The Landscape of Wind Energy in Asia: A Booming Renewable Powerhouse
Asia is rapidly establishing itself as a global leader in wind energy, harnessing the power of its vast coastlines and windswept plains to generate clean, sustainable electricity.
From the towering turbines of China to the emerging potential of Japan, the wind energy landscape in Asia is diverse and dynamic.
China: The Undisputed Leader
China reigns supreme in Asian wind energy, boasting the world’s largest installed capacity. With over 328 gigawatts (GW) of operational wind power as of 2021, China accounts for nearly half of Asia’s total wind energy capacity. This impressive feat is driven by several factors, including:
- Favorable geographic conditions: China’s vast landmass offers diverse wind resources, with strong inland winds and a lengthy coastline ideal for offshore wind farms.
- Government support: China’s ambitious renewable energy targets and supportive policies have spurred significant investment in wind power development.
- Technological advancements: Domestic wind turbine manufacturers have made significant strides in recent years, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Beyond China: Rising Stars in Asian Wind Energy
While China leads the pack, other Asian countries are rapidly catching up. Here are some notable players:
- India: With over 40 GW of installed capacity, India is the second-largest wind energy market in Asia. The country boasts strong wind resources, particularly in its southern states, and is actively pursuing ambitious expansion plans.
- Vietnam: Vietnam has emerged as a rising star in recent years, with its wind energy capacity surging from near zero in 2010 to over 4 GW in 2021. The country’s attractive investment climate and strong wind resources along its coastline have attracted significant foreign investment.
- Japan: Japan, with its limited landmass and stringent regulations, has traditionally lagged behind in wind energy development. However, recent policy changes and a growing focus on offshore wind farms are paving the way for significant expansion in the coming years.
Offshore Wind: The Next Frontier
Offshore wind presents a vast untapped potential for Asian countries. With extensive coastlines and strong offshore winds, Asia is well-positioned to capitalize on this emerging technology. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are already taking the lead, investing heavily in large-scale offshore wind projects.
Wind Farm in Asia
Here’s a list of notable wind farms across Asia, along with their capacities and locations:
-
Gansu Wind Farm, China: With a whopping 7,500 MW capacity, this behemoth in the Gansu province reigns supreme as the largest wind farm in Asia and the world. Imagine over 7,000 turbines spread across a staggering 20,000 square kilometers!
-
Hebei Zhangjiakou Wind Farm, China: This cluster of wind farms in Zhangjiakou, Hebei province, boasts a remarkable capacity exceeding 5,000 MW. It encompasses several impressive farms, including the Ximalin Wind Farm (50 MW) and the Guyuan Wind Farm (100.5 MW).
-
Inner Mongolia Baixo Wind Farm, China: Located in the Baixo Banner of Inner Mongolia, this wind farm packs a punch with a 1,000 MW capacity. Owned and operated by China Guodian Corporation, it began operations in 2010.
-
Muppandal Wind Farm, India: This Tamil Nadu powerhouse in the Ramanathapuram district stands tall with a 1,500 MW capacity. Owned by the Tamil Nadu Generation and Distribution Corporation, it was commissioned in stages between 2005 and 2011.
-
Jaisalmer Wind Park, India: This impressive park in Rajasthan’s Jaisalmer district flaunts a 1,050 MW capacity. Suzlon Energy owns and operates this marvel, commissioned in phases between 2008 and 2012.
-
Taramangalam Wind Farm, India: Another Tamil Nadu gem, this wind farm in the Tirunelveli district, with a 600 MW capacity, is owned and operated by Mytrah Energy (formerly First Wind). Its commissioning spanned from 2008 to 2014.
-
Vietnam Tuy Phong Wind Farm: Located in Vietnam’s Bình Thuận province, this wind farm boasts a 260 MW capacity. Owned and operated by the Power Construction Corporation of Vietnam (EVN Power Construction), it commenced operations in 2019.
-
Japan Kamisu Wind Farm: This wind farm in Japan’s Akita prefecture stands tall with a 102 MW capacity. Owned and operated by Green Power Investment Corporation, it began operations in 2012.
-
South Korea Dokdo Wind Farm: Situated on the Dokdo islands off South Korea’s east coast, this wind farm packs a 30 MW punch. Owned and operated by Korea Western Power, it started operations in 2014.
-
Dharmsala Wind Farm, India: Nestled in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, India, this wind farm offers stunning Himalayan views alongside its 88 MW capacity. Owned and operated by Suzlon Energy, it commenced operations in 2012.
-
Yunnan Longping Wind Farm, China: This wind farm in China’s Yunnan province boasts a 600 MW capacity and stunning scenery amidst the mountains. Owned and operated by China Huadian Corporation, it was commissioned in 2010.
-
Jhimpir Wind Farm, Pakistan: Located in Thatta District, Sindh, Pakistan, this wind farm has a 100 MW capacity. Owned and operated by Sindh Renewable Energy Ltd, it started operations in 2015.
-
Hormozgan Wind Farm, Iran: This wind farm in Iran’s Hormozgan province has a 250 MW capacity. Owned and operated by Mabna نیرو, it went online in 2019.
-
Black Sea Wind Farm, Turkey: Located in Karadeniz Eregli district of Zonguldak Province, Turkey, this wind farm enjoys the Black Sea’s scenic backdrop. It boasts a 120 MW capacity and is owned and operated by ENECO.
Wind Farm Powerhouses of Asia
| Rank | Wind Farm Name | Country | Capacity (MW) | Location | Key Features | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gansu Wind Farm | China | 7,500 | Gansu Province | Largest wind farm in Asia and the world | |
| 2 | Hebei Zhangjiakou Wind Farm | China | 5,000+ | Zhangjiakou, Hebei Province | Cluster of wind farms including Ximalin (50 MW) and Guyuan (100.5 MW) | |
| 3 | Inner Mongolia Baixo Wind Farm | China | 1,000 | Baixo Banner, Inner Mongolia | Commissioned in 2010 | |
| 4 | Muppandal Wind Farm | India | 1,500 | Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu | Commissioned in phases between 2005 and 2011 | |
| 5 | Jaisalmer Wind Park | India | 1,050 | Jaisalmer district, Rajasthan | Commissioned in phases between 2008 and 2012 | |
| 6 | Taramangalam Wind Farm | India | 600 | Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu | Owned and operated by Mytrah Energy (formerly First Wind) | |
| 7 | Vietnam Tuy Phong Wind Farm | Vietnam | 260 | Bình Thuận province | Owned and operated by the Power Construction Corporation of Vietnam (EVN Power Construction) | |
| 8 | Japan Kamisu Wind Farm | Japan | 102 | Akita prefecture | Owned and operated by Green Power Investment Corporation | |
| 9 | South Korea Dokdo Wind Farm | South Korea | 30 | Dokdo islands off the east coast | Owned and operated by Korea Western Power | |
| 10 | Dharmsala Wind Farm | India | 88 | Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh | Stunning Himalayan views | |
| 11 | Yunnan Longping Wind Farm | China | 600 | Yunnan province | Mountainous scenery | |
| 12 | Jhimpir Wind Farm | Pakistan | 100 | Thatta District, Sindh | Owned and operated by Sindh Renewable Energy Ltd | |
| 13 | Hormozgan Wind Farm | Iran | 250 | Hormozgan province | Owned and operated by Mabna نیرو | |
| 14 | Black Sea Wind Farm | Turkey | 120 | Karadeniz Eregli district, Zonguldak Province | Scenic Black Sea backdrop | |
| 15 | Mytrah Energy Wind Farm | India | 100 | Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu | Owned and operated by Mytrah Energy (formerly First Wind) |
Please note that this is just a selection of notable wind farms in Asia and there are many others that could be included in the list.
Statistics of Landscape of Wind Energy in Asia
Wind Energy Landscape in Asia: Statistics that Paint a Powerful Picture
Asia is rapidly establishing itself as a global leader in wind energy, harnessing the power of its vast coastlines and windswept plains to generate clean, sustainable electricity. Let’s delve into some key statistics that illustrate this impressive growth:
Installed Capacity:
- Total: As of 2023, Asia boasts over 557 gigawatts (GW) of installed wind energy capacity, accounting for nearly half of the world’s total.
- China: The undisputed leader, China holds the lion’s share with over 357 GW, contributing over 60% of Asia’s wind power.
- India: Following closely, India has witnessed tremendous growth, reaching over 70 GW and aiming for ambitious expansion plans.
- Other Notable Players: Vietnam, with around 4.5 GW, and Japan, with 5 GW, are quickly catching up, with significant investments in offshore wind projects.
Growth:
- Asia is expected to add 10 GW of new wind power capacity each year, with projections reaching nearly 15 GW by 2030.
- China aims to reach 450 GW by 2030, further solidifying its dominance.
- India has set ambitious targets to reach 100 GW by 2030 and 300 GW by 2035.
Economic Impact:
- The wind energy sector in Asia employs millions of people, contributing significantly to regional economies.
- China alone has over 700,000 jobs directly or indirectly related to wind energy.
- Investments in wind energy infrastructure and technology development are spurring innovation and economic diversification.
Environmental Benefits:
- Wind energy generation is a clean and renewable energy source, contributing to Asia’s fight against air pollution and climate change.
- It reduces reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions, promoting a cleaner and healthier future.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Grid integration and energy storage solutions are crucial for efficient utilization of intermittent wind power.
- Environmental concerns regarding birdlife and marine ecosystems need careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
- Financing large-scale projects requires innovative mechanisms and supportive government policies.
The Future:
With its vast potential, supportive policies, and technological advancements, Asia is poised to remain a dominant force in the global wind energy landscape. Continued investment in onshore and offshore wind farms, coupled with innovative solutions to overcome challenges, will pave the way for a sustainable and clean energy future for the region.
Visualizing the Stats:
- Imagine the colossal Gansu Wind Farm in China, with its over 7,000 turbines spread across a vast 20,000 square kilometers.
- Picture the towering blades of the Muppandal Wind Farm in India, stretching across the landscape of Tamil Nadu.
- Visualize the intricate network of offshore wind farms emerging along the coastlines of Japan and South Korea.
These statistics and images paint a vivid picture of the wind energy landscape in Asia, showcasing its remarkable growth, immense potential, and crucial role in shaping a cleaner future for the region and the world.
Table Landscape of Wind Energy in Asia
Asia’s Wind Energy Landscape: Statistics that Power Forward
Asia is rapidly carving its path as a global wind energy leader, harnessing the wind’s might to generate clean, sustainable electricity. Let’s delve into some key statistics that illustrate this impressive growth:
| Stat | Numbers | Impact | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Installed Capacity | Over 557 GW | Nearly half the world’s total | |
| China’s Dominance | Over 357 GW | Holds 60% of Asia’s wind power | |
| India’s Surge | Over 70 GW | Ambitious expansion plans in place | |
| Other Notable Players | Vietnam: 4.5 GW, Japan: 5 GW | Rapidly catching up with offshore investments | |
| Annual Growth Rate | Expected to be 10 GW, reaching 15 GW by 2030 | Asian leadership solidifying further | |
| China’s Target | 450 GW by 2030 | Reinforcing its global lead | |
| India’s Ambitions | 100 GW by 2030, 300 GW by 2035 | Challenging China’s supremacy | |
| Millions of Jobs | Created by the wind sector across Asia | Boosting regional economies | |
| China’s Workforce | Over 700,000 jobs directly or indirectly linked to wind energy | Significant economic contribution | |
| Clean & Renewable Power | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels and emissions | Combating air pollution and climate change | |
| Grid Integration Challenge | Efficient utilization of intermittent wind power needs solutions | Energy storage development crucial | |
| Environmental Considerations | Birdlife and marine ecosystems require careful attention | Mitigation strategies necessary | |
| Financing Hurdles | Innovative mechanisms and supportive policies needed for large-scale projects | Public-private partnerships key to overcoming challenges |
With its vast potential, supportive policies, and technological advancements, Asia is poised to dominate the global wind energy landscape. Continued investment in onshore and offshore projects, coupled with innovative solutions to overcome challenges, will pave the way for a sustainable and clean energy future for the region and the world.
Challenges and Opportunities Wind Energy in Asia
Despite its impressive growth, the wind energy sector in Asia faces several challenges. These include:
- Grid integration: Integrating large amounts of intermittent wind power into existing grids can be challenging, requiring investments in grid infrastructure and energy storage solutions.
- Environmental concerns: The construction and operation of wind farms can have environmental impacts, such as on birdlife and marine ecosystems. Careful planning and mitigation measures are necessary to address these concerns.
- Financing: Financing large-scale wind projects can be challenging, especially in developing countries. Innovative financing mechanisms and supportive government policies are needed to overcome this hurdle.
However, the opportunities for wind energy in Asia are immense. The growing demand for clean energy, coupled with falling technology costs and supportive government policies, is creating a perfect storm for continued growth. As Asian countries grapple with the challenges of climate change and air pollution, wind energy is poised to play a critical role in building a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Looking Ahead
The future of wind energy in Asia is bright. With its vast potential, supportive policies, and technological advancements, Asia is well on its way to becoming a global leader in this clean and sustainable energy source. The wind turbines that dot the landscapes of Asian countries are not just generating electricity; they are symbols of a region embracing a cleaner and brighter future.
https://www.exaputra.com/2024/01/the-landscape-of-wind-energy-in-asia.html
Renewable Energy
Should We Appease MAGA by Rewriting the Constitution?
 Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Rewriting the U.S. Constitution will take some work, as I’m sure you’re aware.
Renewable Energy
California’s Next Governor?
 What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
Yes, we have traffic, which we hate. But that’s because everybody and his dog wants to be here for our economic opportunities and our natural beauty.
In general, we reject racism, ignorance, corruption, and environmental destruction.
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
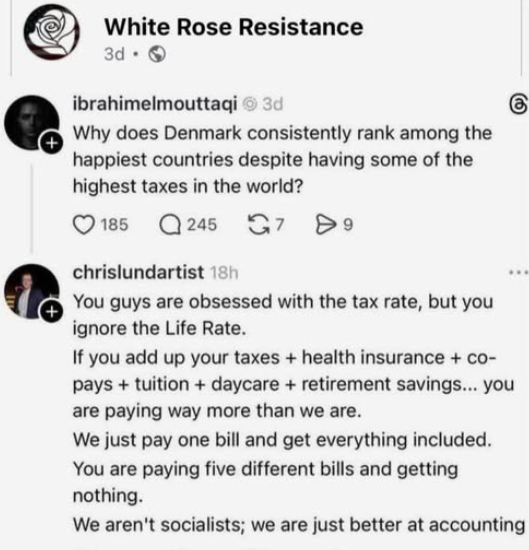 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
















