Clean-energy growth helped China’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions fall by 1% year-on-year in the first half of 2025, extending a declining trend that started in March 2024.
The CO2 output of the nation’s power sector – its dominant source of emissions – fell by 3% in the first half of the year, as growth in solar power alone matched the rise in electricity demand.
The new analysis for Carbon Brief shows that record solar capacity additions are putting China’s CO2 emissions on track to fall across 2025 as a whole.
Other key findings include:
- The growth in clean power generation, some 270 terawatt hours (TWh) excluding hydro, significantly outpaced demand growth of 170TWh in the first half of the year.
- Solar capacity additions set new records due to a rush before a June policy change, with 212 gigawatts (GW) added in the first half of the year.
- This rush means solar is likely to set an annual record for growth in 2025, becoming China’s single-largest source of clean power generation in the process.
- Coal-power capacity could surge by as much as 80-100GW this year, potentially setting a new annual record, even as coal-fired electricity generation declines.
- The use of coal to make synthetic fuels and and chemicals is growing rapidly, climbing 20% in the first half of the year and helping add 3% to China’s CO2 since 2020.
- The coal-chemical industry is planning further expansion, which could add another 2% to China’s CO2 by 2029, making the 2030 deadline for peaking harder to meet.
Even if its emissions fall in 2025 as expected, however, China is bound to miss multiple important climate targets this year.
This includes targets to reduce its carbon intensity – the emissions per unit of GDP – to strictly control coal consumption growth and new coal-power capacity, as well as to increase the share of cleaner electric-arc steelmaking in total steel output.
If policymakers want to make up for these shortfalls, then there will be additional pressure on China’s next “nationally determined contribution” (NDC, its international climate pledge for 2035) and its 15th five-year plan for 2026-30, both due to be finalised in the coming months.
The falling trend in CO2 emissions – and the clean-energy growth that is driving it – could give policymakers greater confidence that more ambitious targets are achievable.
Falling emissions from power, cement and steel
The reduction in emissions in the first half of 2025 was predominantly driven by the power sector, aided by the building materials, steel and heating industries.
Coal use in the power industry fell by 3.4% compared with the same period a year earlier, while gas use increased by 6%, resulting in a 3.2% drop in emissions for the sector overall.
The reduction in CO2 emissions from coal use in the power sector is shown at the bottom of the figure below, along with the small rise due to higher gas-fired electricity generation.
Other changes in CO2 emissions in the first half of 2025, compared with the same period in 2024, are broken down by source and sector in the rest of the figure.
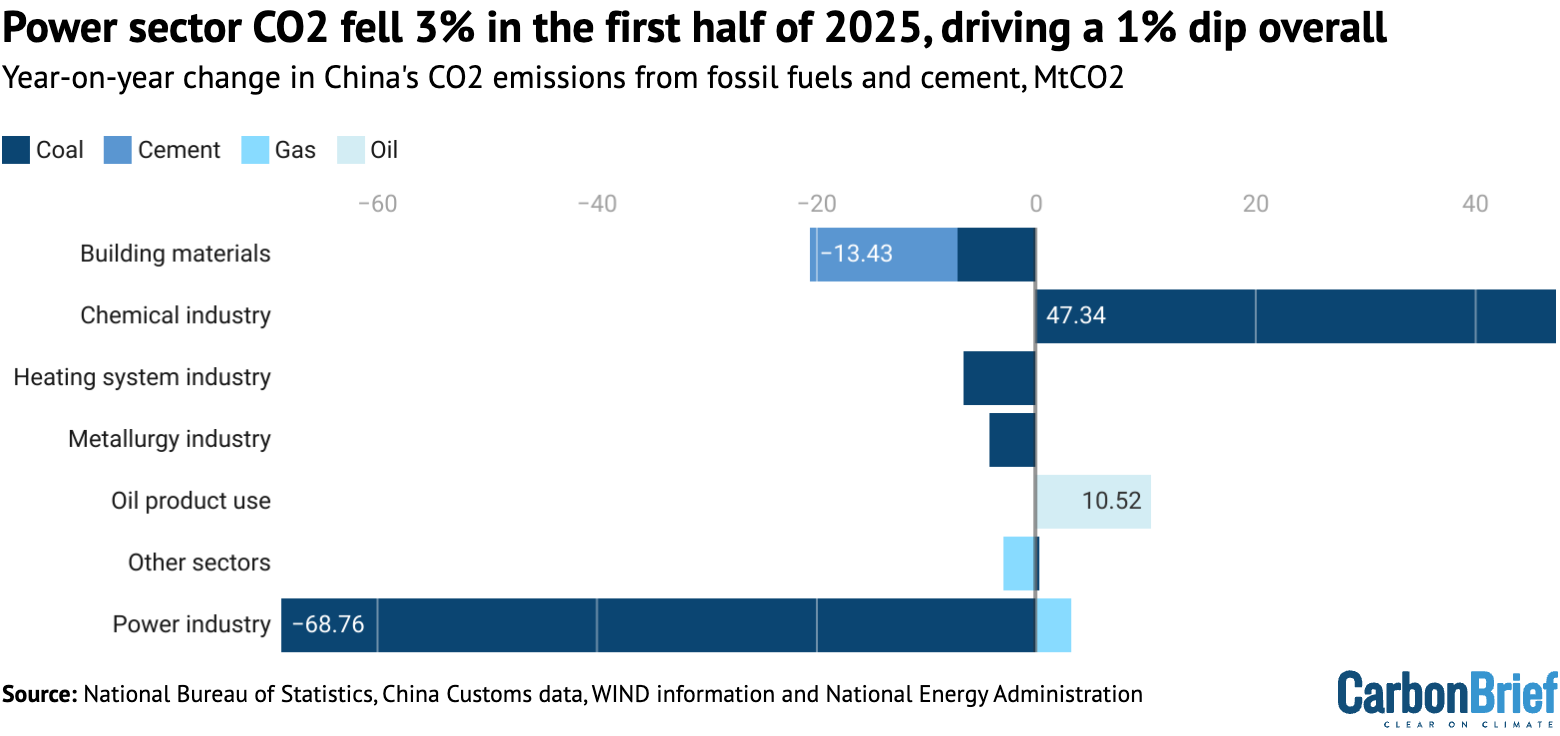
Emissions from the building materials sector fell by 3% and from the metals industry by 1%, with cement falling 4% and steel output 3%. The reason for these reductions is the ongoing contraction in the construction sector, with real estate investment falling 11% and the floor area of new construction starts by 20%. Traditional targets of government infrastructure investment, such as transportation, also showed relatively slow growth.
CO2 reductions resulting from the drop in steel output were limited by a fall in the share of electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking, a much less emissions- and energy-intensive process than the coal-based production of primary steel.
The share of electric-arc output in total production fell from 10.2% in 2024 to 9.8% in the first half of 2025, despite a government target of 15% for this year.
Excess coal-based capacity and a lack of incentives for shifting production mean that electric arc steelmakers, rather than coal-based steel mills, tend to absorb reductions in output, as their operating costs are higher and costs of shutting down and starting up production lines are lower.
Shifting to EAF steel is one of the largest emission reduction opportunities in China over the next decade, according to an analysis by the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air.
Elsewhere, consumption of oil products increased by 1%. However, this growth did not come from transport fuel demand. The production of petrol, diesel and jet fuel all continued to fall, with electric vehicles eating into road-fuel demand. Instead, growth was driven by demand for naphtha from petrochemicals producers, including newly commissioned plants.
Gas use outside the power sector – mainly heating – dropped by 1%, after a fall in the first quarter due to mild winter temperatures and a smaller increase in the second quarter.
Solar boom covers power demand growth
The first half of 2025 saw a new record for the growth of clean power generation excluding hydro, made up of solar, wind, nuclear and biomass.
Clean power generation from solar, wind and nuclear power grew by 270 terawatt hours (TWh), substantially exceeding the 170TWh (3.7%) increase in electricity consumption. Hydropower generation fell by 3% (16TWh), moderating the fall in fossil fuel-fired power generation.
The rise in power generation from solar panels, on its own, covered all of the growth in electricity demand, increasing by 170TWh – equivalent to the national power output of Mexico or Turkey over the same period. Wind power output grew by 80TWh and nuclear by 20TWh.
As a result, the share of low-carbon sources reached 40% of the nation’s electricity generation overall in the first half of the year, up from 36% in the same period of 2024.
The figure below shows how clean-energy sources excluding hydro (columns) have started matching the recent increases in China’s electricity demand (solid line), as well as the average amount of growth in recent years (dashed line).

Strikingly, the record growth of solar and continued expansion of wind mean that both sources of electricity generation overtook hydropower for the first time in the first half of 2025, as shown in the figure below. Despite steady growth, nuclear power is a relatively distant fourth, at less than half of the power generation from each of the other three major non-fossil technologies.

The growth in solar power generation was driven by record capacity growth. China added 212GW of new solar capacity in the first half of the year, double the amount installed in the first half of 2024, which itself had been a new record.
For comparison, the world’s second-largest nation for solar capacity – the US – had only installed 178GW, in total, by the end of 2024, while third-ranked India had 98GW.
Some 93GW of new solar capacity was added to China’s grid in May alone, as the rush to install before a change in pricing policy culminated. This rate of installations translates to approximately 100 solar panels installed every second of the month.
The acceleration was due to a change in the policy on tariffs paid to new wind and solar generators, which started in June. Previously, new plants were guaranteed to receive the benchmark price for coal-fired power output in each province, for each unit of electricity they generate. Under the new policy, new generators have to secure contracts directly with electricity buyers, causing uncertainty and likely putting downward pressure on revenue.
The resulting surge in new capacity means that solar is poised to overtake wind this year – and hydro this year or next – to become the largest source of clean power generation in China.
This is despite solar capacity additions slowing down in June and projections diverging widely on how much growth to expect for the remainder of 2025 and into 2026, under the new policy.
The consensus among forecasters has been one of a sharp slowdown in installations.
After the new pricing policy was announced, the China Electricity Council (CEC) and China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA) projected 210GW and 215-235GW for 2025 as a whole, respectively, implying plummeting additions in the second half of the year. In contrast, the State Grid Energy Research Institute expects 380GW to be added to the grid this year.
After data for May installations became available, the CEC upgraded its forecast for the whole year to 310GW and the CPIA to 270-300GW, implying that 60-100GW would be added in the second half of the year. This would still be a sharp deceleration compared with the second half of 2024, when 173GW was added.
For wind, the State Grid researchers expect 140GW and CEC 110GW, while 51GW was added in the first half of the year. Both numbers indicate larger capacity additions in the second half of 2025 and an increase for the full year compared with 2024.
The State Grid should have detailed knowledge of projects seeking to connect to the electricity grid, so its projections carry extra weight compared with others. If its expectations for wind and solar growth are realised, this would result in around 850TWh of annual clean power generation being added to the grid in 2025, as shown in the figure below.
This new clean power capacity would be more than enough to meet the entire electricity demand of Brazil (760TWh), or Germany and the UK combined (817TWh).
With the State Grid also projecting demand to grow by 400-640TWh (4.0-6.5%), clean-energy growth should push down CO2 from China’s power sector this year – and well into next year.

China’s top economic planner, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), is also taking steps to spur demand for contracts with solar and wind producers.
A new policy – published in July – requires for the first time that steel, cement and polysilicon factories, as well as some new data centres, meet a certain percentage of their demand using renewable electricity.
Previously, such requirements were only applied to provinces, power distribution companies and the aluminum industry. Their mandated renewable energy shares have also now increased.
These changes boost demand for contracts with renewable electricity suppliers, just as new solar and wind plants are having to secure contracts directly with buyers, under their new pricing policy.
The increase in demand for renewable power resulting from these measures broadly matches the low end of the growth projected in solar and wind this year. The renewable quotas therefore offer a backstop of support for the continued growth of clean power, which will be required to meet China’s wider climate and energy targets.
The increase in solar power generation from rising installations could be even larger, but is being limited by issues around grid management and capacity.
The share of potential solar power output that was not utilised rose to 5.7% in the first half of 2025, from 3.2% a year earlier. While technical issues such as uncompleted grid connections could play a role amid the boom, this also implies a significant increase in curtailment.
The average utilisation rate of solar panels fell by 12% in the first quarter of this year, compared with the 2020–2023 average, according to China Electricity Council data accessed through Wind Information. This is a much larger reduction than indicated by the reported curtailment rates. The flipside of this dip in utilisation is that improvements to grid operation and infrastructure will unlock even more generation from existing solar capacity.
Coal power capacity is expected to surge this year, even as demand for power generation from coal contracts. The State Grid predicts 127GW of thermal power added. Some of this will be gas, but based on non-coal thermal power additions expected by the CEC, around 90-100GW is coal, while the CEC projects 80GW of coal power added.
Data from Global Energy Monitor shows 93-109GW of coal-power projects under construction that could be completed this year, assuming a 2.5 to 3-year lead time from issuance of permits to grid connection. The largest amount of coal-fired capacity China has ever connected to the grid in one year is 63GW in 2008, so 2025 seems likely to set a new record by a large margin.
A former senior official at one of China’s largest power firms stated in an interview in June 2025 that companies are building coal power capacity due to central government pressure.
There is little enthusiasm to invest and the target to expand coal-power capacity to 1,360GW in this five-year plan period, covering 2021-2025, is unlikely to be met. Operating coal-power capacity was 1,210GW at the end of June, up from 1,080GW at the end of 2020.
The influx of coal-fired capacity will result in falling utilisation and profitability.
However, oversupply of coal power could also weaken demand for contracts with solar and wind producers, undermining clean-energy growth. This makes measures that offer a backstop of demand for clean power, such as the sector quotas, all the more significant.
Coal chemicals shooting up
The only major sector that saw growth in emissions in the first half of the year was the chemicals sector. Coal use in the sector, both as a fuel and a feedstock, increased by a dramatic 20% year-on-year, on top of a 10% increase in 2024.
Oil use in the chemicals sector increased as well, as reflected in a 9% increase in total consumption of naptha – a key petrochemicals feedstock – estimated from OPEC data.
The growth is driven by the coal-to-chemicals industry, which turns coal into synthetic liquid and gaseous fuels, as well as petrochemical products. This is a sector that China has developed aggressively, to reduce reliance on imported oil and gas, as well as to promote the exploitation of coal resources in the country’s far west – particularly Xinjiang – where coal and coal power exports to the rest of China are limited by transportation capacity and costs.
The sector consumed approximately 390m tonnes of coal in 2024, resulting in an estimated 690m tonnes CO2 emissions (MtCO2), making it responsible for 6% of China’s fossil CO2 emissions and 9% of the country’s coal use in 2024.
Coal use and emissions increased 10% from 2023 while total coal conversion capacity increased only 5%, implying that the utilisation of existing capacity increased as well.
The coal-to-chemicals industry used 155m tonnes of standard coal in 2020 and CO2 emissions were estimated at 320MtCO2. The coal-to-chemicals industry therefore added around 3% to China’s total CO2 emissions from 2020 to 2024, making it one of the sectors responsible for the recent acceleration in the country’s CO2 emissions growth and its shortfall against targets to control increases in CO2 emissions and coal use.
Output from the sector reportedly replaced 100m tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe) of oil and gas in 2024, which implies 250-280MtCO2 emissions avoided from oil and gas use, depending on how the avoided demand breaks down between oil and gas.
The net effect of the industry on CO2 emissions was therefore an increase of around 410-440MtCO2, or 4% of China’s total CO2, highlighting that coal-based chemical production is much more carbon-intensive than its already carbon-intensive oil- and gas-based equivalent.
The sector’s growth in coal use and emissions reflects drastically improved profitability in most segments in recent years. Its profitability depends heavily on the oil price, so the sharp increase in oil prices from the 2015-2020 level in 2021-24 supported output growth, whereas the recent fall in oil prices could temper it.
The chemical industry association still expects the sector to expand capacity for another decade, until 2035, even under China’s CO2 peaking target.
Analysis by Tianfeng Securities touts the years 2025-2030 as the “peak period” for investment in coal to chemicals, claiming that potential annual investment over the next five years could reach three times the 2021-23 level and that half of this potential investment is in Xinjiang province.
Sinolink Securities projects that an average of at least 37m tonnes of coal conversion capacity will be added in the coal-to-chemicals industry each year from 2025 to 2029, with coal-to-oil-and-gas and coal-to-methanol dominating these capacity additions.
This would mean a 40% increase in the industry’s capacity from 2024 to 2029, with the potential to add over 250MtCO2 per year of emissions, increasing total CO2 emissions by over 2%.
The figure below illustrates this potential increase, which would continue recent trends.
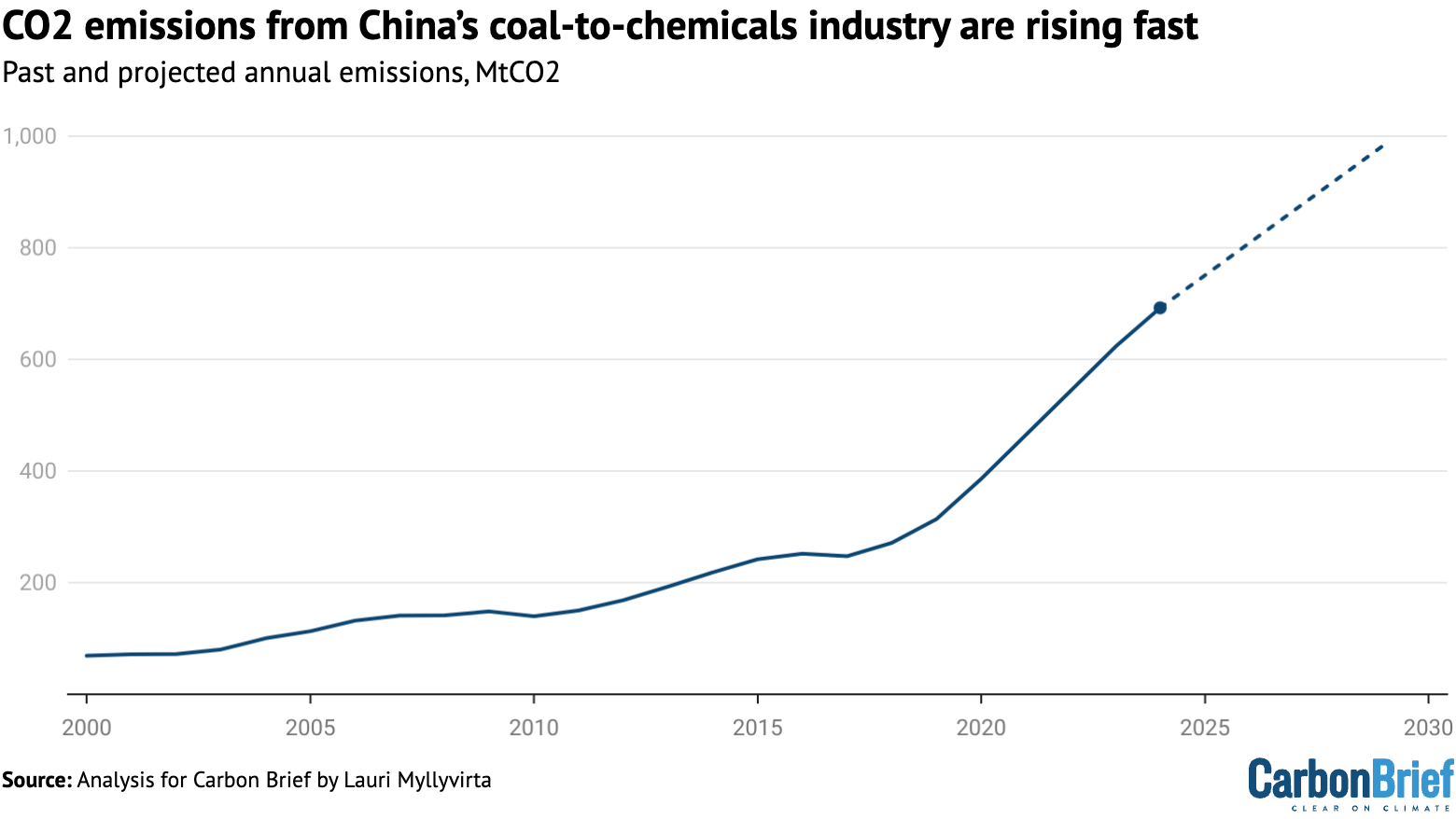
If this further expansion takes place – and assuming new chemicals plants are used at the same rate as the existing fleet is being used today – then it would complicate China’s carbon peaking target and make the CO2 intensity target for 2030 even more challenging to meet.
However, this is not the first time that the industry has been predicted to boom. In 2014, the China Coal Association issued a prediction that the coal-to-chemicals industry would be using 750Mt of coal per year by 2020, converting to about 540Mt of “standard” coal.
In reality, less than a third of this demand was realised – in large part due to low oil prices – and the sector was still only using half of this amount by the end of 2024.
New targets on the horizon
Given the major increase in solar capacity in the first half, as well as expected additions of wind and nuclear throughout the year, China is on track for a fall in emissions in 2025.
This would continue a declining trend that began in early 2024 and leaves open the possibility that China’s emissions could have peaked already, years ahead of its “before 2030” target.
The recent slide in China’s total CO2 emissions is shown in the figure below, with the shallow decline illustrating the potential that this trend could be reversed.

Even if China’s emissions fall by a few percent this year, however, this is unlikely to be sufficient to meet the carbon intensity target for 2025 in the current five-year plan. Still, it would make the country’s 2030 carbon intensity commitment under the Paris Agreement easier to meet.
A continuing fall in emissions, extending the fall that began in early 2024, could also affect target-setting for the next five-year plan – which is being prepared for release in early 2026 – by showing that China could peak and reduce its emissions well ahead of the 2030 deadline.
Yet, despite rapid progress in 2024 and 2025, China is bound to miss multiple emissions-related targets in the 2021-2025 period, due to rapid CO2 rises during and after the Covid pandemic.
These targets include improvements in carbon intensity, “strict” controls of the growth in coal consumption and new coal-fired power plants, as well as the share of cleaner electric arc steelmaking in total steel output.
If China’s policymakers want to make up the shortfall against these 2025 targets and get on track for their 2030 goals, then they would need to set out higher ambitions in the 15th five-year plan, covering 2026-2030. For example, this could include reducing the carbon intensity of China’s economy by more than 20% over the next five years.
China’s new pledge (NDC) under the Paris Agreement, with targets for 2035, is due to be published in the next few months and will provide important indications of their intentions.
The new pricing policy for wind and solar has also increased the importance of target-setting, by making “contracts for difference” available for the amount of capacity needed to meet the central government’s clean-energy targets. An ambitious clean-energy target for 2035 would be a significant new backstop for clean-energy growth, with both climate and economic relevance.
Another major question is how the government will react to the influx of coal-fired capacity, even as power generation from coal recedes. It could either move to close down older coal plants – or to limit clean-energy additions.
With respect to coal power plants, the key point remains, however, that as long as clean power generation keeps growing faster than electricity demand, then increases in coal and gas fired capacity will result in falling utilisation, rather than increased CO2 emissions.
About the data
Data for the analysis was compiled from the National Bureau of Statistics of China, National Energy Administration of China, China Electricity Council and China Customs official data releases, and from WIND Information, an industry data provider.
Wind and solar output, and thermal power breakdown by fuel, was calculated by multiplying power generating capacity at the end of each month by monthly utilisation, using data reported by China Electricity Council through Wind Financial Terminal.
Total generation from thermal power and generation from hydropower and nuclear power was taken from National Bureau of Statistics monthly releases.
Monthly utilisation data was not available for biomass, so the annual average of 52% for 2023 was applied. Power sector coal consumption was estimated based on power generation from coal and the average heat rate of coal-fired power plants during each month, to avoid the issue with official coal consumption numbers affecting recent data.
CO2 emissions estimates are based on National Bureau of Statistics default calorific values of fuels and emissions factors from China’s latest national greenhouse gas emissions inventory, for the year 2021. Cement CO2 emissions factor is based on annual estimates up to 2024.
For oil consumption, apparent consumption is calculated from refinery throughput, with net exports of oil products subtracted.
The post Analysis: Record solar growth keeps China’s CO2 falling in first half of 2025 appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Record solar growth keeps China’s CO2 falling in first half of 2025
Greenhouse Gases
Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting
Half of nations have met a UN deadline to report on how they are tackling nature loss within their borders, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
This includes 11 of the 17 “megadiverse nations”, countries that account for 70% of Earth’s biodiversity.
It also includes all of the G7 nations apart from the US, which is not part of the world’s nature treaty.
All 196 countries that are part of the UN biodiversity treaty were due to submit their seventh “national reports” by 28 February, of which 98 have done so.
Their submissions are supposed to provide key information for an upcoming global report on actions to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030, in addition to a global review of progress due to be conducted by countries at the COP17 nature summit in Armenia in October this year.
At biodiversity talks in Rome in February, UN officials said that national reports submitted late will not be included in the global report due to a lack of time, but could still be considered in the global review.
Tracking nature action
In 2022, nations signed a landmark deal to halt and reverse nature loss by 2030, known as the “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF).
In an effort to make sure countries take action at the domestic level, the GBF included an “implementation schedule”, involving the publishing of new national plans in 2024 and new national reports in 2026.
The two sets of documents were to inform both a global report and a global review, to be conducted by countries at COP17 in Armenia later this year. (This schedule mirrors the one set out for tackling climate change under the Paris Agreement.)
The deadline for nations’ seventh national reports, which contain information on their progress towards meeting the 23 targets of the GBF based on a set of key indicators, was 28 February 2026.
According to Carbon Brief’s analysis of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity’s online reporting platform, 98 out of the 196 countries that are part of the nature convention (50%) submitted on time.
The map below shows countries that submitted their seventh national reports by the UN’s deadline.
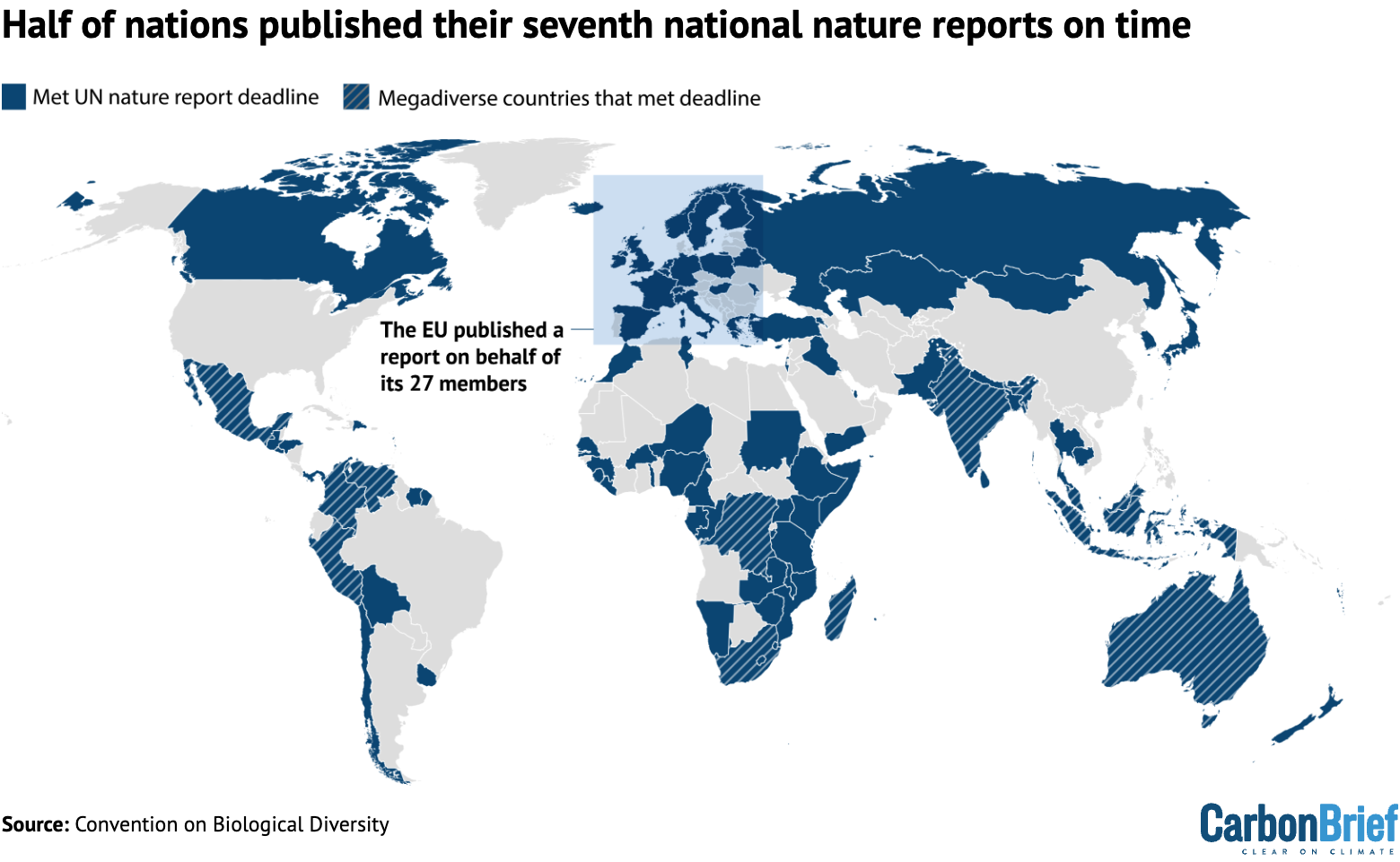
This includes 11 of the 17 “megadiverse nations” that account for 70% of Earth’s biodiversity.
The megadiverse nations to meet the deadline were India, Venezuela, Indonesia, Madagascar, Peru, Malaysia, South Africa, Colombia, Mexico, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Australia.
It also includes all of the G7 nations (France, Germany, the UK, Japan, Italy and Canada), excluding the US, which has never ratified the Convention on Biological Diversity.
The UK’s seventh national report shows that it is currently on track to meet just three of the GBF’s 23 targets.
This is according to a LinkedIn post from Dr David Cooper, former executive secretary of the CBD and current chair of the UK’s Joint Nature Conservation Committee, which coordinated the UK’s seventh national report,
The report shows the UK is not on track to meet one of the headline targets of the GBF, which is to protect 30% of land and sea for nature by 2030.
It reports that the proportion of land protected for nature is 7% in England, 18% in Scotland and 9% in Northern Ireland. (The figure is not given for Wales.)
National plans
In addition to the national reports, the upcoming global report and review will draw on countries’ national plans.
Countries were meant to have submitted their new national plans, known as “national biodiversity strategies and action plans” (NBSAPs), by the start of COP16 in October 2024.
A joint investigation by Carbon Brief and the Guardian found that only 15% of member countries met that deadline.
Since then, the percentage of countries that have submitted a new NBSAP has risen to 39%.
According to the GBF and its underlying documents, countries that were “not in a position” to meet the deadline to submit NBSAPs ahead of COP16 were requested to instead submit national targets. These submissions simply list biodiversity targets that countries will aim for, without an accompanying plan for how they will be achieved.
As of 2 March, 78% of nations had submitted national targets.
At biodiversity talks in Rome in February, UN officials said that national reports submitted late will not be included in the global report due to a lack of time, but could still be considered in the global review.
Funding ‘delays’
At the Rome talks, some countries raised that they had faced “difficulties in submitting [their national reports] on time”, according to the Earth Negotiations Bulletin.
Speaking on behalf of “many” countries, Fiji said that there had been “technical and financial constraints faced by parties” in the preparation of their seventh national reports.
In a statement to Carbon Brief, a spokesperson for the Global Environment Facility, the body in charge of providing financial and technical assistance to countries for the preparation of their national reports, said “delays in fund disbursement have occurred in some cases”, adding:
“In 2023, the GEF council approved support for the development of NBSAPs and the seventh national reports for all 139 eligible countries that requested assistance. This includes national grants of up to $450,000 per country and $6m in global technical assistance delivered through the UN Development Programme and UN Environment Programme.
“As of the end of January 2026, all 139 participating countries had benefited from technical assistance and 93% had accessed their national grants, with 11 countries yet to receive their funds. Delays in fund disbursement have occurred in some cases, compounded by procurement challenges and limited availability of technical expertise.”
The spokesperson added that the fund will “continue to engage closely with agencies and countries to support timely completion of NBSAPs and the seventh national reports”.
The post Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 27 February 2026: Trump’s fossil-fuel talk | Modi-Lula rare-earth pact | Is there a UK ‘greenlash’?
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Absolute State of the Union
‘DRILL, BABY’: US president Donald Trump “doubled down on his ‘drill, baby, drill’ agenda” in his State of the Union (SOTU) address, said the Los Angeles Times. He “tout[ed] his support of the fossil-fuel industry and renew[ed] his focus on electricity affordability”, reported the Financial Times. Trump also attacked the “green new scam”, noted Carbon Brief’s SOTU tracker.
COAL REPRIEVE: Earlier in the week, the Trump administration had watered down limits on mercury pollution from coal-fired power plants, reported the Financial Times. It remains “unclear” if this will be enough to prevent the decline of coal power, said Bloomberg, in the face of lower-cost gas and renewables. Reuters noted that US coal plants are “ageing”.
OIL STAY: The US Supreme Court agreed to hear arguments brought by the oil industry in a “major lawsuit”, reported the New York Times. The newspaper said the firms are attempting to head off dozens of other lawsuits at state level, relating to their role in global warming.
SHIP-SHILLING: The Trump administration is working to “kill” a global carbon levy on shipping “permanently”, reported Politico, after succeeding in delaying the measure late last year. The Guardian said US “bullying” could be “paying off”, after Panama signalled it was reversing its support for the levy in a proposal submitted to the UN shipping body.
Around the world
- RARE EARTHS: The governments of Brazil and India signed a deal on rare earths, said the Times of India, as well as agreeing to collaborate on renewable energy.
- HEAT ROLLBACK: German homes will be allowed to continue installing gas and oil heating, under watered-down government plans covered by Clean Energy Wire.
- BRAZIL FLOODS: At least 53 people died in floods in the state of Minas Gerais, after some areas saw 170mm of rain in a few hours, reported CNN Brasil.
- ITALY’S ATTACK: Italy is calling for the EU to “suspend” its emissions trading system (ETS) ahead of a review later this year, said Politico.
- COOKSTOVE CREDITS: The first-ever carbon credits under the Paris Agreement have been issued to a cookstove project in Myanmar, said Climate Home News.
- SAUDI SOLAR: Turkey has signed a “major” solar deal that will see Saudi firm ACWA building 2 gigawatts in the country, according to Agence France-Presse.
$467 billion
The profits made by five major oil firms since prices spiked following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine four years ago, according to a report by Global Witness covered by BusinessGreen.
Latest climate research
- Claims about the “fingerprint” of human-caused climate change, made in a recent US Department of Energy report, are “factually incorrect” | AGU Advances
- Large lakes in the Congo Basin are releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from “immense ancient stores” | Nature Geoscience
- Shared Socioeconomic Pathways – scenarios used regularly in climate modelling – underrepresent “narratives explicitly centring on democratic principles such as participation, accountability and justice” | npj Climate Action
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
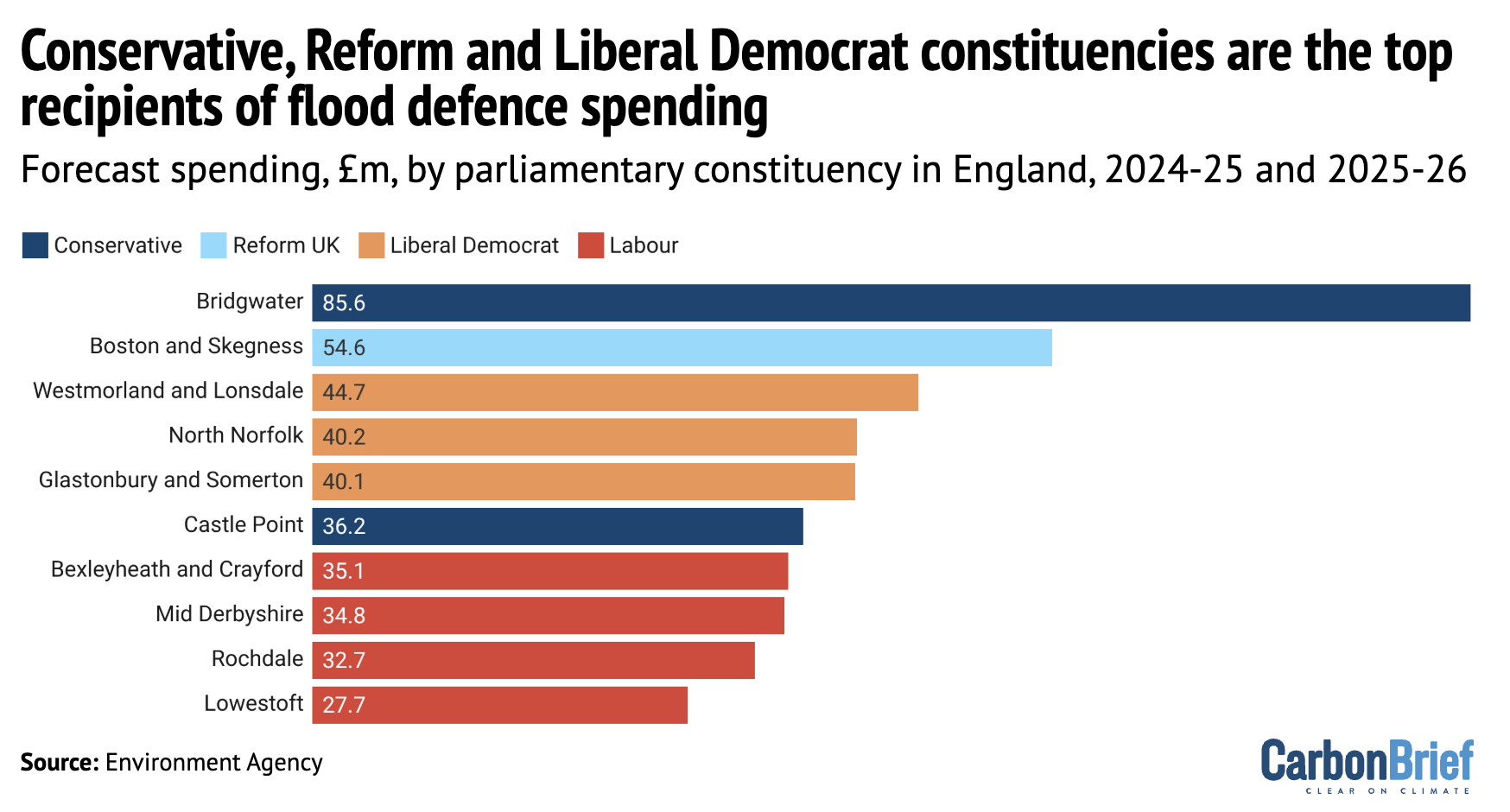
The constituency of Richard Tice MP, the climate-sceptic deputy leader of Reform UK, is the second-largest recipient of flood defence spending in England, according to new Carbon Brief analysis. Overall, the funding is disproportionately targeted at coastal and urban areas, many of which have Conservative or Liberal Democrat MPs.
Spotlight
Is there really a UK ‘greenlash’?
This week, after a historic Green Party byelection win, Carbon Brief looks at whether there really is a “greenlash” against climate policy in the UK.
Over the past year, the UK’s political consensus on climate change has been shattered.
Yet despite a sharp turn against climate action among right-wing politicians and right-leaning media outlets, UK public support for climate action remains strong.
Prof Federica Genovese, who studies climate politics at the University of Oxford, told Carbon Brief:
“The current ‘war’ on green policy is mostly driven by media and political elites, not by the public.”
Indeed, there is still a greater than two-to-one majority among the UK public in favour of the country’s legally binding target to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, as shown below.
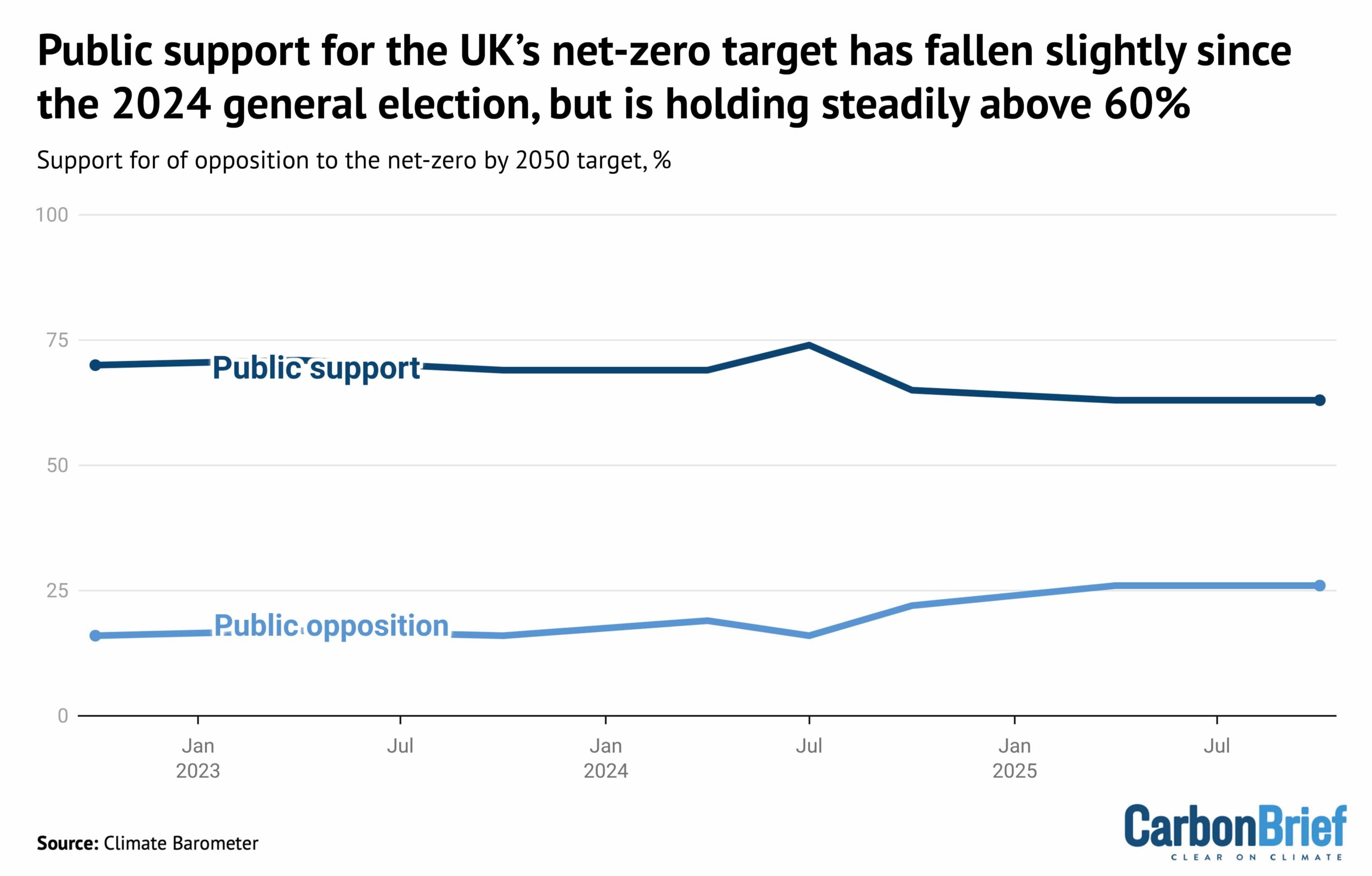
Steve Akehurst, director of public-opinion research initiative Persuasion UK, also noted the growing divide between the public and “elites”. He told Carbon Brief:
“The biggest movement is, without doubt, in media and elite opinion. There is a bit more polarisation and opposition [to climate action] among voters, but it’s typically no more than 20-25% and mostly confined within core Reform voters.”
Conservative gear shift
For decades, the UK had enjoyed strong, cross-party political support for climate action.
Lord Deben, the Conservative peer and former chair of the Climate Change Committee, told Carbon Brief that the UK’s landmark 2008 Climate Change Act had been born of this cross-party consensus, saying “all parties supported it”.
Since their landslide loss at the 2024 election, however, the Conservatives have turned against the UK’s target of net-zero emissions by 2050, which they legislated for in 2019.
Curiously, while opposition to net-zero has surged among Conservative MPs, there is majority support for the target among those that plan to vote for the party, as shown below.
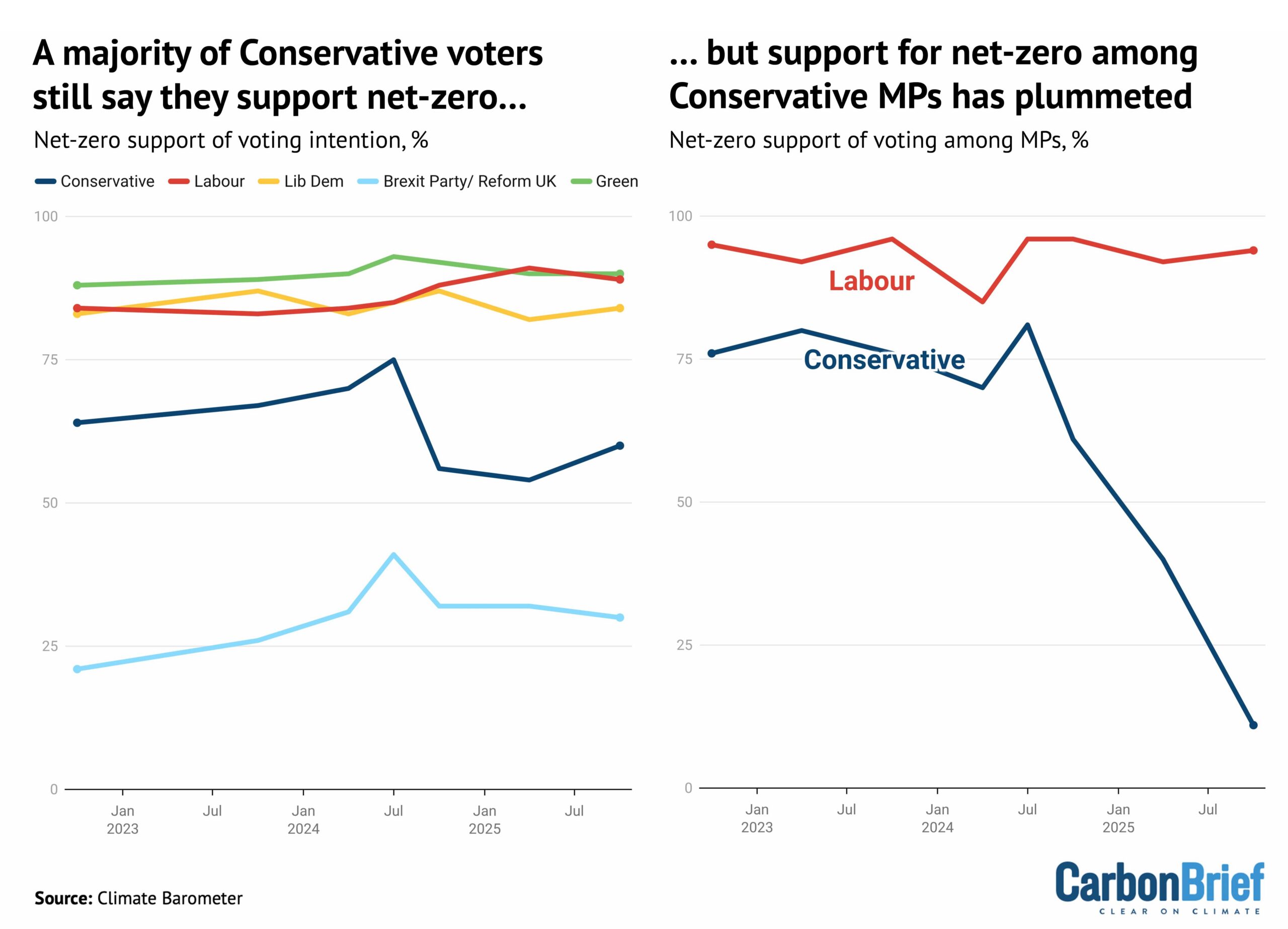
Dr Adam Corner, advisor to the Climate Barometer initiative that tracks public opinion on climate change, told Carbon Brief that those who currently plan to vote Reform are the only segment who “tend to be more opposed to net-zero goals”. He said:
“Despite the rise in hostile media coverage and the collapse of the political consensus, we find that public support for the net-zero by 2050 target is plateauing – not plummeting.”
Reform, which rejects the scientific evidence on global warming and campaigns against net-zero, has been leading the polls for a year. (However, it was comfortably beaten by the Greens in yesterday’s Gorton and Denton byelection.)
Corner acknowledged that “some of the anti-net zero noise…[is] showing up in our data”, adding:
“We see rising concerns about the near-term costs of policies and an uptick in people [falsely] attributing high energy bills to climate initiatives.”
But Akehurst said that, rather than a big fall in public support, there had been a drop in the “salience” of climate action:
“So many other issues [are] competing for their attention.”
UK newspapers published more editorials opposing climate action than supporting it for the first time on record in 2025, according to Carbon Brief analysis.
Global ‘greenlash’?
All of this sits against a challenging global backdrop, in which US president Donald Trump has been repeating climate-sceptic talking points and rolling back related policy.
At the same time, prominent figures have been calling for a change in climate strategy, sold variously as a “reset”, a “pivot”, as “realism”, or as “pragmatism”.
Genovese said that “far-right leaders have succeeded in the past 10 years in capturing net-zero as a poster child of things they are ‘fighting against’”.
She added that “much of this is fodder for conservative media and this whole ecosystem is essentially driving what we call the ‘greenlash’”.
Corner said the “disconnect” between elite views and the wider public “can create problems” – for example, “MPs consistently underestimate support for renewables”. He added:
“There is clearly a risk that the public starts to disengage too, if not enough positive voices are countering the negative ones.”
Watch, read, listen
TRUMP’S ‘PETROSTATE’: The US is becoming a “petrostate” that will be “sicker and poorer”, wrote Financial Times associate editor Rana Forohaar.
RHETORIC VS REALITY: Despite a “political mood [that] has darkened”, there is “more green stuff being installed than ever”, said New York Times columnist David Wallace-Wells.
CHINA’S ‘REVOLUTION’: The BBC’s Climate Question podcast reported from China on the “green energy revolution” taking place in the country.
Coming up
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean, Brasília
- 3 March: UK spring statement
- 4-11 March: China’s “two sessions”
- 5 March: Nepal elections
Pick of the jobs
- The Guardian, senior reporter, climate justice | Salary: $123,000-$135,000. Location: New York or Washington DC
- China-Global South Project, non-resident fellow, climate change | Salary: Up to $1,000 a month. Location: Remote
- University of East Anglia, PhD in mobilising community-based climate action through co-designed sports and wellbeing interventions | Salary: Stipend (unknown amount). Location: Norwich, UK
- TABLE and the University of São Paulo, Brazil, postdoctoral researcher in food system narratives | Salary: Unknown. Location: Pirassununga, Brazil
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 27 February 2026: Trump’s fossil-fuel talk | Modi-Lula rare-earth pact | Is there a UK ‘greenlash’? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding
The Lincolnshire constituency held by Richard Tice, the climate-sceptic deputy leader of the hard-right Reform party, has been pledged at least £55m in government funding for flood defences since 2024.
This investment in Boston and Skegness is the second-largest sum for a single constituency from a £1.4bn flood-defence fund for England, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
Flooding is becoming more likely and more extreme in the UK due to climate change.
Yet, for years, governments have failed to spend enough on flood defences to protect people, properties and infrastructure.
The £1.4bn fund is part of the current Labour government’s wider pledge to invest a “record” £7.9bn over a decade on protecting hundreds of thousands of homes and businesses from flooding.
As MP for one of England’s most flood-prone regions, Tice has called for more investment in flood defences, stating that “we cannot afford to ‘surrender the fens’ to the sea”.
He is also one of Reform’s most vocal opponents of climate action and what he calls “net stupid zero”. He denies the scientific consensus on climate change and has claimed, falsely and without evidence, that scientists are “lying”.
Flood defences
Last year, the government said it would invest £2.65bn on flood and coastal erosion risk management (FCERM) schemes in England between April 2024 and March 2026.
This money was intended to protect 66,500 properties from flooding. It is part of a decade-long Labour government plan to spend more than £7.9bn on flood defences.
There has been a consistent shortfall in maintaining England’s flood defences, with the Environment Agency expecting to protect fewer properties by 2027 than it had initially planned.
The Climate Change Committee (CCC) has attributed this to rising costs, backlogs from previous governments and a lack of capacity. It also points to the strain from “more frequent and severe” weather events, such as storms in recent years that have been amplified by climate change.
However, the CCC also said last year that, if the 2024-26 spending programme is delivered, it would be “slightly closer to the track” of the Environment Agency targets out to 2027.
The government has released constituency-level data on which schemes in England it plans to fund, covering £1.4bn of the 2024-26 investment. The other half of the FCERM spending covers additional measures, from repairing existing defences to advising local authorities.
The map below shows the distribution of spending on FCERM schemes in England over the past two years, highlighting the constituency of Richard Tice.
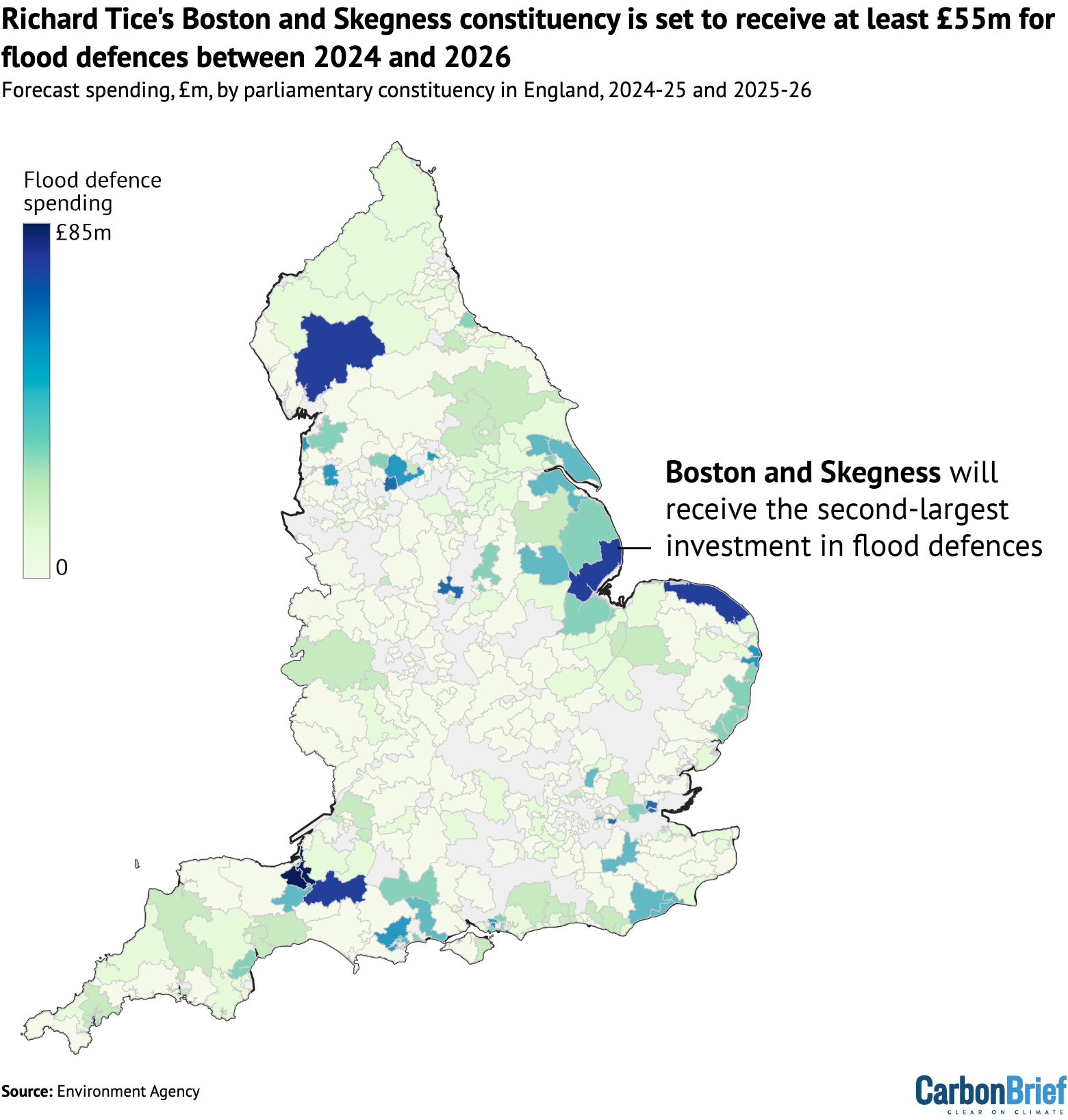
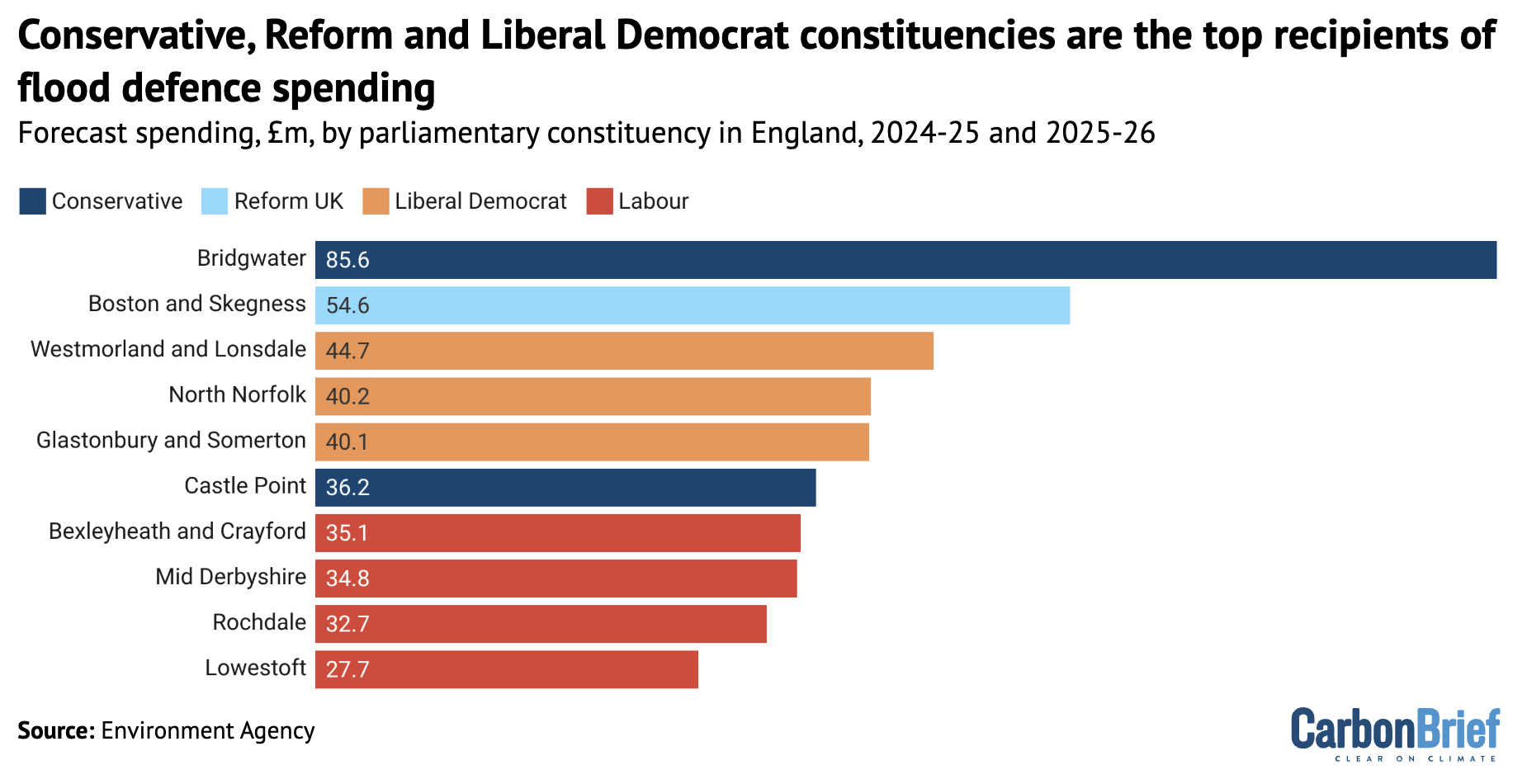
By far the largest sum of money – £85.6m in total – has been committed to a tidal barrier and various other defences in the Somerset constituency of Bridgwater, the seat of Conservative MP Ashley Fox.
Over the first months of 2026, the south-west region has faced significant flooding and Fox has called for more support from the government, citing “climate patterns shifting and rainfall intensifying”.
He has also backed his party’s position that “the 2050 net-zero target is impossible” and called for more fossil-fuel extraction in the North Sea.
Tice’s east-coast constituency of Boston and Skegness, which is highly vulnerable to flooding from both rivers and the sea, is set to receive £55m. Among the supported projects are beach defences from Saltfleet to Gibraltar Point and upgrades to pumping stations.
Overall, Boston and Skegness has the second-largest portion of flood-defence funding, as the chart below shows. Constituencies with Conservative and Liberal Democrat MPs occupied the other top positions.
Overall, despite Labour MPs occupying 347 out of England’s 543 constituencies – nearly two-thirds of the total – more than half of the flood-defence funding was distributed to constituencies with non-Labour MPs. This reflects the flood risk in coastal and rural areas that are not traditional Labour strongholds.
Reform funding
While Reform has just eight MPs, representing 1% of the population, its constituencies have been assigned 4% of the flood-defence funding for England.
Nearly all of this money was for Tice’s constituency, although party leader Nigel Farage’s coastal Clacton seat in Kent received £2m.
Reform UK is committed to “scrapping net-zero” and its leadership has expressed firmly climate-sceptic views.
Much has been made of the disconnect between the party’s climate policies and the threat climate change poses to its voters. Various analyses have shown the flood risk in Reform-dominated areas, particularly Lincolnshire.
Tice has rejected climate science, advocated for fossil-fuel production and criticised Environment Agency flood-defence activities. Yet, he has also called for more investment in flood defences, stating that “we cannot afford to ‘surrender the fens’ to the sea”.
This may reflect Tice’s broader approach to climate change. In a 2024 interview with LBC, he said:
“Where you’ve got concerns about sea level defences and sea level rise, guess what? A bit of steel, a bit of cement, some aggregate…and you build some concrete sea level defences. That’s how you deal with rising sea levels.”
While climate adaptation is viewed as vital in a warming world, there are limits on how much societies can adapt and adaptation costs will continue to increase as emissions rise.
The post Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits