Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Congress passes Trump’s ‘megabill’
TAX CREDITS CRUSHED: A major budget bill passed by US congress this week is “poised to remake American energy by slashing tax breaks for wind and solar power and electric cars”, reported the New York Times. The legislation, which was “muscled” through by Republicans, “provides a boost to fossil fuels and dismantles many of the biggest actions the federal government has ever taken to fight climate change”, the newspaper said.
‘CRACKDOWN’: The version of the bill approved by the Senate on Tuesday included “compromise language” that gave wind and solar projects one year to begin construction to claim current tax credits, noted Politico. “Hard-line” Republicans in the House of Representatives told the outlet that they backed the bill only after receiving assurances from Donald Trump that he would use executive action to further “constrict” wind and solar.
LAB LIABILITY: The bill, which is expected to be signed by Trump today, also “seeks to defund” multiple climate labs, according to CNN. This includes the Mauno Lao laboratory in Hawaii, where measurements since 1958 have produced the iconic “Keeling Curve” of rising atmospheric CO2, the outlet noted. See below for more on the emissions impact of Trump’s bill.
Record-breaking heatwave ‘grips’ Europe
RED ALERTS: At least eight people died across Europe as a heatwave gripped much of the continent, reported Reuters, “triggering health alerts and forest fires and forcing the closure of a nuclear reactor at a Swiss power plant”. The New York Times quoted UN secretary general António Guterres, who said: “Extreme heat is no longer a rare event – it has become the new normal.”
RECORD-BREAKING: Both Spain and England had their hottest June on record, noted BBC News, with the Spanish weather service saying the average of 23.6C “pulverised records”. The outlet added that France registered its second-hottest June, while the Guardian reported that Portugal hit a provisional record high for June of 46.6C.
FLASH FLOODS: Elsewhere, a record downpour in the central Chinese province of Hubei brought a month’s worth of rain in just 12 hours to the city of Xianfeng, reported Reuters. Authorities moved 18,000 people to safety, the newswire said. Flooding in India’s northern state of Himachal Pradesh left five people dead, reported the Hindustan Times.
Around the world
- ‘WATER[ED] DOWN’: The European Commission’s newly proposed target to cut the EU’s carbon emissions by 90% by 2040 has been criticised for allowing up to 3% of the goal to be met with international carbon credits, reported Carbon Brief.
- BRAZIL OIL BID: Brazil’s COP30 president-designate, André Corrêa do Lago, has “played down concerns” on Brazil’s oil expansion after a new analysis found the nation will drive a surge in new production by 2030, reported the Financial Times.
- ‘REPUTATIONAL RISK’: The nomination of an economist from the Saudi Aramco oil company as a coordinating lead author for an Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report has been denounced as “political capture”, reported Politico.
- FLIGHT FEE: A group of countries, including France, Kenya and Barbados, have pledged to tax private jets and premium-class flying in a bid to raise funds for climate action at a summit in Spain, Reuters reported. Climate Home News has all the key climate-finance takeaways from the event.
- ‘MAJOR SETBACK’: A £65m satellite launched last year to detect methane emissions from oil and gas production has been “lost in space”, reported BBC News.
£528m
The amount by which “climate aid” given by the UK government to developing countries was inflated through controversial changes to the way climate finance is now being designated, Carbon Brief analysis showed.
Latest climate research
- Sustained cuts to US military spending could result in annual energy savings by 2032 equivalent to the energy consumption of Slovenia, a study in PLOS Climate found.
- Using satellite data, a study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences revealed a marked increase in surface salinity across the Southern Ocean since 2015, coinciding with a “dramatic decline” in Antarctic sea ice.
- Research in Nature Cities highlighted the “disproportionate flood exposure” faced by urban slum populations in the global south, with one in three living on a floodplain.
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured

Trump’s dismantling of climate policy means the US will add an extra 7bn tonnes of emissions to the atmosphere from now until 2030, compared to meeting its former climate pledge under the Paris Agreement, according to new Carbon Brief analysis of modelling from Princeton University. The approval of Trump’s megabill repealing clean-energy tax credits, alongside a series of executive orders, means that US emissions are now set to drop to just 3% below current levels by 2030 – effectively flatlining – rather than falling 40% as required to hit the now-defunct target, according to the analysis.
Spotlight
Tipping points that worry scientists the most
This week, delegates at the Global Tipping Points 2025 conference in Exeter tell Carbon Brief which potential tipping “element” in the Earth system they are most worried about.
Prof Tim Lenton, founding director of the Global Systems Institute and chair in climate change and Earth system science at the University of Exeter:
“The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC, for sure. The consequences of crashing that would be devastating globally – and also for where I live in the UK. By our own calculation, we could have less than half the viable area for growing a couple of major staple crops, wheat and maize, worldwide. We would have a widespread water crisis. We could have collapses of the monsoons in West Africa and India that would displace hundreds of millions of people. It is hard to see that in anything other than a catastrophe.”
Prof Ricarda Winkelmann, founding director of the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology and professor of climate system analysis at the University of Potsdam:
“So I am thinking about this from a risk perspective – so both the likelihood as well as the impacts – and I think the answer depends on that. Because when it comes to the likelihood and the particular threshold – and we know about those – I’m mostly concerned about the Greenland and the West Antarctic ice sheets. This is because we know that, even at lower warming levels, they’re already at risk of transgressing tipping points in certain regions.
“But when it comes to the impacts and also the timescales over which those play out, there are other tipping elements that worry me most. In particular, regional tipping elements. So, if we think of the mountain glaciers, for instance, these impacts are already experienced right now and several mountain glaciers are undergoing these accelerated changes.”
Prof Gabi Hegerl, chair in climate system science in the school of geosciences at the University of Edinburgh:
“I am worried about all of them. But, for the immediate future, I am particularly worried about tipping points that involve the biosphere and humans due to breaching thresholds for heat or drought that then ripple into food availability, livelihood and ecosystems. The Earth system tipping points will do that, too, but maybe a little bit later. Examples are coral diebacks triggered by marine heatwaves, forest change and fires, and droughts threatening livelihoods and putting people on the move.
“I did a research project on the US dustbowl and the trigger was drought causing vegetation and crop dieback, then [leading to] extreme heat and dust storms in response – and migration, as memorialised in [the 1939 John Steinbeck novel] The Grapes of Wrath. And, now with warming, all droughts get supercharged.”
Prof Carlos Nobre, Brazilian scientist and meteorologist who spearheaded the multi-disciplinary, multinational large-scale biosphere-atmosphere experiment in the Amazon:
“The Amazon is a very serious tipping point, because [dieback] could release around 250bn tonnes of CO2 by 2100 – which will make it impossible to [limit global warming] at 1.5C. We could also lose the largest [host to] biodiversity on the planet, which would induce a tremendous, large number of epidemics and several pandemics. Also, of course, the Amazon forest controls aspects of the global climate. In South America, the climate is entirely controlled by the Amazon forest.”
Carbon Brief will publish further coverage of the Global Tipping Points conference next week.
Watch, read, listen
‘CLIMATE ACTION IS UNSTOPPABLE’: In a talk at the recent TED Countdown Summit 2025 in Nairobi, former US vice-president Al Gore explained why the narrative of “climate realism” is a “myth”.
PROTESTOR IN PRISON: A BBC Radio 4 Currently documentary followed the story of a “law-abiding Middle England mum”, who received a four-year prison sentence for a Just Stop Oil protest on the M25 motorway.
‘FROM THE GREEN TO THE UNSEEN’: In its L is for Labour YouTube show, the Migration Project asked what a “just transition” to electric vehicles would look like for the traditional automotive industry and its workers in India.
Coming up
- 6-7 July: 17th BRICS summit, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
- 8-11 July: AI For Good global summit 2025, Geneva, Switzerland
- 7-11 July: 47th Meeting of the Open-ended Working Group of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol, Bangkok, Thailand
Pick of the jobs
- Climate Policy Initiative, senior communications associate, climate finance | Salary: Unknown. Location: Cape Town, South Africa
- Global Action Plan, partnerships manager and campaigner | Salary: £36,000 and £36,000-£45,000, respectively. Location: London
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, principal manager, nature & climate finance | Salary: Unknown. Location: London
- Cheltenham Borough Council, climate and decarbonisation manager | Salary: £47,227-52,547. Location: Cheltenham, UK
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 4 July 2025: Trump ‘megabill’ guts clean energy; Europe’s record heat; Scientists discuss ‘most worrying’ tipping points appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 10 October 2025: Renewables power past coal; Legacy of UK’s Climate Change Act; Fukushima’s solar future
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Renewables overtake coal
‘HISTORIC FIRST’: Renewables have overtaken coal to become the world’s leading source of electricity for the first six months of this year in a “historic first”, BBC News said. The analysis, from the thinktank Ember, found the world generated “almost a third” more solar power in the first half of the year, compared with the same period in 2024, while wind power grew by “just over 7%,” reported the Guardian.
HEAVY LIFTING: According to the report, China and India were “largely responsible for the surge in renewables”, while the US and Europe “relied more heavily on fossil fuels,” the Guardian wrote. China built more renewables than every other country combined in the first half of this year, the newspaper added.
CONTINENTAL SHIFTS: A second report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicted a “surge” in global wind and solar capacity by 2030, but shaved 5% off its previous forecast, the Financial Times said. The IEA revealed that India is set to become the second-largest growth market for renewables after China, “with capacity expected to increase 2.5 times by 2030”, Down to Earth reported. The IEA also upped its forecast for renewables in the Middle East and north Africa by 23%, “helped by Saudi Arabia rolling out wind turbines and solar panels”, but halved the outlook for the US, the FT noted.
Around the world
- EV BOOM: Sales of electric and hybrid cars made up “more than half” of all new car registrations in the UK last month, a new record, according to data from the Society of Motor Manufacturers, reported BBC News.
- BANKING COLLAPSE: A global banking alliance launched by the UN to get banks to slash the carbon footprint of their loans and investments and help drive the transition to a net-zero economy by 2050 has collapsed after four years, Agence France-Press reported.
- CUTS, CUTS, CUTS: The Trump administration plans to cut nearly $24bn in funding for more than 600 climate projects across the US, according to documents reviewed by the Wall Street Journal.
- PEOPLE POWER: A farmer, a prison guard and a teacher were among those from the Dutch-Caribbean island Bonaire who appeared at the Hague on Tuesday to “accuse the Netherlands of not doing enough to protect them from the effects of climate change”, Politico reported.
400,000
The number of annual service days logged by the US National Guard responding to hurricanes, wildfires and other natural disasters over the past decade, according to a Pentagon report to Congress, Inside Climate News reported.
Latest climate research
- Politicians in the UK “overwhelmingly overestimate the time period humanity has left to bend the temperature curve”, according to a survey of 100 MPs | Nature Communications Earth and Environment
- Fire-driven degradation of the Amazon last year released nearly 800m tonnes of CO2 equivalent, surpassing emissions from deforestation and marking the “worst Amazon forest disturbance in over two decades” | Biogeosciences
- Some 43% of the 200 most damaging wildfires recorded over 1980-2023 occurred in the last decade | Science
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
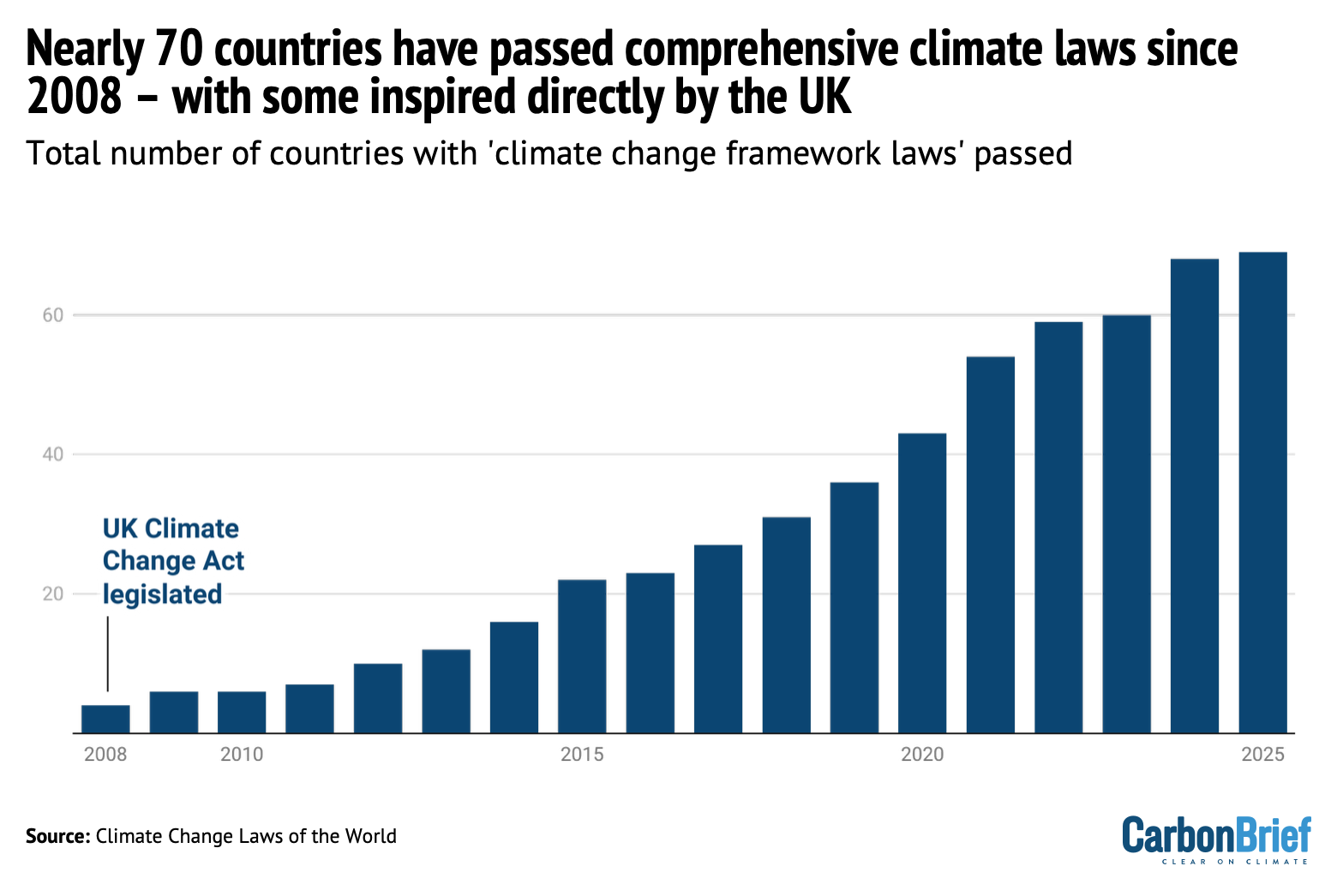
The UK’s Climate Change Act, landmark legislation that guides the nation’s response to climate change, is increasingly coming under attack from anti-net-zero right-leaning politicians. In a factcheck published this week, Carbon Brief explained how the UK’s Climate Change Act was among the first comprehensive national climate laws in the world and the first to include legally binding emissions targets. In total, 69 countries have now passed “framework” climate laws similar to the UK’s Climate Change Act, with laws in New Zealand, Canada and Nigeria among those explicitly based on the UK model. This is up from just four when the act was legislated in 2008. Of these, 14 are explicitly titled the “Climate Change Act”.
Spotlight
Fukushima’s solar future
This week, Carbon Brief examines how Fukushima helped to recover from nuclear disaster by building solar farms on contaminated farmland.
On 11 March 2011, an earthquake off the pacific coast of Japan caused 15m-tall waves to crash into the eastern region of Tōhoku, killing 19,500 people and injuring a further 6,000.
In the aftermath, flooding at the Fukushima Daichi nuclear power plant caused cooling systems to fail, leaching radioactive contaminants into the soil and leading to a major nuclear incident.
Some 1,200km2 around the site was restricted and up to 100,000 people were evacuated – in some cases forever.
In the years following, Japan entered a fraught debate about nuclear energy.
In 2010, nuclear power provided 25% of Japan’s electricity, but, in the years following the disaster, its 54 nuclear reactors were taken offline.
Successive governments have fought over reintroducing nuclear power. Today, some 14 reactors are back online, 27 have been permanently closed and another 19 remain suspended. (Japan’s newly-elected prime minister Sanae Takaichi has promised to make nuclear central to her energy strategy.)
Against this backdrop, Fukushima – a prefecture home to 1.8 million people – has emerged as a surprise leader in the renewables race.
In 2014, the Fukushima Renewable Energy Institute (FREA) opened with the twin goals of promoting research and development into renewable energy, while “making a contribution to industrial clusters and reconstruction”.
That same year, the prefecture declared a target of 100% renewable power by 2040.
Contaminated land
“A lot of these communities, I know, were looking for ways to revitalise their economy,” said Dr Jennifer Sklarew, assistant professor of energy and sustainability at George Mason University and author of “Building Resilient Energy Systems: Lessons from Japan”.
Once evacuation orders were lifted, however, residents in many parts of Fukushima were faced with a dilemma, explained Skarlew:
“Since that area was largely agricultural, and the agriculture was facing challenges due to stigma, and also due to the soil being removed [as part of the decontamination efforts], they had to find something else.”
One solution came in the form of rent, paid to farmers by companies, to use their land as solar farms.
Michiyo Miyamoto, energy finance specialist at the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis, told Carbon Brief:
“The [Fukushima] prefecture mapped suitable sites early and conducted systematic consultations with residents and agricultural groups before projects were proposed. This upfront process reduced land-use conflicts, shortened permitting timelines and gave developers clarity.”
As a result, large-scale solar capacity in Fukushima increased to more than 1,300 megawatts (MW) from 2012 to 2023, according to Miyamoto. Moreover, installed renewable capacity now exceeds local demand, meaning the region can run entirely on clean power when conditions are favourable, Miyamoto said.
Today, aerial pictures of Fukushima reveal how solar panels have proliferated on farmland that was contaminated in the nuclear disaster.
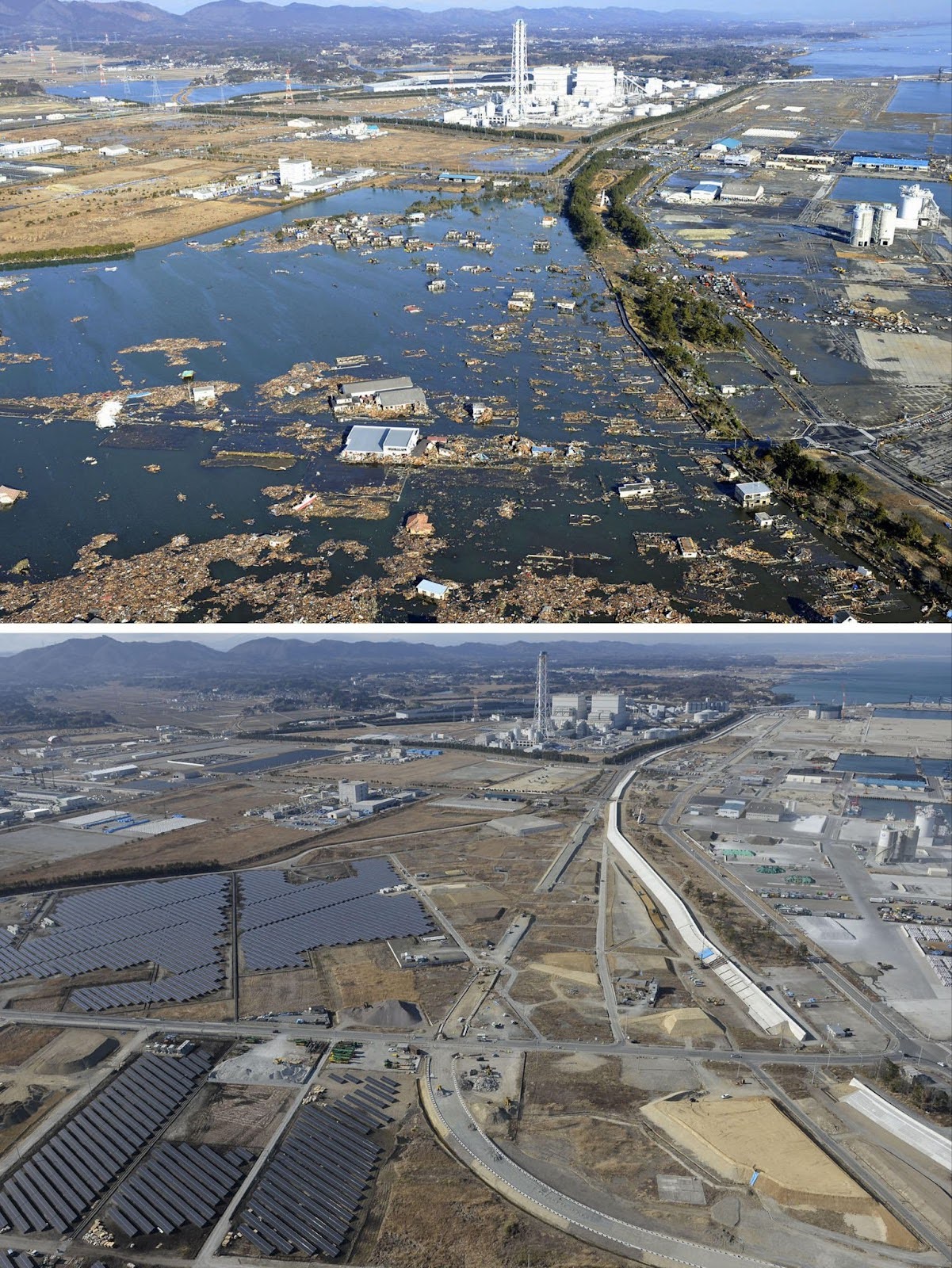

Charging on
Last year, 60% of Fukushima’s electricity was met by renewables, up from 22% in 2011. (The country as a whole still lags behind at 27%.)
And that is set to grow after Japan’s largest onshore windfarm started operations earlier this year in Abukuma, Fukushima, with a capacity of 147MW.
The growth of solar and wind means that Fukushima is already “ahead of schedule” for its 2040 target of 100% renewable power, said Miyamoto:
“The result is a credible pathway from recovery to leadership, with policy, infrastructure and targets working in concert.”
Watch, read, listen
OVERSHOOT: The Strategic Climate Risks Initiative, in partnership with Planet B Productions, has released a four-part podcast series exploring what will happen if global warming exceeds 1.5C.
DRONE WARFARE: On Substack, veteran climate campaigner and author Bill McKibben considered the resilience of solar power amid modern warfare.
CLIMATE AND EMPIRE: For Black history month, the Energy Revolution podcast looked at how “race and the legacies of empire continue to impact the energy transition”.
Coming up
- 12 October: presidential elections, Cameroon
- 13-14 October: Pre-COP, Brasilia, Brazil
- 13-18 October: World Bank Group/IMF annual meetings, Washington DC
- 14-17 October: 2nd extraordinary session of the Marine Environment Protection Committee at the International Maritime Organisation, London
- 15-16 October: Circle of Finance Ministers report
Pick of the jobs
- Buckinghamshire Council, principal climate change officer | Salary: £49,354-£51,759. Location: Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire
- Sustainable NI, sustainable business lead | Salary: £60,000. Location: Belfast, Northern Ireland
- Dialogue Earth, South Asia managing editor | Salary: £1,875 per month. Location: South Asia
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 10 October 2025: Renewables power past coal; Legacy of UK’s Climate Change Act; Fukushima’s solar future appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Guest post: How Caribbean states are shifting climate legislation
The Caribbean region is among the most vulnerable to climate change, despite historically contributing less than half of one percent of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Rising sea levels, extreme heat and more frequent and intense storms – such as the 2024 Hurricane Beryl, which made landfall in Grenada – pose urgent and growing threats to the small island states, coastal nations and overseas territories that comprise the Caribbean region.
With global progress to address climate change still too slow, Caribbean countries are taking matters into their own hands by enacting more robust legislation to help protect against climate risks.
In a new study published in the Carbon and Climate Law Review, we identified 78 climate laws and legally binding decrees across 16 Caribbean states, as well as two constitutional references to climate change and a growing recognition of the right to a healthy environment.
Our analysis suggests that, together, these developments are not only enhancing resilience, but also positioning Caribbean states as influential actors in the global climate arena.
Caribbean climate laws on the rise
Climate governance in the Caribbean has expanded significantly in recent years. In the past decade, countries such as Cuba and the Dominican Republic have embedded climate obligations and programmatic guidelines into their national constitutions.
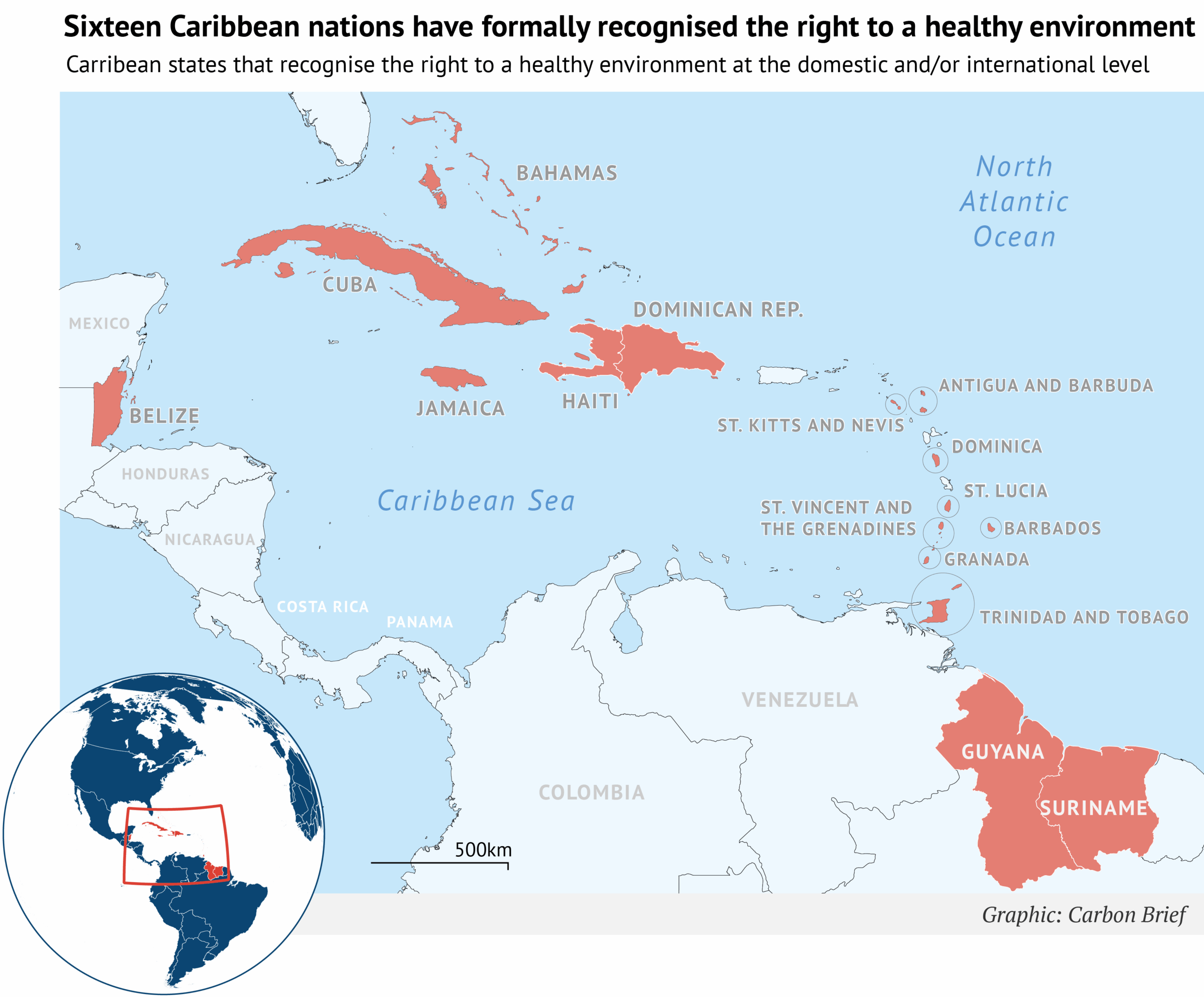
At the same time, legislative recognition of the human right to a healthy environment is gaining momentum across the region. Six Caribbean nations now affirm the right in their constitutions, while 15 have recognised it through international instruments, such as the UN Council, UN Assembly and the Escazu Agreement, as shown in the figure below.
More recently, there has been a notable rise in targeted, sector-specific climate frameworks that go beyond broader environmental statutes.
Saint Lucia stands out as the only country with a climate framework law, or a comprehensive national law that outlines long-term climate strategies across multiple domains. Meanwhile, several other Caribbean governments have adopted climate-specific laws that focus on individual sectors, such as energy, migration and disaster management.
According to our analysis, more than a quarter of climate-relevant legislation in the region – comprising 21 laws and legally binding decrees – now has an explicit focus on climate change, as illustrated in the chart below.
Our research suggests that this represents an ongoing shift in legislative focus, reflecting changes in how climate legislation is being structured in one of the world’s most climate-vulnerable regions.
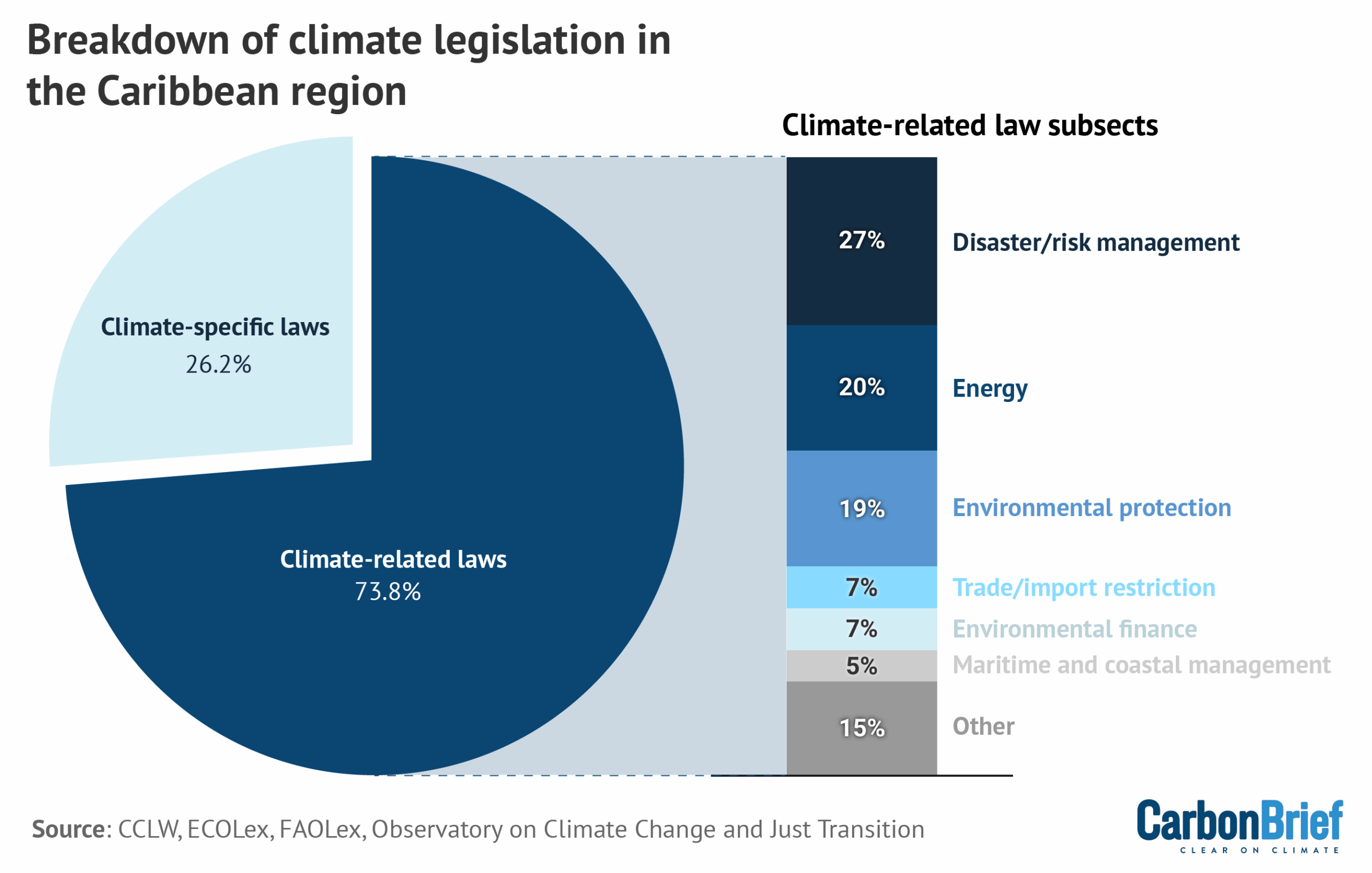
Caribbean nations are also advancing legal reforms to structure and institutionalise climate finance and market mechanisms directly into domestic law, aligned with Article 6.2 of the Paris Agreement.
For example, the Bahamas has introduced provisions for carbon credit trading, while Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados and Grenada have established national climate financing mechanisms to support mitigation and adaptation efforts.
Some states, including Belize and Saint Kitts and Nevis, have incorporated regional bodies such as the Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre – the climate arm of the intergovernmental Caribbean community organisation CARICOM – into national frameworks. This indicates an increasing alignment between regional cooperation and domestic law.
In addition to the influx of regulations specifically addressing climate change, Caribbean nations are also legislating broader environmental issues, which, in turn, could provide increased resilience from climate impacts and risks, as shown in the graph above.
Key trends in these types of climate-related laws include the expansion of disaster risk management governance, which addresses national preparedness for climate-induced weather events or related catastrophes. Likewise, energy law is an increasingly prominent focus, with countries including Antigua and Barbuda and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines integrating renewable energy and energy efficiency goals into national climate governance.
More broadly, many Caribbean nations have adopted wide-ranging and comprehensive environmental laws, many of which were developed in alignment with existing climate commitments. In combination, these legal developments reflect a dynamic and evolving climate governance landscape across the region.
Proactive vs reactive approaches
Despite general alignment with these broader regional trends, our research reveals distinct developmental pathways shaping domestic climate regulation.
In the eastern Caribbean, for example, we saw both proactive, long-term planning strategies and reactive, post-disaster reforms.
Saint Lucia’s multifaceted approach to climate resilience evolved steadily over the course of more than a decade. During this time, the country developed numerous adaptation plans, strengthened cross-sectoral coordination and engaged in institutional climate reforms in areas such as energy, tourism, finance and development.
More recently, the passage of Saint Lucia’s Climate Change Act in 2024 marked a milestone in climate governance, by giving legal force to the country’s obligations under the UNFCCC, the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement – making Saint Lucia one of the few small island states to incorporate global climate commitments into domestic law.
Our research indicates that this strategy has not only positioned the country as a more climate-resilient nation, but also solidified its access to international climate financing.
In contrast, Dominica’s efforts evolved more rapidly in the aftermath of Hurricane Maria in 2017, which destroyed over 200% of the country’s GDP. The storm’s impacts were felt across the country and hit particularly hard for the Kalinago people – the Caribbean’s last Indigenous community – highlighting the role of socioeconomic disparities in shaping climate vulnerability and resilience.
In response, the government passed the Climate Resilience Act, creating the temporary Climate Resilience Execution Agency for Dominica (CREAD).
Beyond establishing an exclusively climate-focused institution, the act aimed to embed resilience into governance by mandating the participation of vulnerable communities – including Indigenous peoples, women, older people and people with disabilities – in shaping and monitoring climate resilience projects.

As noted in a recent statement by the UN special rapporteur on Climate Change, Dr Elisa Morgera, these frameworks underscore the government’s ambition to become the world’s first “climate-resilient nation.”
Although challenges persist, Dominica’s efforts demonstrate how post-disaster urgency can drive institutional change, including the integration of rights and resilience into climate governance.
Uneven progress and structural gaps
Despite significant progress, our research shows that several key opportunities for climate governance across the Caribbean continue to exist, which could enable improvements in both resilience and long-term ambition.
The region’s legal landscape remains somewhat heterogeneous. While Saint Lucia has enacted a comprehensive climate framework law, the rest of the region lacks similar blanket legislation. This includes some states that entirely lack climate-specific laws, instead relying on related laws and frameworks to regulate and respond to climate-related risks.
Other nations have yet to adopt explicit disaster-risk management frameworks, leaving Caribbean populations vulnerable before, during and after climate emergencies. Most have yet to enshrine the right to a healthy environment at the national level.
Our research suggests that outdated legal frameworks are further limiting progress in addressing current climate risks. Because many of the longer-standing environmental laws in the region were adopted well before climate policy became a mainstream concern, some fail to address the nature, frequency and intensity of modern climate challenges, such as sea-level rise, tropical storms, wildfires, floods, droughts and other impacts.
More broadly, many Caribbean climate laws include limited integration of gender equity, Indigenous rights and social justice. As Caribbean nations such as Grenada and the Dominican Republic begin to link climate resilience with these issues, the region has an opportunity to lead by example.
Ultimately, capacity and resource constraints persist as significant barriers to implementation and adaptation.
The Caribbean region faces debt that exacerbates ongoing development challenges, a burden made heavier by the repeated economic shocks of climate-related disasters. Along with regional debt-for-resilience schemes, increased funding from high-emitting countries to support adaptation measures in climate-vulnerable nations – as endorsed under the Paris Agreement – is likely to be critical to ensuring the region’s climate laws can be executed effectively.
Global implications of Caribbean climate law
Our research suggests that Caribbean countries are outpacing other regions in terms of the scope and ambition of their climate laws. This legislation has the potential to serve as a model for climate-vulnerable nations worldwide.
Continuing efforts in the region show that legal frameworks in the field can not only drive resilience, embed rights and strengthen claims to international finance, but also highlight how regional cooperation and diplomacy can enhance global influence.
These findings demonstrate that innovation in climate law need not wait for action from major emitters, but can instead be led by those on the front lines of climate change.
The post Guest post: How Caribbean states are shifting climate legislation appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Guest post: How Caribbean states are shifting climate legislation
Greenhouse Gases
IEA: Renewables have cut fossil-fuel imports for more than 100 countries
More than 100 countries have cut their dependence on fossil-fuel imports and saved hundreds of billions of dollars by continuing to invest in renewables, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
It says nations such as the UK, Germany and Chile have reduced their need for imported coal and gas by around a third since 2010, mainly by building wind and solar power.
Denmark has cut its reliance on fossil-fuel imports by nearly half over the same period.
Renewable expansion allowed these nations to collectively avoid importing 700m tonnes of coal and 400bn cubic metres of gas in 2023, equivalent to around 10% of global consumption.
In doing so, the fuel-importing countries saved more than $1.3tn between 2010 and 2023 that would otherwise have been spent on fossil fuels from overseas.
Reduced reliance
The IEA’s Renewables 2025 report quantifies the benefits of renewable-energy deployment for electricity systems in fossil fuel-importing nations.
It compares recent trends in renewable expansion to an alternative “low renewable-energy source” scenario, in which this growth did not take place.
In this counterfactual, fuel-importing countries stopped building wind, solar and other non-hydropower renewable-energy projects after 2010.
In reality, the world added around 2,500 gigawatts (GW) of such projects between 2010 and 2023, according to the IEA, more than the combined electricity generating capacity of the EU and US in 2023, from all sources. Roughly 80% of this new renewable capacity was built in nations that rely on coal and gas imports to generate electricity.
The chart below shows how 31 of these countries have substantially cut their dependence on imported fossil fuels over the 13-year period, as a result of expanding their wind, solar and other renewable energy supplies. All of these countries are net importers of coal and gas.

In total, the IEA identified 107 countries that had reduced their dependence on fossil fuel imports for electricity generation, to some extent due to the deployment of renewables other than hydropower.
Of these, 38 had cut their reliance on electricity from imported coal and gas by more than 10 percentage points and eight had seen that share drop by more than 30 percentage points.
Security and resilience
The IEA stresses that renewables “inherently strengthen energy supply security”, because they generate electricity domestically, while also “improving…economic resilience” in fossil-fuel importer countries.
This is particularly true for countries with low or dwindling domestic energy resources.
The agency cites the energy crisis exacerbated by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which exposed EU importers to spiralling fossil-fuel prices.
Bulgaria, Romania and Finland – which have historically depended on Russian gas for electricity generation – have all brought their import reliance close to zero in recent years by building renewables.
In the UK, where there has been mounting opposition to renewables from right-wing political parties, the IEA says reliance on electricity generated with imported fossil fuels has dropped from 45% to under 25% in a decade, thanks primarily to the growth of wind and solar power.
Without these technologies, the UK would now be needing to import fossil fuels to supply nearly 60% of its electricity, the IEA says.
Other major economies, notably China and the EU, would also have had to rely on a growing share of coal and gas from overseas, if they had not expanded renewables.
As well as increasing the need for fossil-fuel imports from other countries, switching renewables for fossil fuels would require significantly higher energy usage “due to [fossil fuels’] lower conversion efficiencies”, the IEA notes. Each gigawatt-hour (GWh) of renewable power produced has avoided the need for 2-3GWh of fossil fuels, it explains.
Finally, the IEA points out that spending on renewables rather than imported fossil fuels keeps more investment in domestic economies and supports local jobs.
The post IEA: Renewables have cut fossil-fuel imports for more than 100 countries appeared first on Carbon Brief.
IEA: Renewables have cut fossil-fuel imports for more than 100 countries
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-
Climate Change2 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Greenhouse Gases1 year ago
Greenhouse Gases1 year ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Greenhouse Gases2 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Climate Change1 year ago
Climate Change1 year ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Renewable Energy3 months ago
US Grid Strain, Possible Allete Sale