Wind Energy
Introduction Largest Wind Farm in the world
What is Wind Farm
A wind farm is a collection of wind turbines that are installed in a specific location to generate electricity from wind energy.
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy by using blades to capture the wind and spin a rotor, which turns a generator to produce electricity. Wind farms are typically located in areas with strong and consistent wind patterns, such as coastal areas, hilltops, or open plains.
Wind farms can range in size from a few turbines to hundreds of turbines, and they can generate enough electricity to power a small town or a large city. Wind energy is a renewable and clean source of energy, which means that it does not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants that are harmful to the environment. As a result, wind farms are becoming increasingly popular renewable energy as a way to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
How wind farm works?
Wind farms generate electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind to turn turbines, which in turn generate electricity through a generator.
The basic components of a wind turbine include:
Rotor blades: These are the long, aerodynamic blades that capture the wind and start to turn when wind hits them.
Nacelle: This is the housing that sits atop the tower and contains the gearbox, generator, and other key components.
Tower: This is the tall structure that supports the rotor blades and nacelle.
Control system: This system monitors wind speed and direction and controls the turbine’s yaw system, which turns the nacelle and rotor to face the wind.
Electrical equipment: This includes transformers, switchgear, and power cables, which transmit the electricity generated by the turbine to the power grid.
As the wind blows, it spins the rotor blades, which are connected to the generator in the nacelle. As the rotor blades turn, the generator produces electricity, which is then sent to the power grid. The electricity generated by each turbine is relatively small, but when many turbines are combined in a wind farm, the amount of electricity generated can be significant.
The efficiency of a wind turbine depends on several factors, including the wind speed, the size and design of the rotor blades, and the altitude of the turbine. The optimal wind speed for generating electricity is between 12 and 25 miles per hour.
Benefits of a wind farm
Wind farms have several benefits, including:
Renewable and Clean Energy: Wind energy is a renewable source of energy that does not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants. Wind farms generate clean electricity, which can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Energy Security and Independence: Wind energy is a domestic source of energy that can help reduce dependence on imported energy sources. Wind farms can improve energy security and independence by providing a reliable source of electricity.
Job Creation and Economic Development: Wind farms can create jobs and stimulate economic development in rural areas. The construction and operation of wind farms require skilled workers, and wind energy can provide a new source of income for landowners.
Low Cost: Wind energy has become increasingly cost-competitive with traditional sources of electricity, such as coal and natural gas. As a result, wind farms can provide low-cost electricity to consumers.
Flexibility: Wind farms can be built in a range of sizes, from small-scale projects to large utility-scale projects. Wind energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar energy, to provide a more reliable and flexible source of electricity.
Reduced Carbon Emissions: Wind farms can help reduce carbon emissions by displacing electricity generated from fossil fuels. This can help mitigate climate change and improve air quality.
Wind farms can provide a range of environmental, economic, and social benefits to communities and society as a whole.

20 Largest Wind Farm in the world
The development of renewable energy sources has become a crucial aspect of combating climate change and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. Wind power is a rapidly growing sector, and the 20 largest wind farms in the world are playing a significant role in generating clean and sustainable energy.
These wind farms, located across different countries and continents, collectively have a massive capacity to generate power, with some producing enough electricity to power entire cities. They not only help reduce carbon emissions but also create job opportunities and boost local economies.
As we continue to transition towards a greener and more sustainable future, it is crucial to invest in the development of renewable energy sources such as wind power.
The 20 largest wind farms in the world are a testament to the potential of this sector and serve as an inspiration for future projects.
22,500 MW – State Grid Corporation of China
Gansu Wind Farm Spesification
The Gansu Wind Farm is one of the largest wind power projects in the world, located in Jiuquan, Gansu province, China. The wind farm consists of several clusters of turbines spread out across an area of over 70,000 hectares (173,000 acres) of desert terrain. The farm was built in several phases, with construction starting in 2004 and continuing through 2019.
The Gansu Wind Farm has a total installed capacity of 20,000 MW, generated by over 7,000 wind turbines. The turbines are manufactured by a variety of companies including Goldwind, Vestas, and Sinovel, among others. The turbines range in size from 850 kW to 6 MW, with rotor diameters ranging from 52 to 135 meters.
The wind farm is operated by several different companies, including China Guodian Corporation, China Datang Corporation, and China Huadian Corporation, among others. Together, these companies are responsible for maintaining the turbines and ensuring that the wind farm operates at maximum efficiency.
The Gansu Wind Farm plays an important role in China’s efforts to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and increase its use of renewable energy sources. The project has helped China to become the world’s leading producer of wind power, and has helped to reduce the country’s greenhouse gas emissions. The wind farm also provides a significant source of employment for people in the region, with over 20,000 people estimated to be employed in the wind power industry in Gansu province alone.
2. Jiuquan Wind Power Base, China
20,000 MW – China Guodian Corporation and China Three Gorges Corporation
Jiuquan Wind Power Base, China – spesification
Jiuquan Wind Power Base is one of the largest wind farms in the world, located in Jiuquan, in the Gansu province of China. Here are some specifications of the Jiuquan Wind Power Base:
Total capacity: 20,000 MW
Number of turbines: Over 7,000
Area covered: Approximately 43,000 square kilometers
Investment: Approximately 120 billion yuan (US$18.5 billion)
Annual power generation: Over 40 TWh (terawatt hours)
Carbon dioxide reduction: Over 16 million tons per year
The Jiuquan Wind Power Base is operated by the State Grid Corporation of China and was developed in multiple phases. Construction on the wind farm started in 2006 and was completed in 2020, making it one of the most recent and largest wind power bases in China. The Jiuquan Wind Power Base plays a crucial role in China’s efforts to reduce its carbon emissions and promote the use of renewable energy.
3. Alta Wind Energy Center, USA
1,550 MW – Terra-Gen Power
Alta Wind Energy Center, USA – spesification
The Alta Wind Energy Center is located in the Tehachapi Pass, Kern County, California, USA. It is one of the largest wind farms in the world, with a total installed capacity of 1,548 megawatts (MW). Here are some specifications of the Alta Wind Energy Center:
Total installed capacity: 1,548 MW
Number of wind turbines: 586
Turbine capacity: Varies depending on the model, ranging from 1.5 MW to 3 MW
Owner and operator: Terra-Gen Power LLC
Year of commissioning: The wind farm was built in several phases between 2010 and 2013.
Power output: The wind farm generates enough electricity to power around 450,000 homes annually.
Environmental benefits: The wind farm displaces approximately 5.1 million metric tons of CO2 emissions each year, equivalent to removing over one million cars from the road.
Employment: The wind farm has created approximately 3,000 jobs during the construction phase and 35 permanent jobs for operation and maintenance.
Transmission: The wind farm is connected to the grid via Southern California Edison’s Tehachapi Renewable Transmission Project, which includes a network of new transmission lines and substations to transport the renewable energy from Tehachapi to major population centers in Southern California.
Investment: The total cost of the project was around $2.5 billion, making it one of the largest renewable energy investments in the United States.
781.5 MW – E.ON Climate and Renewables
Roscoe Wind Farm, USA – spesification
Roscoe Wind Farm is a wind power project located in the western part of Texas, USA. Here are some of its specifications:
Capacity: 781.5 MW
Turbines: 627 wind turbines
Turbine Manufacturer: General Electric (GE)
Total Area: Over 100,000 acres
Annual Production: Over 2 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year
CO2 Emissions Avoided: Over 1.5 million metric tons per year
Operator: E.ON Climate & Renewables
Construction Started: 2007
Cost: Approximately $1 billion USD
5. Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center, USA
735.5 MW – NextEra Energy Resources idAmerican Energy
Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center, USA – spesification
Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center is a wind farm located in Taylor and Nolan Counties, Texas, USA. It was the largest wind farm in the world at the time of its completion in 2006, and it is still one of the largest in the world. Here are some specifications of the Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center:
Number of turbines: 421
Total installed capacity: 735 MW
Owner and operator: NextEra Energy Resources
Commissioning date: 2006
Turbine height: 213 feet (65 meters)
Rotor diameter: 331 feet (101 meters)
Blade length: 139 feet (42 meters)
Annual electricity production: Approximately 2 billion kilowatt-hours, which is enough to power around 220,000 homes in the USA
Carbon dioxide emissions avoided annually: Approximately 1.2 million metric tons, which is equivalent to taking around 225,000 cars off the road
The Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center provides a significant amount of clean energy to the Texas power grid and helps to reduce carbon emissions.
6. Shepherds Flat Wind Farm, USA
845 MW – Caithness Energy
Shepherds Flat Wind Farm, USA – spesification
The Shepherds Flat Wind Farm is located in Oregon, USA and is one of the largest wind farms in the world. Here are some of its specifications:
Total capacity: 845 MW
Number of wind turbines: 338
Turbine manufacturer: General Electric
Turbine model: GE 2.5xl
Rotor diameter: 100 meters
Hub height: 80 meters
Blade length: 49 meters
Annual energy output: Approximately 2 billion kilowatt-hours, enough to power about 235,000 homes
Owner and operator: Caithness Energy
Construction of the Shepherds Flat Wind Farm began in 2009 and it began commercial operation in 2012. The wind farm generates clean energy that is delivered to Southern California Edison under a long-term power purchase agreement.
1050 MW – Statkraft and TrønderEnergi
Fosen Vind, Norway – spesification
Fosen Vind is a cluster of six wind farms located on the Fosen peninsula in Trøndelag, Norway. Here are some of its specifications:
Capacity: Fosen Vind has a total installed capacity of 1,056 MW, making it the largest onshore wind farm in Europe.
Number of turbines: There are a total of 278 turbines in Fosen Vind, spread across six different wind farms.
Height: The turbines at Fosen Vind have a hub height of 80 meters and a rotor diameter of 112 meters.
Cost: The total cost of the project was approximately 11 billion Norwegian krone (NOK).
Annual production: The wind farm produces around 3.6 TWh of renewable energy annually, enough to power around 170,000 Norwegian homes.
Ownership: Fosen Vind is jointly owned by the Norwegian power companies TrønderEnergi, Statkraft, and Nordic Wind Power DA.
630 MW – Ørsted, EON, and Masdar
London Array, UK – Spesification
The London Array is a large offshore wind farm located in the outer Thames Estuary in the UK. Here are some specifications:
Capacity: 175 turbines with a total capacity of 630 MW
Turbine type: Siemens SWT-3.6-120
Height: Each turbine has a height of 147 meters (482 feet) from sea level to blade tip
Distance from shore: Located approximately 20km (12.4 miles) off the coast of Kent, UK
Area covered: 100 km² (38.6 mi²)
Annual output: Approximately 2.5 TWh, enough to power around 500,000 UK homes
Commissioned: Fully operational in 2013
Owners: A consortium comprising of EON, DONG Energy, and Masdar.
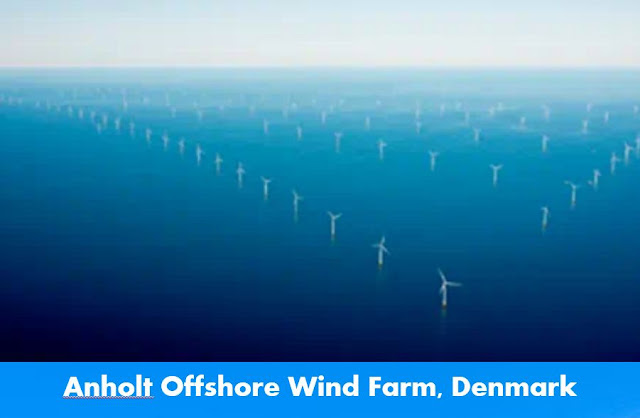
9. Anholt Offshore Wind Farm, Denmark
400 MW – DONG Energy
Anholt Offshore Wind Farm, Denmark – Spesification
The Anholt Offshore Wind Farm is a large-scale offshore wind farm located in the Kattegat Sea, about 20 km off the coast of Djursland, Denmark. It was commissioned in 2013 and is currently one of the largest offshore wind farms in the world. Here are some of its specifications:
The wind farm consists of 111 wind turbines, each with a capacity of 3.6 MW, for a total installed capacity of 400 MW.
The rotor diameter of each turbine is 120 meters, and the hub height is 80 meters above sea level. The blade length is 58.5 meters, making the total height of the turbine 198.5 meters.
The wind farm covers an area of approximately 88 square kilometers and is capable of producing enough electricity to power around 400,000 Danish households per year.
The project was developed by DONG Energy (now Ørsted), and cost around €1.2 billion to build.
The wind farm is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by around 900,000 tonnes per year, compared to traditional fossil fuel power plants.
The Anholt Offshore Wind Farm is connected to the Danish grid via a 150-kilometer-long submarine cable, which brings the electricity ashore at the town of Grenaa on the eastern coast of Jutland.
10. XEMC Darwind Hengtong, China
400 MW – XEMC Group
XEMC Darwind Hengtong, China – Spesification
XEMC Darwind Hengtong is an offshore wind farm located in Fujian province, China. Here are some specifications:
Total capacity: 30 MW
Number of turbines: 7
Turbine model: XD115/4.5MW
Rotor diameter: 115 meters
Hub height: 90 meters
Total height: 141 meters
Water depth: 23-33 meters
Distance to shore: 15 km
Year of commissioning: 2017
The XD115/4.5MW turbines are specifically designed for offshore wind farms and feature a permanent magnet direct drive system, which provides high energy efficiency and reliability. The wind farm is operated by XEMC Darwind, a Dutch wind turbine manufacturer, and Hengtong Group, a Chinese cable manufacturer.
11. Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm, UK
316.8 MW – Equinor, Statkraft, and Green Investment Group
Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm, UK – Spesification
The Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm is located in the North Sea, approximately 17-23 kilometers off the coast of Norfolk, UK. It became operational in 2012 and is owned by Equinor (40%), Green Investment Group (20%), and two utilities from Norway (Stadtwerke München and Agder Energi) with a 20% stake each. Here are some specifications of the wind farm:
Number of turbines: 88 Siemens Gamesa turbines
Turbine capacity: 3.6 MW each
Total capacity: 317 MW
Annual electricity production: Approximately 1.1 TWh, which is enough to power around 290,000 UK homes
Substations: Two offshore substations and one onshore substation
12. Macarthur Wind Farm, Australia
420 MW – AGL Energy and Meridian Energy
Macarthur Wind Farm, Australia – Spesification
The Macarthur Wind Farm is a large-scale wind energy project located in Victoria, Australia. Here are some of its specifications:
The wind farm has a capacity of 420 MW and is one of the largest in the southern hemisphere.
The project consists of 140 Vestas V112-3.0 MW wind turbines, each with a rotor diameter of 112 meters and a hub height of 85 meters.
The turbines are spread over an area of around 5,500 hectares and are connected to a 500 kV substation via a 70 km transmission line.
The Macarthur Wind Farm was developed by AGL Energy and Meridian Energy, with construction starting in 2010 and commercial operations commencing in 2013.
The wind farm generates around 1,500 GWh of clean electricity annually, enough to power around 220,000 Australian homes and offset approximately 1.7 million tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions each year.
13. Gemini Wind Farm, Netherlands
600 MW – Canadian Pension Plan Investment Board, Northland Power, and Siemens Financial Services
Gemini Wind Farm, Netherlands – Spesification
The Gemini Wind Farm is a large offshore wind farm located in the Dutch part of the North Sea, approximately 85 kilometers north of the coast of Groningen. Here are some specifications of the Gemini Wind Farm:
Capacity: 600 MW
Number of turbines: 150 Siemens SWT-4.0-130 turbines
Turbine height: 115 meters (hub height) and 190 meters (tip height)
Turbine rotor diameter: 130 meters
Total area: 68 square kilometers
Distance from shore: 85 kilometers
Developer: Gemini Wind Park B.V.
Owner: Northland Power (60%) and Siemens Financial Services (40%)
Construction started: 2015
Commissioned: 2017
Annual electricity production: Approximately 2.6 TWh, which is enough to power around 1.5 million households and reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 1.25 million tonnes per year.
Gemini Wind Farm is one of the largest offshore wind farms in the world and plays a significant role in the Netherlands’ transition towards renewable energy.
14. Muppandal Wind Farm, India
1500 MW – Suzlon Energy and China Power Investment Corporation
Muppandal Wind Farm, India – Spesification
The Muppandal Wind Farm is located in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It was commissioned in 2001 and has a total installed capacity of 1,500 MW, making it one of the largest wind farms in India. The wind farm comprises of over 3,000 wind turbines, which are spread across the Muppandal hill range and the neighbouring areas. The turbines have a hub height of 50-80 meters and a rotor diameter of 43-46 meters. The wind farm generates over 3 million units of electricity per day, which is supplied to the Tamil Nadu Electricity Board. The project was developed by the Tamil Nadu Electricity Board and has been instrumental in promoting the use of renewable energy in India.
15. Rosarito Wind Farm, Mexico
300 MW – Fuerza Eólica de San Matías
Rosarito Wind Farm, Mexico – Spesification
The Rosarito Wind Farm is a proposed wind energy project located in the municipality of Playas de Rosarito in the state of Baja California, Mexico. Here are some of its specifications:
Capacity: The wind farm is expected to have a capacity of 156 MW, generated by 39 wind turbines.
Turbines: The wind farm will use 39 wind turbines, each with a capacity of 4 MW.
Investment: The project is expected to require an investment of approximately $300 million USD.
Developer: The project is being developed by Eoliatec del Pacífico, a subsidiary of the French energy company Engie.
Electricity production: The wind farm is expected to generate approximately 565 GWh of electricity annually, which is enough to power around 220,000 homes in Mexico.
Carbon dioxide reduction: The Rosarito Wind Farm is expected to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 232,000 metric tons annually, which is equivalent to taking around 50,000 cars off the road.
16. Penonome Wind Farm, Panama
270 MW – InterEnergy Holdings and Actis
Penonome Wind Farm, Panama – Spesification
The Penonomé Wind Farm is a wind power project located in the Penonomé District, Coclé Province, Panama. It is considered the largest wind farm in Central America and the Caribbean. Here are some specifications:
Number of turbines: 220
Total capacity: 555 MW
Turbine manufacturer: General Electric
Turbine model: GE 2.5-116
Annual production: 1,600 GWh
Developer: InterEnergy Holdings
Commissioned: 2015
Investment: $450 million
CO2 savings per year: 400,000 tons
The Penonomé Wind Farm covers an area of approximately 42,000 hectares and is expected to generate around 7% of Panama’s electricity consumption. The wind farm has helped Panama to diversify its energy mix and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to the country’s goal of achieving 70% renewable energy generation by 2050.
17. Tarfaya Wind Farm, Morocco
300 MW – NAREVA Holding and Enel Green Power
Tarfaya Wind Farm, Morocco – Spesification
The Tarfaya Wind Farm is a large wind energy project located in the Tarfaya Province of Morocco. Here are some of its specifications:
The wind farm has a total installed capacity of 301 MW.
It consists of 131 wind turbines manufactured by Siemens Gamesa with a capacity of 2.3 MW each.
The wind turbines have a hub height of 80 meters and a rotor diameter of 108 meters.
The wind farm covers an area of 8,900 hectares (22,000 acres).
The project was developed by Moroccan utility company Nareva Holding in partnership with the French energy company Engie.
It started operations in 2014 and supplies electricity to over 1.5 million people in Morocco.
The project cost around $560 million and is expected to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 900,000 tons annually.
18. Rampion Offshore Wind Farm, UK
400 MW – EON, Green Investment Group, and Canadian Pension Plan Investment Board
Rampion Offshore Wind Farm, UK – Spesification
The Rampion Offshore Wind Farm is a wind farm located in the English Channel off the coast of Sussex, UK. Here are some specifications:
Total capacity: 400 MW
Number of turbines: 116
Turbine manufacturer: Siemens Gamesa
Turbine capacity: 3.45 MW each
Total project cost: £1.3 billion
Annual electricity generation: equivalent to the needs of around 350,000 homes
CO2 savings: equivalent to taking around 200,000 cars off the road
Owned by: E.ON (50.1%), UK Green Investment Rampion Ltd (25%), and Enbridge (24.9%)
Operational since: 2018
19. Ocotillo Wind Energy Facility
The Ocotillo Wind Energy Facility is a wind farm located in the Ocotillo area of Imperial County, California, United States.
Here are some of its specifications:
Capacity: 265 MW
Turbines: 112 Siemens 2.37 MW turbines
Rotor diameter: 101 meters
Blade length: 49 meters
Total height: 140 meters
Annual output: Approximately 850,000 MWh
Commissioned: 2013
Operator: Pattern Energy
Land area: 12,436 acres
Location: Ocotillo, Imperial County, California, United States
Cost: Approximately $600 million
Carbon offset: Approximately 464,000 metric tons of CO2 per year
20. West of Duddon Sands Wind Farm
West of Duddon Sands – Spesification
West of Duddon Sands is an offshore wind farm located in the Irish Sea, about 14 kilometers (8.7 miles) from the Cumbrian coast of England and about 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) south-west of the Walney Island wind farm.
Here are some of its specifications:
The wind farm was completed in 2014 and has a capacity of 389 MW, enough to power approximately 280,000 homes in the UK.
It comprises 108 turbines with a rotor diameter of 130 meters (427 feet) and a total height of 190 meters (623 feet).
The turbines were manufactured by Siemens and feature a direct-drive system.
The wind farm is jointly owned by Ørsted (formerly DONG Energy) and ScottishPower Renewables.
The project was built at a cost of approximately £1.6 billion ($2.2 billion USD).
It has a total area of approximately 67 square kilometers (26 square miles) and is located in water depths of up to 20 meters (66 feet).
The electricity generated by the wind farm is transmitted to shore via subsea cables to an onshore substation at Heysham, Lancashire.
Conclusion for 20 Largest Wind Farm in the world and their Capacity
The world’s largest wind farms are primarily located in China and the United States, with a few notable exceptions in Europe, Australia, India, Mexico, Panama, Morocco, and the Netherlands.
The largest wind farm in the world is the Gansu Wind Farm in China, with a total installed capacity of 22,500 MW. Other large wind farms include the Jiuquan Wind Power Base in China, the Alta Wind Energy Center in the USA, and the Fosen Vind in Norway. These wind farms provide significant amounts of clean and renewable energy, which can help reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change.
Wind energy is one of the fastest-growing sources of renewable energy worldwide, with a total installed capacity of over 743 GW.
The 20 largest wind farms listed earlier, there are many other notable wind farms around the world, including:
Walney Extension, UK – 659 MW
Shiloh Wind Power Plant, USA – 300 MW
Whitelee Wind Farm, UK – 539 MW
Clyde Wind Farm, UK – 523 MW
Kaunisvaara Wind Power Plant, Sweden – 235 MW
Lake Turkana Wind Power, Kenya – 310 MW
These wind farms, along with many others, are contributing to the global transition to clean and renewable energy. Wind energy has the potential to provide a significant share of the world’s electricity needs, and as technology continues to improve, it is likely that wind farms will continue to grow in size and capacity.
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/04/20-largest-wind-farm-in-world-and-their.html
Renewable Energy
Should We Appease MAGA by Rewriting the Constitution?
 Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Rewriting the U.S. Constitution will take some work, as I’m sure you’re aware.
Renewable Energy
California’s Next Governor?
 What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
Yes, we have traffic, which we hate. But that’s because everybody and his dog wants to be here for our economic opportunities and our natural beauty.
In general, we reject racism, ignorance, corruption, and environmental destruction.
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
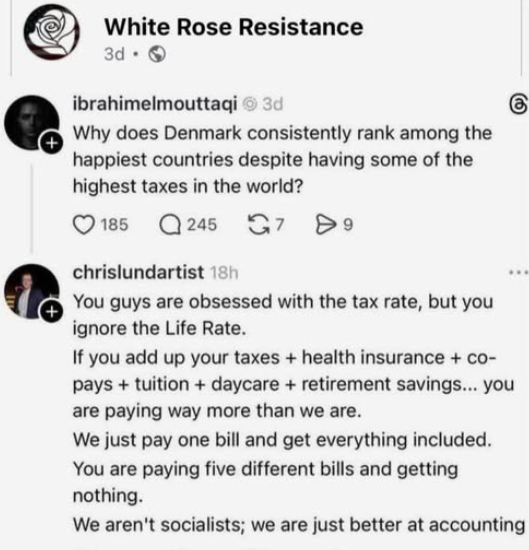 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits


























