Sustainable Aviation Fuel
Definition of Algal Biofuel
Algal biofuel refers to a type of renewable fuel that is derived from algae, specifically microalgae or macroalgae (seaweed).
It is produced through the cultivation and harvesting of algae, followed by the extraction and conversion of their biomass into various forms of usable fuel.
Algae are photosynthetic organisms that can efficiently convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into energy-rich compounds through the process of photosynthesis. Certain types of algae, particularly microalgae, have a high lipid (oil) content, which can be extracted and processed to produce biofuels.
In the quest for renewable and sustainable energy sources, algal biofuels have emerged as a promising solution. Algae, microscopic photosynthetic organisms, possess the remarkable ability to convert sunlight and carbon dioxide into biomass and oils. This article explores the potential of algal biofuels, their production methods, benefits, and challenges, highlighting their role in achieving a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Algal Biofuel Production Methods
The production of algal biofuels typically involves the following steps:
Cultivation: Algae are grown in large-scale cultivation systems, such as open ponds, closed photobioreactors, or raceway ponds. They are provided with sunlight, water, nutrients, and carbon dioxide to facilitate their growth.
Harvesting: Once the algae have reached the desired density or lipid content, they are harvested. Various methods, such as centrifugation, filtration, flocculation, or sedimentation, are employed to separate the algae from the growth medium.
Extraction: The harvested algae biomass undergoes an extraction process to separate the lipids or oils from the rest of the biomass. Common extraction methods include mechanical pressing, solvent extraction, or supercritical fluid extraction.
Conversion: The extracted lipids can be processed through different conversion methods to produce biofuels. The most common approach is transesterification, where the lipids are reacted with alcohol (e.g., methanol) to produce biodiesel. Alternatively, the lipids can be processed through hydrothermal liquefaction, pyrolysis, or fermentation to produce bio-oil, biogas, or bioethanol, respectively.
Algal biofuels have gained attention as a potential renewable energy source due to several advantages. Algae can be grown on non-arable land, using wastewater or seawater, which minimizes competition with food production. They have a high growth rate and can yield a higher oil productivity per unit area compared to conventional oil crops. Algal biofuels also have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
However, there are still challenges to overcome in terms of improving the efficiency and scalability of algal cultivation, optimizing extraction methods, and addressing the economic viability of large-scale production. Ongoing research and technological advancements aim to further develop and commercialize algal biofuels as a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Benefits of Algal Biofuels:
High productivity: Algae can achieve significantly higher oil yields per unit area compared to traditional biofuel feedstocks. They have a rapid growth rate and can produce substantial amounts of biomass and oil in a short period.
Reduced environmental impact: Algal biofuels have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, as algae consume carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Algae can also grow in wastewater or with the use of nutrient-rich effluents, thereby providing an opportunity for wastewater treatment and nutrient recycling.
Versatility: Algal biofuels can be processed into various types of fuels, including biodiesel, green gasoline, and renewable diesel, making them compatible with existing infrastructure and vehicles.
Potential for co-product generation: Algal biomass can serve as a valuable resource for the production of other products, such as animal feed, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and bio-based chemicals, creating additional revenue streams.
Challenges and Consideration for Algal Biofuel
Strain selection and cultivation: Identifying suitable algal strains with high oil content and optimizing their cultivation conditions remain important challenges. Researchers are actively exploring genetic engineering and selective breeding techniques to enhance productivity.
Cost-effectiveness and scalability: Algal biofuel production is currently more expensive compared to conventional fuels. Achieving cost reductions through improved cultivation systems, harvesting methods, and processing technologies is crucial for commercial viability.
Water and nutrient requirements: Algae cultivation requires a consistent supply of water and essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus. Exploring sustainable sourcing options and efficient nutrient recycling systems are necessary to minimize environmental impacts and operational costs.
Land and resource use: Large-scale algae cultivation may require significant land area, potentially conflicting with other land uses. Utilizing non-arable land or exploring alternative cultivation methods, such as algae grown on floating structures or wastewater treatment facilities, can mitigate land use concerns.
Conclusion for Algae for a Sustainable Energy Future
Algal biofuels hold tremendous promise as a renewable and sustainable energy source.
Their high productivity, reduced environmental impact, versatility, and potential for co-product generation make them an attractive option for a cleaner energy future. Addressing challenges related to strain selection, cultivation techniques, cost-effectiveness, and resource management will pave the way for widespread adoption of algal biofuels. Continued research, development, and collaboration among scientists, industry, and policymakers are crucial for unlocking the full potential of algal biofuels and accelerating the transition to a more sustainable energy landscape.
In conclusion, algal biofuels hold great promise as a renewable energy source with numerous potential benefits. The cultivation and utilization of algae for biofuel production offer advantages such as high lipid content, rapid growth, and the ability to grow on non-arable land using wastewater or seawater. Algal biofuels have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decrease dependence on fossil fuels, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
However, several challenges need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of algal biofuels. These include improving the efficiency and scalability of algal cultivation systems, optimizing extraction and conversion processes, and addressing the economic viability of large-scale production. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on overcoming these challenges and advancing the commercialization of algal biofuels.
Despite the challenges, the continued exploration of algal biofuels holds promise for creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system. As technology advances and our understanding of algae biology and cultivation techniques improves, algal biofuels may play an increasingly significant role in the transition to a low-carbon future. By harnessing the power of algae, we can potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote energy security, and pave the way for a greener and more sustainable world.
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/05/algae-for-sustainable-energy-future.html
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
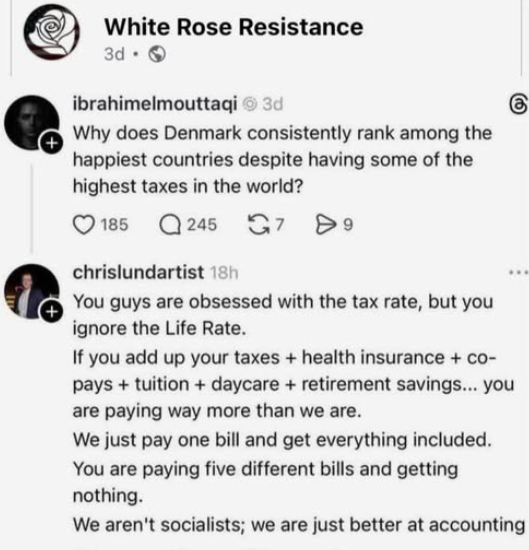 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
Renewable Energy
What Kids Need from Their Parents
 Well, here’s a controversial statement.
Well, here’s a controversial statement.
Apparently, there are people who believe kids should be raised by dishonest imbeciles.
https://www.2greenenergy.com/2026/03/05/what-kids-need-from-their-parents/
Renewable Energy
How and When Did We Become a Country of Assholes?
When I was a boy, growing up in the 1960s, the United States was certainly not a nation of assholes. We valued personal liberty, which meant the freedom to say and think and do anything we wanted, and to do anything we wanted as long as we weren’t hurting anyone. This is what it meant to be an American.
Our allies also valued that freedom, and our enemies were the dictatorships that demanded mindless conformity to arbitrary positions held by the autocrat.
All this has gone totally out the window.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits