Outlook Green Mobility in Freiburg
Public Transportation and Cycling Culture
Munich, the capital of Bavaria, Germany, excels in sustainable transportation and fostering a cycling culture. The city’s comprehensive public transportation network, including trams, buses, and suburban trains, encourages residents and visitors to rely less on private cars. Munich also promotes cycling as a primary mode of transportation, with a vast network of cycling lanes and bike-sharing programs available throughout the city. By prioritizing public transportation and cycling infrastructure, Munich reduces traffic congestion and contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable urban environment.
Renewable Energy and Climate Action
Munich is at the forefront of Germany’s transition to renewable energy sources and climate action. The city has made significant investments in renewable energy projects, particularly solar and wind power. Munich’s commitment to sustainability is exemplified by initiatives like the installation of solar panels on public buildings, district heating systems, and energy-efficient retrofits. The city has also set ambitious climate goals of becoming carbon neutral and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Munich actively engages in climate action through public awareness campaigns, energy-saving initiatives, and partnerships with local businesses and organizations, demonstrating its dedication to a sustainable and low-carbon future.
Green Building and Urban Design
Munich promotes green building practices and sustainable urban design to create energy-efficient and environmentally friendly spaces. The city encourages the construction of energy-efficient buildings with green certifications, such as LEED and Passive House standards. Munich’s urban planning integrates green spaces, pedestrian-friendly streets, and mixed-use developments, fostering a sense of community and reducing the need for long-distance commuting. By prioritizing green building and sustainable urban design, Munich creates a harmonious balance between the built environment and nature.
Waste Management and Recycling
Munich has implemented a comprehensive waste management system with a strong focus on recycling and waste reduction. The city encourages residents to separate their waste into different categories, including organic, recyclable, and residual waste. Munich’s recycling programs cover a wide range of materials, including paper, plastic, glass, and metal. The city also promotes composting initiatives for organic waste and educates residents about the importance of waste reduction and recycling. Munich’s commitment to effective waste management contributes to resource conservation and the circular economy.
Green Spaces and Parks
Munich is renowned for its abundant green spaces and parks, which play a vital role in enhancing the city’s sustainability and residents’ quality of life. The English Garden, one of the world’s largest urban parks, offers vast green expanses, meandering paths, and a serene atmosphere for relaxation and recreation. Munich’s commitment to preserving and expanding green spaces creates a healthy urban environment, promotes biodiversity, and provides natural habitats for wildlife. The city actively engages in urban greening projects, planting trees and flowers to enhance the aesthetic appeal and ecological balance of the urban landscape.
Local and Organic Food Initiatives
Munich promotes local and organic food initiatives, supporting sustainable agriculture and reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production and transportation. The city encourages residents to choose locally sourced and organic products by promoting farmers’ markets, community-supported agriculture programs, and organic food cooperatives. Munich’s commitment to sustainable food systems ensures access to fresh, healthy, and environmentally friendly food choices while supporting local farmers and reducing the reliance on long-distance food transportation.
Conclusion Green Mobility in Freiburg
Munich stands as a prime example of a sustainable city that combines tradition and innovation to create a thriving urban environment.
The city’s commitment to public transportation, cycling infrastructure, renewable energy, green building practices, waste management, green spaces, and local food initiatives showcases its dedication to sustainability and quality of life for its residents. As other cities navigate the challenges of urbanization and climate change, Munich’s sustainable practices offer valuable lessons and inspiration for creating vibrant, resilient, and eco-friendly urban communities.
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/06/munich-germany-sustainable-city.html
Renewable Energy
Gutting America’s Healthcare in Rural (MAGA) Areas
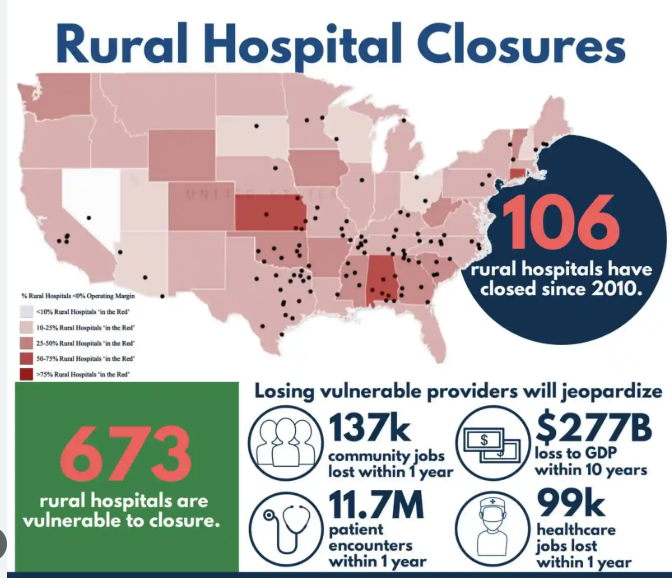 Here’s a short video that addresses the assault that the U.S. federal government is conducting on the health of people in red states and counties.
Here’s a short video that addresses the assault that the U.S. federal government is conducting on the health of people in red states and counties.
Of course, this is another fine example of what Lyndon Johnson said: “If you can convince the lowest white man that he’s better than the finest black man, he’ll open up his wallet to you.”
In this case, uneducated white people don’t care about their own ignorance or poverty or disease, as long as their president is vigorously punishing non-whites.
Renewable Energy
Cynicism Incarnate
 To the point being made at left, I’m a progressive, but I honestly couldn’t care less if white people of the American south want to wallow in incest, disease, poverty, and ignorance.
To the point being made at left, I’m a progressive, but I honestly couldn’t care less if white people of the American south want to wallow in incest, disease, poverty, and ignorance.
On the other hand, I am concerned about the plight of hungry children, homeless veterans, the collapse of the environment, the destruction of the educational system, and the criminal psychosis of the U.S. president.
Renewable Energy
The Coming Apocalypse
 I had a friend who co-coached my son’s all-star soccer team with me 20+ years ago who told me, when I told him that I was an environmentalist, “Oh no, Craig, we must hasten to destroy the Earth, so as to welcome the return of Jesus Christ,” by which, of course, he meant the rapture, the apocalypse as discussed at length in Revelation.
I had a friend who co-coached my son’s all-star soccer team with me 20+ years ago who told me, when I told him that I was an environmentalist, “Oh no, Craig, we must hasten to destroy the Earth, so as to welcome the return of Jesus Christ,” by which, of course, he meant the rapture, the apocalypse as discussed at length in Revelation.
I have heard some twisted s*** in my time, but this stands at or near the top.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits














