EGU is the largest European geoscientific conference, and it is no surprise that many FYORD members attended. This month for the FYORD Travel Grant reports you will find some more EGU reports. Stay tuned to find out where the FYORD members travel to in the next month!
Naveen’s impression of EGU 2024
I am Naveen, in my third year of my PhD. I am part of the MarDATA graduate school, affiliated with both GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research and the University of Kiel. I have a background in scientific computing. My interest in machine learning led me to apply for this interesting project in MarDATA, which revolves around the application of machine learning in the global prediction of total organic carbon burial rates in marine sediments.
As an interdisciplinary researcher, I find the European Geosciences Union in Vienna to be the perfect platform to network with other researchers working in the field of machine learning and geosciences. In the past, I always presented my work in a machine learning session, and this was the first time I presented in an ocean biogeochemistry session. I needed the feedback from the people who actually use my results, and this was a perfect way to do it. I presented my work in front of people, whose names I had previously only on papers that I cited. When I shared the same podium with them, I felt very much part of the science community.

Though it triggered my intrinsic imposter syndrome, I felt very much welcome. Even though machine learning was not the strongest field in the session, the topic was still welcomed by the researchers. They were eager for my publication, that is in preparation. I received a lot of feedback and ideas for my work, which I can implement and think about in the next phase of my research. EGU24 was also a doorway to numerous interesting works, plenary sessions from your idols, and workshops that cater to the needs of ECRs like myself.
I always found it challenging to choose between different parallel talks and sessions. Five days of conference can be long and taxing, with the number of inputs that you have to take in. But at the end of all the talks and the poster sessions, we could always relax with the beer with the attendees there and share a light moment for dinner. From the traditional pasta dinner on the welcome day to the final beer on Friday, there was always something to look forward to, to learn about, to cherish, to wonder, to think. For an ECR, it might be a bit overwhelming, but you feel part of the community very easily here. On the whole, I would recommend all the ECRs to attend this conference and I would definitely be there next year.
Naveen Kumar Parameswaran
Science in a Crowd
EGU is one of the largest geoscience conferences and attended by researchers from all over the world. It is informative, thought-provoking, and exciting to learn about the latest in geoscience research. However, it is also loud, crowded, and overwhelming!
My name is Rebecca Englert and I am a postdoctoral researcher in the Marine Geophysics and Hydroacoustics group at Kiel University. I am from Canada and because I completed my education at Canadian institutions, I never had the opportunity to attend EGU before – it was too far and expensive compared to North American conferences. When my current supervisor asked who wanted to attend EGU, I raised my hand and was able to attend this past April with the help of a FYORD travel grant.

My research is in marine sedimentology and I study how sediments, such as mud and sand, are transported by currents in the ocean. My work is inherently multidisciplinary and draws on aspects of oceanography, sedimentology, geophysics, and geomorphology. This made EGU the perfect venue for sharing and learning about topics related to my research because it includes a broad range of sessions.
Overall, I had a productive and valuable experience at EGU. I presented a poster on my recent work, which investigates the formation of sediment waves (undulations on the seafloor) along the northwest African margin. I attended a variety of sessions on different topics, which I understood to varying degrees but always learned something from the experience. There were also many non-scientific sessions that were very useful about how to manage a career in research.

I would recommend attending EGU to anyone looking to broaden their network or knowledge, or perhaps efficiently connect with colleagues from around the world. However, some planning is certainly required to make the most of the experience. The schedule and the venue are huge and it can take 10 – 20 minutes to find your way between sessions amongst hoards of people. It is easy to miss an event that is relevant. Although overwhelming at times, I was able to make many new contacts and reconnect with old colleagues – there were always friendly faces in the crowd.
Rebecca Englert
FYORD Travel Grant Reports: Impressions from EGU 2024 (Part 2)
Ocean Acidification
What is Coral Bleaching and Why is it Bad News for Coral Reefs?
Coral reefs are beautiful, vibrant ecosystems and a cornerstone of a healthy ocean. Often called the “rainforests of the sea,” they support an extraordinary diversity of marine life from fish and crustaceans to mollusks, sea turtles and more. Although reefs cover less than 1% of the ocean floor, they provide critical habitat for roughly 25% of all ocean species.
Coral reefs are also essential to human wellbeing. These structures reduce the force of waves before they reach shore, providing communities with vital protection from extreme weather such as hurricanes and cyclones. It is estimated that reefs safeguard hundreds of millions of people in more than 100 countries.
What is coral bleaching?
A key component of coral reefs are coral polyps—tiny soft bodied animals related to jellyfish and anemones. What we think of as coral reefs are actually colonies of hundreds to thousands of individual polyps. In hard corals, these tiny animals produce a rigid skeleton made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). The calcium carbonate provides a hard outer structure that protects the soft parts of the coral. These hard corals are the primary building blocks of coral reefs, unlike their soft coral relatives that don’t secrete any calcium carbonate.
Coral reefs get their bright colors from tiny algae called zooxanthellae. The coral polyps themselves are transparent, and they depend on zooxanthellae for food. In return, the coral polyp provides the zooxanethellae with shelter and protection, a symbiotic relationship that keeps the greater reefs healthy and thriving.
When corals experience stress, like pollution and ocean warming, they can expel their zooxanthellae. Without the zooxanthellae, corals lose their color and turn white, a process known as coral bleaching. If bleaching continues for too long, the coral reef can starve and die.
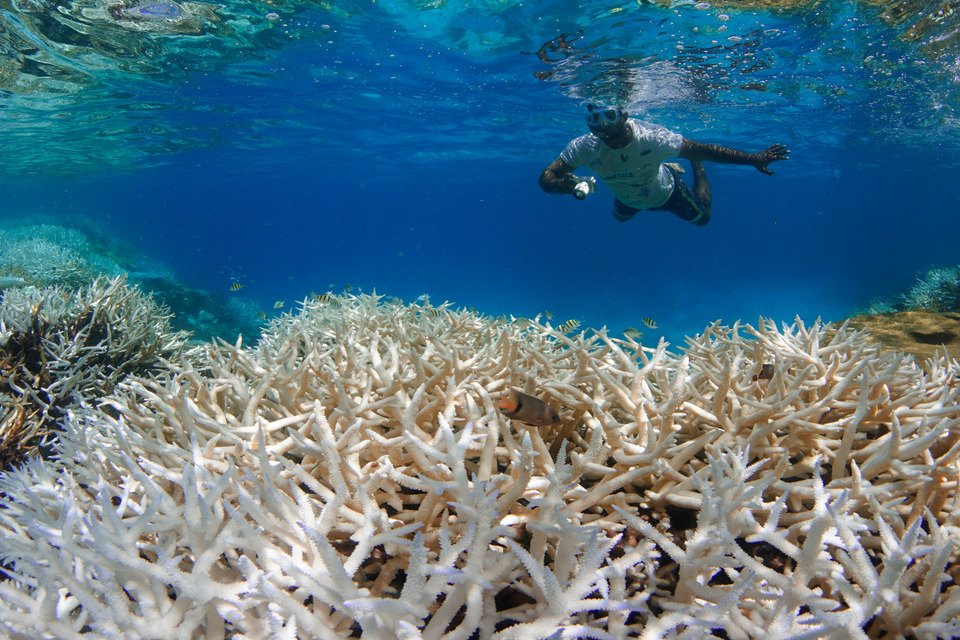

Ocean warming and coral bleaching
Human-driven stressors, especially ocean warming, threaten the long-term survival of coral reefs. An alarming 77% of the world’s reef areas are already affected by bleaching-level heat stress.
The Great Barrier Reef is a stark example of the catastrophic impacts of coral bleaching. The Great Barrier Reef is made up of 3,000 reefs and is home to thousands of species of marine life. In 2025, the Great Barrier Reef experienced its sixth mass bleaching since 2016. It should also be noted that coral bleaching events are a new thing because of ocean warming, with the first documented in 1998.
Get Ocean Updates in Your Inbox
Sign up with your email and never miss an update.
How you can help
The planet is changing rapidly, and the stakes have never been higher. The ocean has absorbed roughly 90% of the excess heat caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, and the consequences, including coral die-offs, are already visible. With just 2℃ of planetary warming, global coral reef losses are estimated to be up to 99% — and without significant change, the world is on track for 2.8°C of warming by century’s end.
To stop coral bleaching, we need to address the climate crisis head on. A recent study from Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the first of its kind to include damage to ocean ecosystems into the economic cost of climate change – resulting in nearly a doubling in the social cost of carbon. This is the first time the ocean was considered in terms of economic harm caused by greenhouse gas emissions, despite the widespread degradation to ocean ecosystems like coral reefs and the millions of people impacted globally.
This is why Ocean Conservancy advocates for phasing out harmful offshore oil and gas and transitioning to clean ocean energy. In this endeavor, Ocean Conservancy also leads international efforts to eliminate emissions from the global shipping industry—responsible for roughly 1 billion tons of carbon dioxide every year.
But we cannot do this work without your help. We need leaders at every level to recognize that the ocean must be part of the solution to the climate crisis. Reach out to your elected officials and demand ocean-climate action now.
The post What is Coral Bleaching and Why is it Bad News for Coral Reefs? appeared first on Ocean Conservancy.
What is Coral Bleaching and Why is it Bad News for Coral Reefs?
Ocean Acidification
What is a Snipe Eel?
From the chilly corners of the polar seas to the warm waters of the tropics, our ocean is bursting with spectacular creatures. This abundance of biodiversity can be seen throughout every depth of the sea: Wildlife at every ocean zone have developed adaptations to thrive in their unique environments, and in the deep sea, these adaptations are truly fascinating.
Enter: the snipe eel.
What Does a Snipe Eel Look Like?
These deep-sea eels have a unique appearance. Snipe eels have long, slim bodies like other eels, but boast the distinction of having 700 vertebrae—the most of any animal on Earth. While this is quite a stunning feature, their heads set them apart in even more dramatic fashion. Their elongated, beak-like snouts earned them their namesake, strongly resembling that of a snipe (a type of wading shorebird). For similar reasons, these eels are also sometimes called deep-sea ducks or thread fish.
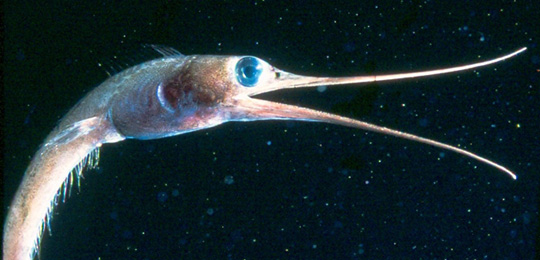
How Many Species of Snipe Eel are There?
There are nine documented species of snipe eels currently known to science, with the slender snipe eel (Nemichthys scolopaceus) being the most studied. They are most commonly found 1,000 to 2,000 feet beneath the surface in tropical to temperate areas around the world, but sightings of the species have been documented at depths exceeding 14,000 feet (that’s more than two miles underwater)!
How Do Snipe Eels Hunt and Eat?
A snipe eel’s anatomy enables them to be highly efficient predators. While their exact feeding mechanisms aren’t fully understood, it’s thought that they wiggle through the water while slinging their beak-like heads back and forth with their mouths wide open, catching prey from within the water column (usually small invertebrates like shrimp) on their hook-shaped teeth.
How Can Snipe Eels Thrive So Well in Dark Depths of the Sea?
Snipe eels’ jaws aren’t the only adaptation that allows them to thrive in the deep, either. They also have notably large eyes designed to help them see nearby prey or escape potential predators as efficiently as possible. Their bodies are also pigmented a dark grey to brown color, a coloring that helps them stay stealthy and blend into dark, dim waters. Juveniles are even harder to spot than adults; like other eel species, young snipe eels begin their lives as see-through and flat, keeping them more easily hidden from predators as they mature.
Get Ocean Updates in Your Inbox
Sign up with your email and never miss an update.
How Much Do Scientists Really Know About Snipe Eels?
Residence in the deep sea makes for a fascinating appearance, but it also makes studying animals like snipe eels challenging. Scientists are still learning much about the biology of these eels, including specifics about their breeding behaviors. While we know snipe eels are broadcast spawners (females release eggs into the water columns at the same time as males release sperm) and they are thought to only spawn once, researchers are still working to understand if they spawn in groups or pairs. Beyond reproduction, there’s much that science has yet to learn about these eels.
Are Snipe Eels Endangered?
While the slender snipe eel is currently classified as “Least Concern” on the International Union for the Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species, what isn’t currently known is whether worldwide populations are growing or decreasing. And in order to know how to best protect these peculiar yet equally precious creatures, it’s essential we continue to study them while simultaneously working to protect the deep-sea ecosystems they depend on.
How Can We Help Protect Deep-Sea Species Like Snipe Eels?
One thing we can do to protect the deep sea and the wildlife that thrive within it is to advocate against deep-sea mining and the dangers that accompany it. This type of mining extracts mineral deposits from the ocean floor and has the potential to result in disastrous environmental consequences. Take action with Ocean Conservancy today and urge your congressional representative to act to stop deep-sea mining—animals like snipe eels and all the amazing creatures of the deep are counting on us to act before it’s too late.
The post What is a Snipe Eel? appeared first on Ocean Conservancy.
Ocean Acidification
5 Animals That Need Sea Ice to Thrive
Today, we’re getting in the winter spirit by spotlighting five remarkable marine animals that depend on cold and icy environments to thrive.
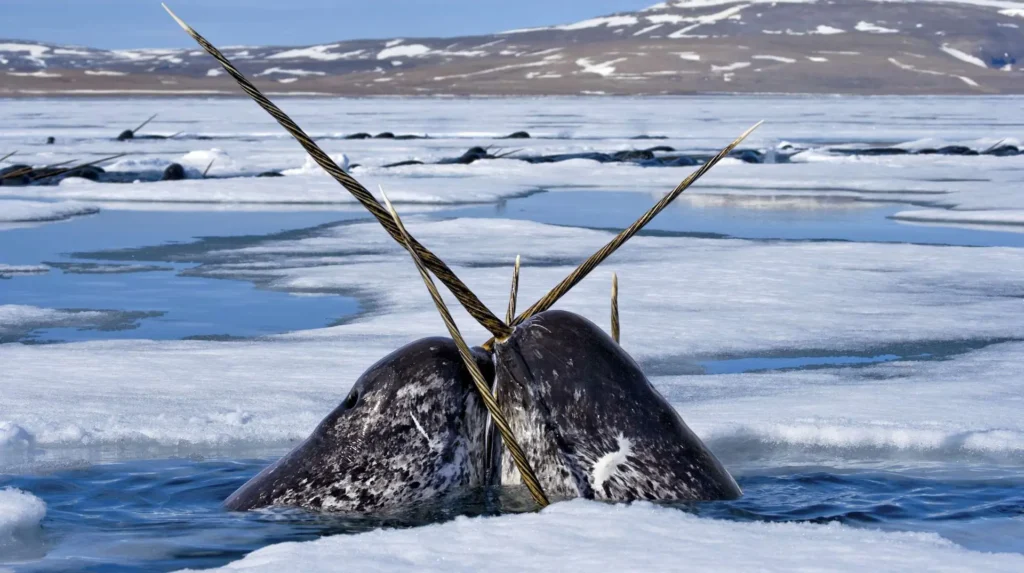
1. Narwhals
Narwhals are often called the “unicorns of the sea” because of their long, spiraled tusk. Here are a few more fascinating facts about them:
- Believe it or not, their tusk is actually a tooth used for sensing their environment and sometimes for sparring.
- Narwhals are whales. While many whale species migrate south in the winter, narwhals spend their entire lives in the frigid waters of the circumpolar Arctic near Canada, Greenland and Russia.
- Sea ice provides narwhals with protection as they travel through unfamiliar waters.
2. Walruses
Walruses are another beloved Arctic species with remarkable adaptations for surviving the cold:
- Walruses stay warm with a thick layer of blubber that insulates their bodies from icy air and water.
- Walruses can slow their heart rate to conserve energy and withstand freezing temperatures both in and out of the water.
- Walruses use sea ice to rest between foraging dives. It also provides a vital and safe platform for mothers to nurse and care for their young.
Get Ocean Updates in Your Inbox
Sign up with your email and never miss an update.
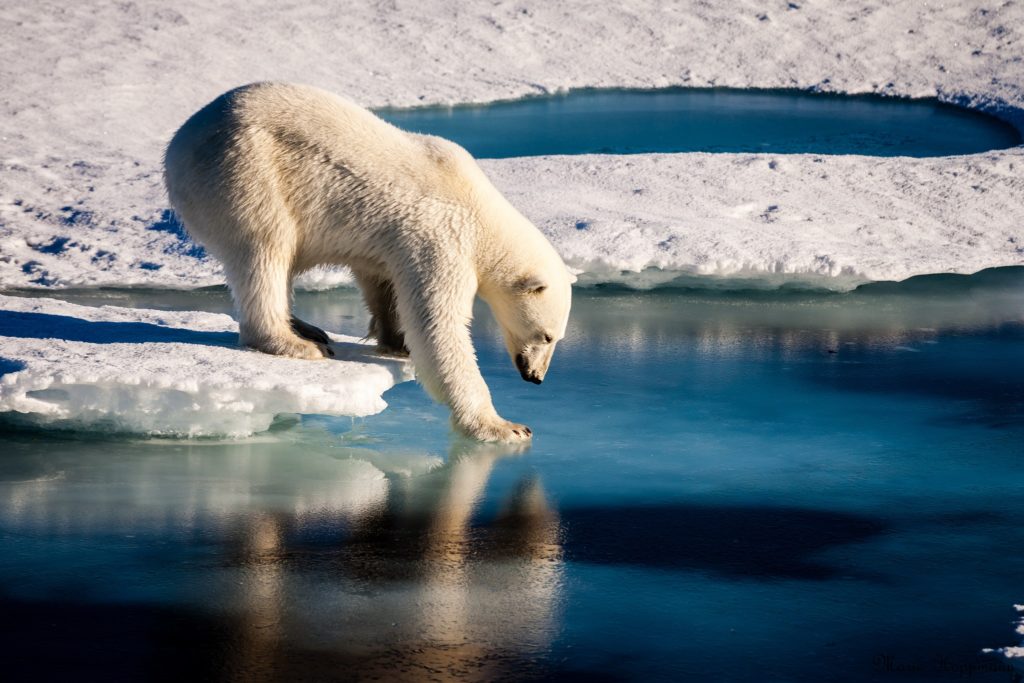
3. Polar Bears
Polar bears possess several unique traits that help them thrive in the icy Arctic:
- Although polar bear fur appears white, each hair is hollow and transparent, reflecting light much like ice.
- Beneath their thick coats, polar bears have black skin that absorbs heat from the sun. This helps keep polar bears warm in their icy habitat.
- Polar bears rely on sea ice platforms to access their primary prey, seals, which they hunt at breathing holes in the ice.
4. Penguins
Penguins are highly adapted swimmers that thrive in icy waters, but they are not Arctic animals:
- Penguins live exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere, mainly Antarctica, meaning they do not share the frigid northern waters with narwhals, walruses and polar bears.
- Penguins spend up to 75% of their lives in the water and are built for efficient aquatic movement.
- Sea ice provides a stable platform for nesting and incubation, particularly for species like the Emperor penguin, which relies on sea ice remaining intact until chicks are old enough to fledge.
5. Seals
Seals are a diverse group of carnivorous marine mammals found in both polar regions:
- There are 33 seal species worldwide, with some living in the Arctic and others in the Antarctic.
- There are two groups of seals: Phocidae (true seals) and Otariidae (sea lions and fur seals). The easiest way to tell seals and sea lions apart is by their ears: true seals have ear holes with no external flaps, while sea lions and fur seals have small external ear flaps.
- Seals need sea ice for critical life functions including pupping, nursing and resting. They also use ice for molting—a process in which they shed their fur in the late spring or early summer.
Defend the Central Arctic Ocean Action
Some of these cold-loving animals call the North Pole home, while others thrive in the polar south. No matter where they live, these marine marvels rely on sea ice for food, safety, movement and survival.
Unfortunately, a rapidly changing climate is putting critical polar ecosystems, like the Central Arctic Ocean, at risk. That is why Ocean Conservancy is fighting to protect the Central Arctic Ocean from threats like carbon shipping emissions, deep-sea mining and more. Take action now to help us defend the Central Arctic Ocean.
Learn more
Did you enjoy these fun facts? Sign up for our mobile list to receive trivia, opportunities to take action for our ocean and more!
The post 5 Animals That Need Sea Ice to Thrive appeared first on Ocean Conservancy.
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits










