By: Annika Barth, Ellie Potter
November 6, 2023
What is the Transmission Needs Study and Why Does it Matter?
The U.S. grid needs to significantly expand its regional and interregional transmission capacity to meet future electricity demand, improve overall grid reliability and resilience, alleviate system congestion, and connect cleaner energy resources, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) concluded in its final National Transmission Needs Study released on Oct. 30, 2023. The Needs Study is an assessment of more than 120 reports on current and anticipated future needs of the electricity grid. It helps inform regional and interregional planning and the use of DOE’s various authorities and funding streams, such as those included in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
The DOE projected that regional transmission capacity will need to more than double by 2035 while interregional capacity must grow by more than fivefold to realize the full economic benefits and clean energy potential of the IRA. As shown in the figure below, for this analysis, the DOE assessed projected needs based upon multiple drivers, including improving reliability, reducing congestion, alleviating interregional transfer limits, and accessing lower-cost generation.

Source: U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Deployment Office
Yet transmission investments have slowed considerably since 2015 in various regions. On average, the U.S. energized only 70 circuit miles of interregional transmission annually from 2011 to 2020, out of a total of 3,300 circuit miles.
What Stakeholders Need to Know
Regional Need
Regional transmission capacity will need to increase 20% by 2035 to accommodate a future with moderate load and clean energy growth. However, under scenarios with high clean energy growth – which most closely align with anticipated sector needs given state and federal policies – these regional needs increase to 64%. Accounting for the high load growth likely to occur under an expansion of building electrification, electric vehicle adoption, and other drivers, would require more than double the existing regional system, a 128% increase.
Scenarios with moderate load and high clean energy growth by 2035 forecast significant capacity growth needs compared to the 2020 system in specific geographic areas: 140% in Texas, 119% in the Plains, 112% in the Midwest, 90% in the Mountain region, and 77% in the Southeast. The needed increase for this timeframe under a high load growth scenario is even greater: 408% in the Plains, 231% in the Delta, 174% in the Midwest, and 173% in the Mountain regions.
 Source: U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Deployment Office
Source: U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Deployment Office
Interregional Need
The capacity needed for two regions to transfer power between one another is expected to increase significantly in the coming years, particularly under scenarios with high load growth or large additions of clean energy sources. Existing interregional transfer capacity must double to meet moderate load and high clean energy growth and quintuple to meet high load and clean energy growth futures by 2035.
Compared to 2020, the DOE projects that by 2035 interregional transfer capacity will need to grow by 414% between the Delta and Plains regions; 255% between New England and New York; 175% between the Midwest and Plains; and 156% between the Mid-Atlantic and Midwest to accommodate moderate load and high clean energy growth future scenarios.
 Source: U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Deployment Office
Source: U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Deployment Office
What’s Next for DOE
National Interest Electric Transmission Corridor (NIETC) Designation
Findings in the Needs Study will help inform the DOE’s designation of NIETCs, which will be critically important to alleviating current and anticipated transmission constraints identified in the Study. The Federal Power Act authorizes the DOE to designate a location as a NIETC if the Department finds that current or anticipated transmission capacity constraints or congestion is adversely affecting consumers. DOE designation of NIETCs can catalyze transmission development through several means. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) may grant permits for transmission lines sited within NIETCs if states do not have authority to site the line, have not acted on an application in over a year, or have denied an application. A NIETC designation also enables transmission projects to be eligible for public-private partnerships under the Transmission Facilitation Program and for loan support under the Transmission Facility Financing program.
The DOE’s designation process for NIETCs is still underway. In May 2023, the Department issued a Notice of Intent and Request for Information (RFI) on a proposal to evaluate the designation of NIETCs on an applicant-driven, route-specific basis. This approach would allow developers to weigh the benefits and risks of applying for such a designation and potentially limit local opposition. The DOE will release guidance on the NIETC designation process after reviewing comments on the RFI, which were submitted in July 2023.
Grid Deployment Office Funding Opportunities
The Needs Study will also help inform implementation of the DOE’s funding programs for transmission, authorized through the IRA and IIJA. Two of these programs include the Transmission Facilitation Program (TFP) and Grid Resilience and Innovation Partnership Program (GRIP).
Under the TFP, the DOE is authorized to borrow up to $2.5 billion to support the construction or upgrade of interregional transmission lines. In addition to releasing the Needs Study on Oct. 30, the DOE announced the first round of TFP funding, totaling $1.3 billion for three selected applicants. The projects include Cross-Tie, planned by TransCanyon, a joint venture between ACORE member Berkshire Hathaway and Pinnacle West Capital subsidiaries, that will connect Nevada and Utah; Southline, developed by Black Forest Partners and GU Southline LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of ACORE member Grid United, that will connect Arizona and New Mexico; and Twin States Clean Energy Link, planned by National Grid, which will run between Vermont and New Hampshire. Southline and Cross-Tie addressed critical regional needs identified by the Needs Study. The DOE anticipates releasing a second round of TFP funding in the first half of 2024.
The DOE also recently announced a total of $3.46 billion in GRIP funding for 58 projects, including the Joint Targeted Interconnection Queue projects that would connect MISO and SPP. GRIP funding is intended to enhance grid flexibility and resilience during extreme weather events, which the DOE expects to become more frequent and severe in the coming years. The Needs Study finds that extreme weather necessitates planning beyond the footprint of individual utilities and regions to assure reliable delivery of power. The DOE expects the next round of GRIP funding to open to applications at the end of 2023.
Conclusion
Having reviewed 120 public reports released in recent years on the issue, the Needs Study authors determined that considerable regional and interregional transmission development is required to meet increased electricity demand and public policy goals across the nation now and in the future. Its release comes just months after the passage of the debt ceiling deal that directing the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) to FERC on the need for more interregional transmission, followed by another year for FERC to make recommendations on any rule changes. But given the DOE’s findings, we clearly cannot afford for FERC to wait so long to take action. We need FERC to act as quickly as possible to ensure there is comprehensive multi-value regional and interregional transmission planning. It is clear that FERC must also establish a minimum interregional transfer capacity standard to spur development of the interregional lines critical to ensuring affordable, reliable power.
It’s time to shift the nation’s focus from studying these lines to building them.
The post Need for Speed: Connecting the Nation with Transmission appeared first on ACORE.
Renewable Energy
California’s Next Governor?
 What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
Yes, we have traffic, which we hate. But that’s because everybody and his dog wants to be here for our economic opportunities and our natural beauty.
In general, we reject racism, ignorance, corruption, and environmental destruction.
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
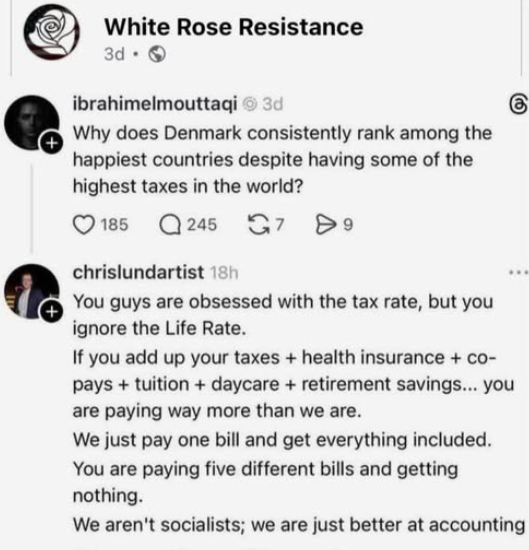 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
Renewable Energy
What Kids Need from Their Parents
 Well, here’s a controversial statement.
Well, here’s a controversial statement.
Apparently, there are people who believe kids should be raised by dishonest imbeciles.
https://www.2greenenergy.com/2026/03/05/what-kids-need-from-their-parents/
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits



