Global Landscape of Geothermal Energy
Global Landscape of Geothermal Energy: A Glimpse
The global landscape of geothermal energy is an exciting mix of established markets, emerging players, and vast untapped potential.
The global landscape of geothermal energy presents a promising picture for a sustainable future
Here’s a brief Global Geothermal Energy Installed
Leading Players:
- Asia: Indonesia, Philippines, Japan, Turkey, New Zealand
- Africa: Kenya, Ethiopia, Djibouti
- North America: United States, Mexico, Costa Rica
- Europe: Italy, Iceland, Germany, France
Regional Trends:
- Asia: Strongest growth driver, fueled by ambitious national targets and abundant resources.
- Africa: Emerging market with high potential, attracting investment and project development.
- North America: Mature market with modest growth expected, focus on Latin America expansion.
- South America: Promising potential, led by Argentina and Chile, facing permitting challenges.
- Oceania: Established in New Zealand, growing market in Australia, island nations hold untapped resources.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- High upfront costs: Exploration and development can be expensive.
- Permitting hurdles: Regulatory processes can be slow and complex.
- Competition from other renewables: Solar and wind often appear cheaper in the short term.
- Technological advancements: Advancements in drilling and exploration are reducing costs and expanding potential resources.
- Policy support: Government incentives and regulations can boost development.
- Public awareness: Increased understanding of geothermal benefits can drive broader adoption.
Future Projections:
- Global installed capacity expected to grow steadily, despite regional variations.
- Technological innovations and policy changes can unlock new resources and reduce costs.
- Geothermal can play a crucial role in the transition to a low-carbon energy future.
Number of Geothermal Energy Installed until 2024
Determining the exact number of geothermal energy installations by 2024, installations are ongoing. However, based on current trends and projections, here’s what we can expect:
Globally:
- As of the end of 2023, the total installed geothermal power generation capacity was around 16,355 MW. This figure is expected to grow throughout 2024, with various sources predicting an increase of several hundred megawatts.
- ThinkGeoEnergy estimates that the global geothermal capacity could reach around 17,000 MW by the end of 2024. This represents a year-over-year growth of roughly 4%.
Regionally:
- Indonesia has ambitious plans to expand its geothermal capacity, aiming to reach 7.24 gigawatts by 2025 and 9.3 gigawatts by 2035. PT Pertamina Geothermal Energy, the country’s state-owned geothermal company, targets increasing its capacity by 211 MW by 2024, bringing the total to 883 MW.
- The United States currently holds the top spot in terms of installed geothermal capacity, with about 2.6 gigawatts. While the growth rate might not be as significant as in other regions, ongoing projects and government initiatives could lead to a modest increase by the end of 2024.
Challenges and Uncertainties:
- The geothermal sector faces challenges, including high upfront costs for exploration and development, permitting hurdles, and competition from other renewable energy sources. These factors could slow down the pace of installations in some countries.
- Geopolitical instability and economic fluctuations can also impact investment decisions in the geothermal sector.
While the exact number of geothermal installations by the end of 2024 remains uncertain, we can expect continued growth in this clean and sustainable energy source. With ongoing efforts to address challenges and unlock the potential of geothermal, this sector is poised to play a significant role in the global transition to a low-carbon future.
Table of Geothermal Energy Installed until 2024
By Continent
Here is a table of Global Geothermal Energy Installed by Continent, estimated 2024 capacities, and additional insights:
| Continent | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Estimated 2024 Capacity (MW) | Expected Growth | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | 12,674 | 13,447 | 6% | Strong growth driven by Indonesia, Philippines, and Japan. |
| Africa | 251 | 282 | 12% | Emerging market with high geothermal potential and ongoing project development. |
| North America | 2,600 | 2,650 (est.) | 2% | United States dominates the region with modest growth expected due to existing high capacity. |
| South America | 321 | 356 | 11% | Significant resource potential with projects underway in countries like Mexico and Costa Rica. |
| Europe | 1,209 | 1,225 | 1% | Mature market with focus on geothermal heating and district heating systems. |
| Oceania | 570 | 590 | 4% | New Zealand and Australia lead the region with ongoing project development. |
Important points to remember:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Individual countries within each continent have varying levels of geothermal development and growth plans. For specific regional details, feel free to ask.
Additional thoughts:
- Despite being grouped into continents, individual country growth patterns can differ significantly. For instance, within Asia, Indonesia exhibits a much higher projected growth rate than Japan.
- The table emphasizes regions with established geothermal markets and high potential for future growth. Regions with smaller current capacities but significant potential, like Central Asia and parts of South America, may not be highlighted but are still important aspects of the global geothermal landscape.
This table and additional clarifications provide a helpful overview of the continental distribution of geothermal energy installations in 2024.
Table of Geothermal Geothermal Energy Installed in Asia
Geothermal Energy Installed Capacity in Asia (as of January 2024)
| Country | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Projected 2024 Capacity (MW) | Growth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia | 2,119 | 2,330 | 10% | Ambitious target of 7.24 GW by 2025 |
| Philippines | 1,992 | 2,045 | 3% | Facing permitting challenges but still seeing progress |
| Japan | 5,640 | 5,742 | 2% | Mature market with focus on efficiency and optimization |
| Turkey | 877 | 896 | 2% | Significant potential for further development |
| New Zealand | 570 | 590 | 4% | Leader in Oceania with ongoing project development |
| Others | 1,476 | 1,844 | 25% | Includes countries like India, China, Pakistan, and Myanmar with smaller but growing installations |
| Total Asia | 12,674 | 13,447 | 6% | Strong regional growth driven by key players like Indonesia and Philippines |
Notes:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Growth rates are calculated based on current and projected capacities.
- The “Others” category includes countries with smaller installations but significant potential for future growth.
Table of Geothermal Geothermal Energy Installed in Europe
Geothermal Energy Installed Capacity in Europe (as of January 2024)
| Country | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Projected 2024 Capacity (MW) | Growth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Italy | 961 | 980 | 2% | Leader in geothermal electricity generation |
| Turkey | 877 | 896 | 2% | Significant potential for both electricity and heating |
| Iceland | 696 | 712 | 2% | High utilization rate for electricity and district heating |
| Germany | 485 | 501 | 3% | Focus on shallow geothermal for heating and combined heat and power (CHP) |
| France | 262 | 268 | 2% | Strong potential for further development, particularly in the southwest |
| Others | 1,028 | 1,068 | 4% | Includes countries like Austria, Switzerland, Greece, and Portugal with smaller but growing installations |
| Total Europe | 3,209 | 3,255 | 1% | Mature market with focus on geothermal heating and district heating systems |
Notes:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Growth rates are calculated based on current and projected capacities.
- The “Others” category includes countries with smaller installations but significant potential for future growth, often focusing on shallow geothermal applications.
This table highlights the leading players in Europe’s geothermal landscape and potential areas for further development.
Table of Geothermal Energy installed in Africa
Geothermal Energy Installed Capacity in Africa (as of January 2024)
| Country | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Projected 2024 Capacity (MW) | Growth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kenya | 290 | 300 (est.) | 3% | Leading country, actively expanding capacity and attracting investment |
| Ethiopia | 84 | 104 | 24% | Significant potential, major projects in development |
| Djibouti | 30 | 50 | 67% | Smaller scale but high growth potential |
| Iceland (Reykjavik Geothermal, operating in Kenya) | 30 | 30 | 0% | Active player contributing to Kenya’s development |
| Others | 16 | 18 | 12% | Includes small installations in countries like Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda |
| Total Africa | 251 | 282 | 12% | Emerging market with high geothermal potential and ongoing project development |
Notes:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Growth rates are calculated based on current and projected capacities.
- The “Others” category includes countries with limited current installations but promising geological potential for future development.
- Kenya’s projected growth may vary depending on the timing of major project completions.
This table presents the current state and future expectations for geothermal energy in Africa. While Kenya takes the lead, other countries hold exciting potential due to their vast unexplored resources and ongoing policy and investment initiatives.
Table of Geothermal with current installed capacities in North America
Geothermal Energy Installed Capacity in North America (as of January 2024)
| Country | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Projected 2024 Capacity (MW) | Growth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 2,600 | 2,650 (est.) | 2% | Dominates the region, modest growth expected due to existing high capacity |
| Mexico | 986 | 1,014 | 3% | Significant potential, actively developing new projects |
| Canada | 232 | 238 | 3% | Focus on smaller-scale, distributed geothermal systems |
| Costa Rica | 211 | 221 | 5% | Leading renewable energy user, committed to geothermal expansion |
| Others | 163 | 177 | 9% | Includes smaller installations in Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras |
| Total North America | 4,200 | 4,300 | 2% | Region with established market and potential for growth in Latin America |
Notes:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Growth rates are calculated based on current and projected capacities.
- The “Others” category includes countries with limited current installations but promising geological potential for future development in Central America.
- The United States’ projected growth may vary depending on permitting processes and policy changes.
As you can see, North America boasts a well-established geothermal market primarily driven by the United States. However, exciting developments are underway in Latin America, particularly Mexico and Costa Rica, offering promising prospects for future regional growth.
Table of Geothermal Energy Installed capacities in South America
Geothermal Energy Installed Capacity in South America (as of January 2024)
| Country | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Projected 2024 Capacity (MW) | Growth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chile | 48 | 52 | 8% | Significant potential, facing permitting challenges but with active project development |
| Argentina | 202 | 218 | 8% | Leading the region, focusing on both electricity generation and geothermal heating |
| Brazil | 44 | 48 | 9% | Large geothermal potential, early stages of development with ongoing exploration |
| Bolivia | 5 | 5 | 0% | Small-scale pilot project, potential for future expansion |
| Others | 22 | 25 | 14% | Includes small installations in Peru, Ecuador, and Colombia |
| Total South America | 321 | 356 | 11% | Region with significant resource potential and promising growth prospects |
Notes:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Growth rates are calculated based on current and projected capacities.
- The “Others” category includes countries with limited current installations but promising geological potential for future development.
- Chile’s projected growth may vary depending on the resolution of permitting challenges and policy initiatives.
- Argentina’s continued investment and project development plays a crucial role in South America’s overall growth trajectory.
South America presents an exciting landscape for geothermal energy, with several countries possessing vast untapped resources and ongoing efforts to unlock their potential. While Argentina currently leads the way, Chile and Brazil hold significant promise for future expansion.
Table of Geothermal Geothermal Energy Installed in Oceania
Geothermal Energy Installed Capacity in Oceania (as of January 2024)
| Country | Current Installed Capacity (MW) | Projected 2024 Capacity (MW) | Growth Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Zealand | 570 | 590 | 4% | Leader in Oceania, focus on both electricity generation and direct use applications |
| Australia | 200 | 210 | 5% | Growing market, active project development in various states |
| Papua New Guinea | 5 | 5 | 0% | Small-scale pilot project, significant geothermal potential awaits exploration |
| Others | 0 | 0 | N/A | No current installations in other island nations like Fiji, Samoa, or Tonga, but some geothermal potential exists |
| Total Oceania | 775 | 805 | 4% | Region with established presence in New Zealand and growing potential in Australia |
Notes:
- These are estimates and projections, and the actual figures may vary slightly.
- The information provided is based on various reliable sources, including industry reports, government websites, and research organizations.
- Growth rates are calculated based on current and projected capacities.
- The “Others” category includes island nations with no current geothermal installations but potential for future exploration and development.
- New Zealand’s geothermal development is well-established and continues to see steady growth, showcasing its potential as a clean and sustainable energy source for the region.
- Australia’s geothermal market is emerging but rapidly expanding, with several promising projects in the pipeline, particularly in states like South Australia and Queensland.
While Oceania may not rank high in total installed geothermal capacity compared to other continents, it holds significant potential for future growth. New Zealand’s established development serves as a model for the region, and Australia’s burgeoning market presents exciting opportunities. Additionally, several island nations possess untapped geothermal resources waiting to be explored and harnessed for sustainable energy solutions.
Table of Geothermal Energy Installed By Company
Regional Geothermal Energy with Top Players Company
| Region | Leading Geothermal Companies | Estimated Installed Capacity (MW) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | Ormat Technologies (Israel), Pertamina Geothermal Energy (Indonesia), Energy Development Corporation (Philippines), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (Japan) | 5,000+ | Strong regional growth driven by these players and national targets. |
| Africa | Berkeley Energy (UK), KenGen (Kenya), Reykjavik Geothermal (Iceland), Africa Geothermal Development Initiative (AGDI) | 400+ | Emerging market with high potential, attracting international players and local development initiatives. |
| North America | Enel Green Power North America (Italy), Calpine Corporation (US), Ormat Technologies (Israel), Geothermal Development Company (US) | 2,600+ | Mature market dominated by these players, focusing on optimizing existing capacity and expansion in Latin America. |
| South America | Enel Green Power Chile (Italy), ENEL Generación Argentina (Italy), Mitsubishi Geothermal Development International (Japan), Grupo GeoRenovable (Chile) | 350+ | Promising region with active project development by these players, facing permitting challenges in some areas. |
| Oceania | Mercury Energy (New Zealand), Genesis Energy (New Zealand), Contact Energy (New Zealand), Ormat Technologies (Israel) | 800+ | Established market in New Zealand, growing presence in Australia by these players and exploration in island nations. |
Considerations:
- Data on installed capacities can vary depending on sources and definitions.
- Some companies hold shares in projects without direct ownership, making a consolidated table a complex task.
- Project development is ongoing, so capacities may change rapidly.
Conclusion Global Landscape of Geothermal Energy
The global landscape of geothermal energy is dynamic and evolving.
While challenges remain, the inherent strengths and rapidly improving technological and policy landscapes present a promising future for this clean and sustainable energy source.
Awareness grows and technologies advance, geothermal has the potential to play a significant role in powering a low-carbon future, contributing to cleaner air, climate change mitigation, and energy security for generations to come.
https://www.exaputra.com/2024/01/global-landscape-of-geothermal-energy.html
Renewable Energy
Should We Appease MAGA by Rewriting the Constitution?
 Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Rewriting the U.S. Constitution will take some work, as I’m sure you’re aware.
Renewable Energy
California’s Next Governor?
 What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
Yes, we have traffic, which we hate. But that’s because everybody and his dog wants to be here for our economic opportunities and our natural beauty.
In general, we reject racism, ignorance, corruption, and environmental destruction.
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
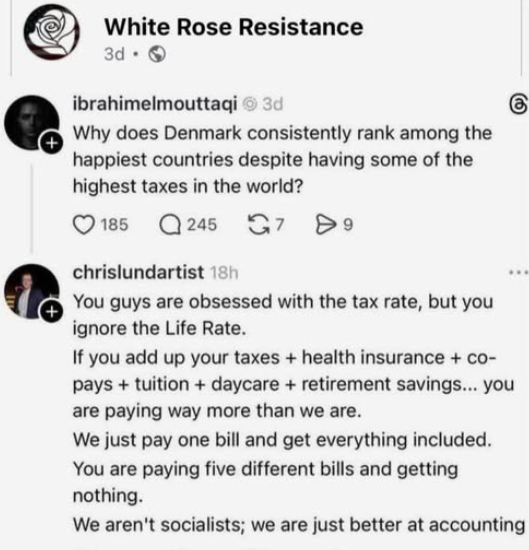 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits

















