Weather Guard Lightning Tech

How Low Cost CMS Stops Catastrophic Damage
We discuss how using continuous monitoring systems (CMS) can prevent catastrophic blade damage from transportation and lightning. We also share insights from GE Vernova CEO Scott Strazik on potential industry growth. And TPI Composites has hit the milestone of manufacturing their 100,000th blade.
Fill out our Uptime listener survey and enter to win an Uptime mug!
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly email update on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary Barnes’ YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
Allen Hall: On this week’s Uptime Wind Energy Podcast, we discuss how continuous monitoring systems could prevent catastrophic blade damage due to transportation issues and lightning strikes. And that’s a good discussion. GE Renova, CEO Scott Straza sees a soft entree wind market through early 2025, highlighting potential growth in Repowering projects.
TPI composites manufactures their 100,000th blade. Congratulations. And our wind farm of the week is the Jericho Rise Wind Farm in upstate New York.
You’re listening to the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast brought to you by bill turbines.com. Learn, train, and be a part of the Clean Energy Revolution. Visit build turbines.com today.
Now here’s your hosts, Allen Hall, Joel Saxum, Phil Totaro, and Rosemary Barnes.
Allen Hall: in his first appearance at Barclays Conference. Since GE Vernova’s spinoff, CEO Scott Strazik offered a sobering assessment of their wind business while highlighting some positive developments. Now, Strazik, uh, described the onshore wind market.
Is currently very soft, quote unquote, with weak order expectations for the first half of 2025, though he noted opportunities in Repowering projects and certain international markets that could, uh, at least partially offset North American weakness. Now, one of the things that was mentioned during the Scott Straza, um, conference or discussion was that they are doing internal inspections and a lot of them using crawlers, which I, I believe is are from Aeros, where they’re looking at.
Uh, the blades at the factory internally after transportation, and then once they’re up on tower trying to capture any defects that are happening. And this, at, at, when I saw this, I thought, oh, it goes back to Phil’s comment that a lot of damage is actually happening during transportation. And that there maybe they’re trying to, uh, work on that transportation piece or at least be able to make some claims that their blades have been damaged during transportation.
That’s a unique piece ’cause I don’t know any other. OEM that is doing that many inspections at the moment. Joel, do you know any of
Joel Saxum: others that are doing that? I know they should be. Uh, but, but, uh, yeah, same page. I don’t know anybody that actually is. I think it’s a, a bit of a. It’s good market response, to be honest with you, from my opinion, because I mean, you know, we’ve, we’ve seen so many blades that are brand new or within warranty having issues.
Well now you can trace them back. If you get that inspection done at the factory, you put in a, uh, basically a, a. Data point of traceability. If it was good then and it got to site and then all of a sudden there’s a damage, well that happened during transportation and handling. So you can start to say, that was your fault.
This is who should pay for this. These are the things that are being traced. Right. Um, and we did see in a presentation, uh, just yesterday or two days ago from Arons that they were putting statistics to the findings of their internal crawlers. And one of them was rad at like that. 70% from root to tip mark where that handling happens.
There was a spike in damages that they’re finding. And it was mostly all related to handling, so I don’t know of any others. I know it’s actually kind of hard to get anybody as, even as an operator, get any of these OEMs or blade manufacturers to agree to get inspections done of the factory.
Allen Hall: Joel, do you think that some of the damage is caused by the cradles or the saddles that are used during transport, or is it more about just the roughness of the roads and the, the trucks that are used to move the
Joel Saxum: blades around?
Well, it’s ha, it’s handling. Uh, for the most part because if you can eliminate how many times you have to handle anything, you can avoid damages. This is why offshore wind farms have a, a problem as well, because if you’re going to move, even if the factory is key, the factory’s close to keyside for those blades, you still have to get them out of the factory, into the lay down yard to the key, and then craned onto the vessel, and then crane, you know, moved on the vessel and then craned off the vessel.
And if you’re in that Jones Act situation, like we are here in this. States, you’ve got to move them twice offshore. That’s just not good, right? Uh, you don’t want to be, you want to handle these things as minimal amounts as possible, because at the end of the day, they’re fragile. How many blades Allen have we seen where like the trailing edge has like a little.
Crunch in it, you know, a lot too, way too many.
Allen Hall: Rosemary. Is there a lot of structural reinforcement that happens on these longer blades for the lifting points and the transportation points?
Rosemary Barnes: No, they don’t. Uh, I, I mean they definitely, um, consider that, uh, as a potential failure mode, but they’re not.
Necessarily trying to reinforce a blade as they are trying to make the cradle so that it won’t damage the blade and put it in a location where there is some, um, reinforcement there. I’m not a hundred percent sure that it’s like purely one way direction. They might, you know, know where the cradles roughly have to go and make sure that there is, you know, like a bulkhead or something there that can, um, stiffen, stiffen up that area a bit locally.
But they’re definitely, they definitely don’t want, you know, a bunch of extra weight added purely for the. Point of transportation, because then it’s up there on the turbine weighing more than it needs to for 20, 30 years. And that affects every, every other component. The, you know, bearings, the. Um, drive, train the tower.
The foundations all need to be beefed up a little bit extra because of the extra weight.
Allen Hall: Phil, what is the cost to the industry due to transportation damage? I think that number’s big.
Phil Totaro: Yeah. It’s, it’s in the millions and we’ve actually been rerunning our calculations, um, recently. So, um, blade transportation damage is actually now number three.
Um, lightning damage to blades has actually overtaken it as being the number one issue. Um, which may or may not be a good thing, I guess, depending on what area of the business you’re in. Certainly if you’re selling people lightning protection technology, uh, maybe that’s good. Um, but, uh, blade root cracking, uh, is also now a big issue.
But all three of those, so. Lightning damage, blade root cracking and transportation damage are like your top three, uh, issues. And it’s all well into the hundreds of millions of dollars a year, uh, in annual, um, operations and maintenance expenditure just for the US market alone. Unfortunately, we don’t have data on, um, the faults and failure rates in other countries yet.
Um, but based on recent conversations, uh, with my new friends in Australia that. Uh, it looks like we may get some data.
Allen Hall: Alright, so after the break, I want to highlight what Phil was discussing here about the hundreds of millions of dollars in transportation expenses do to damage and what we’re doing about it or what we can do about it.
Don’t let blade damage catch you off Guard the logics. Ping sensors detect issues before they become expensive, time consuming problems. From ice buildup and lightning strikes to pitch misalignment in internal blade cracks. OGs Ping has you covered The cutting edge sensors are easy to install, giving you the power to stop damage before it’s too late.
Visit eLog ping.com and take control of your turbine’s health today. Okay, Phil. If there’s so much damage happening from transportation and lightning, by the way, it does seem like CMS should be used to detect it. Now it looks like GE is actually gonna use the internal rovers from Aeros to inspect them, but are there any CMS systems on a.
Truck or on the cradle when blades are being transported at the minute?
Phil Totaro: No. No way. That’s that’s way more sophisticated than this industry would ever employ. And way more expensive than anything we would ever choose to do if we can’t even get people to put CMS systems on turbines. Um, you know, even 4, 5, 6 megawatt turbines, then we’re not gonna have, you know, any kind of, uh, fault and failure detection on the, the transportation systems themselves.
Not to say that that wouldn’t probably catch certain issues and, you know, you can certainly put like strain gauges and accelerometers on the truck, uh, or on a cradle. Um, and some people may in rare occasions use things like that. Um, but it’s not standard
Joel Saxum: for sure. Yeah, Phil, I was gonna mention that. Not standard as well, right?
So in Hamburg, two years ago, I ran into a company that was doing just this. They had a sensor that was about the size of a cell phone, and it’s really basic sensor, to be honest with you. It’s just GPS communications, a battery, and then an accelerometer and a gyro inside of it. And they were, it’s the same kind of stuff that’s used to track fleet vehicles, right?
Like, oh, this is this vehicle, this is, so, you can see where it is if they hit the brakes hard, these kind of things. But they were wanting to put them, that was their goal. We’re gonna put ’em on turbine blades from the factory. So locationally geographically, we can track them, uh, wherever they go. And then also if they hit a bump hard, if they do something, if they get dropped or whatever, you can see the different G-forces on the blades themselves.
But. You know, when I was speaking with him, I was like, that’s cool. I said, probably the locational part, because at the, to be honest with you, you’d have to put a half a dozen of these things on different parts of the blade to start to see if the root bending moments moved a bunch or something of that sort.
And at the end of the day, you’re not gonna get, like, blades don’t show up cracked in half, you know what I mean? Mostly it’s lifting damage or something like that. So the accelerometer thing, I don’t know if that’s really a valid, but people have tried to do it. It just has never, could, never caught on.
Allen Hall: Okay, Rosemary, when a CMS system should be installed, there must be some sort of criteria here, and I want, I want to get your thoughts about this because there is a lot of discussions about CMS and monitoring of blades and monitoring of gear boxes, and there’s a spec gonna come out in the next, I don’t know, it’s a couple of weeks, I suppose, and.
There is so much discussion about it, but I want to hear some sane thoughts about when you should use a CMS system.
Rosemary Barnes: You know what? I think that it’s got a lot to do with, um, the amount of. Um, spare time that your operators have on their hands, people that working in operations and maintenance and, um, all of those sort of, you know, like afterwards things, um, they’re so pressed for time.
They do not have enough time to do all of the things that they already know they have to do. They kind of don’t want to know about additional things. And so when you say how much should you have, they should have that CMS because it will ultimately make their job smaller. Right? That, um. You that that will instead of.
Having to replace, you know, some gearbox component or some bearings that means, you know, like a shutdown of a turbine for a long time and all of a sudden an emergency to, you know, get this fixed quickly. Instead of that, they would be able to, you know, monitor across the fleet. They would know, okay, we’ve got a few that are coming up and we’ll need to be replaced soon, so we’ll make a campaign and we’ll get them all together.
But, um, yeah, so that’s, that’s what should be happening. The industry would work much smoother, but I know that the reality of it is that people are too pressed to start thinking about stuff like that.
Allen Hall: Phil, what are the top four or five money losers? On turbines at the minute?
Phil Totaro: Uh, well, generally blades, I mean, I can’t, you know, again, I can’t really categorize everything, um, specifically ’cause we don’t have enough information about all the faults and failure modes, but blades number one, uh, gear boxes, particularly bearings and anything having to do with kind of the drivetrain overall, uh, main shaft, et cetera.
So that’s all kinda lumped in there. Um. Jaw bearing and pitch bearing. Those are, those are kind of your top three or four.
Allen Hall: Okay. Let’s look. Let’s look at sources of problems. It was lightning’s number one, right? In terms of sources of problems
Phil Totaro: for
Allen Hall: blades? Yes.
Phil Totaro: And for tower. And for tower collapses, potentially, yes.
I mean,
Allen Hall: right tower collapses. Catastrophic lightning has gotta be close to the top. The insurance companies will tell you that.
Phil Totaro: Uh, yeah. Again, I don’t have the data to say that if an insurance company will tell you that, then I’ll believe it because that seems logical that, you know, I mean, how a blade is even able to strike the tower to kind of knock it down is if the blade’s got some kind of damage and there’s a load imbalance, um, it’s hard to just get a load imbalance from some other.
You know, like you’re not gonna get a load imbalance from leading edge erosion, let’s put it that way. I mean, you’d have to have ridiculous leading edge erosion to have a load imbalance on the blade or the rotor
Allen Hall: catastrophic. The things that will take down turbines today are light. It gotta be lightning.
It’s gotta be number one. It’s not even a close second to that, I don’t think. Some sort of serial defect in blades. De bonding. Yeah, de bonding, right. Something that’s just. Almost immediate, but uh, but, but a structural problem, right? A structural problem that’s probably a factory issue, a quality issue.
After that, it gets pretty consistent, right? You’re talking about gearbox failures, which are really. Time driven, some sort of bearing failure
Rosemary Barnes: loose bolts in the tower. Right? Haven’t we seen a few of, a few of those
Allen Hall: root blade root cracks, which are a manufacturing issue and yeah. The tightening of bolts.
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah. Root inserts,
Allen Hall: right Root inserts,
Rosemary Barnes: detaching. Also foundation problems can cause it. Um, and, uh, could I just, uh, go off on a, a tiny tangent that you said, you know, lightning obviously I was talking to somebody recently, um, ’cause there was a, a tower collapse in Australia and they’re saying it was probably lightning.
And anecdotally in the Australian wind industry, people are rolling their eyes going, oh, come on. As if that’s the case. So I don’t think it’s necessarily obvious. Um, I mean, I, I know that we all, we all know. That anything that can damage a blade so much that it, you know, falls in half or folds in half, or, um, you know, gets a big crack so it hits a tower, then you’ve got a big enough imbalance that your tower’s gonna start wobbling around like a noodle and then it’s gonna, you know, it’s gonna fall over.
Right. Um, so it doesn’t, it’s not that the lightning. Struck the tower down, you know, even though, I mean, lightning can do that, we’ve all seen trees fall down right. From being struck by, struck by lightning. So I guess it, it, it could happen, but that’s not what the failure modes we’re talking about, right?
It’s, it’s any, anything that can make the blades, um, damage, get damaged so much that they have strike the tower or a big chunk falls off and sets the, sets the tower wobbling.
Allen Hall: I, I totally agree. And if those are the big money losers. The why are they’re not CMS systems installed to protect against the million two, four, $5 million loss.
We’re focused on, weirdly enough gearbox monitoring, which is great, you know, but it, it is a time, long time derivative problem. It’s gonna degrade slowly. And we know what those curves are like, is just like leading edge erosion, right? So why wouldn’t you do the simplest. One first lightning transportation lifts.
Then you’re looking at sort of serial defects. I think if, you know you got a, a root cracking issue in a particular kind of blade, then we put a CMS on it. But the, the gearbox monitoring and the oil monitoring all great, but are they, they’re not, wouldn’t be top priority in terms of money. Saved. Right.
Rosemary Barnes: But I think it’s in terms of how easy it is to monitor these things, because I mean, maybe there are blade monitoring solutions today, I, I, maybe I’m not a hundred percent up to date, but at least until recently, there were ways to monitor it, but not cheap and not.
Easy to actually monitor. You know, like it’s really hard to say, like, you know, um, wind turbines are, are, are cracking and stuff all the time. It’s like impossible to say, when is a crack gonna turn into something that I need to worry about? And unless you’ve got strain sensors like covering a blade like a net, you’re not actually gonna be sure that you’re gonna catch every single big crack that might happen.
So I think that that one. Hard. Lightning I know is easy, but I don’t think it’s well understood how easy it is to monitor for lightning.
Allen Hall: It’s a couple hundred dollars per turbine, right? Today. It’s cheap compared to a drone inspection, but I don’t think that’s
Rosemary Barnes: well
Allen Hall: known. Rosie would, would you say that the, all the cracks and the leading edge erosion and even some of those serial defects, because we’ve have drone inspections happening in some cases mandatory quarterly, quarterly.
Yeah, quarterly. Would you, would you put a CMS system in, or we just rely on the internal external drone inspections as your quote unquote CMS?
Rosemary Barnes: Well, I, I mean, I don’t think, I think you might end up with a false of a sense of false security by putting CMS to monitor cracks that were identified in drone inspections.
I mean, if it’s a big enough crack to be worried about, it needs to be getting repaired right away. Um, it, and then there’s the next category down where. You wanna monitor it and see how it grows, then? Yeah. I mean. I dunno, it’s hard to say. I can see CMSI, I don’t know if even know if it counts in CMS ’cause CMS to me sounds like a, you know, like a monitoring while normal operation is happening.
But when you know you’ve got a bad crack or maybe you’ve got like a serial defect issue and you know you’ve got 10 affected turbines in your site and it’s, you know, taking your long time to get, maybe you need even replacement blades or you know, you need to take them down and do a month long repair on each one.
Um, sometimes you would really like to keep badly damaged blades operating. If possible, and then I can definitely see a case for you, you know, you’ve got an, a specific area that you’re monitoring, put some, there are systems that you can put in place to monitor a known one location of a, a crack. And then yes, definitely then you can, you know, run, you don’t have to be as cautious about shutting down your whole potentially affected, um, you know, uh, uh, population of, of turbines and, and blades.
But beyond that, I actually, I don’t think that. Drone inspections are good enough and definitely not on their own. I mean, they don’t capture all of the inside stuff. Even the internal inspections don’t capture all of the inside stuff. I just think that you’re not actually like, you’ll get a little bit closer.
Um, to knowing what’s going on with your blades, but not close enough to not have to worry about it.
Joel Saxum: Yeah. I think that there’s a, there’s a couple of new advancements in, in CMS for blade cracks as well, so of course there’s, there’s multiple of these solutions actually out there, right? Uh, we have, we have a good friend of the show that’s installing cameras inside of.
Blades to monitor cracks right now too. Uh, but also Aeros was doing that. They talked about it at Blades USA this week, uh, putting cracks in or cameras into monitor specific cracks. But there’s also been advances in CMS at that really minute level of ac accelerometers and vibration where, so a blade is inherently stiff, you know, the frequency of vibrates that if you start to get a crack in it.
It reduces the stiffness, so the frequency changes in the whole blade. So it’s one of those things where like, if that happens, then it’s a flag come and look at me, I think. But, but I think where we’re at here now is this, Alan, you raised a great point with this conversation because if you were to ask Phil, Phil, what are the numbers for failures in the most expensive ones?
10 years ago, it would’ve been gear boxes. So in, in response to that, the industry was like, we need to monitor gear boxes. We need to monitor oil, we need to monitor all this stuff. And we have solved that. Not solved, but we have greatly reduced the cost of that problem as an industry. I. Right. So now we’re at the next stage.
It’s like the industry has forgot that that’s how we solve that problem. And now we have the next iteration of problem, which is blades, and we have solutions for it, but nobody’s implementing them.
Phil Totaro: Well, and the other, the other real issue for blades was about 15 years ago when a lot of companies were developing very sophisticated.
You know, blade monitoring systems. They had, you know, fiber Bragg sensors that they wanted to put into everything. And I mean, but these, these systems were all so fantastically expensive and unfortunately unreliable, particularly as it, as these systems and the sensors on the blades interacted with lightning.
Um, you know, you, you end up with. Uh, you know, a boondoggle that doesn’t really pay for itself. Uh, and so a lot of companies were just like, you know what, we’ll rely on drones. Which, you know, even again, going back 10 years, were cheap and still relatively are, um, to, to do that kind of an inspection as opposed to having a full fledged CMS system integrated into the blade as CMS technology gets cheaper.
That increases the rate of adoption. Um, the reality is that the industry still needs solutions, but it needs more cost effective and targeted solutions. It sounds like
Allen Hall: That’s what I’m saying is that I can go back to Phil’s point. You gotta have RROI, high, ROI on any kind of CMS. You put on your most expensive.
Losses are catastrophic. Go cover those at a minimum. And the cost of those sensors to catch the catastrophic before they turn catastrophic are incredibly low. They’re in the hundreds of dollars well below a thousand dollars. Lightning ones are about $250 at the minute. They’re crazy low, they’re way less expensive than pretty much any other CMS on, on the turbine right now.
Put them on, at least you’re gonna. Protect your
Joel Saxum: huge downside loss. Yeah. Think about the simple math on that one. Alan. 250 bucks a turbine for lightning sensors so you know exactly when a tower got struck. And if you use them properly in operations, you can, you can instrument a thousand turbines. For the cost of one insurance deductible.
Allen Hall: As Wind energy professionals staying informed is crucial, and let’s face it difficult. That’s why the Uptime podcast recommends PES Wind Magazine. PES Wind offers a diverse range of in-depth articles and expert insights that dive into the most pressing issues facing our energy future. Whether you’re an industry veteran or new to.
Wind, PES Wind has the high quality content you need. Don’t miss out. Visit PES wind.com today. CPI composites, A major supplier in the wind energy industry has celebrated the production of its 100,000. Uh, the milestone highlights the company’s longstanding role in supporting the growth of wind energy through, uh, blade manufacturing across multiple global facilities.
So, you know, obviously you do the math. 100,000 divided by three is like 33. Thousand turbines plus. That’s a lot of wind turbines. I was trying to do the math on where most of those blades were built. That, my guess is that a significant portion were built or, or are built right
Joel Saxum: now down in Mexico. Right?
Yeah. Everybody you talked to is like that. Yeah. That factory. That factory in Mexico. I think there’s three factories in Mexico. Two. I know there’s two. I think there’s three, but to me that seems, doesn’t that I, I honestly con congrats to TPI for the a hundred thousand to play, but. 30. Then when you do the math, Alan, you said 33,000 turbines.
There’s almost 500,000 turbines in the world right now. That seems low. I would think that TPI would have a larger share.
Allen Hall: Yeah, it does seem low. I, I would say they would have a lot more, so the a hundred thousand doesn’t make sense except that they were kind of, Johnny come lately in a sense that, that they were doing small production runs for a while.
Mostly in the States when they started, they were making blades, I think in Rhode Island for a while. And then once it got to scale mostly in Mexico and Turkey and some other places, then it really picked up, right?
Phil Totaro: Yeah. And then, but then they mothballed the, the Newton, Iowa factory in 2021 to shift production down to Mexico and India, where it was cheaper cost of labor and, um, you still had access to, to raw materials.
Um, but. They’re now talking about, in part because of the, the threat of tariffs that are to be imposed on, on Mexico, potentially. They’re talking about restarting the, or accelerating the restarting of the Newton, Iowa factory, um, specifically to meet the demand for GE
Joel Saxum: Renova. Oh, that’s cool. I mean, ge like the, the article you said today, Alan Scott Straza said a softening of the market there, but they still have order book.
They still gotta create a lot of blades. I mean. They’re we’re, we’re, we’re built. Just think about the Sun Zia project. They’ve got hundreds of turbines just for that one project that they’ve gotta build. So, uh, yeah, I think maybe the TPI thing in my mind about why I thought it would be a bigger market share is just because a lot of the projects that, uh, that Alan, you and I, or our compadres in the industry work on.
I have TPI blades in ’em. So maybe that’s just why my mind was going that way.
Allen Hall: Well, and our friends at Vestas have opened up another presence in the United States. They opened some offices in Houston, Texas to much a great fanfare. Uh, they used to have an office in Houston years ago, as Phil has pointed out before we started recording today.
Uh, but they’re back at it and it looks like they’re trying to get more of a foothold into the United States. They have about. 500 employees in Texas at the minute, but it does seem a lot of the manufacturing and production is coming out of Colorado. And obviously as Joel pointed out, you know, sun Z is a big project that Vestas is also involved with.
Uh, so what does the growth outlook look like for Vestas and why the move right
Joel Saxum: now? I, I don’t know what the growth outlook looks like, but I do know that being a person who lived in Houston and works and plays there still. There’s so many good engineers in Houston, and it’s not just mechanical electrical engineers.
It’s every sort of engineer you can imagine, and a lot of it from that oil and gas world, right? So Houston as the. Energy capital of the world for oil and gas. Now that city is starting to rebrand itself as the energy transition capital of the world. They’re all the trade organizations are trying to do this.
They’re grabbing people at oil and gas to be engineers. So there’s a lot of really good, smart people that understand the energy industry in Houston. If you’re gonna put an office in the United States and as a wind company, it’s a good place to be or or to do an event. Uh, this week’s wind farm of the week is the Jericho Rise Wind Farm.
It’s an EDPR wind farm and it’s really close to the Canadian border, so it’s up in the northern part of New York state. And we’ll do a little bit of a wind farm, uh, by the numbers this week for the wind farm of the week. So, uh, this wind farm 37 S-G-R-E-G 1 14 2 0.1 megawatt machines, uh, that creates a total of 77.
Point seven megawatts, uh, coming outta this wind farm. But the scope of work for some of the build out was, is kind of interesting. 55, 50 5,000 linear feet of access. Roads, 175,000 tons of sub based placed for roads and pads, 3.6 million pounds of rebar. Procured and installed for foundations. 23,300 cubic yards of concrete.
Procured and installed 60,000 cubic yards of backfill, a hundred acres of trees. Uh, $132 million. Went into this wind farm with, uh, 76 construction jobs and six jobs created locally. So it gives you a little bit of the scale of what it takes to. Build one of these wind farms, uh, and this is 37 turbines, right?
We’re seeing wind farms a hundred, a hundred fifty, two hundred, three hundred, even more than that for wind turbine numbers. So the, the size and scale of these things is, is growing and growing. So Jericho Rise Wind Farm, up at upstate New York by the Canadian border from EDPR, you are the Wind Farm of the week.
And that’s gonna
Allen Hall: do it for this week’s Uptime with Energy podcast. Thanks for listening. Give us a five star rating on your podcast platform and subscribe it in the show notes below to Uptime, tech News or Substack Newsletter. And if you haven’t joined us on YouTube yet, we’re getting close to a million subscribers.
So you. Better click in there before we cross that magic number. We have to have some sort of giveaway at a million if we can figure out who that person is. That would be kind of cool. So we’ll see you here next week on the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast.
https://weatherguardwind.com/low-cost-cms-damage/
Renewable Energy
The United States Run Amok
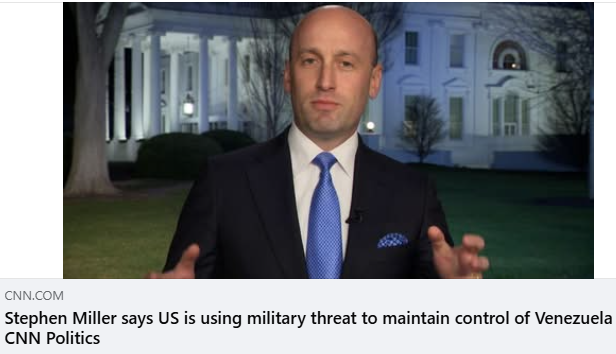 An old school chum writes:
An old school chum writes:
“We live in a world … that is governed by strength … by force … and by power.” – Stephen Miller (see @ 5:55). For the record, that’s what Hitler said in 1939.
The United States has lost its place in this world. We’ve been taken over by a lunatic president and his “nazi” henchmen.
Renewable Energy
Solar Compliance & Regulations Every Australian Business Must Know
Renewable Energy
US Offshore Wind Halts, Japan Launches First Floating Farm
Weather Guard Lightning Tech

US Offshore Wind Halts, Japan Launches First Floating Farm
Allen, Joel, Rosemary, and Yolanda discuss the ongoing federal halt on US offshore wind projects and mounting lawsuits from Equinor, Ørsted, and Dominion Energy. Plus Japan’s Goto floating wind farm begins commercial operation with eight Hitachi turbines on hybrid SPAR-type foundations, and Finnish investigators seize a vessel suspected of severing Baltic Sea cables.
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly newsletter on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on YouTube, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary’s “Engineering with Rosie” YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
The Uptime Wind Energy Podcast brought to you by Strike Tape, protecting thousands of wind turbines from lightning damage worldwide. Visit striketape.com. And now your hosts, Allen Hall, Rosemary Barnes, Joel Saxum and Yolanda Padron. Welcome to the
Allen Hall: Uptime Wind Energy Podcast. I’m your host, Alan Hall. I’m here with Rosie Barnes, Joel Saxum, and Yolanda Padron.
Many things on the docket this week. The, the big one is the five US offshore wind projects that are facing cancellation after the federal halt. And on December 22nd, as we all know, the US Department of Interior ordered construction halted on every offshore wind project in American waters. Uh, the recent given and still given is national security.
Uh, developers see it way differently and they’ve been going to court to try to. Get this issue resolved. Ecuador, Ted and Dominion Energy have all filed lawsuits at this point. EOR says [00:01:00] a 90 day pause, which is what this is right now, will likely mean cancellation of their empire. Project Dominion is losing more than about $5 million a day, and everybody is watching to see what happens.
Orton’s also talking about taking some action here. Uh, there’s a, a lot of moving pieces. Essentially, as it stands right now, a lot of lawsuits, nothing happening in the water, and now talks mostly Ecuador of just completely canceling the project. That will have big implications to US. Electricity along the east coast,
Joel Saxum: right Joel?
Yeah. We need it. Right? So I, I hate to beat a dead horse here because we’ve been talking about this for so long. Um, but. We’ve got energy demand growth, right? We’re sitting at three to 5% year on year demand growth in the United States, uh, which is unprecedented. Since, since, and this is a crazy thing. Since air [00:02:00] conditioning was invented for residential homes, we have not had this much demand for electricity growth.
We’ve been pretty flat for the last 20 years. Uh, so we need it, right? We wanna be the AI data center superpower. We wanna do all this stuff. So we need electrons. Uh, these electrons are literally the quickest thing gonna be on the grid. Uh, up and down that whole eastern seaboard, which is a massive population center, a massive industrial and commercial center of the United States, and now we’re cutting the cord on ’em.
Uh, so it is going to drive prices up for all consumers. That is a reality, right? Um, so we, we hear campaign promises up and down the things about making life more affordable for the. Joe Schmo on the street. Um, this is gonna hurt that big time. We’re already seeing. I think it was, um, we, Alan, you and I talked with some people from PGM not too long ago, and they were saying 20 to 30% increases already early this year.
Allen Hall: Yeah. The, the increases in electricity rates are not being driven by [00:03:00] offshore wind. You see that in the press constantly or in commentary. The reason electricity rates are going up along the east coast is because they’re paying for. The early shutdown of cold fire generation, older generation, uh, petroleum based, uh, dirty, what I’ll call dirty electricity generation, they’re paying to shut those sites down early.
So that’s why your rates are going up. Putting offshore wind into the equation will help lower some of those costs, and onshore wind and solar will help lower those costs. But. The East Coast, especially the Northeast, doesn’t have a lot of that to speak of at the minute. So, uh, Joel, my question is right now, what do you think the likelihood is of the lawsuits that are being filed moving within the next 90 days?
Joel Saxum: I mean, it takes a long time to put anything through any kind of, um, judicial process in the United States, however. There’s enough money, power [00:04:00] in play here that what I see this as is just like the last time we saw an injunction happen like this is, it’s more of a posturing move. I have the power to do this, or we have the power to do this.
It’s, it’s, uh, the, it’s to get power. Over some kind of decision making process. So once, once people come to the table and start talking, I think these things will be let, let back loose. Uh, I don’t, I don’t think it will go all the way to, we need to have lawsuits and stuff. It’ll just be the threat of lawsuits.
There’ll be a little bit of arbitration. They’ll go back to work. Um, the problem that I see. One of the problems, I guess, is if we get to the point where people, companies start saying like, you know what, we can’t do this anymore. Like, we can’t keep having these breaks, these pauses, these, this, you know, if it’s 90 days at $5 million a day, I mean that’s 450 million bucks.
That’s crazy. But that nobody, nobody could absorb that.
Allen Hall: Will they leave the mono piles and transition pieces and some [00:05:00] towers just sitting in the water. That’s what
Joel Saxum: I was gonna say next is. What happens to all of the assets, all of the steel that’s in the water, all the, all the, if there’s cable, it lays if there’s been rock dumps or the companies liable to go pick them up.
I don’t know what the contracts look like, right? I don’t know what the Boem leases say. I don’t know about those kind of things, but most of that stuff is because they go back to the oil field side of things, right? You have a 20 year lease at the end of your 20 year lease. You gotta clean it up. So if you put the things in the water, do they have 20 years to leave ’em out there before they plan on how they’re gonna pull ’em out or they gotta pull ’em out now?
I don’t know.
Allen Hall: Would just bankrupt the LLCs that they formed to create these, uh, wind
Joel Saxum: farms. That’s how the oil field does it bankrupt. The LC move on. You’ve, you’ve more than likely paid a bond when you, you signed that lease and that, but that bond in like in a lot of. Things is not enough. Right. A bond to pull mono piles out would have to be, [00:06:00] I mean, you’re already at billions of dollars there, right?
So, and, and if you look again to the oil and gas world, which is our nearest mirror to what happens here, when you go and decommission an old oil platform in the Gulf of Mexico, you don’t pull the mono piles out. You go down to as close to the sea floor as you can get, and you just cut ’em off with a diamond saw.
So it’s just like a big clamp that goes around. It’s like a big band saw. And you cut the foundations off and then pull the steel back to shore, so that can be done. Um, it’s not cheap.
Allen Hall: You know what I would, what I would do is the model piles are in, the towers are up, and depending on what’s on top of them, whether it’s in the cell or whatever, I would sure as hell put the red flashing lights on top and I would turn those things on and let ’em run just so everybody along the East coast would know that there could be power coming out of these things.
But there’s not. So if you’re gonna look at their red flashy lights, you might as well get some, uh, megawatts out of them. That’s what I would do.
Joel Saxum: You’d have to wonder if the contracts, what, what, what it says in the contracts about. [00:07:00] Uh, utilization of this stuff, right? So if there’s something out there, does the FAA say, if you got a tower out there, it’s gotta have a light on it anyways.
Allen Hall: It has to or a certain height. So where’s the power coming from? I don’t know. Solar panel. Solar panel. That’s what it have to be, right? Yeah. This is ridiculous. But this is the world we live in today.
Speaker 4: Australia’s wind farms are growing fast, but are your operations keeping up? Join us February 17th and 18th at Melbourne’s Pullman on the park for Wind energy o and M Australia 2026, where you’ll connect with the experts solving real problems in maintenance asset management.
And OEM relations. Walk away with practical strategies to cut costs and boost uptime that you can use the moment you’re back on site. Register now at W OM a 2020 six.com. Wind Energy o and m Australia is created by wind professionals for wind professionals. Because this industry needs solutions, not speeches, [00:08:00]
Allen Hall: the dominoes keep falling.
In American offshore wind, last year it was construction halts this year, contract delays. Massachusetts has pushed back the signing of two offshore wind agreements that were supposed to be done. Months ago, ocean Winds and Berroa won their bids in September of 2024. The paperwork is still unsigned more than a year later, a year and a half later.
State officials blame Federal uncertainty. Uh, the new target is June and offshore wind for these delays are really becoming a huge problem, especially if you don’t have an offtake agreements signed, Joel.
Joel Saxum: I don’t see how the, I mean, again, I’m not sitting in those rooms. I’m not a fly on the wall there, but I don’t see how you can have something sitting out there for, it’s just say September 24.
Yeah. Yeah. You’re at 18 months now, right? 17, 18 months without an agreement signed. Why is, why is Massachusetts doing this? What’s, what’s the, what’s the thing there? I mean, you’re an, [00:09:00] you are, uh, an ex Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Ian, is that what it’s called?
Allen Hall: Yeah. I, I think they would like to be able to change the pricing for the offtake is most likely what is happening as, uh, the Trump administration changes the agreements or trying to change the agreements, uh, the price can go up or down.
So maybe the thing to do is to not sign it and wait this out to see what the courts say. Maybe something will happen in your favor. That’s a real shame. Right. Uh, there’s thousands of employees that have been sidelined. Uh, the last number I saw was around 4,000. That seems on the low end.
Joel Saxum: Yeah. I think about, um, the, the vessels too.
Like you’re the, like the Eco Edison that was just built last year. I think it’s upwards of 500 million bucks or something to build that thing down in Louisiana, being sent up there. And you have all these other specialized, uh, vessels coming over from Europe to do all this construction. Um, you know. Of course if they’re coming over from Europe, those are being hot bunked and being paid standby rates, which [00:10:00] is crazy ’cause the standby rates are insane.
Uh, ’cause you still gotta run fuel, you still gotta keep the thing running. You still gotta cook food. You still have all those things that have to happen on that offshore vessel. Uh, but they’re just gonna be sitting out there on DP doing nothing.
Yolanda Padron: You have the vessels, you have people’s jobs. You have.
Regular people who are unrelated to energy at all suffering because of their prices going up for energy and just their cost of living overall going up. All because they don’t look pretty.
Joel Saxum: Yeah. The entire, that entire supply chain is suffering. I mean, Yolanda, you’re, you, you used to work with a company involved in offshore wind.
How many people have, um, you know, have we seen across LinkedIn losing their jobs? Hey, we’re pivoting away from this. I gotta go find something else. And with that. In the United States, if you’re not from the States, you don’t know this, but there’s not that much wind, onshore wind on the East coast. So many of those families had to relocate out there, uproot your family, go out to Massachusetts, New Jersey, [00:11:00] Virginia, wherever, put roots back down and now you’re what?
What happens? You gotta move back.
Yolanda Padron: Good luck to you. Especially, I mean, you know, it’s, it’s a lot of projects, right? So it’s not like you can just move on to the next wind farm. It’s a really unfortunate situation.
Allen Hall: Well, for years the promise of floating wind turbines has dangled just out of reach and the technology works, and the engineers have been saying for quite a while.
We just needed someone to prove it at scale. Well, Japan just did the go-to floating wind farm began commercial operation this past week. Eight turbines on hybrid spar foundations anchored in water is too deep for anything fixed. Bottom, uh, it’s the first. Wind farm of his kind in Japan and signals to the rest of Asia that floating wind is possible.
Now, uh, Rosemary, their turbines that are being used are Hitachi turbines, 2.1 megawatt machines. I don’t know a lot about this hybrid spark [00:12:00] type floater technology, which looks to be relatively new in terms of application. Is this gonna open up a large part of the Japanese shoreline to offshore wind?
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah, I mean, at the first glance it’s like two megawatt turbine turbines. That’s micro, even for onshore these days, that’s a really small turbine. Um, and for offshore, you know, usually when you hear about offshore announcements, it’s like 20 megawatt, 40 megawatt monstrosities. However, I, I think that if you just look at the size of it, then it really underestimates the significance of it, especially for Japan.
Because they, one, don’t have a lot of great space to put turbines on shore or solar power on shore. Um, and two, they don’t have any, any good, um, locations for fixed bottom offshore. So this is not like this floating offshore wind farm. It’s not competing against many onshore um, options at all. For Japan, it’s competing against energy imports.
I’m really happy to see [00:13:00] a proper wind farm. Um, in Japan and they’ll learn a lot from this. And I hope that it goes smoothly and that, you know, the next one can be bigger and better. And then it’s also, you know, Japan traditionally has been a really great manufacturing country and not so much with wind energy, but this could be their chance.
If they’re the country that’s really on scale developing the floating offshore industry, they will necessarily, you know, like just naturally as a byproduct of that, they’re gonna develop manufacturing, at least supporting manufacturing and probably. Some major components and then bring down the cost. You know, the more that, um, these early projects might start out expensive, but get cheaper, fast.
That’s how we hope it’ll go. And then they’ll push out into other areas that could benefit from offshore wind, but um, not at the cost. Somewhere like California, you know, they have the ability to have onshore wind. They’d really like some offshore wind, some floating offshore wind. But it is a hard sell there at the moment because it is so much more expensive.
But if it gets cheaper because, you know, projects like [00:14:00] this help push the price down, then I think it will open things up a lot. So yeah, I am, I’m quite excited to see this project.
Allen Hall: Will it get cheaper at the two to six megawatt range instead of the 15 to 20 megawatt range?
Joel Saxum: That’s what I was gonna comment on.
Like there’s, there’s a, there’s a key here that the general public misses. For a floating offshore wind farm. So if you’re gonna do this cost effectively, that’s why they did it with the 2.1 megawatts ones because with a, with the spar product that they’re using basically. And, and I was sourcing this off at my desk, so here you go,
Rosemary Barnes: Joel.
We need a closed caption version for those listening on the podcast and not watching on YouTube. Joel’s holding like a foam, a foam model of a wind turbine. Looks like it’s got a stubby, stubby holder on the bottom.
Joel Saxum: This is. Turbine. Steel. Steel to a transition piece and then concrete, right? So this is basically a concrete tube like, um, with, with, uh, structural members on the inside of it.
And you can float this thing or you can drag these, you can float ’em key side and then drag ’em out, and [00:15:00] then it just fill ’em halfway or three quarters away with ballast sea seawater. So you just open a valve, fill the thing up to three quarters of the way with seawater, and it sinks it down into the water a little bit.
Water level sits about. Right at the transition piece and then it’s stable. And that’s a hybrid. Spar product is very simple. So to make this a easy demonstrate project, keyside facility is the key, is the big thing. So your Keyside facility, and you need a deep water keyside facility to make this easy. So if you go up to Alan, like you said, a two to six, to eight to 10 to 15 megawatt machine.
You may have to go and take, you may have to barge the spars out and then dump ’em off the spar and then bring the turbines out and put ’em on. That’s not ideal. Right? But if you can do this all keyside, if you can have a crane on shore and you can float the spars and then put the, build the whole turbine, and then drag that out as it sits, that’s a huge cost reduction in the installation operations.
So it, it’s all about how big is the subsea portion of the spar? How? How deep is your [00:16:00] deep water keyside port? To make it efficient to build. Right. So they’re looking at 10 gigawatts of floating offshore wind by 2030. Now it’s 2026. That’s only four years away, so 10 gigawatts. You’re gonna have to scale up the size of the turbines.
It’ll be interesting how they do it, right? Because to me, flipping spars off of a barge is not that hard. That’s how jackets and spars have been installed in the past. Um, for, um, many industries, construction industries, whether it’s oil and gas or just maritime, construction can be done. Not a problem. Um, it’s just not as efficient.
So we’ll see what, we’ll see what they do.
Allen Hall: You would need 5,000 turbines at two megawatts to get to 10 gigawatts, 5,000 turbines. They make 5,000 cars in a day. The, the Japanese manufacturing is really efficient. I wouldn’t put anything by the Japanese capabilities there.
Joel Saxum: The problem with that is the cost of the, the inter array cables and [00:17:00] export cables for 5,000 turbines is extreme.
Allen Hall: We also know that. Some of the best technology has come out of Japan for the last 50 years, and then maybe there’s a solution to it. I, I’m really curious to see where this goes, because it’s a Hitachi turbine. It’s a 2.1 megawatt turbine, as Rosemary’s pointed out. That’s really old technology, but it is inexpensive to manufacture and easy to move around.
Has benefits.
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah. It also means like they, they’re not gonna be surprised with like, you know, all of. When you make a 20 megawatt offshore wind turbine, you’re not only in the offshore environment, you’re also dealing with, you know, all your blade issues from a blade that long and 2.1 megawatt turbine has blades of the size that, you know, just so mature, reliable, robust.
They can at least rule those headaches out of their, um, you know, out of their. Development phase and focus on the, the new stuff.
Joel Saxum: Does anybody know who [00:18:00] makes blades for Hitachi?
Allen Hall: Rosie? Was it lm? I, I, I know we have on a number of Hitachi turbines over time, but I don’t know who makes the blades.
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah, I don’t know.
But I mean, also it’s like, um, it doesn’t mean that they’re locked into 2.1 megawatts for forever, right? So, um, if the economics suggest that it is be beneficial to scale up. Presumably there will be a lot that they have learned from the smaller scale that will be de-risking the, the bigger ones as well.
So, you know, um, it’s, there’s advantages to doing it both ways. It’s probably a slower, more steady progress from starting small and incrementally increasing compared to the, you know, like big, um, fail fast kind of, um, approach where you just do a big, big, huge turbine and just find out everything wrong with it all at once.
Um, but. You know, pros and cons to both.
Allen Hall: Hitachi buys TPI. They got the money. They got the money, and they got the brain power. [00:19:00] Delamination and bottom line. Failures and blades are difficult problems to detect early. These hidden issues can cost you millions in repairs and lost energy production.
C-I-C-N-D-T are specialists to detect these critical flaws before they become expensive burdens. Their non-destructive test technology penetrates deep to blade materials to find voids and cracks. Traditional inspections completely. Miss C-I-C-N-D-T Maps. Every critical defect delivers actionable reports and provides support to get your blades back in service.
So visit cic ndt.com because catching blade problems early will save you millions.
The Baltic Sea has become a chessboard under sea. Cables carry data. Pipelines carry energy as we’ve all seen and someone keeps cutting them. Finnish investigators are now saying a cargo ship dragged its anchor [00:20:00] across the seabed for tens of kilometers before severing a telecommunications cable. On New Year’s Eve, special forces seize the vessel.
Four crew members are detained, but the questions still remain. Who or what is trying to cut cables and pipelines at the bottom of the Baltic Sea.
Joel Saxum: It’s not accidents like it happened on New Year’s Eve and it was, and you drug an anchor for tens of kilometers. That’s on purpose. There’s, there’s no way that this is someone, oh, we forgot to pull the anchor up.
You know how much more throttle you have to put on one of these? Have you seen an anchor for an offshore vessel? They’re the size of a fricking house,
Allen Hall: so they’re investigating it right now. And four, the 14 crew members are under detention. Travel restrictions, we’ll see how long that lasts. Crew includes nationals from of all places, Russia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, and Azerbaijan.
So there is a, a Russian element to this. [00:21:00] I don’t know if you were all watching, I don’t know, a week or two ago when there’s a YouTube video from and oral, which makes undersea. Equipment and defense, uh, related, uh, products. And Palmer Lucky who runs that company basically said, there are microphones all over the bottom of the ocean, all around the world.
Everything is monitored. There’s no way you can drag an anchor for a kilometer without somebody knowing. So I’m a little surprised this took so long to grab hold of, but. Maybe the New Year’s Eve, uh, was a good time to pick because everybody is kind of relaxed and not thinking about a ship, dragging an anchor and breaking telecommunication cables, wind turbines have to be really careful about this.
There, there have to be some sort of monitoring, installation sensors that are going on around the, all the wind power that exists up in that region and all [00:22:00] the way down in, in the North Sea. To prevent this from happening, the sabotage is ridiculous. At this point,
Joel Saxum: yeah. I mean, even, even with mattresses over the export cables, or the inter array cables or, or rock bags or rock dumps or, or burials, these anchors are big enough to, to cut those, to drag and cut ’em like it, it’s just a, it’s a reality.
It’s a risk. But someone needs to be monitoring these things closer if they’re not yet. ’cause you are a hundred percent correct. There’s, so, there’s, there’s private, there’s public sides of the acoustic monitoring, right? So like the United States military monitors, there’s, there’s acoustic monitoring all up and down.
I can’t actually never, I looked into it quite a while ago. There’s a name for the whole system. It’s called the blah, blah, blah, and it monitors our coastline. Like ev, there’s a sensor. Every man, it’s a couple miles. Like all, all around the EEZ of the United States. And that exists everywhere. So like you think like in international waters, guarantee that the United States has got microphones out listening to, [00:23:00] right.
So, but if you’re in the Baltic Sea, it’s a little bit different of an, of a confined space. But you have Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, all along the southern and eastern coast and the, and Russia. And then you have the Fins, Swedes, Norwegian, Denmark, Germany. Everybody is Poland. Everybody’s monitoring that for sure.
It’s just like a postmortem investigation is, is doable.
Allen Hall: Yolanda, how are they gonna stop this? Should they board the ships, pull the people off and sink them? What is it gonna take for this to end?
Yolanda Padron: I don’t know. In the meantime, I think Joel has a movie going on in his head about how exactly he’s gonna portray this.
Um, yeah, it’s. I mean, I’d say better monitoring, but I, I’m not sure. I guess keep a closer eye on it next time. I mean, I really hope it’s, there’s not a next time, but there seems to be a pattern developing. Right.
Allen Hall: I forgot how many of those happened.
Joel Saxum: Yeah. The maritime, this is a, this is a tough reality about the maritime world.
[00:24:00] ’cause I, I’ve done some work done in Africa and down there it’s specifically the same thing. There’s say there’s a vessel. Okay, so a vessel is flagged from. S Cy Malta, a lot of vessels are flagged Malta or Cyprus, right? Because of the laws. The local laws there that Cyprus flagged vessel may be owned by a company based in, um, Bermuda that’s owned by a company based in Russia that’s owned by a company based in India.
All of these things are this way. There’s shell companies and hidden that you don’t know who owns vessels unless they’re even, even the specific ones. Like if you go to a Maersk vessel. And you’re like, oh, that’s Maersk, they’re Danish. Nope. That thing will be, that thing will be flagged somewhere else, hidden somewhere else.
And it’s all about what port you go to and how much taxes you can hide from, and you’ll never be able to chase down the actual parties that own these vessels and that are responsible you, you, it, it’s so [00:25:00] difficult. You’re literally just going to have to deal with the people on board, and you can try to chase the channels to who owns that boat, but you’ll never find them.
That’s the, that’s the trouble with it.
Allen Hall: It does seem like a Jean Claude Van Dam situation will need to happen pretty soon. Maybe as Steven Segal, something has to happen. It can’t continue to go on it over the next couple of months with as much attention as being paid to international waters and.
Everything that’s happening around the world, you’d think that, uh, ships Defense Department ships from Denmark, Finland, Germany. We will all be watching this really closely UK be watching this and trying to stop these things before they really even happened. Interesting times. That wraps up another episode of the Uptime Wind Energy Podcasts.
If today’s discussion sparked any questions or ideas. We’d love to hear from you. Reach out to us on LinkedIn and don’t forget to subscribe so you never miss an episode. [00:26:00] And if you found value in today’s conversation, please leave us a review. It really helps other wind energy professionals discover the show for Rosie, Yolanda and Joel.
I’m Alan Hall and we’ll catch you next week on the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast.
-
Greenhouse Gases5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits




