To help meet the needs of the energy transition, global demand for copper – a mineral critical for making electric vehicles, wind turbines and solar panels – is set to rise more than 40% by 2040, fuelling concern over the risks its extraction poses to the environment and human rights, new data shows.
In its latest Global Trade Update, UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD) projected this week that 80 new copper mines and $250 billion in investment would be required by 2030 to meet demand and avoid a looming shortfall that could stall the world’s shift to clean energy and digital infrastructure.
The report called copper the “new strategic raw material” for the green and digital economy – and a test case for how global trade systems handle resource pressures under strain.
“Copper is no longer just a commodity – it’s a strategic asset,” Luz María de la Mora, director of UNCTAD’s Division on International Trade and Commodities, said in a statement.
“Its market exposes the power asymmetries that still shape global trade. That’s why we need to invest in local value addition, scale up recycling and remove trade barriers that limit opportunity.”
A separate new study, meanwhile, has warned that ramping up copper production could come at a human and environmental cost.


In its Transition Minerals Tracker published on Wednesday, the Business and Human Rights Resource Centre (BHRRC), a global research and advocacy group, singled out copper as associated with 513 allegations of human rights abuses recorded between 2010 and 2024, accounting for about 60% of a total of 835 cases linked to the mining of transition minerals.
The tracker monitors abuses associated with the extraction of eight key transition minerals – copper, bauxite, cobalt, lithium, manganese, nickel, zinc and iron ore.
These minerals, used to produce technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines and electric vehicles, have become more sought after in the global push towards clean energy and electrification.
But Caroline Avan, head of just transition and natural resources at BHRRC, warned that the urgency of the energy transition should not be used to “justify an unprincipled scramble for transition minerals” that is driving widespread human rights abuses, environmental destruction and growing community conflict.
A transition built on exploitative minerals supply chains “is not simply unjust – it is unstable, unpredictable, and ultimately unsustainable”, she said, adding that “the path to net zero cannot be paved with more injustice and global inequality”.
Hidden cost of copper extraction
With copper reserves concentrated in five countries – Chile, Peru, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Australia and Russia – the researchers found that the highest number of allegations in the 15-year period occurred in three of those countries, including 14% of the total in Peru, 11% in Chile and 10% in the DRC.
In 2024 alone, more than half of the 156 abuse allegations linked to minerals projects and mines were associated with copper extraction, which over the years has faced significant operational threats as a result of conflicts with communities and associated legal challenges, the researchers said.
Central and South America featured as hotspots for copper-related legal cases. The researchers also found that 52% of copper mines located in high water stress areas had impacts on water access and/or pollution.
Ending poverty and gangs: How Zambia seeks to cash in on the global drive for EVs
This year, four copper mining companies operating in Zambia, including one British and three Chinese firms, have been accused of releasing toxic mining waste into the Kafue River’s watershed in one of the country’s worst environmental disasters.
The most devastating spill occurred in February, when the tailings dam holding mining waste from Chinese company Sino-Metals Leach Zambia burst its walls and released acidic effluent into the river.
The pollution killed fish, burned maize and groundnut crops and led to the deaths of livestock, wiping out livelihoods and causing the water supply to the nearby town of Kitwe to be shut down.


Indigenous peoples on the frontline
The alleged abuses in BHRRC’s Transition Minerals Tracker usually affect individuals and families living near mining sites and their environment, with three in five involving local communities and another 77 infringing on Indigenous Peoples’ rights, including violation of their right to Free, Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC) about projects.
Edson Krenak, Brazil cultural survival lead, wrote in a forward to the research: “Rushing to extract more minerals without reducing consumption or showing true respect for our rights is not only reckless – it is unjust and unfair,” adding that the world must listen more to Indigenous voices.
In her contribution, Annabella Rosemberg, senior advisor on just transition with Climate Action Network (CAN) International, called for “a rights-based approach throughout renewable energy value chains, where all human rights are respected, where workers are treated fairly – and where the opportunities of this extraordinary and unprecedented global effort are harnessed to build shared prosperity”.
Mining firms lack human rights policies
The researchers found that just 20 companies have been associated with 60% of allegations and attacks since 2010, with the top five companies for 2024 listed as Georgian American Alloys, China Minmetals, Codelco, Grupo México and Sinomine Resource Group.
Additionally, the tracker documented 157 attacks against human rights and environmental defenders, accounting for one in five of the total abuse allegations recorded.
Despite the problems recorded, less than half of all mines associated with at least one allegation in the tracker are covered by a corporate human rights policy. And fewer than 30 mines are associated with 50% of allegations, demonstrating that while human rights issues are widespread in the sector, some mines have become a focus for allegations of abuses and conflict.
Rosemberg of CAN International wrote in the report that the enormous impacts of “unchecked mining” on the world’s most marginalised groups – already disproportionately affected by climate change – should not be left out of climate conversations.
“Conversely, we need to be clear that extracting more minerals, at all costs, and without a serious look at reducing energy and material demand, notably in the richest countries, will not answer the climate crisis nor the hopes of economic prosperity in resource-rich countries,” she added.
The post Rising copper demand fuels concern over pollution and rights abuses appeared first on Climate Home News.
Rising copper demand fuels concern over pollution and rights abuses
Climate Change
A Little-Used Maneuver Could Mean More Drilling and Mining in Southern Utah’s Redrock Country
Two Utah Congress members have introduced a resolution that could end protections for Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument. Conservation groups worry similar maneuvers on other federal lands will follow.
Lawmakers from Utah have commandeered an obscure law to unravel protections for the Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, potentially delivering on a Trump administration goal of undoing protections for public conservation lands across the country.
A Little-Used Maneuver Could Mean More Drilling and Mining in Southern Utah’s Redrock Country
Climate Change
Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes
Drought and heatwaves occurring together – known as “compound” events – have “surged” across the world since the early 2000s, a new study shows.
Compound drought and heat events (CDHEs) can have devastating effects, creating the ideal conditions for intense wildfires, such as Australia’s “Black Summer” of 2019-20 where bushfires burned 24m hectares and killed 33 people.
The research, published in Science Advances, finds that the increase in CDHEs is predominantly being driven by events that start with a heatwave.
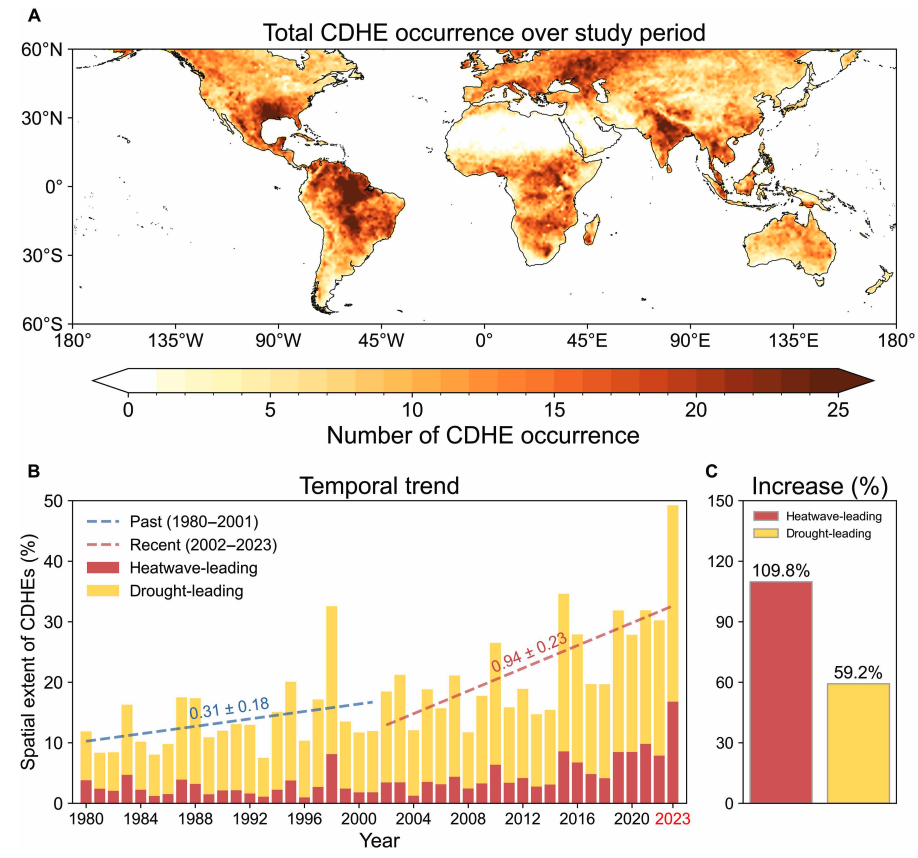
The global area affected by such “heatwave-led” compound events has more than doubled between 1980-2001 and 2002-23, the study says.
The rapid increase in these events over the last 23 years cannot be explained solely by global warming, the authors note.
Since the late 1990s, feedbacks between the land and the atmosphere have become stronger, making heatwaves more likely to trigger drought conditions, they explain.
One of the study authors tells Carbon Brief that societies must pay greater attention to compound events, which can “cause severe impacts on ecosystems, agriculture and society”.
Compound events
CDHEs are extreme weather events where drought and heatwave conditions occur simultaneously – or shortly after each other – in the same region.
These events are often triggered by large-scale weather patterns, such as “blocking” highs, which can produce “prolonged” hot and dry conditions, according to the study.
Prof Sang-Wook Yeh is one of the study authors and a professor at the Ewha Womans University in South Korea. He tells Carbon Brief:
“When heatwaves and droughts occur together, the two hazards reinforce each other through land-atmosphere interactions. This amplifies surface heating and soil moisture deficits, making compound events more intense and damaging than single hazards.”
CDHEs can begin with either a heatwave or a drought.
The sequence of these extremes is important, the study says, as they have different drivers and impacts.
For example, in a CDHE where the heatwave was the precursor, increased direct sunshine causes more moisture loss from soils and plants, leading to a drought.
Conversely, in an event where the drought was the precursor, the lack of soil moisture means that less of the sun’s energy goes into evaporation and more goes into warming the Earth’s surface. This produces favourable conditions for heatwaves.
The study shows that the majority of CDHEs globally start out as a drought.
In recent years, there has been increasing focus on these events due to the devastating impact they have on agriculture, ecosystems and public health.
In Russia in the summer of 2010, a compound drought-heatwave event – and the associated wildfires – caused the death of nearly 55,000 people, the study notes.

The record-breaking Pacific north-west “heat dome” in 2021 triggered extreme drought conditions that caused “significant declines” in wheat yields, as well as in barley, canola and fruit production in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada, says the study.
Increasing events
To assess how CDHEs are changing, the researchers use daily reanalysis data to identify droughts and heatwaves events. (Reanalysis data combines past observations with climate models to create a historical climate record.) Then, using an algorithm, they analyse how these events overlap in both time and space.
The study covers the period from 1980 to 2023 and the world’s land surface, excluding polar regions where CDHEs are rare.
The research finds that the area of land affected by CDHEs has “increased substantially” since the early 2000s.
Heatwave-led events have been the main contributor to this increase, the study says, with their spatial extent rising 110% between 1980-2001 and 2002-23, compared to a 59% increase for drought-led events.
The map below shows the global distribution of CDHEs over 1980-2023. The charts show the percentage of the land surface affected by a heatwave-led CDHE (red) or a drought-led CDHE (yellow) in a given year (left) and relative increase in each CDHE type (right).
The study finds that CDHEs have occurred most frequently in northern South America, the southern US, eastern Europe, central Africa and south Asia.
Threshold passed
The authors explain that the increase in heatwave-led CDHEs is related to rising global temperatures, but that this does not tell the whole story.
In the earlier 22-year period of 1980-2001, the study finds that the spatial extent of heatwave-led CDHEs rises by 1.6% per 1C of global temperature rise. For the more-recent period of 2022-23, this increases “nearly eightfold” to 13.1%.
The change suggests that the rapid increase in the heatwave-led CDHEs occurred after the global average temperature “surpasse[d] a certain temperature threshold”, the paper says.
This threshold is an absolute global average temperature of 14.3C, the authors estimate (based on an 11-year average), which the world passed around the year 2000.
Investigating the recent surge in heatwave-leading CDHEs further, the researchers find a “regime shift” in land-atmosphere dynamics “toward a persistently intensified state after the late 1990s”.
In other words, the way that drier soils drive higher surface temperatures, and vice versa, is becoming stronger, resulting in more heatwave-led compound events.
Daily data
The research has some advantages over other previous studies, Yeh says. For instance, the new work uses daily estimations of CDHEs, compared to monthly data used in past research. This is “important for capturing the detailed occurrence” of these events, says Yeh.
He adds that another advantage of their study is that it distinguishes the sequence of droughts and heatwaves, which allows them to “better understand the differences” in the characteristics of CDHEs.
Dr Meryem Tanarhte is a climate scientist at the University Hassan II in Morocco, and Dr Ruth Cerezo Mota is a climatologist and a researcher at the National Autonomous University of Mexico. Both scientists, who were not involved in the study, agree that the daily estimations give a clearer picture of how CDHEs are changing.
Cerezo-Mota adds that another major contribution of the study is its global focus. She tells Carbon Brief that in some regions, such as Mexico and Africa, there is a lack of studies on CDHEs:
“Not because the events do not occur, but perhaps because [these regions] do not have all the data or the expertise to do so.”
However, she notes that the reanalysis data used by the study does have limitations with how it represents rainfall in some parts of the world.
Compound impacts
The study notes that if CDHEs continue to intensify – particularly events where heatwaves are the precursors – they could drive declining crop productivity, increased wildfire frequency and severe public health crises.
These impacts could be “much more rapid and severe as global warming continues”, Yeh tells Carbon Brief.
Tanarhte notes that these events can be forecasted up to 10 days ahead in many regions. Furthermore, she says, the strongest impacts can be prevented “through preparedness and adaptation”, including through “water management for agriculture, heatwave mitigation measures and wildfire mitigation”.
The study recommends reassessing current risk management strategies for these compound events. It also suggests incorporating the sequences of drought and heatwaves into compound event analysis frameworks “to enhance climate risk management”.
Cerezo-Mota says that it is clear that the world needs to be prepared for the increased occurrence of these events. She tells Carbon Brief:
“These [risk assessments and strategies] need to be carried out at the local level to understand the complexities of each region.”
The post Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes
Climate Change
DeBriefed 6 March 2026: Iran energy crisis | China climate plan | Bristol’s ‘pioneering’ wind turbine
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Energy crisis
ENERGY SPIKE: US-Israeli attacks on Iran and subsequent counterattacks across the Middle East have sent energy prices “soaring”, according to Reuters. The newswire reported that the region “accounts for just under a third of global oil production and almost a fifth of gas”. The Guardian noted that shipping traffic through the strait of Hormuz, which normally ferries 20% of the world’s oil, “all but ground to a halt”. The Financial Times reported that attacks by Iran on Middle East energy facilities – notably in Qatar – triggered the “biggest rise in gas prices since Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine”.
‘RISK’ AND ‘BENEFITS’: Bloomberg reported on increases in diesel prices in Europe and the US, speculating that rising fuel costs could be “a risk for president Donald Trump”. US gas producers are “poised to benefit from the big disruption in global supply”, according to CNBC. Indian government sources told the Economic Times that Russia is prepared to “fulfil India’s energy demands”. China Daily quoted experts who said “China’s energy security remains fundamentally unshaken”, thanks to “emergency stockpiles and a wide array of import channels”.
‘ESSENTIAL’ RENEWABLES: Energy analysts said governments should cut their fossil-fuel reliance by investing in renewables, “rather than just seeking non-Gulf oil and gas suppliers”, reported Climate Home News. This message was echoed by UK business secretary Peter Kyle, who said “doubling down on renewables” was “essential” amid “regional instability”, according to the Daily Telegraph.
China’s climate plan
PEAK COAL?: China has set out its next “five-year plan” at the annual “two sessions” meeting of the National People’s Congress, including its climate strategy out to 2030, according to the Hong Kong-based South China Morning Post. The plan called for China to cut its carbon emissions per unit of gross domestic product (GDP) by 17% from 2026 to 2030, which “may allow for continued increase in emissions given the rate of GDP growth”, reported Reuters. The newswire added that the plan also had targets to reach peak coal in the next five years and replace 30m tonnes per year of coal with renewables.
ACTIVE YET PRUDENT: Bloomberg described the new plan as “cautious”, stating that it “frustrat[es] hopes for tighter policy that would drive the nation to peak carbon emissions well before president Xi Jinping’s 2030 deadline”. Carbon Brief has just published an in-depth analysis of the plan. China Daily reported that the strategy “highlights measures to promote the climate targets of peaking carbon dioxide emissions before 2030”, which China said it would work towards “actively yet prudently”.
Around the world
- EU RULES: The European Commission has proposed new “made in Europe” rules to support domestic low-carbon industries, “against fierce competition from China”, reported Agence France-Presse. Carbon Brief examined what it means for climate efforts.
- RECORD HEAT: The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has said there is a 50-60% chance that the El Niño weather pattern could return this year, amplifying the effect of global warming and potentially driving temperatures to “record highs”, according to Euronews.
- FLAGSHIP FUND: The African Development Bank’s “flagship clean energy fund” plans to more than double its financing to $2.5bn for African renewables over the next two years, reported the Associated Press.
- NO WITHDRAWAL: Vanuatu has defied US efforts to force the Pacific-island nation to drop a UN draft resolution calling on the world to implement a landmark International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruling on climate, according to the Guardian.
98
The number of nations that submitted their national reports on tackling nature loss to the UN on time – just half of the 196 countries that are part of the UN biodiversity treaty – according to analysis by Carbon Brief.
Latest climate research
- Sea levels are already “much higher than assumed” in most assessments of the threat posed by sea-level rise, due to “inadequate” modelling assumptions | Nature
- Accelerating human-caused global warming could see the Paris Agreement’s 1.5C limit crossed before 2030 | Geophysical Research Letters covered by Carbon Brief
- Future “super El Niño events” could “significantly lower” solar power generation due to a reduction in solar irradiance in key regions, such as California and east China | Communications Earth & Environment
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
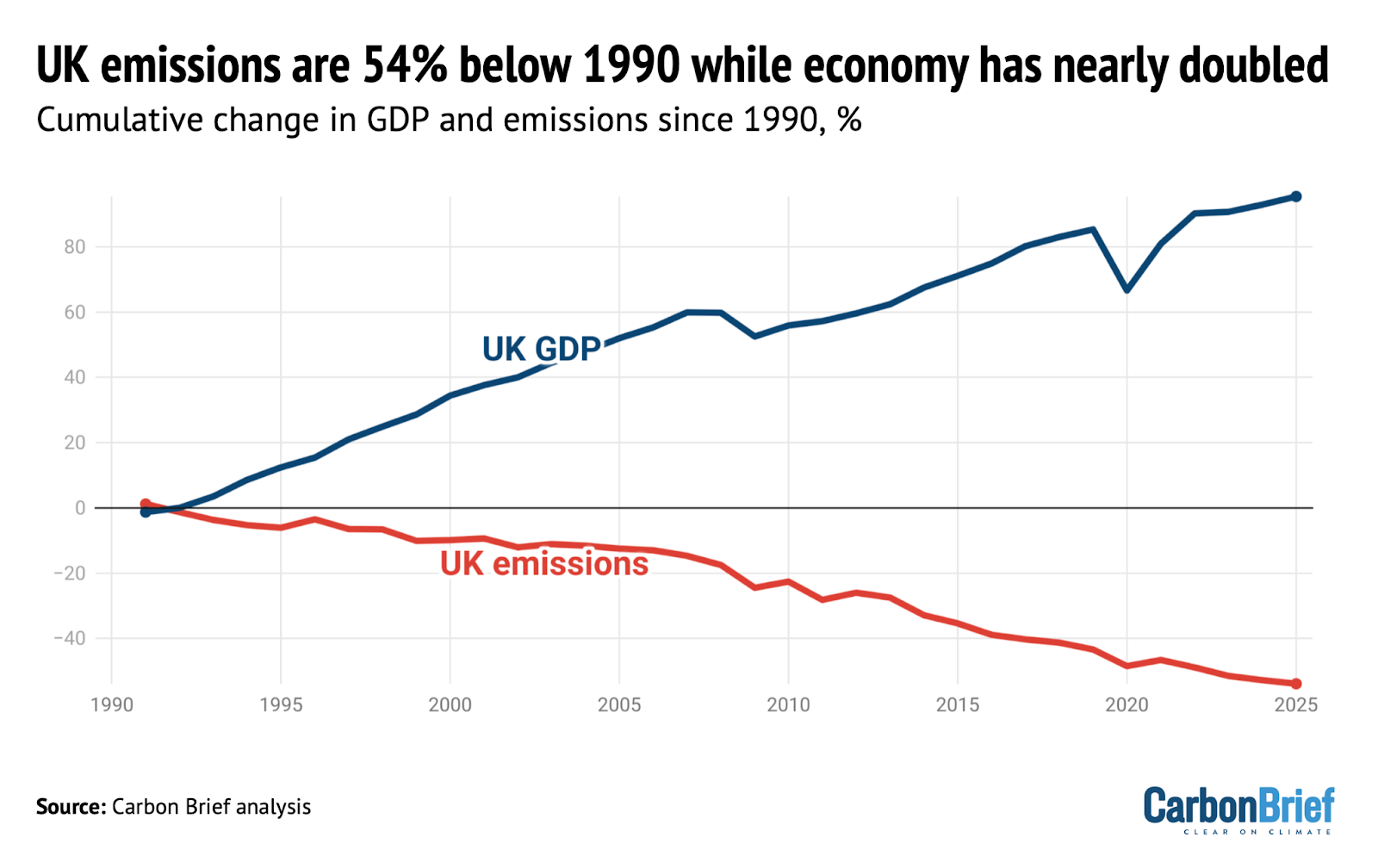
UK greenhouse gas emissions in 2025 fell to 54% below 1990 levels, the baseline year for its legally binding climate goals, according to new Carbon Brief analysis. Over the same period, data from the World Bank shows that the UK’s economy has expanded by 95%, meaning that emissions have been decoupling from growth.
Spotlight
Bristol’s ‘pioneering’ community wind turbine
Following the recent launch of the UK government’s local power plan, Carbon Brief visits one of the country’s community-energy success stories.
The Lawrence Weston housing estate is set apart from the main city of Bristol, wedged between the tree-lined grounds of a stately home and a sprawl of warehouses and waste incinerators. It is one of the most deprived areas in the city.
Yet, just across the M5 motorway stands a structure that has brought the spoils of the energy transition directly to this historically forgotten estate – a 4.2 megawatt (MW) wind turbine.
The turbine is owned by local charity Ambition Lawrence Weston and all the profits from its electricity sales – around £100,000 a year – go to the community. In the UK’s local power plan, it was singled out by energy secretary Ed Miliband as a “pioneering” project.
‘Sustainable income’
On a recent visit to the estate by Carbon Brief, Ambition Lawrence Weston’s development manager, Mark Pepper, rattled off the story behind the wind turbine.
In 2012, Pepper and his team were approached by the Bristol Energy Cooperative with a chance to get a slice of the income from a new solar farm. They jumped at the opportunity.
“Austerity measures were kicking in at the time,” Pepper told Carbon Brief. “We needed to generate an income. Our own, sustainable income.”
With the solar farm proving to be a success, the team started to explore other opportunities. This began a decade-long process that saw them navigate the Conservative government’s “ban” on onshore wind, raise £5.5m in funding and, ultimately, erect the turbine in 2023.
Today, the turbine generates electricity equivalent to Lawrence Weston’s 3,000 households and will save 87,600 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) over its lifetime.

‘Climate by stealth’
Ambition Lawrence Weston’s hub is at the heart of the estate and the list of activities on offer is seemingly endless: birthday parties, kickboxing, a library, woodworking, help with employment and even a pop-up veterinary clinic. All supported, Pepper said, with the help of a steady income from community-owned energy.
The centre itself is kitted out with solar panels, heat pumps and electric-vehicle charging points, making it a living advertisement for the net-zero transition. Pepper noted that the organisation has also helped people with energy costs amid surging global gas prices.
Gesturing to the England flags dangling limply on lamp posts visible from the kitchen window, he said:
“There’s a bit of resentment around immigration and scarcity of materials and provision, so we’re trying to do our bit around community cohesion.”
This includes supper clubs and an interfaith grand iftar during the Muslim holy month of Ramadan.
Anti-immigration sentiment in the UK has often gone hand-in-hand with opposition to climate action. Right-wing politicians and media outlets promote the idea that net-zero policies will cost people a lot of money – and these ideas have cut through with the public.
Pepper told Carbon Brief he is sympathetic to people’s worries about costs and stressed that community energy is the perfect way to win people over:
“I think the only way you can change that is if, instead of being passive consumers…communities are like us and they’re generating an income to offset that.”
From the outset, Pepper stressed that “we weren’t that concerned about climate because we had other, bigger pressures”, adding:
“But, in time, we’ve delivered climate by stealth.”
Watch, read, listen
OIL WATCH: The Guardian has published a “visual guide” with charts and videos showing how the “escalating Iran conflict is driving up oil and gas prices”.
MURDER IN HONDURAS: Ten years on from the murder of Indigenous environmental justice advocate Berta Cáceres, Drilled asked why Honduras is still so dangerous for environmental activists.
TALKING WEATHER: A new film, narrated by actor Michael Sheen and titled You Told Us To Talk About the Weather, aimed to promote conversation about climate change with a blend of “poetry, folk horror and climate storytelling”.
Coming up
- 8 March: Colombia parliamentary election
- 9-19 March: 31st Annual Session of the International Seabed Authority, Kingston, Jamaica
- 11 March: UN Environment Programme state of finance for nature 2026 report launch
Pick of the jobs
- London School of Economics and Political Science, fellow in the social science of sustainability | Salary: £43,277-£51,714. Location: London
- NORCAP, innovative climate finance expert | Salary: Unknown. Location: Kyiv, Ukraine
- WBHM, environmental reporter | Salary: $50,050-$81,330. Location: Birmingham, Alabama, US
- Climate Cabinet, data engineer | Salary: hourly rate of $60-$120 per hour. Location: Remote anywhere in the US
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 6 March 2026: Iran energy crisis | China climate plan | Bristol’s ‘pioneering’ wind turbine appeared first on Carbon Brief.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits









