Nearly a decade on from the Paris Agreement, there is still not an agreed way to measure progress towards its “global goal on adaptation” (GGA).
Yet climate impacts are increasingly being felt around the world, with the weather becoming more extreme and the risk to vulnerable populations growing.
At COP30, which takes place next month, negotiators are set to finalise a list of indicators that can be used to measure progress towards the GGA.
This is expected to be one of the most significant negotiated outcomes from the UN climate summit in Belém, Brazil.
In a series of open letters running up to the summit, COP30 president-designate André Corrêa do Lago wrote that adaptation was “no longer a choice” and that countries needed to seize a “window of opportunity”:
“There is a window of opportunity to define a robust framework to track collective progress on adaptation. This milestone will…lay the groundwork for the future of the adaptation agenda.”
However, progress on producing an agreed list of indicators has been difficult, with nearly 90 experts working over two years to narrow down a list of almost 10,000 potential indicators to a final set of just 100, which is supposed to be adopted at COP30.
Below, Carbon Brief explores what the GGA is, why progress on adaptation has been so challenging and what a successful outcome would look like in Belém.
What is the GGA?
The GGA was signed into being within the Paris Agreement in 2015, but the treaty included limited detail on exactly what the goal would look like, how it would be achieved and how progress would be tracked.
The need to adapt to climate change has long been established, with the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, adopted in 1992, noting that parties “shall…cooperate in preparing for adaptation to the impacts of climate change”.
In the subsequent years, the issue received limited focus, however. Then, in 2013, the African Group of Negotiators put forward a proposed GGA, setting out a target for adaptation.
This was then formally established under article 7.1 of the Paris text two years later. The text of the treaty says that the GGA is to “enhanc[e] adaptive capacity, strengthen…resilience and reduc[e] vulnerability to climate change”.

According to the World Resources Institute (WRI), the GGA was designed to set “specific, measurable targets and guidelines for global adaptation action, as well as enhancing adaptation finance and other types of support for developing countries”.
However, unlike the goal to cut emissions – established in article 4 of the Paris Agreement – measuring progress on adaptation is “inherently challenging”.
Emilie Beauchamp, lead for monitoring, evaluation and learning (MEL) for adaptation at the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD), tells Carbon Brief that this challenge relates to the context-specific nature of what adaptation means. She says:
“The main [reason] it’s hard to measure progress on adaptation is because adaptation is very contextual, and so resilience and adapting mean different things to different people, and different things in different places. So it’s not always easy to quantify or qualify…You need to integrate really different dimensions and different lived experiences when you assess progress on adaptation. And that’s why it’s been hard.”
Beyond this, attribution of the impact of adaptive measures remains a “persistent challenge”, according to Dr Portia Adade Williams, a research scientist at the CSIR-Science and Technology Policy Research Institute and Carbon Brief contributing editor, “as observed changes in vulnerability or resilience may result from multiple climatic and non-climatic factors”. She adds:
“In many contexts, data limitations and inconsistent monitoring systems, particularly in developing countries, constrain systematic tracking of adaptation efforts. Existing monitoring frameworks tend to emphasise outputs, such as infrastructure built or trainings conducted, rather than outcomes that reflect actual reductions in vulnerability or enhanced resilience.”
Despite these challenges, the need for increased progress on adaptation is clear. Nearly half of the global population – around 3.6 billion people – are currently highly vulnerable to these impacts. This includes vulnerability to droughts, floods, heat stress and food insecurity.
However, for six years following the adoption of the Paris Agreement, the GGA did not feature on the agenda at COP summits and there was limited progress on the matter.
This changed in 2021, at COP26 in Glasgow, when parties initiated the two-year Glasgow-Sharm el-Sheikh work program to begin establishing tangible adaptation targets.
This work culminated at COP28 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, with the GGA “framework”.
Agreeing the details of this framework and developing indicators to measure adaptation progress has been the main focus of negotiations in recent years.
What progress has been made?
Following the establishment of the GGA, there was – for many years – only limited progress towards agreeing how to track countries’ adaptation efforts.
COP28 was seen as a “pivotal juncture” for the GGA, with the creation of the framework and a new two-year plan to develop indicators, which is supposed to culminate at COP30.
Negotiations across the two weeks in Dubai in 2023 were tense. It took five days for a draft negotiating text on the GGA framework to emerge, due to objections from the G77 and China group of developing countries around the inclusion of adaptation finance.
Within the GGA – as with many negotiating tracks under the UNFCCC – finance to support developing nations is a common sticking point. Other disagreements included the principle of “common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities” (CBDR–RC).
Ultimately, a text containing weakened language around both CBDR-RC and finance was waved through at the end of COP28 and a framework for the GGA was adopted.
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Ana Mulio Alvarez, a researcher on adaptation at thinktank E3G, said that the framework was the “first real step to fulfilling” the adaptation mandate laid out in the Paris Agreement, adding:
“The GGA is the equivalent of the 1.5C commitment for mitigation – a north star to guide efforts. It will be hugely symbolic if the GGA indicators are agreed at COP and the GGA can be implemented.”
The framework agreed at COP28 includes 11 targets to guide progress against the GGA. Of these, four are related to what it describes as an “iterative adaptation cycle” – risk assessment, planning, implementation and learning – and seven to thematic targets.
These “themes” cover water, food, health, ecosystems, infrastructure, poverty eradication and cultural heritage.
Within these, there are subgoals for countries to work towards. For example, within the water theme, there is a subgoal of achieving universal access to clean water.
While this framework was broadly welcomed as a step forward for adaptation work, there remains concern from some experts about the focus of the programme.
Prof Lisa Schipper, a professor of development geography at the University of Bonn, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) author and Carbon Brief contributing editor, tells Carbon Brief that without the framework there would likely have been continued delays, but there was still “significant scientific pushback against this approach to adaptation”.
She notes that the IPCC’s sixth assessment report (AR6) “didn’t necessarily provide any concrete inputs that could be useful for the GGA”. Beyond this, there are political challenges that the framework does not address, Schipper adds, continuing:
“There are also political reasons why global-north countries or annex-one countries don’t necessarily want specificity [in adaptation targets], because they also don’t want to be held accountable and to be forced to pay for things, right? So, the science was pathetic in one way, it was just not sufficient. And then you have a political agenda that’s fighting against clarity on this.
“So, even though [the framework] came together, it was still not very concrete, right? It was a framework, but it didn’t have a lot in it.”
As with the language around finance, thematic targets within the GGA were weakened over the course of the negotiations. Additionally, parties ultimately did not agree to set up a specific, recurring agenda item to continue discussing the GGA.
However, a further two-year programme was established at COP28. The UAE-Belém work programme was designed to establish concrete “indicators” that can be used to measure progress on adaptation going forward.
Why is it hard to choose adaptation indicators?
In the two years following COP28, work has been ongoing to narrow down a potential list of more than 9,000 indicators under the GGA to just 100.
At the UNFCCC negotiations in June 2024 in Bonn, parties agreed to ask for a group of technical experts to be convened to help with this process.
This led to a group of 78 experts meeting in September 2024. They were split into eight working groups – one for each of the seven themes and one for the iterative adaptation cycle – to begin work reviewing a list of more than 5,000 indicators, which had already been compiled from submissions to the UNFCCC.
In October 2024, a second workshop was held under the UAE-Belém work programme, at which the experts agreed that they should also consider an additional 5,000 indicators compiled by the Adaptation Committee, another body within the UN climate regime.
One key challenge, Beauchamp tells Carbon Brief, was that the group of experts had very limited time and a lack of resources. She expands:
“They had to finish their work by the end of the summer [of 2025]. This means they’ve not even had a year [and] they have no funding. So of the 78 experts, the number of whom could actually contribute was much lower, and it’s not by lack of desire and expertise. But [because] they have day jobs, they have families…And the lack of clear instructions from parties also didn’t help.”
COP29 formed the mid-way point in the work programme to develop adaptation indicators, with parties stressing it was “critical” to come away with a decision from the summit.
As with previous sessions, finance quickly became a sticking point in negotiations, however, alongside the notion of “transformational adaptation”.
This is a complex concept centred around the idea of driving systemic shifts – in infrastructure, governance or society more broadly – so as to address the root causes of vulnerability to climate change.
Ultimately, COP29 adopted a decision that made reference to finance as “means of implementation” (MOI), recognised transformational adaptation and launched the Baku Adaptation Roadmap (BAR). The BAR is designed to advance progress towards the GGA, however, the details of how it will operate are still unclear.
Going into the Bonn climate negotiations in June 2025, the list of potential indicators had been “miraculously” refined to a list of 490 through further work by the group of experts. While this was a major step forward, it was still a long way off the aim of agreeing to a final set of just 100 indicators at COP30.
Once again, disagreement quickly arose in Bonn around finance and this dominated much of the two weeks of negotiations. As such, a final text did not get uploaded until mid-way through the final plenary meeting of the negotiations.
This was seen as contentious, as some parties complained that they did not have time to fully assess it, before it was gavelled through.
Bethan Laughlin, senior policy specialist at the Zoological Society of London, tells Carbon Brief:
“Adaptation finance has consistently lagged behind mitigation for decades, despite growing recognition of the urgent need to build resilience to climate shocks. The gap between the needs of countries and the funding provided is stark, with an adaptation financing gap in the hundreds of billions annually.
“Within the GGA negotiations, the implications of this finance issue are clear. Disagreements persist over how MoI [finance] should be measured in the indicator set, particularly around whether private finance should count, how support from developed countries is defined, and how national budgets are tracked versus international climate finance.”
The final text produced in Bonn was split into two, with an agreed section capturing the GGA indicators and a separate “informal note” covering the BAR and transformation adaptation.
Importantly, the main text invited the experts to continue working on the indicators and to submit a final technical report with a list of potential indicators by August 2025.
As this work continued, one of the biggest challenges was “balancing technical rigour with political feasibility while ensuring ambition”, says Laughlin, adding:
“The scale and diversity of adaptation action means a diverse menu of indicators per target is needed, but this must not be so vast as to be unfeasible for countries to measure, especially those countries with limited resources and capacity.”
Meetings took place subsequently, within which experts focused on “ensuring adaptation relevance of indicators, reducing redundancy and ensuring coverage across thematic indicators”, according to a technical report.
Beauchamp notes the importance of these themes for continued work on adaptation, saying:
“The themes were really helpful to bring some attention and to communicate about the GGA. They echo more easily what adaptation results can look like, because people find it difficult to talk about processes. But they’re really important. Without the targets on the adaptation cycle, we can too easily forget that you need resilient processes to have resilient outcomes.”
The table below, from the same technical report, shows how nearly 10,000 adaptation indicators have been whittled down to a proposed final list of 100. The table also shows how the indicators are split between the themes (9a-g) and iterative adaptation cycle (10a-d) of the GGA framework.
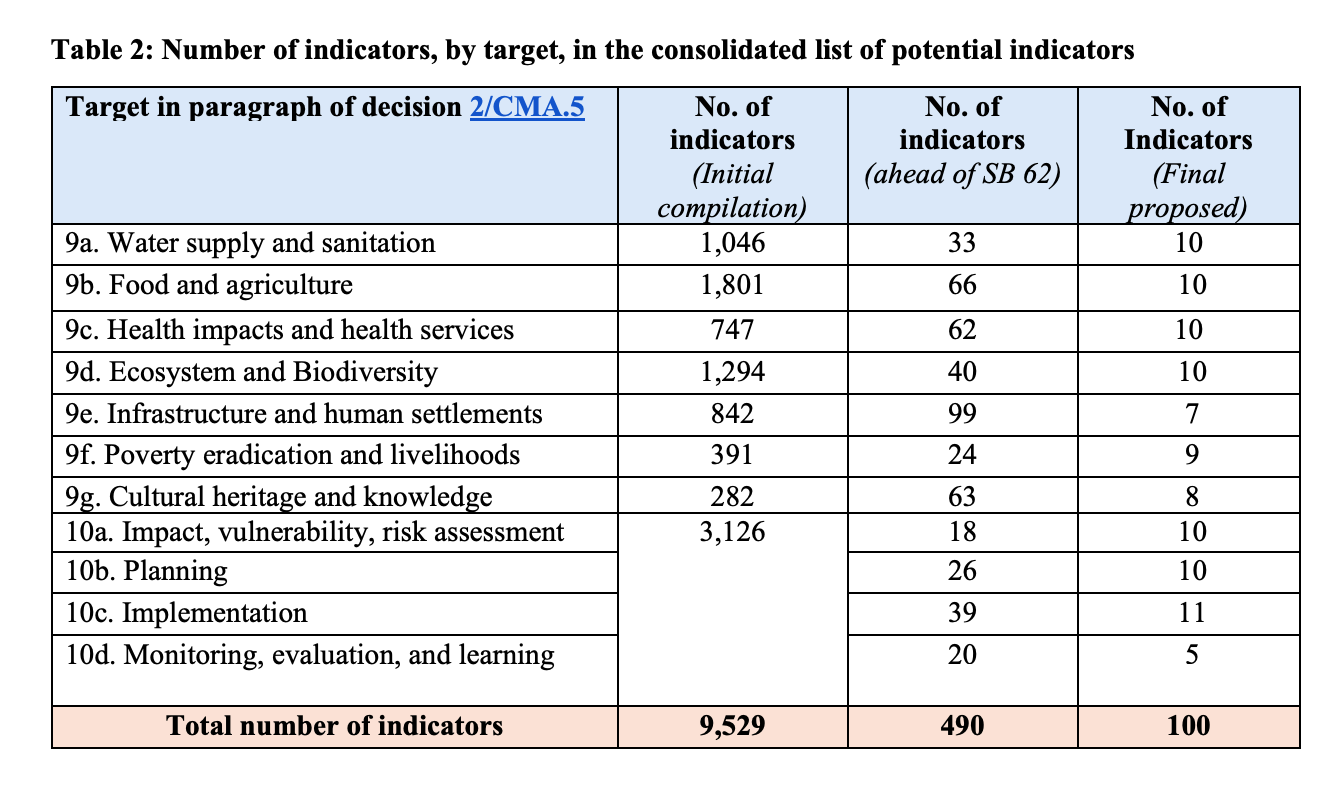
Source: GGA technical report.
Further consultations took place in September and the final workshop under the UAE-Belém work programme took place on 3-4 October.
Following on from the numerous sessions held under the GGA, negotiators are now able to go into COP30 with a consolidated list of indicators to discuss, agree and bring into use, allowing progress towards the adaptation goal in Paris to be finally measured.
What to expect from COP30?
A final decision on the adaptation indicators is expected at COP30, potentially marking a significant milestone under the GGA.
In his third letter, COP30 president-designate Correa do Lago noted that a “special focus” was to be given to the GGA indicators at the summit.
He wrote that adaptation is “the visible face of the global response to climate change” and a “central pillar for aligning climate action with sustainable development”.
Therefore, he said COP30 should focus on “delivering tangible benefits for societies, ecosystems and economies by advancing and concluding the key mandates in this agenda”. These “key mandates” are the GGA and the related topic of National Adaptation Plans (NAPs).
Correa do Lago’s letter added:
“There is a window of opportunity to define a robust framework to track collective progress on adaptation. This milestone will also lay the groundwork for the future of the adaptation agenda.”
Indeed, adaptation has moved up the political agenda this year, with the topic being discussed during the “climate day” at the UN general assembly in September. This included a “leaders’ dialogue” on the sidelines of the assembly, where Carbon Brief understands that leaders of climate-vulnerable nations pushed for specific adaptation targets.
Elsewhere, nearly three-quarters (73%) of new country climate pledges include adaptation components, further emphasising the increased focus the topic is now receiving.
Despite the increased attention, there are still likely to be challenges at COP30, including the continued fight over finance. This will likely be felt particularly keenly, given that the COP26 commitment to double adaptation finance comes to an end this year.
This was part of the “Glasgow dialogue”, which saw parties commit to “at least double” adaptation finance between 2019 and 2025.
Adade Williams tells Carbon Brief:
“A major expectation [at COP30] is that parties will tackle the gaps in adaptation finance, consider how to link MoI – finance, technology, capacity‐building – with the GGA indicators and possibly set new finance ambitions or roadmaps. The emphasis on MoI means capacity building, data systems, technology transfer and institutional strengthening will gain more traction.”
Adaptation finance was also a key topic during pre-COP meetings in Brasilia in October, with E3G noting that it is a “political litmus test for success in Belém, with vulnerable countries signalling urgency and demanding greater clarity that finance will flow”.
Laughlin tells Carbon Brief that she expects discussions on finance to “dominate in Belém” – in particular, given the legacy of the “new collective quantified goal” (NCQG) for climate finance agreed at COP29, which many developing countries were “starkly disappointed” by.
Additionally, there may be challenges around the process of negotiations on the GGA indicators, notes Beauchamp, adding:
“We’ve not agreed yet if it is acceptable to open up text of some indicators [to negotiation]. We have 100 of them and, as a technical expert, on one hand [it] is quite worrying, because changing one term in an indicator can change its entire methodology, right? But, at the same time, there is definitely more work that can be done on the indicators.
“So, are we only keeping indicators that can work or that everybody is happy with now, and then we review the set later, for example, with the review of the UAE framework in 2028? Or do we open the whole Pandora’s box and then we start hashing out some new indicators? That’s the first big challenge parties need to grapple with at COP30.”
Despite the challenges, Mulio Alvarez says she would expect a final list of indicators to be adopted at COP30, even if some change during the negotiation process. She adds:
“The Brazilian presidency knows that this is the biggest negotiated outcome of COP30 and they want it to go through smoothly. The adoption of the list would officially launch the UAE framework so that it can begin to track and guide efforts.”
While agreement on indicators would be seen as a political win at COP30, several experts highlighted that it is only a step towards enabling further adaptation work, with Beauchamp noting that parties “need to see this as an opportunity”.
Laughlin adds:
“Although finalising the indicator list is a core deliverable, it is also important that COP30 makes progress on the next steps for the GGA following COP30, including the expectations for reporting, and regular updates to the indicator list so it keeps up with the latest science.”
What will the GGA mean for vulnerable communities?
COP30 kicks off on 10 November and negotiators are hoping to hit the ground running with the condensed list of indicators to discuss.
There remain key questions about what the GGA could mean for adaptation around the world – in particular, for those most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Mulio Alvarez notes:
“In the short term, the GGA metrics [indicators] will likely paint a very challenging picture of the needs for adaptation. In the medium to long term, we hope the GGA will be embedded in policy planning and implementation – supporting risk assessments, helping identify gaps, driving planning and resources and even unlocking investments.”
Others are more cautious about the potential impact of the GGA, the associated framework and its indicators, in terms of driving real progress for adaptation.
Schipper notes that, while the GGA indicators are welcome from a political perspective, “from a scientific perspective, and I think from a development perspective, I think there’s a sort of a high risk that this ends up making people worse off in the end”.
She adds that the incremental approach currently being taken for adaptation is not working and that the indicators can “at best” show us incremental progress.
Schipper notes that there is a risk that the indicators narrow the approach to adaptation to the extent that they are either ineffective or actually produce maladaptive outcomes. She adds:
“I’m not saying that we should abandon the indicators, but I think it’s important to recognise that this is not enough. This is nowhere near enough.”
Others are more optimistic about the long-term potential of the GGA. Laughlin suggests that the indicators could help build systemic resilience, adding that if they were successfully implemented it could mean adaptation is integrated into national development and planning, “making sure that climate resilience becomes a core part of policymaking”. She says:
“For vulnerable populations, this means moving from a reactive approach to a proactive one – embedding resilience into development planning, restoring ecosystems and empowering local communities.
“The success of the GGA in delivering for vulnerable populations hinges on political will, finance and inclusive governance – many of which are currently lacking.”
Beyond COP30, the GGA framework agreed at COP28 includes a number of overarching targets to help guide countries in developing and implementing their NAPs, although these targets are not quantified.
The targets include countries conducting risk assessments to identify the impact of climate change and areas of particular vulnerability, by 2030. The framework says this would inform a country’s NAP and that “by 2030 all parties have in place” adaptation planning processes or strategies, as shown in the image below.

Adade Williams tells Carbon Brief that if the GGA is “effectively implemented” it could help develop systemic resilience in the long term, helping to address “not just climate hazards but also underlying structural vulnerabilities”. She adds:
“However, this long-term potential depends heavily on the extent of political will, sustained finance and capacity support available to developing countries. Without these, the GGA risks becoming a reporting framework rather than a transformative mechanism for resilience.”
The post Q&A: COP30 could – finally – agree how to track the ‘global goal on adaptation’ appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Q&A: COP30 could – finally – agree how to track the ‘global goal on adaptation’
Climate Change
We must invest in early-warning systems to tackle crises like Kenya’s drought
Dancliff Mbura is the advocacy and communications manager at Action Against Hunger Kenya. He works to influence policy and resource allocation and is an expert on multisectoral nutrition interventions.
Just four years since the last devastating drought, when five consecutive rainy seasons failed, 3.3 million people in Kenya’s arid and semi-arid counties are facing acute hunger as yet another drought crisis deepens. It is visible everywhere – in the parched riverbeds, weakened animals, and the children, who are too quiet.
Six months ago, the number of people facing acute hunger was 1.8 million. If nothing changes, by August, it will climb to 3.7 million, underscoring the need for urgent aid.
We know the answers. Cash transfers allow families to purchase food in markets that are still functioning. Mobile health and nutrition outreach teams must meet communities where they are, not where facilities happen to be located, which could make them inaccessible. Emergency water provision is essential.
But the resources are not there to address the growing needs. A coalition of humanitarian organisations working across Kenya’s drought-hit regions with the government has estimated the drought response would cost more than 30 billion Kenyan shillings ($232 million). Kenya’s government has released just 6 billion shillings so far.
Reducing the damage
Beyond the immediate response, however, we need to invest in systems that reduce the damage of future drought cycles in this climate-vulnerable region.
Kenya has systems that support the generation of early-warning systems, such as the National Drought Management Authority’s monthly county and national early-warning bulletins with detailed early-warning data. What we need is a means to ensure that information reaches communities in time for them to act on it and make sure they have the resources they need to do that.
One approach could be the establishment of village-level climate change and disaster hubs. These hubs would provide communities with simplified, actionable information, sometimes via dashboards on weather patterns and forecasts, and support them in generating locally relevant, cost-effective early actions.
By engaging communities in this process, the government and development partners can complement these efforts with additional resources where needed. This approach fosters community ownership while simultaneously enhancing resilience to climate-related risks.
With better technology, including AI-assisted climate modeling, we can generate precise early-warning information. When shared in a timely manner with communities and accompanied by support for early or anticipatory actions, this can help build resilience to frequent droughts and other crises.
For example, with access to early-warning information, vulnerable communities could store water ahead of droughts, switch to short-maturity crops when reduced rainfall is forecast, and move livestock and food stocks to higher ground before floods hit. They could also apply preventative treatments to protect crops and animals from pest or disease outbreaks, and make smarter market decisions, such as selling livestock early before prices drop, to safeguard their income.
Different in scale
I have spent 15 years working on humanitarian response in Kenya. I have seen drought cycles come and go. But what is happening right now across our arid and semi-arid lands – the ASAL counties that cover nearly 80% of the country – is different in scale and in the depth of suffering it is causing.
The October-December 2025 short rains delivered only 30 to 60% of the long-term average, making it one of the driest seasons since 1981. In some areas, rainfall failed almost entirely. More than 90% of open water sources have dried up in most parts of ASAL counties. Families are walking up to 20 km (12 miles) or more just to find water.
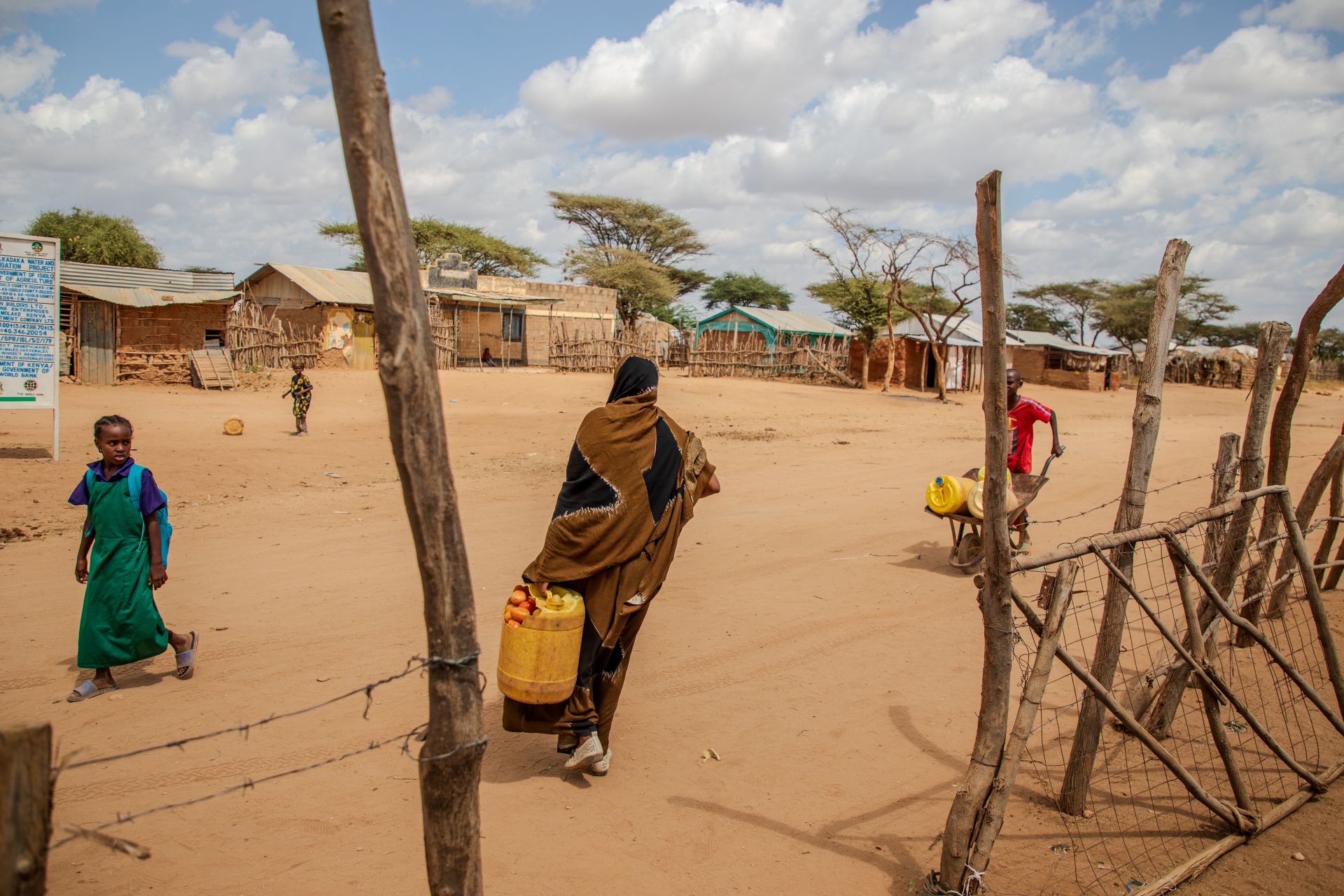


Now, as we approach Kenya’s more reliable rainy season from March to May, projections are well below average across the hardest-hit northern counties, and we may be heading into a fourth consecutive poor season. For communities who have already exhausted every coping mechanism they have, another failed season could be catastrophic.
More than 810,000 children between the ages of six months and five years are acutely malnourished. Nearly 117,000 pregnant and breastfeeding mothers are also acutely malnourished. The cycle of nutrition that healthy communities depend on is breaking down.
And yet approximately half of severe acute malnutrition cases are going untreated. Only 24% of the nutrition and health outreach sites mapped across the arid and semi-arid counties are currently functioning.
Impossible choices
The economic devastation compounds everything. Livestock is the backbone of life in these pastoral lands. But in Marsabit county alone, more than 50,000 sheep and goats have died. Mandera has lost nearly 30,000 animals. Milk production has plummeted by 55%. As animals grow weaker, families receive less and less when they sell them. Livelihoods are collapsing in slow motion, and families are running out of options.
That can lead to desperate decisions: more daughters are married off early in exchange for dowry like livestock, a practice that rises sharply in times of crisis. Girls are subjected to female genital mutilation so they can be considered ready for marriage. Children drop out of school as families are forced to move in search of better land.
Every week that passes without a scaled-up response is a week in which children go hungry, animals die, and families make impossible choices. We are at a point where, if we do not act, lives will be lost – preventably.
Not because we lacked the knowledge, not because we lacked the warning, but because we were not able to move fast enough.
The post We must invest in early-warning systems to tackle crises like Kenya’s drought appeared first on Climate Home News.
https://www.climatechangenews.com/2026/03/10/we-must-invest-in-early-warning-systems-to-tackle-crises-like-kenyas-drought/
Climate Change
A Warmer Climate Means Bigger Hail
New attribution research shows how extra heat in the atmosphere can turn thunderstorms into factories for dangerous, softball-size hail.
Regions that are often pummeled by severe storms—like the Midwestern United States under last weekend’s powerful thunderstorms and deadly tornadoes—could also face the threat of more extreme hail.
Climate Change
States Blast Federal Playbook of Potential Colorado River Options
Possible scenarios could include significant water reductions in lower-basin states or creating new incentives for states to conserve water.
The sluggish Colorado River negotiations have entered a new phase: Long and fiery letter writing.
States Blast Federal Playbook of Potential Colorado River Options
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits







