Greenland is closing in on three decades of continuous annual ice loss, with 1995-96 being the last year in which the giant ice sheet grew in size.
With another melt season over, Greenland lost 105bn tonnes of ice in 2024-25.
The past year has seen some notable events, including ongoing ice melt into the month of September – well beyond the end of August when Greenland’s short summer typically draws to a close.
In a hypothetical world not impacted by human-caused climate change, ice melt in Greenland would rarely occur in September – and, if it did, it would generally be confined to the south.
In this article, we explore how Greenland’s ice sheets fared over the 12 months to August 2025, including the evidence that the territory’s summer melting season is lengthening.
(For our previous analyses of Greenland’s ice cover, see coverage in 2024, 2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019, 2018, 2017, 2016 and 2015.)
Surface mass balance
The seasons in Greenland are overwhelmingly dominated by winter.
The bitterly cold, dark winter lasts up to ten months, depending on where you are. In contrast, the summer period is generally rather short, starting in late May in southern Greenland and in June in the north, before ending in late August.
Greenland’s annual ice cycle is typically measured from 1 September through to the end of August.
This is because the ice sheet largely gains snow on the surface from September, accumulating ice through autumn, winter and into spring.
Then, as temperatures increase, the ice sheet begins to lose more ice through surface melt than it gains from snowfall, generally from mid-June. The melt season usually continues until the middle or end of August.
Over this 12-month period, scientists track the “surface mass balance” (SMB) of the ice sheet. This is the balance between ice gains and losses at the surface.
To calculate ice gain and losses, scientists use data collected by high-resolution regional climate models and Sentinel satellites.
The SMB does not consider all ice losses from Greenland – we will come to that later – but instead provides a gauge of changes at the surface of the ice sheet.
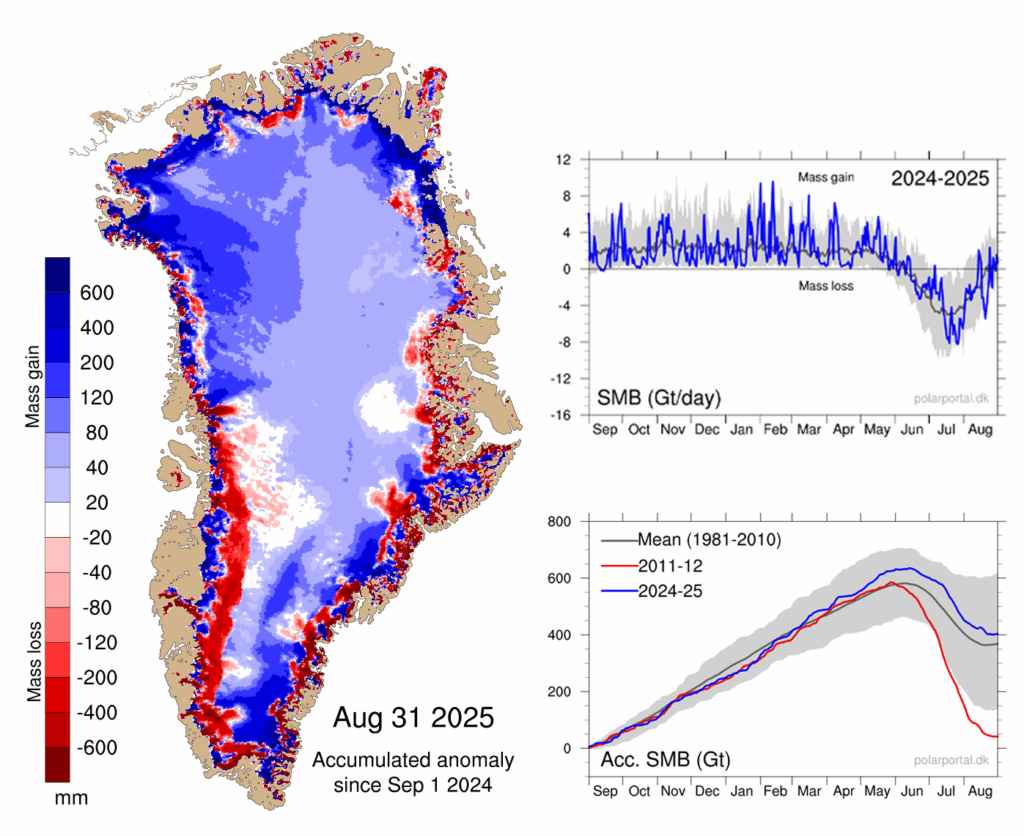
According to our calculations, Greenland ended the year 2024-25 with an overall SMB of about 404bn tonnes. This is the 15th highest SMB in a dataset that goes back 45 years, exceeding the 1981-2010 average by roughly 70bn tonnes.
This year’s SMB is illustrated in the maps and charts below, based on data from the Polar Portal.
The blue line in the upper chart shows the day-to-day SMB. Large snowfall events become visible as “spikes”. The blue line in the lower chart depicts the accumulated SMB since 1 September 2024. In grey, the long-term average and its variability are shown. For comparison, the red line shows the record-low year of 2011-12.
The map shows the geographic spread of SMB gains (blue) and losses (red) for 2024-25, compared to the long-term average.
It illustrates that southern and north-western Greenland had a relatively wet year compared to the long-term average, while there was mass loss along large sections of the coast, in particular in the south-west. The spikes of snow and melt are clearly visible in the graphs on the right.
Lengthening summer
Scientists have traditionally pinned the start of the “mass balance year” in Greenland to 1 September, given that this is when the ice sheet typically starts to gain mass.
However, evidence has started to emerge of a lengthening of the summer season in Greenland – as predicted some time ago by climate models.
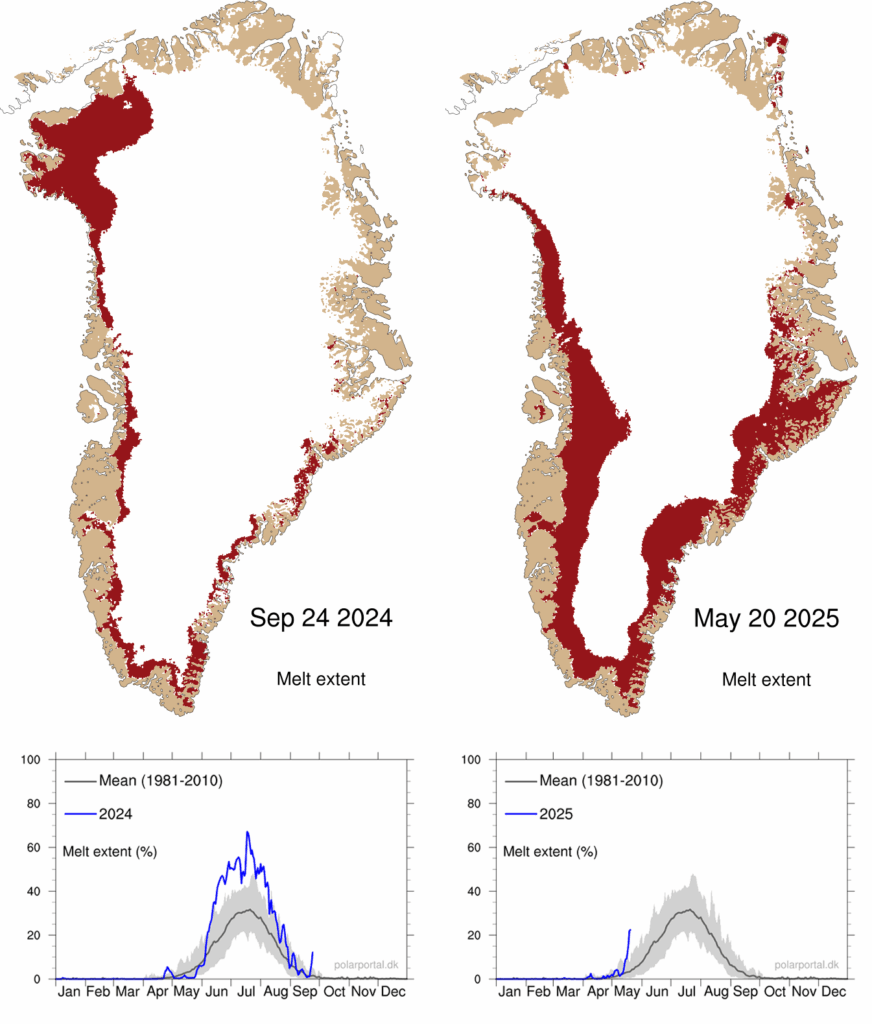
The start of the 2024-25 mass balance year in Greenland saw ice melt continuing into September. This included a particularly unusual spike in ice melt in the northern part of the territory in September as well as all down the west coast.
In a world without human-caused climate change, ice melt in September would be very rare – and generally confined to the south.
Greenland also saw an early start to the summer melt season in 2025. The onset of the melting season, defined as the first of at least three days in a row with melting over more than 5% of the ice sheet, was on 14 May. This is 12 days earlier than the 1981-2025 average.
The maps below show the extent of melt (red shading) across the ice sheet on 24 September 2024 (left) and 20 May 2025 (right). The blue lines in charts beneath show the percentage melt in 2024 (left) and 2025 (right), up to these dates, compared to the 1981-2010 average (grey).
The melt season began with a significant spike of melting across the southern part of the ice sheet. This happened in combination with sea ice breaking up particularly early in north-west Greenland, allowing the traditional narwhal hunt to start much earlier than usual.
Surface melt
The ablation season, which covers the period in the year when Greenland is losing ice, started a little late. The onset of the season – defined as the first of at least three days in a row with an SMB below -1bn tonnes – began on 15 June, which is two days later than the 1981-2010 average.
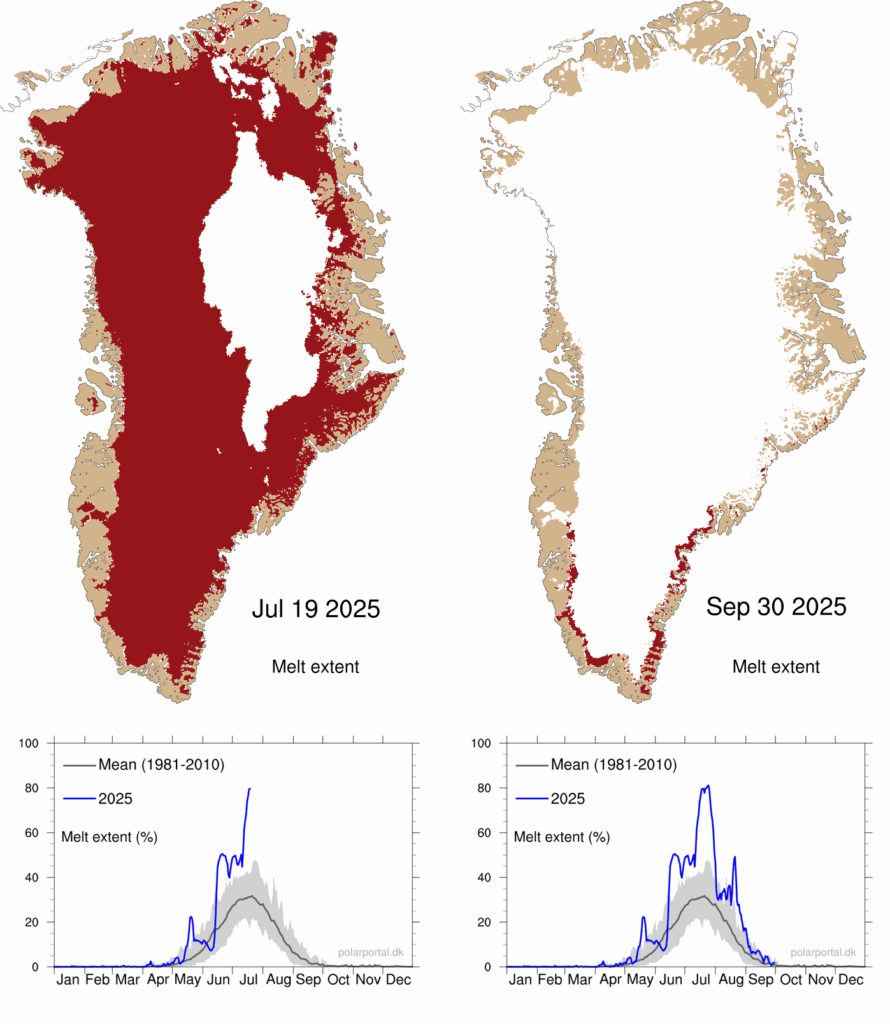
Overall, during the 2025 summer, a remarkably large percentage of the ice sheet was melting at once. This area was larger than the 1981-2010 average for three and a half months (mid-June to end of September).
In mid-July, melting occurred over a record area. For three days in a row, melting was present over more than 80% of the area of the ice sheet – peaking at 81.2%. This is the highest value in our dataset, which started in 1981.
The red shading in the maps below shows the extent of melting across Greenland on 19 July (left) and 30 September (right) 2025. The charts beneath show the daily extent of melting through 2025 (blue line), up to these dates, compared to the 1981-2010 average.
Snowfall
However, the SMB is not just about ice melt.
There was a lack of snowfall in the early winter months (September to January), particularly in south-east Greenland, which is typically the wettest part of the territory. The months that followed then saw abundant snow, which brought snowfall totals up closer to average by the start of summer.
A cold period at the end of May and in June protected the ice sheet from excessive ice loss. Melt then continued rather weakly until mid-July.
This was followed by strong melting rates in the second half of July and again in mid-August.
Overall, with both ice melt and snowfall exceeding their historical averages for the year as a whole, the SMB of the Greenland ice sheet ended above the 1981-2010 average.
These increases in snowfall and melt are in line with what scientists expect in a warming climate. This is because air holds more water vapour as it warms – leading to more snowfall and rain. Warmer temperatures also lead to more ice melt.
Total mass balance
The surface mass balance is just one component of the “total” mass balance (TMB) of the Greenland ice sheet.
The total mass balance of Greenland is the sum of the SMB, the marine mass balance (MMB) and basal mass balance (BMB). In other words, it brings together calculations from the surface, sides and base of the ice sheet.
The MMB measures the impact of the breaking off – or “calving” – of icebergs, as well as the melting of the front of glaciers where they meet the warm sea water. The MMB is always negative and has increased towards more negative values over the last decades.
BMB refers to ice losses from the base of the ice sheet. This makes a small negative contribution to the TMB.
(The only way for the ice sheet to gain mass is through snowfall.)
The continued mass loss observed in Greenland is primarily due to a weakening of the SMB – caused by rising melt combined with insufficient compensation of lost ice through snowfall.
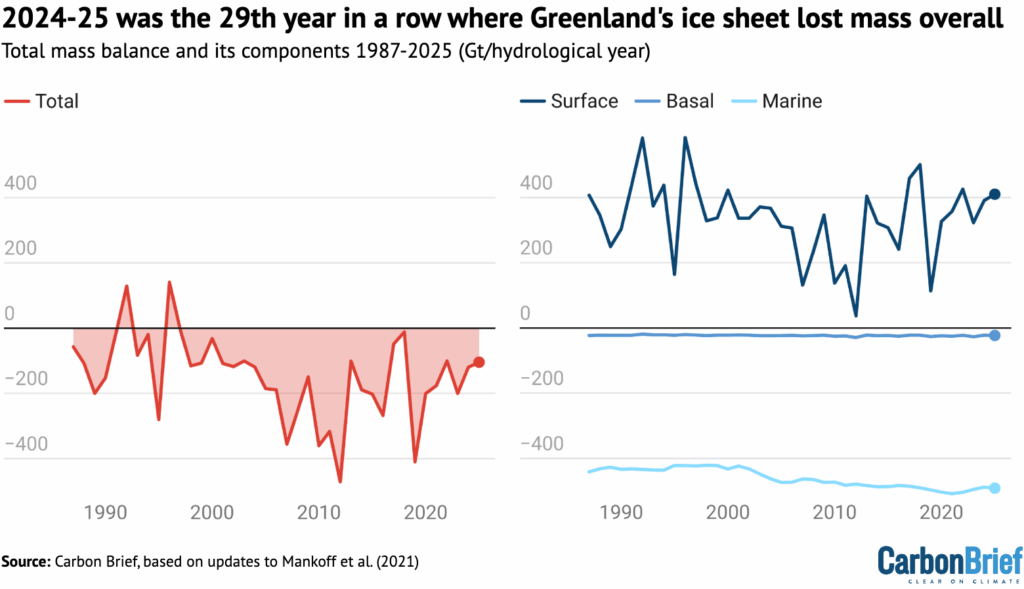
The figure below shows how much ice the Greenland ice sheet has lost (red) going back to 1987, which includes the SMB (dark blue), MMB (mid blue) and BMB (light blue). The analysis, which uses data from three models, is based on 2021 research published in Earth System Science.
Despite a relatively high SMB, high calving rates meant that Greenland lost 105bn tonnes of ice over the 12-month period.
This means that 2024-25 was the 29th year in a row with a Greenland ice sheet overall mass loss. As the chart shows, Greenland last saw an annual net gain of ice in 1996.
Satellite data
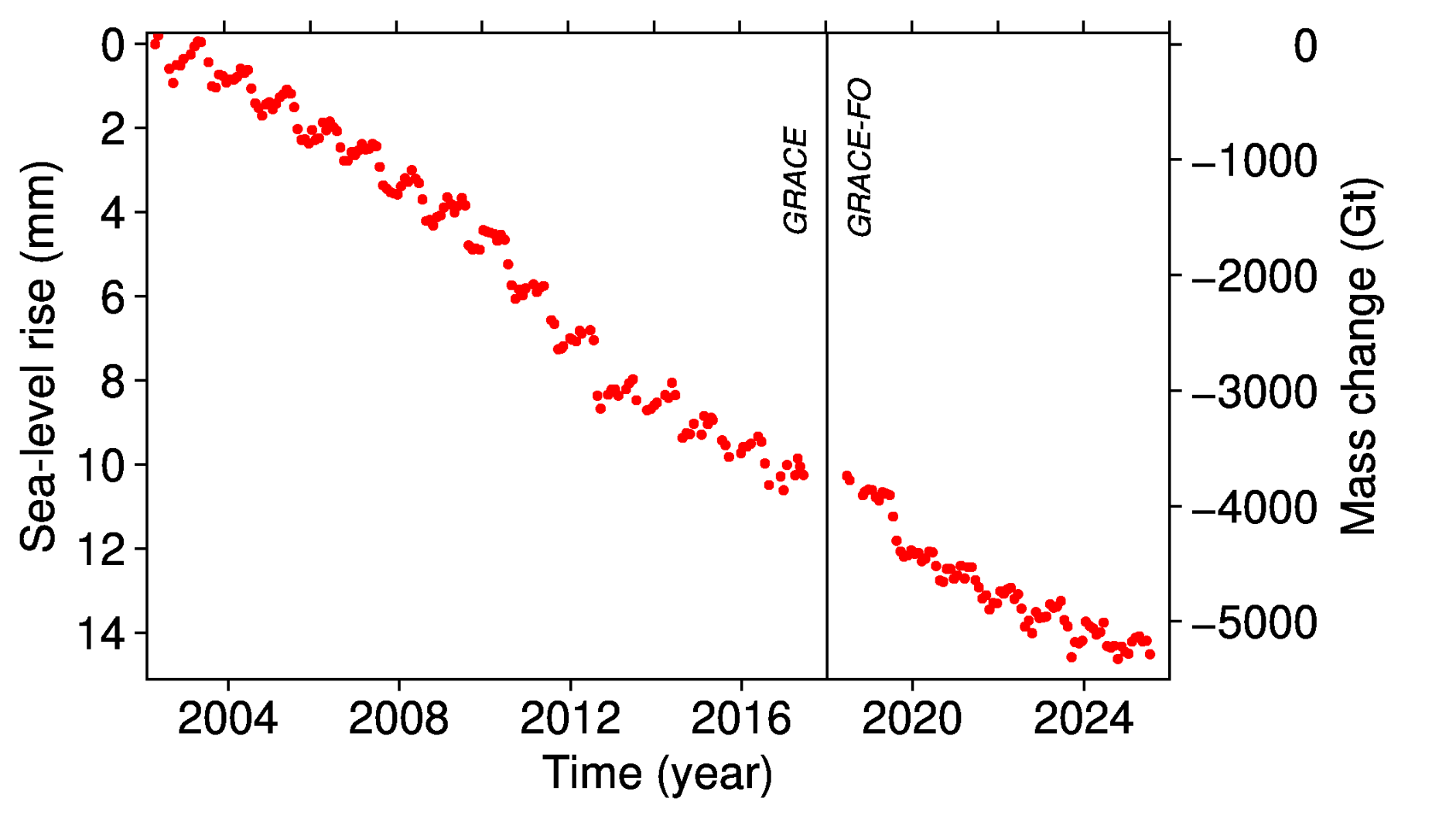
The mass balance of the Greenland ice sheet can also be measured by looking at the Earth’s gravitational field, using data captured by the Grace and Grace-FO satellite missions – a joint initiative from NASA and the German Aerospace Center.
The Grace satellites are twin satellites that follow each other closely at a distance of about 220km, which is why they are nicknamed “Tom and Jerry”. The distance between the two depends on gravity – which is, in turn, related to changes in mass on Earth, including ice loss.
Therefore, the distance between the two satellites, which can be measured very precisely, can be used to calculate loss of mass from the Greenland ice sheet.
Overall, the satellite data reveals that Greenland’s ice sheet lost around 55bn tonnes of ice over the 2024-25 season.
There is reasonably good agreement between the Grace satellite data and the model data, which, as noted above, finds that 105bn tonnes of ice was lost in Greenland over the same period.
However, the alignment of the two datasets – which are fully independent of each other – becomes more clear once a longer time period is considered.
In the 22-year period between April 2002 and May 2024, the Grace data shows that Greenland lost 4,911bn tonnes of ice. The modelling approach, on the other hand, calculates that 4,766bn tonnes of ice was lost.
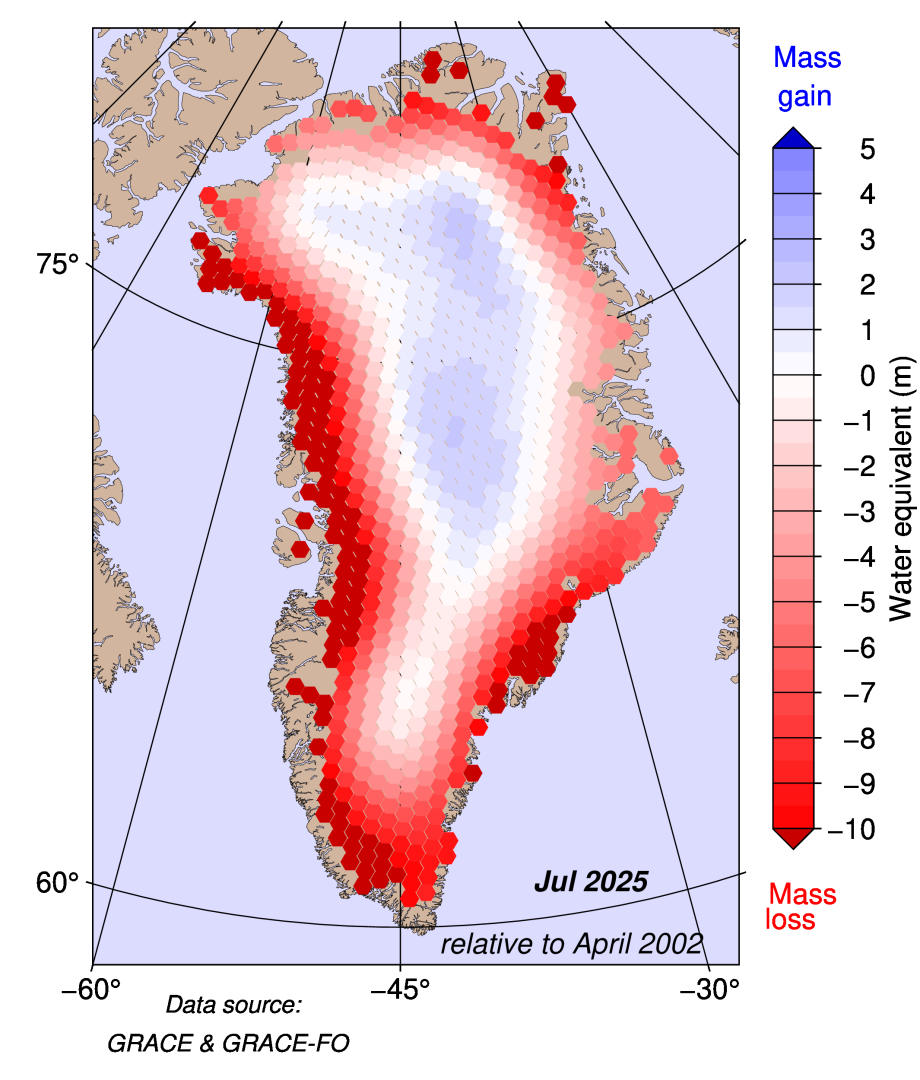
The figure below shows gain and loss in the total mass of ice of the Greenland ice sheet, calculated using Grace satellite measurements. It reveals that, over the past 23 years, there has been mass loss in the order of several metres along the coasts of Greenland, with the most significant losses seen on the western coast. Over the central parts of the ice sheet, there has been a small mass gain.
The lower figure shows the contribution of Greenland mass change to sea level rise over the last 23 years, according to the satellite data. It illustrates that more than 5,000bn tonnes of ice have been lost over the time period – contributing to roughly 1.5cm of sea level rise.
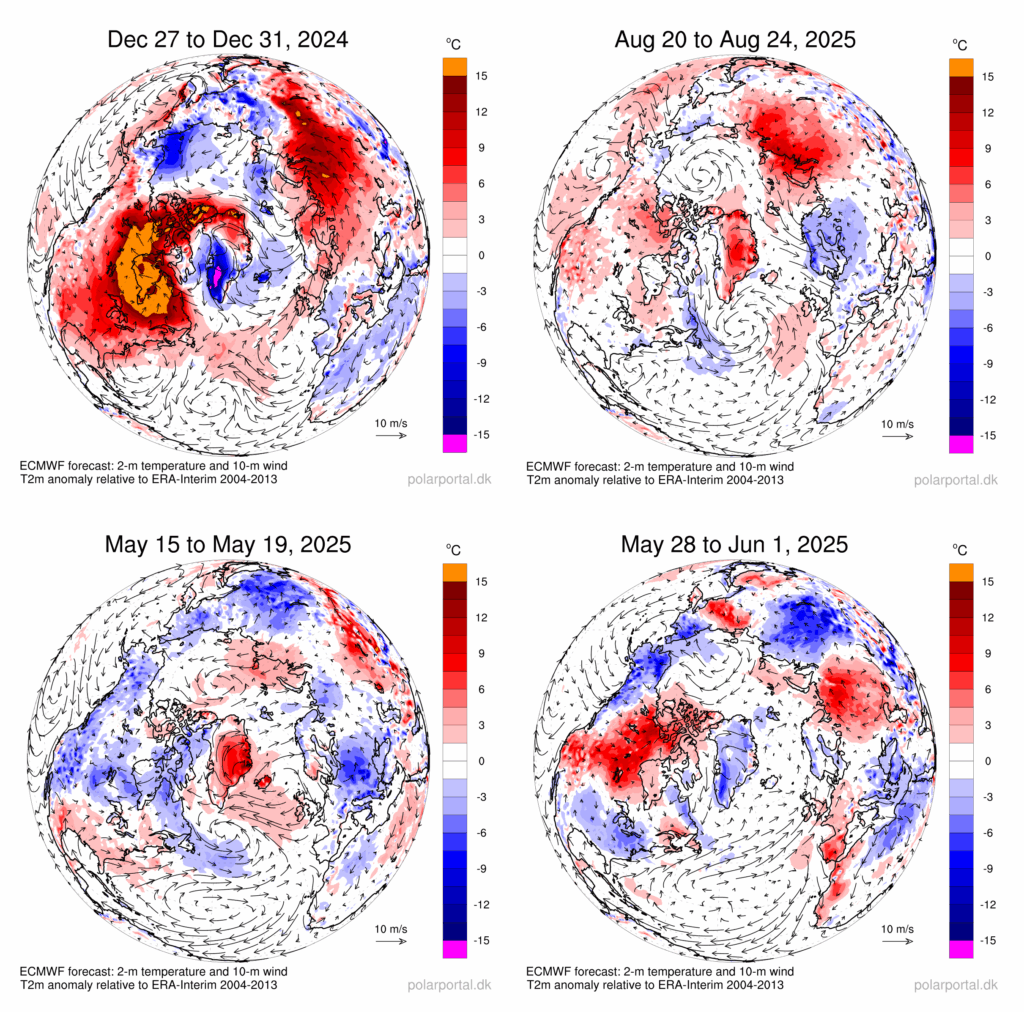
Warm over Europe and North America, cool over Greenland
As always, the weather systems across the northern hemisphere play a key role in the melt and snowfall that Greenland sees each year.
As in previous years, multiple heatwaves were observed in southern Europe and North America over the summer of 2025.
And, just like in 2024, there was only modest heat in northern Europe – with the notable exception of Arctic Scandinavia – with a comparably cool and rainy July followed by a warmer and sunnier August.
The high-pressure weather systems that bring heatwaves have a wide-ranging impact on weather extremes across the northern hemisphere.
Strong blocking patterns over North America and Europe were repeatedly present in the course of the summer of 2025. In such a blocked flow, the jet stream – fast-moving winds that blow from west to east high in the atmosphere – is shaped like the Greek capital letter Omega (Ω).
The jet stream bulged up to the north over Canada and northern Europe. West and east of these ridges, low pressure troughs were found at both “feet” of the Omega. One of these troughs was located over Greenland (top left panel in next figure).
This resulted in widespread heat near the cores of these high-pressure systems, fuelling fires in several countries, including large wildfires in Canada. Smoke from these wildfires reached Greenland and Europe in late May.
Unlike in previous years, no heavy precipitation events were observed near the “feet” of the Omega.
If the Omega pattern is displaced by half a wavelength, the opposite – warm over Greenland, with cool continents – is also possible.
This circulation pattern occurred in August 2025 and is shown in the top right panel of the figure below. The bottom panel depicts the large temperature variability in May 2025.
The post Guest post: How the Greenland ice sheet fared in 2025 appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Analysis: UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
The UK’s fleet of wind, solar and biomass power plants all set new records in 2025, Carbon Brief analysis shows, but electricity generation from gas still went up.
The rise in gas power was due to the end of UK coal generation in late 2024 and nuclear power hitting its lowest level in half a century, while electricity exports grew and imports fell.
In addition, there was a 1% rise in UK electricity demand – after years of decline – as electric vehicles (EVs), heat pumps and data centres connected to the grid in larger numbers.
Other key insights from the data include:
- Electricity demand grew for the second year in a row to 322 terawatt hours (TWh), rising by 4TWh (1%) and hinting at a shift towards steady increases, as the UK electrifies.
- Renewables supplied more of the UK’s electricity than any other source, making up 47% of the total, followed by gas (28%), nuclear (11%) and net imports (10%).
- The UK set new records for electricity generation from wind (87TWh, +5%), solar (19TWh, +31%) and biomass (41TWh, +2%), as well as for renewables overall (152TWh, +6%).
- The UK had its first full year without any coal power, compared with 2TWh of generation in 2024, ahead of the closure of the nation’s last coal plant in September of that year.
- Nuclear power was at its lowest level in half a century, generating just 36TWh (-12%), as most of the remaining fleet paused for refuelling or outages.
Overall, UK electricity became slightly more polluting in 2025, with each kilowatt hour linked to 126g of carbon dioxide (gCO2/kWh), up 2% from the record low of 124gCO2/kWh, set last year.
The National Energy System Operator (NESO) set a new record for the use of low-carbon sources – known as “zero-carbon operation” – reaching 97.7% for half an hour on 1 April 2025.
However, NESO missed its target of running the electricity network for at least 30 minutes in 2025 without any fossil fuels.
The UK inched towards separate targets set by the government, for 95% of electricity generation to come from low-carbon sources by 2030 and for this to cover 100% of domestic demand.
However, much more rapid progress will be needed to meet these goals.
Carbon Brief has published an annual analysis of the UK’s electricity generation in 2024, 2023, 2021, 2019, 2018, 2017 and 2016.
Record renewables
The UK’s fleet of renewable power plants enjoyed a record year in 2025, with their combined electricity generation reaching 152TWh, a 6% rise from a year earlier.
Renewables made up 47% of UK electricity supplies, another record high. The rise of renewables is shown in the figure below, which also highlights the end of UK coal power.
While the chart makes clear that gas-fired electricity generation has also declined over the past 15 years, there was a small rise in 2025, with output from the fuel reaching 91TWh. This was an increase of 5TWh (5%) and means gas made up 28% of electricity supplies overall.
The rise in gas-fired generation was the result of rising demand and another fall in nuclear power output, which reached the lowest level in half a century, while net imports and coal also declined.

The year began with the UK’s sunniest spring and by mid-December had already become the sunniest year on record. This contributed to a 5TWh (31%) surge in electricity generation from solar power, helped by a jump of roughly one-fifth in installed generating capacity.
The new record for solar power generation of 19TWh in 2025 comes after years of stagnation, with electricity output from the technology having climbed just 15% in five years.
The UK’s solar capacity reached 21GW in the third quarter of 2025. This is a substantial increase of 3 gigawatts (GW) or 18% year-on-year.
These are the latest figures available from the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ). The DESNZ timeseries has been revised to reflect previously missing data.
UK wind power also set a new record in 2025, reaching 87TWh, up 4TWh (5%). Wind conditions in 2025 were broadly similar to those in 2024, with the uptick in generation due to additional capacity.
The UK’s wind capacity reached 33GW in the third quarter of 2025, up 1GW (4%) from a year earlier. The 1.2GW Dogger Bank A in the North Sea has been ramping up since autumn 2025 and will be joined by the 1.2GW Dogger Bank B in 2026, as well as the 1.4GW Sofia project.
These sites were all awarded contracts during the government’s third “contracts for difference” (CfD) auction round and will be paid around £53 per megawatt hour (MWh) for the electricity they generate. This is well below current market prices, which currently sit at around £80/MWh.
Results from the seventh auction round, which is currently underway, will be announced in January and February 2026. Prices are expected to be significantly higher than in the third round, as a result of cost inflation.
Nevertheless, new offshore wind capacity is expected to be deliverable at “no additional cost to the billpayer”, according to consultancy Aurora Energy Research.
The UK’s biomass energy sites also had a record year in 2025, with output nudging up by 1TWh (2%) to 41TWh. Approximately two-thirds (roughly 27TWh) of this total is from wood-fired power plants, most notably the Drax former coal plant in Yorkshire, which generated 15TWh in 2024.
The government recently awarded new contracts to Drax that will apply from 2027 onwards and will see the amount of electricity it generates each year roughly halve, to around 6TWh. The government is also consulting on how to tighten sustainability rules for biomass sourcing.
Rising demand
The UK’s electricity demand has been falling for decades due to a combination of more efficient appliances and lightbulbs, as well as ongoing structural shifts in the economy.
Experts have been saying for years that at some point this trend would be reversed, as the UK shifts to electrified heat and transport supplies using EVs and heat pumps.
Indeed, the Climate Change Committee (CCC) has said that demand would more than double by 2050, with electrification forming a key plank of the UK’s efforts to reach net-zero.
Yet there has been little sign of this effect to date, with electricity demand continuing to fall outside single-year rebounds after economic shocks, such as the 2020 Covid lockdowns.
The data for 2025 shows hints that this turning point for electricity demand may finally be taking place. UK demand increased by 4TWh (1%) to 322TWh in 2025, after a 1TWh rise in 2024.
After declining for more than two decades since a peak in 2005, this is the first time in 20 years that UK demand has gone up for two years in a row, as shown in the figure below.
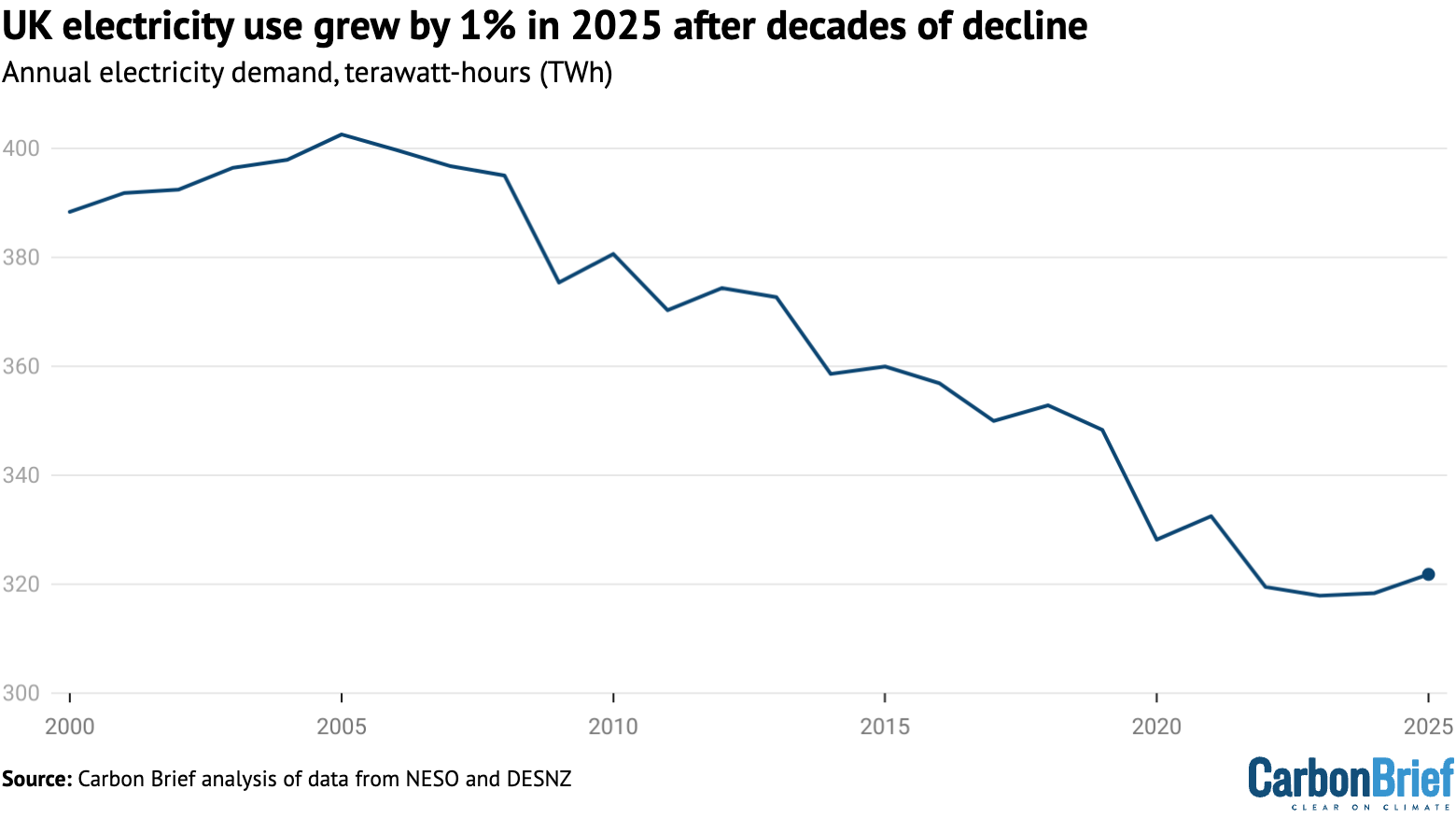
While detailed data on underlying electricity demand is not available, it is clear that the shift to EVs and heat pumps is playing an important role in the recent uptick.
There are now around 1.8m EVs on the UK’s roads and another 1m plug-in hybrids. Of this total, some 0.6m new EVs and plug-in hybrids were bought in 2025 alone. In addition, around 100,000 heat pumps are being installed each year. Sales of both technologies are rising fast.
Estimates from the NESO “future energy scenarios” point to an additional 2.0TWh of demand from new EVs in 2025, compared with 2024. They also suggest that newly installed heat pumps added around 0.2TWh of additional demand, while data centres added 0.4TWh.
By 2030, NESO’s scenarios suggest that electricity use for these three sources alone will rise by around 30TWh, equivalent to around 10% of total demand in 2025.
EVs would have the biggest impact, adding 17TWh to demand by 2030, NESO says, with heat pumps adding another 3TWh. Data-centre growth is highly uncertain, but could add 12TWh.
Gas growth
At the same time as UK electricity demand was growing by 4TWh in 2025, the country also lost a total of 10TWh of supply as a result of a series of small changes.
First, 2025 was the UK’s first full year without coal power since 1881, resulting in the loss of 2TWh of generation. Second, the UK’s nuclear fleet saw output falling to the lowest level in half a century, after a series of refuelling breaks and outages, which cut generation by 5TWh.
Third, after a big jump in imports in 2024, the UK saw a small decline in 2025, as well as a more notable increase in the amount of electricity exported to other countries. This pushed the country’s net imports down by 1TWh (4%).
The scale of cross-border trade in electricity is expected to increase as the UK has significantly expanded the number of interconnections with other markets.
However, the government’s clean-power targets for 2030 imply that the UK would become a net exporter, sending more electricity overseas than it receives from other countries. At present, it remains a significant net importer, with these contributions accounting for 109% of supplies.
Finally, other sources of generation – including oil – also declined in 2025, reducing UK supplies by another 2TWh, as shown in the figure below.
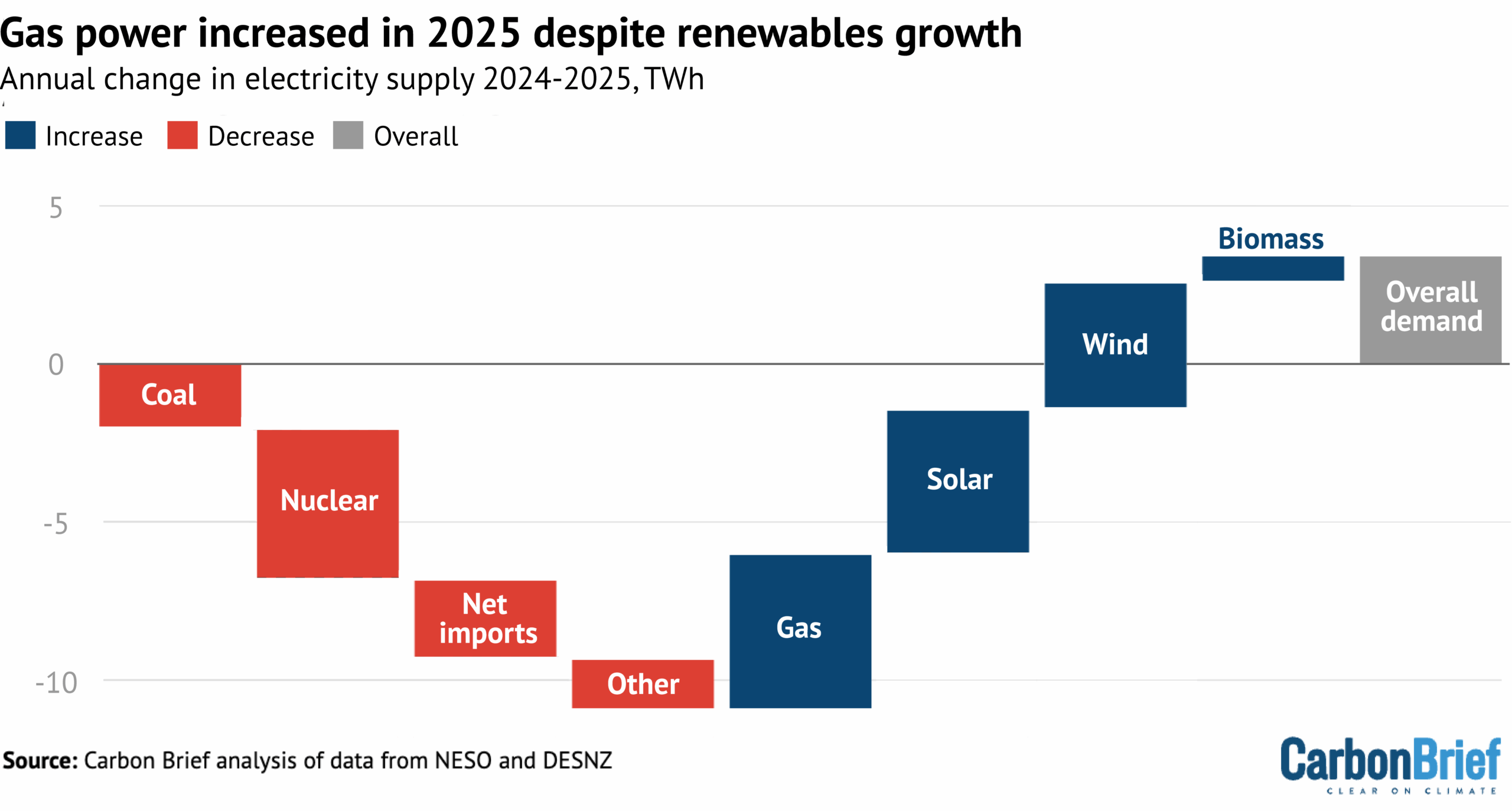
These losses in UK electricity supply were met by the already-mentioned increases in generation from gas, solar, wind and biomass, as shown in the figure above.
The government’s targets for decarbonising the UK’s electricity supplies will face similar challenges in the years to come as electrification – and, potentially, data centres – continue to push up demand.
All but one of the UK’s existing nuclear power plants are set to retire by 2030, meaning the loss of another 27TWh of nuclear generation.
This will be replaced by new nuclear capacity, but only slowly. The 3.2GW Hinkley Point C plant in Somerset is set to start operating in 2030 at the earliest and its sister plant, Sizewell C in Suffolk, not until at least another five years later.
Despite backing from ministers for small modular reactors, the timeline for any buildout is uncertain, with the latest government release referring to the “mid-2030s”.
Meanwhile, biomass generation is likely to decline as the output of Drax is scaled back from 2027.
Stalling progress
Taken together, the various changes in the UK’s electricity supplies in 2025 mean that efforts to decarbonise the grid stalled, with a small increase in emissions per unit of generation.
The 2% increase in carbon intensity to 126gCO2/kWh is illustrated in the figure below and comes after electricity was the “cleanest ever” in 2024, at 124gCO2/kWh.
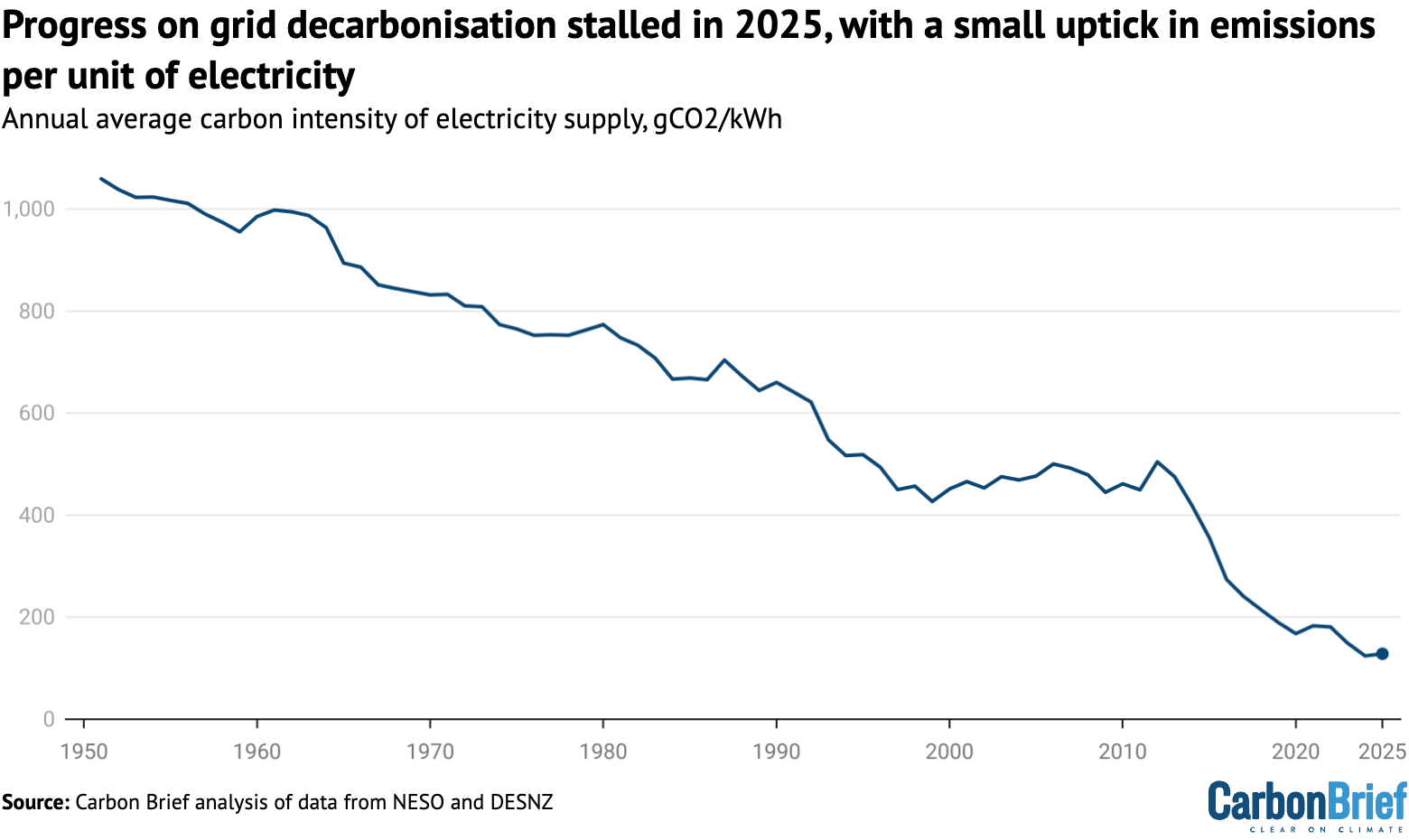
The stalling progress on cleaning up the UK’s grid reflects the balance of record renewables, rising demand and rising gas generation, along with poor output from nuclear power.
Nevertheless, a series of other new records were set during 2025.
NESO ran the transmission grid on the island of Great Britain (GB; namely, England, Wales and Scotland) with a record 97.7% “zero-carbon operation” (ZCO) on 1 April 2025.
Note that this measure excludes gas plants that also generate heat – known as combined heat and power, or CHP – as well as waste incinerators and all other generators that do not connect to the transmission network, which means that it does not include most solar or onshore wind.
NESO was unable to meet its target – first set in 2019 – for 100% ZCO during 2025, meaning it did not succeed in running the transmission grid without any fossil fuels for half an hour.
Other records set in 2025 include:
- GB ran on 100% clean power, after accounting for exports, for a record 87 hours in 2025, up from 64.5 hours in 2024.
- Total GB renewable generation from wind, solar, biomass and hydro reached a record 31.3GW from 13:30-14:00 on 4 July 2025, meeting 84% of demand.
- GB wind generation reached a record 23.8GW for half an hour on 5 December 2025, when it met 52% of GB demand.
- GB solar reached a record 14.0GW at 13:00 on 8 July 2025, when it met 40% of demand.
The government has separate targets for at least 95% of electricity generation and 100% of demand on the island of Great Britain to come from low-carbon sources by 2030.
These goals, similar to the NESO target, exclude Northern Ireland, CHP and waste incinerators. However, they include distributed renewables, such as solar and onshore wind.
These definitions mean it is hard to measure progress independently. The most recent government figures show that 74% of qualifying generation in GB was from low-carbon sources in 2024.
Carbon Brief’s figures for the whole UK show that low-carbon sources made up a record 58% of electricity supplies overall in 2025, up marginally from a year earlier.
Similarly, low-carbon sources made up 65% of electricity generation in the UK overall. This was unchanged from a year earlier.
Methodology
The figures in the article are from Carbon Brief analysis of data from DESNZ Energy Trends, chapter 5 and chapter 6, as well as from NESO. The figures from NESO are for electricity supplied to the grid in Great Britain only and are adjusted here to include Northern Ireland.
In Carbon Brief’s analysis, the NESO numbers are also adjusted to account for electricity used by power plants on site and for generation by plants not connected to the high-voltage national grid.
NESO already includes estimates for onshore windfarms, but does not cover industrial gas combined heat and power plants and those burning landfill gas, waste or sewage gas.
Carbon intensity figures from 2009 onwards are taken directly from NESO. Pre-2009 estimates are based on the NESO methodology, taking account of fuel use efficiency for earlier years.
The carbon intensity methodology accounts for lifecycle emissions from biomass. It includes emissions for imported electricity, based on the daily electricity mix in the country of origin.
DESNZ historical electricity data, including years before 2009, is adjusted to align with other figures and combined with data on imports from a separate DESNZ dataset. Note that the data prior to 1951 only includes “major” power producers.
The post Analysis: UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
Greenhouse Gases
Ricky Bradley named Citizens’ Climate Executive Director after strategic and legislative progress during interim leadership role
Ricky Bradley named Citizens’ Climate Executive Director after strategic and legislative progress during interim leadership role
 Dec. 22, 2025 – After a six month interim period, Ricky Bradley has been appointed Executive Director of Citizens’ Climate Lobby and Citizens’ Climate Education. The decision was made by the CCL and CCE boards of directors in a unanimous vote during their final joint board meeting of 2025.
Dec. 22, 2025 – After a six month interim period, Ricky Bradley has been appointed Executive Director of Citizens’ Climate Lobby and Citizens’ Climate Education. The decision was made by the CCL and CCE boards of directors in a unanimous vote during their final joint board meeting of 2025.
“Citizens’ Climate Lobby is fortunate to have someone with Ricky Bradley’s experience, commitment, and demeanor to lead the organization,” said CCL board chair Bill Blancato. “I can’t think of anyone with as much knowledge about CCL and its mission who is held in such high regard by CCL’s staff and volunteers.”
Bradley has been active with Citizens’ Climate for more than 13 years. Prior to his former roles as Interim Executive Director and Vice President of Field Operations, he has also served as a volunteer Group Leader and volunteer Regional Coordinator, all of which ground him in Citizens’ Climate’s grassroots model. Bradley has also led strategic planning and implementation efforts at HSBC, helping a large team adopt new approaches and deliver on big organizational goals.
“We are confident that Ricky has the skills to guide CCL during a challenging time for organizations trying to make a difference on climate change,” Blancato added.
Since stepping into the Interim Executive Director role in July 2025, Bradley has led Citizens’ Climate through a season of high volunteer engagement and effective advocacy on Capitol Hill. Under his leadership, CCL staff and volunteers organized a robust virtual lobby week with 300+ constituent meetings, despite an extended government shutdown, and executed a targeted mobilization to support the bipartisan passage of climate-friendly forestry legislation through the Senate Agriculture Committee.
“We have heard nothing but glowing descriptions of Ricky’s ability as a leader, as a manager, and as a team player,” said CCE board chair Dr. Sandra Kirtland Turner. “We’ve been absolutely thrilled with how Ricky’s brought the team together over the last six months to deliver on a new strategic plan for the organization.”
The strategic plan, which launched during CCL’s Fall Conference in November, details Citizens’ Climate’s unique role in the climate advocacy space, its theory of change for effectively moving federal climate legislation forward, and its strategic goals for 2026.
“Ricky has the heart of a CCLer and the strategic chops to take us into the next chapter as an organization,” Dr. Kirtland Turner said.
Bradley shared his vision for that next chapter in his conference opening remarks last month and, most recently, during the organization’s December monthly meeting.
“There’s a lot that we don’t control in today’s politics, but we do know who we are. The power of our persistent, nonpartisan advocacy is unmistakable,” Bradley said. “If we stay true to that, deepen our skills, and walk forward together, I know we’re going to meet this moment and deliver real results for the climate.”
CONTACT: Flannery Winchester, CCL Vice President of Marketing and Communications, 615-337-3642, flannery@citizensclimate.org
###
Citizens’ Climate Lobby is a nonprofit, nonpartisan, grassroots advocacy organization focused on national policies to address climate change. Learn more at citizensclimatelobby.org.
The post Ricky Bradley named Citizens’ Climate Executive Director after strategic and legislative progress during interim leadership role appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 19 December 2025: EU’s petrol car U-turn; Trump to axe ‘leading’ research lab; What climate scientists are reading
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
EU easing up
HITTING THE BREAKS: The EU “walked back” its target to ban the sale of petrol and diesel cars by 2035, “permitting some new combustion engine cars”, reported Agence-France Presse. Under the original plan, the bloc would have had to cut emissions entirely by 2035 on new vehicles, but will now only have to cut emissions by 90% by that date, compared to 2021 levels. However, according to the Financial Times, some car manufacturers have “soured” on the reversal.
ADJUSTING CBAM: Meanwhile, the Financial Times reported that the EU is making plans to “close loopholes” in the bloc’s carbon border adjustment mechanism (CBAM) before it goes into effect in January. CBAM is set to be the world’s first carbon border tax and has drawn ire from key trading partners. The EU has also finalised a plan to delay its anti-deforestation legislation for another year, according to Carbon Pulse.
Around the world
- NCAR NO MORE: The Trump administration is moving to “dismantle” the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Colorado, said USA Today, describing it as “one of the world’s leading climate research labs”.
- DEADLY FLOODS: The deadliest flash flooding in Morocco in a decade killed “at least” 37 people, while residents accused the government of “ignoring known flood risks and failing to maintain basic infrastructure”, reported Radio France Internationale.
- FAILING GRADE: The past year was the “warmest and wettest” ever recorded in the Arctic, with implications for “global sea level rise, weather patterns and commercial fisheries”, according to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s 2025 Arctic report card, covered by NPR.
- POWER TO THE PEOPLE: Reuters reported that Kenya signed a $311m agreement with an African infrastructure fund and India’s Power Grid Corporation for the “construction of two high-voltage electricity transmission lines” that could provide power for millions of people.
- BP’S NEW EXEC: BP has appointed Woodside Energy Group’s Meg O’Neill as its new chief executive amid a “renewed push to…double down on oil and gas after retreating from an ambitious renewables strategy”, said Reuters.
29
The number of consecutive years in which the Greenland ice sheet has experienced “continuous annual ice loss”, according to a Carbon Brief guest post.
Latest climate research
- Up to 4,000 glaciers could “disappear” per year during “peak glacier extinction”, projected to occur sometime between 2041 and 2055 | Nature Climate Change
- The rate of sea level rise across the coastal US doubled over the past century | AGU Advances
- Repression and criminalisation of climate and environmentally focused protests are a “global phenomena”, according to an analysis of 14 countries | Environmental Politics
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured

The latest coal market report from the International Energy Agency said that global coal use will reach record levels in 2025, but will decline by the end of the decade. Carbon Brief analysis of the report found that projected coal use in China for 2027 has been revised downwards by 127m tonnes, compared to the projection from the 2024 report – “more than cancelling out the effects of the Trump administration’s coal-friendly policies in the US”.
Spotlight
What climate scientists are curious about
This week, Carbon Brief spoke to climate scientists attending the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union in New Orleans, Louisiana, about the most interesting research papers they read this year.
Their answers have been lightly edited for length and clarity.
Dr Christopher Callahan, assistant professor at Indiana University Bloomington
The most interesting research paper I read was a simple thought experiment asking when we would have known humans were changing the climate if we had always had perfect observations. The authors show that we could have detected a human influence on the climate as early as the 1880s, since we have a strong physical understanding of how those changes should look. This paper both highlights that we have been discernibly changing the climate for centuries and emphasises the importance of the modern climate observing network – a network that is currently threatened by budget cuts and staff shortages.
Prof Lucy Hutyra, distinguished professor at Boston University
The most interesting paper I read was in Nature Climate Change, where the researchers looked at how much mortality was associated with cold weather versus hot weather events and found that many more people died during cold weather events. Then, they estimated how much of a protective factor in the urban heat island is on those winter deaths and suggested that the winter benefits exceed the summer risks of mitigating extreme heat, so perhaps we shouldn’t mitigate extreme heat in cities.
This paper got me in a tizzy…It spurred an exciting new line of research. We’ll be publishing a response to this paper in 2026. I’m not sure their conclusion was correct, but it raised really excellent questions.
Dr Kristina Dahl, vice president for science at Climate Central
This year was when we saw source attribution studies, such as Chris Callahan‘s, really start to break through and be able to connect the emissions of specific emitters…to the impact of those emissions through heat or some other sort of damage function. [This] is really game-changing.
What [Callahan’s] paper showed is that the emissions of individual companies have an impact on extreme heat, which then has an impact on the GDP of the countries experiencing that extreme heat. And so, for the first time, you can really say: “Company X caused this condition which then led to this economic damage.”
Dr Antonia Hadjimichael, assistant professor at Pennsylvania State University
It was about interdisciplinary work – not that anything in it is ground-shakingly new, but it was a good conversation around interdisciplinary teams and what makes them work and what doesn’t make them work. And what I really liked about it is that they really emphasise the role of a connector – the scientist that navigates this space in between and makes sure that the things kind of glue together…The reason I really like this paper is that we don’t value those scientists in academia, in traditional metrics that we have.
Dr Santiago Botía, researcher at Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry
The most interesting paper I’ve read this year was about how soil fertility and water table depth control the response to drought in the Amazon. They found very nicely how the proximity to soil water controls the anomalies in gross primary productivity in the Amazon. And, with that methodology, they could explain the response of recent droughts and the “greening” of the forest during drought, which is kind of a counterintuitive [phenomenon], but it was very interesting.
Dr Gregory Johnson, affiliate professor at the University of Washington
This article explores the response of a fairly coarse spatial resolution climate model…to a scenario in which atmospheric CO2 is increased at 1% a year to doubling and then CO2 is more gradually removed from the atmosphere…[It finds] a large release of heat from the Southern Ocean, with substantial regional – and even global – climate impacts. I find this work interesting because it reminds us of the important – and potentially nonlinear – roles that changing ocean circulation and water properties play in modulating our climate.
Cecilia Keating also contributed to this spotlight.
Watch, read, listen
METHANE MATTERS: In the Guardian, Barbados prime minister Mia Mottley wrote that the world must “urgently target methane” to avoid the worst impacts of climate change.
CLIMATE WRAPPED: Grist summarised the major stories for Earth’s climate in 2025 – “the good, the bad and the ugly”.
COASTING: On the Coastal Call podcast, a biogeochemist spoke about “coastal change and community resilience” in the eastern US’s Long Island Sound.
Coming up
- 27 December: Cote D’Ivoire parliamentary elections
- 28 December: Central African Republic presidential and parliamentary elections
- 28 December: Guinean presidential election
Pick of the jobs
- BirdLife International, forest programme administrator | Salary: £28,000-£30,000. Location: Cambridge, UK
- World Resources Institute, power-sector transition senior manager | Salary: $116,000-$139,000. Location: Washington DC
- Fauna & Flora, operations lead for Liberia | Salary: $61,910. Location: Monrovia, Liberia
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 19 December 2025: EU’s petrol car U-turn; Trump to axe ‘leading’ research lab; What climate scientists are reading appeared first on Carbon Brief.
-
Greenhouse Gases5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval















