After Brazil’s COP30 presidency insisted on its plan to gavel through a political package on some of the most divisive issues at the UN climate talks “very late” on Wednesday, promised new draft texts had yet to materialise by early evening.
Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva is in town for a series of high-level meetings, including talks with delegations from the EU and China. UN Secretary-General António Guterres is also conducting bilateral engagements on the sidelines.
Key sticking points – from trade and finance from developed countries to a proposed roadmap for transitioning away from fossil fuels – remain unresolved. Brazilian negotiators are pushing to bridge divisions in hopes of securing an early win.
China and Russia oppose critical minerals in draft
Minerals needed for the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy systems made their first appearance in a draft COP text last week. But not everyone is happy about it.
Observers at the talks say China has opposed the inclusion of language on minerals in the text on ensuring a just energy transition within and among countries, while one with access to the negotiation rooms told Climate Home News that Russia is also resisting.
The current draft text for an area of the negotiations known as the Just Transition Work Programme (JTWP) includes an option to recognise the social and environmental risks from extracting minerals needed to manufacture batteries, solar panels and wind turbines. If adopted it would be the first mention of energy-transition minerals in the UN climate regime.
The same option also recalls principles and recommendations outlined by a UN of experts convened by UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres, which suggested that human rights must be “at the core” of mining for transition minerals.
Observers say China has been adamant about dropping all references to critical minerals in the COP30 draft. Russia took particular aim at the reference to the UN panel and wants it removed.
COP30 draft text includes energy transition minerals in UN climate first
To pressure China away from its current position, a group of activists sought to approach China’s second-in-command at COP30, Xia Yingxian, director general of the Department of Climate Change at China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE).
After he concluded an appearance in an unrelated event at the WWF pavilion, a group of activists approached Xia to give him a letter “respectfully” calling on China to agree to the inclusion of minerals in the text, arguing that “China’s support would carry significant weight” and signal climate leadership.
“The explicit inclusion of critical energy transition minerals is a paramount priority for key delegates and partners across the Global South and developing parties here at COP30,” the letter read.
After being offered the letter, Xia rejected the document several times and, after the activists insisted, he sped away towards delegation offices.


China is a dominant actor in the transition minerals supply chain, producing more than 70% of the world’s refined lithium, 78% of the world’s refined cobalt and 91% of rare earth minerals, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
China wants a transition towards renewables
Battling the deafening roar of pouring rain in a remote corner of the COP venue, Xia Yingxian, director general of China’s Department of Climate Change, dropped subtle hints on where the country stands on the transition away from fossil fuels.
Speaking in English at the WWF pavilion, Yingxian said “we are trying to push for a transition to renewables, transitioning away from fossil fuels…how to make it just, orderly and fair. We understand it’s not easy, but this is the journey we have to go together.”
He suggested that, while there has been lots of talk about transitioning away, “such kind of narrative” could be reframed to overcome divisions.
How could we promote renewables? Trying to change the tone from negative to positive. This will be more than welcome,” he added.
Xia concluded his speech saying that a change in framing to “positive prosperity” could help “unite all of us” and send the message that “we can do it together”. He added the framing should not be about “losing” but “how we can win”.
China – the world’s largest producer of solar and wind technologies – has so far not publicly voiced a position on calls for a roadmap to transition away from fossil fuels at COP30.
Yesterday, more than 80 countries asked that a process to craft a roadmap to shift the world away from oil, coal and gas be agreed as one of the main outcomes from Belém.


Roadmap to end deforestation lags fossil fuel plan at Amazon COP
As countries ramp up pressure for a COP30 decision on a roadmap to transition away from fossil fuels, they have yet to push hard in the Amazon city of Belém for another much-anticipated roadmap to end deforestation.
Discussions on both mechanisms took off after Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva told world leaders at the summit’s opening that COP30 must deliver “roadmaps to plan in a fair way the reversal of deforestation, reducing the dependency on fossil fuels and to mobilise the necessary resources to reach these objectives”.
Since then, more than 80 countries have rallied behind a fossil fuel transition roadmap – yet negotiators from tropical countries and observers say a roadmap to end deforestation has not gained the same momentum at the UN climate talks.
At least 42 countries have expressed support for a deforestation roadmap – among them the European Union, the AILAC group of Latin American countries and the Environmental Integrity Group which includes Mexico, Liechtenstein, Monaco, South Korea, Switzerland and Georgia.
World failing on goal to halt deforestation by 2030, raising stakes for Amazon COP
Current negotiating drafts include an option to convene a dialogue of ministers on the creation of national roadmaps to end deforestation, which observers told Climate Home News is a weak option that must be improved with more pressure from countries.
Panama’s head of delegation Juan Carlos Monterrey told an event hosted by Climate Home News this week that a plan to protect forests has to be one of the key outcomes of COP30. “If we don’t get a roadmap to end deforestation at the Amazonia COP, we will never get it,” he said.
Latin America issues joint call for adaptation indicators in Belém
Latin American countries in the AILAC group advocated for a strong adaptation outcome at COP30, after African countries called for a two-year delay in the adoption of metrics to track climate resilience – a key deliverable at the summit.
Countries are discussing a set of indicators under the Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA), which they are expected to use to track progress on how they are coping with the impacts of climate change. But African countries want to hold off unless developed countries agree to triple adaptation finance to $120 billion a year by 2030, saying the metrics are meaningless without money to help them ramp up resilience.
Poorest countries appeal for more adaptation finance at COP30
The current draft texts of the “Mutirão” pact – the main expected outcome at COP30 – and the GGA both include options to establish a finance goal for adaptation. COP30 president André Correa do Lago said the two decisions are “interlinked”.
“It’s very important that we finish the indicators here. We’ve had two years of work. Technical teams have made progress on a list. It’s not perfect – nothing is – but it exists. We need that list approved so we can begin to implement it,” said Chile’s Environment Minister Maisa Rojas.
“We can’t leave a Latin American COP here in Belém without that set of indicators that can help us make progress in this area,” she added.


As dozens of reporters surrounded the group of Latin American ministers in an impromptu press huddle, the heads of delegation reiterated the need for finance to back up those indicators, which the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) appealed for on Tuesday.
Edwin Castellanos, environment minister of Guatemala, said vulnerable countries “cannot keep adapting with our own resources”, adding that developed countries must provide accessible finance.
“We cannot keep waiting for years while projects are developed and our communities keep suffering the impacts of climate change,” he said.
A UN report issued in the run-up to COP30 said developing countries will need to spend between $310 billion and $365 billion per year on measures to adapt to worsening climate change impacts by 2035.
Rojas of Chile said “we must ensure that finance reaches communities”, adding that one option would be to allocate a share of last year’s finance goal agreed in Baku for adaptation. It promises to mobilise $300 billion a year by 2035 in public finance for climate action in developing countries.
This is the preferred option of European countries, which have opposed reopening finance talks in Belem.
Gender Action Plan negotiations still haggling over definitions
The latest draft of the Gender Action Plan (GAP) was released yesterday and has six footnotes, four of them about the mere definition of gender. They were added by Paraguay, Argentina, Iran and the Vatican.
There are also two placeholders for footnotes from Indonesia, also related to the same topic. Climate Home News understands that, even if Russia doesn’t have a footnote to its name, it is one of the main countries pushing for the use of “women and girls” instead of the word “gender”. Other blockers include Saudi Arabia and Iran.
“We’ve always had fights on the Gender Action Plan… but this is different. This is trying to actually push women back by having this binary definition,” said Mary Robinson, former Irish president who is now a member of the Elders. “It’s so cruel. I mean, it’s actually unbelievable that this would enter into our space.”
Campaigners say that this row over gender hasn’t been limited to the GAP negotiations, but forms part of a bigger, coordinated effort to backtrack on human rights language. A recent press release by the Women and Gender Constituency shows that gender references have received pushback in the negotiations on adaptation, mitigation, the Global Stocktake of climate action and the Green Climate Fund.
Bridget Burns, from the Women’s Environment and Development Organization (WEDO), told a press conference that in the past two years those wanting to undermine gender progress have been “emboldened by elections around the world that have shifted countries to the right”, including in the US election. In turn, she added that has triggered “a much stronger and more coordinated pushback to the pushback.”
On day one of COP, 92 countries signed a “Global Statement on Gender Equality and Climate Action Ahead of COP30”, reaffirming their commitment to a strong GAP, “because there was an awareness of what we might face in this process,” said Burns.
As the days went by and the negotiations seemed to unfold in a more or less peaceful way, the “Belém GAP” was supposed to appear on the first “Mutirão” decision package, but in the end it was left out as COP30 President André Correa do Lago said it was not directly related to the issues addressed in that planned decision. The topic is now being discussed in consultations led by ministers, as with other negotiating tracks.
“I would like to remind President Lula and the negotiators from Brazil that President Lula was mainly elected by women in this country,” said Michelle Ferreti, founder of the Brazilian Instituto Alzira. “It’s time to honour those who put them into power.”
The post COP30 Bulletin Day 9: China and Russia oppose critical minerals mention in draft text appeared first on Climate Home News.
COP30 Bulletin Day 9: Belém package elusive as Lula steals the show
Climate Change
The Voracious Vine That ‘Ate the South’ Can Also Fuel Wildfires
Brought to the United States as an ornamental porch decoration, the kudzu vine has reshaped itself into ladder fuel for wildfires.
Nearly every Monday morning, five restorationists with Conserving Carolina guide volunteers through the steep hills of Norman Wilder Forest in Tryon, North Carolina. Armed with chainsaws, thick gloves and a pickaxe-like mattock, the group goes hunting for a wily prey: kudzu.
The Voracious Vine That ‘Ate the South’ Can Also Fuel Wildfires
Climate Change
New Jersey’s Balancing Act: Cut Utility Bills Without Derailing Clean Energy
Governor Mikie Sherrill wants to tap clean-energy funds to cushion residents from rising electricity bills.
Halfway through her inaugural speech in front of thousands of New Jerseyans in late January, newly elected governor Mikie Sherrill paused to write her signature on two documents. They were her first two executive orders.
New Jersey’s Balancing Act: Cut Utility Bills Without Derailing Clean Energy
Climate Change
Q&A: What does Trump’s repeal of US ‘endangerment finding’ mean for climate action?
On 12 February, US president Donald Trump revoked the “endangerment finding”, the bedrock of federal climate policy.
The 2009 finding concluded that six key greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), were a threat to human health – triggering a legal requirement to regulate them.
It has been key to the rollout of policies such as federal emission standards for vehicles, power plants, factories and other sources.
Speaking at the White House, US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) administrator Lee Zeldin claimed that the “elimination” of the endangerment finding would save “trillions”.
The revocation is expected to face multiple legal challenges, but, if it succeeds, it is expected to have a “sweeping” impact on federal emissions regulations for many years.
Nevertheless, US emissions are expected to continue falling, albeit at a slower pace.
Carbon Brief takes a look at what the endangerment finding was, how it has shaped US climate policy in the past and what its repeal could mean for action in the future.
- What is the ‘endangerment finding’?
- How has it shaped federal climate policy?
- How is the finding being repealed and will it face legal challenge?
- What does this mean for federal efforts to address climate change?
- What has the reaction been?
- What will the repeal mean for US emissions?
What is the ‘endangerment finding’?
The challenges of passing climate legislation in the US have meant that the federal government has often turned instead to regulations – principally, under the 1970 Clean Air Act.
The act requires the EPA to regulate pollutants, if they are found to pose a danger to public health and the environment.
In a 2007 legal case known as Massachusetts vs EPA, the Supreme Court ruled that greenhouse gases qualify as pollutants under the Clean Air Act. It also directed the EPA to determine whether these gases posed a threat to human health.
The 2009 “endangerment finding” was the result of this process and found that greenhouse gas emissions do indeed pose such a threat. Subsequently, it has underpinned federal emissions regulations for more than 15 years.
In developing the endangerment finding, the EPA pulled together evidence from its own experts, the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine and the wider scientific community.
On 7 December 2009, it concluded that US greenhouse gas emissions “in the atmosphere threaten the public health and welfare of current and future generations”.
In particular, the finding highlighted six “well-mixed” greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide (CO2); methane (CH4); nitrous oxide (N2O); hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs); perfluorocarbons (PFCs); and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
A second part of the finding stated that new vehicles contribute to the greenhouse gas pollution that endangers public health and welfare, opening the door to these emissions being regulated.
At the time, the EPA noted that, while the finding itself does not impose any requirements on industry or other entities, “this action was a prerequisite for implementing greenhouse gas emissions standards for vehicles and other sectors”.
On 15 December 2009, the finding was published in the federal register – the official record of US federal legislation – and the final rule came into effect on 14 January 2010.
At the time, then-EPA administrator Lisa Jackson said in a statement:
“This finding confirms that greenhouse gas pollution is a serious problem now and for future generations. Fortunately, it follows President [Barack] Obama’s call for a low-carbon economy and strong leadership in Congress on clean energy and climate legislation.
“This pollution problem has a solution – one that will create millions of green jobs and end our country’s dependence on foreign oil.”
How has it shaped federal climate policy?
The endangerment finding originated from a part of the Clean Air Act regulating emissions from new vehicles and so it was first applied in that sector.
However, it came to underpin greenhouse gas emission regulation across a range of sectors.
In May 2010, shortly after the Obama EPA finalised the finding, it was used to set the country’s first-ever limits on greenhouse gas emissions from light-duty engines in motor vehicles.
The following year, the EPA also released emissions standards for heavy-duty vehicles and engines.
However, findings made under one part of the Clean Air Act can also be applied to other articles of the law. David Widawsky, director of the US programme at the World Resources Institute (WRI), tells Carbon Brief:
“You can take that finding – and that scientific basis and evidence – and apply it in other instances where air pollutants are subject or required to be regulated under the Clean Air Act or other statutes.
“Revoking the endangerment finding then creates a thread that can be pulled out of not just vehicles, but a whole lot of other [sources].”
Since being entered into the federal register, the endangerment finding has also been applied to stationary sources of emissions, such as fossil-fuelled power plants and factories, as well as an expanded range of non-stationary emissions sources, including aviation.
(In fact, the EPA is compelled to regulate emissions of a pollutant – such as CO2 as identified in the endangerment finding – from stationary sources, once it has been regulated anywhere else under the Clean Air Act.)
In 2015, the EPA finalised its guidance on regulating emissions from fossil-fuelled power plants. These performance standards applied to newly constructed plants, as well as those that underwent major modifications.
This ruling noted that “because the EPA is not listing a new source category in this rule, the EPA is not required to make a new endangerment finding…in order to establish standards of performance for the CO2”.
The following year, the agency established rules on methane emissions from oil and gas sources, including wells and processing plants. Again, this was based on the 2009 finding.
The 2016 aircraft endangerment finding also explicitly references the vehicle-emissions endangerment finding. That rule says that the “body of scientific evidence amassed in the record for the 2009 endangerment finding also compellingly supports an endangerment finding” for aircraft.
The endangerment finding has also played a critical role in shaping the trajectory of climate litigation in the US.
In a 2011 case, American Electric Power Co. vs Connecticut, the Supreme Court unanimously found that, because greenhouse gas emissions were already regulated by the EPA under the Clean Air Act, companies could not be sued under federal common law over their greenhouse gas emissions.
Widawsky tells Carbon Brief that repealing the endangerment finding therefore “opens the door” to climate litigation of other kinds:
“When plaintiffs would introduce litigation in federal courts, the answer or the courts would find that EPA is ‘handling it’ and there’s not necessarily a basis for federal litigation. By removing the endangerment finding…it actually opens the door to the question – not necessarily successful litigation – and the courts will make that determination.”
How is the finding being repealed and will it face legal challenge?
The official revocation of the endangerment finding is yet to be posted to the federal register. It will be effective 60 days after the text is published in the journal.
It is set to face no shortage of legal challenges. The state of California has “vowed” to sue, as have a number of environmental groups, including Sierra Club, Earthjustice and the National Resources Defense Council.
Dena Adler, an adjunct professor of law at New York University School of Law, tells Carbon Brief there are “significant legal and analytical vulnerabilities” in the EPA’s ruling. She explains:
“This repeal will only stick if it can survive legal challenge in the courts. But it could take months, if not years, to get a final judicial decision.”
At the heart of the federal agency’s argument is that it claims to lack the authority to regulate greenhouse gas emissions in response to “global climate change concerns” under the Clean Air Act.
In the ruling, the EPA says the section of the Act focused on vehicle emissions is “best read” as authorising the agency to regulate air pollution that harms the public through “local or regional exposure” – for instance, smog or acid rain – but not pollution from “well-mixed” greenhouse gases that, it claims, “impact public health and welfare only indirectly”.
This distinction directly contradicts the landmark 2007 Supreme Court decision in Massachusetts vs EPA. (See: What is the ‘endangerment finding’?)
The EPA’s case also rests on an argument that the agency violated the “major questions doctrine” when it started regulating greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles.
This legal principle holds that federal agencies need explicit authorisation from Congress to press ahead with actions in certain “extraordinary” cases.
In a policy brief in January, legal experts from New York University School of Law’s Institute of Policy Integrity argued that the “major questions doctrine” argument “fails for several reasons”.
Regulating greenhouse gas emissions under the Clean Air Act is “neither unheralded nor transformative” – both of which are needed for the legal principle to apply, the lawyers said.
Furthermore, the policy brief noted that – even if the doctrine were triggered – the Clean Air Act does, in fact, supply the EPA with the “clear authority” required.
Mark Drajem, director of public affairs at NRDC, says the endangerment finding has been “firmly established in the courts”. He tells Carbon Brief:
“In 2007, the Supreme Court directed EPA to look at the science and determine if greenhouse gases pose a risk to human health and welfare. EPA did that in 2009 and federal courts rejected a challenge to that in 2012.
“Since then, the Supreme Court has considered EPA’s greenhouse gas regulations three separate times and never questioned whether it has the authority to regulate greenhouse gases. It has only ruled on how it can regulate that pollution.”
However, experts have noted that the Trump administration is banking on legal challenges making their way to the Supreme Court – and the now conservative-leaning bench then upholding the repeal of the endangerment finding.
Elsewhere, the EPA’s new ruling argues that regulating emissions from vehicles has “no material impact on global climate change concerns…much less the adverse public health or welfare impacts attributed to such global climate trends”.
“Climate impact modelling”, it continues, shows that “even the complete elimination of all greenhouse gas emissions” of vehicles in the US would have impacts that fall “within the standard margin of error” for global temperature and sea level rise.
In this context, it argues, regulations on emissions are “futile”.
(The US is more historically responsible for climate change than any other country. In its 2022 sixth assessment report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change said that further delaying action to cut emissions would “miss a brief and rapidly closing window of opportunity to secure a liveable and sustainable future for all”.)
However, the final rule stops short of attempting to justify the plans by disputing the scientific basis for climate change.
Notably, the EPA has abandoned plans to rely on the findings of a controversial climate science report commissioned by the Department of Energy (DoE) last year.
This is a marked departure from the draft ruling, published in August, which argued there were “significant questions and ambiguities presented by both the observable realities of the past nearly two decades and the recent findings of the scientific community, including those summarised in the draft CWG [‘climate working group’] report”.
The CWG report – written by five researchers known for rejecting the scientific consensus on human influence on global warming – faced significant criticism for inaccurate conclusions and a flawed review process. (Carbon Brief’s factcheck found more than 100 misleading or false statements in the report.)
A judge ruled in January that the DoE had broken the law when energy secretary Chris Wright “hand-picked five researchers who reject the scientific consensus on climate change to work in secret on a sweeping government report on global warming”, according to the New York Times.
In a press release in July, the EPA said “updated studies and information” set out in the CWG report would serve to “challenge the assumptions” of the 2009 finding.
But, in the footnotes to its final ruling, the EPA notes it is not relying on the report for “any aspect of this final action” in light of “concerns raised by some commenters”.
Legal experts have argued that the pivot away from arguments undermining climate science is designed with future legal battles over the attempted repeal in mind.
What does this mean for federal efforts to address climate change?
As mentioned above, a number of groups have already filed legal actions against the Trump administration’s move to repeal the endangerment finding – leaving the future uncertain.
However, if the repeal does survive legal challenges, it would have far-reaching implications for federal efforts to address greenhouse gas emissions, experts say.
In a blog post, the WRI’s Widawsky said that the repeal would have a “sweeping” impact on federal emissions regulations for cars, coal-fired power stations and gas power plants, adding:
“In practical terms, without the endangerment finding, regulating greenhouse gas emissions is no longer a legal requirement. The science hasn’t changed, but the obligation to act on it has been removed.”
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Widawsky adds that, despite this large immediate impact, there are “a lot of mechanisms” future US administrations might be able to pursue if they wanted to reinstate the federal government’s obligation to address greenhouse gas emissions:
“Probably the most direct way – rather than talk about ‘pollutants’, in general, and the EPA, say, making a science-specific finding for that pollutant – [is] for Congress simply to declare a particular pollutant to be a hazard for human health and welfare. [This] has been done in other instances.”
If federal efforts to address greenhouse gas emissions decline, there will likely still be attempts to regulate at the state level.
Previous analysis from the University of Oxford noted that, despite a walkback on federal climate policy in Trump’s second presidential term, 19 US states – covering nearly half of the country’s population – remain committed to net-zero targets.
Widawksy tells Carbon Brief that it is possible that states may be able to leverage legislation, including the Clean Air Act, to enact regulations to address emissions at the state level.
However, in some cases, states may be prevented from doing so by “preemption”, a US legal doctrine where higher-level federal laws override lower-level state laws, he adds:
“There are a whole lot of other sections of the Clean Air Act that may either inhibit that kind of ability for states to act through preemption or allow for that to happen.”
What has the reaction been?
The Trump administration’s decision has received widespread global condemnation, although it has been celebrated by some right-wing newspapers, politicians and commentators.
In the US, former US president Barack Obama said on Twitter that the move will leave Americans “less safe, less healthy and less able to fight climate change – all so the fossil-fuel industry can make even more money”.
Similarly, California governor Gavin Newsom called the decision “reckless”, arguing that it will lead to “more deadly wildfires, more extreme heat deaths, more climate-driven floods and droughts and greater threats to communities nationwide”.
Former US secretary of state and climate envoy John Kerry called the decision “un-American”, according to a story on the frontpage of the Guardian. He continued:
“[It] takes Orwellian governance to new heights and invites enormous damage to people and property around the world.”
An editorial in the Guardian dubbed the repeal as “just one part of Trump’s assault on environmental controls and promotion of fossil fuels”, but added that it “may be his most consequential”.
Similarly, an editorial in the Hindu said that Trump is “trying to turn back the clock on environmental issues”.
In China, state-run news agency Xinhua published a cartoon depicting Uncle Sam attempting to turn an ageing car, marked “US climate policy”, away from the road marked “green development”, back towards a city engulfed in flames and pollution that swells towards dark clouds labelled “greenhouse gas catastrophe”.
Conversely, Trump described the finding as “the legal foundation for the green new scam”, which he claimed “the Obama and Biden administration used to destroy countless jobs”.
Similarly, Al Jazeera reported that EPA administrator Zeldin said the endangerment finding “led to trillions of dollars in regulations that strangled entire sectors of the US economy, including the American auto industry”. The outlet quoted him saying:
“The Obama and Biden administrations used it to steamroll into existence a left-wing wish list of costly climate policies, electric vehicle mandates and other requirements that assaulted consumer choice and affordability.”
An editorial in the Washington Post also praises the move, saying “it’s about time” that the endangerment finding was revoked. It argued – without evidence – that the benefits of regulating emissions are “modest” and that “free-market-driven innovation has done more to combat climate change than regulatory power grabs like the ‘endangerment finding’ ever did”.
The Heritage Foundation – the climate-sceptic US lobby group that published the influential “Project 2025” document before Trump took office – has also celebrated the decision.
Time reported that the group previously criticised the endangerment finding, saying that it was used to “justify sweeping restrictions on CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions across the economy, imposing huge costs”. The magazine added that Project 2025 laid out plans to “establish a system, with an appropriate deadline, to update the 2009 endangerment finding”.
Climate scientists have also weighed in on the administration’s repeal efforts. Prof Andrew Dessler, a climate scientist at Texas A&M University in College Station, argued that there is “no legitimate scientific rationale” for the EPA decision.
Similarly, Dr Katharine Hayhoe, chief scientist at the Nature Conservancy, said in a statement that, since the establishment of the 2009 endangerment finding, the evidence showing greenhouse gases pose a threat to human health and the environment “has only grown stronger”.
Dr Gretchen Goldman, president and CEO of the Union of Concerned Scientists and a former White House official, gave a statement, arguing that “ramming through this unlawful, destructive action at the behest of polluters is an obvious example of what happens when a corrupt administration and fossil fuel interests are allowed to run amok”.
In the San Francisco Chronicle, Prof Michael Mann, a climate scientist at the University of Pennsylvania, and Bob Ward, policy and communications director at the Grantham Research Institute, wrote that Trump is “slowing climate progress”, but that “it won’t put a stop to global climate action”. They added:
“The rest of the world is moving on and thanks to Trump’s ridiculous insistence that climate change is a ‘hoax’, the US now stands to lose out in the great economic revolution of the modern era – the clean-energy transition.”
What will the repeal mean for US emissions?
Federal regulations and standards underpinned by the endangerment finding have been at the heart of US government plans to reduce the nation’s emissions.
For example, NRDC analysis of EPA data suggests that Biden-era vehicle standards, combined with other policies to boost electric cars, were set to avoid nearly 8bn tonnes of CO2 equivalent (GtCO2e) over the next three decades.
By removing the legal requirement to regulate greenhouse gases at a federal level from such high-emitting sectors, the EPA could instead be driving higher emissions.
Nevertheless, some climate experts argue that the repeal is more of a “symbolic” action and that EPA regulations have not historically been the main drivers of US emissions cuts.
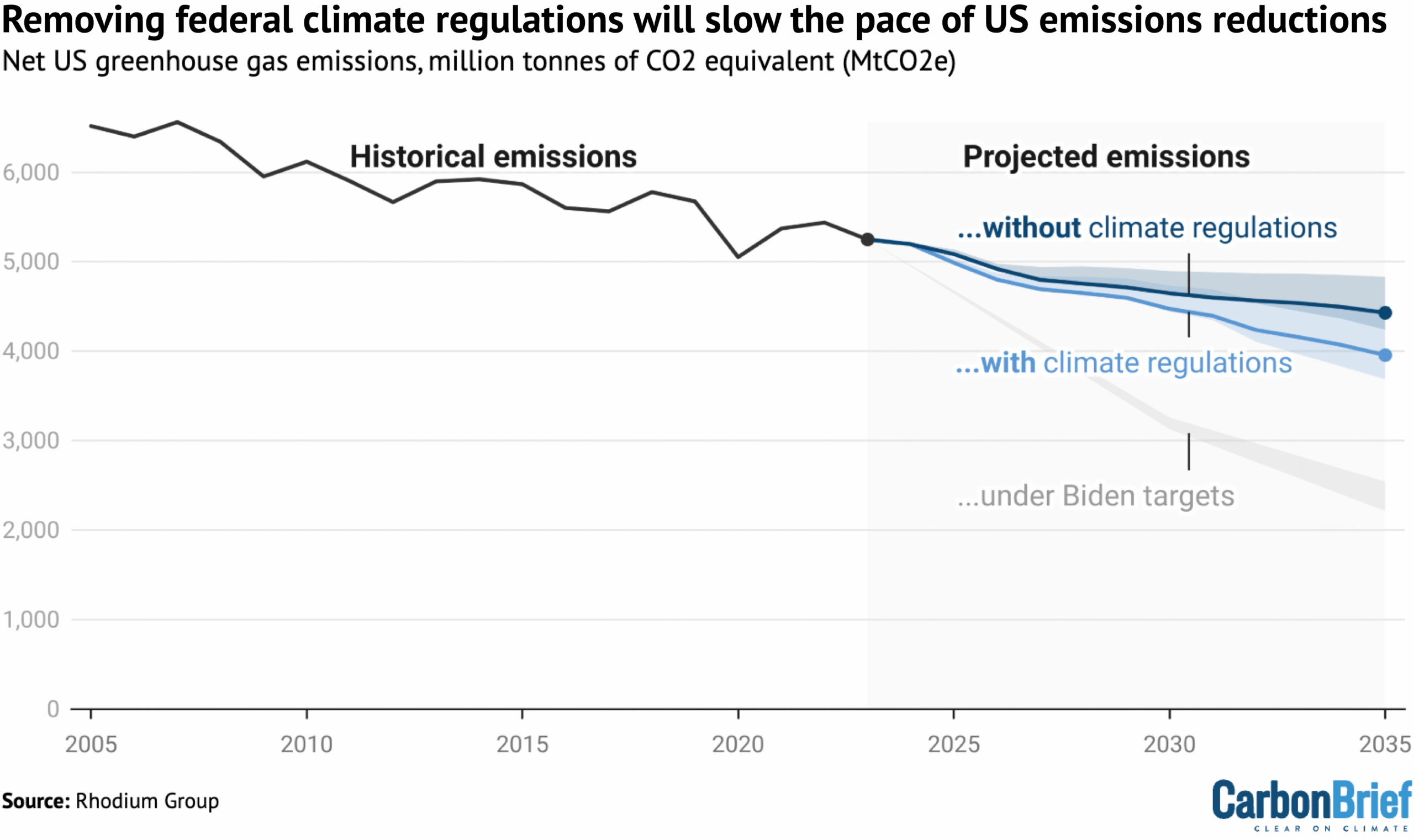
Rhodium Group analysis last year estimated the impact of the EPA removing 31 regulatory policies, including the endangerment finding and “actions that rely on that finding”. Most of these had already been proposed for repeal independently by the Trump administration.
Ben King, the organisation’s climate and energy director, tells Carbon Brief this “has the same effect on the system as repealing the endangerment finding”.
The Rhodium Group concluded that, in this scenario, emissions would continue falling to 26-35% below 2005 levels by 2035, as the chart below shows. If the regulations remained in place, it estimated that emissions would fall faster, by around 32-44%.
(Notably, neither of these scenarios would be in line with the Biden administration’s international climate pledge, which was a 61-66% reduction by 2035).
There are various factors that could contribute to continued – albeit slower – decline in US emissions, in the absence of federal regulations. These include falling costs for clean technologies, higher fossil-fuel prices and state-level legislation.
Despite Trump’s rhetoric, coal plants have become uneconomic to operate in the US compared with cheaper renewables and gas. As a result, Trump has overseen a larger reduction in coal-fired capacity than any other US president.
Meanwhile, in spite of the openly hostile policy environment, relatively low-cost US wind and solar projects are competitive with gas power and are still likely to be built in large numbers.
The vast majority of new US power capacity in recent years has been solar, wind and storage. Around 92% of power projects seeking electricity interconnection in the US are solar, wind and storage, with the remainder nearly all gas.
The broader transition to low-carbon transport is well underway in the US, with electric vehicle sales breaking records during nearly every month in 2025.
This can partly be attributed to federal tax credits, which the Trump administration is now cutting. However, cheaper models, growing consumer preference and state policies are likely to continue strengthening support.
Even if emissions continue on a downward trajectory, repealing the endangerment finding could make it harder to drive more ambitious climate action in the future. Some climate experts also point to the uncertainty of future emissions reductions.
“[It] depends on a number of technology, policy, economic and behavioural factors. Other folks are less sanguine about greenhouse gas declines,” WRI’s Widawsky tells Carbon Brief.
The post Q&A: What does Trump’s repeal of US ‘endangerment finding’ mean for climate action? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Q&A: What does Trump’s repeal of US ‘endangerment finding’ mean for climate action?
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits









