Nikola, America’s favorite zero-emissions truck brand, released its first Sustainability Impact Report. This report provides a comprehensive picture of Nikola’s environmental and social initiatives and explains their progress toward sustainability goals.
Nikola owns battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and hydrogen fuel cell (FCEV) Class 8 trucks, designed specifically to make the environment safer and cleaner. Most significantly, HYLA’s hydrogen refueling ecosystem offers a robust hydrogen infrastructure to support the shift to sustainable fuel sources.
Driving Towards a Zero-Emission Future
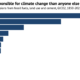
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reports that transportation generates around 28% of direct U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Medium- and heavy-duty trucks alone account for about 23% of these emissions. However, the EPA also highlighted that with the rise in transportation costs and freight demands, zero-emission vehicles can be a solution for a sustainable future.

So Nikola’s mission is clear: to lead the transition to zero-emission technology across critical routes. Thereby, supporting a climate-friendly future for commercial transportation.
Steve Girsky, President and CEO of Nikola, stated,
“Our focus is on zero-emission technologies and the infrastructure to support them, decarbonizing what has been known as a very ‘dirty’ market segment, Class 8 trucks. Medium- and heavy-duty trucks produce more emissions than passenger cars and rail combined. Our commitment—our mission, really—to improving air quality, avoiding emissions, and mitigating our contributions to climate change is why most of us work for Nikola. What we are most proud of, besides our dedicated team, is bringing our battery electric truck to market while developing and launching our hydrogen fuel cell electric truck shortly thereafter.”
Nikola’s sustainability report reveals an interesting piece of information. The company was founded to tackle transportation emissions, specifically. In addition to its net-zero goals, it prioritizes drivers’ health, safety, and community well-being where Class 8 trucks operate.
The truck giant strongly believes that zero-emission transportation is achievable, which is why the company aims to expand its impact throughout the nation.
Environmental Impact and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Nikola recognizes the risks of climate change and the opportunities that proactive measures offer. The company has taken the following actions to address these risks and capitalize on opportunities:
- Investment in clean technology and innovation
- Measurement and identification of emission sources
- Commitment to renewable energy and energy efficiency in operations
- Installation of EV charging infrastructure for Nikola trucks and employees
- Adoption of circularity principles and waste diversion strategies for improved sustainability
In 2023, Nikola’s total emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2) were 5,155.56 MT CO₂e.

Hydrogen Trucks Hit the Highway
In Q4 2023, the company introduced hydrogen fuel cell electric trucks on the road in North America. By year-end, 42 trucks were manufactured, with 35 delivered to dealers and seven retained for ongoing testing and fleet demonstrations.
Early in 2024, the first HYLA modular refueling station was launched in Ontario, California, alongside a new partnership with FirstElement Fuel to offer hydrogen fueling solutions in both Northern and Southern California, including Oakland.
Nikola views both battery electric trucks powered by the grid and hydrogen fuel cell electric trucks as essential to reducing emissions in heavy-duty transportation. The company remains dedicated to advancing both vehicle technologies and fueling infrastructure for broad deployment.
The 3-R Approach to Battery Lifecycles
Nikola is committed to a circular economy, where truck and battery components are built to last long. They can be reused and recycled efficiently. The company collaborates with partners to manage materials responsibly at every stage of a vehicle’s life, focusing on durability and resource efficiency.
Regarding battery sustainability, Nikola has a battery circularity policy based on the 3 Rs: remanufacture, reuse, and recycle all pre-consumer and production batteries. Currently, Nikola’s recycling partners recover up to 95% of materials from lithium-ion batteries, aiming to recycle 100% of scrapped batteries. Notably, last year, the truck titan reused 192 metric tons of batteries.
The company also believes in extending battery life as the most sustainable choice. They use advanced vehicle software to receive over-the-air (OTA) updates that improve battery efficiency and extend battery life before recycling.
Waste and Water Management
The report also highlights the company’s dedication to improving manufacturing practices and minimizing environmental impact. A Waste Management Committee meets regularly to measure performance and implement strategies. They prioritize recycling materials such as steel, aluminum, lithium-ion batteries, plastic, and cardboard. Additionally, Nikola is mindful of water usage, primarily using water for vehicle quality testing and recycling.
Nikola’s environmental impact data for the last year is as follows:

Resource and Energy Efficiency at Nikola Facility
Nikola is committed to maximizing its resource efficiency and minimizing its manufacturing impact. The 670,000-square-foot Coolidge facility uses advanced eco-friendly technologies, including energy-efficient LED lighting, HVAC systems, and daylighting to cut artificial lighting needs.
Additionally, smart-controlled energy systems optimize resource use, while on-site solar panels and EV charging stations support sustainable practices. Nikola has also deployed electric automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and forklifts to further reduce emissions.
The total energy consumption at the facility is 7,491,559 kWh, of which 771,960 kWh is generated through solar.
By embracing these initiatives, Nikola is paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Disclaimer: Data and visuals- Nikola Sustainability Impact Report
- FURTHER READING: Truck Titans Clash: Tesla Semi vs. Nikola Hydrogen
The post A Green Journey: Key Insights from Nikola’s First Sustainability Report appeared first on Carbon Credits.
Carbon Footprint
How BESS and Lithium Demand Are Shaping Energy Storage: Global Shipments to Surge 50% in 2025
Disseminated on behalf of Surge Battery Metals Inc.
The global Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market is growing at a rapid pace. The expansion is driven by the rise of renewable energy, the increasing need for grid stability, and the growth of electric vehicles (EVs).
BESS allows electricity to be stored when supply exceeds demand and released when demand is higher than supply. This technology is becoming essential for utilities, commercial users, and residential applications.
Powering Demand: EVs and Energy Storage Drive Growth
J.P. Morgan’s recent analysis shows that shipments of stationary energy storage batteries will rise by 50% in 2025 and 43% in 2026. This surge is causing the lithium supply to move into a deficit.

Analysts estimate that BESS will account for about 30% of global lithium demand by 2026, rising to 36% by 2030. Global lithium demand in lithium-carbonate-equivalent (LCE) terms could reach ~2.8 million tonnes by 2030.
Demand is rising not only from energy storage but also from the EV sector. J.P. Morgan has increased its forecast for EV-related lithium demand by 3–5% for the years 2025 to 2030. This change shows that more people are adopting electric vehicles globally.

The rising demand is further amplified by policies encouraging renewable energy adoption. Many countries are setting goals for renewable energy and cleaner grids. This opens up new chances for energy storage.
Utilities are using BESS more widely. They do this to manage peak loads, integrate renewable energy, and offer services like frequency regulation and black-start capability.
Price Sparks: Lithium Supply and Market Tightness
Despite growing demand, supply faces significant constraints. Many lithium producers hesitate to restart idle production. They want prices to rise enough for them to profit.
J.P. Morgan highlights that prices of $1,200–1,500 per tonne of spodumene are needed to bring new supply online. Spot prices have already risen from around $800/t to ~ $950/t, highlighting tightness in the market.

Lithium price forecasts have also been upgraded to reflect these market conditions:
- 2026/27: $1,100–1,200/t
- Long-term: $1,300/t
Higher price levels boost the economics of lithium projects. This benefits companies with strong ties to the BESS market. Higher prices also create incentives for new players to enter the market and expand existing projects.
Key Market Trends for BESS
The BESS market is evolving rapidly with several structural trends:
- Grid-scale storage growth: Large-scale BESS deployments are increasing to help utilities manage intermittent renewable generation and maintain grid stability.
- Distributed energy storage: Behind-the-meter storage for commercial, industrial, and residential users is rising as battery costs fall.
- Advances in battery technology: Lithium-ion battery performance is improving, with longer lifespans, higher efficiency, and better safety.
- Policy support: Governments worldwide are providing incentives and creating regulations that encourage energy storage adoption.
- Supply-chain risks: Lithium, nickel, cobalt, and other critical minerals remain a bottleneck, and securing a reliable supply is a key challenge for the industry.
J.P. Morgan says that high demand and limited supply are creating a structural deficit in the lithium market. This is pushing prices up and making companies that supply lithium for BESS applications more appealing.
Spotlight on Surge Battery Metals: A Rising Player
Surge Battery Metals (TSXV: NILI | OTCQX: NILIF) is advancing the highest-grade lithium clay resource currently reported in the United States. With this level of grade and consistency, the Nevada North Lithium Project (NNLP) represents the type of high-quality, domestic lithium supply that battery makers and grid-scale energy storage developers have been looking for – an “American-made” resource that strengthens U.S. supply chains and reduces dependence on imported material.
With the lithium market emerging from a prolonged downturn, high-quality projects with strong fundamentals are beginning to stand out. Surge Battery Metals is well-positioned in this environment as the company has:
- BLM approval for its Exploration Plan of Operations,
- Hosts the highest-grade lithium clay resource currently reported in the USA, and
- Maintains a strong treasury to advance the NNLP. NNLP holds an inferred resource of 11.24 Mt of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) at 3,010 ppm Li, showcasing the scale and potential quality of its lithium assets.
These advantages – combined with a high-grade, near-surface deposit located in mining-friendly Nevada – position Surge as one of the few lithium explorers with the potential to advance meaningfully toward production as market conditions improve. Demand for BESS is rising quickly, which boosts its potential advantage.

Forecasts and Industry Analysis: Lithium and BESS Outlook
The BESS market is expected to continue growing sharply over the next decade. According to J.P. Morgan, stationary energy storage will account for 30–36% of lithium demand by 2030. Utility-scale projects will lead this growth. However, commercial and residential installations will also play a big role.
Price trends are likely to remain supportive for suppliers. Spot prices are near $950/t, with long-term forecasts at $1,300/t. Companies that produce and supply lithium efficiently can capture significant value.
Industry analysts also highlight several emerging trends:
- Integration of smart-grid technology: AI and software solutions are being deployed to optimize energy storage and distribution.
- Hybrid energy storage solutions: Combining batteries with other forms of storage, such as pumped hydro or thermal storage, is becoming more common.
- Recycling and secondary supply chains: As BESS adoption grows, recycling lithium and other critical metals will become increasingly important.
These trends should boost the flexibility, efficiency, and sustainability of power networks globally.
Strategic Moves: Surge’s Path to Market Leadership
Surge Battery Metals is positioned to benefit from these industry dynamics. Its focus on high-quality lithium assets aligns with the rising demand for BESS. Key strategic considerations for the company include:
- Advancing projects efficiently to meet growing market demand.
- Forming strategic partnerships with battery manufacturers and utility companies to secure offtake agreements.
- Maintaining operational discipline and cost efficiency to maximize project returns.
Surge Battery Metals is currently advancing lithium exploration at its Nevada North Lithium Project with the goal of defining resources that could support future production. Its metallurgical testing has shown promising results. These include lithium carbonate of 99% purity, but the company is still working toward a full feasibility study. If development proceeds as planned, Surge could become a significant future supplier for the BESS market, although current supply remains limited.

The Bright Future of Energy Storage
Battery Energy Storage Systems are no longer a niche market. The growing use of renewable energy, the rise of electric vehicles, and updates to the grid are increasing the demand for lithium and other battery materials.
Moreover, the outlook for BESS is positive. Demand growth, tech improvements, and policy support all suggest the market will keep expanding. Supply limits and higher prices are opening doors for companies that can deliver lithium effectively.
By 2030, BESS could account for more than one-third of global lithium demand. Surge Battery Metals and similar companies are key to this shift. They help create cleaner, stronger, and more efficient electricity systems.
As the market grows, execution, timing, and partnerships will decide which companies benefit the most. Surge Battery Metals can shine in the energy storage market by focusing on high-quality lithium resources, smart development, and staying aligned with market trends.
- READ MORE: Lithium’s Surge: Why Global X Lithium & Battery Tech ETF (LIT) Is Outperforming NVIDIA Stock in 2025
DISCLAIMER
New Era Publishing Inc. and/or CarbonCredits.com (“We” or “Us”) are not securities dealers or brokers, investment advisers, or financial advisers, and you should not rely on the information herein as investment advice. Surge Battery Metals Inc. (“Company”) made a one-time payment of $50,000 to provide marketing services for a term of two months. None of the owners, members, directors, or employees of New Era Publishing Inc. and/or CarbonCredits.com currently hold, or have any beneficial ownership in, any shares, stocks, or options of the companies mentioned.
This article is informational only and is solely for use by prospective investors in determining whether to seek additional information. It does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities. Examples that we provide of share price increases pertaining to a particular issuer from one referenced date to another represent arbitrarily chosen time periods and are no indication whatsoever of future stock prices for that issuer and are of no predictive value.
Our stock profiles are intended to highlight certain companies for your further investigation; they are not stock recommendations or an offer or sale of the referenced securities. The securities issued by the companies we profile should be considered high-risk; if you do invest despite these warnings, you may lose your entire investment. Please do your own research before investing, including reviewing the companies’ SEDAR+ and SEC filings, press releases, and risk disclosures.
It is our policy that information contained in this profile was provided by the company, extracted from SEDAR+ and SEC filings, company websites, and other publicly available sources. We believe the sources and information are accurate and reliable but we cannot guarantee them.
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT AND FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION
Certain statements contained in this news release may constitute “forward-looking information” within the meaning of applicable securities laws. Forward-looking information generally can be identified by words such as “anticipate,” “expect,” “estimate,” “forecast,” “plan,” and similar expressions suggesting future outcomes or events. Forward-looking information is based on current expectations of management; however, it is subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated.
These factors include, without limitation, statements relating to the Company’s exploration and development plans, the potential of its mineral projects, financing activities, regulatory approvals, market conditions, and future objectives. Forward-looking information involves numerous risks and uncertainties and actual results might differ materially from results suggested in any forward-looking information. These risks and uncertainties include, among other things, market volatility, the state of financial markets for the Company’s securities, fluctuations in commodity prices, operational challenges, and changes in business plans.
Forward-looking information is based on several key expectations and assumptions, including, without limitation, that the Company will continue with its stated business objectives and will be able to raise additional capital as required. Although management of the Company has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially, there may be other factors that cause results not to be as anticipated, estimated, or intended.
There can be no assurance that such forward-looking information will prove to be accurate, as actual results and future events could differ materially. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking information. Additional information about risks and uncertainties is contained in the Company’s management’s discussion and analysis and annual information form for the year ended December 31, 2024, copies of which are available on SEDAR+ at www.sedarplus.ca.
The forward-looking information contained herein is expressly qualified in its entirety by this cautionary statement. Forward-looking information reflects management’s current beliefs and is based on information currently available to the Company. The forward-looking information is made as of the date of this news release, and the Company assumes no obligation to update or revise such information to reflect new events or circumstances except as may be required by applicable law.
The post How BESS and Lithium Demand Are Shaping Energy Storage: Global Shipments to Surge 50% in 2025 appeared first on Carbon Credits.
Carbon Footprint
BYD Overtakes Tesla as World’s Biggest EV Seller in 2025
In 2025, China’s automotive maker BYD became the world’s largest seller of electric vehicles (EVs), overtaking U.S. EV pioneer Tesla for the first time. Data from multiple industry trackers shows that BYD sold about 2.26 million battery electric vehicles (BEVs) in 2025.
In contrast, Tesla delivered about 1.64 million EVs in the same year, marking a decline from its 2024 figures. This shift marks a major change in the global EV market.
From Challenger to Market Leader: BYD’s Breakthrough Year
BYD’s EV sales showed strong momentum throughout 2025. Its pure battery electric vehicle deliveries rose by roughly 28% year on year, reaching more than 2.25 million units worldwide. This steady growth allowed BYD to move ahead of Tesla in total annual BEV sales.
Tesla, by comparison, reported a decline of about 9-10% in overall vehicle deliveries versus the previous year. As a result, 2025 marked the first full calendar year in which BYD sold more battery electric vehicles than Tesla.

The gap became more visible in the second half of the year. Demand for EVs softened in some of Tesla’s key markets, particularly as higher interest rates and reduced incentives affected consumer spending. BYD, however, continued to benefit from strong demand in China and improving sales abroad.
By year’s end, the gap in total EV deliveries between the two companies grew to several hundred thousand units. This marked a clear shift in market leadership.
Quarterly data reinforced this trend. In the fourth quarter of 2025, Tesla delivered around 418,000 vehicles, representing a 15–16% drop from the same period in 2024. This decline reflected slower sales growth and increased competition.
BYD’s fourth-quarter BEV deliveries, in contrast, continued to rise. Its consistent quarterly growth helped push its full-year sales past Tesla’s and confirmed its position as the world’s largest EV seller by volume.
Why China’s EV Champion Is Scaling Faster
Several factors helped drive BYD’s expansion in global EV sales during 2025. A key driver was strong domestic demand in China, the world’s largest electric vehicle market.
Chinese automakers lead in local EV sales. This is thanks to consumer trust in domestic brands and a strong charging network in big cities. BYD benefited directly from this environment.
From January to November, industry estimates China’s NEV wholesale sales are about 13.78 million units. This shows a 29% increase compared to last year, and BYD captured a dominant 32% domestic share. This home-market strength fueled its global BEV leadership.

The product range also played an important role. BYD offers a wide lineup of EV models, including many lower-priced options that appeal to cost-conscious buyers. These vehicles attracted customers looking for practical electric cars rather than premium models. This broader appeal helped BYD reach a larger customer base than some competitors.
At the same time, BYD’s exports hit 1.05 million units in 2025, up 200% from the previous year. Europe and Latin America are key drivers of this growth. Globally, BYD claimed 12.1% of the BEV market in 2025, ahead of Tesla’s 8.8% and Volkswagen’s 5.2%, cementing the competitive shift.
Competitive pricing and improving vehicle quality helped BYD gain traction in these markets. Policy support also contributed, as incentives and trade policies in several regions made imported EVs more competitive.
Together, these factors allowed BYD to sustain sales growth even as demand softened for some rival brands.
Tesla Under Pressure in a Crowded EV Arena
Tesla’s sales declines in 2025 were linked to several challenges, including:
- Reduced demand after EV tax incentives ended in the United States, particularly the federal EV tax credit that expired in late 2025. This had encouraged buyers to purchase earlier in the year.
- Stronger competition from Chinese brands, not only BYD but also other manufacturers, is entering global markets.
- Market saturation in some regions, where potential customers postponed purchases or chose alternatives.
Tesla remains a major EV maker, but it saw its first consecutive annual drop in deliveries. By contrast, BYD increased its volume while expanding into new regions.
The EV Market Is Still Growing—But Leadership Is Shifting
The global EV market continues to grow, with total EV sales rising annually as more countries push toward cleaner transport. Analysts see strong demand for electric cars continuing this decade. Climate goals and stricter emissions rules in many areas support this trend.
Industry forecasts say global EV deliveries might keep growing until 2030. This growth is due to lower battery costs and more models from various automakers.
Industry forecasts project global EV sales reaching 40–50% of total car sales by 2030, up from ~20 million units in 2025. Battery pack prices have fallen to $115/kWh in 2024. They could further drop to $80–$99/kWh by 2026 (50% decline), enabling price parity with gas cars.

Nations in Europe and Asia are pushing zero‑emission vehicle targets as part of their climate commitments, which may further expand EV adoption.
Europe targets 90% CO2 cut by 2035 for new cars (easing from 100%, allowing some e-fuels/PHEVs). China aims for ~60–90% EV/NEV sales by 2030.
Still, challenges remain. EV buyer incentives vary by country and can affect sales patterns, as seen in the U.S. when federal credits expired. Some regions face infrastructure gaps, like limited charging networks, which can slow growth. Continued cost reductions and broader infrastructure rollouts will be key to sustaining EV adoption long term.
Emissions, Energy, and the Bigger Climate Picture
Electric vehicles are central to efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from transport by 70–90% over their lifecycle compared to gasoline cars. This holds even with current grids.
- For EVs, emissions range from 200–500 gCO2/km, while ICEVs emit 200–300 gCO2/km.
Global transport represents 24% of CO2 emissions (8 GtCO2e). EVs could slash this by 40% by 2030 at 40% adoption. Clean grids, renewables >60% by 2030, boost EV advantage to near-total decarbonization.

Also, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions and can lower overall carbon output when charged with renewable electricity. As more power grids shift toward clean energy sources, the lifetime emissions advantage of EVs grows.
BYD’s sales surge contributes to this global transition. As one of the largest EV producers, its growth means more EVs are on the road worldwide. This supports international efforts to cut emissions from passenger cars, which remain a major source of global greenhouse gases.
However, the environmental impact of EV manufacturing, especially battery production, remains a focus of industry and policy discussions. Sustainable practices in sourcing materials and recycling batteries will be crucial to maximizing the environmental benefits of EV growth.
A New Global Auto Order Takes Shape
BYD’s rise to the top reflects broader changes in the global auto sector:
- Chinese carmakers are gaining ground internationally, not just in their home market.
- Competition in EV segments is increasing, pushing companies to innovate faster on cost, range, and technology.
- Tesla’s leadership is challenged, even as it pushes into areas like autonomous driving and energy products.
The shift also highlights how consumer preferences are evolving, with buyers showing strong interest in different EV brands and models beyond traditional market leaders. As EV technology matures, more brands are expected to capture market share and expand globally.
The post BYD Overtakes Tesla as World’s Biggest EV Seller in 2025 appeared first on Carbon Credits.
Carbon Footprint
DOE’s $2.7 Billion Push for Uranium Enrichment Rebuilds U.S. Energy Security
The post DOE’s $2.7 Billion Push for Uranium Enrichment Rebuilds U.S. Energy Security appeared first on Carbon Credits.
-
Greenhouse Gases5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval