The World Bank has called for governments in wealthy countries to shift subsidies from high-emitting to low-emitting foods in a landmark new report, but stopped short of criticising meat or telling people what to eat.
While scientists have long recognised that vegan and vegetarian diets are far better for the climate than typical Western meat-eating ones, governments and international bodies have often shied away from explicit calls for the public to consume fewer animal products.
Experts told Climate Home that diets are an emotive issue. Western politicians and lobbyists opposed to climate action have spread disinformation about green policies that affect food, falsely claiming that governments will limit hamburgers, tax T-bones or make citizens eat low-carbon forms of protein like insects.
Shift subsidies
The bank’s new “Recipe for a Livable Planet” report outlines a “menu of solutions” governments can take to reduce their planet-warming emissions from food production, including using more renewable energy, harvesting food from trees instead of cutting them down, and restoring forests.
It calls on high-income countries, whose diets are most polluting for the planet, to take the lead by providing finance for green measures to low and middle-income nations and by shifting subsidies away from high-emitting food sources like cattle for beef. This “would reveal their full price and help make low-emission food options cheaper in comparison”, the report says.
UN agrees carbon market safeguards to tackle green land grabs
Report author William Sutton, the bank’s lead on climate-smart agriculture, told Climate Home an example of a subsidy that is “not necessarily helpful for the environment” is providing free or cheap land for grazing livestock. While Sutton declined to single out countries, the US government, for example, allows cows to graze on public land for a knock-down price.
If subsidies for meat were reduced in line with its “true cost” to the planet, prices would be 20-60% higher, Sutton said. “Allow the price of meat to more accurately reflect its true cost and let consumers decide whether that’s what they want to consume or whether they would rather consume lower-emissions, lower-cost alternatives,” he added.
Options not prescriptions
Despite its report, the World Bank is not keen to be seen telling people what to eat or arguing for veganism. “The approach that we’ve taken is not to be prescriptive – not to tell people what they should and shouldn’t do – but to provide options on what they could do if they should so choose,” Sutton said.
The report contrasts high-emitting foods like red meat and dairy with “low-emission foods like poultry or fruits or vegetables”. While poultry meat, which is mainly chicken, is much less emissions-intensive than lamb or particularly beef, it is more polluting than plant-based proteins, as the report’s data shows.

This table from the report shows that vegan diets are the lowest emissions (Screenshot/World Bank)
Sutton said that changing to a more sustainable diet “doesn’t mean eliminating meat necessarily. It could be switching from beef or lamb to something like chicken or even pork.” But, he added, people “could also switch to soy or other types of beans… That will reduce emissions even more but we don’t think it’s useful to prescribe that.”
Greenpeace EU food campaigner Sini Eräjää agreed that promoting full vegetarianism or veganism is too “black and white”. But, she added, encouraging poultry consumption gives out the wrong message. “I know that there are different kinds of calculations between different kinds of meats,” she said, but “first and foremost we need to change to more plant-based diets”.
Paul Behrens, an environmental change professor at Leiden University, agreed, telling Climate Home that chicken farms drive zoonotic disease and antimicrobial resistance and pollute rivers and air, while poultry feed causes deforestation.
The World Bank still has investments in the meat and dairy sector. Last year, its International Finance Corporation arm loaned $47.3m for a company to develop a pig-rearing complex in China and invested $32.6m in a Brazilian dairy producer, despite opposition from environmentalists.
Asked about this, Sutton said the organisation had to “walk the talk” and had increased its support for adapting farming to climate change and reducing its emissions.
But, he added, the bank does support some investments in livestock “after careful consideration”, if it thinks it can improve a company’s approach by increasing efficiency, cutting emissions, and providing jobs and nutritious food to the poor.
Political hot-potato
Other international bodies have avoided criticising meat too explicitly. Former officials of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have said their employers censored them when they tried to criticise livestock. Meanwhile scientists have accused the FAO of misusing their research to underplay the role that changing diets can play in cutting climate-heating emissions.
In 2021, scientists working with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change faced pressure from Brazil and Argentina – two major beef and animal feed producers – to remove from a report a mention of plant-based diets and reduction of meat and dairy consumption as being good for the climate.
Edward Davey, an advisor to the Food and Land Use Coalition, said that national governments in particular “tend to be quite shy about talking about this issue because they fear the political repercussions of being perceived to be telling people what to eat”.
The US government has made no moves to reduce meat consumption but right-wing media outlets like Fox News have falsely claimed that “Biden’s climate requirements” will restrict Americans to “one burger per month”.
The Australian government likewise has no policies to curb meat-eating. But opposition politicians there have spread misinformation that the country signing up to a global methane pledge amounts to a “T-bone tax” and the end of the Australian barbeque.
We heard warnings about an end to the Aussie barbeque, a T-bone tax and so on if Australia joins 120 other countries in signing a pledge to reduce methane emissions.
But for rhetorical flourish – no one was ever going to outdo Barnaby Joyce.#Insiders #auspol pic.twitter.com/ZHYkbS0HJ2
— Insiders ABC (@InsidersABC) October 15, 2022
Greenpeace EU’s Eräjää said she had seen early drafts of European Commission documents that included warnings about red meat’s health impact before those warnings were stripped out of the final version. “Meat is a four-letter word,” she said.
David Powell has researched the issue for Climate Outreach, a group that specialises in communicating effectively on climate change. He said that “what we see as normal to eat is closely linked with our identities and is very personal”.
“For most people, climate arguments alone won’t help persuade them to change what they eat,” he said, adding it is better to talk about the health benefits of eating less meat and dairy in a positive way rather than shaming people.

High-income countries eat more servings of animal-sourced products than the global average
Both Sutton and Davey stressed that the debate over meat-eating is largely a wealthy country concern. People in higher-income regions eat three times as many servings of meat, seafood, eggs and dairy per day than their counterparts in South Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa.
“Many, many people in the world – typically richer people in wealthier societies but also in unequal middle-income countries – need to eat much less meat for the purpose of their health, as well as for the climate, and many of the world’s poorer people need to eat more animal protein for their health, well-being and nutrition,” said Davey.
(Reporting by Joe Lo; editing by Megan Rowling)
The post World Bank tiptoes into fiery debate over meat emissions appeared first on Climate Home News.
Climate Change
On the Farm, the Hidden Climate Cost of America’s Broken Health Care System
American farmers are drowning in health insurance costs, while their German counterparts never worry about medical bills. The difference may help determine which country’s small farms are better prepared for a changing climate.
Samantha Kemnah looked out the foggy window of her home in New Berlin, New York, at the 150-acre dairy farm she and her husband, Chris, bought last year. This winter, an unprecedented cold front brought snowstorms and ice to the region.
On the Farm, the Hidden Climate Cost of the Broken U.S. Health Care System
Climate Change
A Little-Used Maneuver Could Mean More Drilling and Mining in Southern Utah’s Redrock Country
Two Utah Congress members have introduced a resolution that could end protections for Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument. Conservation groups worry similar maneuvers on other federal lands will follow.
Lawmakers from Utah have commandeered an obscure law to unravel protections for the Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, potentially delivering on a Trump administration goal of undoing protections for public conservation lands across the country.
A Little-Used Maneuver Could Mean More Drilling and Mining in Southern Utah’s Redrock Country
Climate Change
Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes
Drought and heatwaves occurring together – known as “compound” events – have “surged” across the world since the early 2000s, a new study shows.
Compound drought and heat events (CDHEs) can have devastating effects, creating the ideal conditions for intense wildfires, such as Australia’s “Black Summer” of 2019-20 where bushfires burned 24m hectares and killed 33 people.
The research, published in Science Advances, finds that the increase in CDHEs is predominantly being driven by events that start with a heatwave.
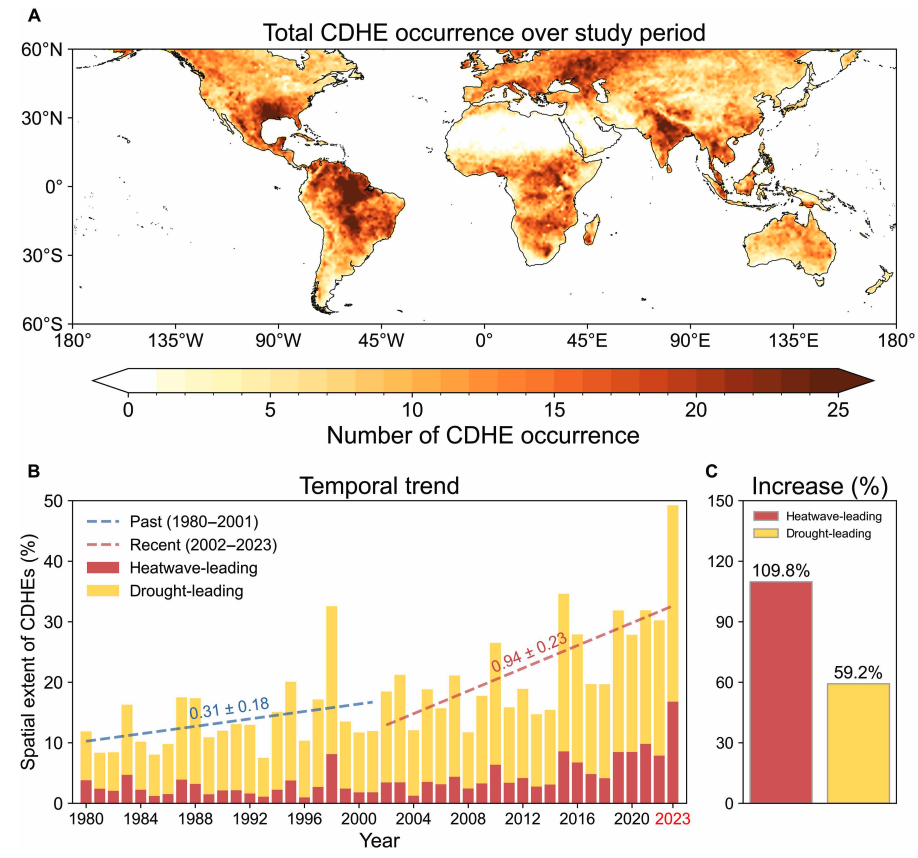
The global area affected by such “heatwave-led” compound events has more than doubled between 1980-2001 and 2002-23, the study says.
The rapid increase in these events over the last 23 years cannot be explained solely by global warming, the authors note.
Since the late 1990s, feedbacks between the land and the atmosphere have become stronger, making heatwaves more likely to trigger drought conditions, they explain.
One of the study authors tells Carbon Brief that societies must pay greater attention to compound events, which can “cause severe impacts on ecosystems, agriculture and society”.
Compound events
CDHEs are extreme weather events where drought and heatwave conditions occur simultaneously – or shortly after each other – in the same region.
These events are often triggered by large-scale weather patterns, such as “blocking” highs, which can produce “prolonged” hot and dry conditions, according to the study.
Prof Sang-Wook Yeh is one of the study authors and a professor at the Ewha Womans University in South Korea. He tells Carbon Brief:
“When heatwaves and droughts occur together, the two hazards reinforce each other through land-atmosphere interactions. This amplifies surface heating and soil moisture deficits, making compound events more intense and damaging than single hazards.”
CDHEs can begin with either a heatwave or a drought.
The sequence of these extremes is important, the study says, as they have different drivers and impacts.
For example, in a CDHE where the heatwave was the precursor, increased direct sunshine causes more moisture loss from soils and plants, leading to a drought.
Conversely, in an event where the drought was the precursor, the lack of soil moisture means that less of the sun’s energy goes into evaporation and more goes into warming the Earth’s surface. This produces favourable conditions for heatwaves.
The study shows that the majority of CDHEs globally start out as a drought.
In recent years, there has been increasing focus on these events due to the devastating impact they have on agriculture, ecosystems and public health.
In Russia in the summer of 2010, a compound drought-heatwave event – and the associated wildfires – caused the death of nearly 55,000 people, the study notes.

The record-breaking Pacific north-west “heat dome” in 2021 triggered extreme drought conditions that caused “significant declines” in wheat yields, as well as in barley, canola and fruit production in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada, says the study.
Increasing events
To assess how CDHEs are changing, the researchers use daily reanalysis data to identify droughts and heatwaves events. (Reanalysis data combines past observations with climate models to create a historical climate record.) Then, using an algorithm, they analyse how these events overlap in both time and space.
The study covers the period from 1980 to 2023 and the world’s land surface, excluding polar regions where CDHEs are rare.
The research finds that the area of land affected by CDHEs has “increased substantially” since the early 2000s.
Heatwave-led events have been the main contributor to this increase, the study says, with their spatial extent rising 110% between 1980-2001 and 2002-23, compared to a 59% increase for drought-led events.
The map below shows the global distribution of CDHEs over 1980-2023. The charts show the percentage of the land surface affected by a heatwave-led CDHE (red) or a drought-led CDHE (yellow) in a given year (left) and relative increase in each CDHE type (right).
The study finds that CDHEs have occurred most frequently in northern South America, the southern US, eastern Europe, central Africa and south Asia.
Threshold passed
The authors explain that the increase in heatwave-led CDHEs is related to rising global temperatures, but that this does not tell the whole story.
In the earlier 22-year period of 1980-2001, the study finds that the spatial extent of heatwave-led CDHEs rises by 1.6% per 1C of global temperature rise. For the more-recent period of 2022-23, this increases “nearly eightfold” to 13.1%.
The change suggests that the rapid increase in the heatwave-led CDHEs occurred after the global average temperature “surpasse[d] a certain temperature threshold”, the paper says.
This threshold is an absolute global average temperature of 14.3C, the authors estimate (based on an 11-year average), which the world passed around the year 2000.
Investigating the recent surge in heatwave-leading CDHEs further, the researchers find a “regime shift” in land-atmosphere dynamics “toward a persistently intensified state after the late 1990s”.
In other words, the way that drier soils drive higher surface temperatures, and vice versa, is becoming stronger, resulting in more heatwave-led compound events.
Daily data
The research has some advantages over other previous studies, Yeh says. For instance, the new work uses daily estimations of CDHEs, compared to monthly data used in past research. This is “important for capturing the detailed occurrence” of these events, says Yeh.
He adds that another advantage of their study is that it distinguishes the sequence of droughts and heatwaves, which allows them to “better understand the differences” in the characteristics of CDHEs.
Dr Meryem Tanarhte is a climate scientist at the University Hassan II in Morocco, and Dr Ruth Cerezo Mota is a climatologist and a researcher at the National Autonomous University of Mexico. Both scientists, who were not involved in the study, agree that the daily estimations give a clearer picture of how CDHEs are changing.
Cerezo-Mota adds that another major contribution of the study is its global focus. She tells Carbon Brief that in some regions, such as Mexico and Africa, there is a lack of studies on CDHEs:
“Not because the events do not occur, but perhaps because [these regions] do not have all the data or the expertise to do so.”
However, she notes that the reanalysis data used by the study does have limitations with how it represents rainfall in some parts of the world.
Compound impacts
The study notes that if CDHEs continue to intensify – particularly events where heatwaves are the precursors – they could drive declining crop productivity, increased wildfire frequency and severe public health crises.
These impacts could be “much more rapid and severe as global warming continues”, Yeh tells Carbon Brief.
Tanarhte notes that these events can be forecasted up to 10 days ahead in many regions. Furthermore, she says, the strongest impacts can be prevented “through preparedness and adaptation”, including through “water management for agriculture, heatwave mitigation measures and wildfire mitigation”.
The study recommends reassessing current risk management strategies for these compound events. It also suggests incorporating the sequences of drought and heatwaves into compound event analysis frameworks “to enhance climate risk management”.
Cerezo-Mota says that it is clear that the world needs to be prepared for the increased occurrence of these events. She tells Carbon Brief:
“These [risk assessments and strategies] need to be carried out at the local level to understand the complexities of each region.”
The post Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits






