Andreas Sieber is the Associate Director of Policy and Campaigns at 350.org.
Trump has such a passion for tariffs he even imposed them on Antarctic islands – home only to penguins, who presumably pose a grave threat to American industry.
Now that the dust is settling – with global stock markets down and US dollar inflation up – two things are clear: the US president’s enthusiasm far outstrips his economic competence; and his shiny new tariffs won’t stop the global energy transition, no matter how hard he tries.
Donald Trump’s tariffs will harm the US economy and working families. But different from what some might fear, the tariffs won’t stop wind and solar energy. The United States’ share in the global cleantech trade is simply too marginal to dictate its terms in this sector. Other than Antarctic penguins, the global energy transition is safe from Trump’s tariffs.
Emerging economies set to dominate
A decade ago, Trump’s tariffs could have delivered a significant blow to the global energy transition: developed economies dominated solar and wind installations – accounting for roughly 70% of solar and 50% of wind capacity additions between 2010 and 2015.
Since then, two major developments must be taken into account. First, emerging economies’ share in renewable installations and the cleantech trade have boomed while the share of installations in advanced economies, including the US, has shrunk significantly. In 2009, about one in four solar panels was installed in the United States. In 2024, less than one in 12 renewable projects globally were added in the US.
According to the International Energy Agency, emerging and developing economies are set to dominate clean energy markets by 2030 – claiming 70% of solar PV, 60% of wind, and 60% of battery storage capacity.
Fossil fuel nations to see value of their economies shrink under new UN-agreed measure
Additionally, the US has not only isolated itself on cleantech in the last week, it has increasingly done so over the past 10 years. Today, China is by far the world’s largest producer and exporter of solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicles – yet only 4% of those products go to the US, compared to 15% of China’s overall exports. In a market with growth dynamics like the green tech market has, tariffs on a 4% share of this market are a mere footnote.
China exported 235.93 gigawatts (GW) of solar modules in 2024, a market it dominates in an unparalleled manner, marking a 13% year-on-year increase from 207.99 GW in 2023. While impressive, the 13% of solar panel exports are small compared to other cleantech: China’s exports of wind turbines surged by over 70% last year. In the global cleantech race, the US is becoming a shrinking, isolated player.
Too poor to buy American luxury goods
None of this suggests Trump’s tariffs are harmless. Far from it – they will hit working families and poorer nations hardest. The former president insists he understands economic policy, but reality paints a different picture. Not only has he repeatedly conflated trade deficits with tariffs – a confusion that would earn a failing grade in any Economics 101 course – but analysts now expect U.S. inflation to rise faster than in almost any other major economy, surpassing even Canada, the EU, and many of the very countries targeted by his trade measures.
It’s the working people he claims to defend who will bear the brunt of these price hikes. Ironically, if the revenue from tariffs is used for anything by the Trump administration, it will be to pay for massive tax cuts for the wealthy.
Meanwhile, markets are stumbling, and the erratic choreography of tariff threats, reversals, and ultimatums has spooked investors, in particular in the US. No one really knows what’s next. Should they swallow the cost of more expensive imports, or gamble on domestic production in uncertainty? With investor confidence sliding to levels unseen since the COVID-19 shock, “America First” increasingly resembles “Economics Last”.
Comment: Finance for renewable energy in sub-Saharan Africa is defying the odds
The persistent conflation of trade deficits with tariffs does more than reveal economic illiteracy – it inflicts real harm, particularly on poorer nations. The notion that all countries must maintain perfectly balanced trade is, at best, a fantasy. Consider Madagascar, where GDP per capita hovers just above $500. The US imports vanilla and critical minerals from the country. Yet the United States imposes trade penalties on Madagascar and many similar countries as if it were a competitive threat – despite the obvious reality that no one in Antananarivo, Cambodia, or Botswana is lining up to buy a Tesla.
Free trade is no silver bullet, and forcing developing economies in particular to open up their markets has historically done harm. But now, Trump is punishing people for being too poor to buy American luxury goods.
Protectionism or co-operation by the rest of the world?
The more urgent question now is how the rest of the world might recalibrate trade relations with each other – not just in retaliation against the United States. Will Trump’s tariffs trigger a broader shift toward protectionism, prompting countries to erect new trade barriers among themselves under the guise of “strategic autonomy”? This could indeed threaten the pace of transition efforts.
The US is drifting into economic isolation. Canada and Mexico have previously aligned their tariff responses; China, Japan and South Korea, though not formally coordinated, seem to be synchronising their strategies with more or less quiet efficiency.
Climate and the energy transition remain textbook examples of why Trump’s zero-sum instincts are wholly unfit for purpose. Global cooperation on climate is not optional. Even countries locked in geopolitical tension must find ways to collaborate on decarbonization – unless, of course, the plan is to compete all the way to climate collapse.
COP30 chief calls for global unity on climate action as cooperation falters
For too long, European leaders have indulged in the futile art of appeasing Donald Trump – among various avenues, by pledging to absorb vast surpluses of American liquefied natural gas. The irony, of course, is that this LNG isn’t needed; worse still, it risks locking Europe into years of inflated energy costs for consumers.
The strategy of placation has plainly failed. Doubling down on dependency through new US LNG deals is short-sighted on multiple levels – not just for those concerned about climate, but for anyone with even a passing interest in economic sovereignty.
Trump may have shocked the world, but he has equally exposed himself as a bully – one whose policies are not only reckless and unreliable but, frankly, embarrassingly misguided. The good news is the US cannot dictate the terms of cleantech trade and the energy transition. The world should move forward without him and keep climate and renewables as a critical area of cooperation and prosperity.
The post Trump’s tariff tantrum won’t stop the global energy transition appeared first on Climate Home News.
Trump’s tariff tantrum won’t stop the global energy transition
Climate Change
North Carolina Regulators Nix $1.2 Billion Federal Proposal to Dredge Wilmington Harbor
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers failed to explain how it would mitigate environmental harms, including PFAS contamination.
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers can’t dredge 28 miles of the Wilmington Harbor as planned, after North Carolina environmental regulators determined the billion-dollar proposal would be inconsistent with the state’s coastal management policies.
North Carolina Regulators Nix $1.2 Billion Federal Proposal to Dredge Wilmington Harbor
Climate Change
Australia’s renewable energy opportunity
Australia has some of the largest areas of high volume, consistent solar and wind energy anywhere in the world. It is a natural advantage that many countries in our region and across Europe will envy as they ramp up their efforts to reduce carbon pollution.
Australia has an amazing opportunity to utilise this abundance of reliable energy not only to transform our own energy systems but also that of our neighbours – if we get the policy settings right.
We are, in fact, already seeing the benefits of renewable energy flowing into our electricity grids. With all the inflation pressures on our bank accounts it looks like electricity pricing may be one cost that could be turning a corner – largely thanks to cheap solar and wind energy.
Renewables are Bringing Down the Cost of Producing Electricity

Here at Greenpeace, while we think there are some important questions to ask about renewable energy, it is clear that solar and wind are certainly the cheapest energy options available.
In contrast, coal, oil and gas are not only big on pollution, they are also proving costlier as they struggle to cope with the changing nature of our electricity systems. Plus, fossil fuels are much more exposed to international price fluctuations – as we all experienced when our electricity bills rapidly rose following the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Wouldn’t it be great if we instead had energy independence, sourced from an infinite supply of clean energy?
Solar and wind (backed by batteries) can do just that and the reality is that they are already out-competing the old guard of gas and coal simply because they are quicker and cheaper to deploy. Which is good news for electricity prices!
Although whether energy retailers are passing on those savings to customers is another question. Short answer: no, they’re not – but it is a bit complex.
Why are my electricity bills still high?
There are a number of elements that make up the final amount we see on our bills. The graph below shows the breakdown of energy costs covered by our bills.
You will see roughly a third (36.2% in 2025-26) of the cost goes to maintenance and build out of the electricity grid. This includes the transmission lines needed to connect to new renewable energy sites and to connect states so they can better share their energy resources. The ‘network’ costs have been increasing but so have other components of our bill, most notably the ‘wholesale’ cost of producing electricity.
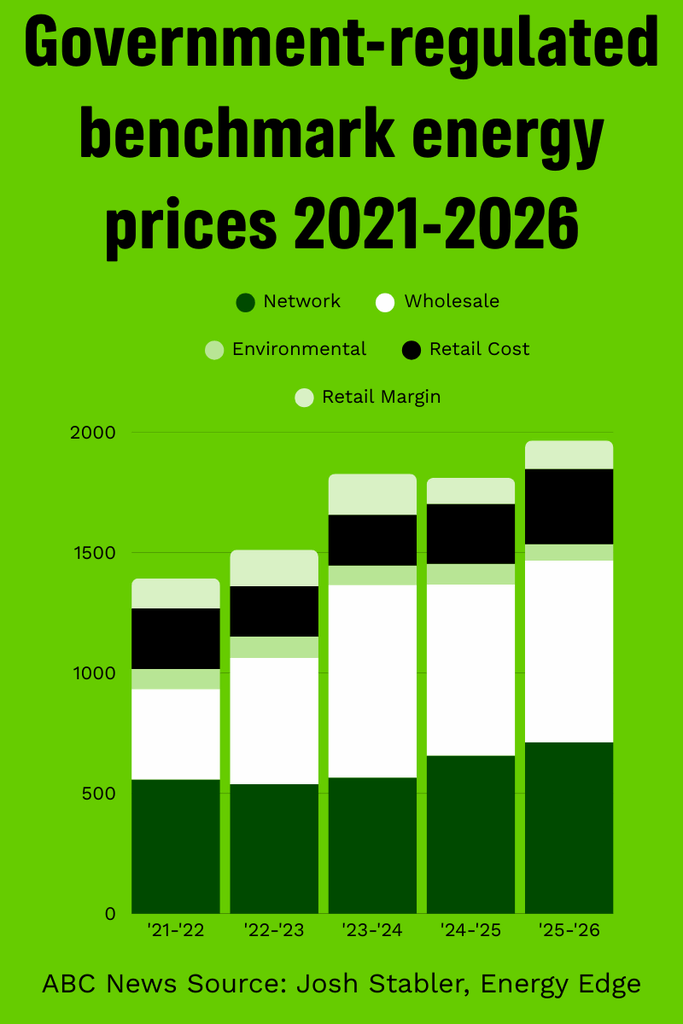
Thankfully, the cost of producing the electricity is now starting to go down (thanks to renewables and batteries), but they are coming off record highs thanks to the exorbitant cost of gas and the unreliability of coal power stations that are old and no longer fit for purpose.
During high demand times (eg, when we all get home from work on a hot day and turn on the air conditioning) spot prices can quickly jump. Add to that a couple of coal power plants breaking down (as they increasingly do), and expensive gas fired power use spikes in the system. This can quickly cancel out any of the cost savings solar power may have created during the day when prices can actually go negative.
The good news is that this is exactly the problem batteries can solve. Batteries are great at soaking up the surplus supply of solar during the middle of the day, which creates a more efficient system, and then rapidly pumping out that power during the evening peak at a cheaper rate than gas.
How much have costs come down?
According to the Australian energy regulator (AEMO), wholesale electricity prices across the east coast have dropped by 44% when comparing prices in quarter 4 of 2025 to the same period in 2024.
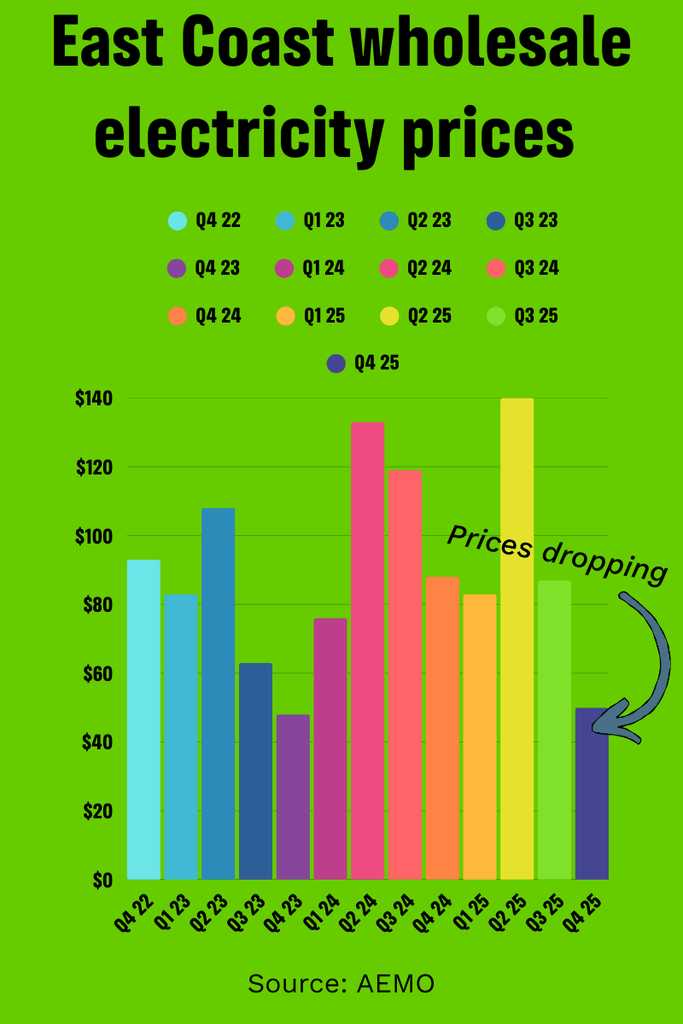
AEMO directly attributes the change to the significant growth in wind (up 29%), solar (up 15%), and batteries (3,796 MW of new battery capacity added). This influx of cheap renewable energy has seen a corresponding decrease in the use of polluting fossil fuels to power the grid. Coal fired power dropped by 4.6% and gas fired power fell by a staggering 27%.
The same trend can be seen in the world’s largest standalone grid in WA where renewable energy and storage supplied a record 52.4% of the grid’s energy across the final 3 months of 2025. That is an impressive result given there is no interstate connection to borrow energy from and there is no hydroelectric power in the system.
As a result, WA has seen a 13% drop in wholesale electricity prices thanks to a 5.8% reduction in coal fired power and a 16.4% reduction in gas fired power.
Australian Households Lead the Way on Solar and Batteries
Despite all the attempts to discredit clean energy by Trump and other conservative politicians, Aussie households have long known the value of renewable energy. In fact, Australia now holds the title for the highest rate of solar energy per capita in the world.
This is now being followed by the rapid takeup of household batteries with the Clean Energy Regulator being overwhelmed with interest in the Cheaper Home Batteries Program. They now expect to receive “around 175,000 valid battery applications corresponding to a total usable capacity of 3.9 GWh by the end of 2025.”’
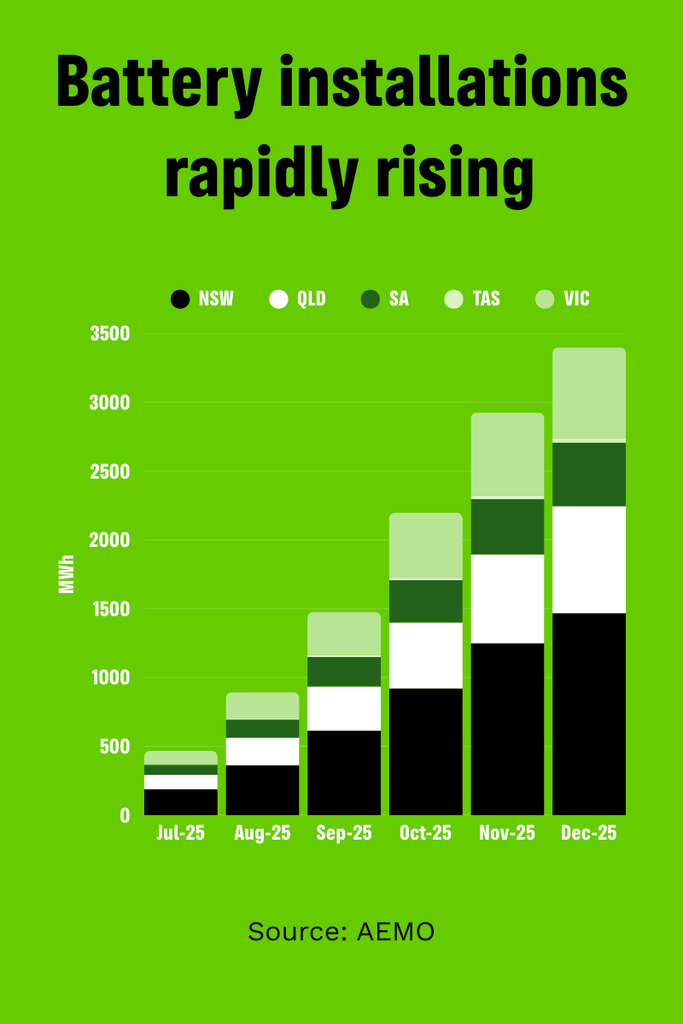
All these extra batteries storing the surplus solar energy across our neighbourhoods during the day is not only creating drastic bill reductions for those households who are installing them, it is helping the whole grid. Which eventually will help everyone’s electricity bills.
If Australia as a whole follows the lead of suburban families by switching to cheap solar (plus wind) backed-up by batteries, it has an unparalleled opportunity to build its economy on the back of unlimited, local, clean energy harnessed from the sun and wind.
Powering our Future Economy
If there was ever something Australia has a natural advantage in, its sun and wind. But given the growing demand for electricity from data centres and the electrification of heavy industry, we are going to need more than just rooftop solar panels.
That’s where Australia has the potential, more than almost any other country, to become a renewable energy powerhouse and punch above our weight in the fight against climate change. See for example the unique opportunity to enter into the production and export of green iron.
While there is still quite a way to go before our electricity is fully sourced from solar and wind, we are well on the way. The clean energy charge is gathering pace – and our communities, oceans, wildlife and bank balances will be the better for it.
Climate Change
Whale Entanglements in Fishing Gear Surge Off U.S. West Coast During Marine Heatwaves
New research finds that rising ocean temperatures are shrinking cool-water feeding grounds, pushing humpbacks into gear-heavy waters near shore. Scientists say ocean forecasting tool could help fisheries reduce the risk.
Each spring, humpback whales start to feed off the coast of California and Oregon on dense schools of anchovies, sardines and krill—prey sustained by cool, nutrient-rich water that seasonal winds draw up from the deep ocean.
Whale Entanglements in Fishing Gear Surge Off U.S. West Coast During Marine Heatwaves
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits



