Introduction Top Rated Modern Agriculture Countries
The landscape of top-rated agricultural countries is dynamic and influenced by a myriad of factors encompassing productivity, innovation, and sustainability.
Prominent nations include the United States, where advanced technology, research, and large-scale farming contribute to its agricultural prowess. China, with its vast land resources and commitment to modernizing agriculture, also stands among the leaders, focusing on improving yields and food security.
Brazil has become a global agricultural powerhouse, excelling in the production of soybeans, beef, and poultry. The country’s adoption of modern farming techniques and extensive agribusiness initiatives has propelled it to the forefront of the agricultural world. India, with its diverse agro-climatic zones and a large farming community, is another key player, continually working on enhancing productivity through technology adoption and sustainable practices.
In addition to these giants, smaller nations like the Netherlands and Israel have gained recognition for their innovative approaches.
The evolving landscape of top-rated agricultural countries underscores the importance of adaptability, sustainability, and technological innovation in shaping the future of global food production. For the latest and most accurate information, it’s advisable to refer to recent reports from agricultural organizations or government sources.
Top Rated Modern Agriculture Countries
Some top-rated modern agriculture countries include the United States, China, Brazil and India. These nations are recognized for advanced farming technologies, large-scale production, and innovation in agricultural practices.
Here is a short list for Top Rated Modern Agriculture Countries.
1. United States
The United States is a leading force in modern agriculture, known for its large-scale farming operations, advanced machinery, and innovative technologies.
Precision farming practices, including GPS-guided tractors and drones, contribute to increased efficiency and yields. The U.S. agricultural sector is diverse, producing a wide range of crops and livestock. Research institutions and private companies continually invest in developing cutting-edge solutions to address challenges and enhance productivity.
Key data for modern agriculture in the United States
Here are some key facts and data about modern agriculture in the United States:
1. Technology Adoption:
– Precision Agriculture: The U.S. has widely adopted precision farming techniques, including GPS-guided tractors, drones, and sensors. These technologies enable farmers to optimize field-level management with regard to crop farming.
– Biotechnology: Genetically modified (GM) crops, such as genetically modified corn and soybeans, are extensively cultivated in the U.S., contributing to increased yields and pest resistance.
2. Crop Production:
– Corn and Soybeans: The U.S. is a major producer of corn and soybeans. These crops are not only essential for domestic consumption but also play a crucial role in international trade.
– Wheat: Wheat cultivation is significant, particularly in states like Kansas and North Dakota.
3. Livestock Production:
– The U.S. is a leading producer of beef, pork, and poultry. Modern livestock farming practices focus on efficiency, nutrition, and animal welfare.
– Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs) are common, especially in the production of poultry and swine.
4. Organic Farming:
– The organic farming sector has been growing, with an increasing number of farms adopting organic practices. Consumer demand for organic products has driven this trend.
5. Farm Size and Consolidation:
– Agriculture in the U.S. is characterized by a mix of large-scale commercial farming and smaller family-owned operations.
– There has been a trend toward consolidation, with larger farms utilizing advanced technologies to manage extensive acreages.
6. Environmental Stewardship:
– Sustainable and conservation practices are gaining importance. Farmers are adopting practices like cover cropping and precision nutrient management to minimize environmental impact.
Here are some key data points related to modern agriculture in the United States.
1. Crop Production:
– In 2021, the USDA estimated corn production at around 14.5 billion bushels, with soybean production at approximately 4.4 billion bushels.
– Wheat production was estimated at around 1.7 billion bushels in the same year.
2. Livestock Production:
– The U.S. is one of the largest producers of beef globally. In 2021, the country produced around 27.1 billion pounds of beef.
– Pork production in the U.S. was approximately 28.8 billion pounds in 2021.
– Chicken production reached around 42.1 billion pounds in the same year.
3. Organic Farming:
– Organic farming has been on the rise. In 2019, the USDA reported that there were over 5 million certified organic acres, including both crop and pastureland.
– Sales of organic products reached $7.6 billion in 2019.
4. Farm Size and Structure:
– The average farm size in the U.S. was around 444 acres in 2020.
– Large family farms and non-family farms accounted for the majority of agricultural production, with smaller family farms contributing significantly to the overall number of farms.
5. Biotechnology:
– Genetically modified (GM) crops are widely cultivated. In 2020, approximately 94% of soybean acreage and 92% of corn acreage in the U.S. were planted with genetically engineered varieties.
6. Environmental Stewardship:
– Conservation practices are increasingly adopted. According to the USDA, in 2020, farmers enrolled over 140 million acres in conservation programs, focusing on practices like cover cropping and resource-efficient land management.
These figures provide a snapshot of the state of modern agriculture in the U.S.
2. China
China, with its vast land resources and a significant portion of the population engaged in agriculture, plays a crucial role in global food production. The country has been focusing on modernizing its agricultural practices, incorporating technologies like precision farming, biotechnology, and smart irrigation systems.
The Chinese government has implemented policies to support rural development and enhance agricultural sustainability. The scale of agricultural operations in China and its commitment to research and development contribute to its prominence in the global agricultural landscape.
Key data for modern agriculture in China
Here are some key facts and data related to modern agriculture in China.
1. Crop Production:
– China is the world’s largest producer of rice, wheat, and various other crops. In 2021, the country produced over 212 million metric tons of rice and around 135 million metric tons of wheat.
– Corn production has been increasing steadily, reaching over 260 million metric tons in 2021.
2. Precision Agriculture and Technology:
– Precision farming practices, such as the use of GPS-guided tractors and drones, have gained popularity in China. These technologies contribute to increased efficiency and optimized resource utilization.
– The Chinese government has been investing in the development and adoption of smart farming technologies to enhance agricultural productivity.
3. Biotechnology:
– China has been actively engaged in agricultural biotechnology. Genetically modified (GM) crops, including cotton and papaya, have been commercially grown.
– Research and development in biotechnology aim to address challenges such as pest resistance and improve crop yields.
4. Livestock Production:
– China is a major producer of pork, with a significant impact on the global market. In 2021, the country produced over 45 million metric tons of pork.
– Poultry and beef production have also seen growth in response to changing dietary patterns.
5. Organic Farming:
– The organic farming sector is expanding in China. As of my last knowledge update, the country had around 3 million hectares of certified organic farmland.
– There is a growing interest in organic products, both domestically and internationally.
6. Sustainable Agriculture:
– China has been working on sustainable agricultural practices to address environmental concerns. Efforts include soil conservation, water management, and the promotion of eco-friendly farming techniques.
7. Rural Development Policies:
– The Chinese government has implemented policies to support rural development, increase agricultural efficiency, and improve the livelihoods of farmers.
Here are some key data points related to modern agriculture in China.
1. Crop Production:
– In 2021, China produced over 670 million metric tons of rice, making it the world’s largest producer of rice.
– Wheat production exceeded 135 million metric tons, solidifying China’s position as a leading global wheat producer.
– Corn production reached over 260 million metric tons, indicating a significant contribution to the global corn market.
2. Livestock Production:
– China produced over 45 million metric tons of pork in 2021, making it the world’s largest pork producer.
– Poultry production was over 22 million metric tons, and beef production exceeded 7 million metric tons in the same year.
3. Organic Farming:
– China had around 3 million hectares of certified organic farmland, showcasing a growing interest in organic agriculture.
– The organic food market in China has been expanding, reflecting consumer preferences for organic products.
4. Biotechnology:
– Genetically modified (GM) crops, including cotton and papaya, have been commercially grown in China.
– Research and development efforts in agricultural biotechnology aim to enhance crop traits and improve yields.
5. Precision Agriculture and Technology:
– China has been actively adopting precision farming practices. The use of GPS-guided tractors and drones contributes to increased efficiency.
– Investments in smart farming technologies underscore China’s commitment to modernizing its agricultural sector.
6. Sustainable Agriculture:
– Sustainable agricultural practices, including soil conservation and water management, are part of China’s efforts to address environmental concerns.
– Policies promoting eco-friendly farming techniques aim to balance agricultural development with environmental sustainability.
3. Brazil
Brazil has emerged as a key player in modern agriculture, particularly in the production of soybeans, beef, and poultry. The country utilizes extensive agricultural lands and employs advanced farming techniques, contributing significantly to global food exports.
Brazil’s emphasis on agribusiness and sustainable farming practices has boosted its international standing. Ongoing efforts in research and development aim to further enhance productivity while addressing environmental concerns associated with agriculture.
Key data for modern agriculture in Brazil
Here are some key facts and data related to modern agriculture in Brazil.
1. Soybean Production:
– Brazil is a global powerhouse in soybean production. In the 2020/2021 season, the country produced over 133 million metric tons of soybeans, making it the world’s largest exporter of soybeans.
2. Beef Production:
– Brazil is one of the largest producers and exporters of beef. In 2021, beef production in Brazil exceeded 10 million metric tons, solidifying its position as a major player in the global beef market.
3. Corn Production:
– Corn cultivation is significant in Brazil, and the country is among the top global producers. In the 2020/2021 season, Brazil produced over 105 million metric tons of corn.
4. Cattle Ranching and Livestock:
– Extensive cattle ranching is a key component of Brazilian agriculture. The country has one of the largest commercial cattle herds globally.
– Brazil has been working on improving the sustainability of its livestock sector, addressing environmental concerns associated with deforestation.
5. Agribusiness and Export:
– Brazil’s agribusiness sector plays a crucial role in its economy. The country is a major exporter of agricultural products, including soybeans, beef, poultry, and coffee.
– The agribusiness industry contributes significantly to Brazil’s GDP and provides employment to a substantial portion of the population.
6. Precision Agriculture and Technology:
– Brazil has adopted modern farming technologies, including precision agriculture techniques and machinery. GPS-guided tractors and advanced irrigation systems are commonly used.
7. Environmental Concerns:
– Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest has raised environmental concerns globally. Efforts to balance agricultural development with conservation have been ongoing, with initiatives aimed at reducing deforestation rates.
8. Sugar and Ethanol Production:
– Brazil is a major producer of sugarcane and a leading global producer of ethanol. The country’s biofuel industry has grown significantly, contributing to both domestic and international energy markets.
Here are some key data points related to modern agriculture in Brazil.
1. Soybean Production:
– In the 2021/2022 season, Brazil produced over 144 million metric tons of soybeans, maintaining its position as the world’s largest exporter of soybeans.
2. Beef Production:
– In 2021, Brazil produced over 10.4 million metric tons of beef, solidifying its status as one of the largest beef-producing nations globally.
3. Corn Production:
– Brazil produced around 107 million metric tons of corn in the 2021/2022 season, making it one of the top global producers of corn.
4. Cattle Ranching and Livestock:
– Brazil has one of the world’s largest commercial cattle herds, with over 232 million head of cattle.
– The country has been implementing sustainable practices and initiatives to address environmental concerns associated with cattle ranching.
5. Agribusiness and Exports:
– Brazil’s agribusiness exports reached around $109 billion in 2021, contributing significantly to the country’s economy.
– Major export products include soybeans, beef, poultry, sugar, and coffee.
6. Biofuel Production:
– Brazil produced over 33 billion liters of ethanol in the 2020/2021 season, utilizing sugarcane as a primary feedstock.
– The biofuel industry in Brazil plays a crucial role in the country’s energy matrix and contributes to global biofuel markets.
7. Precision Agriculture and Technology:
– Precision agriculture technologies, including GPS-guided tractors and advanced irrigation systems, are widely adopted in Brazil to enhance efficiency and productivity.
8. Deforestation and Conservation:
– Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest has been a global concern. Efforts to address deforestation and promote sustainable land use have been ongoing, with increased focus on environmental conservation.
These data points provide an overview of Brazil’s prominence in global agriculture.
4. India
India, with its diverse agro-climatic zones and a large farming community, is a major player in global agriculture. The country has been working on improving agricultural productivity through technology adoption, water management, and sustainable practices.
Initiatives such as the Green Revolution have played a pivotal role in transforming India into a major food producer. Ongoing government programs and collaborations with the private sector aim to address challenges and modernize the agricultural sector for increased efficiency and sustainability.
Key data for modern agriculture in India
Here are some key facts and data related to modern agriculture in India.
1. Crop Production:
– In the 2020-2021 crop year, India produced over 303 million metric tons of food grains, including rice, wheat, and coarse grains.
– India is a major producer of various crops, including rice, wheat, pulses, and oilseeds.
2. Horticulture Production:
– India is a leading global producer of fruits and vegetables. In the 2019-2020 fiscal year, horticulture production exceeded 320 million metric tons.
3. Livestock Production:
– India has one of the world’s largest populations of livestock. The country produced over 32 million metric tons of milk in the 2020-2021 fiscal year, making it the largest milk-producing nation globally.
– Poultry and meat production have also seen growth, contributing to the overall agricultural sector.
4. Green Revolution and Technological Adoption:
– The Green Revolution in the 1960s and 1970s played a significant role in transforming Indian agriculture. The adoption of high-yielding crop varieties, irrigation, and fertilizers led to increased productivity.
– Modern technologies, including precision farming, are gradually being adopted to enhance agricultural efficiency.
5. Organic Farming:
– India has witnessed a growing interest in organic farming. As of my last update, the country had over 3.6 million hectares of certified organic farmland.
– The organic food market has been expanding, with increased awareness and demand for organic products.
6. Sustainable Agriculture:
– Sustainable agriculture practices are gaining attention. Initiatives focus on water management, soil conservation, and promoting environmentally friendly farming techniques.
7. Government Initiatives:
– The Indian government has implemented various schemes to support farmers, including the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) income support program and the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
8. Challenges and Opportunities:
– Indian agriculture faces challenges such as fragmented land holdings, water scarcity, and the need for modernization.
– Opportunities exist for leveraging technology, improving infrastructure, and promoting agribusiness to enhance the sector’s sustainability.
Here are some key data points related to modern agriculture in India.
1. Crop Production:
– In the 2020-2021 crop year, India produced approximately 120 million metric tons of rice and around 109 million metric tons of wheat.
– Pulses production exceeded 24 million metric tons, and oilseeds production was around 37 million metric tons in the same period.
2. Horticulture Production:
– Horticulture production in the 2019-2020 fiscal year reached over 320 million metric tons. Fruits and vegetables play a crucial role in India’s agricultural landscape.
3. Livestock Production:
– Milk production in India surpassed 194 million metric tons in the 2020-2021 fiscal year, making it the world’s largest milk-producing country.
– Poultry production reached around 103 billion eggs and over 4 million metric tons of meat in the same period.
4. Organic Farming:
– India had over 3.6 million hectares of certified organic farmland, showcasing a growing interest in organic agriculture.
– The organic food market in India has been expanding, with increased consumer awareness and demand.
5. Sustainable Agriculture:
– The National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) aims to promote sustainable agriculture practices. Initiatives include watershed management, soil health cards, and organic farming.
6. Government Initiatives:
– The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) income support program provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
– Various other schemes, such as the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), aim to mitigate risks associated with crop losses.
7. Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
– Agriculture contributes significantly to India’s greenhouse gas emissions. Efforts are underway to address emissions through sustainable farming practices and carbon sequestration initiatives.
8. Challenges and Opportunities:
– Indian agriculture faces challenges such as water scarcity, fragmented land holdings, and the need for modernization.
– Opportunities exist for leveraging technology, improving infrastructure, and promoting agribusiness to enhance the sector’s sustainability.
Conclusion for Top Rated Modern Agriculture Countries
The top-rated modern agriculture countries, including the United States, China, Brazil, and India, collectively shape the global agricultural landscape.
These nations exhibit distinct characteristics that contribute to their prominence in the field:
The United States stands out for its advanced technology adoption, large-scale farming operations, and diverse agricultural output. Precision farming and biotechnology play key roles in enhancing productivity, making the U.S. a major player in international trade.
China, with its vast population, has strategically focused on modernizing agriculture to meet domestic demand and ensure food security. The country’s adoption of advanced technologies and active participation in global markets, especially as a major importer of commodities like soybeans, solidifies its position.
Brazil leverages its extensive arable land, favorable climate, and agribusiness expertise to excel in soybean and beef production. The nation’s market penetration is evident through its significant contributions to international trade and supply chains.
India, with its diverse agricultural practices and a growing emphasis on modernization, plays a crucial role in the global market. The country’s traditional strengths in crops and spices are complemented by a burgeoning export market for fruits, vegetables, and processed foods.
Collectively, these countries not only feed their populations but also contribute substantially to global food production and trade. Their adoption of modern technologies, sustainable practices, and active engagement in international markets underscore their influence in shaping the future of agriculture on a global scale. However, challenges such as environmental sustainability, evolving consumer preferences, and the need for inclusive agricultural development remain areas that these nations and the global community must address to ensure a resilient and sustainable agricultural future.
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/12/top-rated-modern-agriculture-countries.html
Renewable Energy
BladeBUG Tackles Serial Blade Defects with Robotics
Weather Guard Lightning Tech

BladeBUG Tackles Serial Blade Defects with Robotics
Chris Cieslak, CEO of BladeBug, joins the show to discuss how their walking robot is making ultrasonic blade inspections faster and more accessible. They cover new horizontal scanning capabilities for lay down yards, blade root inspections for bushing defects, and plans to expand into North America in 2026.
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly newsletter on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on YouTube, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary’s “Engineering with Rosie” YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
Welcome to Uptime Spotlight, shining Light on Wind. Energy’s brightest innovators. This is the Progress Powering Tomorrow.
Allen Hall: Chris, welcome back to the show.
Chris Cieslak: It’s great to be back. Thank you very much for having me on again.
Allen Hall: It’s great to see you in person, and a lot has been happening at Blade Bugs since the last time I saw Blade Bug in person. Yeah, the robot. It looks a lot different and it has really new capabilities.
Chris Cieslak: So we’ve continued to develop our ultrasonic, non-destructive testing capabilities of the blade bug robot.
Um, but what we’ve now added to its capabilities is to do horizontal blade scans as well. So we’re able to do blades that are in lay down yards or blades that have come down for inspections as well as up tower. So we can do up tower, down tower inspections. We’re trying to capture. I guess the opportunity to inspect blades after transportation when they get delivered to site, to look [00:01:00] for any transport damage or anything that might have been missed in the factory inspections.
And then we can do subsequent installation inspections as well to make sure there’s no mishandling damage on those blades. So yeah, we’ve been just refining what we can do with the NDT side of things and improving its capabilities
Joel Saxum: was that need driven from like market response and people say, Hey, we need, we need.
We like the blade blood product. We like what you’re doing, but we need it here. Or do you guys just say like, Hey, this is the next, this is the next thing we can do. Why not?
Chris Cieslak: It was very much market response. We had a lot of inquiries this year from, um, OEMs, blade manufacturers across the board with issues within their blades that need to be inspected on the ground, up the tap, any which way they can.
There there was no, um, rhyme or reason, which was better, but the fact that he wanted to improve the ability of it horizontally has led the. Sort of modifications that you’ve seen and now we’re doing like down tower, right? Blade scans. Yeah. A really fast breed. So
Joel Saxum: I think the, the important thing there is too is that because of the way the robot is built [00:02:00] now, when you see NDT in a factory, it’s this robot rolls along this perfectly flat concrete floor and it does this and it does that.
But the way the robot is built, if a blade is sitting in a chair trailing edge up, or if it’s flap wise, any which way the robot can adapt to, right? And the idea is. We, we looked at it today and kind of the new cage and the new things you have around it with all the different encoders and for the heads and everything is you can collect data however is needed.
If it’s rasterized, if there’s a vector, if there’s a line, if we go down a bond line, if we need to scan a two foot wide path down the middle of the top of the spa cap, we can do all those different things and all kinds of orientations. That’s a fantastic capability.
Chris Cieslak: Yeah, absolutely. And it, that’s again for the market needs.
So we are able to scan maybe a meter wide in one sort of cord wise. Pass of that probe whilst walking in the span-wise direction. So we’re able to do that raster scan at various spacing. So if you’ve got a defect that you wanna find that maximum 20 mil, we’ll just have a 20 mil step [00:03:00] size between each scan.
If you’ve got a bigger tolerance, we can have 50 mil, a hundred mil it, it’s so tuneable and it removes any of the variability that you get from a human to human operator doing that scanning. And this is all about. Repeatable, consistent high quality data that you can then use to make real informed decisions about the state of those blades and act upon it.
So this is not about, um, an alternative to humans. It’s just a better, it’s just an evolution of how humans do it. We can just do it really quick and it’s probably, we, we say it’s like six times faster than a human, but actually we’re 10 times faster. We don’t need to do any of the mapping out of the blade, but it’s all encoded all that data.
We know where the robot is as we walk. That’s all captured. And then you end up with really. Consistent data. It doesn’t matter who’s operating a robot, the robot will have those settings preset and you just walk down the blade, get that data, and then our subject matter experts, they’re offline, you know, they are in their offices, warm, cozy offices, reviewing data from multiple sources of robots.
And it’s about, you know, improving that [00:04:00] efficiency of getting that report out to the customer and letting ’em know what’s wrong with their blades, actually,
Allen Hall: because that’s always been the drawback of, with NDT. Is that I think the engineers have always wanted to go do it. There’s been crush core transportation damage, which is sometimes hard to see.
You can maybe see a little bit of a wobble on the blade service, but you’re not sure what’s underneath. Bond line’s always an issue for engineering, but the cost to take a person, fly them out to look at a spot on a blade is really expensive, especially someone who is qualified. Yeah, so the, the difference now with play bug is you can have the technology to do the scan.
Much faster and do a lot of blades, which is what the de market demand is right now to do a lot of blades simultaneously and get the same level of data by the review, by the same expert just sitting somewhere else.
Chris Cieslak: Absolutely.
Joel Saxum: I think that the quality of data is a, it’s something to touch on here because when you send someone out to the field, it’s like if, if, if I go, if I go to the wall here and you go to the wall here and we both take a paintbrush, we paint a little bit [00:05:00] different, you’re probably gonna be better.
You’re gonna be able to reach higher spots than I can.
Allen Hall: This is true.
Joel Saxum: That’s true. It’s the same thing with like an NDT process. Now you’re taking the variability of the technician out of it as well. So the data quality collection at the source, that’s what played bug ducts.
Allen Hall: Yeah,
Joel Saxum: that’s the robotic processes.
That is making sure that if I scan this, whatever it may be, LM 48.7 and I do another one and another one and another one, I’m gonna get a consistent set of quality data and then it’s goes to analysis. We can make real decisions off.
Allen Hall: Well, I, I think in today’s world now, especially with transportation damage and warranties, that they’re trying to pick up a lot of things at two years in that they could have picked up free installation.
Yeah. Or lifting of the blades. That world is changing very rapidly. I think a lot of operators are getting smarter about this, but they haven’t thought about where do we go find the tool.
Speaker: Yeah.
Allen Hall: And, and I know Joel knows that, Hey, it, it’s Chris at Blade Bug. You need to call him and get to the technology.
But I think for a lot of [00:06:00] operators around the world, they haven’t thought about the cost They’re paying the warranty costs, they’re paying the insurance costs they’re paying because they don’t have the set of data. And it’s not tremendously expensive to go do. But now the capability is here. What is the market saying?
Is it, is it coming back to you now and saying, okay, let’s go. We gotta, we gotta mobilize. We need 10 of these blade bugs out here to go, go take a scan. Where, where, where are we at today?
Chris Cieslak: We’ve hads. Validation this year that this is needed. And it’s a case of we just need to be around for when they come back round for that because the, the issues that we’re looking for, you know, it solves the problem of these new big 80 a hundred meter plus blades that have issues, which shouldn’t.
Frankly exist like process manufacturer issues, but they are there. They need to be investigated. If you’re an asset only, you wanna know that. Do I have a blade that’s likely to fail compared to one which is, which is okay? And sort of focus on that and not essentially remove any uncertainty or worry that you have about your assets.
’cause you can see other [00:07:00] turbine blades falling. Um, so we are trying to solve that problem. But at the same time, end of warranty claims, if you’re gonna be taken over these blades and doing the maintenance yourself, you wanna know that what you are being given. It hasn’t gotten any nasties lurking inside that’s gonna bite you.
Joel Saxum: Yeah.
Chris Cieslak: Very expensively in a few years down the line. And so you wanna be able to, you know, tick a box, go, actually these are fine. Well actually these are problems. I, you need to give me some money so I can perform remedial work on these blades. And then you end of life, you know, how hard have they lived?
Can you do an assessment to go, actually you can sweat these assets for longer. So we, we kind of see ourselves being, you know, useful right now for the new blades, but actually throughout the value chain of a life of a blade. People need to start seeing that NDT ultrasonic being one of them. We are working on other forms of NDT as well, but there are ways of using it to just really remove a lot of uncertainty and potential risk for that.
You’re gonna end up paying through the, you know, through the, the roof wall because you’ve underestimated something or you’ve missed something, which you could have captured with a, with a quick inspection.
Joel Saxum: To [00:08:00] me, NDT has been floating around there, but it just hasn’t been as accessible or easy. The knowledge hasn’t been there about it, but the what it can do for an operator.
In de-risking their fleet is amazing. They just need to understand it and know it. But you guys with the robotic technology to me, are bringing NDT to the masses
Chris Cieslak: Yeah.
Joel Saxum: In a way that hasn’t been able to be done, done before
Chris Cieslak: that. And that that’s, we, we are trying to really just be able to roll it out at a way that you’re not limited to those limited experts in the composite NDT world.
So we wanna work with them, with the C-N-C-C-I-C NDTs of this world because they are the expertise in composite. So being able to interpret those, those scams. Is not a quick thing to become proficient at. So we are like, okay, let’s work with these people, but let’s give them the best quality data, consistent data that we possibly can and let’s remove those barriers of those limited people so we can roll it out to the masses.
Yeah, and we are that sort of next level of information where it isn’t just seen as like a nice to have, it’s like an essential to have, but just how [00:09:00] we see it now. It’s not NDT is no longer like, it’s the last thing that we would look at. It should be just part of the drones. It should inspection, be part of the internal crawlers regimes.
Yeah, it’s just part of it. ’cause there isn’t one type of inspection that ticks all the boxes. There isn’t silver bullet of NDT. And so it’s just making sure that you use the right system for the right inspection type. And so it’s complementary to drones, it’s complimentary to the internal drones, uh, crawlers.
It’s just the next level to give you certainty. Remove any, you know, if you see something indicated on a a on a photograph. That doesn’t tell you the true picture of what’s going on with the structure. So this is really about, okay, I’ve got an indication of something there. Let’s find out what that really is.
And then with that information you can go, right, I know a repair schedule is gonna take this long. The downtime of that turbine’s gonna be this long and you can plan it in. ’cause everyone’s already got limited budgets, which I think why NDT hasn’t taken off as it should have done because nobody’s got money for more inspections.
Right. Even though there is a money saving to be had long term, everyone is fighting [00:10:00] fires and you know, they’ve really got a limited inspection budget. Drone prices or drone inspections have come down. It’s sort, sort of rise to the bottom. But with that next value add to really add certainty to what you’re trying to inspect without, you know, you go to do a day repair and it ends up being three months or something like, well
Allen Hall: that’s the lightning,
Joel Saxum: right?
Allen Hall: Yeah. Lightning is the, the one case where every time you start to scarf. The exterior of the blade, you’re not sure how deep that’s going and how expensive it is. Yeah, and it always amazes me when we talk to a customer and they’re started like, well, you know, it’s gonna be a foot wide scarf, and now we’re into 10 meters and now we’re on the inside.
Yeah. And the outside. Why did you not do an NDT? It seems like money well spent Yeah. To do, especially if you have a, a quantity of them. And I think the quantity is a key now because in the US there’s 75,000 turbines worldwide, several hundred thousand turbines. The number of turbines is there. The number of problems is there.
It makes more financial sense today than ever because drone [00:11:00]information has come down on cost. And the internal rovers though expensive has also come down on cost. NDT has also come down where it’s now available to the masses. Yeah. But it has been such a mental barrier. That barrier has to go away. If we’re going going to keep blades in operation for 25, 30 years, I
Joel Saxum: mean, we’re seeing no
Allen Hall: way you can do it
Joel Saxum: otherwise.
We’re seeing serial defects. But the only way that you can inspect and or control them is with NDT now.
Allen Hall: Sure.
Joel Saxum: And if we would’ve been on this years ago, we wouldn’t have so many, what is our term? Blade liberations liberating
Chris Cieslak: blades.
Joel Saxum: Right, right.
Allen Hall: What about blade route? Can the robot get around the blade route and see for the bushings and the insert issues?
Chris Cieslak: Yeah, so the robot can, we can walk circumferentially around that blade route and we can look for issues which are affecting thousands of blades. Especially in North America. Yeah.
Allen Hall: Oh yeah.
Chris Cieslak: So that is an area that is. You know, we are lucky that we’ve got, um, a warehouse full of blade samples or route down to tip, and we were able to sort of calibrate, verify, prove everything in our facility to [00:12:00] then take out to the field because that is just, you know, NDT of bushings is great, whether it’s ultrasonic or whether we’re using like CMS, uh, type systems as well.
But we can really just say, okay, this is the area where the problem is. This needs to be resolved. And then, you know, we go to some of the companies that can resolve those issues with it. And this is really about played by being part of a group of technologies working together to give overall solutions
Allen Hall: because the robot’s not that big.
It could be taken up tower relatively easily, put on the root of the blade, told to walk around it. You gotta scan now, you know. It’s a lot easier than trying to put a technician on ropes out there for sure.
Chris Cieslak: Yeah.
Allen Hall: And the speed up it.
Joel Saxum: So let’s talk about execution then for a second. When that goes to the field from you, someone says, Chris needs some help, what does it look like?
How does it work?
Chris Cieslak: Once we get a call out, um, we’ll do a site assessment. We’ve got all our rams, everything in place. You know, we’ve been on turbines. We know the process of getting out there. We’re all GWO qualified and go to site and do their work. Um, for us, we can [00:13:00] turn up on site, unload the van, the robot is on a blade in less than an hour.
Ready to inspect? Yep. Typically half an hour. You know, if we’ve been on that same turbine a number of times, it’s somewhere just like clockwork. You know, muscle memory comes in, you’ve got all those processes down, um, and then it’s just scanning. Our robot operator just presses a button and we just watch it perform scans.
And as I said, you know, we are not necessarily the NDT experts. We obviously are very mindful of NDT and know what scans look like. But if there’s any issues, we have a styling, we dial in remote to our supplement expert, they can actually remotely take control, change the settings, parameters.
Allen Hall: Wow.
Chris Cieslak: And so they’re virtually present and that’s one of the beauties, you know, you don’t need to have people on site.
You can have our general, um, robot techs to do the work, but you still have that comfort of knowing that the data is being overlooked if need be by those experts.
Joel Saxum: The next level, um, commercial evolution would be being able to lease the kit to someone and or have ISPs do it for [00:14:00] you guys kinda globally, or what is the thought
Chris Cieslak: there?
Absolutely. So. Yeah, so we to, to really roll this out, we just wanna have people operate in the robots as if it’s like a drone. So drone inspection companies are a classic company that we see perfectly aligned with. You’ve got the sky specs of this world, you know, you’ve got drone operator, they do a scan, they can find something, put the robot up there and get that next level of information always straight away and feed that into their systems to give that insight into that customer.
Um, you know, be it an OEM who’s got a small service team, they can all be trained up. You’ve got general turbine technicians. They’ve all got G We working at height. That’s all you need to operate the bay by road, but you don’t need to have the RAA level qualified people, which are in short supply anyway.
Let them do the jobs that we are not gonna solve. They can do the big repairs we are taking away, you know, another problem for them, but giving them insights that make their job easier and more successful by removing any of those surprises when they’re gonna do that work.
Allen Hall: So what’s the plans for 2026 then?
Chris Cieslak: 2026 for us is to pick up where 2025 should have ended. [00:15:00] So we were, we were meant to be in the States. Yeah. On some projects that got postponed until 26. So it’s really, for us North America is, um, what we’re really, as you said, there’s seven, 5,000 turbines there, but there’s also a lot of, um, turbines with known issues that we can help determine which blades are affected.
And that involves blades on the ground, that involves blades, uh, that are flying. So. For us, we wanna get out to the states as soon as possible, so we’re working with some of the OEMs and, and essentially some of the asset owners.
Allen Hall: Chris, it’s so great to meet you in person and talk about the latest that’s happening.
Thank you. With Blade Bug, if people need to get ahold of you or Blade Bug, how do they do that?
Chris Cieslak: I, I would say LinkedIn is probably the best place to find myself and also Blade Bug and contact us, um, through that.
Allen Hall: Alright, great. Thanks Chris for joining us and we will see you at the next. So hopefully in America, come to America sometime.
We’d love to see you there.
Chris Cieslak: Thank you very [00:16:00] much.
Renewable Energy
Understanding the U.S. Constitution
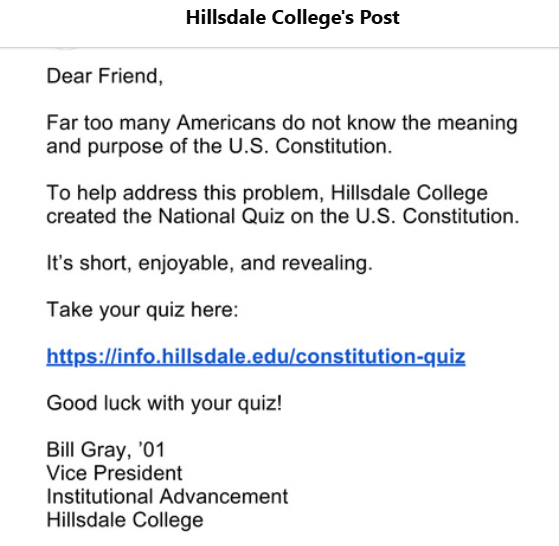 Hillsdale College is a rightwing Christian extremist organization that ostensibly honors the United States Constitution.
Hillsdale College is a rightwing Christian extremist organization that ostensibly honors the United States Constitution.
Here’s their quiz, which should be called the “Constitutional Trivia Quiz.”, whose purpose is obviously to convince Americans of their ignorance.
When I teach, I’m going for understanding of the topic, not the memorization of useless information.
Renewable Energy
Bravery Meets Tragedy: An Unending Story
 Here’s a story:
Here’s a story:
He had 3 days left until graduation.
Kendrick Castillo was 18. A robotics student. College bound. Accepted into an engineering program. The final week of school felt like countdown, not crisis.
Then a weapon appeared inside a classroom.
Students froze.
Kendrick did not.
Witnesses say he moved instantly. He lunged toward the attacker. No hesitation. No calculation.
Two other students followed his lead.
Gunfire erupted.
Kendrick was fatally sh*t.
But his movement changed the room.
Classmates were able to tackle and restrain the attacker until authorities arrived. Investigators later stated that the confrontation disrupted the attack and likely prevented additional casualties.
In seconds, an 18-year-old made a decision most adults pray they never face.
Afterward, the silence was heavier than the noise.
At graduation, his name was called.
His diploma was awarded posthumously. The arena stood in collective applause. An empty seat. A cap and gown without the student inside it.
His robotics teammates remembered him as curious. Competitive. Kind. Someone who solved problems instead of avoiding them.
He had planned to build machines.
Instead, he built a moment.
A moment that classmates say gave them time.
Time to escape.
Two points:
If you can read this without tears welling up in your eyes, you’re a far more stoic person than I.
Since Big Money has made it impossible for the United States to implement the same common-sense gun laws that exist in the rest of the planet, this story will reduplicate itself into perpetuity.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits















