Local officials are often viewed as relatively weak actors in China’s governance structure, largely implementing policies issued from the central level.
However, a new book – “Implementing a low-carbon future: climate leadership in Chinese cities” – argues that these officials play an important role in designing innovative and enduring climate policy.
The book follows how four cities – Shenzhen, Zhenjiang, Xiamen and Nanchang – approached developing low-carbon policies over the course of almost a decade.
It identifies “bridge leaders” – mid-level local bureaucrats who have a strong interest in a specific policy area and who are unlikely to move often between different posts – as key to effective local climate policymaking.
Carbon Brief interviews author Weila Gong, non-resident scholar at the UC San Diego School of Global Policy and Strategy’s 21st Century China Center and visiting scholar at UC Davis, on her research.
The interview has been edited for length and clarity.
- Gong on why cities are important: “Over 85% of China’s carbon emissions come from cities. The majority of Chinese people live in cities, so the extent to which cities can become truly low-carbon will also influence China’s climate success.”
- On what motivates local policymakers: “Mid-level bureaucrats need to think about how to create unique, innovative and visible policy actions to help draw attention to their region and their bosses.”
- On cities as a way to test new policies: “Part of the function of local governments in China is to experiment with policy at a local level, thereby helping national-level officials develop responses to emerging policy challenges.”
- On how local policymakers get results: “Even though we tend to think that local officials are very constrained in terms of policy or financial resources, they can often have the leverage and space to build coalitions.”
- On uneven city-level engagement: “To begin with, all regions received political support if they joined the [low-carbon city] pilot programme. But over the years, different regions have engaged very differently.”
- On the need for ‘entrepreneurial bureaucrats’: “China will always need local officials willing to introduce new legislations or try new policy instruments…For that, it needs entrepreneurial bureaucrats who are willing to turn ideas into actions.”
- On international cooperation: “Even with how geopolitics is really complicating things, many cities continue to have common challenges. For example, collaboration between Shanghai and Los Angeles on green shipping corridors is still ongoing”.
- On the effectiveness of mid-level bureaucrats: “They are creative, they know how to convince their boss about the importance of climate action and they know how that can bring opportunities for themselves and their boss. And because of how long they have worked in one area, they understand the local politics, policy processes and the coalitions needed to provide solutions.”
Carbon Brief: You’ve just written a book about climate policy in Chinese cities. Could you explain why subnational governments are important for China’s climate policy in general?
Weila Gong: China is the world’s largest carbon emitter, so the extent to which global efforts to address climate change can actually reach their goal is largely influenced by China’s efforts.
If you look at the structure of China’s carbon emissions, over 85% of China’s carbon emissions come from cities. The majority of Chinese people live in cities, so the extent to which cities can become truly low-carbon will also influence China’s climate success. That’s why I started to look at this research area.
We tend to think of China as a centralised, big system and a unitary state – state-run and top-down – but it actually also has multi-level governance. No climate action or national climate targets can be achieved without local engagement.
We also tend to think subnational level [actors], including the provincial, city and township levels, are barriers for environmental protection, because they are focused on promoting economic growth.
But I observed these actors participating in China’s low-carbon city pilot programme [as part of my fieldwork spanning most of the 2010s]. I was really surprised to see so many cities wanted to participate in the pilot, even though at the time there was no specific evaluation system that would reward their efforts.
We think of local governments just as implementers of central-level policy. When it comes to issues like climate change and also low-carbon development – in 2010 [policymakers found these concepts] very vague…So I was curious why those local officials would want to take on this issue, given that there was no immediate reward, either in terms of career development or in terms of increasing financial support from the central government.
CB: Could you help us understand the mindset of these bureaucrats? How do local-level officials design policies in China?
WG: The role of different local officials in promoting low-carbon policy is not very well understood. We tend to focus on top political figures, such as mayors or [municipal] party secretaries, because we see them as the most important policymakers.
But that is not entirely true. Those top local politicians are very important in supporting efforts to tackle problem areas…but the focus in my book is the mid-level bureaucrats.
Unlike mayors and party secretaries, mid-level officials tend to stay in one locality for their entire career. That helps us to understand why climate policy can become durable in some places and not others.
Mayors and party secretaries are important for [pushing through policy solutions to problem] issues, but they can also be key barriers for ensuring continuation of those policies – particularly when they change positions…as they tend to move to another locality every three to five years.
Therefore, these top-level officials are not the ones implementing low-carbon policies. That’s why I looked at the mid-level bureaucrats instead.
The conventional understanding of these bureaucrats is that they are obedient and only follow their bosses’ guidance. But actually, when low-carbon policies emerged as an important area for the central government in 2010, opportunities appeared for local governments to develop pilot projects.
Mid-level local officials saw this as a way to help their bosses – the mayors and party secretaries – increase their chances of getting promoted, which in turn would help the mid-level bureaucrats to advance their own career.
Impressing central government officials isn’t really a consideration for these officials…but their bosses need visible or more reliable local actions to show their ability to enforce low-carbon development.
As such, mid-level bureaucrats need to think about how to create unique, innovative and visible policy actions to help draw attention to their region and their bosses.
Secondly, mid-level bureaucrats are more interested in climate issues if it is in the interest of their agency or local government.
For example, Zhenjiang [a city in east China] came to be known as a leader in promoting low-carbon development due to a series of early institutional efforts to establish low-carbon development. In particular, in part because of this, it was chosen for a visit by president Xi Jinping in 2014.
As a result, the city created a specialised agency [on low-carbon development]. This made it one of the first regions to have full-time local officials that followed through on low-carbon policy implementation.
This increased their ability to declare their regulatory authority on low-carbon issues, by being able to promote new regulations, standards and so on, as well as enhancing the region’s and the local policymakers’ reputations by building institutions to ensure long-term enforcement.
Another motivation for many local governments is accessing finance through the pilot programmes. If their ideas impress the central-level government, local policymakers could get access to investment or other forms of financial resources from higher levels of government.
In the city of Nanchang, for example, officials were trying to negotiate access to external investment, because the main central government fund for low-carbon initiatives only provided minimal finance.
Nanchang officials tried to partner with the Austrian government on sustainable agriculture, working through China’s National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC).
It didn’t materialise in the end, but they still created a platform to attract international investment, and gathered tens of millions of yuan [millions of dollars] in central-level support because the fact they showed they were innovating allowed them to access more money through China’s institutional channels.
CB: Could you give an example of what drives innovative local climate policies?
WG: National-level policies and pilot programme schemes provide openings for local governments to really think about how and whether they should engage more in addressing climate change.
The national government has participated in international negotiations on climate for decades…but subnational-level cities and provinces only joined national efforts to address climate issues from the 2010s – starting with the low-carbon city programme.
So we can see that local responses to addressing climate change have been shaped by the opportunities provided by the national government, [who in turn] want more local-level participation to give them successful case studies to take to international conferences.
Local carbon emission trading systems (ETSs) are an example of giving local governments opportunities to experiment.
In my book, I look at the case of Shenzhen, which launched China’s first local ETS. [Shenzhen was one of seven regions selected to run a pilot ETS, ahead of the national ETS being established in 2018.]
Part of the function of local governments in China is to experiment with policy at a local level, thereby helping national-level officials develop responses to emerging policy challenges.
I remember a moment during my field research in 2012, when I was with a group of officials from both the national and local government.
The national government officials asked the local officials to come up with some best practices and solutions, to help them envision what could be done at the national level.
Then there are drivers at the international level, which I think is very interesting.
I observed that the officials particularly willing to take on climate issues usually had access to international training.
During the early stages of subnational climate engagement, organisations such as the German Agency for International Cooperation (GIZ) worked with the NDRC and other national-level agencies to train local officials across the country.
This created more opportunities to help local officials understand what climate change and carbon markets were, and how to use policy instruments to support low-carbon development.
In Shenzhen, local bureaucrats also turned to their international partners to help them design policy.
The city created a study group to visit partners working on the EU ETS and learn how it was designed. They learned about price volatility in the EU ETS and pushed legislation through the local people’s congress [to mitigate this in their own system].
One thing that made the Shenzhen ETS so successful is what I call “entrepreneurial bureaucrats” [who have the ability to design, push through and maintain new local-level climate policies].
Shenzhen’s vice mayor worked with the local people’s congress to push the ETS legislation through. This was the first piece of legislation in China to require compulsory participation by more than 600 local industrial actors. It also granted the local government authority to decide the quotas and scope of the ETS.
These 600 entities also included Shenzhen’s public building sector[, a powerful local interest group].
This shows that, even though we tend to think that local officials are very constrained in terms of policy or financial resources, they can often have the leverage and space to build coalitions – even in China’s more centralised political system – and know how to mobilise political support.
CB: You chose to look at the effectiveness of four cities – Shenzhen, Zhenjiang, Xiamen and Nanchang – in climate policymaking. Why did you choose these cities and how representative are they of the rest of China?
WG: We tend to believe that only economically-advanced areas or environmentally-friendly cities will become champions for low-carbon development…But I was surprised, because Zhenjiang and Nanchang are not known for having an advanced economy, but [they nevertheless built impactful climate] institutions – regulations, standards and legislation that shape individual and organisational behaviours in the long term. I thought they were interesting examples of how local regions can really create those institutions.
Then there was Xiamen, which is seen as an environmentally-friendly city and economically is comparable to Shenzhen when you look at GDP per capita. Xiamen actually did not turn its low-carbon policy experimentation into long-term institutions, instead randomly proposing new initiatives [that were not sustained].
I conducted more than 100 interviews, talking with policy-practitioners inside and outside of government about specific policies, their processes and implementation.
I found that, over the course of eight years, these [cities] showed very different levels of engagement.
Some I categorised into substantive engagement, where the local government delivered on their climate goals. [Shenzhen falls into this category.]
Then there is performative engagement – such as in the case of Nanchang – where the local government was more interested in [using climate policies to] attract external investment and access projects from higher levels of government.
But they were not able to enforce the policies, because impressing higher levels of government became the primary motivation.
Zhenjiang was a case of symbolic engagement. It actually created a lot of institutions, such as a specialised agency and a screening system to ensure new [low-carbon] investment. When I was observing Zhenjiang, from 2012 to 2018, officials recognised they needed to be carbon-constrained.
The problem was that Zhenjiang has a very strong power sector – mainly coal power – which supplies the whole eastern coast. That meant, even though the government was very determined to promote low-carbon policies, they faced [opposition from] very strong local actors – meaning the government could only partially implement the targets they set.
Then there is sporadic engagement, as seen in Xiamen. [The city’s approach to climate policy was incremental and cautious] because of a lack of political support [from officials in Xiamen], as well as local coalitions between key actors. So instead, we find random initiatives being promoted.
This explains the uneven policy implementation in China. To begin with, all regions received political support if they joined the pilot programme. But over the years, different regions have engaged very differently, in terms of the regulations, standards and legislation they have introduced, and whether those were paired with enforcement by a group of trained personnel to follow through on those initiatives.
CB: What needs to be done to strengthen sub-national climate policy making?
WG: It’s very important to have groups of personnel trained on climate policy. Since 2010, when I started studying the low-carbon pilot programme, there were no provincial-level people or agencies fully responsible for climate change. Back then, there was only the [central-level] department of climate change under the NDRC.
By the time I finished the book, provincial-level departments of climate change had been created across all provinces. But almost nothing has been established at the city level, so most city-level climate initiatives are being managed under the agencies responsible for air quality.
That means climate change is only one of those local officials’ day-to-day responsibilities. Only a handful of cities have dedicated staff working on climate issues: Beijing, Shanghai, Zhenjiang, Shenzhen and Guiyang.
Nanchang devised some of China’s first legislation to include an annual [financial] budget for low-carbon development. But when I revisited the city, officials were not actually sure about how and whether that budget was being used, because there wasn’t a person responsible for it.
Therefore, even if there are resources available, they can go unused because local officials at the city level are so busy. If climate policy is not prioritised, or written into their job responsibilities, that can be a challenge for sustaining implementation.
In China’s governance structure, the national government comes up with ideas, and the provincial level transfers these ideas down to local-level governments. City-level governments are the ones implementing these ideas.
So we need full-time staff to follow through on policies from the beginning right up to implementation.
Secondly, while almost all cities have now made carbon-peaking plans, one area in which the Chinese government can make further progress is in data.
China has recently emphasised the need to strengthen carbon-emissions data collection and monitoring. But when I was conducting my research, most Chinese cities had not yet established regular carbon-accounting systems.
As such, inadequate energy statistics and insufficient detail remain key barriers to effective climate-policy implementation.
In addition, the relevant data usually is owned by China’s National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), which does not always share it with other agencies. Local agencies can’t always access detailed data.
When I visited Xiamen, officials told me the local government is now improving emissions monitoring systems. But there should be more systematic and rigorous data collection, covering both carbon emissions and non-CO2 greenhouse gases. Also, much of the company-level data is self-reported, which could affect the accuracy of carbon-emissions statistics.
For continued climate action, it’s also important that the central government ensures that local officials have the institutional support needed to experiment and propose new ideas.
…China will always need local officials willing to introduce new legislations or try new policy instruments – like Shenzhen with its ETS, or establishing new carbon-monitoring platforms.
For that, it needs entrepreneurial bureaucrats who are willing to turn ideas into actions. Ensuring that local governments have the right set of conditions to do this is very important.
CB: What did you find most surprising when researching this book?
WG: That international collaboration is still very important. I found that many officials learnt about climate change through international engagement.
In the current situation, I think international engagement is still very important – particularly given how, even with how geopolitics is really complicating things, many cities continue to have common challenges. For example, collaboration between Shanghai and Los Angeles on green shipping corridors is still ongoing.
That can bring opportunities for continuing climate action at the city level in the face of rising international tensions, as long as national governments give them space to be involved in international climate action.
Another surprise was the factors of what exactly made climate action durable. I was really surprised that many of the cities that I revisited were still involved in the pilot programmes, despite the central government restructuring that shifted the climate change portfolio from the NDRC to the Ministry of Ecology and Environment – which created challenges for the local governments who had to navigate this.
I also thought that the change in mayors for all four cities would lead to climate initiatives falling off the agenda.
But actually, Zhenjiang, Xiamen and Nanchang all maintained their low-carbon initiatives, despite these changes. This showed it isn’t only strong mayors that bring success, but rather a group of trained personnel building and enforcing regulations and standards. So the importance of bureaucrats and bureaucracy in making climate action durable was actually way beyond my initial expectations.
I was also surprised that bureaucrats can be entrepreneurial, even though they work in a centralised system. They are creative, they know how to convince their boss about the importance of climate action and they know how that can bring opportunities for themselves and their boss. And because of how long they have worked in one area, they understand the local politics, policy processes and the coalitions needed to provide solutions.
The post Interview: How ‘mid-level bureaucrats’ are helping to shape Chinese climate policy appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Interview: How ‘mid-level bureaucrats’ are helping to shape Chinese climate policy
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 6 February 2026: US secret climate panel ‘unlawful’ | China’s clean energy boon | Can humans reverse nature loss?
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Secrets and layoffs
UNLAWFUL PANEL: A federal judge ruled that the US energy department “violated the law when secretary Chris Wright handpicked five researchers who rejected the scientific consensus on climate change to work in secret on a sweeping government report on global warming”, reported the New York Times. The newspaper explained that a 1972 law “does not allow agencies to recruit or rely on secret groups for the purposes of policymaking”. A Carbon Brief factcheck found more than 100 false or misleading claims in the report.
DARKNESS DESCENDS: The Washington Post reportedly sent layoff notices to “at least 14” of its climate journalists, as part of a wider move from the newspaper’s billionaire owner, Jeff Bezos, to eliminate 300 jobs at the publication, claimed Climate Colored Goggles. After the layoffs, the newspaper will have five journalists left on its award-winning climate desk, according to the substack run by a former climate reporter at the Los Angeles Times. It comes after CBS News laid off most of its climate team in October, it added.
WIND UNBLOCKED: Elsewhere, a separate federal ruling said that a wind project off the coast of New York state can continue, which now means that “all five offshore wind projects halted by the Trump administration in December can resume construction”, said Reuters. Bloomberg added that “Ørsted said it has spent $7bn on the development, which is 45% complete”.
Around the world
- CHANGING TIDES: The EU is “mulling a new strategy” in climate diplomacy after struggling to gather support for “faster, more ambitious action to cut planet-heating emissions” at last year’s UN climate summit COP30, reported Reuters.
- FINANCE ‘CUT’: The UK government is planning to cut climate finance by more than a fifth, from £11.6bn over the past five years to £9bn in the next five, according to the Guardian.
- BIG PLANS: India’s 2026 budget included a new $2.2bn funding push for carbon capture technologies, reported Carbon Brief. The budget also outlined support for renewables and the mining and processing of critical minerals.
- MOROCCO FLOODS: More than 140,000 people have been evacuated in Morocco as “heavy rainfall and water releases from overfilled dams led to flooding”, reported the Associated Press.
- CASHFLOW: “Flawed” economic models used by governments and financial bodies “ignor[e] shocks from extreme weather and climate tipping points”, posing the risk of a “global financial crash”, according to a Carbon Tracker report covered by the Guardian.
- HEATING UP: The International Olympic Committee is discussing options to hold future winter games earlier in the year “because of the effects of warmer temperatures”, said the Associated Press.
54%
The increase in new solar capacity installed in Africa over 2024-25 – the continent’s fastest growth on record, according to a Global Solar Council report covered by Bloomberg.
Latest climate research
- Arctic warming significantly postpones the retreat of the Afro-Asian summer monsoon, worsening autumn rainfall | Environmental Research Letters
- “Positive” images of heatwaves reduce the impact of messages about extreme heat, according to a survey of 4,000 US adults | Environmental Communication
- Greenland’s “peripheral” glaciers are projected to lose nearly one-fifth of their total area and almost one-third of their total volume by 2100 under a low-emissions scenario | The Cryosphere
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
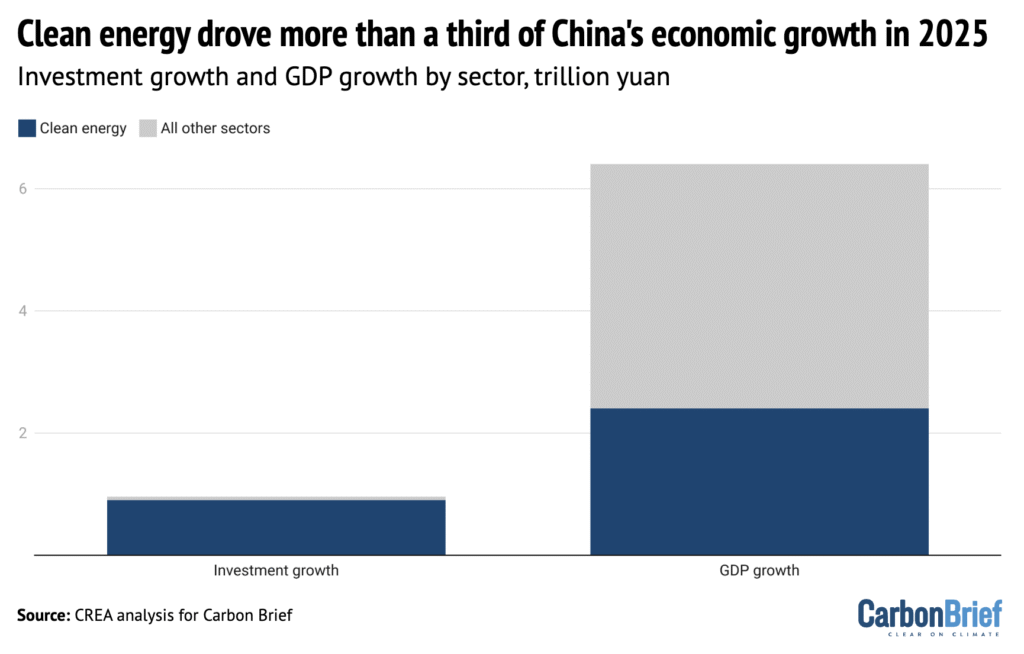
Solar power, electric vehicles and other clean-energy technologies drove more than a third of the growth in China’s economy in 2025 – and more than 90% of the rise in investment, according to new analysis for Carbon Brief (shown in blue above). Clean-energy sectors contributed a record 15.4tn yuan ($2.1tn) in 2025, some 11.4% of China’s gross domestic product (GDP) – comparable to the economies of Brazil or Canada, the analysis said.
Spotlight
Can humans reverse nature decline?
This week, Carbon Brief travelled to a UN event in Manchester, UK to speak to biodiversity scientists about the chances of reversing nature loss.
Officials from more than 150 countries arrived in Manchester this week to approve a new UN report on how nature underpins economic prosperity.
The meeting comes just four years before nations are due to meet a global target to halt and reverse biodiversity loss, agreed in 2022 under the landmark “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF).
At the sidelines of the meeting, Carbon Brief spoke to a range of scientists about humanity’s chances of meeting the 2030 goal. Their answers have been edited for length and clarity.
Dr David Obura, ecologist and chair of Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES)
We can’t halt and reverse the decline of every ecosystem. But we can try to “bend the curve” or halt and reverse the drivers of decline. That’s the economic drivers, the indirect drivers and the values shifts we need to have. What the GBF aspires to do, in terms of halting and reversing biodiversity loss, we can put in place the enabling drivers for that by 2030, but we won’t be able to do it fast enough at this point to halt [the loss] of all ecosystems.
Dr Luthando Dziba, executive secretary of IPBES
Countries are due to report on progress by the end of February this year on their national strategies to the Convention on Biological Diversity [CBD]. Once we get that, coupled with a process that is ongoing within the CBD, which is called the global stocktake, I think that’s going to give insights on progress as to whether this is possible to achieve by 2030…Are we on the right trajectory? I think we are and hopefully we will continue to move towards the final destination of having halted biodiversity loss, but also of living in harmony with nature.
Prof Laura Pereira, scientist at the Global Change Institute at Wits University, South Africa
At the global level, I think it’s very unlikely that we’re going to achieve the overall goal of halting biodiversity loss by 2030. That being said, I think we will make substantial inroads towards achieving our longer term targets. There is a lot of hope, but we’ve also got to be very aware that we have not necessarily seen the transformative changes that are going to be needed to really reverse the impacts on biodiversity.
Dr David Cooper, chair of the UK’s Joint Nature Conservation Committee and former executive secretary of the Convention on Biological Diversity
It’s important to look at the GBF as a whole…I think it is possible to achieve those targets, or at least most of them, and to make substantial progress towards them. It is possible, still, to take action to put nature on a path to recovery. We’ll have to increasingly look at the drivers.
Prof Andrew Gonzalez, McGill University professor and co-chair of an IPBES biodiversity monitoring assessment
I think for many of the 23 targets across the GBF, it’s going to be challenging to hit those by 2030. I think we’re looking at a process that’s starting now in earnest as countries [implement steps and measure progress]…You have to align efforts for conserving nature, the economics of protecting nature [and] the social dimensions of that, and who benefits, whose rights are preserved and protected.
Neville Ash, director of the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre
The ambitions in the 2030 targets are very high, so it’s going to be a stretch for many governments to make the actions necessary to achieve those targets, but even if we make all the actions in the next four years, it doesn’t mean we halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030. It means we put the action in place to enable that to happen in the future…The important thing at this stage is the urgent action to address the loss of biodiversity, with the result of that finding its way through by the ambition of 2050 of living in harmony with nature.
Prof Pam McElwee, Rutgers University professor and co-chair of an IPBES “nexus assessment” report
If you look at all of the available evidence, it’s pretty clear that we’re going to keep experiencing biodiversity decline. I mean, it’s fairly similar to the 1.5C climate target. We are not going to meet that either. But that doesn’t mean that you slow down the ambition…even though you recognise that we probably won’t meet that specific timebound target, that’s all the more reason to continue to do what we’re doing and, in fact, accelerate action.
Watch, read, listen
OIL IMPACTS: Gas flaring has risen in the Niger Delta since oil and gas major Shell sold its assets in the Nigerian “oil hub”, a Climate Home News investigation found.
LOW SNOW: The Washington Post explored how “climate change is making the Winter Olympics harder to host”.
CULTURE WARS: A Media Confidential podcast examined when climate coverage in the UK became “part of the culture wars”.
Coming up
- 2-8 February: 12th session of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), Manchester, UK
- 8 February: Japanese general election
- 8 February: Portugal presidential election
- 11 February: Barbados general election
- 11-12 February: UN climate chief Simon Stiell due to speak in Istanbul, Turkey
Pick of the jobs
- UK Met Office, senior climate science communicator | Salary: £43,081-£46,728. Location: Exeter, UK
- Canadian Red Cross, programme officer, Indigenous operations – disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation | Salary: $56,520-$60,053. Location: Manitoba, Canada
- Aldersgate Group, policy officer | Salary: £33,949-£39,253. Location: London (hybrid)
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 6 February 2026: US secret climate panel ‘unlawful’ | China’s clean energy boon | Can humans reverse nature loss? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
China Briefing 5 February 2026: Clean energy’s share of economy | Record renewables | Thawing relations with UK
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s China Briefing.
China Briefing handpicks and explains the most important climate and energy stories from China over the past fortnight. Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
Solar and wind eclipsed coal
‘FIRST TIME IN HISTORY’: China’s total power capacity reached 3,890 gigawatts (GW) in 2025, according to a National Energy Administration (NEA) data release covered by industry news outlet International Energy Net. Of this, it said, solar capacity rose 35% to 1,200GW and wind capacity was up 23% to 640GW, while thermal capacity – which is mostly coal – grew 6% to just over 1,500GW. This marks the “first time in history” that wind and solar capacity has outranked coal capacity in China’s power mix, reported the state-run newspaper China Daily. China’s grid-related energy storage capacity exceeded 213GW in 2025, said state news agency Xinhua. Meanwhile, clean-energy industries “drove more than 90%” of investment growth and more than half of GDP growth last year, said the Guardian in its coverage of new analysis for Carbon Brief. (See more in the spotlight below.)

DAWN FOR SOLAR: Solar power capacity alone may outpace coal in 2026, according to projections by the China Electricity Council (CEC), reported business news outlet 21st Century Business Herald. It added that non-fossil sources could account for 63% of the power mix this year, with coal falling to 31%. Separately, the China Renewable Energy Society said that annual wind-power additions could grow by between 600-980GW over the next five years, with annual additions of 120GW expected until 2028, said industry news outlet China Energy Net. China Energy Net also published the full CEC report.
STATE MEDIA VOICE: Xinhua published several energy- and climate-related articles in a series on the 15th five-year plan. One said that becoming a low-carbon energy “powerhouse” will support decarbonisation efforts, strengthen industrial innovation and improve China’s “global competitive edge and standing”. Another stated that coal consumption is “expected” to peak around 2027, with continued “growth” in the power and chemicals sector, while oil has already peaked. A third noted that distributed energy systems better matched the “characteristics of renewable energy” than centralised ones, but warned against “blind” expansion and insufficient supporting infrastructure. Others in the series discussed biodiversity and environmental protection and recycling of clean-energy technology. Meanwhile, the communist party-affiliated People’s Daily said that oil will continue to play a “vital role” in China, even after demand peaks.
Starmer and Xi endorsed clean-energy cooperation
CLIMATE PARTNERSHIP: UK prime minister Keir Starmer and Chinese president Xi Jinping pledged in Beijing to deepen cooperation on “green energy”, reported finance news outlet Caixin. They also agreed to establish a “China-UK high-level climate and nature partnership”, said China Daily. Xi told Starmer that the two countries should “carry out joint research and industrial transformation” in new energy and low-carbon technologies, according to Xinhua. It also cited Xi as saying China “hopes” the UK will provide a “fair” business environment for Chinese companies.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “China Briefing” email newsletter. All you need to know about the latest developments relating to China and climate change. Sent to your inbox every Thursday.
OCTOPUS OVERSEAS: During the visit, UK power-trading company Octopus Energy and Chinese energy services firm PCG Power announced they would be starting a new joint venture in China, named Bitong Energy, reported industry news outlet PV Magazine. The move “marks a notable direct entry” of a foreign company into China’s “tightly regulated electricity market”, said Caixin.
PUSH AND PULL: UK policymakers also visited Chinese clean-energy technology manufacturer Envision in Shanghai, reported finance news outlet Yicai. It quoted UK business secretary Peter Kyle emphasising that partnering with companies “like Envision” on sustainability is a “really important part of our future”, particularly in terms of job creation in the UK. Trade minister Chris Bryant told Radio Scotland Breakfast that the government will decide on Chinese wind turbine manufacturer Mingyang’s plans for a Scotland factory “soon”. Researchers at the thinktank Oxford Institute for Energy Studies wrote in a guest post for Carbon Brief that greater Chinese competition in Europe’s wind market could “help spur competition in Europe”, if localisation rules and “other guardrails” are applied.
More China news
- LIFE SUPPORT: China will update its coal capacity payment mechanism, which will raise thresholds for coal-fired power plants and expand to cover gas-fired power and pumped and new-energy storage, reported current affairs outlet China News.
- FRONTIER TECH: The world’s “largest compressed-air power storage plant” has begun operating in China, said Bloomberg.
- PARTNERSHIP A ‘MISTAKE’: The EU launched a “foreign subsidies” probe into Chinese wind turbine company Goldwind, said the Hong Kong-based South China Morning Post. EU climate chief Wopke Hoekstra said the bloc must resist China’s pull in clean technologies, according to Bloomberg.
- TRADE SPAT: The World Trade Organization “backed a complaint by China” that the US Inflation Reduction Act “discriminated against” Chinese cleantech exports, said Reuters.
- NEW RULES: China has set “new regulations” for the Waliguan Baseline Observatory, which provides “key scientific references for the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”, said the People’s Daily.
Captured

New or reactivated proposals for coal-fired power plants in China totalled 161GW in 2025, according to a new report covered by Carbon Brief.
Spotlight
Clean energy drove China’s economic growth in 2025
New analysis for Carbon Brief finds that clean-energy sectors contributed the equivalent of $2.1tn to China’s economy last year, making it a key driver of growth. However, headwinds in 2026 could restrict growth going forward – especially for the solar sector.
Below is an excerpt from the article, which can be read in full on Carbon Brief’s website.
Solar power, electric vehicles (EVs) and other clean-energy technologies drove more than a third of the growth in China’s economy in 2025 – and more than 90% of the rise in investment.
Clean-energy sectors contributed a record 15.4tn yuan ($2.1tn) in 2025, some 11.4% of China’s gross domestic product (GDP)
Analysis shows that China’s clean-energy sectors nearly doubled in real value between 2022-25 and – if they were a country – would now be the 8th-largest economy in the world.
These investments in clean-energy manufacturing represent a large bet on the energy transition in China and overseas, creating an incentive for the government and enterprises to keep the boom going.
However, there is uncertainty about what will happen this year and beyond, particularly due to a new pricing system, worsening industrial “overcapacity” and trade tensions.
Outperforming the wider economy
China’s clean-energy economy continues to grow far more quickly than the wider economy, making an outsized contribution to annual growth.
Without these sectors, China’s GDP would have expanded by 3.5% in 2025 instead of the reported 5.0%, missing the target of “around 5%” growth by a wide margin.
Clean energy made a crucial contribution during a challenging year, when promoting economic growth was the foremost aim for policymakers.
In 2024, EVs and solar had been the largest growth drivers. In 2025, it was EVs and batteries, which delivered 44% of the economic impact and more than half of the growth of the clean-energy industries.
The next largest subsector was clean-power generation, transmission and storage, which made up 40% of the contribution to GDP and 30% of the growth in 2025.
Within the electricity sector, the largest drivers were growth in investment in wind and solar power generation capacity, along with growth in power output from solar and wind, followed by the exports of solar-power equipment and materials.
But investment in solar-panel supply chains, a major growth driver in 2022-23, continued to fall for the second year, as the government made efforts to rein in overcapacity and “irrational” price competition.
Headwinds for solar
Ongoing investment of hundreds of billions of dollars represents a gigantic bet on a continuing global energy transition.
However, developments next year and beyond are unclear, particularly for solar. A new pricing system for renewable power is creating uncertainty, while central government targets have been set far below current rates of clean-electricity additions.
Investment in solar-power generation and solar manufacturing declined in the second half of the year.
The reduction in the prices of clean-energy technology has been so dramatic that when the prices for GDP statistics are updated, the sectors’ contribution to real GDP – adjusted for inflation or, in this case deflation – will be revised down.
Nevertheless, the key economic role of the industry creates a strong motivation to keep the clean-energy boom going. A slowdown in the domestic market could also undermine efforts to stem overcapacity and inflame trade tensions by increasing pressure on exports to absorb supply.
Local governments and state-owned enterprises will also influence the outlook for the sector.
Provincial governments have a lot of leeway in implementing the new electricity markets and contracting systems for renewable power generation. The new five-year plans, to be published this year, will, therefore, be of major importance.
This spotlight was written for Carbon Brief by Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst at Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), and Belinda Schaepe, China policy analyst at CREA. CREA China analysts Qi Qin and Chengcheng Qiu contributed research.
Watch, read, listen
PROVINCE INFLUENCE: The Institute for Global Decarbonization Progress, a Beijing-based thinktank, published a report examining the climate-related statements in provincial recommendations for the 15th five-year plan.
‘PIVOT’?: The Outrage + Optimism podcast spoke with the University of Bath’s Dr Yixian Sun about whether China sees itself as a climate leader and what its role in climate negotiations could be going forward.
COOKING FOR CLEAN-TECH: Caixin covered rising demand for China’s “gutter oil” as companies “scramble” to decarbonise.
DON’T GO IT ALONE: China News broadcast the Chinese foreign ministry’s response to the withdrawal of the US from the Paris Agreement, with spokeswoman Mao Ning saying “no country can remain unaffected” by climate change.
$6.8tn
The current size of China’s green-finance economy, including loans, bonds and equity, according to Dr Ma Jun, the Institute of Finance and Sustainability’s president,in a report launch event attended by Carbon Brief. Dr Ma added that “green loans” make up 16% of all loans in China, with some areas seeing them take a 34% share.
New science
- China’s official emissions inventories have overestimated its hydrofluorocarbon emissions by an average of 117m tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (mtCO2e) every year since 2017 | Nature Geoscience
- “Intensified forest management efforts” in China from 2010 onwards have been linked to an acceleration in carbon absorption by plants and soils | Communications Earth and Environment
Recently published on WeChat
China Briefing is written by Anika Patel and edited by Simon Evans. Please send tips and feedback to china@carbonbrief.org
The post China Briefing 5 February 2026: Clean energy’s share of economy | Record renewables | Thawing relations with UK appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Analysis: Clean energy drove more than a third of China’s GDP growth in 2025
Solar power, electric vehicles (EVs) and other clean-energy technologies drove more than a third of the growth in China’s economy in 2025 – and more than 90% of the rise in investment.
Clean-energy sectors contributed a record 15.4tn yuan ($2.1tn) in 2025, some 11.4% of China’s gross domestic product (GDP) – comparable to the economies of Brazil or Canada.
The new analysis for Carbon Brief, based on official figures, industry data and analyst reports, shows that China’s clean-energy sectors nearly doubled in real value between 2022-25 and – if they were a country – would now be the 8th-largest economy in the world.
Other key findings from the analysis include:
- Without clean-energy sectors, China would have missed its target for GDP growth of “around 5%”, expanding by 3.5% in 2025 instead of the reported 5.0%.
- Clean-energy industries are expanding much more quickly than China’s economy overall, with their annual growth rate accelerating from 12% in 2024 to 18% in 2025.
- The “new three” of EVs, batteries and solar continue to dominate the economic contribution of clean energy in China, generating two-thirds of the value added and attracting more than half of all investment in the sectors.
- China’s investments in clean energy reached 7.2tn yuan ($1.0tn) in 2025, roughly four times the still sizable $260bn put into fossil-fuel extraction and coal power.
- Exports of clean-energy technologies grew rapidly in 2025, but China’s domestic market still far exceeds the export market in value for Chinese firms.
These investments in clean-energy manufacturing represent a large bet on the energy transition in China and overseas, creating an incentive for the government and enterprises to keep the boom going.
However, there is uncertainty about what will happen this year and beyond, particularly for solar power, where growth has slowed in response to a new pricing system and where central government targets have been set far below the recent rate of expansion.
An ongoing slowdown could turn the sectors into a drag on GDP, while worsening industrial “overcapacity” and exacerbating trade tensions.
Yet, even if central government targets in the next five-year plan are modest, those from local governments and state-owned enterprises could still drive significant growth in clean energy.
This article updates analysis previously reported for 2023 and 2024.
Clean-energy sectors outperform wider economy
China’s clean-energy economy continues to grow far more quickly than the wider economy. This means that it is making an outsize contribution to annual economic growth.
The figure below shows that clean-energy technologies drove more than a third of the growth in China’s economy overall in 2025 and more than 90% of the net rise in investment.

In 2022, China’s clean-energy economy was worth an estimated 8.4tn yuan ($1.2tn). By 2025, the sectors had nearly doubled in value to 15.4tn yuan ($2.1tn).
This is comparable to the entire output of Brazil or Canada and positions the Chinese clean-energy industry as the 8th-largest economy in the world. Its value is roughly half the size of the economy of India – the world’s fourth largest – or of the US state of California.
The outperformance of the clean-energy sectors means that they are also claiming a rising share of China’s economy overall, as shown in the figure below.

This share has risen from 7.3% of China’s GDP in 2022 to 11.4% in 2025.
Without clean-energy sectors, China’s GDP would have expanded by 3.5% in 2025 instead of the reported 5.0%, missing the target of “around 5%” growth by a wide margin.
Clean energy thus made a crucial contribution during a challenging year, when promoting economic growth was the foremost aim for policymakers.
The table below includes a detailed breakdown by sector and activity.
| Sector | Activity | Value in 2025, CNY bln | Value in 2025, USD bln | Year-on-year growth | Growth contribution | Value contribution | Value in 2025, CNY trn | Value in 2024, CNY trn | Value in 2023, CNY trn | Value in 2022, CNY trn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVs | Investment: manufacturing capacity | 1,643 | 228 | 18% | 10.4% | 10.7% | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.9 |
| EVs | Investment: charging infrastructure | 192 | 27 | 58% | 2.9% | 1.2% | 0.192 | 0.122 | 0.1 | 0.08 |
| EVs | Production of vehicles | 3,940 | 548 | 29% | 36.4% | 25.6% | 3.94 | 3.065 | 2.26 | 1.65 |
| Batteries | Investment: battery manufacturing | 277 | 38 | 35% | 3.0% | 1.8% | 0.277 | 0.205 | 0.32 | 0.15 |
| Batteries | Exports: batteries | 724 | 101 | 51% | 10.1% | 4.7% | 0.724 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.34 |
| Solar power | Investment: power generation capacity | 1,182 | 164 | 15% | 6.3% | 7.7% | 1.182 | 1.031 | 0.808 | 0.34 |
| Solar power | Investment: manufacturing capacity | 506 | 70 | -23% | -6.5% | 3.3% | 0.506 | 0.662 | 0.95 | 0.51 |
| Solar power | Electricity generation | 491 | 68 | 33% | 5.1% | 3.2% | 0.491 | 0.369 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Solar power | Exports of components | 681 | 95 | 21% | 4.9% | 4.4% | 0.681 | 0.562 | 0.5 | 0.35 |
| Wind power | Investment: power generation capacity, onshore | 612 | 85 | 47% | 8.1% | 4.0% | 0.612 | 0.417 | 0.397 | 0.21 |
| Wind power | Investment: power generation capacity, offshore | 96 | 13 | 98% | 2.0% | 0.6% | 0.096 | 0.048 | 0.086 | 0.06 |
| Wind power | Electricity generation | 510 | 71 | 13% | 2.4% | 3.3% | 0.51 | 0.453 | 0.4 | 0.34 |
| Nuclear power | Investment: power generation capacity | 173 | 24 | 18% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Nuclear power | Electricity generation | 216 | 30 | 8% | 0.7% | 1.4% | 0.216 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| Hydropower | Investment: power generation capacity | 54 | 7 | -7% | -0.2% | 0.3% | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Hydropower | Electricity generation | 582 | 81 | 3% | 0.6% | 3.8% | 0.582 | 0.567 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| Rail transportation | Investment | 902 | 125 | 6% | 2.1% | 5.8% | 0.902 | 0.851 | 0.764 | 0.714 |
| Rail transportation | Transport of passengers and goods | 1,020 | 142 | 3% | 1.3% | 6.6% | 1.02 | 0.99 | 0.964 | 0.694 |
| Electricity transmission | Investment: transmission capacity | 644 | 90 | 6% | 1.5% | 4.2% | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.5 |
| Electricity transmission | Transmission of clean power | 52 | 7 | 14% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.052 | 0.046 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Energy storage | Investment: Pumped hydro | 53 | 7 | 5% | 0.1% | 0.3% | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Energy storage | Investment: Grid-connected batteries | 232 | 32 | 52% | 3.3% | 1.5% | 0.232 | 0.152 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| Energy storage | Investment: Electrolysers | 11 | 2 | 29% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0 | 0 |
| Energy efficiency | Revenue: Energy service companies | 620 | 86 | 17% | 3.8% | 4.0% | 0.62 | 0.528003 | 0.52 | 0.45 |
| Total | Investments | 7,198 | 1001 | 15% | 38.2% | 46.7% | 7.20 | 6.28 | 6.00 | 4.11 |
| Total | Production of goods and services | 8,216 | 1,143 | 22% | 61.8% | 53.3% | 8.22 | 6.73 | 5.58 | 4.32 |
| Total | Total GDP contribution | 15,414 | 2144 | 18% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 15.41 | 13.01 | 11.58 | 8.42 |
EVs and batteries were the largest drivers of GDP growth
In 2024, EVs and solar had been the largest growth drivers. In 2025, it was EVs and batteries, which delivered 44% of the economic impact and more than half of the growth of the clean-energy industries. This was due to strong growth in both output and investment.
The contribution to nominal GDP growth – unadjusted for inflation – was even larger, as EV prices held up year-on-year while the economy as a whole suffered from deflation. Investment in battery manufacturing rebounded after a fall in 2024.
The major contribution of EVs and batteries is illustrated in the figure below, which shows both the overall size of the clean-energy economy and the sectors that added the most to the rise from year to year.

The next largest subsector was clean-power generation, transmission and storage, which made up 40% of the contribution to GDP and 30% of the growth in 2025.
Within the electricity sector, the largest drivers were growth in investment in wind and solar power generation capacity, along with growth in power output from solar and wind, followed by the exports of solar-power equipment and materials.
Investment in solar-panel supply chains, a major growth driver in 2022-23, continued to fall for the second year. This was in line with the government’s efforts to rein in overcapacity and “irrational” price competition in the sector.
Finally, rail transportation was responsible for 12% of the total economic output of the clean-energy sectors, but saw relatively muted growth year-on-year, with revenue up 3% and investment by 6%.
Note that the International Energy Agency (IEA) world energy investment report projected that China invested $627bn in clean energy in 2025, against $257bn in fossil fuels.
For the same sectors as the IEA report, this analysis puts the value of clean-energy investment in 2025 at a significantly more conservative $430bn. The higher figures in this analysis overall are therefore the result of wider sectoral coverage.
Electric vehicles and batteries
EVs and vehicle batteries were again the largest contributors to China’s clean-energy economy in 2025, making up an estimated 44% of value overall.
Of this total, the largest share of both total value and growth came from the production of battery EVs and plug-in hybrids, which expanded 29% year-on-year. This was followed by investment into EV manufacturing, which grew 18%, after slower growth rates in 2024.
Investment in battery manufacturing also rebounded after a drop in 2024, driven by new battery technology and strong demand from both domestic and international markets. Battery manufacturing investment grew by 35% year-on-year to 277bn yuan.
The share of electric vehicles (EVs) will have reached 12% of all vehicles on the road by the end of 2025, up from 9% a year earlier and less than 2% just five years ago.
The share of EVs in the sales of all new vehicles increased to 48%, from 41% in 2024, with passenger cars crossing the 50% threshold. In November, EV sales crossed the 60% mark in total sales and they continue to drive overall automotive sales growth, as shown below.

Electric trucks experienced a breakthrough as their market share rose from 8% in the first nine months of 2024 to 23% in the same period in 2025.
Policy support for EVs continues, for example, with a new policy aiming to nearly double charging infrastructure in the next three years.
Exports grew even faster than the domestic market, but the vast majority of EVs continue to be sold domestically. In 2025, China produced 16.6m EVs, rising 29% year-on-year. While exports accounted for only 21% or 3.4m EVs, they grew by 86% year-on-year. Top export destinations for Chinese EVs were western Europe, the Middle East and Latin America.
The value of batteries exported also grew rapidly by 41% year-on-year, becoming the third largest growth driver of the GDP. Battery exports largely went to western Europe, north America and south-east Asia.
In contrast with deflationary trends in the price of many clean-energy technologies, average EV prices have held up in 2025, with a slight increase in average price of new models, after discounts. This also means that the contribution of the EV industry to nominal GDP growth was even more significant, given that overall producer prices across the economy fell by 2.6%. Battery prices continued to drop.
Clean-power generation
The solar power sector generated 19% of the total value of the clean-energy industries in 2025, adding 2.9tn yuan ($41bn) to the national economy.
Within this, investment in new solar power plants, at 1.2tn yuan ($160bn), was the largest driver, followed by the value of solar technology exports and by the value of the power generated from solar. Investment in manufacturing continued to fall after the wave of capacity additions in 2023, reaching 0.5tn yuan ($72bn), down 23% year-on-year.
In 2025, China achieved another new record of wind and solar capacity additions. The country installed a total of 315GW solar and 119GW wind capacity, adding more solar and two times as much wind as the rest of the world combined.
Clean energy accounted for 90% of investment in power generation, with solar alone covering 50% of that. As a result, non-fossil power made up 42% of total power generation, up from 39% in 2024.
However, a new pricing policy for new solar and wind projects and modest targets for capacity growth have created uncertainty about whether the boom will continue.
Under the new policy, new clean-power generation has to compete on price against existing coal power in markets that place it at a disadvantage in some key ways.
At the same time, the electricity markets themselves are still being introduced and developed, creating investment uncertainty.
Investment in solar power generation increased year-on-year by 15%, but experienced a strong stop-and-go cycle. Developers rushed to finish projects ahead of the new pricing policy coming into force in June and then again towards the end of the year to finalise projects ahead of the end of the current 14th five-year plan.
Investment in the solar sector as a whole was stable year-on-year, with the decline in manufacturing capacity investment balanced by continued growth in power generation capacity additions. This helped shore up the utilisation of manufacturing plants, in line with the government’s aim to reduce “disorderly” price competition.
By late 2025, China’s solar manufacturing capacity reached an estimated 1,200GW per year, well ahead of the global capacity additions of around 650GW in 2025. Manufacturers can now produce far more solar panels than the global market can absorb, with fierce competition leading to historically low profitability.
China’s policymakers have sought to address the issue since mid-2024, warning against “involution”, passing regulations and convening a sector-wide meeting to put pressure on the industry. This is starting to yield results, with losses narrowing in the third quarter of 2025.
The volume of exports of solar panels and components reached a record high in 2025, growing 19% year-on-year. In particular, exports of cells and wafers increased rapidly by 94% and 52%, while panel exports grew only by 4%.
This reflects the growing diversification of solar-supply chains in the face of tariffs and with more countries around the world building out solar panel manufacturing capacity. The nominal value of exports fell 8%, however, due to a fall in average prices and a shift to exporting upstream intermediate products instead of finished panels.
Hydropower, wind and nuclear were responsible for 15% of the total value of the clean-energy sectors in 2025, adding some 2.2tn yuan ($310bn) to China’s GDP in 2025.
Nearly two-thirds of this (1.3tn yuan, $180bn) came from the value of power generation from hydropower, wind and nuclear, with investment in new power generation projects contributing the rest.
Power generation grew 33% from solar, 13% from wind, 3% from hydropower and 8% from nuclear.
Within power generation investment, solar remained the largest segment by value – as shown in the figure below – but wind-power generation projects were the largest contributor to growth, overtaking solar for the first time since 2020.
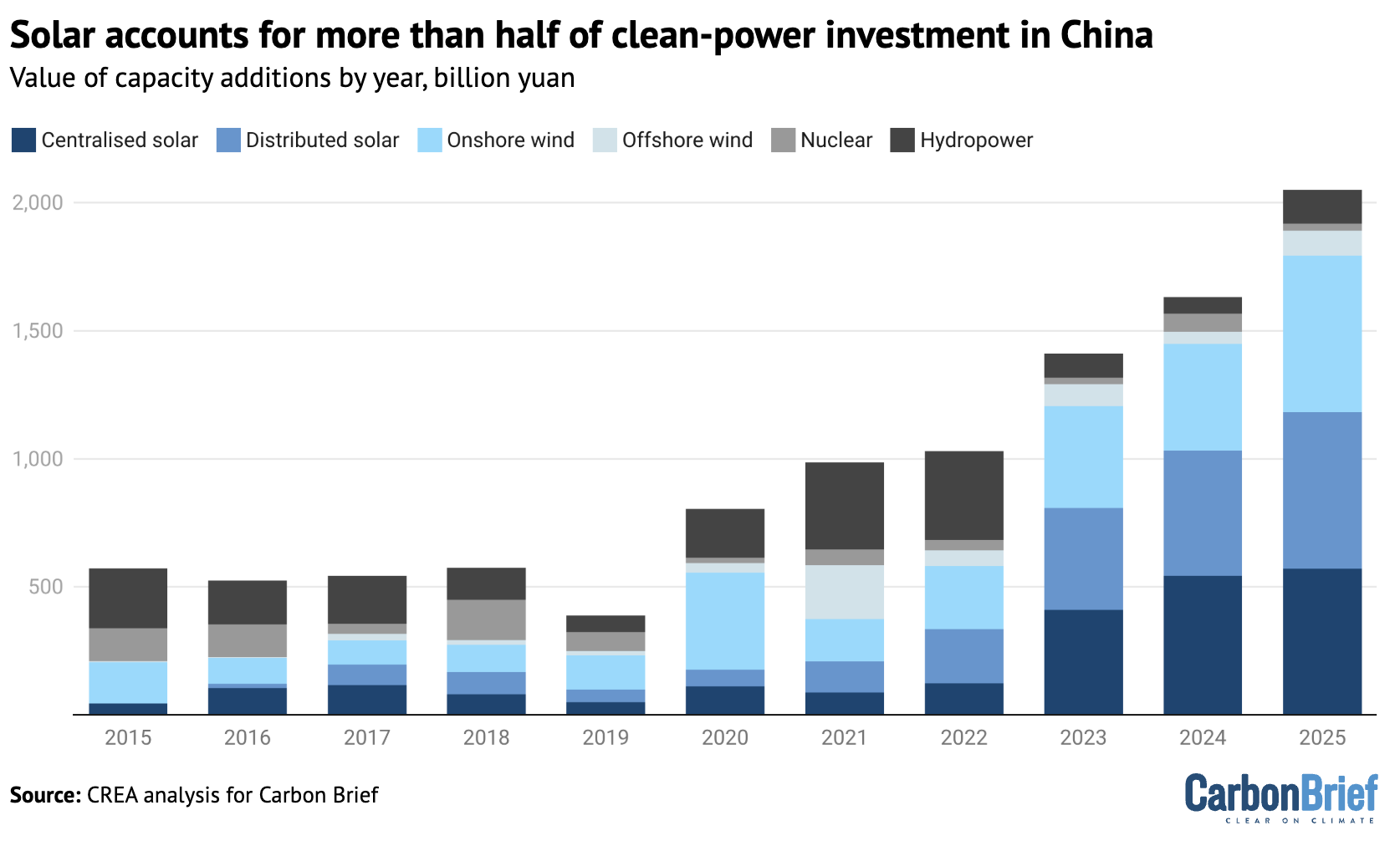
In particular, offshore wind power capacity investment rebounded as expected, doubling in 2025 after a sharp drop in 2024.
Investment in nuclear projects continued to grow but remains smaller in total terms, at 17bn yuan. Investment in conventional hydropower continued to decline by 7%.
Electricity storage and grids
Electricity transmission and storage were responsible for 6% of the total value of the clean-energy sectors in 2025, accounting for 1.0 tn yuan ($140bn).
The most valuable sub-segment was investment in power grids, growing 6% in 2025 and reaching $90bn. This was followed by investment in energy storage, including pumped hydropower, grid-connected battery storage and hydrogen production.
Investment in grid-connected batteries saw the largest year-on-year growth, increasing by 50%, while investments in electrolysers also grew by 30%. The transmission of clean power increased an estimated 13%, due to rapid growth in clean-power generation.
China’s total electricity storage capacity reached more than 213GW, with battery storage capacity crossing 145GW and pumped hydro storage at 69GW. Some 66GW of battery storage capacity was added in 2025, up 52% year-on-year and accounting for more than 40% of global capacity additions.
Notably, capacity additions accelerated in the second half of the year, with 43GW added, compared with the first half, which saw 23GW of new capacity.
The battery storage market initially slowed after the renewable power pricing policy, which banned storage mandates after May, but this was quickly replaced by a “market-driven boom”. Provincial electricity spot markets, time-of-day tariffs and increasing curtailment of solar power all improved the economics of adding storage.
By the end of 2025, China’s top five solar manufacturers had all entered the battery storage market, making a shift in industry strategy.
Investment in pumped hydropower continued to increase, with 15GW of new capacity permitted in the first half of 2025 alone and 3GW entering operation.
Railways
Rail transportation made up 12% of the GDP contribution of the clean-energy sectors, with revenue from passenger and goods rail transportation the largest source of value. Most growth came from investment in rail infrastructure, which increased 6% year-on-year
The electrification of transport is not limited to EVs, as rail passenger, freight and investment volumes saw continued growth. The total length of China’s high-speed railway network reached 50,000km in 2025, making up more than 70% of the global high-speed total.
Energy efficiency
Investment in energy efficiency rebounded strongly in 2025. Measured by the aggregate turnover of large energy service companies (ESCOs), the market expanded by 17% year-on-year, returning to growth rates last seen during 2016-2020.
Total industry turnover has also recovered to its previous peak in 2021, signalling a clear turnaround after three years of weakness.
Industry projections now anticipate annual turnover reaching 1tn yuan in annual turnover by 2030, a target that had previously been expected to be met by 2025.
China’s ESCO market has evolved into the world’s largest. Investment within China’s ESCO market remains heavily concentrated in the buildings sector, which accounts for around 50% of total activity. Industrial applications make up a further 21%, while energy supply, demand-side flexibility and energy storage together account for approximately 16%.
Implications of China’s clean-energy bet
Ongoing investment of hundreds of billions of dollars into clean-energy manufacturing represents a gigantic economic and financial bet on a continuing global energy transition.
In addition to the domestic investment covered in this article, Chinese firms are making major investments in overseas manufacturing.
The clean-energy industries have played a crucial role in meeting China’s economic targets during the five-year period ending this year, delivering an estimated 40%, 25% and 37% of all GDP growth in 2023, 2024 and 2025, respectively.
However, the developments next year and beyond are unclear, particularly for solar power generation, with the new pricing system for renewable power generation leading to a short-term slowdown and creating major uncertainty, while central government targets have been set far below current rates of clean-electricity additions.
Investment in solar-power generation and solar manufacturing declined in the second half of the year, while investment in generation clocked growth for the full year, showing the risk to the industries under the current power market set-ups that favour coal-fired power.
The reduction in the prices of clean-energy technology has been so dramatic that when the prices for GDP statistics are updated, the sectors’ contribution to real GDP – adjusted for inflation or, in this case deflation – will be revised down.
Nevertheless, the key economic role of the industry creates a strong motivation to keep the clean-energy boom going. A slowdown in the domestic market could also undermine efforts to stem overcapacity and inflame trade tensions by increasing pressure on exports to absorb supply.
A recent CREA survey of experts working on climate and energy issues in China found that the majority believe that economic and geopolitical challenges will make the “dual carbon” goals – and with that, clean-energy industries – only more important.
Local governments and state-owned enterprises will also influence the outlook for the sector. Their previous five-year plans played a key role in creating the gigantic wind and solar power “bases” that substantially exceeded the central government’s level of ambition.
Provincial governments also have a lot of leeway in implementing the new electricity markets and contracting systems for renewable power generation. The new five-year plans, to be published this year, will therefore be of major importance.
About the data
Reported investment expenditure and sales revenue has been used where available. When this is not available, estimates are based on physical volumes – gigawatts of capacity installed, number of vehicles sold – and unit costs or prices.
The contribution to real growth is tracked by adjusting for inflation using 2022-2023 prices.
All calculations and data sources are given in a worksheet.
Estimates include the contribution of clean-energy technologies to the demand for upstream inputs such as metals and chemicals.
This approach shows the contribution of the clean-energy sectors to driving economic activity, also outside the sectors themselves, and is appropriate for estimating how much lower economic growth would have been without growth in these sectors.
Double counting is avoided by only including non-overlapping points in value chains. For example, the value of EV production and investment in battery storage of electricity is included, but not the value of battery production for the domestic market, which is predominantly an input to these activities.
Similarly, the value of solar panels produced for the domestic market is not included, as it makes up a part of the value of solar power generating capacity installed in China. However, the value of solar panel and battery exports is included.
In 2025, there was a major divergence between two different measures of investment. The first, fixed asset investment, reportedly fell by 3.8%, the first drop in 35 years. In contrast, gross capital formation saw the slowest growth in that period but still inched up by 2%.
This analysis uses gross capital formation as the measure of investment, as it is the data point used for GDP accounting. However, the analysis is unable to account for changes in inventories, so the estimate of clean-energy investment is for fixed asset investment in the sectors.
The analysis does not explicitly account for the small and declining role of imports in producing clean-energy goods and services. This means that the results slightly overstate the contribution to GDP but understate the contribution to growth.
For example, one of the most important import dependencies that China has is for advanced computing chips for EVs. The value of the chips in a typical EV is $1,000 and China’s import dependency for these chips is 90%, which suggests that imported chips represent less than 3% of the value of EV production.
The estimates are likely to be conservative in some key respects. For example, Bloomberg New Energy Finance estimates “investment in the energy transition” in China in 2024 at $800bn. This estimate covers a nearly identical list of sectors to ours, but excludes manufacturing – the comparable number from our data is $600bn.
China’s National Bureau of Statistics says that the total value generated by automobile production and sales in 2023 was 11tn yuan. The estimate in this analysis for the value of EV sales in 2023 is 2.3tn yuan, or 20% of the total value of the industry, when EVs already made up 31% of vehicle production and the average selling prices for EVs was slightly higher than for internal combustion engine vehicles.
The post Analysis: Clean energy drove more than a third of China’s GDP growth in 2025 appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Clean energy drove more than a third of China’s GDP growth in 2025
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-
Renewable Energy2 years ago
GAF Energy Completes Construction of Second Manufacturing Facility












