October is National Seafood Month, a time to celebrate the incredible diversity of ocean life and the hardworking communities that rely on the ocean for food, livelihoods, recreation and other benefits. At Ocean Conservancy, we are dedicated to protecting these marine ecosystems and supporting the sustainable fisheries that rely on them. However, this year, we must also recognize the severe challenges facing one of Alaska’s most iconic and most valuable fisheries: Bering Sea snow crab. In 2022, for the first time in history, this fishery was closed due to a sudden, dramatic decline in the abundance of adult and juvenile crabs. While it was recently announced that the fishery will be reopened for the upcoming season—a welcome relief for the fishers and communities hit hard by the closures—this remains a climate-vulnerable stock. The reopening brings hope, but the collapse serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing threats climate change poses to marine ecosystems.
See more wonderful ocean animals!
Enter your email and never miss an update
What happened to the crabs?
The collapse of the Bering Sea snow crab population was swift and devastating. Following the 2018-2019 marine heatwave, nearly 47 billion crabs (yes, that’s 47 billion) disappeared from the region by 2021, representing population declines in excess of 90%. This event represents a catastrophic loss of marine life due to climate change, resulting in profound consequences for communities and marine systems in Alaska. Especially impacted is the island of St. Paul, home to the world’s largest crab processing plant. This mostly Indigenous community is highly dependent on the snow crab fishery and declared a cultural, economic and social emergency in the wake of the plant’s closure. In some cases, town officials turned to external fundraising to maintain critical municipal functions such as emergency medical services.

Understanding the mortality event
Research from NOAA Fisheries links the snow crab fishery collapse to a marine heatwave that struck the Bering Sea between 2018 and 2019. Temperature rise and associated ecological changes emerged as the key culprits. While snow crabs could tolerate the warmer waters caused by the heatwave, warmer temperatures meant higher metabolisms, requiring them to consume nearly twice as much food to meet the increased metabolic demands. At the same time, those warmer waters meant both less suitable habitats and reduced prey availability—this pushed the crabs into smaller, more densely populated areas. The combination of higher caloric demands and increased competition for limited resources led to mass starvation, which scientists have determined was the immediate cause of snow crab deaths. Bycatch and habitat impacts from the trawl fleet (which uses large trawl nets to fish on the bottom of the ocean for groundfish) are also contributing factors, and continued harvest of crab by the trawl fleet when the directed fishery is closed impedes recovery.
Borealization: an ongoing ecological shift
The changing environmental conditions and subsequent collapse of the snow crab fishery are indicative of a larger ecosystem trend known as borealization: an ecological shift poleward from Arctic to sub-Arctic—or boreal—conditions, in this case driven by anthropogenic climate change. The southeastern Bering Sea is what’s known as a marginal ice zone, meaning its ecology is deeply influenced by the presence or absence of winter sea ice. As sea ice continues to retreat due to rising temperatures from climate change, the region is shifting toward conditions more characteristic of boreal (sub-Arctic rather than Arctic) ocean ecosystems. A recent study showed that, compared to the pre-industrial era, this change to boreal conditions is more than 200 times more likely to occur now, highlighting the profound impact of climate change on these kinds of marine ecosystems.
The implications of borealization are significant for the future of marine life and resources, as evidenced by what’s happened to the snow crab fishery. With studies anticipating a future with more boreal-condition years in the Bering Sea region, the traditional grounds of this fishery may continue to shift northward. As other fish stocks move northward there is pressure from industrial fishing fleets to move north with the fish, bringing devastating impacts from bycatch, habitat destruction and disruption to predator/prey relationships. In Alaska this is particularly harmful to Alaska Native Tribes whose lives and cultures are deeply connected to a healthy ocean ecosystem.
The path forward: adaptation and resilience
A 2022 bottom-trawl survey revealed some encouraging signs for the short-term recovery in the abundance of snow crab, namely lower seafloor temperatures and a higher population of juvenile crabs. This optimism is further reinforced by the announcement that the fishery will reopen for the 2024/25 season. While this news is heartening for fishing communities, NOAA Fisheries anticipates that Arctic conditions in the southeastern Bering Sea will not persist, suggesting a double-edged sword of short-term recovery and long-term uncertainty. And to date, NOAA Fisheries and the North Pacific Fishery Management Council have not taken any steps to reduce impacts on snow crab from the trawl fleet. This reality emphasizes the need for adaptive management that can secure the future of snow crab—and other marine resources—for future generations of fishing communities, subsistence users and consumers.

Particularly, the snow crab collapse underscores the need for adaptive management strategies that account for rapid ecological changes. Traditional management models, which rely on the assumption that the future will roughly resemble the past, are increasingly unreliable in a world where climate change is driving major paradigmatic shifts across ecosystems. Instead, forward-looking scientists and managers are advocating for a more integrated and climate-ready approach that takes into account the interconnectedness of species and their habitats and for climate change. For example, the borealization index developed for the snow crab study combined several ecological indicators (including ice cover and temperature) to track the ecosystem’s transition from Arctic to boreal conditions. This kind of study could provide a template for determining the impacts of ecosystem changes on other commercially important species, a critical input for management considerations.
The collapse of the Bering Sea snow crab population is a stark reminder of the urgent need to adapt quickly and secure the future of our seafood. For fishing communities in Alaska, the closure of the snow crab fishery has been a devastating blow, but it is also a wake-up call for policymakers and managers. As we observe National Seafood Month, let us not only celebrate what the ocean provides but commit ourselves to protecting it. That means that NOAA Fisheries must continue to rebuild fisheries and provide better tools to help managers and fishers adapt to increasing climate impacts. At Ocean Conservancy, we are actively working with NOAA and other managers, scientists and communities to develop those adaptive strategies for sustainable management. By advocating for evidence-based policies and supporting conservation efforts, we are striving to protect marine biodiversity and the livelihoods of those who depend on a healthy ocean. Please consider donating to Ocean Conservancy to make a difference today.
The post The Bering Sea Snow Crab Collapse: A Climate-Driven Crisis appeared first on Ocean Conservancy.
Ocean Acidification
What is the High Seas Treaty and Why Does It Matter?
You may have seen headlines recently about a new global treaty that went into effect just as news broke that the United States would be withdrawing from a number of other international agreements. It’s a confusing time in the world of environmental policy, and Ocean Conservancy is here to help make it clearer while, of course, continuing to protect our ocean.
What is the High Seas Treaty?
The “High Seas Treaty,” formally known as the Agreement on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement, went into effect on January 17, 2026. We celebrated this win last fall, when the agreement reached the 60 ratifications required for its entry into force. (Since then, an additional 23 countries have joined!) It is the first comprehensive international legal framework dedicated to addressing the conservation and sustainable use of the high seas (the area of the ocean that lies 200 miles beyond the shorelines of individual countries).
To “ensure the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity” of these areas, the BBNJ addresses four core pillars of ocean governance:
- Marine genetic resources: The high seas contain genetic resources (genes of plants, animals and microbes) of great value for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and food production. The treaty will ensure benefits accrued from the development of these resources are shared equitably amongst nations.
- Area-based management tools such as the establishment of marine protected areas (MPAs) in international waters. Protecting important areas of the ocean is essential for healthy and resilient ecosystems and marine biodiversity.
- Environmental impact assessments (EIA) will allow us to better understand the potential impacts of proposed activities that may harm the ocean so that they can be managed appropriately.
- Capacity-building and the transfer of marine technology with particular emphasis on supporting developing states. This section of the treaty is designed to ensure all nations benefit from the conservation and sustainable use of marine biodiversity through, for example, the sharing of scientific information.
Get Ocean Updates in Your Inbox
Sign up with your email and never miss an update.
Why is the High Seas Treaty Important?
The BBNJ agreement is legally binding for the countries that have ratified it and is the culmination of nearly two decades of negotiations. Its enactment is a historic milestone for global ocean governance and a significant advancement in the collective protection of marine ecosystems.
The high seas represent about two-thirds of the global ocean, and yet less than 10% of this area is currently protected. This has meant that the high seas have been vulnerable to unregulated or illegal fishing activities and unregulated waste disposal. Recognizing a major governance gap for nearly half of the planet, the agreement puts in place a legal framework to conserve biodiversity.
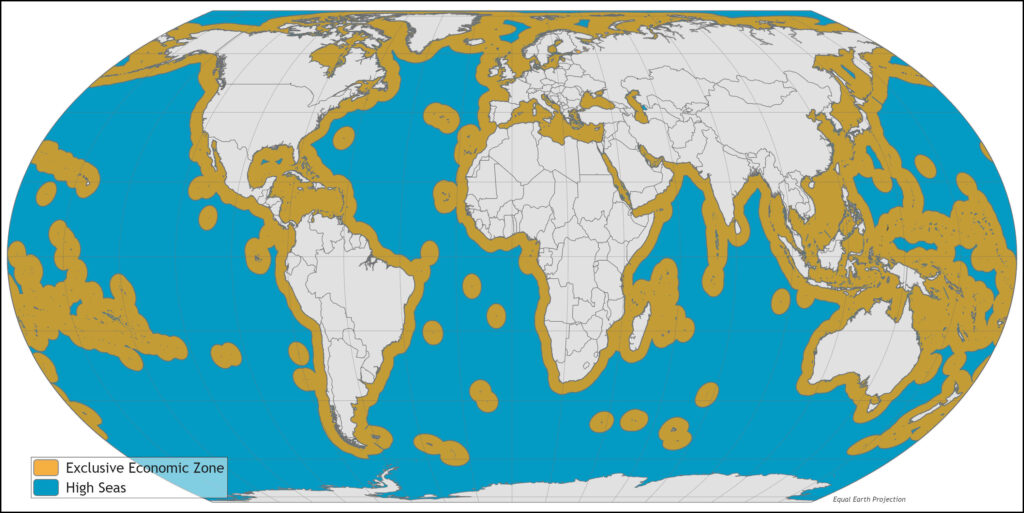
As it promotes strengthened international cooperation and accountability, the agreement will establish safeguards aimed at preventing and reversing ocean degradation and promoting ecosystem restoration. Furthermore, it will mobilize the international community to develop new legal, scientific, financial and compliance mechanisms, while reinforcing coordination among existing treaties, institutions and organizations to address long-standing governance gaps.
How is Ocean Conservancy Supporting the BBNJ Agreement?
Addressing the global biodiversity crisis is a key focal area for Ocean Conservancy, and the BBNJ agreement adds important new tools to the marine conservation toolbox and a global commitment to better protect the ocean.
Ocean Conservancy’s efforts to protect the “ocean twilight zone”—an area of the ocean 200-1000m (600-3000 ft) below the surface—is a good example of why the BBNJ agreement is so important. The ocean twilight zone (also known as the mesopelagic zone) harbors incredible marine biodiversity, regulates the climate and supports the health of ocean ecosystems. By some estimates, more than 90% of the fish biomass in the ocean resides in the ocean twilight zone, attracting the interest of those eager to develop new sources of protein for use in aquaculture feed and pet foods.
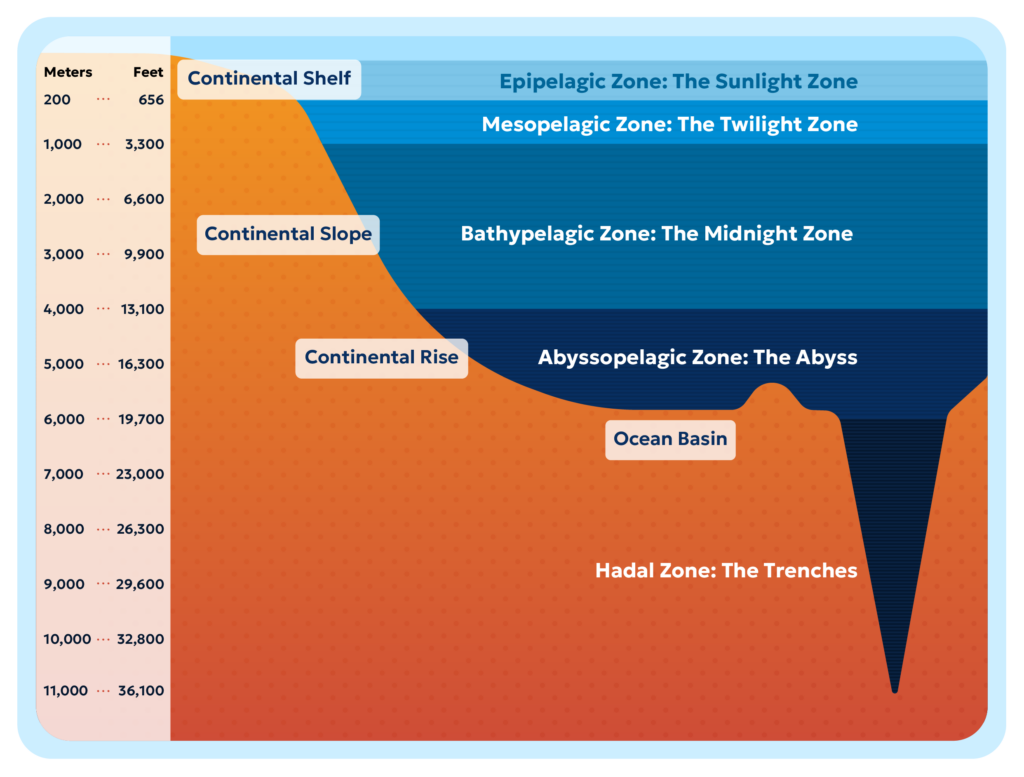
Done poorly, such development could have major ramifications for the health of our planet, jeopardizing the critical role these species play in regulating the planet’s climate and sustaining commercially and ecologically significant marine species. Species such as tunas (the world’s most valuable fishery), swordfish, salmon, sharks and whales depend upon mesopelagic species as a source of food. Mesopelagic organisms would also be vulnerable to other proposed activities including deep-sea mining.
A significant portion of the ocean twilight zone is in the high seas, and science and policy experts have identified key gaps in ocean governance that make this area particularly vulnerable to future exploitation. The BBNJ agreement’s provisions to assess the impacts of new activities on the high seas before exploitation begins (via EIAs) as well as the ability to proactively protect this area can help ensure the important services the ocean twilight zone provides to our planet continue well into the future.
What’s Next?
Notably, the United States has not ratified the treaty, and, in fact, just a few days before it went into effect, the United States announced its withdrawal from several important international forums, including many focused on the environment. While we at Ocean Conservancy were disappointed by this announcement, there is no doubt that the work will continue.
With the agreement now in force, the first Conference of the Parties (COP1), also referred to as the BBNJ COP, will convene within the next year and will play a critical role in finalizing implementation, compliance and operational details under the agreement. Ocean Conservancy will work with partners to ensure implementation of the agreement is up to the challenge of the global biodiversity crisis.
The post What is the High Seas Treaty and Why Does It Matter? appeared first on Ocean Conservancy.
https://oceanconservancy.org/blog/2026/02/25/high-seas-treaty/
Ocean Acidification
Hälsningar från Åland och Husö biological station
On Åland, the seasons change quickly and vividly. In summer, the nights never really grow dark as the sun hovers just below the horizon. Only a few months later, autumn creeps in and softly cloaks the island in darkness again. The rhythm of the seasons is mirrored by the biological station itself; researchers, professors, and students arrive and depart, bringing with them microscopes, incubators, mesocosms, and field gear to study the local flora and fauna peaking in the mid of summer.
This year’s GAME project is the final chapter of a series of studies on light pollution. Together, we, Pauline & Linus, are studying the effects of artificial light at night (ALAN) on epiphytic filamentous algae. Like the GAME site in Japan, Akkeshi, the biological station Husö here on Åland experiences very little light pollution, making it an ideal place to investigate this subject.
We started our journey at the end of April 2025, just as the islands were waking up from winter. The trees were still bare, the mornings frosty, and the streets quiet. Pauline, a Marine Biology Master’s student from the University of Algarve in Portugal, arrived first and was welcomed by Tony Cederberg, the station manager. Spending the first night alone on the station was unique before the bustle of the project began.
Linus, a Marine Biology Master’s student at Åbo Akademi University in Finland, joined the next day. Husö is the university’s field station and therefore Linus has been here for courses already. However, he was excited to spend a longer stretch at the station and to make the place feel like a second home.

Our first days were spent digging through cupboards and sheds, reusing old materials and tools from previous years, and preparing the frames used by GAME 2023. We chose Hamnsundet as our experimental site, (i.e. the same site that was used for GAME 2023), which is located at the northeast of Åland on the outer archipelago roughly 40 km from Husö. We got permission to deploy the experiments by the local coast guard station, which was perfect. The location is sheltered from strong winds, has electricity access, can be reached by car, and provides the salinity conditions needed for our macroalga, Fucus vesiculosus, to survive.
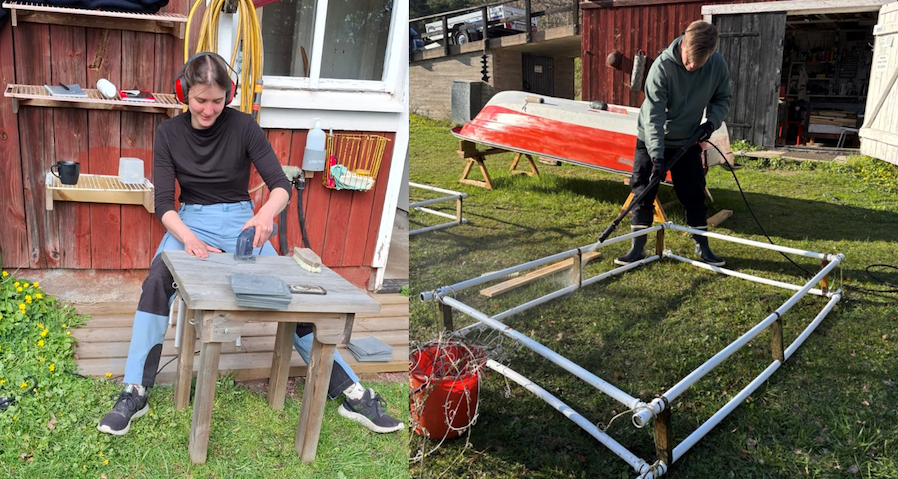

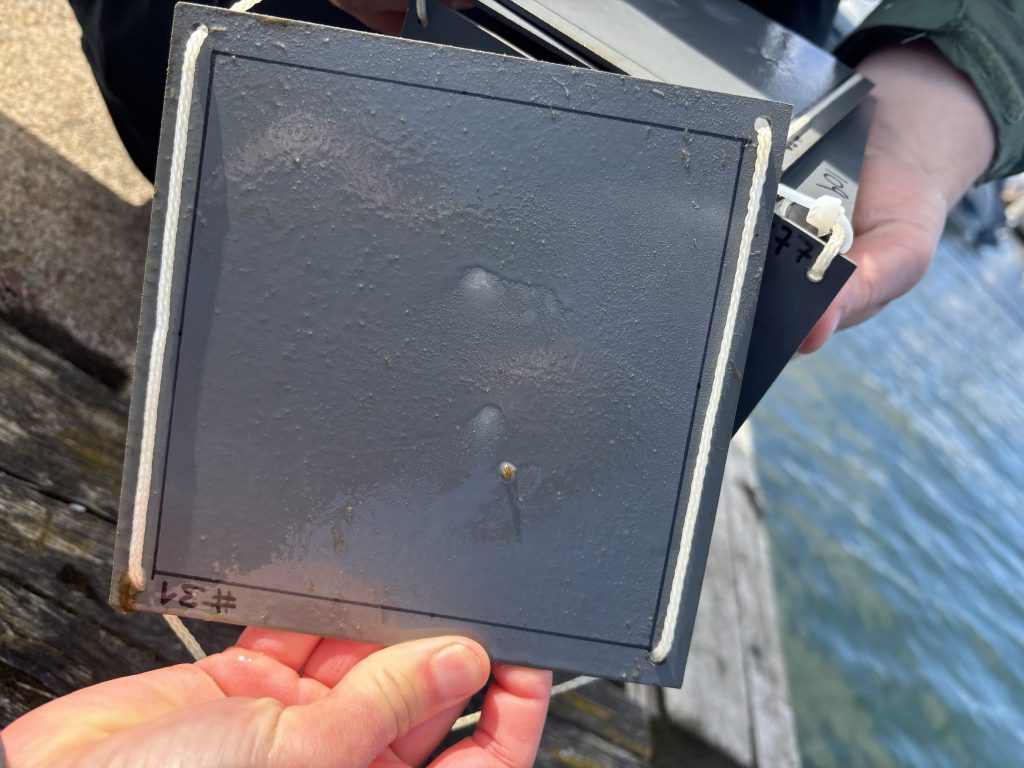
To assess the conditions at the experimental site, we deployed a first set of settlement panels in late April. At first, colonization was slow; only a faint biofilm appeared within two weeks. With the water temperature being still around 7 °C, we decided to give nature more time. Meanwhile, we collected Fucus individuals and practiced the cleaning and the standardizing of the algal thalli for the experiment. Scraping epiphytes off each thallus piece was fiddly, and agreeing on one method was crucial to make sure our results would be comparable to those of other GAME teams.

By early May, building the light setup was a project in itself. Sawing, drilling, testing LEDs, and learning how to secure a 5-meter wooden beam over the water. Our first version bent and twisted until the light pointed sideways instead of straight down onto the algae. Only after buying thicker beams and rebuilding the structure, we finally got a stable and functional setup that could withstand heavy rain and wind. The day we deployed our first experiment at Hamnsundet was cold and rainy but also very rewarding!


Outside of work, we made the most of the island life. We explored Åland by bike, kayak, rowboat, and hiking, visited Ramsholmen National Park during the ramson/ wild garlic bloom, and hiked in Geta with its impressive rock formations and went out boating and fishing in the archipelago. At the station on Husö, cooking became a social event: baking sourdough bread, turning rhubarb from the garden into pies, grilling and making all kind of mushroom dishes. These breaks, in the kitchen and in nature, helped us recharge for the long lab sessions to come.

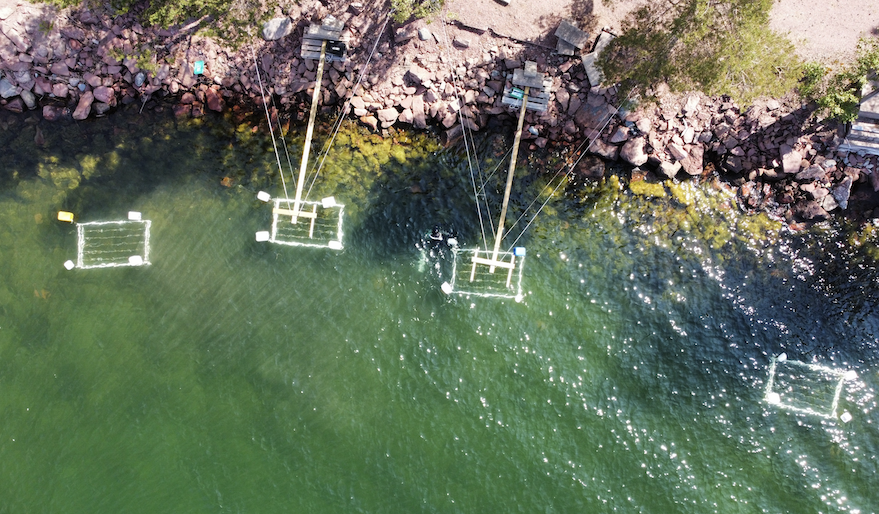
Every two weeks, it was time to collect and process samples. Snorkeling to the frames, cutting the Fucus and the PVC plates from the lines, and transferring each piece into a freezer bag became our routine. Sampling one experiment took us 4 days and processing all the replicates in the lab easily filled an entire week. The filtering and scraping process was even more time-consuming than we had imagined. It turned out that epiphyte soup is quite thick and clogs filters fastly. This was frustrating at times, since it slowed us down massively.
Over the months, the general community in the water changed drastically. In June, water was still at 10 °C, Fucus carried only a thin layer of diatoms and some very persistent and hard too scrape brown algae (Elachista). In July, everything suddenly exploded: green algae, brown algae, diatoms, cyanobacteria, and tiny zooplankton clogged our filters. With a doubled filtering setup and 6 filtering units, we hoped to compensate for the additional growth.
However, what we had planned as “moderate lab days” turned into marathon sessions. In August, at nearly 20 °C, the Fucus was looking surprisingly clean, but on the PVC a clear winner had emerged. The panels were overrun with the green alga Ulva and looked like the lawn at an abandoned house. Here it was not enough to simply filter the solution, but bigger pieces had to be dried separately. In September, we concluded the last experiment with the help of Sarah from the Cape Verde team, as it was not possible for her to continue on São Vicente, the Cape Verdean island that was most affected by a tropical storm. Our final experiment brought yet another change into community now dominated by brown algae and diatoms. Thankfully our new recruit, sunny autumn weather, and mushroom picking on the side made the last push enjoyable.

By the end of summer, we had accomplished four full experiments. The days were sometimes exhausting but also incredibly rewarding. We learned not only about the ecological effects of artificial light at night, but also about the very practical side of marine research; planning, troubleshooting, and the patience it takes when filtering a few samples can occupy half a day.

Ocean Acidification
What is Coral Bleaching and Why is it Bad News for Coral Reefs?
Coral reefs are beautiful, vibrant ecosystems and a cornerstone of a healthy ocean. Often called the “rainforests of the sea,” they support an extraordinary diversity of marine life from fish and crustaceans to mollusks, sea turtles and more. Although reefs cover less than 1% of the ocean floor, they provide critical habitat for roughly 25% of all ocean species.
Coral reefs are also essential to human wellbeing. These structures reduce the force of waves before they reach shore, providing communities with vital protection from extreme weather such as hurricanes and cyclones. It is estimated that reefs safeguard hundreds of millions of people in more than 100 countries.
What is coral bleaching?
A key component of coral reefs are coral polyps—tiny soft bodied animals related to jellyfish and anemones. What we think of as coral reefs are actually colonies of hundreds to thousands of individual polyps. In hard corals, these tiny animals produce a rigid skeleton made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). The calcium carbonate provides a hard outer structure that protects the soft parts of the coral. These hard corals are the primary building blocks of coral reefs, unlike their soft coral relatives that don’t secrete any calcium carbonate.
Coral reefs get their bright colors from tiny algae called zooxanthellae. The coral polyps themselves are transparent, and they depend on zooxanthellae for food. In return, the coral polyp provides the zooxanethellae with shelter and protection, a symbiotic relationship that keeps the greater reefs healthy and thriving.
When corals experience stress, like pollution and ocean warming, they can expel their zooxanthellae. Without the zooxanthellae, corals lose their color and turn white, a process known as coral bleaching. If bleaching continues for too long, the coral reef can starve and die.
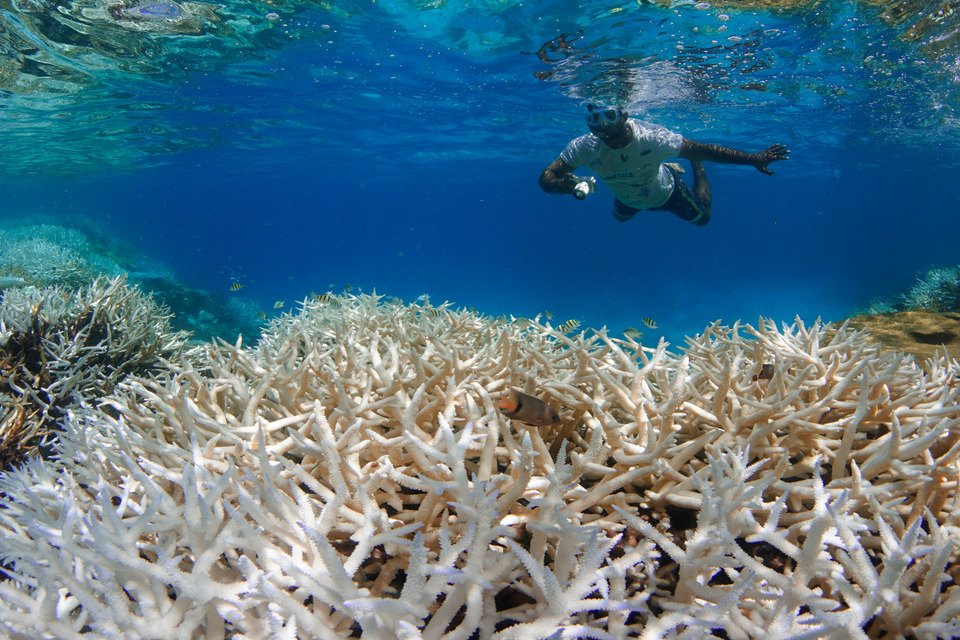

Ocean warming and coral bleaching
Human-driven stressors, especially ocean warming, threaten the long-term survival of coral reefs. An alarming 77% of the world’s reef areas are already affected by bleaching-level heat stress.
The Great Barrier Reef is a stark example of the catastrophic impacts of coral bleaching. The Great Barrier Reef is made up of 3,000 reefs and is home to thousands of species of marine life. In 2025, the Great Barrier Reef experienced its sixth mass bleaching since 2016. It should also be noted that coral bleaching events are a new thing because of ocean warming, with the first documented in 1998.
Get Ocean Updates in Your Inbox
Sign up with your email and never miss an update.
How you can help
The planet is changing rapidly, and the stakes have never been higher. The ocean has absorbed roughly 90% of the excess heat caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, and the consequences, including coral die-offs, are already visible. With just 2℃ of planetary warming, global coral reef losses are estimated to be up to 99% — and without significant change, the world is on track for 2.8°C of warming by century’s end.
To stop coral bleaching, we need to address the climate crisis head on. A recent study from Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the first of its kind to include damage to ocean ecosystems into the economic cost of climate change – resulting in nearly a doubling in the social cost of carbon. This is the first time the ocean was considered in terms of economic harm caused by greenhouse gas emissions, despite the widespread degradation to ocean ecosystems like coral reefs and the millions of people impacted globally.
This is why Ocean Conservancy advocates for phasing out harmful offshore oil and gas and transitioning to clean ocean energy. In this endeavor, Ocean Conservancy also leads international efforts to eliminate emissions from the global shipping industry—responsible for roughly 1 billion tons of carbon dioxide every year.
But we cannot do this work without your help. We need leaders at every level to recognize that the ocean must be part of the solution to the climate crisis. Reach out to your elected officials and demand ocean-climate action now.
The post What is Coral Bleaching and Why is it Bad News for Coral Reefs? appeared first on Ocean Conservancy.
What is Coral Bleaching and Why is it Bad News for Coral Reefs?
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits


