Norway: A Hydropower Wonderland
Norway, the land of majestic fjords, breathtaking mountains, and charming fishing villages, also boasts a title less widely known but equally impressive: the hydropower capital of Europe.
With its abundant rainfall and rugged topography, Norway has harnessed the power of water to become a global leader in clean and sustainable energy generation.
A Legacy of Hydropower:
- 96% of Norway’s electricity comes from hydropower, a staggering figure compared to the global average of around 16%. This dependence on hydro began in the late 19th century, driven by the need for energy for industrialization.
- Over 1,500 hydropower plants dot the Norwegian landscape, from the snow-capped peaks of the north to the lush valleys of the south. These plants range in size, with some generating enough electricity for entire towns, while others feed into the national grid.
Norway’s Hydropower Journey: From Waterfall Thunder to Clean Energy Leader
Norway’s embrace of hydropower is a captivating saga, intertwined with industrialization, innovation, and a deep respect for the natural world. Let’s trace the path of this remarkable journey:
Early Sparks (19th Century):
- 1870s: The seeds are sown with early electricity experiments and the establishment of Norway’s first small hydro plants.
- 1891: Hammerfest, nestled above the Arctic Circle, takes the plunge, becoming the first town lit by hydropower.
- 1892: Prime Minister Knutsen champions national electricity generation, advocating for hydro as the clean and sustainable choice.
Industrial Takeoff (Early 20th Century):
- 1905: Independence paves the way for rapid industrialization, fueling the demand for clean energy.
- 1911: Vemork power plant near Rjukan, then the world’s largest, powers fertilizer production and lays the foundation for a burgeoning industry.
- 1920s: Hydropower reaches every corner of the country, transforming rural communities and powering urban growth.
Golden Age and Expansion (Mid-20th Century):
- 1950s-1980s: A national hydropower boom sees massive capacity expansion, with iconic projects like Folgefonn and Glomfjord.
- 1960s: Surplus electricity fuels export agreements, solidifying Norway’s position as a regional energy supplier.
- 1970s: Environmental concerns emerge, leading to stricter regulations and a focus on cleaner technologies.
Modern Challenges and Advancements (21st Century):
- Balancing Demand and Supply: Fluctuations in renewable resources necessitate innovative solutions like pumped storage and smart grid technologies.
- Environmental Impact: Striking a balance between energy needs and preserving ecosystems is crucial, with careful planning and mitigation strategies.
- Sharing Knowledge: Norway’s expertise is actively shared, providing valuable lessons for other countries transitioning to clean energy.
The Future Unfolds:
As climate change casts its shadow, Norway’s commitment to hydropower remains firm, but with a focus on increased efficiency, environmental sustainability, and integration with other renewable sources. The legacy of the waterfall pioneers continues to guide Norway on its path to a clean and vibrant future.
Hydroelectric Power Plant in Norway
A Hydroelectric Wonderland: Exploring Norway’s Mighty Power Plants
Norway’s majestic landscape isn’t just about breathtaking fjords and snow-capped peaks. Dotted throughout the country are hundreds of hydroelectric power plants, silent giants harnessing the power of rushing water to provide clean energy.
These marvels of engineering not only illuminate homes and fuel industries, but also stand as testaments to Norway’s commitment to a sustainable future.
Powering the Fjords: More Mighty Hydroelectric Wonders of Norway
1. Aurland Hydroelectric Power Station:
Nestled within the Aurlandsdalen valley, this colossal complex is a true powerhouse. Comprising three separate plants – Aurland 1, 2, and 3 – it boasts a combined capacity of 1,128 MW, making it the second-largest in Norway. Imagine the sheer force of water coursing through its turbines, generating enough electricity to power over a million homes! The iconic Stegastein viewpoint offers jaw-dropping panoramas of Aurland 2, the power station blending seamlessly with the dramatic beauty of the valley.
2. Sima Kraftverk:
Venture deep inside a mountain near Odda and you’ll discover Sima Kraftverk, a testament to human ingenuity. This remarkable power station utilizes a 1,483-meter-long pressure tunnel, carving its way through the heart of the mountain. This makes it the deepest power station in Europe, its turbines whirring with the power of water plummeting from a staggering height. The entrance to the power station itself is a sight to behold, a stark concrete portal contrasting with the surrounding natural splendor.
3. Folgefonn Hydroelectric Power Station:
Located near Hardangerfjord, Folgefonn harnesses the power of one of Norway’s largest glaciers, the Folgefonn. Imagine glacial meltwater rushing through tunnels and pipes, channeled into turbines that generate 522 MW of clean energy. This power station plays a vital role in supplying western Norway, its contribution evident in the brightly lit towns and thriving industries. Standing at the dam, the vast expanse of the Folgefonn glacier stretching towards the horizon is a powerful reminder of the natural forces at play.
4. Morkedalselva Hydroelectric Power Station:
Head north to Nord-Trøndelag county and you’ll encounter Morkedalselva, a series of three power plants built over several decades. With a combined capacity of 824 MW, it’s a major contributor to the national grid. Its dams and reservoirs create stunning artificial lakes, their mirror-like surfaces reflecting the surrounding mountains and forests. Picture kayakers paddling peacefully across the water, surrounded by the serene beauty of nature.
5. Nedre Otta Hydroelectric Power Station:
Travel back in time to Oppland county and you’ll find Nedre Otta, a classic example of early 20th-century hydroelectric engineering. Built in 1914, it played a crucial role in powering Norway’s industrialization. Its red brick facade and sturdy construction exude a timeless charm, a reminder of the pioneering spirit that fueled Norway’s transition to clean energy. Imagine the excitement when the first lights flickered on in homes and factories, powered by the mighty Otta River.
6. Kvilldal Hydroelectric Power Station:
Hidden within the mountains of Rogaland, Kvilldal reigns supreme as the most powerful hydroelectric plant in Norway. This behemoth boasts four Francis turbines, generating a staggering 1,240 MW – enough to illuminate over 1.2 million homes! Picture the sheer volume of water cascading through its tunnels, churning the turbines with raw power. Kvilldal’s intricate water system, utilizing both natural reservoirs and man-made tunnels, is a fascinating example of engineering expertise.
7. Saurdal Hydroelectric Power Station:
In the lush valleys of Rogaland, another hydropower giant stands tall: Saurdal. Its 640 MW capacity plays a crucial role in powering homes and industries across the region. Imagine the serene contrast between the power station’s sleek, modern design and the surrounding verdant meadows, showcasing the potential for clean energy to coexist with nature. Saurdal also boasts an innovative pumped-storage system, allowing it to store excess energy during off-peak hours and release it when demand increases, a testament to Norway’s commitment to flexible and sustainable energy solutions.
8. Vemork Power Station:
Travel back in time to Rjukan, where history and hydropower intertwine at the iconic Vemork power station. Built in 1911, it was once the world’s largest, powering a fertilizer factory and illuminating homes during a time of rapid industrialization. Its impact on Norway’s development is undeniable, making it a landmark of ingenuity and innovation. Today, Vemork serves as a museum, showcasing the evolution of hydropower and its role in shaping the nation’s future.
9. Glomfjord Hydroelectric Power Station:
In the heart of Northern Norway, amidst snow-capped mountains and dramatic fjords, lies Glomfjord. This massive complex, constructed in the 1940s, holds the title of the largest pumped-storage facility in the world. Imagine vast reservoirs nestled high in the mountains, connected by a network of tunnels, ready to unleash their stored energy when needed. Glomfjord plays a crucial role in balancing the Norwegian grid, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of clean electricity even during fluctuating demand periods.
These are just a few of the countless hydroelectric power plants that grace Norway’s landscape. Each one embodies a unique story of innovation, environmental consciousness, and dedication to sustainable energy. As you explore this majestic country, keep your eyes peeled for these silent giants, for they are not just power stations, but symbols of Norway’s commitment to a brighter, cleaner future.
Whether you’re an engineer fascinated by the technology, an environmentalist passionate about clean energy, or simply a traveler intrigued by human ingenuity, Norway’s hydroelectric power plants offer something for everyone. So, embark on your own hydro adventure, explore these fascinating structures, and let the power of nature inspire you.
Norway’s Majestic Hydroelectric Powerhouses: A Tabular View
Norway’s landscape is not just painted by breathtaking fjords and snow-capped mountains, but also dotted with awe-inspiring hydroelectric power plants. These remarkable feats of engineering harness the power of rushing water to provide clean energy, illuminating homes, fueling industries, and standing as testaments to the country’s commitment to a sustainable future. Let’s explore some of these mighty marvels through a detailed table:
| Power Station | Location | Capacity (MW) | Key Features | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aurland Hydroelectric Power Station | Aurlandsdalen valley | 1,128 | Second-largest in Norway, three separate plants, breathtaking Stegastein viewpoint | |
| Sima Kraftverk | Near Odda | 185 | Deepest power station in Europe (1,483m pressure tunnel), unique mountain location, popular tourist destination | |
| Folgefonn Hydroelectric Power Station | Near Hardangerfjord | 522 | Harnesses power of Folgefonn glacier, major contributor to western Norway, picturesque dam and reservoir | |
| Morkedalselva Hydroelectric Power Station | Nord-Trøndelag county | 824 | Series of three plants built over decades, stunning artificial lakes, recreational opportunities | |
| Nedre Otta Hydroelectric Power Station | Oppland county | 150 | Classic 20th-century example, powered Norway’s industrialization, historical significance | |
| Kvilldal Hydroelectric Power Station | Rogaland | 1,240 | Most powerful in Norway, intricate water system, hidden within mountains | |
| Saurdal Hydroelectric Power Station | Rogaland | 640 | Modern design amidst verdant meadows, innovative pumped-storage system | |
| Vemork Power Station | Rjukan | 150 | Once the world’s largest, powered fertilizer factory, historical landmark and museum | |
| Glomfjord Hydroelectric Power Station | Northern Norway | 1,450 | Largest pumped-storage facility in the world, vast reservoirs and tunnel network, balances the national grid |
This table offers a glimpse into the diversity and impressive capabilities of Norway’s hydroelectric power plants. From awe-inspiring capacity to historical significance and innovative solutions, each one tells a unique story within the wider narrative of clean energy and a sustainable future.
Benefits of Hydropower In Norway
Here is the Benefits of Hydropower In Norway
- Renewable and Clean: Unlike fossil fuels, hydropower is a renewable energy source that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions. This makes it a crucial player in the fight against climate change.
- Reliable and Stable: Hydropower plants can be easily adjusted to meet changing electricity demands, providing a stable and reliable source of power. This is particularly important for Norway’s energy-intensive industries, such as aluminum production.
- Economic Engine: The hydropower industry is a major driver of the Norwegian economy, creating jobs in construction, operation, and maintenance. It also generates significant export revenue, as Norway sells surplus electricity to neighboring countries.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Environmental Impact: While generally considered clean, hydropower projects can have negative environmental impacts on ecosystems and local communities. The construction of dams and reservoirs can disrupt fish migration patterns and flood valuable land.
- Social Impact: Resettlement of communities and cultural heritage loss can be associated with hydropower projects.
- Balancing Demand and Supply: Managing the water flow in reservoirs to meet seasonal electricity demand fluctuations can be challenging.
Data Highlights:
- Electricity generation: 122.7 TWh (2020)
- Installed hydropower capacity: 33 GW (2020)
- Average annual precipitation: 1,322 mm
- Number of rivers suitable for hydropower: Over 25,000
Norway’s Hydropower – A Statistical Powerhouse
Norway’s reliance on hydropower is as impressive as its majestic fjords. Let’s dive into some key statistics highlighting this clean energy dominance:
Generation:
- 96% of Norway’s electricity comes from hydropower, dwarfing the global average of 16%.
- 122.7 TWh of electricity generated in 2020, enough to power over 12 million homes annually.
- 143.7 TWh record high achieved in 2021, showcasing potential production.
Capacity:
- 33 GW of installed hydropower capacity as of 2020, making Norway a European leader.
- Over 1,500 hydropower plants spread across the country, from mighty giants to local contributors.
- 84 large hydropower plants (over 100 MW), ensuring significant baseload supply.
Resources:
- 1,322 mm average annual precipitation across Norway, fueling the hydro potential.
- Over 25,000 rivers deemed suitable for hydropower development, a vast untapped resource.
Economic Impact:
- Hydropower industry is a major economic driver, creating jobs in construction, operation, and maintenance.
- Significant export revenue generated by selling surplus electricity to neighboring countries.
Challenges:
- Environmental impact of dams and reservoirs on ecosystems and local communities needs careful consideration.
- Balancing water flow in reservoirs to meet fluctuating demand can be challenging.
- Social impact of potential resettlement and cultural heritage loss must be addressed with sensitivity.
Future:
- Research and development aimed at improving efficiency and environmental sustainability of hydropower plants.
- Exploring pumped-hydro storage solutions to address demand fluctuations.
- Norway’s leadership in hydropower inspires other countries aiming towards clean energy goals.
Norway’s Hydropower: A Statistical Overview
| Statistic | Value | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity Generation | |||
| * Share of total electricity | 96% | % | 2020 |
| * Annual production | 122.7 | TWh | 2020 |
| * Record high annual production | 143.7 | TWh | 2021 |
| Hydropower Capacity | |||
| * Installed capacity | 33 | GW | 2020 |
| * Number of plants | > 1,500 | ||
| * Large plants (over 100 MW) | 84 | ||
| Water Resources | |||
| * Average annual precipitation | 1,322 | mm | |
| * Rivers suitable for hydropower | > 25,000 |
Key Takeaway:
Norway’s hydropower statistics paint a picture of a clean energy champion, relying heavily on this renewable resource. However, balancing environmental and social considerations remains crucial for sustainable development.
This comprehensive statistical overview, I hope, provides a clear understanding of the strength and complexities of Norway’s hydropower landscape.
Norway’s Hydropower Landscape: A Model for the World
The Future of Hydropower in Norway:
Hydropower remains a cornerstone of Norway’s energy strategy. The country is continuously investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and environmental sustainability of its hydropower plants. Additionally, exploring pumped-hydro storage to address the issue of fluctuating demand is being actively pursued.
Norway’s success in harnessing hydropower offers valuable lessons for other countries seeking to transition to clean energy. By carefully considering the environmental and social impacts of hydropower projects, and by investing in technological advancements, Norway can continue to be a leader in sustainable energy generation and inspire others to follow suit.
Norway’s hydropower landscape is a testament to the country’s commitment to clean energy and sustainable development. By harnessing the power of its abundant water resources, Norway has not only secured its own energy independence but also provided a model for other countries aspiring to a greener future.
https://www.exaputra.com/2024/01/norway-hydro-energy-lansdcape.html
Renewable Energy
Should We Appease MAGA by Rewriting the Constitution?
 Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Do you think this will change American lives for the better? If so, how?
Rewriting the U.S. Constitution will take some work, as I’m sure you’re aware.
Renewable Energy
California’s Next Governor?
 What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
Yes, we have traffic, which we hate. But that’s because everybody and his dog wants to be here for our economic opportunities and our natural beauty.
In general, we reject racism, ignorance, corruption, and environmental destruction.
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
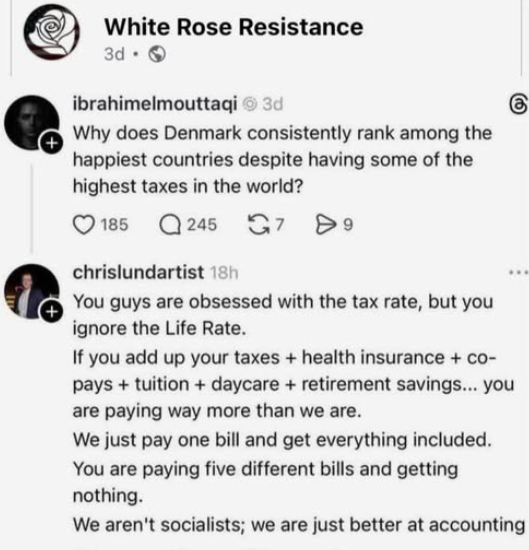 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
















