Renewable Energy In United States of Amerika
The United States is a federal republic located in North America, consisting of 50 states, a federal district, and several territories. It is the third-largest country in the world by population, with over 330 million people.
The country has a diverse geography, ranging from the Appalachian Mountains in the east to the Rocky Mountains in the west, and from the frozen tundras of Alaska to the sunny beaches of Hawaii. The country is bordered by Canada to the north, Mexico to the south, and the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans to the east and west, respectively.
The United States is known for its rich history, having been colonized by European powers in the 16th and 17th centuries before gaining independence from Great Britain in 1776. The country has played a significant role in global events such as World War I and II, and has been a superpower in the post-war era.
The United States is a diverse and multicultural country, with a large immigrant population from all over the world. It is home to many famous landmarks, such as the Statue of Liberty, the Golden Gate Bridge, and Mount Rushmore. The country is also known for its iconic institutions, such as Hollywood, the Ivy League universities, and the Smithsonian museums.
The United States is a global economic power, with the world’s largest economy in terms of gross domestic product (GDP). It is also home to many of the world’s largest corporations and is a leader in technological innovation.
The government of the United States is a federal republic with a presidential system. The country has a complex system of checks and balances between its three branches of government – the executive, legislative, and judicial – which is designed to ensure that no one branch of government has too much power.
Overall, the United States is a vast and diverse country with a rich history and culture, and is known for its economic and political power on the world stage.
The United States’ Vision of Renewable Energy
The United States’ vision of renewable energy is centered around the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy system that reduces the country’s dependence on fossil fuels, mitigates climate change, and creates new jobs and economic opportunities.
The country has set ambitious goals to increase the use of renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, geothermal, and hydropower, and to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in order to address the urgent challenge of climate change. In 2021, the Biden administration announced a goal to achieve a carbon-free power sector by 2035, and to achieve a net-zero economy-wide emissions target by 2050.
To achieve these goals, the country is investing in research and development, incentivizing the deployment of renewable energy technologies, and encouraging innovation in the private sector. There are also various tax credits, subsidies, and grants available to individuals and businesses that invest in renewable energy projects, such as installing solar panels on rooftops or developing wind farms.
The United States’ vision of renewable energy also emphasizes the need to ensure that the benefits of the transition to a clean energy economy are shared equitably, and that communities that have historically been impacted by fossil fuel extraction and pollution are not left behind.
Implementation of Renewable Energy in the United States government
The United States government has implemented several policies and programs to promote the development and use of renewable energy in the country.
Here are some examples:
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): Some states in the United States have adopted RPS policies that require utilities to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable energy sources. This has helped to increase the demand for renewable energy and incentivize the development of new renewable energy projects.
Investment Tax Credits (ITC): The federal government has offered ITCs for solar, wind, and other renewable energy projects. The ITC reduces the tax liability of individuals and businesses that invest in renewable energy, making it more attractive to invest in these projects.
Department of Energy (DOE) programs: The DOE has several programs that provide funding and technical assistance to promote the development of renewable energy. For example, the SunShot Initiative is aimed at reducing the cost of solar energy, and the Wind Energy Technologies Office supports research and development of wind energy.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations: The EPA has implemented regulations such as the Clean Power Plan, which sets targets for reducing carbon emissions from power plants. This has incentivized utilities to shift towards renewable energy sources to meet these targets.
Department of Defense (DOD) initiatives: The DOD has implemented initiatives to increase the use of renewable energy on military bases and reduce the military’s dependence on fossil fuels. This has helped to increase the demand for renewable energy and drive down costs.
The United States government has implemented a range of policies and programs to promote the development and use of renewable energy in the country. While progress has been made, there is still a long way to go to achieve the goal of a carbon-free power sector by 2035 and a net-zero economy-wide emissions target by 2050.
United States Nett Zero Carbon Target
In January 2021, President Joe Biden signed an executive order to rejoin the Paris Agreement on climate change, which commits the United States to reaching net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. This is a significant commitment, as the United States is one of the world’s largest emitters of greenhouse gases and its participation in global climate efforts is critical to addressing the global climate crisis.
Achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 will require a significant and rapid transformation of the United States’ energy system. To achieve this goal, the Biden administration has proposed a range of measures to accelerate the deployment of renewable energy, increase energy efficiency, and reduce emissions in the transportation and building sectors.
Some of the key measures proposed by the administration include:
Investing in clean energy research, development, and deployment to drive innovation and reduce the cost of renewable energy technologies.
Establishing a national clean energy standard to require a certain percentage of electricity to come from renewable sources.
Promoting energy efficiency in buildings through incentives and standards for new and existing construction.
Supporting the adoption of electric vehicles through incentives and investments in charging infrastructure.
Accelerating the deployment of carbon capture and storage technologies to reduce emissions from fossil fuel power plants.
The Biden administration has also pledged to make environmental justice a key part of its climate policy, recognizing that communities of color and low-income communities are disproportionately impacted by climate change and environmental pollution.
The United States’ commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 is a critical step towards addressing the global climate crisis. However, achieving this goal will require sustained effort and investment from both the public and private sectors, as well as continued innovation and collaboration across industries and communities.

Solar Energy Project in the United States
There are many solar energy projects in the United States, ranging from small residential installations to large utility-scale projects.
Here are a few examples of notable solar energy projects in the country:
Solar Star: The Solar Star project in California is one of the largest solar energy projects in the world, with a capacity of 579 megawatts (MW). The project consists of two sites, each with over 1.7 million solar panels.
Topaz Solar Farm: The Topaz Solar Farm in California has a capacity of 550 MW and is one of the largest solar energy projects in the world. The project consists of over 9 million solar panels spread across 9.5 square miles.
Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System: The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System in California is a concentrated solar power (CSP) project with a capacity of 392 MW. The project uses mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto boilers, which generate steam that drives turbines to generate electricity.
SolarReserve Crescent Dunes: The SolarReserve Crescent Dunes project in Nevada is a CSP project with a capacity of 110 MW. The project uses molten salt to store thermal energy, allowing it to generate electricity even when the sun is not shining.
Brooklyn Microgrid: The Brooklyn Microgrid is a community-based solar energy project that allows residents of Brooklyn, New York to buy and sell solar energy within their community. The project consists of rooftop solar panels installed on homes and businesses throughout the community.
There are many solar energy projects in the United States, ranging from large utility-scale projects to community-based initiatives. These projects are helping to drive the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy system and create new jobs and economic opportunities.

Hydro Energy Project in the United States
Hydro energy is an important source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are many hydro energy projects across the country.
Here are a few examples:
Grand Coulee Dam: The Grand Coulee Dam, located on the Columbia River in Washington state, is the largest hydroelectric power station in the United States, with a capacity of 6,809 MW. The dam generates over 21 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity each year.
Hoover Dam: The Hoover Dam, located on the Colorado River on the border between Arizona and Nevada, has a capacity of 2,080 MW. The dam generates over 4 billion kWh of electricity each year.
Glen Canyon Dam: The Glen Canyon Dam, also located on the Colorado River in Arizona, has a capacity of 1,312 MW. The dam generates over 4 billion kWh of electricity each year.
Bonneville Dam: The Bonneville Dam, located on the Columbia River in Oregon and Washington, has a capacity of 1,080 MW. The dam generates over 8 billion kWh of electricity each year.
Niagara Falls: The Niagara Falls hydroelectric power plants, located on the Niagara River in New York and Ontario, Canada, have a combined capacity of 4.4 GW. The plants generate over 21 billion kWh of electricity each year.
Hydro energy is an important source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are many hydro energy projects across the country. These projects provide clean, renewable energy to millions of homes and businesses, and help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.

Wind Energy Project in the United States
Wind energy is a rapidly growing source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are many wind energy projects across the country.
Here are a few examples:
Alta Wind Energy Center: The Alta Wind Energy Center, located in California, is one of the largest wind energy projects in the United States, with a capacity of 1,550 MW. The project consists of 586 wind turbines spread across several sites.
Shepherds Flat Wind Farm: The Shepherds Flat Wind Farm, located in Oregon, has a capacity of 845 MW and is one of the largest wind energy projects in the world. The project consists of 338 wind turbines spread across 30 square miles.
Roscoe Wind Farm: The Roscoe Wind Farm, located in Texas, has a capacity of 781.5 MW and was the largest wind energy project in the world when it was completed in 2009. The project consists of 627 wind turbines spread across 100,000 acres.
Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center: The Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center, also located in Texas, has a capacity of 735 MW and is one of the largest wind energy projects in the United States. The project consists of 421 wind turbines spread across 47,000 acres.
Block Island Wind Farm: The Block Island Wind Farm, located off the coast of Rhode Island, has a capacity of 30 MW and was the first offshore wind energy project in the United States. The project consists of five wind turbines that generate enough electricity to power over 17,000 homes.
Wind energy is a rapidly growing source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are many wind energy projects across the country. These projects provide clean, renewable energy to millions of homes and businesses, and help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.

Geothermal Energy Project in the United States
Geothermal energy is a significant source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are several geothermal energy projects across the country.
Here are a few examples:
The Geysers: The Geysers, located in California, is the largest geothermal energy project in the world with a capacity of 1.5 GW. The project consists of 22 power plants that generate electricity using steam from more than 350 geothermal wells.
Salton Sea: The Salton Sea geothermal project, located in California, has a capacity of 340 MW. The project consists of 10 power plants that generate electricity using steam from more than 100 geothermal wells.
Nevada Geothermal Power: The Nevada Geothermal Power project, located in Nevada, has a capacity of 69 MW. The project consists of two power plants that generate electricity using steam from geothermal wells.
Raft River: The Raft River geothermal project, located in Idaho, has a capacity of 10.5 MW. The project consists of a single power plant that generates electricity using steam from geothermal wells.
Chena Hot Springs: The Chena Hot Springs geothermal project, located in Alaska, has a capacity of 440 kW. The project consists of a single power plant that generates electricity using steam from a geothermal well.
Geothermal energy is an important source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are several geothermal energy projects across the country. These projects provide clean, renewable energy to homes and businesses and help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.

Bio mass energy Project in the United States
Biomass energy is a significant source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are several biomass energy projects across the country.
Here are a few examples:
Drax Power Station: The Drax Power Station, located in Mississippi, is one of the largest biomass energy projects in the world with a capacity of 3.9 GW. The project consists of six biomass-fired power plants that generate electricity using wood pellets.
Dominion Energy: Dominion Energy, located in Virginia, operates several biomass energy projects with a combined capacity of 163 MW. These projects generate electricity using wood waste, agricultural waste, and other biomass materials.
Amager Bakke: Amager Bakke, located in Massachusetts, is a biomass energy project that generates electricity and heat from waste materials. The project consists of a waste-to-energy plant that burns municipal waste to generate electricity.
Blue Lake Power: Blue Lake Power, located in California, is a biomass energy project that generates electricity using wood waste. The project has a capacity of 12 MW and provides renewable energy to homes and businesses in the area.
New Hope Power Company: The New Hope Power Company, located in Florida, is a biomass energy project that generates electricity using wood waste. The project has a capacity of 140 MW and provides renewable energy to homes and businesses in the area.
Biomass energy is an important source of renewable energy in the United States, and there are several biomass energy projects across the country. These projects provide clean, renewable energy while also helping to reduce waste and support sustainable forestry practices.
How to utilize renewable energy in the transportation sector in the United States
The transportation sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. However, there are several ways to utilize renewable energy in this sector.
Here are some examples:
Electric vehicles (EVs): The most direct way to utilize renewable energy in the transportation sector is by using EVs. EVs are powered by electricity, which can be generated from renewable sources such as wind, solar, or hydropower. EVs are becoming increasingly popular in the United States, and many car manufacturers now offer electric models.
Biofuels: Biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, are renewable fuels made from organic matter. They can be used in conventional gasoline or diesel engines without modification. Biofuels can be produced from various sources, including agricultural crops, waste biomass, and algae.
Hydrogen fuel cells: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity, which can be used to power vehicles. Hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources such as wind or solar power, and when used in fuel cells, it produces no emissions, only water.
Solar-powered charging stations: Solar-powered charging stations can be installed along highways, in parking lots, or other locations to charge EVs with renewable energy.
Public transportation: Public transportation systems, such as buses and trains, can be powered by renewable energy sources such as electricity or biofuels.
Utilizing renewable energy in the transportation sector can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote a cleaner and more sustainable future. The United States government has implemented policies to support the development of renewable energy in transportation, such as tax incentives for EVs and biofuel production, and funding for research and development of new renewable energy technologies.

Implementation of Renewable Energy in the tourism sector in the United States
The tourism sector in the United States is increasingly implementing renewable energy initiatives to reduce its environmental impact and promote sustainability.
Here are some examples of renewable energy implementation in the tourism sector:
Solar power: Many hotels, resorts, and tourist attractions have installed solar panels to generate renewable energy. For example, Walt Disney World Resort in Florida has installed over 500,000 solar panels to generate renewable energy and reduce its carbon footprint.
Energy efficiency: The tourism sector is also implementing energy efficiency measures to reduce energy consumption and costs. These measures include upgrading lighting systems, installing energy-efficient HVAC systems, and using advanced energy management systems.
Geothermal power: Some tourist destinations have implemented geothermal energy projects to provide heating and cooling for their facilities. For example, the Chena Hot Springs Resort in Alaska uses geothermal energy to provide hot water for its pools and heating for its facilities.
Wind power: Some tourist destinations, such as Cape Cod, Massachusetts, have implemented wind power projects to generate renewable energy.
Electric vehicles: Some tourist destinations are also using electric vehicles for transportation, such as shuttle buses or rental cars. This not only reduces carbon emissions but also provides a unique and sustainable travel experience for visitors.
The tourism sector in the United States is recognizing the importance of implementing renewable energy initiatives to reduce its environmental impact, enhance sustainability, and provide a unique and sustainable travel experience for visitors. By doing so, the tourism sector can lead the way towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Companies that contribute greatly to the implementation of renewable energy in the United States
There are many companies that have contributed greatly to the implementation of renewable energy in the United States.
Here are a few examples:
Tesla: Tesla is a leading electric vehicle manufacturer and has also made significant contributions to renewable energy through its production of solar panels, solar roofs, and battery storage solutions. The company’s Gigafactory in Nevada is one of the largest facilities for producing batteries for electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
NextEra Energy: NextEra Energy is a leading renewable energy company in the United States and operates the largest fleet of wind and solar projects in North America. The company has been instrumental in developing new renewable energy projects and expanding the use of renewable energy across the country.
Duke Energy: Duke Energy is one of the largest utilities in the United States and has set ambitious goals to transition to a cleaner energy system. The company plans to invest $56 billion in renewable energy and grid modernization over the next decade.
Amazon: Amazon has made significant investments in renewable energy, including signing power purchase agreements (PPAs) for wind and solar projects that will provide the company with renewable energy to power its operations. In 2019, Amazon announced its commitment to be carbon neutral by 2040.
Google: Google has also made significant investments in renewable energy, including purchasing renewable energy certificates (RECs) and signing PPAs for wind and solar projects. The company has also invested in research and development of new renewable energy technologies.
There are many companies in the United States that are making significant contributions to the implementation of renewable energy. These companies are playing a critical role in driving down the cost of renewable energy and accelerating the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy system.
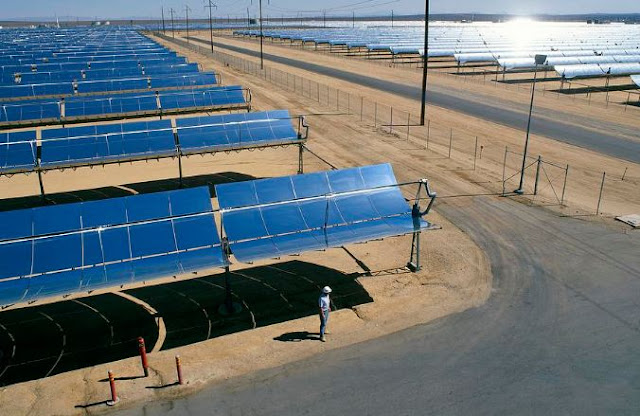

The largest Renewable Energy Project in the United States
The largest renewable energy project in the United States is the Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) located in California. SEGS is a series of nine solar thermal power plants located in the Mojave Desert, which collectively generate a total of 354 megawatts (MW) of electricity, enough to power over 200,000 homes.
The SEGS project was built in the 1980s and 1990s, and at the time of its construction, it was the largest solar power project in the world. The project consists of over 1.2 million mirrors, known as heliostats, which reflect sunlight onto a receiver that contains a heat transfer fluid. The fluid is heated by the concentrated sunlight, and the resulting steam drives turbines that generate electricity.
SEGS was built by Luz Industries, a company that was later acquired by the energy company, FPL Energy. The project has been in operation for over 30 years and has provided a reliable source of renewable energy to Southern California Edison, the utility that purchases the electricity generated by SEGS.
In recent years, other large-scale renewable energy projects have been developed in the United States, such as the Alta Wind Energy Center in California, which is the largest wind farm in the country with a total capacity of 1,550 MW, and the Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System in California, which is a 392 MW solar thermal power plant. However, SEGS remains the largest renewable energy project in the United States in terms of installed capacity.

What is the composition of renewable energy in the overall energy sector in the United States
Renewable energy has been growing in importance in the United States, but it still accounts for a relatively small share of the overall energy sector. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2020, renewable energy sources accounted for about 12% of total U.S. energy consumption and about 20% of electricity generation.
Breaking down the composition of renewable energy in the United States, the largest sources of renewable energy in 2020 were:
Hydroelectric power: Hydroelectric power accounted for about 6% of total U.S. energy consumption and about 7% of electricity generation. Hydroelectric power is generated from flowing water, usually in dams.
Wind power: Wind power accounted for about 2.8% of total U.S. energy consumption and about 8% of electricity generation. Wind power is generated from the kinetic energy of wind turbines.
Biomass: Biomass, including wood, biofuels, and waste, accounted for about 4% of total U.S. energy consumption and about 1% of electricity generation.
Solar power: Solar power accounted for about 1% of total U.S. energy consumption and about 3% of electricity generation. Solar power is generated from photovoltaic panels that convert sunlight into electricity.
Other renewable energy sources, such as geothermal and tidal power, accounted for a very small percentage of total U.S. energy consumption.
It is worth noting that the share of renewable energy in the United States’ energy mix has been growing steadily in recent years, and the government has set targets to increase the use of renewable energy further.
Conclusions on the implementation of renewable energy in the United States
The United States has made significant progress in implementing renewable energy in recent years. There has been a growing awareness of the importance of transitioning to a cleaner and more sustainable energy system, and the government has implemented various policies to support the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies.
Some of the key developments in the implementation of renewable energy in the United States include:
Significant growth in renewable energy capacity and generation, with renewable energy sources accounting for about 12% of total U.S. energy consumption and about 20% of electricity generation in 2020.
Major investments in renewable energy by both the public and private sectors, including the Department of Defense and leading corporations such as Google and Apple.
The implementation of policies such as tax incentives, renewable portfolio standards, and funding for research and development to support the growth of renewable energy.
The adoption of innovative renewable energy technologies such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, as well as emerging technologies such as geothermal and tidal power.
Despite these positive developments, there are still challenges to the widespread implementation of renewable energy in the United States. These include issues related to grid integration, energy storage, and the availability of financing for renewable energy projects. However, with continued investment, innovation, and policy support, the United States can continue to make progress towards a more sustainable and clean energy future.
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/04/implementation-of-renewable-energy-in.html
Renewable Energy
How Is U.S. Insanity Affecting Tourism?
 It’s probably a bit too soon to have useable statistics on this subject, but it’s certainly not too early to apply some common sense.
It’s probably a bit too soon to have useable statistics on this subject, but it’s certainly not too early to apply some common sense.
There are at two factors at play here:
1) America is broadly regarded as a rogue country. Do you want to visit North Korea? Do Canadians want to spend money in a country that wants to annex them?
2) America is now understood to be unsafe. Do you want to visit Palestine? Ukraine? Iran?
Renewable Energy
Commercial Solar Solutions: Real Case Studies by Cyanergy
The post Commercial Solar Solutions: Real Case Studies by Cyanergy appeared first on Cyanergy.
https://cyanergy.com.au/blog/commercial-solar-solutions-real-case-studies-by-cyanergy/
Renewable Energy
Inside ATT and SSE’s Faskally Safety Leadership Centre
Weather Guard Lightning Tech

Inside ATT and SSE’s Faskally Safety Leadership Centre
Allen visits the Faskally Safety Leadership Centre with Mark Patterson, Director of Safety, Health, and Environment at SSE, and Dermot Kerrigan, Director and Co-Founder of Active Training Team. They discuss how SSE has put over 9,000 employees and 2,000 contract partners through ATT’s innovative training program, which uses actors and realistic scenarios to create lasting behavioral change across the entire workforce chain, from executives to technicians. Reach out to SSE and ATT to learn more!
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly newsletter on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on YouTube, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary’s “Engineering with Rosie” YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
Welcome to Uptime Spotlight, shining Light on Wind. Energy’s brightest innovators. This is the Progress Powering tomorrow.
Allen Hall: Mark and Turnt. Welcome to the show. Thank you.
Mark Patterson: Thank you.
Allen Hall: We’re in Scotland, present Scotland and per Scotland, which is a place most people probably haven’t ventured to in the United States, but it is quite lovely, although chilly and rainy. It’s Scotland. We’re in December. Uh, and we’re here to take a look at the SSE Training Center.
And the remarkable things that active training team is doing here, because we had seen this in Boston in a smaller format, uh, about a year ago almost now.
Dermot Kerrigan: Just Yeah,
Allen Hall: yeah. Six months
Dermot Kerrigan: ago.
Allen Hall: Yeah. Yeah. It hasn’t been that long ago. Uh, but IC was on me to say, you gotta come over. You gotta come over. You gotta see the, the whole, uh, environment where we put you into the police room and some of the things we wanna talk about, uh, because it, [00:01:00] it does play different.
And you’re right, it does play different. It is very impactful. And it, and maybe we should start off first of Mark, you’re the head of basically health and safety and environment for SSE here in Perth. This is a remarkable facility. It is unlike anything I have seen in the States by far. And SSE has made the commitment to do this sort of training for.
Everybody in your employment and outside of your employment, even contractors.
Mark Patterson: We have been looking at some quite basic things in safety as everybody does. And there’s a fundamental thing we want to do is get everybody home safe. And uh, it’s easier said than done because you’ve gotta get it right for every single task, every single day.
And that’s a massive challenge. And we have like 15,000. 15,000 people in SSE, we probably work with about 50,000 contract [00:02:00] partners and we’re heavily dependent, uh, on get our contract partners to get our activities done. And they’re crucial.
Speaker: Mm-hmm.
Mark Patterson: And in that it’s one community and we need to make sure everybody there gets home safe.
And that’s what drove us to think about adding more rules isn’t gonna do it. Um, you need to give people that sense of a feeling, uh, when a really serious sense of cars and then equip them with tools to, to deal with it. So. We’ve all probably seen training that gives that sense of doom and dread when something goes badly wrong, but actually that needs to be.
Coupled with something which is quite powerful, is what are the tools that help people have the conversations that gets everybody home safe. So kind of trying to do two things.
Allen Hall: Well, SSC is involved in a number of large projects. You have three offshore wind farms, about a more than a thousand turbines right now.
Wind turbines onshore, offshore, and those offshore projects are not easy. There’s a lot of complexity to them.
Mark Patterson: Absolutely. So look, I I think [00:03:00] that’s, that’s something that. You’ve gotta partner with the right people. If you wanna be successful, you need to make it easy for people to do the right thing. Yeah, as best you possibly can.
You need to partner with the right people, and you need to get people that you need to have a sense that you need to keep checking that as you’re growing your business. The chinks in your armor don’t grow too. But fundamentally there’s something else, which is a sense of community. When people come together to, to do a task, there is a sense of community and people work, put a lot of discretionary effort into to get, uh, big projects done.
And in that, um, it’s a sense of community and you wanna make sure everybody there gets home safe to their friends and family. ’cause if we’re all being honest about it, you know, SSE is a brilliant company. What we do is absolutely worth doing. I love SC. But I love my family a fair amount more. And if you bought into that, you probably bought into the strategy that we’re trying to adopt in terms of safety.
Uh, it’s really simple messaging. Um,
Allen Hall: yeah. That, that is very clear. Yeah. And it should be [00:04:00]well communicated outside of SSEI hope because it is a tremendous, uh, value to SSE to do that. And I’m sure the employees appreciate it because you have a culture of safety. What. Trigger that. How long ago was that trigger?
Is this, this is not something you thought up yesterday for sure.
Mark Patterson: No, look, this, the, the, what we’ve done in the immersive training center, um, really reinforces a lot of things that we’ve had in place for a while, and it, it takes it to the, the next level. So we’ve been working probably more than 10 years, but, uh, certainly the.
Seven years we’ve been talking very much about our safety family, that’s the community and SSE with our contract partners and what we need to do. And part of that is really clear language about getting people home safe. Uh, a sense that you’ve, everybody in it that works with us has a safety license. And that license is, if it’s not safe, we don’t do it.
It’s not a rural based thing. It’s how we roll. It’s part of the culture. We’d, we, uh, have a culture where, and certainly trying to instill for everybody a culture. Where [00:05:00] they’ve got that license. If, if they think something’s not right, we’ll stop the job and get it right. And even if they’re wrong, we’ll still listen to them because ultimately we need to work our way through, right?
So we’ve been, we’ve thought hard about the language we wanted to use to reinforce that. So the importance of plan, scan and adapt. So planning our work well, thinking through what we need to do. Not just stopping there though, keeping scanning for what could go wrong. That sense that you can’t remember everything.
So you need to have immediate corrective actions and that immediate sort of see it, sort of report it. If you see something that isn’t right, do something about it. And that sense of community caring for the community that you work with. And those are the essence of our, our language on safety and the immersive training.
Uh, is not trying to shove that language down everybody’s throats again, particularly our contract partners, but it’s, it’s helping people see some really clear things. One is if a [00:06:00] really serious incident occurs at what, what it feels like here. And I’ve spent a lot of time in various industries and people are different when they’ve been on a site or involved when there’s been a really serious incident and you need to do something to.
Get that sense of a feeling of what it feels like and actually make people feel slightly uncomfortable in the process. ’cause that’s part of it,
Allen Hall: right? Yes.
Mark Patterson: Because you know,
Allen Hall: you remember that.
Mark Patterson: You remember that. Yeah. We’ve had, you know, we’ve had people say, well, I felt very uncomfortable in that bit of the training.
It was okay. But was, I felt very uncomfortable. And you know, we’ve talked about that a lot.
Allen Hall: Yeah.
Mark Patterson: We know you kinda should because if there’s something wrong with you, if you don’t feel uncomfortable about that. But what’s super powerful on the guys in at TT do brilliantly. Is have facilitators that allow you to have that conversation and understand what do you need to do differently?
How do you influence somebody who’s more senior? How do you, how do you bring people with you so that they’re gonna [00:07:00] do what you want ’em to do after you’ve left the building? And. Just pointing the finger at people and shouting at them. Never does that. Right? Uh, rarely does that. You’ve gotta get that sense of how do you get people to have a common belief?
And,
Allen Hall: and I think that’s important in the way that SSE addresses that, is that you’re not just addressing technicians, it’s the whole chain. It’s everybody is involved in this action. And you can break the link anywhere in there. I wanna get through the description of why that. Process went through ATTs head to go.
We need to broaden the scope a little bit. We need to think about the full chain from the lowest entry worker just getting started to the career senior executive. Why chain them all together? Why put them in the same room together? Yeah. Why do you do that?
Dermot Kerrigan: Well, behavioral safety or behavioral base safety kind of got a bad rep because it was all about.
If we could just [00:08:00] make those guys at the front line behave themselves,
Allen Hall: then everything’s fine,
Dermot Kerrigan: then everything’s fine.
Allen Hall: Yes.
Dermot Kerrigan: But actually that’s kind of a, the wrong way of thinking. It didn’t work. I, I think,
Allen Hall: yeah, it didn’t work.
Dermot Kerrigan: What the mess, the central message we’re trying to get across is that actually operational safety is not just the business of operational people.
It’s everybody’s business.
Allen Hall: Right.
Dermot Kerrigan: You know? Um, and. Yeah, everybody has a role to p play in that, you know? Right. So site based teams, back office support functions, everybody has a role to play. And, you know, there’s a strand in, in this scenario where, uh, an incident takes place because people haven’t been issued with the right piece of equipment.
Which is a lifting cage.
Allen Hall: Yes.
Dermot Kerrigan: And there’s a whole story about that, which goes through a procurement decision made somewhere where somebody hit a computer and a computer said no because they’d asked for too many lifting cages when they, somebody could have said, you’ve asked for five lifting cages, it’s takes you over the procurement cap.
Would four do it? [00:09:00] Yes, that would be fine. That would be fine. Yeah. As it is, they come to a crucial piece of operation. This incr this, you know, this crucial piece of kit simply isn’t there. So in order to hit the deadline and try and make people happy, two ordinary guys, two technicians, put two and two together, make five, and, and one of them gets killed, you know?
Yeah. So it’s, we’re, we’re trying to show that, that this isn’t just operational people. It’s everybody’s business.
Mark Patterson: Well, that’s why we worked with you in this, because, um, we saw. Why you got it in terms of that chain? Um, so in, in the scenario, it’s very clear there’s a senior exec talking to the client and actually as SSE.
We’re sometimes that client, we’ve got big principal contractors that are doing our big construction activities. We’ve got a lot in renewables and onshore and offshore wind obviously, but, and the transmission business and in thermal, so, uh, and distribution. So I’ll list all our businesses and including customer’s business, but we’ve got some big project activities where we’re the client sometime we’re the principal contractor [00:10:00] ourselves.
And we need to recognize that in each chain, each link in that chain, there’s a risk that we say the wrong thing, put the wrong pressure on. And I think what’s really helpful is we have in the center that sort of philosophy here that we get everybody in together mixed up. Probably at least half of our board have done this.
Our executive team have all done this. Um, people are committed to it at that level, and they’re here like everybody else sitting, waiting for this thing to start. Not being quite sure what they’re gonna go through in the day. Um, and it’s actually really important you’ve got a chief exec sitting with somebody who’s, um, a scaffolder.
That’s really important. ’cause the scaffolder is probably the more likely person to get hurt rather than chief exec. So actually everybody seeing what it’s like and the pressures that are under at each level is really important.
Allen Hall: SSC is such a good example for the industry. I watched you from outside in America for a long time and you just watch the things that happened.
[00:11:00] Here you go. Wow. Okay. SSC is organized. They know what they’re doing, they understand what the project is, they’re going about it. Mm-hmm. Nothing is perfect, but I, I think when we watch from the United States, we see, oh, there’s order to it. There’s a reason they’re doing these things. They’re, they’re measuring what is happening.
And I think that’s one of the things about at t is the results. Have been remarkable, not just here, but in several different sites, because a TT touches a lot of massive infrastructure projects in the uk and the success rate has been tremendous. Remember? You wanna just briefly talk about that?
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah. But we, we run a number of centers.
We also run mobile programs, which you got from having seen us in the States. Um, but the first, uh, center that we, we, we opened was, was called. Epic, which stood for Employers Project Induction Center, and that was the Thames Tideway Tunnel Project, which is now more or less finished. It’s completed. And that was a 10 year project, 5 billion pounds.
Allen Hall: Wow.
Dermot Kerrigan: Um, [00:12:00] and you know, unfortunately the fact is on, on that kind of project, you would normally expect to hurt a number of people, sometimes fatally. That would be the expectation.
Allen Hall: Right. It’s a complicated
Dermot Kerrigan: project, statistic underground. So, you know, we, and, and of course Tide, we are very, very. Very pleased that, uh, in that 10 year span, they didn’t even have one, uh, serious life-changing injury, uh, let alone a fatality.
Um, so you know that that’s, and I’m I’m not saying that what ATTs work, uh, what we do is, is, is, is directly responsible for that, but certainly Epic, they would say Tideway was the cornerstone for the safety practices, very good safety practices that they, they put out. Uh, on that project, again, as a cultural piece to do with great facilities, great leadership on the part of the, of the, of the executive teams, et cetera, and stability.
It was the same ex executive team throughout that whole project, which is quite unusual.
Allen Hall: No.
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah. [00:13:00] Um, so yeah, it, it, it seems to work, you know, uh, always in safety that the, the, the, the tricky thing is trying to prove something works because it hasn’t happened. You know?
Allen Hall: Right, right. Uh, prove the negative.
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah. Um,
Allen Hall: but in safety, that’s what you want to have happen. You, you do know, not want an outcome.
Dermot Kerrigan: No, absolutely not.
Allen Hall: No reports, nothing.
Dermot Kerrigan: No. So, you know, you have to give credit to, to organizations. Organizations like SSE. Oh, absolutely. And projects like Tideway and Sted, uh, on their horn projects. Who, who have gone down this, frankly, very left field, uh, route.
We we’re, you know, it is only in the last 10 years that we’ve been doing this kind of thing, and it hasn’t, I mean, you know, Tideway certainly is now showing some results. Sure. But, you know, it’s, it’s, it, it wasn’t by any means a proven way of, of, of dealing with safety. So
Mark Patterson: I don’t think you could ever prove it.
Dermot Kerrigan: No.
Mark Patterson: And actually there’s, there’s something [00:14:00]fundamentally of. It, it kind of puts a stamp on the culture that you want, either you talked about the projects in SSE, we’ve, we’ve done it for all of our operational activities, so we’ve had about 9,000 people through it for SSE and so far about 2000 contract partners.
Um, we’re absolutely shifting our focus now. We’ve got probably 80% of our operational teams have been through this in each one of our businesses, and, uh, we. We probably are kind of closing the gaps at the moment, so I was in Ireland with. I here guys last week, um, doing a, a mobile session because logistically it was kind of hard to come to Perth or to one of the other centers, but we’re, we’re gradually getting up to that 80%, uh, for SSE colleagues and our focus is shifting a bit more to contract partners and making sure they get through.
And look, they are super positive about this. Some of them have done that themselves and worked with a TT in the past, so they’re. Really keen to, to use the center that we have [00:15:00] here in Perth, uh, for their activities. So when, when they’re working with us, we kind of work together to, to make that happen. Um, but they can book that separately with you guys.
Yeah. Uh, in, in the, uh, Fastly Center too.
Allen Hall: I think we should describe the room that we’re in right now and why this was built. This is one of three different scenes that, that each of the. Students will go through to put some realism to the scenario and the scenario, uh, a worker gets killed. This is that worker’s home?
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah. So each of the spaces that we have here that, that they denote antecedents or consequences, and this is very much consequences. Um, so the, the, the participants will be shown in here, uh, as they go around the center, uh, and there’s a scene that takes place where they meet the grown up daughter of the young fella who’s been right, who’s been, who’s been tragically killed.
Uh, and she basically asks him, uh, asks [00:16:00] them what happened. And kind of crucially this as a subtext, why didn’t you do something about it?
Allen Hall: Mm-hmm.
Dermot Kerrigan: Because you were there,
Allen Hall: you saw it, why it was played out in front of you. You saw, you
Dermot Kerrigan: saw what happened. You saw this guy who was obviously fast asleep in the canteen.
He was exhausted. Probably not fit for work. Um, and yet being instructed to go back out there and finish the job, um, with all the tragic consequences that happen,
Allen Hall: right?
Dermot Kerrigan: But it’s important to say, as Mark says, that. It’s not all doom and gloom. The first part of the day is all about showing them consequences.
Allen Hall: Sure. It’s
Dermot Kerrigan: saying it’s a,
Allen Hall: it’s a Greek tragedy
Dermot Kerrigan: in
Allen Hall: some
Dermot Kerrigan: ways, but then saying this doesn’t have to happen. If you just very subtly influence other people’s behavior, it’s
Allen Hall: slight
Dermot Kerrigan: by thinking about how you behave and sure adapting your behavior accordingly, you can completely change the outcome. Uh, so long as I can figure out where you are coming from and where that behavior is coming from, I might be able to influence it,
Allen Hall: right.
Dermot Kerrigan: And if I can, then I can stop that [00:17:00] hap from happening. And sure enough, at the end of the day, um, the last scene is that the, the, the daughter that we see in here growing up and then going back into this tragic, uh, ending, uh. She’s with her dad, then it turned out he was the one behind the camera all along.
So he’s 45 years old, she’s just passed the driving test and nobody got her 21 years ago. You know,
Mark Patterson: I think there, there is, there’s a journey that you’ve gotta take people through to get to believe that. And kind of part of that journey is as, as we look around this room, um, no matter who it is, and we’ve talked to a lot of people, they’ll be looking at things in this room and think, well, yeah, I’ve got a cup like that.
And yes. Yeah. When my kids were, we, we had. That play toy for the kids. Yes. So there is something that immediately hooks people and children hook
Allen Hall: people.
Mark Patterson: Absolutely. And
Allen Hall: yes,
Mark Patterson: they get to see that and understand that this is, this is, this is, could be a real thing. And also in the work site, uh, view, there’s kind of a work site, there’s a kind of a boardroom type thing [00:18:00] and you can actually see, yeah, that’s what it kind of feels like.
The work sites a little bit. You know, there’s scuffs in the, on the line, on the floor because that’s what happens in work sites and there’s a sense of realism for all of this, uh, is really important.
Allen Hall: The realism is all the way down to the outfits that everybody’s worn, so they’re not clean safety gear.
It’s. Dirty, worn safety gear, which is what it should be. ’cause if you’re working, that’s what it should look like. And it feels immediately real that the, the whole stage is set in a, in the canteen, I’ll call it, I don’t know, what do you call the welfare area? Yeah. Okay.
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah.
Allen Hall: Okay. Uh, wanna use the right language here.
But, uh, in the states we call it a, a break room. Uh, so you’re sitting in the break room just minding your own business and boom. An actor walks in, in full safety gear, uh, speaking Scottish very quickly, foreign American. But it’s real.
Mark Patterson: I think
Allen Hall: it feels real because you, you, I’ve been in those situations, I’ve seen that that break the,
Mark Patterson: the language is real and, uh, [00:19:00] perhaps not all, uh, completely podcast suitable.
Um, but when you look at it, the feedback we’ve got from, from people who are closer to the tools and at all levels, in fact is, yeah. This feels real. It’s a credible scenario and uh, you get people who. I do not want to be in a safety training for an entire day. Um, and they’re saying arms folded at the start of the day and within a very short period of time, they are absolutely watching what the heck’s going on here.
Yes. To understand what’s happening, what’s going on. I don’t understand. And actually it’s exactly as you say, those subtle things that you, not just giving people that experience, but the subtle things you can nudge people on to. There’s some great examples of how do you nudge people, how do you give feedback?
And we had some real examples where people have come back to us and said even things to do with their home life. We were down in London one day, um, and I was sitting in on the training and one of the guys said, God, you’ve just taught me something about how I can give feedback to people in a really impactful [00:20:00] way.
So you, so you explain the behavior you see, which is just the truth of what the behavior is. This is what I saw you do, this is what happened, but actually the impact that that has. How that individual feels about it. And the example that they used was, it was something to do with their son and how their son was behaving and interacting.
And he said, do you know what? I’ve struggled to get my son to toe the line to, to look after his mom in the right way. I’m gonna stop on the way home and I’m gonna have a conversation with him. And I think if I. Keep yourself cool and calm and go through those steps. I think I can have a completely different conversation.
And that was a great example. Nothing to do with work, but it made a big difference to that guy. But all those work conversations where you could just subtly change your tone. Wind yourself back, stay cool and calm and do something slightly different. And I think that those, those things absolutely make a difference,
Allen Hall: which is hard to do in the moment.
I think that’s what the a TT training does make you think of the re the first reaction, [00:21:00] which is the impulsive reaction. We gotta get this job done. This has gotta be done. Now I don’t have the right safety gear. We’ll, we’ll just do it anyway to, alright, slow. Just take a breather for a second. Think about what the consequences of this is.
And is it worth it at the end of the day? Is it worth it? And I think that’s the, the reaction you want to draw out of people. But it’s hard to do that in a video presentation or
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah.
Allen Hall: Those things just
Dermot Kerrigan: don’t need to practice.
Allen Hall: Yeah. It doesn’t stick in your brain.
Dermot Kerrigan: You need to give it a go And to see, right.
To see how to see it happen. And, and the actors are very good. They’re good if they, you know. What, whatever you give them, they will react to.
Mark Patterson: They do. That’s one of the really powerful things. You’ve got the incident itself, then you’ve got the UNP of what happened, and then you’ve got specific, uh, tools and techniques and what’s really good is.
Even people who are not wildly enthusiastic at the start of the day of getting, being interactive in, in, in a session, they do throw themselves into it ’cause they recognize they’ve been through [00:22:00] something. It’s a common sense of community in the room.
Dermot Kerrigan: Right.
Mark Patterson: And they have a bit of fun with it. And it is fun.
Yeah. You know, people say they enjoy the day. Um, they, they, they recognize that it’s challenged them a little bit and they kinda like that, but they also get the opportunity to test themselves. And that testing is really important in terms of, sure. Well, how do you challenge somebody you don’t know and you just walking past and you see something?
How do you have that conversation in a way that just gets to that adult To adult communication? Yeah. And actually gets the results that you need. And being high handed about it and saying, well, those are the rules, or, I’m really important, just do it. That doesn’t give us a sustained improvement.
Dermot Kerrigan: PE people are frightened of failure, you know?
Sure. They’re frightened of getting things wrong, so give ’em a space where they, where actually just fall flat in your face. Come back up again and try again. You know, give it a go. And, because no one’s, this is a safe space, you know, unlike in the real world,
Allen Hall: right?
Dermot Kerrigan: This is as near to the real world as you want to get.
It’s pretty real. It’s safe, you know, uh, it’s that Samuel Beckett thing, you know, fail again, [00:23:00] fail better,
Allen Hall: right?
Mark Patterson: But there’s, there’s a really good thing actually because people, when they practice that they realize. Yeah, it’s not straightforward going up and having a conversation with somebody about something they’re doing that could be done better.
And actually that helps in a way because it probably makes people a little bit more generous when somebody challenges them on how they’re approaching something. Even if somebody challenges you in a bit of a cat handed way, um, then you can just probably take a breath and think this. This, this guy’s probably just trying to have a conversation with me,
Allen Hall: right.
Mark Patterson: So that I get home to my family.
Allen Hall: Right.
Mark Patterson: It’s hard to get annoyed when you get that mindset. Mindset
Allen Hall: someone’s looking after you just a little bit. Yeah. It does feel nice.
Mark Patterson: And, and even if they’re not doing it in the best way, you need to be generous with it. So there’s, there’s good learnings actually from both sides of the, the, the interaction.
Allen Hall: So what’s next for SSE and at t? You’ve put so many people through this project in, in the program and it has. Drawn great results.
Mark Patterson: Yeah.
Allen Hall: [00:24:00] How do you, what do you think of next?
Mark Patterson: So what’s next? Yeah, I guess, uh, probably the best is next to come. Next to come. We, I think there’s a lot more that we can do with this.
So part of what we’ve done here is establish with a big community of people, a common sense of what we’re doing. And I think we’ve got an opportunity to continue with that. We’ve got, um, fortunate to be in a position where we’ve got a good level of growth in the business.
Allen Hall: Yes,
Mark Patterson: we do. Um, there’s a lot going on and so there’s always a flow of new people into an organization, and if people, you know, the theory of this stuff better than I do, would say that you need to maintain a, a sense of community that’s kind of more than 80%.
If you want a certain group of people to act in a certain way, you need about 80% of the people plus to act in that way, and then it’ll sustain. But if it starts. To drift so that only 20% of people are acting a certain way, then that is gonna ex extinguish that elements of the culture. So we need to keep topping up our Sure, okay.
Our, our [00:25:00] immersive training with people, and we’re also then thinking about the contract partners that we have and also leaving a bit of a legacy. For the communities in Scotland, because we’ve got a center that we’re gonna be using a little bit less because we’ve fortunate to get the bulk of our people in SSE through, uh, we’re working with contract partners.
They probably want to use it for. For their own purposes and also other community groups. So we’ve had all kinds of people from all these different companies here. We’ve had the Scottish first Minister here, we’ve had loads of people who’ve been really quite interested to see what we’re doing. And as a result of that, they’ve started to, uh, to, to step their way through doing something different themselves.
So,
Allen Hall: so that may change the, the future of at t also. And in terms of the slight approach, the scenarios they’re in. The culture changes, right? Yeah. Everybody changes. You don’t wanna be stuck in time.
Dermot Kerrigan: No, absolutely.
Allen Hall: That’s one thing at t is not,
Dermot Kerrigan: no, it’s not
Allen Hall: stuck in time.
Dermot Kerrigan: But, uh, I mean, you know, we first started out with the centers, uh, accommodating project.
Yeah. So this would [00:26:00] be an induction space. You might have guys who were gonna work on a project for two weeks, other guys who were gonna work on it for six months. They wanted to put them through the same experience. Mm. So that when they weren’t on site. That they could say, refer back to the, the, the, the induction and say, well, why ask me to do that?
You know, we, we, we both have that experience, so I’m gonna challenge you and you’re gonna accept challenge, et cetera. So it was always gonna be a short, sharp shock. But actually, if you’re working with an organization, you don’t necessarily have to take that approach. You could put people through a little bit of, of, of, of the training, give ’em a chance to practice, give ’em a chance to reflect, and then go on to the next stage.
Um. So it, it becomes more of a, a journey rather than a single hard, a single event experience. Yeah. You don’t learn to drive in a day really, do you? You know, you have to, well, I do transfer it to your right brain and practice, you know?
Allen Hall: Right. The more times you see an experience that the more it’s memorable and especially with the, the training on how to work with others.[00:27:00]
A refresh of that is always good.
Dermot Kerrigan: Yeah.
Allen Hall: Pressure changes people and I think it’s always time to reflect and go back to what the culture is of SSE That’s important. So this, this has been fantastic and I, I have to. Thank SSC and a TT for allowing us to be here today. It was quite the journey to get here, but it’s been really enlightening.
Uh, and I, I think we’ve been an advocate of a TT and the training techniques that SSC uses. For well over a year. And everybody we run into, and in organizations, particularly in win, we say, you, you gotta call a TT, you gotta reach out because they’re doing things right. They’re gonna change your safety culture, they’re gonna change the way you work as an organization.
That takes time. That message takes time. But I do think they need to be reaching out and dermo. How do they do that? How do, how do they reach att?
Dermot Kerrigan: Uh, they contact me or they contact att. So info at Active Trading Team, us.
Allen Hall: Us. [00:28:00] There you go.
Dermot Kerrigan: or.co uk. There you go. If you’re on the other side of the pond. Yeah.
Allen Hall: Yes. And Mark, because you just established such a successful safety program, I’m sure people want to reach out and ask, and hopefully a lot of our US and Australian and Canadian to listen to this podcast. We’ll reach out and, and talk to you about how, what you have set up here, how do they get ahold of you?
Mark Patterson: I’ll give you a link that you can access in the podcast, if that. Great. And uh, look. The, the risk of putting yourself out there and talking about this sort of thing is you sometimes give the impression you’ve got everything sorted and we certainly don’t in SSE. And if the second you think you’ve got everything nailed in terms of safety in your approach, then, then you don’t.
Um, so we’ve got a lot left to do. Um, but I think this particular thing has made a difference to our colleagues and, and contract partners and just getting them home safe.
Allen Hall: Yes. Yes, so thank you. Just both of you. Mark Dermott, thank you so much for being on the podcast. We appreciate both [00:29:00] of you and yeah, I’d love to attend this again, this is.
Excellent, excellent training. Thanks, Alan. Thanks.
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits