A new study warns that global declines in soil moisture in the 21st century could mark a “permanent” shift in the world’s water cycle.
Combining data from satellites, sea level measurements and observations of “polar motion”, the research shows how soil moisture levels have decreased since the year 2000.
The findings, published in Science, suggest the decline is primarily driven by an increasingly thirsty atmosphere as global temperatures rise, as well as shifts in rainfall patterns.
Consequently, the researchers warn the observed changes are likely to be “permanent” if current warming trends continue.
An accompanying perspective article says the study provides “robust evidence” of an “irreversible shift” in terrestrial water sources under climate change.
The drying out of soil “increases the severity and frequency” of major droughts, with consequences for humans, ecosystems and agriculture, explains Dr Benjamin Cook, an interdisciplinary Earth system scientist working at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and Columbia University, who was not involved in the research.
He tells Carbon Brief:
“Droughts are one of the most impactful, expensive natural hazards out there, because they are typically persistent and long lasting. Everything needs water – ecosystems need water, agriculture needs water. People need water. If you don’t have enough water – you’re in trouble.”
Drying soil
Every year, around 6tn tonnes of water cycles through Earth’s land surface. When rain falls on land it gets held up in soil, wetlands, groundwater, lakes and reservoirs on its journey back to the oceans.
Soil moisture forms a critical part of the Earth’s system, helping to irrigate soil, cycle nutrients and regulate the climate.
The amount of water contained in the soil is sensitive to a range of factors, including changes in rainfall, evaporation, vegetation and climate – as well as human activity, such as intensive agriculture.
The research points to a “gradual decline” in soil moisture levels in the 21st century, kickstarted by a period of “sharp depletion” in the three years over 2000-02.
Specifically, the researchers find the depletion of soil moisture resulted in a total loss of 1,614bn tonnes (gigatonnes, or Gt) of water over 2000-02 and then 1,009Gt between 2002 and 2016.
(For context, ice loss in Greenland resulted in 900Gt of water loss over 2002-06.)
Soil moisture has not recovered as of 2021, according to the research, and is unlikely to pick up under present climate conditions.
Joint-lead author Prof Dongryeol Ryu, professor of hydrology and remote sensing at the University of Melbourne, explains to Carbon Brief:
“We observed a stepwise decline [in soil moisture] twice in the past two decades, interspersed within a continuously declining trend in soil moisture. We haven’t seen this trend earlier, so that is why this is very concerning.”
Ryu explains the decision to analyse changes to soil moisture on a global scale meant the researchers could confirm trends difficult to see in smaller geographic datasets:
“The unique thing we found through analysing these larger-scale measures is that – even if we have seen widely fluctuating ups and downs in precipitation and increasing temperature – the total water contained in the soil, as soil moisture and groundwater, has been declining gradually from around the beginning of this century.“
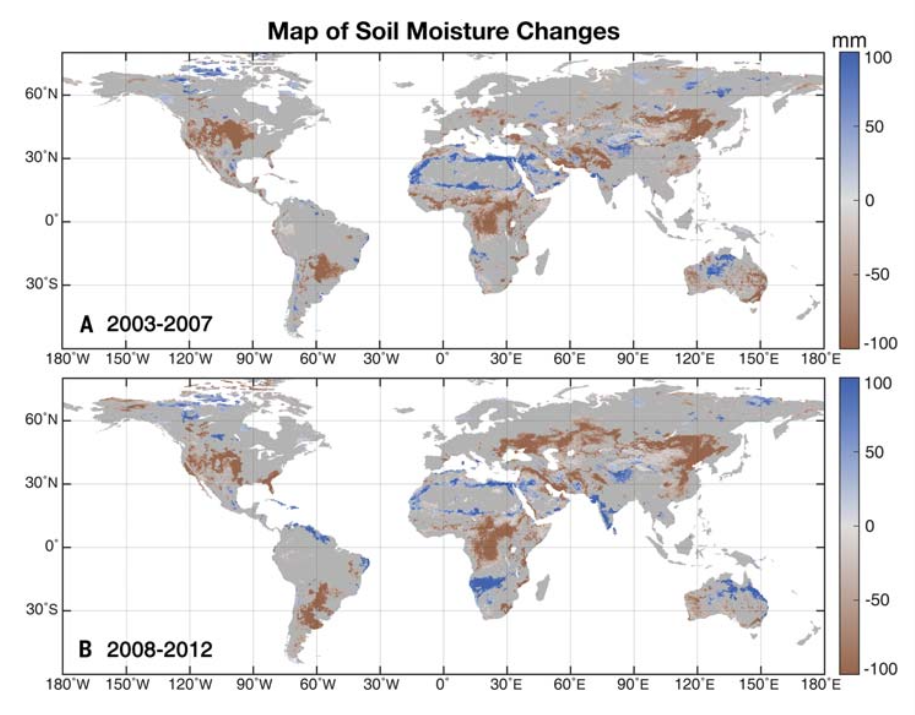
The maps below illustrate soil moisture changes in 2003-07 and 2008-12 against a 1995-99 baseline, as estimated by the ERA5-Land reanalysis dataset. The areas marked on the map in brown saw a drop in soil moisture and the areas marked in blue an increase in soil moisture.
The top map shows soil moisture depletion across large regions in eastern and central Asia, central Africa and North and South America over 2003-07. The lower map shows that “replenishment” in the years that followed occurred in relatively small parts of South America, India, Australia and North America.
Climate change
Ryu says the researchers “suspect that increasing temperature played an important role” in the decline in terrestrial water storage and soil moisture in the 21st century.
The study points to two factors driving gradual depletion of soil moisture over the last quarter century: fluctuations to rainfall patterns and increasing “evaporative demand”.
Evaporative demand refers to the atmosphere’s “thirst” for water, or how much moisture it can take from the land, vegetation and surface water.
Studies have highlighted how global evaporative demand has been increasing over the last two decades globally, impacting water availability, hurting crops and causing drought.
The new study notes that “increasing evaporative demand driven by a warming climate” suggests a “more consistent and widespread trend toward drying as temperatures rise”.
Ryu says the “very unusual” drop in water moisture observed over 2000-02 could be attributed to low levels of rainfall globally, which coincided with the “period when evaporative demand started increasing”.
Another – less pronounced – period of rapid soil moisture decline seen over 2015-16 can be attributed to droughts triggered by the 2014-16 El Niño event, Ryu notes.
Ryu says the study findings indicate that soil moisture can no longer bounce back from a dry year, as it has in the past:
“It used to be that when precipitation goes up again, we recover water in the soil. But because of this increasing evaporative demand, once we have strong El Niño years – which lead to much less rainfall for a year or two – it seems that we are not recovering the water fully because of increasing evaporative demand. Because of that – even if we have a wet year following dry years – the water in the soil doesn’t seem to recover.”
Cross-validation
Measuring changes in global soil moisture has historically presented a challenge to scientists, given the lack of comprehensive and direct observations of water in soil.
The researchers attempt to reduce this uncertainty by corroborating the ERA5-Land reanalysis dataset from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) with three geophysical measurement datasets.
ERA5’s land surface modelling system uses meteorological and other input data to estimate water within the upper few metres of the soil.
These figures were compared with data collected by the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission – a joint satellite mission between NASA and the German Aerospace Center.
Running since 2002, the GRACE mission tracks changes to the Earth’s gravity by collecting data on groundwater depletion, ice sheet loss and sea level rise. These observations have revealed a persistent loss of water from land to the ocean.
The scientists also cross-reference the ERA5 reanalysis data with a century-old dataset that measures fluctuations in the rotation of the Earth as the distribution of mass on the planet changes.
(The redistribution of ice and water, such as melting ice sheets and depleting groundwater, causes the planet to wobble as it spins and its axis to shift slightly. This is known as “polar motion”.)
The third set of measurements the scientists use is global mean sea level height, which is collected by satellites.
To extract soil moisture changes from this set of data, the researchers subtracted other components of sea level rise from the overall total – including Greenland ice melt, Antarctica ice melt, the impact of increasing sea surface temperature (which expands water volume) and the contribution of groundwater.
This process of elimination left researchers with an estimate of the contribution of soil moisture to global sea level rise.
The study notes that both the sea surface height and polar motion observations “support the conclusion that the abrupt change in soil moisture is genuine”.
Ryu says using global average sea level rise and “Earth wobble” to track water redistribution on land is the “main innovation” applied in the paper.
He adds the value of “reverse engineering” the ERA5 dataset is to understand how to enhance land surface modelling in the future:
“By explaining all the contributing factors to this measurement, you can understand the process. And if you understand the process, you can actually predict what’s going to happen in the future if any of these factors change in a certain manner.”
NASA’s Dr Cook says the “corroborating evidence” supplied by the paper offers a “really strong case that there has been a large-scale decline in soil moisture in recent decades”.
However, he says the relatively short reference period of the study means that identifying the cause of the decline is less clear cut:
“Whether [the decline] is permanent or not is much more uncertain…On these timescales, internal natural variability can be really, really strong. Attributing this decline to something specific – either climate change or internal variability – is much much more difficult.”
Sea level rise
A notable finding in the study’s sea level rise analysis is that terrestrial water storage may have been the dominant driver of sea level rise in the early 21st century.
Specifically, the paper notes that the decline in terrestrial water storage over 2000-02 – when soil moisture plummeted – led to global average sea level rise of almost 2mm annually.
The researchers note this rate of sea level rise is “unprecedented” and “significantly higher” than the rate of sea level rise attributed to Greenland ice mass loss, which they note is approximately 0.8mm a year.
Prof Reed Maxwell, a professor at the High Meadows Environmental Institute at Princeton University, who was also not involved in the study, says the researchers’ efforts to compare soil moisture with other global water stores was “novel” and “opens the door to future study of a more holistic global water balance”.
‘Creeping disaster’
The paper notes that land surface and hydrological models require “substantial improvement” to accurately simulate changes in soil moisture in changing climate.
Current models do not factor the impacts of agricultural intensification, nor the ongoing “greening” of semi-arid regions – both of which “may contribute” to a further decline in soil moisture, it states.
Writing in a perspectives article published in Science, Prof Luis Samaniego from the department of computational hydrosystems at the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research says that it is “essential” that next-generation models incorporate human-caused influences such as farming, large dams and irrigation systems.
The study posits that the “innovative methods” for estimating changes in global soil moisture presented in the study provide opportunities to “improve the present state of modelling at global and continental scales”.
More broadly, advances in scientific understanding of changes to soil moisture can help improve the world’s preparedness for drought.
Drought is often described as a “creeping disaster” – because by the time it is identified, it is usually already well under way,
Paper author Ryu explains:
“Unlike a flood and heatwaves, drought comes very very slowly – and has prolonged and delayed consequences. We better be prepared earlier than later, because once drought comes you can expect a long period of consequences.”
Dr Shou Wang, associate professor at the Hydroclimate Extremes Lab and the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, who was not involved in the study, says the research findings are “crucial” for advancing understanding of the “potential drivers and dynamics” of “unprecedented hydrological extremes in a warming climate”. He tells Carbon Brief:
“This is breakthrough work that uncovers the drivers of hydrological regime changes, which are leading to unprecedented hydrological extremes such as compound and consecutive drought-flood events.”
The post Global soil moisture in ‘permanent’ decline due to climate change appeared first on Carbon Brief.
https://www.carbonbrief.org/global-soil-moisture-in-permanent-decline-due-to-climate-change/
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 20 February 2026: EU’s ‘3C’ warning | Endangerment repeal’s impact on US emissions | ‘Tree invasion’ fuelled South America’s fires
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Preparing for 3C
NEW ALERT: The EU’s climate advisory board urged countries to prepare for 3C of global warming, reported the Guardian. The outlet quoted Maarten van Aalst, a member of the advisory board, saying that adapting to this future is a “daunting task, but, at the same time, quite a doable task”. The board recommended the creation of “climate risk assessments and investments in protective measures”.
‘INSUFFICIENT’ ACTION: EFE Verde added that the advisory board said that the EU’s adaptation efforts were so far “insufficient, fragmented and reactive” and “belated”. Climate impacts are expected to weaken the bloc’s productivity, put pressure on public budgets and increase security risks, it added.
UNDERWATER: Meanwhile, France faced “unprecedented” flooding this week, reported Le Monde. The flooding has inundated houses, streets and fields and forced the evacuation of around 2,000 people, according to the outlet. The Guardian quoted Monique Barbut, minister for the ecological transition, saying: “People who follow climate issues have been warning us for a long time that events like this will happen more often…In fact, tomorrow has arrived.”
IEA ‘erases’ climate
MISSING PRIORITY: The US has “succeeded” in removing climate change from the main priorities of the International Energy Agency (IEA) during a “tense ministerial meeting” in Paris, reported Politico. It noted that climate change is not listed among the agency’s priorities in the “chair’s summary” released at the end of the two-day summit.
US INTERVENTION: Bloomberg said the meeting marked the first time in nine years the IEA failed to release a communique setting out a unified position on issues – opting instead for the chair’s summary. This came after US energy secretary Chris Wright gave the organisation a one-year deadline to “scrap its support of goals to reduce energy emissions to net-zero” – or risk losing the US as a member, according to Reuters.
Around the world
- ISLAND OBJECTION: The US is pressuring Vanuatu to withdraw a draft resolution supporting an International Court of Justice ruling on climate change, according to Al Jazeera.
- GREENLAND HEAT: The Associated Press reported that Greenland’s capital Nuuk had its hottest January since records began 109 years ago.
- CHINA PRIORITIES: China’s Energy Administration set out its five energy priorities for 2026-2030, including developing a renewable energy plan, said International Energy Net.
- AMAZON REPRIEVE: Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon has continued to fall into early 2026, extending a downward trend, according to the latest satellite data covered by Mongabay.
- GEZANI DESTRUCTION: Reuters reported the aftermath of the Gezani cyclone, which ripped through Madagascar last week, leaving 59 dead and more than 16,000 displaced people.
20cm
The average rise in global sea levels since 1901, according to a Carbon Brief guest post on the challenges in projecting future rises.
Latest climate research
- Wildfire smoke poses negative impacts on organisms and ecosystems, such as health impacts on air-breathing animals, changes in forests’ carbon storage and coral mortality | Global Ecology and Conservation
- As climate change warms Antarctica throughout the century, the Weddell Sea could see the growth of species such as krill and fish and remain habitable for Emperor penguins | Nature Climate Change
- About 97% of South American lakes have recorded “significant warming” over the past four decades and are expected to experience rising temperatures and more frequent heatwaves | Climatic Change
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
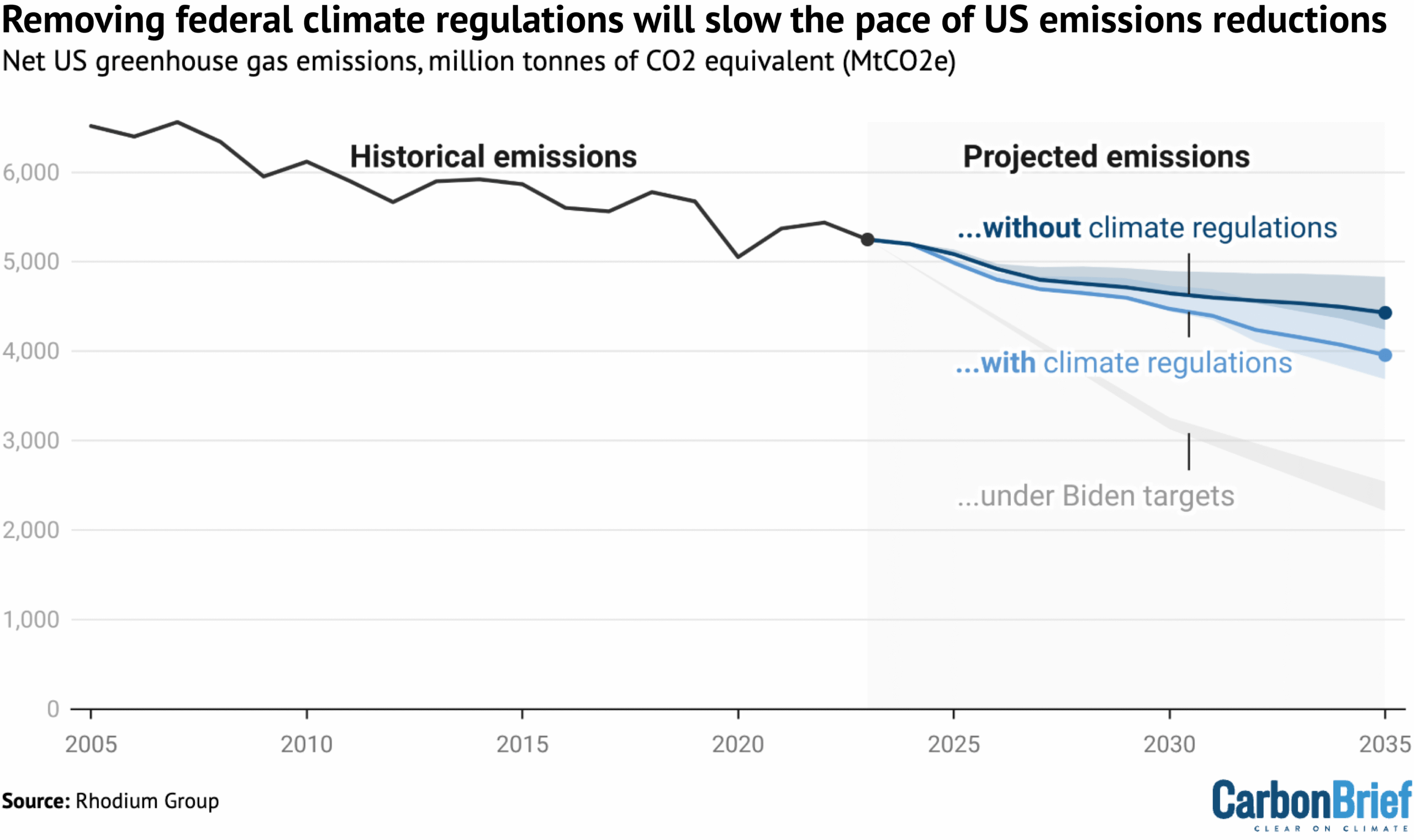
Repealing the US’s landmark “endangerment finding”, along with actions that rely on that finding, will slow the pace of US emissions cuts, according to Rhodium Group visualised by Carbon Brief. US president Donald Trump last week formally repealed the scientific finding that underpins federal regulations on greenhouse gas emissions, although the move is likely to face legal challenges. Data from the Rhodium Group, an independent research firm, shows that US emissions will drop more slowly without climate regulations. However, even with climate regulations, emissions are expected to drop much slower under Trump than under the previous Joe Biden administration, according to the analysis.
Spotlight
How a ‘tree invasion’ helped to fuel South America’s fires
This week, Carbon Brief explores how the “invasion” of non-native tree species helped to fan the flames of forest fires in Argentina and Chile earlier this year.
Since early January, Chile and Argentina have faced large-scale and deadly wildfires, including in Patagonia, which spans both countries.
These fires have been described as “some of the most significant and damaging in the region”, according to a World Weather Attribution (WWA) analysis covered by Carbon Brief.
In both countries, the fires destroyed vast areas of native forests and grasslands, displacing thousands of people. In Chile, the fires resulted in 23 deaths.
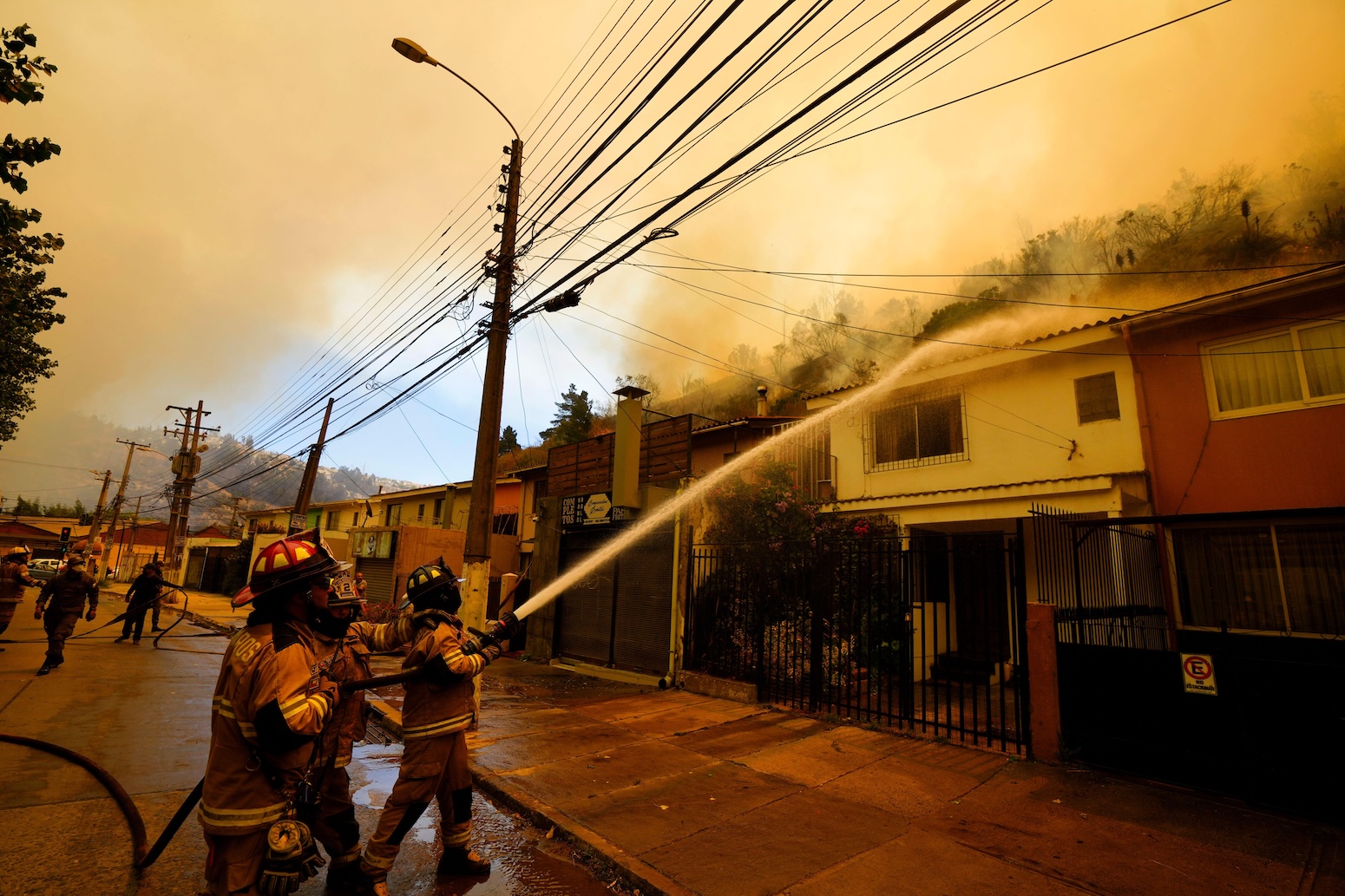

Multiple drivers contributed to the spread of the fires, including extended periods of high temperatures, low rainfall and abundant dry vegetation.
The WWA analysis concluded that human-caused climate change made these weather conditions at least three times more likely.
According to the researchers, another contributing factor was the invasion of non-native trees in the regions where the fires occurred.
The risk of non-native forests
In Argentina, the wildfires began on 6 January and persisted until the first week of February. They hit the city of Puerto Patriada and the Los Alerces and Lago Puelo national parks, in the Chubut province, as well as nearby regions.
In these areas, more than 45,000 hectares of native forests – such as Patagonian alerce tree, myrtle, coigüe and ñire – along with scrubland and grasslands, were consumed by the flames, according to the WWA study.
In Chile, forest fires occurred from 17 to 19 January in the Biobío, Ñuble and Araucanía regions.
The fires destroyed more than 40,000 hectares of forest and more than 20,000 hectares of non-native forest plantations, including eucalyptus and Monterey pine.
Dr Javier Grosfeld, a researcher at Argentina’s National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) in northern Patagonia, told Carbon Brief that these species, introduced to Patagonia for production purposes in the late 20th century, grow quickly and are highly flammable.
Because of this, their presence played a role in helping the fires to spread more quickly and grow larger.
However, that is no reason to “demonise” them, he stressed.
Forest management
For Grosfeld, the problem in northern Patagonia, Argentina, is a significant deficit in the management of forests and forest plantations.
This management should include pruning branches from their base and controlling the spread of non-native species, he added.
A similar situation is happening in Chile, where management of pine and eucalyptus plantations is not regulated. This means there are no “firebreaks” – gaps in vegetation – in place to prevent fire spread, Dr Gabriela Azócar, a researcher at the University of Chile’s Centre for Climate and Resilience Research (CR2), told Carbon Brief.
She noted that, although Mapuche Indigenous communities in central-south Chile are knowledgeable about native species and manage their forests, their insight and participation are not recognised in the country’s fire management and prevention policies.
Grosfeld stated:
“We are seeing the transformation of the Patagonian landscape from forest to scrubland in recent years. There is a lack of preventive forestry measures, as well as prevention and evacuation plans.”
Watch, read, listen
FUTURE FURNACE: A Guardian video explored the “unbearable experience of walking in a heatwave in the future”.
THE FUN SIDE: A Channel 4 News video covered a new wave of climate comedians who are using digital platforms such as TikTok to entertain and raise awareness.
ICE SECRETS: The BBC’s Climate Question podcast explored how scientists study ice cores to understand what the climate was like in ancient times and how to use them to inform climate projections.
Coming up
- 22-27 February: Ocean Sciences Meeting, Glasgow
- 24-26 February: Methane Mitigation Europe Summit 2026, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 25-27 February: World Sustainable Development Summit 2026, New Delhi, India
Pick of the jobs
- The Climate Reality Project, digital specialist | Salary: $60,000-$61,200. Location: Washington DC
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), science officer in the IPCC Working Group I Technical Support Unit | Salary: Unknown. Location: Gif-sur-Yvette, France
- Energy Transition Partnership, programme management intern | Salary: Unknown. Location: Bangkok, Thailand
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 20 February 2026: EU’s ‘3C’ warning | Endangerment repeal’s impact on US emissions | ‘Tree invasion’ fuelled South America’s fires appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Q&A: How Trump is threatening climate science in Earth’s polar regions
Since Donald Trump returned to the White House last year, his administration in the US has laid off thousands of scientists and frozen research grants worth billions of dollars.
The cutbacks have had far-reaching consequences for all areas of scientific research, extending all the way to Earth’s fragile polar regions, researchers say.
Speaking to Carbon Brief, polar researchers explain how Trump’s attacks on science have affected efforts to study climate change at Earth’s poles, including by disrupting fieldwork, preventing data collection and even forcing researchers to leave the US.
One climate scientist tells Carbon Brief that the administration’s decision to terminate the only US icebreaker used in Antarctica forced her to cancel her fieldwork at the last minute – with her scientific cargo still held up in Chile.
As US polar scientists reel from the cuts, Trump has caused a geopolitical storm with threats to take control of Greenland, the self-ruling island which is part of the Kingdom of Denmark and located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans.
Below, Carbon Brief speaks to experts about what Trump’s sweeping changes could mean for climate science at Earth’s poles
- Why is the US important for polar research?
- How has Trump affected US polar research in his second term?
- What could the changes mean for international climate research at Earth’s poles?
- What could be the impact of Trump’s threats to take control of Greenland on climate research?
Why is the US important for polar research?
The US’s wealth, power and geography have made it a key player in polar research for more than a century.
Ahead of Trump’s second term, the National Science Foundation (NSF), a federal agency that funds US science, was the largest single funder of polar research globally, with its Office of Polar Programs overseeing extensive research in both the Arctic and Antarctica.
The US has three permanent bases in Antarctica: McMurdo Station, Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station and Palmer Station.
In Alaska, which the US purchased from Russia in 1867, there is the Toolik Field Station and the Barrow Arctic Research Center. The US also has the Summit Station in Greenland.
US institutes operate several satellites that provide scientists across the world with key data on the polar regions.
This includes the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System, which provides data used for extreme weather forecasting.
Over the past few years, US institutes have led and provided support for the world’s largest polar expeditions.
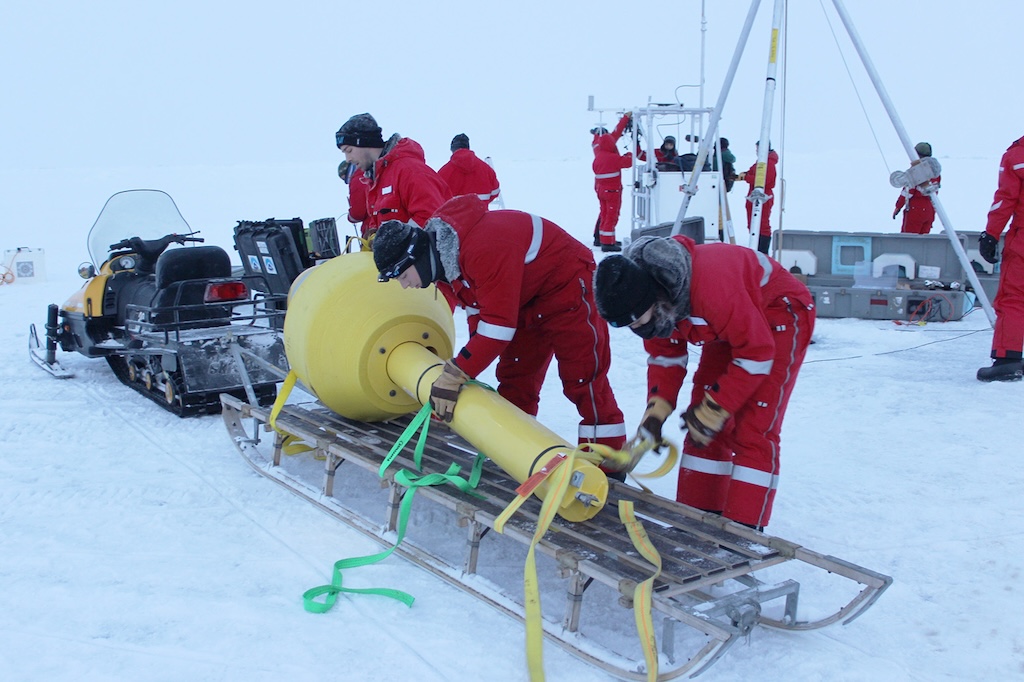

This includes MOSAiC, the largest Arctic expedition on record, which took place from 2019-20 and was co-led by research institutes from the US and Germany. [Carbon Brief joined the expedition for its first leg and covered it in depth with a series of articles.]
The US has historically been “incredibly valuable” to research efforts in the Arctic and Antarctica, a senior US polar scientist currently living in Europe, who did not wish to be named, tells Carbon Brief.
“For a lot of the international collaborations, the US is a big component, if not the largest,” the scientist says.
“We do a lot of collaborative work with other countries,” adds Dr Jessie Creamean, an atmospheric scientist working in polar regions based at Colorado State University. “Doing work in the polar regions is really an international thing.”
How has Trump affected US polar research in his second term?
Since returning to office, the Trump administration has frozen or terminated 7,800 research grants from federal science agencies and laid off 25,000 scientists and personnel.
This includes nearly 2,000 research grants from the NSF, which is responsible for the Office for Polar Programs and for funding a broad range of climate and polar research.
Courts have since made orders to reinstate thousands of these grants and some universities have settled with the federal government to unfreeze funding. However, it is unclear whether scientists have yet received those funds.
As with other areas of US science, the impact of Trump’s attacks on polar research have been far-reaching and difficult to quantify, scientists tell Carbon Brief.
Key scientific institutions affected include NASA, NOAA and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado.
In December, the Trump administration signalled that it planned to dismantle NCAR, calling it a source of “climate alarmism”. At the end of January, the NSF published a letter that “doubled down” on the administration’s promise to “restructure” and “privatise” NCAR.
NCAR has been responsible for a host of polar research in recent years, with several NCAR scientists involved in the MOSAiC expedition.
“NCAR is kind of like a Mecca for atmospheric research,” the US polar scientist who did not want to be named tells Carbon Brief. “They’ve done so much. Now their funding is drying up and people are scrambling.”
At NOAA, one of the major polar programmes to be affected is the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), which regularly issues updates about Arctic and Antarctic sea ice.
Last July, Space reported that researchers at NSIDC were informed by the Department of Defense – now renamed the Department of War under Trump – that they would lose access to data from a satellite operated by the US air force, which was used to calculate sea ice changes.
Although the Department of Defense reversed the decision following a public outcry, the uncertainty drove the researchers at NSIDC to switch to sourcing data from a Japanese satellite instead, explains Dr Zack Labe. Labe is a climate scientist who saw his position at NOAA terminated under the Trump administration and now works at the nonprofit research group Climate Central. He tells Carbon Brief:
“It looked like they were losing access to that data and, after public outcry, they regained access to the data. And then, later this year, they had to switch to another satellite.”
He adds that the Trump administration’s layoffs and budget cuts has also forced the programme to scale back its communications initiatives:
“A big loss at NSIDC is that they used to put out these monthly summaries of current conditions in Greenland, the Arctic and Antarctic called Sea Ice Today. It was a really important resource to describe the current weather and sea ice conditions in these regions.
“These reports went to stakeholders, they went to Indigenous communities within the Arctic. And that has stopped in the past year due to budget cuts.”
Elsewhere, the New York Times reported that a director at the Office for Polar Programs found out she was being laid off while on a trip to Antarctica.
US polar research took another hit in September, when the NSF announced that it was terminating the lease for the Nathaniel B Palmer, the only US icebreaker dedicated to Antarctic research.
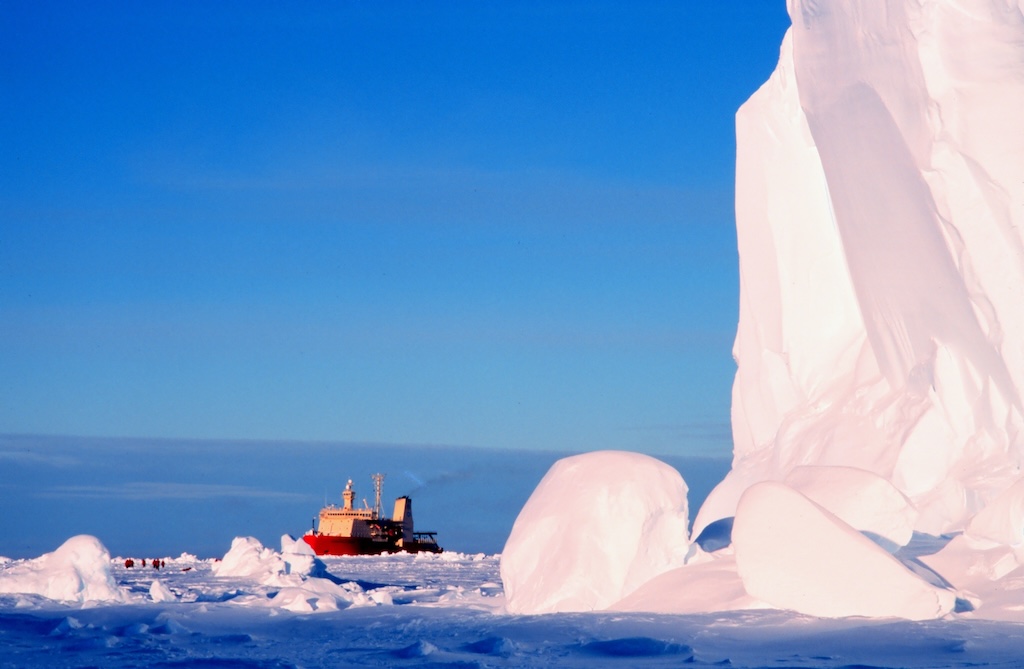

The statement gave just one month’s notice, saying that the vessel would be returned to its operator in October.
Creamean was among the scientists who were affected by the termination. She tells Carbon Brief:
“I was supposed to go on that icebreaker in September. I have a project funded at Palmer Station, along with colleagues from Scripps Institution of Oceanography. We were supposed to go set up for an 18-month study there. We have the money for the project, but we just didn’t get to go because the icebreaker got decommissioned.
“It was a big bummer. We shipped everything down to South America. All of our cargo is still sitting in Punta Arenas [in Chile].”
Elsewhere, other scientists have warned that the termination of the icebreaker could affect the continuity of Antarctic data collection.
In a statement, Dr Naomi Ochwat, a glaciologist at the University of Colorado, Boulder, said that decades of data on changes to Antarctic glaciers taken from the deck of the Palmer had been vital to her research.
For some, one of the most worrying impacts of Trump’s attacks on US polar science is on the careers of scientists, which will likely lead to many of them leaving the country.
All of the researchers that Carbon Brief spoke to said they had heard many stories of US polar scientists deciding to relocate outside of the country or to leave the profession altogether.
Creamean is one of the polar scientists to make the difficult decision to temporarily leave the US. She says:
“I’m actually moving to Sweden for a year starting in May. I’m going to do a visiting science position [at Stockholm University]. I’m hoping to come back. But if things are not looking good and things are looking more positive in Sweden, maybe I’ll stay there. I don’t know.”
Labe tells Carbon Brief that the “brain drain” of US scientists is the “biggest story” when it comes to Trump’s impact on polar research:
“I think one of the long-term repercussions is just how many people will be forced out of science due to a lack of opportunities. I think this is something that will grow in 2026. There were a lot of grants that were two-to-three years and, so, were still running, but they will be ending now.”
What could the changes mean for international climate research at Earth’s poles?
With all research at Earth’s poles relying heavily on international collaboration, Trump’s attacks on science are likely to have far-reaching implications outside of the US, scientists tell Carbon Brief.
One implication of budget and personnel cuts could be the loss of continuous data from US researchers, bases and satellites.
Many US polar datasets have been collected for decades and are relied upon by scientists and institutes around the world. This includes records for Arctic and Antarctica’s oceans, sea ice, atmosphere and wildlife.
Trump’s impact has highlighted to scientific organisations outside of the US how vulnerable US datasets can be to political changes, says Labe, adding:
“From a climate perspective, you need a consistent data record over a long period of time. Even a small gap in data caused by uncertainty can cause major issues in understanding long-term trends in the polar regions.
“Other scientific organisations around the world are realising that they’re going to have to find alternative sources for data.”
Creamean tells Carbon Brief that, while some datasets have been discontinued, researchers have made an effort to keep records going despite personnel and budget constraints. She says:
“I know at Summit Station in Greenland they had some instruments that were pulled out that had been measuring things like the surface energy budget for a long time. That dataset has been discontinued.
“Thankfully, some programmes have been able to somehow hold on and continue to do baseline measurements. There’s a station up in Alaska [Barrow] where, as far as I know, measurements have been maintained there. That’s good because some measurements up there have been happening since the 60s and 70s.”

Trump’s changes could also cast uncertainty over the US’s role in taking part and offering support to upcoming collaborative Arctic and Antarctic expeditions.
In addition to helping scientists better understand the impact of climate change on Earth’s polar regions, these expeditions have also enabled countries with testy geopolitical relationships to come together for a common goal, the US polar scientist who did not want to be named tells Carbon Brief.
For example, the MOSAiC expedition from 2019-20 saw the US and Germany work alongside Russian and Chinese research institutes to study the impact of climate change on the Arctic, says the scientist, adding:
“It was an international collaboration that involved people who should be geopolitical enemies. Science is a way that we seem to be able to work together, to solve problems together, because we all live on one planet. And, right now, to see these changes in the US, it’s quite concerning [for these kinds of collaborations].”

The retreat of the US from polar research might see other powers step up to fill the gap, scientists tell Carbon Brief.
Several scientists mentioned the Nordic countries as possibly taking a larger role in leading polar research, while one said that “China seems to be picking up the slack that’s left behind”.
China currently has five Antarctic research stations – Great Wall, Zhongshan, Kunlun, Taishan and Qinling – along with one Arctic station in Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard.
The Financial Times recently reported on China’s growing ambitions for Arctic exploration, involving its fleet of five icebreakers.
What could be the impact of Trump’s threats to take control of Greenland on climate research?
In recent months, Trump has whipped up a media frenzy with threats to take control of Greenland, the world’s largest island lying between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, which is self-governing and part of the Kingdom of Denmark.
Last month, he clarified that he will not try to take Greenland “by force”, but that he is seeking “immediate negotiations” to acquire the island for “national security reasons”.
Trump’s interest in the island is likely influenced by the rapid melting away of Arctic sea ice due to climate change, which is opening up new sea routes and avenues for potential resource exploitation, reported the Washington Post.
His comments have sparked condemnation from a wide range of US scientists who conduct fieldwork in Greenland.
An open letter signed by more than 350 scientists “vehemently opposes” Trump’s threats to take control of Greenland and expresses “solidarity and gratitude” to Greenland’s population. It says:
“Greenland deserves the world’s attention: it occupies a key position geopolitically and geophysically. As climate warms, rapid loss of Greenland’s ice affects coastal cities and communities worldwide.”
A breakdown in diplomatic relations between the US and Greenland could prevent scientists from being able to carry out their climate research on the island, one of the scientists to sign the letter wrote in a supporting statement:
“Scientific access to Arctic environments is essential for research which secures our shared future and, directly, materially benefits American citizens. It is deeply upsetting that these essential relationships are being undermined, perhaps irreparably, by the Trump administration.”
Dr Yarrow Axford, one of the letter’s organisers who is a palaeoclimatologist and science communicator based in Massachusetts, told Nature that Trump’s comments could put Greenland climate research at risk, saying:
“We Americans have benefited from all these decades of peaceful partnership with Greenland. Scientific understanding of climate change has benefited tremendously. I hope scientists can reach out to Congress and point out what a wonderful partnership that is.”
In addition to the US-run Summit Station, there are at least eight other research stations in Greenland, operated by a range of institutions from across the world.
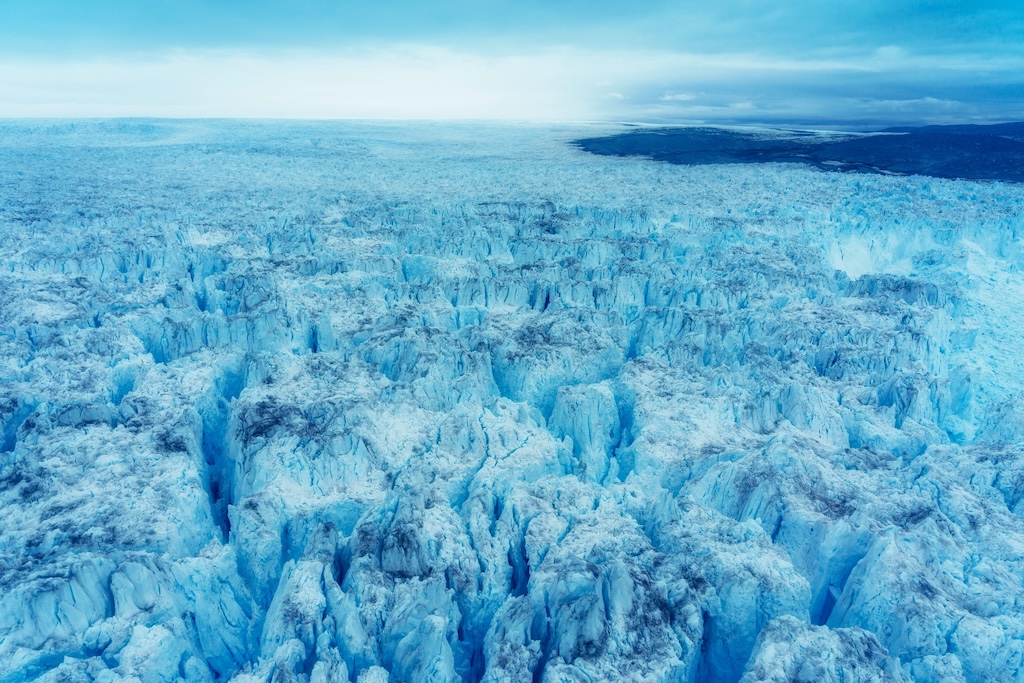

A major focus of research efforts in the region is the Greenland ice sheet, Earth’s second-largest body of ice which is rapidly melting away because of climate change.
The ice sheet holds enough freshwater to raise global sea levels by around more than seven metres, if melted completely.
Any political moves that could “jeopardise” the study of the Greenland ice sheet would be detrimental, says Creamean:
“Greenland is a ‘tipping point’ in that, the ice sheet melting, that could be one of the biggest contributors to sea level rise. It’s not like we can wait to study it, it needs to be understood now.”
The post Q&A: How Trump is threatening climate science in Earth’s polar regions appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Q&A: How Trump is threatening climate science in Earth’s polar regions
Greenhouse Gases
Limiting warming to 2C is ‘crucial’ to protect pristine Antarctic Peninsula
Keeping global warming to less than 2C above pre-industrial temperatures is “crucial” for limiting damage to the Antarctic Peninsula’s unique ecosystems, according to a new study.
The paper, published in Frontiers in Environmental Science, reviews the latest literature on the impacts of warming on Antarctica’s most biodiverse region.
The Antarctic Peninsula is home to many types of penguins, whales and seals, as well as the continent’s only two flowering plant species.
The study also analyses previously published data and model output to create a fuller picture of the potential futures facing the peninsula under different levels of global warming.
Under a low-emissions scenario that keeps global temperature rise to less than 2C, the Antarctic Peninsula will still face 2.28C of warming by the end of the century, the study says, while higher-emissions futures could push the region’s warming above 5C.
Limiting warming to 2C would avoid the more dramatic impacts associated with higher emissions, such as ice-shelf collapse, increasingly frequent extreme weather events and extinction of some of the peninsula’s native species, according to the paper.
However, warming of 4C would result in “dramatic and irreversible” damages, it adds.
Importantly, the paper shows that the outlook for the peninsula is “dependent on the choices we make now and in the near future”, a researcher not involved in the study tells Carbon Brief.
‘Alternative futures’
The Antarctic Peninsula juts northwards from West Antarctica, stretching towards the tip of South America.
The region is made up of the main peninsula, which spans around 232,000 square kilometres (km2) and a series of islands and archipelagos that cover another 80,000km2. The mainland peninsula is nearly entirely covered in ice, while its islands – many of which are further north – are around 92% covered.
Taken as a whole, the Antarctic Peninsula is the most biodiverse region of the icy continent, and a “beautiful, pristine environment”, says Prof Bethan Davies, a glaciologist at Newcastle University, who led the new work.
It hosts many species of penguins and whales, as well as apex predators, such as orcas and leopard seals. Each spring, more than 100m birds nest there to rear their young. It is also home to hundreds of species of moss and lichens, along with the only two flowering plant species on the continent.
The peninsula is also the part of Antarctica that is undergoing the most significant changes due to climate change, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC’s) sixth assessment report.
In 2019, a group of researchers published a study on the fate of the Antarctic Peninsula at 1.5C of global warming above pre-industrial temperatures. However, it has since “become apparent” that keeping warming below this limit is no longer in reach, Davies says.
The team selected three warming scenarios for their study:
- a low-emissions scenario, SSP1-2.6
- a high-emissions scenario characterised by growing nationalism, SSP3-7.0
- a very-high-emissions scenario, SSP5-8.5
SSP1-2.6 represents the “new goal” of keeping warming less than 2C, Davies says.
SSP3-7.0 and SSP5-8.5 represent “alternative futures” – with the former being one that “felt quite relevant” to the current state of the world and the latter being “useful to consider as a high end”, she adds.
For each potential future, the researchers conducted a literature review to assess the changes to different parts of the peninsula’s physical and biological systems. To fill gaps in the published literature, the team also reanalysed existing datasets and results from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project 6 (CMIP6) group of models developed for the IPCC’s latest assessment cycle.
Dr Sammie Buzzard, a glaciologist at the Centre for Polar Observation and Modelling, tells Carbon Brief:
“By choosing three different emissions scenarios, they’ve shown just how much variability there is in the possible future of the Antarctica Peninsula that is dependent on the choices we make now and in the near future.”
Buzzard, who was not involved in the new study, adds that it “highlights the consequences of this [change] for the glaciers, sea ice and unique wildlife habitats in this region”.
Physical changes
The Antarctic Peninsula is already experiencing climate change, with one record showing sustained warming over nearly a century. The peninsula is also warming more rapidly than the global average.
For the new study, Davies and her team assess the changes in temperature for the decade 2090-99 across 19 CMIP6 models.
They find that under the low-emissions scenario, the Antarctic Peninsula is projected to warm by 2.28C compared to pre-industrial temperatures, or about 0.55C above its current level of warming. Under the high- and very-high-emissions scenarios, the peninsula will reach temperatures of 5.22C and 6.10C above pre-industrial levels, respectively.
They also analyse output from 12 sea ice models.
In each scenario, they find that the western side of the Antarctic Peninsula experiences the largest declines in sea ice concentration during the winter months of June, July and August. For the southern hemisphere’s summertime, it is the eastern side of the peninsula that shows the largest decreases.
The maps below show the projected change in sea-ice concentration around the Antarctic Peninsula for each season (left to right) under low (top), high (middle) and very high (bottom) emissions. Decreasing concentrations are shown in blue and increasing concentrations are shown in red.

The paper gives a “great overview of the current literature on the Antarctic Peninsula, examining multiple aspects of the region holistically”, Dr Tri Datta, a climate scientist at the Delft University of Technology, tells Carbon Brief.
However, Datta – who was not involved in the study – notes that the coarse resolution of CMIP6 models means that the “most vulnerable regions are too poorly represented to capture important feedbacks”, such as the forming of meltwater ponds on the tops of glaciers, which warm much more than the icy surface around them.
Ecosystem impacts
The study also looks at potential futures for the Antarctic Peninsula’s marine and terrestrial ecosystems – albeit, much more briefly than it examines the physical changes.
This is because modelling ecosystem change is very difficult, Davies explains:
“If you’re going to model an ecosystem, you have to model the climate and the ocean and the ice and how that changes. Exactly how that ecosystem responds to those changes is still beyond most of our Earth system models.”
Still, by looking at trends in the Antarctic over the past several decades, as well as changes that have occurred in other high-latitude regions, the researchers piece together some of the potential impacts of warming.
They conclude that under SSP1, the changes experienced by ecosystems are “uncertain”, but will “likely” be similar to present day – with some terrestrial species, such as its flowering plants, even benefitting from increased habitat area and water availability.

However, under higher-emissions scenarios, species will become “increasingly likely” to experience warmer temperatures than they are suited for.
Other changes that may occur in the very-high-emissions scenario are closely linked to the projected reductions in sea ice. These include the increased spread of invasive alien species, reduced ranges for krill and the displacement of animals unable to tolerate the warmer temperatures by those more able to adapt.
Prof Scott Doney, an oceanographer and biogeochemist at the University of Virginia, notes that some of these changes are already happening. Doney, who was not involved in the study, is part of an ongoing research programme on the Antarctic Peninsula known as the Palmer Long-Term Ecological Research project.
He tells Carbon Brief that Adélie penguins, which are a polar species, have “seen a massive drop in their breeding population” at their research sites. Meanwhile, gentoo penguins – whose range extends into the subpolar regions – “have been quite opportunistic” in colonising those breeding sites.
‘Changes here first’
Antarctica is home to 50 year-round research stations and dozens of summer-only ones, operated by more than 30 countries.
Around a dozen year-round stations are found on the peninsula and its islands, including the oldest permanent settlement in Antarctica – Argentina’s Base Orcadas, established in 1903 by the Scottish national Antarctic expedition.
The continent is home to commercially important fisheries – particularly krill, which also play a critical role in the Antarctic marine food chain.
Increasingly, the Antarctic Peninsula is also a tourist destination.
Climate change poses a threat to all of these activities, Davies says.
For example, much of the research infrastructure on the Antarctic Peninsula was “built to assume dry, snowy conditions”, she says. Rain can “cause quite a lot of difficulty”, she adds.
(In an article published last year, Carbon Brief looked at the causes of rain in sub-zero temperatures in West Antarctica.)
Decreased sea ice cover can impact krill populations. It can also lead to increased ship traffic, as more of the continent becomes accessible throughout more of the year.
Furthermore, Davies says, the changes occurring on the peninsula will reverberate across Antarctica and around the world. She tells Carbon Brief:
“We’ll see changes here first and those changes will continue to be felt in West Antarctica and continent-wide…What happens in Antarctica doesn’t stay in Antarctica.”
The post Limiting warming to 2C is ‘crucial’ to protect pristine Antarctic Peninsula appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Limiting warming to 2C is ‘crucial’ to protect pristine Antarctic Peninsula
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits