▶️ Powering Up North: Finland’s Landscape of Renewable Energy
Finland, the land of a thousand lakes and endless forests, is also forging a path towards a sustainable future fueled by renewable energy sources.
With ambitious goals and a commitment to green innovation, the country is rapidly transforming its energy landscape, offering valuable insights for other nations aiming for similar transitions.
Finland’s impressive progress in embracing renewable energy demonstrates the potential for a sustainable future. The country’s commitment to ambitious goals, coupled with strategic investments and technological innovation, serves as an inspiration for other nations on their paths toward a cleaner and greener tomorrow. As Finland continues its journey, the lessons learned and solutions developed will undoubtedly contribute to a global shift towards a renewable energy future.
▶️ History of Renewable Energy Development in Finland: A Path Less Traveled
Finland’s journey towards renewables hasn’t always been a smooth path, but it’s a fascinating one nonetheless. Here’s a glimpse into its key milestones:
Early Reliance on Hydropower (Pre-1970s):
- Finland’s hydropower potential was tapped early on, with the first major hydroelectric plant (Imatra) commissioned in 1929.
- Hydropower became the dominant source of electricity, especially in the post-WWII era, reaching its peak share of over 90% in the 1970s.
Oil Embargo and Diversification (1970s-1990s):
- The 1973 oil crisis exposed Finland’s dependence on imported fossil fuels, prompting a shift towards diversification.
- Nuclear power entered the scene, with four plants built between 1972 and 1995.
- Biomass gained traction, particularly for district heating and combined heat and power (CHP) generation.
- Wind power saw its first pilot projects in the 1980s, but development remained slow.
Renewables Gain Momentum (2000s-Present):
- The 2000s witnessed a renewed focus on renewables, driven by EU mandates and environmental concerns.
- Wind power experienced significant growth, particularly with the construction of large onshore farms like Kalajoki.
- Biomass continued to play a crucial role, but concerns about sustainability led to a shift towards more responsible practices.
- Solar power started gaining traction, initially through large-scale solar thermal projects and gradually shifting towards distributed generation with rooftop panels.
Reaching for New Heights (2020s-Onwards):
- Finland set ambitious targets for renewable energy, aiming for 55% by 2025 and 70% by 2035.
- Offshore wind development received major impetus, with projects like HaiSea poised to significantly boost wind power capacity.
- Investments in innovative technologies like biofuels and energy storage are accelerating.
- Public acceptance of renewables continues to grow, paving the way for smoother development and integration.
Key Takeaways:
- Finland’s historical reliance on hydropower laid the foundation for renewable energy development.
- Geopolitical and environmental factors have continuously shaped the country’s energy choices.
- Diversification has become crucial, with wind, biomass, and solar playing increasingly important roles.
- Ambitious targets and technological advancements are propelling Finland towards a sustainable future powered by renewables.
Additional Points:
- Finland’s unique geographic location influences its energy choices, with abundant forests favoring biomass and strong winds supporting wind power development.
- The country fosters close collaboration between research institutions, industries, and policymakers to drive innovation and overcome challenges.
- While Finland has achieved remarkable progress, challenges remain, including grid integration, public acceptance in certain areas, and balancing environmental sustainability with economic considerations.
▶️ Finland’s Renewable Energy Landscape: Key Statistics
Leading the Charge with Renewables:
- Current Status: As of 2022, renewable energy accounted for 58% of Finland’s final electricity consumption, surpassing the national target of 55%. This impressive share is further broken down as:
- Hydropower: 35%
- Wind power: 12%
- Biomass: 9%
- Solar power: 2%
- Future Goals: By 2035, Finland aims to achieve carbon neutrality, with renewables expected to provide 70% of the country’s total energy demand. Additionally, the government plans to phase out coal entirely by 2029.
Key Players and Technologies:
- Hydropower: Remains the backbone of Finland’s renewable energy mix, with several large hydroelectric plants contributing significantly. However, new investments are focusing on smaller-scale, run-of-the-river projects.
- Wind power: The wind energy sector is experiencing rapid growth, with both onshore and offshore projects gaining momentum. Finland boasts the largest onshore wind farm in Europe (Kalajoki) and has ambitious plans for offshore wind development in the Baltic Sea.
- Biomass: Primarily sourced from wood waste and biofuels, biomass plays a crucial role in heating and combined heat and power (CHP) generation. Research and development are underway to explore advanced biofuels for transportation and other sectors.
- Solar power: While currently a smaller contributor, solar energy is seeing significant growth, particularly in the distributed generation segment with rooftop solar panels.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Geographic factors: Finland’s dispersed population and harsh winter conditions pose challenges for grid integration and infrastructure development, particularly for wind and solar projects.
- Public acceptance: While generally supportive of renewable energy, concerns about visual impact and land use require careful consideration and community engagement.
- Technology advancements: Continued advancements in storage solutions, smart grids, and renewable energy technologies are crucial for further optimization and integration.
Finland’s Renewable Energy Landscape: Key Statistics Table
| Statistic | Value (Year) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Share of Final Electricity Consumption | 58% (2022) | Ministry of Economic Affairs and Employment of Finland |
| Hydropower Contribution | 35% (2022) | Finnish Energy Industries |
| Wind Power Contribution | 12% (2022) | Finnish Wind Power Association |
| Biomass Contribution | 9% (2022) | Finnish Energy Industries |
| Solar Power Contribution | 2% (2022) | Finnish Energy Industries |
| Target for Renewable Energy Share of Total Energy Demand (2035) | 70% | Ministry of Economic Affairs and Employment of Finland |
| Target for Coal Phase-Out | 2029 | Ministry of Economic Affairs and Employment of Finland |
| Rank in 2023 Climate Change Performance Index | 4th | Germanwatch & Climate Action Tracker |
| Per Capita Greenhouse Gas Emissions (compared to EU) | Among the lowest | Eurostat |
| Share of District Heating from Renewables | Over 90% | Finnish Energy Industries |
Additional Notes:
- Data for specific technology contributions may vary slightly depending on the source.
- Greenhouse gas emissions and district heating statistics refer to the latest available data, which may not be from 2022.
Additional Statistics:
- Finland ranks 4th in the world in the 2023 Climate Change Performance Index.
- The country’s per capita greenhouse gas emissions are among the lowest in the European Union.
- Over 90% of Finland’s district heating comes from renewable sources.
▶️ Gazing into the Crystal Ball: Future of Renewable Energy Development in Finland
Predicting the future is always tricky, but Finland’s commitment to renewable energy and ongoing advancements paint a promising picture. Here’s a peek into what the future might hold:
Dominant Duo: Wind and Solar Take Center Stage:
- Offshore Wind: With the recent green light for large-scale projects like HaiSea, offshore wind is poised to become a major player, potentially contributing up to 50% of Finland’s electricity demand by 2050.
- Solar Power: Technological advancements and cost reductions are expected to propel solar energy growth, particularly in the distributed generation segment with rooftop panels and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV).
Biomass Transformation:
- Focus on Sustainability: Sustainable forestry practices and advanced biofuels like bioethanol and biogas are likely to dominate, ensuring responsible biomass utilization.
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP): Biomass will continue to play a vital role in CHP plants, especially for district heating, but integration with other renewables requires optimization.
Technological Twists:
- Energy Storage: Advancements in battery storage and other technologies will be crucial for managing the variability of wind and solar power, enabling smoother grid integration.
- Smart Grids: Digitalization and intelligent grid management systems will optimize energy distribution and facilitate the integration of diverse renewable sources.
- Hydrogen: While still in its early stages, hydrogen might emerge as a clean fuel option for transportation and industrial applications, requiring further research and infrastructure development.
Community and Collaboration:
- Public Engagement: Continued efforts to increase public awareness and address concerns about visual impact and land use will be crucial for ensuring social acceptance of renewable projects.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: Collaboration with neighboring countries on issues like grid infrastructure and energy trading can contribute to regional decarbonization efforts.
Challenges to Navigate:
- Economic Viability: Balancing the need for affordable energy with investments in new technologies will require innovative financing models and cost-competitive solutions.
- Policy Stability: Clear and long-term policy frameworks are essential to attract investments and ensure market stability in the renewable energy sector.
- Grid Modernization: Upgrading the existing grid infrastructure is crucial to accommodate the increasing share of variable renewables and ensure network stability.
Overall Outlook:
Despite the challenges, Finland’s future appears bright, with renewables expected to dominate its energy mix. Continued innovations, strategic investments, and collaborative efforts will be key to achieving climate goals and securing a sustainable energy future for the nation.
https://www.exaputra.com/2024/02/finlands-landscape-of-renewable-energy.html
Renewable Energy
BladeBUG Tackles Serial Blade Defects with Robotics
Weather Guard Lightning Tech

BladeBUG Tackles Serial Blade Defects with Robotics
Chris Cieslak, CEO of BladeBug, joins the show to discuss how their walking robot is making ultrasonic blade inspections faster and more accessible. They cover new horizontal scanning capabilities for lay down yards, blade root inspections for bushing defects, and plans to expand into North America in 2026.
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly newsletter on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on YouTube, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary’s “Engineering with Rosie” YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
Welcome to Uptime Spotlight, shining Light on Wind. Energy’s brightest innovators. This is the Progress Powering Tomorrow.
Allen Hall: Chris, welcome back to the show.
Chris Cieslak: It’s great to be back. Thank you very much for having me on again.
Allen Hall: It’s great to see you in person, and a lot has been happening at Blade Bugs since the last time I saw Blade Bug in person. Yeah, the robot. It looks a lot different and it has really new capabilities.
Chris Cieslak: So we’ve continued to develop our ultrasonic, non-destructive testing capabilities of the blade bug robot.
Um, but what we’ve now added to its capabilities is to do horizontal blade scans as well. So we’re able to do blades that are in lay down yards or blades that have come down for inspections as well as up tower. So we can do up tower, down tower inspections. We’re trying to capture. I guess the opportunity to inspect blades after transportation when they get delivered to site, to look [00:01:00] for any transport damage or anything that might have been missed in the factory inspections.
And then we can do subsequent installation inspections as well to make sure there’s no mishandling damage on those blades. So yeah, we’ve been just refining what we can do with the NDT side of things and improving its capabilities
Joel Saxum: was that need driven from like market response and people say, Hey, we need, we need.
We like the blade blood product. We like what you’re doing, but we need it here. Or do you guys just say like, Hey, this is the next, this is the next thing we can do. Why not?
Chris Cieslak: It was very much market response. We had a lot of inquiries this year from, um, OEMs, blade manufacturers across the board with issues within their blades that need to be inspected on the ground, up the tap, any which way they can.
There there was no, um, rhyme or reason, which was better, but the fact that he wanted to improve the ability of it horizontally has led the. Sort of modifications that you’ve seen and now we’re doing like down tower, right? Blade scans. Yeah. A really fast breed. So
Joel Saxum: I think the, the important thing there is too is that because of the way the robot is built [00:02:00] now, when you see NDT in a factory, it’s this robot rolls along this perfectly flat concrete floor and it does this and it does that.
But the way the robot is built, if a blade is sitting in a chair trailing edge up, or if it’s flap wise, any which way the robot can adapt to, right? And the idea is. We, we looked at it today and kind of the new cage and the new things you have around it with all the different encoders and for the heads and everything is you can collect data however is needed.
If it’s rasterized, if there’s a vector, if there’s a line, if we go down a bond line, if we need to scan a two foot wide path down the middle of the top of the spa cap, we can do all those different things and all kinds of orientations. That’s a fantastic capability.
Chris Cieslak: Yeah, absolutely. And it, that’s again for the market needs.
So we are able to scan maybe a meter wide in one sort of cord wise. Pass of that probe whilst walking in the span-wise direction. So we’re able to do that raster scan at various spacing. So if you’ve got a defect that you wanna find that maximum 20 mil, we’ll just have a 20 mil step [00:03:00] size between each scan.
If you’ve got a bigger tolerance, we can have 50 mil, a hundred mil it, it’s so tuneable and it removes any of the variability that you get from a human to human operator doing that scanning. And this is all about. Repeatable, consistent high quality data that you can then use to make real informed decisions about the state of those blades and act upon it.
So this is not about, um, an alternative to humans. It’s just a better, it’s just an evolution of how humans do it. We can just do it really quick and it’s probably, we, we say it’s like six times faster than a human, but actually we’re 10 times faster. We don’t need to do any of the mapping out of the blade, but it’s all encoded all that data.
We know where the robot is as we walk. That’s all captured. And then you end up with really. Consistent data. It doesn’t matter who’s operating a robot, the robot will have those settings preset and you just walk down the blade, get that data, and then our subject matter experts, they’re offline, you know, they are in their offices, warm, cozy offices, reviewing data from multiple sources of robots.
And it’s about, you know, improving that [00:04:00] efficiency of getting that report out to the customer and letting ’em know what’s wrong with their blades, actually,
Allen Hall: because that’s always been the drawback of, with NDT. Is that I think the engineers have always wanted to go do it. There’s been crush core transportation damage, which is sometimes hard to see.
You can maybe see a little bit of a wobble on the blade service, but you’re not sure what’s underneath. Bond line’s always an issue for engineering, but the cost to take a person, fly them out to look at a spot on a blade is really expensive, especially someone who is qualified. Yeah, so the, the difference now with play bug is you can have the technology to do the scan.
Much faster and do a lot of blades, which is what the de market demand is right now to do a lot of blades simultaneously and get the same level of data by the review, by the same expert just sitting somewhere else.
Chris Cieslak: Absolutely.
Joel Saxum: I think that the quality of data is a, it’s something to touch on here because when you send someone out to the field, it’s like if, if, if I go, if I go to the wall here and you go to the wall here and we both take a paintbrush, we paint a little bit [00:05:00] different, you’re probably gonna be better.
You’re gonna be able to reach higher spots than I can.
Allen Hall: This is true.
Joel Saxum: That’s true. It’s the same thing with like an NDT process. Now you’re taking the variability of the technician out of it as well. So the data quality collection at the source, that’s what played bug ducts.
Allen Hall: Yeah,
Joel Saxum: that’s the robotic processes.
That is making sure that if I scan this, whatever it may be, LM 48.7 and I do another one and another one and another one, I’m gonna get a consistent set of quality data and then it’s goes to analysis. We can make real decisions off.
Allen Hall: Well, I, I think in today’s world now, especially with transportation damage and warranties, that they’re trying to pick up a lot of things at two years in that they could have picked up free installation.
Yeah. Or lifting of the blades. That world is changing very rapidly. I think a lot of operators are getting smarter about this, but they haven’t thought about where do we go find the tool.
Speaker: Yeah.
Allen Hall: And, and I know Joel knows that, Hey, it, it’s Chris at Blade Bug. You need to call him and get to the technology.
But I think for a lot of [00:06:00] operators around the world, they haven’t thought about the cost They’re paying the warranty costs, they’re paying the insurance costs they’re paying because they don’t have the set of data. And it’s not tremendously expensive to go do. But now the capability is here. What is the market saying?
Is it, is it coming back to you now and saying, okay, let’s go. We gotta, we gotta mobilize. We need 10 of these blade bugs out here to go, go take a scan. Where, where, where are we at today?
Chris Cieslak: We’ve hads. Validation this year that this is needed. And it’s a case of we just need to be around for when they come back round for that because the, the issues that we’re looking for, you know, it solves the problem of these new big 80 a hundred meter plus blades that have issues, which shouldn’t.
Frankly exist like process manufacturer issues, but they are there. They need to be investigated. If you’re an asset only, you wanna know that. Do I have a blade that’s likely to fail compared to one which is, which is okay? And sort of focus on that and not essentially remove any uncertainty or worry that you have about your assets.
’cause you can see other [00:07:00] turbine blades falling. Um, so we are trying to solve that problem. But at the same time, end of warranty claims, if you’re gonna be taken over these blades and doing the maintenance yourself, you wanna know that what you are being given. It hasn’t gotten any nasties lurking inside that’s gonna bite you.
Joel Saxum: Yeah.
Chris Cieslak: Very expensively in a few years down the line. And so you wanna be able to, you know, tick a box, go, actually these are fine. Well actually these are problems. I, you need to give me some money so I can perform remedial work on these blades. And then you end of life, you know, how hard have they lived?
Can you do an assessment to go, actually you can sweat these assets for longer. So we, we kind of see ourselves being, you know, useful right now for the new blades, but actually throughout the value chain of a life of a blade. People need to start seeing that NDT ultrasonic being one of them. We are working on other forms of NDT as well, but there are ways of using it to just really remove a lot of uncertainty and potential risk for that.
You’re gonna end up paying through the, you know, through the, the roof wall because you’ve underestimated something or you’ve missed something, which you could have captured with a, with a quick inspection.
Joel Saxum: To [00:08:00] me, NDT has been floating around there, but it just hasn’t been as accessible or easy. The knowledge hasn’t been there about it, but the what it can do for an operator.
In de-risking their fleet is amazing. They just need to understand it and know it. But you guys with the robotic technology to me, are bringing NDT to the masses
Chris Cieslak: Yeah.
Joel Saxum: In a way that hasn’t been able to be done, done before
Chris Cieslak: that. And that that’s, we, we are trying to really just be able to roll it out at a way that you’re not limited to those limited experts in the composite NDT world.
So we wanna work with them, with the C-N-C-C-I-C NDTs of this world because they are the expertise in composite. So being able to interpret those, those scams. Is not a quick thing to become proficient at. So we are like, okay, let’s work with these people, but let’s give them the best quality data, consistent data that we possibly can and let’s remove those barriers of those limited people so we can roll it out to the masses.
Yeah, and we are that sort of next level of information where it isn’t just seen as like a nice to have, it’s like an essential to have, but just how [00:09:00] we see it now. It’s not NDT is no longer like, it’s the last thing that we would look at. It should be just part of the drones. It should inspection, be part of the internal crawlers regimes.
Yeah, it’s just part of it. ’cause there isn’t one type of inspection that ticks all the boxes. There isn’t silver bullet of NDT. And so it’s just making sure that you use the right system for the right inspection type. And so it’s complementary to drones, it’s complimentary to the internal drones, uh, crawlers.
It’s just the next level to give you certainty. Remove any, you know, if you see something indicated on a a on a photograph. That doesn’t tell you the true picture of what’s going on with the structure. So this is really about, okay, I’ve got an indication of something there. Let’s find out what that really is.
And then with that information you can go, right, I know a repair schedule is gonna take this long. The downtime of that turbine’s gonna be this long and you can plan it in. ’cause everyone’s already got limited budgets, which I think why NDT hasn’t taken off as it should have done because nobody’s got money for more inspections.
Right. Even though there is a money saving to be had long term, everyone is fighting [00:10:00] fires and you know, they’ve really got a limited inspection budget. Drone prices or drone inspections have come down. It’s sort, sort of rise to the bottom. But with that next value add to really add certainty to what you’re trying to inspect without, you know, you go to do a day repair and it ends up being three months or something like, well
Allen Hall: that’s the lightning,
Joel Saxum: right?
Allen Hall: Yeah. Lightning is the, the one case where every time you start to scarf. The exterior of the blade, you’re not sure how deep that’s going and how expensive it is. Yeah, and it always amazes me when we talk to a customer and they’re started like, well, you know, it’s gonna be a foot wide scarf, and now we’re into 10 meters and now we’re on the inside.
Yeah. And the outside. Why did you not do an NDT? It seems like money well spent Yeah. To do, especially if you have a, a quantity of them. And I think the quantity is a key now because in the US there’s 75,000 turbines worldwide, several hundred thousand turbines. The number of turbines is there. The number of problems is there.
It makes more financial sense today than ever because drone [00:11:00]information has come down on cost. And the internal rovers though expensive has also come down on cost. NDT has also come down where it’s now available to the masses. Yeah. But it has been such a mental barrier. That barrier has to go away. If we’re going going to keep blades in operation for 25, 30 years, I
Joel Saxum: mean, we’re seeing no
Allen Hall: way you can do it
Joel Saxum: otherwise.
We’re seeing serial defects. But the only way that you can inspect and or control them is with NDT now.
Allen Hall: Sure.
Joel Saxum: And if we would’ve been on this years ago, we wouldn’t have so many, what is our term? Blade liberations liberating
Chris Cieslak: blades.
Joel Saxum: Right, right.
Allen Hall: What about blade route? Can the robot get around the blade route and see for the bushings and the insert issues?
Chris Cieslak: Yeah, so the robot can, we can walk circumferentially around that blade route and we can look for issues which are affecting thousands of blades. Especially in North America. Yeah.
Allen Hall: Oh yeah.
Chris Cieslak: So that is an area that is. You know, we are lucky that we’ve got, um, a warehouse full of blade samples or route down to tip, and we were able to sort of calibrate, verify, prove everything in our facility to [00:12:00] then take out to the field because that is just, you know, NDT of bushings is great, whether it’s ultrasonic or whether we’re using like CMS, uh, type systems as well.
But we can really just say, okay, this is the area where the problem is. This needs to be resolved. And then, you know, we go to some of the companies that can resolve those issues with it. And this is really about played by being part of a group of technologies working together to give overall solutions
Allen Hall: because the robot’s not that big.
It could be taken up tower relatively easily, put on the root of the blade, told to walk around it. You gotta scan now, you know. It’s a lot easier than trying to put a technician on ropes out there for sure.
Chris Cieslak: Yeah.
Allen Hall: And the speed up it.
Joel Saxum: So let’s talk about execution then for a second. When that goes to the field from you, someone says, Chris needs some help, what does it look like?
How does it work?
Chris Cieslak: Once we get a call out, um, we’ll do a site assessment. We’ve got all our rams, everything in place. You know, we’ve been on turbines. We know the process of getting out there. We’re all GWO qualified and go to site and do their work. Um, for us, we can [00:13:00] turn up on site, unload the van, the robot is on a blade in less than an hour.
Ready to inspect? Yep. Typically half an hour. You know, if we’ve been on that same turbine a number of times, it’s somewhere just like clockwork. You know, muscle memory comes in, you’ve got all those processes down, um, and then it’s just scanning. Our robot operator just presses a button and we just watch it perform scans.
And as I said, you know, we are not necessarily the NDT experts. We obviously are very mindful of NDT and know what scans look like. But if there’s any issues, we have a styling, we dial in remote to our supplement expert, they can actually remotely take control, change the settings, parameters.
Allen Hall: Wow.
Chris Cieslak: And so they’re virtually present and that’s one of the beauties, you know, you don’t need to have people on site.
You can have our general, um, robot techs to do the work, but you still have that comfort of knowing that the data is being overlooked if need be by those experts.
Joel Saxum: The next level, um, commercial evolution would be being able to lease the kit to someone and or have ISPs do it for [00:14:00] you guys kinda globally, or what is the thought
Chris Cieslak: there?
Absolutely. So. Yeah, so we to, to really roll this out, we just wanna have people operate in the robots as if it’s like a drone. So drone inspection companies are a classic company that we see perfectly aligned with. You’ve got the sky specs of this world, you know, you’ve got drone operator, they do a scan, they can find something, put the robot up there and get that next level of information always straight away and feed that into their systems to give that insight into that customer.
Um, you know, be it an OEM who’s got a small service team, they can all be trained up. You’ve got general turbine technicians. They’ve all got G We working at height. That’s all you need to operate the bay by road, but you don’t need to have the RAA level qualified people, which are in short supply anyway.
Let them do the jobs that we are not gonna solve. They can do the big repairs we are taking away, you know, another problem for them, but giving them insights that make their job easier and more successful by removing any of those surprises when they’re gonna do that work.
Allen Hall: So what’s the plans for 2026 then?
Chris Cieslak: 2026 for us is to pick up where 2025 should have ended. [00:15:00] So we were, we were meant to be in the States. Yeah. On some projects that got postponed until 26. So it’s really, for us North America is, um, what we’re really, as you said, there’s seven, 5,000 turbines there, but there’s also a lot of, um, turbines with known issues that we can help determine which blades are affected.
And that involves blades on the ground, that involves blades, uh, that are flying. So. For us, we wanna get out to the states as soon as possible, so we’re working with some of the OEMs and, and essentially some of the asset owners.
Allen Hall: Chris, it’s so great to meet you in person and talk about the latest that’s happening.
Thank you. With Blade Bug, if people need to get ahold of you or Blade Bug, how do they do that?
Chris Cieslak: I, I would say LinkedIn is probably the best place to find myself and also Blade Bug and contact us, um, through that.
Allen Hall: Alright, great. Thanks Chris for joining us and we will see you at the next. So hopefully in America, come to America sometime.
We’d love to see you there.
Chris Cieslak: Thank you very [00:16:00] much.
Renewable Energy
Understanding the U.S. Constitution
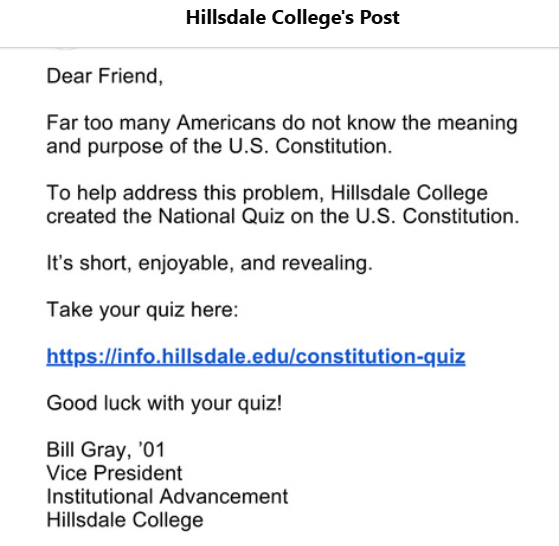 Hillsdale College is a rightwing Christian extremist organization that ostensibly honors the United States Constitution.
Hillsdale College is a rightwing Christian extremist organization that ostensibly honors the United States Constitution.
Here’s their quiz, which should be called the “Constitutional Trivia Quiz.”, whose purpose is obviously to convince Americans of their ignorance.
When I teach, I’m going for understanding of the topic, not the memorization of useless information.
Renewable Energy
Bravery Meets Tragedy: An Unending Story
 Here’s a story:
Here’s a story:
He had 3 days left until graduation.
Kendrick Castillo was 18. A robotics student. College bound. Accepted into an engineering program. The final week of school felt like countdown, not crisis.
Then a weapon appeared inside a classroom.
Students froze.
Kendrick did not.
Witnesses say he moved instantly. He lunged toward the attacker. No hesitation. No calculation.
Two other students followed his lead.
Gunfire erupted.
Kendrick was fatally sh*t.
But his movement changed the room.
Classmates were able to tackle and restrain the attacker until authorities arrived. Investigators later stated that the confrontation disrupted the attack and likely prevented additional casualties.
In seconds, an 18-year-old made a decision most adults pray they never face.
Afterward, the silence was heavier than the noise.
At graduation, his name was called.
His diploma was awarded posthumously. The arena stood in collective applause. An empty seat. A cap and gown without the student inside it.
His robotics teammates remembered him as curious. Competitive. Kind. Someone who solved problems instead of avoiding them.
He had planned to build machines.
Instead, he built a moment.
A moment that classmates say gave them time.
Time to escape.
Two points:
If you can read this without tears welling up in your eyes, you’re a far more stoic person than I.
Since Big Money has made it impossible for the United States to implement the same common-sense gun laws that exist in the rest of the planet, this story will reduplicate itself into perpetuity.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits















