The UK government’s “high-risk” research funding agency last week announced that it will invest £57m ($76m) in a new solar geoengineering research programme.
“Solar geoengineering” refers to methods that aim to address some of the impacts of a warming climate by reflecting away more sunlight from the Earth.
The programme, spearheaded by the Advanced Research and Invention Agency (Aria), will fund 21 projects globally.
This includes small-scale outdoor experiments, involving attempts to thicken Arctic sea ice and brighten clouds above Australia’s Great Barrier Reef to reflect away sunlight.
The news was reported breathlessly by the UK media, with some outlets conjuring images of the government one day “dimming the sun” or trying to modify the weather and others focusing on the “secretive” nature of Aria and its research.
The reaction was even more exaggerated on social media, where anonymous accounts seized upon the news to spread misinformation about existing “secret” government schemes to “control” the weather.
At the same time, the programme – first reported last year – has sparked legitimate debate among climate scientists, who have long held diverging views on whether more research funding should be channelled into solar geoengineering.
Below, Carbon Brief explains what the new solar geoengineering research programme consists of and explores the social and ethical concerns surrounding the technology.
- What is the UK’s new solar geoengineering research programme?
- How does this compare to past solar geoengineering efforts in the UK and globally?
- Why do some scientists say solar geoengineering research is needed?
- Why are there social and ethical concerns around solar geoengineering?
What is the UK’s new solar geoengineering research programme?
Solar geoengineering is a term used to describe a group of hypothetical technologies that could, in theory, counteract temperature rise by reflecting more sunlight away from the Earth’s surface. (It is also sometimes called “solar radiation modification”.)
The most commonly proposed idea is to introduce reflective aerosols high up into the stratosphere, which would lower global temperatures in a similar way to a volcanic eruption.
Other ideas include deliberately modifying clouds to make them more reflective or sending giant mirrors into space.
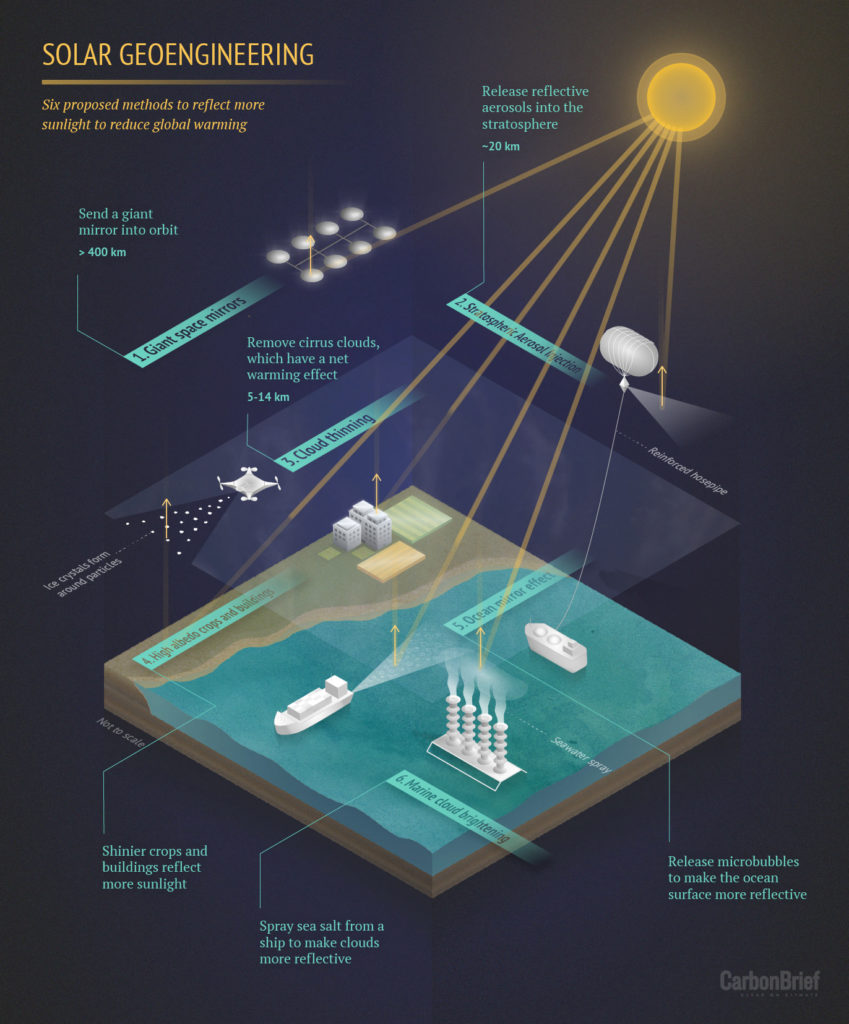
The proposals may sound futuristic, but the notion of engineering the climate in order to limit sunlight has been debated by scientists and politicians for more than 50 years.
However, these debates have always proved controversial, meaning – apart from studies based on computer simulations – little field research into solar geoengineering has been carried out. (See: How does this compare to past solar geoengineering efforts in the UK and globally?)
Aria’s new research programme aims to invest £57m in 21 solar geoengineering research projects globally.
This – along with a separate £10m scheme from the UK Research and Innovation body – means the UK is now one of the world’s biggest funders of solar geoengineering research.
Announcing the details of the scheme, Aria said its motivation for launching the research programme was “the possibility of encountering damaging climate tipping points”.
Out of the £57m, around £24.5m ($33m) will be spent on “controlled, small-scale outdoor experiments”, according to Aria.
These include attempts to thicken Arctic sea ice, brighten clouds above Australia’s Great Barrier Reef and to float weather balloons containing natural minerals high in the stratosphere, which will be retrieved after “hours or weeks”.
All outdoor experiments will be “scrutinised” by an oversight committee chaired by Prof Piers Forster, a leading climate scientist who is the founding director of the Priestley Centre for Climate Futures at the University of Leeds.
In a note released alongside news of the research funding, the oversight committee said it does “not exist to legitimise this programme”, adding:
“We advise Aria on the risks and benefits of supporting proposed creator projects and how best to work with and across creator teams to support learning and to help ensure that findings are contextualised and communicated appropriately alongside [climate] mitigation and adaptation options.”
Aria is a “high-risk, high-reward” government research agency that was formally established through an act of parliament in 2023.
It was originally conceptualised by Dominic Cummings, a controversial former adviser of then prime minister Boris Johnson.
According to Nature, Aria was modelled on the “famed US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or DARPA, which helped to pioneer some of the world’s most consequential technologies, including the internet and personal computers”.
In its recent coverage, the Daily Telegraph described Aria as a “secretive government unit”.

Aria itself has said that it aims to be fully transparent about its solar geoengineering programme, which was its motivation for publicly announcing its spending on the 21 projects involved.
How does this compare to past solar geoengineering efforts in the UK and globally?
As mentioned above, the idea of solar geoengineering has been debated for more than 50 years. However, its controversial nature has meant that, until now, very few field experiments have been carried out.
In 2010, there was an attempt to carry out field research in the UK by the Stratospheric Particle Injection for Climate Engineering (SPICE) project, which was headed by Dr Matthew Watson at the University of Bristol and involved scientists from the University of Oxford, the University of Cambridge and the University of Edinburgh.
The project aimed to “investigate the effectiveness” of solar geoengineering, in part by releasing the equivalent of a bathtub of water high into the atmosphere above Norfolk.
However, it was met with fierce opposition by some campaign groups. In 2012, the team ended the project, citing issues with intellectual property and discomfort with the current lack of regulation and governance of solar geoengineering research.
(Watson is one of the recipients of Aria’s new research programme. His team has been awarded £4.3m ($5.7m) to build specialised drones to study emissions from regularly erupting volcanoes in Guatemala, Montserrat and Chile.)
Outside of the UK, another high-profile solar geoengineering experiment headed by researchers at Harvard University, called the Stratospheric Controlled Perturbation Experiment (Scopex), was also forced to disband following public disapproval.
In the private sector, a US start-up called Make Sunsets has begun releasing high-altitude balloons containing sulphur dioxide into the stratosphere, in an attempt to geoengineer the planet. It funds its activities by selling “cooling credits”.
The company has been banned in Mexico, where it previously launched balloons, and is currently being investigated by the US Environmental Protection Agency.
According to the online publication SRM360, funding for solar geoengineering has increased from $34.9m in 2010-14 to $112.1m in 2020-24. The vast majority of funding is concentrated in global-north countries and about half of all funding comes from philanthropic sources.
This week, scientists and policymakers are meeting in Cape Town, South Africa for the largest summit to date on the scientific, social and political implications of solar geoengineering.
Countries have agreed to a de facto moratorium on large-scale solar geoengineering under the Convention on Biological Diversity, a UN treaty that aims to protect biodiversity. (However, it is not legally binding.)
Why do some scientists say solar geoengineering research is needed?
Scientists agree that cutting global greenhouse emissions as soon as possible is key to tackling climate change.
But global emissions are still rising – and the prospect of limiting global warming to 1.5C above pre-industrial levels, the ambition of the landmark Paris Agreement, without first “overshooting” the target is fast vanishing.
This has led some scientists to call for more research into solar geoengineering ideas, including through small-scale experiments and trials.
Research based on computer modelling indicates that artificially cooling the planet by releasing reflective aerosols into the stratosphere using specialised planes could be effective at offsetting a range of climate impacts, such as more intense heatwaves and flooding, melting sea ice and higher tropical storm risk.
(One solar geoengineering scientist has estimated that halving global warming with reflective aerosols would involve a specialised fleet of about 100 planes releasing 1m tonnes of sulfuric acid each year by 2070.)
However, this type of solar geoengineering would not address rising CO2 levels, which are causing oceans to become more acidic and crops to become less nutritious, among other issues.
Some scientists have raised concerns that, if aerosols were used to address global warming, the world could be left at risk of a “termination shock”. That is, if aerosols were released and then suddenly stopped – as a result of political disagreement or a terrorist attack, for example – global temperatures could rapidly rebound.
This sharp temperature change could be “catastrophic” for wildlife, modelling studies have suggested. However, other research argues that the likelihood of a termination shock has been “overplayed” and that measures could be put in place to ensure that the risk is minimised.
There is also a risk that deploying aerosols from just one spot on Earth could cause uneven impacts for people. One research paper based on modelling found that releasing aerosols in just the northern hemisphere could lead to a decrease in rainfall – and, therefore, an enhanced drought risk – in India and the African Sahel.
Ultimately, advocates of solar geoengineering research tend to argue that the only way to understand more about the efficacy and risks of the technology is to study it further, whereas opponents say more research could be a “slippery slope” towards deployment.
Why are there social and ethical concerns around solar geoengineering?
As well as scientific uncertainties, experts have long warned that solar geoengineering poses large social, ethical and governance challenges.
Some scientists and campaigners are fundamentally opposed to the idea of manipulating the climate further in order to try to repair some of the damage caused by fossil-fuel emissions.
Writing in the Guardian, climate scientists Prof Raymond Pierrehumbert and Dr Michael Mann described Aria’s research programme as “like using aspirin for cancer”.
Indigenous groups have strongly opposed the idea of solar geoengineering and its research, often arguing it goes against their beliefs about living in harmony with nature.
Some scientists and campaign groups also believe that solar geoengineering could be viewed by politicians and the public as a quick “technofix” to climate change. If more research and development is channelled into these techniques, they argue, people may start to backpedal on their promises to cut their emissions.
This is often referred to as the “moral hazard” dilemma.
But other researchers have urged caution on this idea. One reason for this is that social experiments conducted with members of the public have found little evidence of the moral hazard problem existing in practice.
Advocates of solar geoengineering research say it should be viewed as a “supplement” to climate mitigation efforts rather than a “substitute” or “quick fix”.
However, many experts and commentators have pointed out that the technology presents a very large global governance challenge.
A fair and just deployment of solar geoengineering would require agreement between countries, experts have reasoned. At present, it is difficult to picture a global forum that could garner such collaboration, they say.
Prof Alan Robock, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at Rutgers University, summarised this issue neatly in a conversation with Carbon Brief in 2018, when he said:
“You’re asking if the world can come together and agree on geoengineering without agreeing on mitigation. I think the answer is for us to agree on mitigation. Paris is the first step, the pledges made there aren’t enough but have got to increase.”
Another concern is the “free-driver problem”, an idea that refers to the potential for a single country, group or even individual to unilaterally deploy solar geoengineering, even if it might cause negative impacts for others. This concern arises from the fact that solar geoengineering would be relatively cheap to carry out.
It has been argued that the free-driver problem poses a larger concern than ever in today’s increasingly polarised world, where lone politicians and billionaires hold large amounts of power.
These serious social and governance issues prompt some experts to say solar geoengineering should not be researched at all, but others to say it should be researched to try to address concerns.
Out of Aria’s £57m for solar geoengineering research, around £2.8m ($3.7m) is earmarked for governance and ethics projects.
In its latest assessment for how the world can address climate change, the world’s authority on climate science, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), notes that there is “high agreement” among research papers that solar geoengineering “cannot be the main policy response to climate change and is, at best, a supplement to achieving sustained net-zero”.
The assessment also notes that solar geoengineering “may introduce novel risks for international collaboration and peace”.
The post Factcheck: How the UK is – and is not – studying solar geoengineering appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Factcheck: How the UK is – and is not – studying solar geoengineering
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 27 February 2026: Trump’s fossil-fuel talk | Modi-Lula rare-earth pact | Is there a UK ‘greenlash’?
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Absolute State of the Union
‘DRILL, BABY’: US president Donald Trump “doubled down on his ‘drill, baby, drill’ agenda” in his State of the Union (SOTU) address, said the Los Angeles Times. He “tout[ed] his support of the fossil-fuel industry and renew[ed] his focus on electricity affordability”, reported the Financial Times. Trump also attacked the “green new scam”, noted Carbon Brief’s SOTU tracker.
COAL REPRIEVE: Earlier in the week, the Trump administration had watered down limits on mercury pollution from coal-fired power plants, reported the Financial Times. It remains “unclear” if this will be enough to prevent the decline of coal power, said Bloomberg, in the face of lower-cost gas and renewables. Reuters noted that US coal plants are “ageing”.
OIL STAY: The US Supreme Court agreed to hear arguments brought by the oil industry in a “major lawsuit”, reported the New York Times. The newspaper said the firms are attempting to head off dozens of other lawsuits at state level, relating to their role in global warming.
SHIP-SHILLING: The Trump administration is working to “kill” a global carbon levy on shipping “permanently”, reported Politico, after succeeding in delaying the measure late last year. The Guardian said US “bullying” could be “paying off”, after Panama signalled it was reversing its support for the levy in a proposal submitted to the UN shipping body.
Around the world
- RARE EARTHS: The governments of Brazil and India signed a deal on rare earths, said the Times of India, as well as agreeing to collaborate on renewable energy.
- HEAT ROLLBACK: German homes will be allowed to continue installing gas and oil heating, under watered-down government plans covered by Clean Energy Wire.
- BRAZIL FLOODS: At least 53 people died in floods in the state of Minas Gerais, after some areas saw 170mm of rain in a few hours, reported CNN Brasil.
- ITALY’S ATTACK: Italy is calling for the EU to “suspend” its emissions trading system (ETS) ahead of a review later this year, said Politico.
- COOKSTOVE CREDITS: The first-ever carbon credits under the Paris Agreement have been issued to a cookstove project in Myanmar, said Climate Home News.
- SAUDI SOLAR: Turkey has signed a “major” solar deal that will see Saudi firm ACWA building 2 gigawatts in the country, according to Agence France-Presse.
$467 billion
The profits made by five major oil firms since prices spiked following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine four years ago, according to a report by Global Witness covered by BusinessGreen.
Latest climate research
- Claims about the “fingerprint” of human-caused climate change, made in a recent US Department of Energy report, are “factually incorrect” | AGU Advances
- Large lakes in the Congo Basin are releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from “immense ancient stores” | Nature Geoscience
- Shared Socioeconomic Pathways – scenarios used regularly in climate modelling – underrepresent “narratives explicitly centring on democratic principles such as participation, accountability and justice” | npj Climate Action
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
The constituency of Richard Tice MP, the climate-sceptic deputy leader of Reform UK, is the second-largest recipient of flood defence spending in England, according to new Carbon Brief analysis. Overall, the funding is disproportionately targeted at coastal and urban areas, many of which have Conservative or Liberal Democrat MPs.
Spotlight
Is there really a UK ‘greenlash’?
This week, after a historic Green Party byelection win, Carbon Brief looks at whether there really is a “greenlash” against climate policy in the UK.
Over the past year, the UK’s political consensus on climate change has been shattered.
Yet despite a sharp turn against climate action among right-wing politicians and right-leaning media outlets, UK public support for climate action remains strong.
Prof Federica Genovese, who studies climate politics at the University of Oxford, told Carbon Brief:
“The current ‘war’ on green policy is mostly driven by media and political elites, not by the public.”
Indeed, there is still a greater than two-to-one majority among the UK public in favour of the country’s legally binding target to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, as shown below.
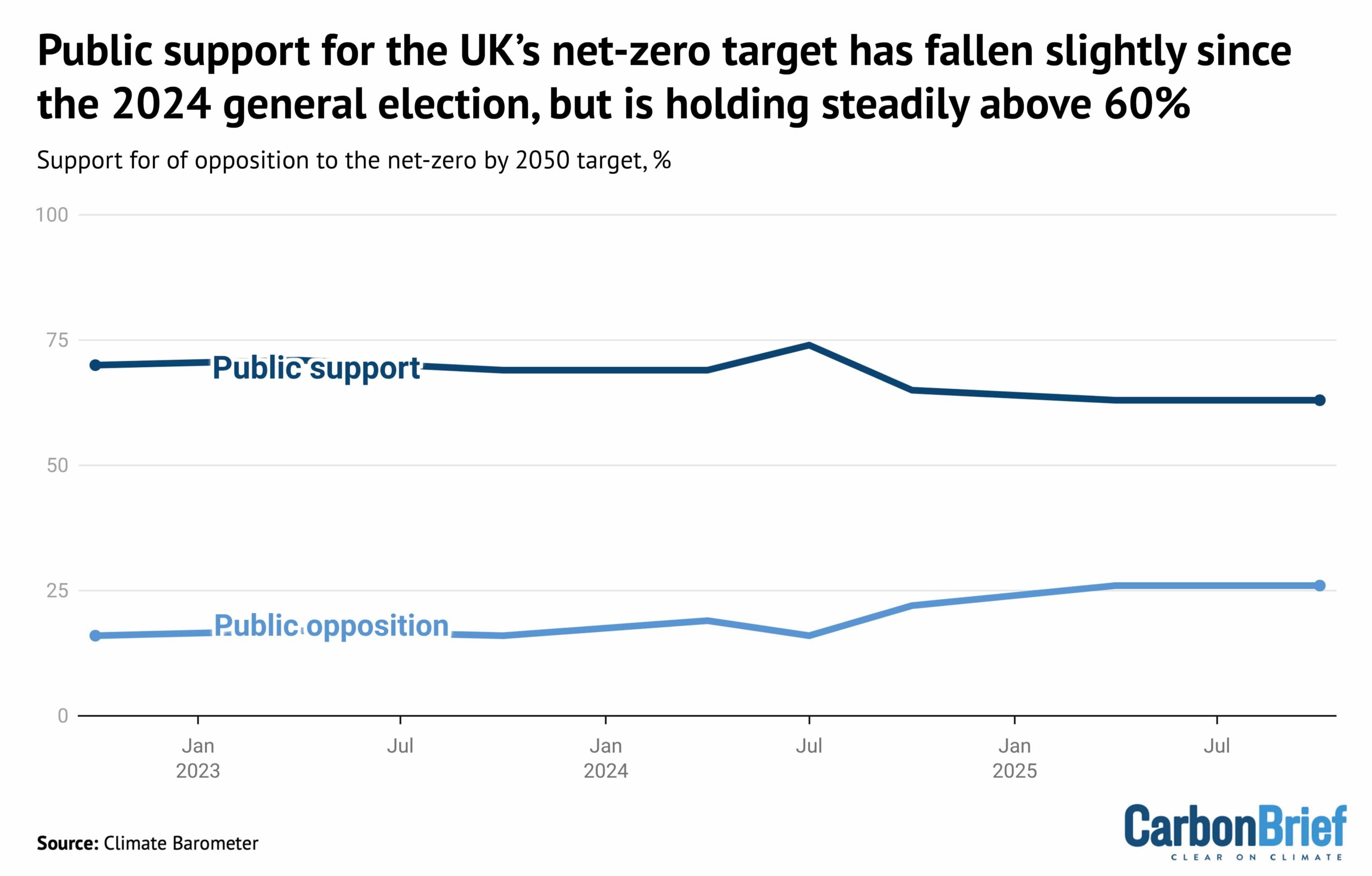
Steve Akehurst, director of public-opinion research initiative Persuasion UK, also noted the growing divide between the public and “elites”. He told Carbon Brief:
“The biggest movement is, without doubt, in media and elite opinion. There is a bit more polarisation and opposition [to climate action] among voters, but it’s typically no more than 20-25% and mostly confined within core Reform voters.”
Conservative gear shift
For decades, the UK had enjoyed strong, cross-party political support for climate action.
Lord Deben, the Conservative peer and former chair of the Climate Change Committee, told Carbon Brief that the UK’s landmark 2008 Climate Change Act had been born of this cross-party consensus, saying “all parties supported it”.
Since their landslide loss at the 2024 election, however, the Conservatives have turned against the UK’s target of net-zero emissions by 2050, which they legislated for in 2019.
Curiously, while opposition to net-zero has surged among Conservative MPs, there is majority support for the target among those that plan to vote for the party, as shown below.
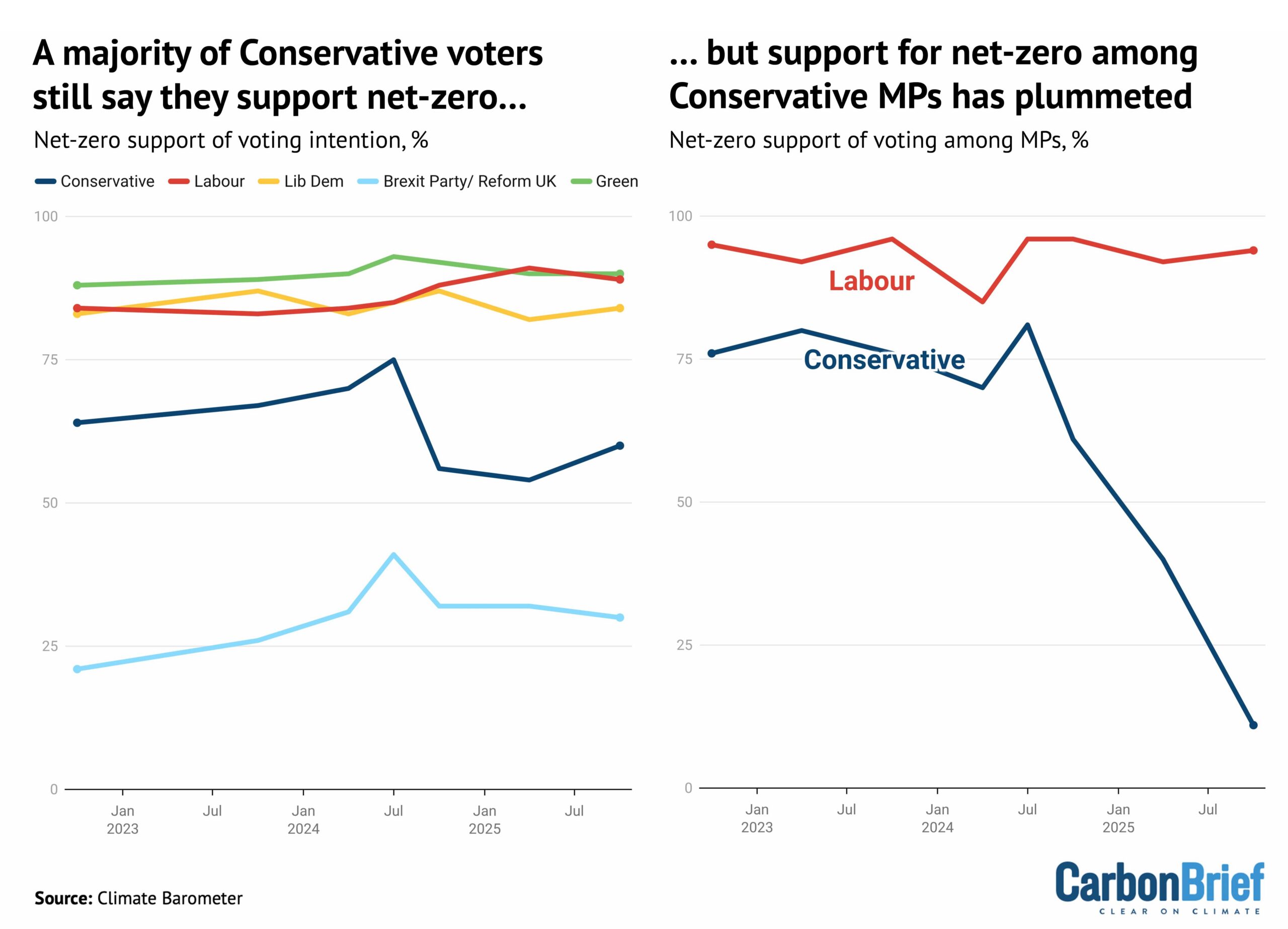
Dr Adam Corner, advisor to the Climate Barometer initiative that tracks public opinion on climate change, told Carbon Brief that those who currently plan to vote Reform are the only segment who “tend to be more opposed to net-zero goals”. He said:
“Despite the rise in hostile media coverage and the collapse of the political consensus, we find that public support for the net-zero by 2050 target is plateauing – not plummeting.”
Reform, which rejects the scientific evidence on global warming and campaigns against net-zero, has been leading the polls for a year. (However, it was comfortably beaten by the Greens in yesterday’s Gorton and Denton byelection.)
Corner acknowledged that “some of the anti-net zero noise…[is] showing up in our data”, adding:
“We see rising concerns about the near-term costs of policies and an uptick in people [falsely] attributing high energy bills to climate initiatives.”
But Akehurst said that, rather than a big fall in public support, there had been a drop in the “salience” of climate action:
“So many other issues [are] competing for their attention.”
UK newspapers published more editorials opposing climate action than supporting it for the first time on record in 2025, according to Carbon Brief analysis.
Global ‘greenlash’?
All of this sits against a challenging global backdrop, in which US president Donald Trump has been repeating climate-sceptic talking points and rolling back related policy.
At the same time, prominent figures have been calling for a change in climate strategy, sold variously as a “reset”, a “pivot”, as “realism”, or as “pragmatism”.
Genovese said that “far-right leaders have succeeded in the past 10 years in capturing net-zero as a poster child of things they are ‘fighting against’”.
She added that “much of this is fodder for conservative media and this whole ecosystem is essentially driving what we call the ‘greenlash’”.
Corner said the “disconnect” between elite views and the wider public “can create problems” – for example, “MPs consistently underestimate support for renewables”. He added:
“There is clearly a risk that the public starts to disengage too, if not enough positive voices are countering the negative ones.”
Watch, read, listen
TRUMP’S ‘PETROSTATE’: The US is becoming a “petrostate” that will be “sicker and poorer”, wrote Financial Times associate editor Rana Forohaar.
RHETORIC VS REALITY: Despite a “political mood [that] has darkened”, there is “more green stuff being installed than ever”, said New York Times columnist David Wallace-Wells.
CHINA’S ‘REVOLUTION’: The BBC’s Climate Question podcast reported from China on the “green energy revolution” taking place in the country.
Coming up
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean, Brasília
- 3 March: UK spring statement
- 4-11 March: China’s “two sessions”
- 5 March: Nepal elections
Pick of the jobs
- The Guardian, senior reporter, climate justice | Salary: $123,000-$135,000. Location: New York or Washington DC
- China-Global South Project, non-resident fellow, climate change | Salary: Up to $1,000 a month. Location: Remote
- University of East Anglia, PhD in mobilising community-based climate action through co-designed sports and wellbeing interventions | Salary: Stipend (unknown amount). Location: Norwich, UK
- TABLE and the University of São Paulo, Brazil, postdoctoral researcher in food system narratives | Salary: Unknown. Location: Pirassununga, Brazil
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 27 February 2026: Trump’s fossil-fuel talk | Modi-Lula rare-earth pact | Is there a UK ‘greenlash’? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding
The Lincolnshire constituency held by Richard Tice, the climate-sceptic deputy leader of the hard-right Reform party, has been pledged at least £55m in government funding for flood defences since 2024.
This investment in Boston and Skegness is the second-largest sum for a single constituency from a £1.4bn flood-defence fund for England, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
Flooding is becoming more likely and more extreme in the UK due to climate change.
Yet, for years, governments have failed to spend enough on flood defences to protect people, properties and infrastructure.
The £1.4bn fund is part of the current Labour government’s wider pledge to invest a “record” £7.9bn over a decade on protecting hundreds of thousands of homes and businesses from flooding.
As MP for one of England’s most flood-prone regions, Tice has called for more investment in flood defences, stating that “we cannot afford to ‘surrender the fens’ to the sea”.
He is also one of Reform’s most vocal opponents of climate action and what he calls “net stupid zero”. He denies the scientific consensus on climate change and has claimed, falsely and without evidence, that scientists are “lying”.
Flood defences
Last year, the government said it would invest £2.65bn on flood and coastal erosion risk management (FCERM) schemes in England between April 2024 and March 2026.
This money was intended to protect 66,500 properties from flooding. It is part of a decade-long Labour government plan to spend more than £7.9bn on flood defences.
There has been a consistent shortfall in maintaining England’s flood defences, with the Environment Agency expecting to protect fewer properties by 2027 than it had initially planned.
The Climate Change Committee (CCC) has attributed this to rising costs, backlogs from previous governments and a lack of capacity. It also points to the strain from “more frequent and severe” weather events, such as storms in recent years that have been amplified by climate change.
However, the CCC also said last year that, if the 2024-26 spending programme is delivered, it would be “slightly closer to the track” of the Environment Agency targets out to 2027.
The government has released constituency-level data on which schemes in England it plans to fund, covering £1.4bn of the 2024-26 investment. The other half of the FCERM spending covers additional measures, from repairing existing defences to advising local authorities.
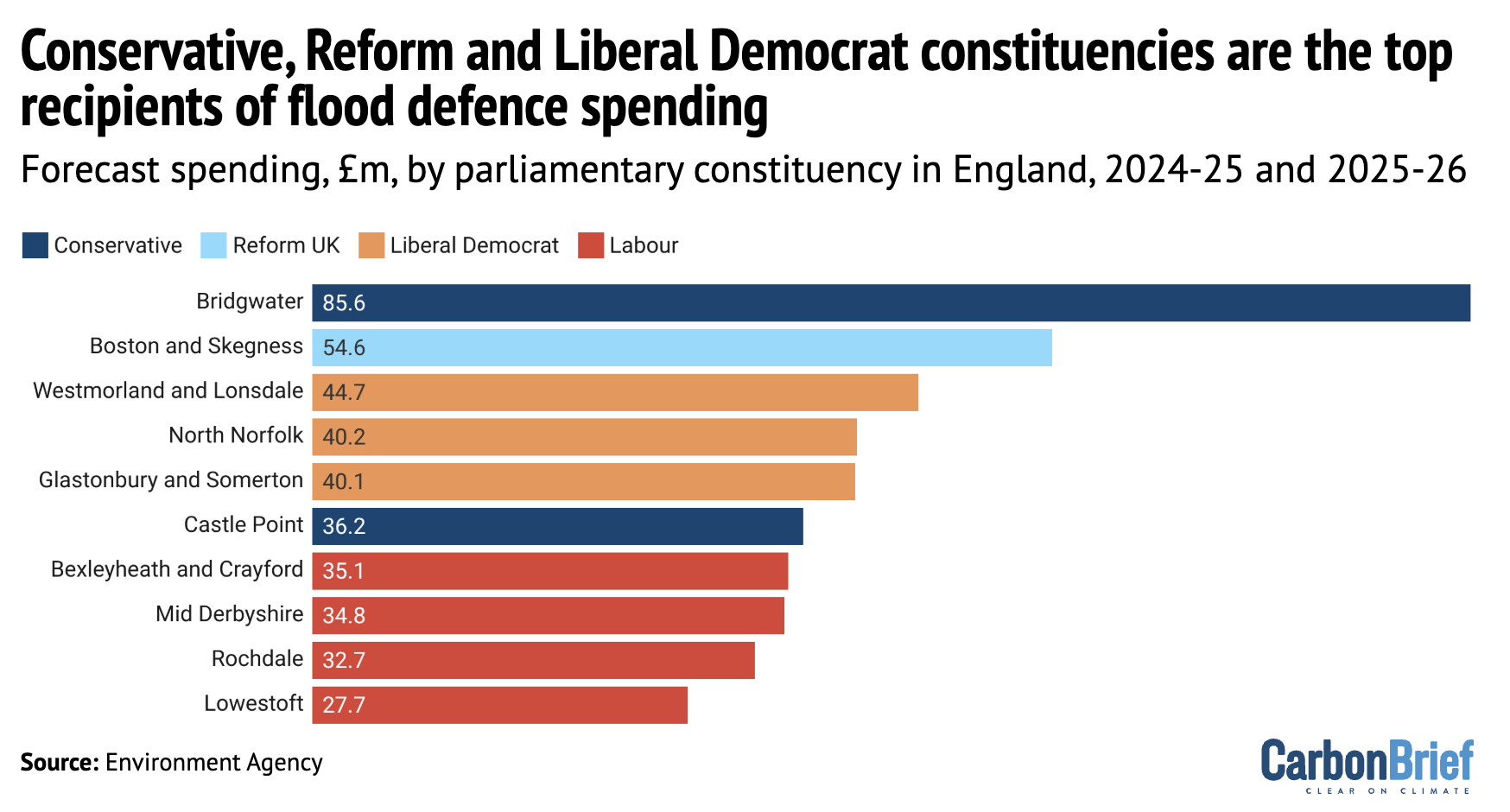
The map below shows the distribution of spending on FCERM schemes in England over the past two years, highlighting the constituency of Richard Tice.
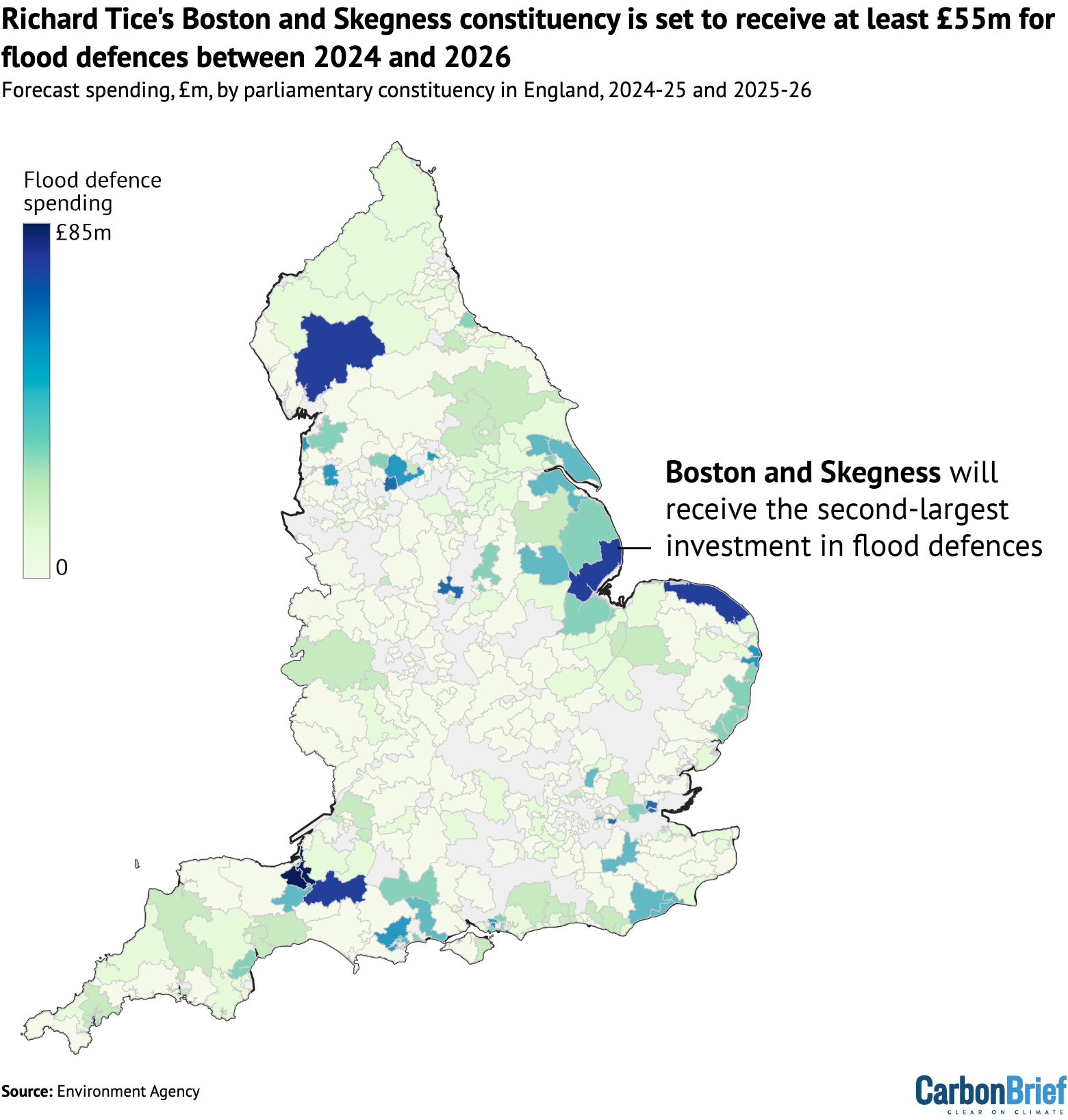
By far the largest sum of money – £85.6m in total – has been committed to a tidal barrier and various other defences in the Somerset constituency of Bridgwater, the seat of Conservative MP Ashley Fox.
Over the first months of 2026, the south-west region has faced significant flooding and Fox has called for more support from the government, citing “climate patterns shifting and rainfall intensifying”.
He has also backed his party’s position that “the 2050 net-zero target is impossible” and called for more fossil-fuel extraction in the North Sea.
Tice’s east-coast constituency of Boston and Skegness, which is highly vulnerable to flooding from both rivers and the sea, is set to receive £55m. Among the supported projects are beach defences from Saltfleet to Gibraltar Point and upgrades to pumping stations.
Overall, Boston and Skegness has the second-largest portion of flood-defence funding, as the chart below shows. Constituencies with Conservative and Liberal Democrat MPs occupied the other top positions.
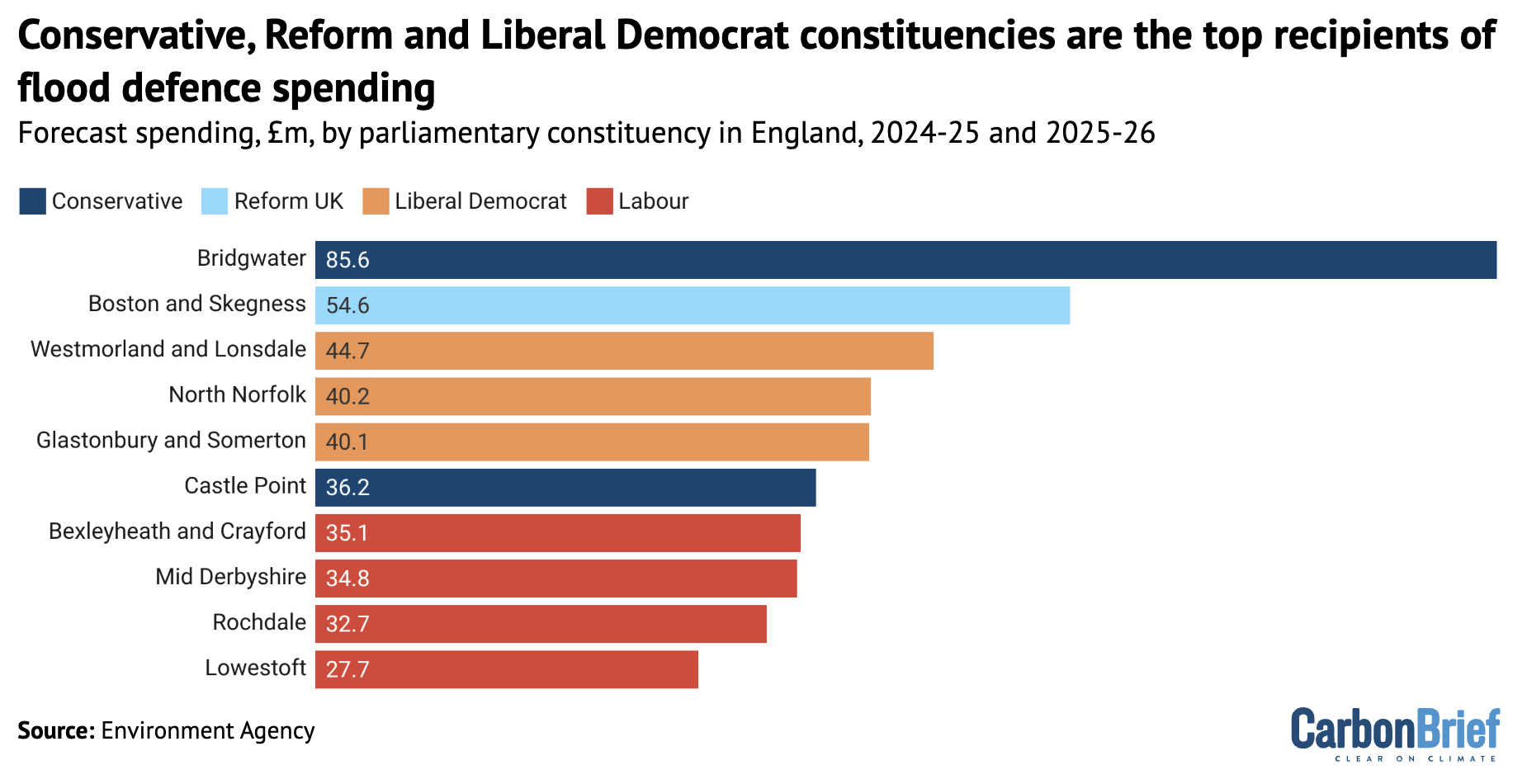
Overall, despite Labour MPs occupying 347 out of England’s 543 constituencies – nearly two-thirds of the total – more than half of the flood-defence funding was distributed to constituencies with non-Labour MPs. This reflects the flood risk in coastal and rural areas that are not traditional Labour strongholds.
Reform funding
While Reform has just eight MPs, representing 1% of the population, its constituencies have been assigned 4% of the flood-defence funding for England.
Nearly all of this money was for Tice’s constituency, although party leader Nigel Farage’s coastal Clacton seat in Kent received £2m.
Reform UK is committed to “scrapping net-zero” and its leadership has expressed firmly climate-sceptic views.
Much has been made of the disconnect between the party’s climate policies and the threat climate change poses to its voters. Various analyses have shown the flood risk in Reform-dominated areas, particularly Lincolnshire.
Tice has rejected climate science, advocated for fossil-fuel production and criticised Environment Agency flood-defence activities. Yet, he has also called for more investment in flood defences, stating that “we cannot afford to ‘surrender the fens’ to the sea”.
This may reflect Tice’s broader approach to climate change. In a 2024 interview with LBC, he said:
“Where you’ve got concerns about sea level defences and sea level rise, guess what? A bit of steel, a bit of cement, some aggregate…and you build some concrete sea level defences. That’s how you deal with rising sea levels.”
While climate adaptation is viewed as vital in a warming world, there are limits on how much societies can adapt and adaptation costs will continue to increase as emissions rise.
The post Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding
Greenhouse Gases
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter.
Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
Food inflation on the rise
DELUGE STRIKES FOOD: Extreme rainfall and flooding across the Mediterranean and north Africa has “battered the winter growing regions that feed Europe…threatening food price rises”, reported the Financial Times. Western France has “endured more than 36 days of continuous rain”, while farmers’ associations in Spain’s Andalusia estimate that “20% of all production has been lost”, it added. Policy expert David Barmes told the paper that the “latest storms were part of a wider pattern of climate shocks feeding into food price inflation”.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “Cropped” email newsletter. A fortnightly digest of food, land and nature news and views. Sent to your inbox every other Wednesday.
NO BEEF: The UK’s beef farmers, meanwhile, “face a double blow” from climate change as “relentless rain forces them to keep cows indoors”, while last summer’s drought hit hay supplies, said another Financial Times article. At the same time, indoor growers in south England described a 60% increase in electricity standing charges as a “ticking timebomb” that could “force them to raise their prices or stop production, which will further fuel food price inflation”, wrote the Guardian.
‘TINDERBOX’ AND TARIFFS: A study, covered by the Guardian, warned that major extreme weather and other “shocks” could “spark social unrest and even food riots in the UK”. Experts cited “chronic” vulnerabilities, including climate change, low incomes, poor farming policy and “fragile” supply chains that have made the UK’s food system a “tinderbox”. A New York Times explainer noted that while trade could once guard against food supply shocks, barriers such as tariffs and export controls – which are being “increasingly” used by politicians – “can shut off that safety valve”.
El Niño looms
NEW ENSO INDEX: Researchers have developed a new index for calculating El Niño, the large-scale climate pattern that influences global weather and causes “billions in damages by bringing floods to some regions and drought to others”, reported CNN. It added that climate change is making it more difficult for scientists to observe El Niño patterns by warming up the entire ocean. The outlet said that with the new metric, “scientists can now see it earlier and our long-range weather forecasts will be improved for it.”
WARMING WARNING: Meanwhile, the US Climate Prediction Center announced that there is a 60% chance of the current La Niña conditions shifting towards a neutral state over the next few months, with an El Niño likely to follow in late spring, according to Reuters. The Vibes, a Malaysian news outlet, quoted a climate scientist saying: “If the El Niño does materialise, it could possibly push 2026 or 2027 as the warmest year on record, replacing 2024.”
CROP IMPACTS: Reuters noted that neutral conditions lead to “more stable weather and potentially better crop yields”. However, the newswire added, an El Niño state would mean “worsening drought conditions and issues for the next growing season” to Australia. El Niño also “typically brings a poor south-west monsoon to India, including droughts”, reported the Hindu’s Business Line. A 2024 guest post for Carbon Brief explained that El Niño is linked to crop failure in south-eastern Africa and south-east Asia.
News and views
- DAM-AG-ES: Several South Korean farmers filed a lawsuit against the country’s state-owned utility company, “seek[ing] financial compensation for climate-related agricultural damages”, reported United Press International. Meanwhile, a national climate change assessment for the Philippines found that the country “lost up to $219bn in agricultural damages from typhoons, floods and droughts” over 2000-10, according to Eco-Business.
- SCORCHED GRASS: South Africa’s Western Cape province is experiencing “one of the worst droughts in living memory”, which is “scorching grass and killing livestock”, said Reuters. The newswire wrote: “In 2015, a drought almost dried up the taps in the city; farmers say this one has been even more brutal than a decade ago.”
- NOUVELLE VEG: New guidelines published under France’s national food, nutrition and climate strategy “urged” citizens to “limit” their meat consumption, reported Euronews. The delayed strategy comes a month after the US government “upended decades of recommendations by touting consumption of red meat and full-fat dairy”, it noted.
- COURTING DISASTER: India’s top green court accepted the findings of a committee that “found no flaws” in greenlighting the Great Nicobar project that “will lead to the felling of a million trees” and translocating corals, reported Mongabay. The court found “no good ground to interfere”, despite “threats to a globally unique biodiversity hotspot” and Indigenous tribes at risk of displacement by the project, wrote Frontline.
- FISH FALLING: A new study found that fish biomass is “falling by 7.2% from as little as 0.1C of warming per decade”, noted the Guardian. While experts also pointed to the role of overfishing in marine life loss, marine ecologist and study lead author Dr Shahar Chaikin told the outlet: “Our research proves exactly what that biological cost [of warming] looks like underwater.”
- TOO HOT FOR COFFEE: According to new analysis by Climate Central, countries where coffee beans are grown “are becoming too hot to cultivate them”, reported the Guardian. The world’s top five coffee-growing countries faced “57 additional days of coffee-harming heat” annually because of climate change, it added.
Spotlight
Nature talks inch forward
This week, Carbon Brief covers the latest round of negotiations under the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), which occurred in Rome over 16-19 February.
The penultimate set of biodiversity negotiations before October’s Conference of the Parties ended in Rome last week, leaving plenty of unfinished business.
The CBD’s subsidiary body on implementation (SBI) met in the Italian capital for four days to discuss a range of issues, including biodiversity finance and reviewing progress towards the nature targets agreed under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
However, many of the major sticking points – particularly around finance – will have to wait until later this summer, leaving some observers worried about the capacity for delegates to get through a packed agenda at COP17.
The SBI, along with the subsidiary body on scientific, technical and technological advice (SBSTTA) will both meet in Nairobi, Kenya, later this summer for a final round of talks before COP17 kicks off in Yerevan, Armenia, on 19 October.
Money talks
Finance for nature has long been a sticking point at negotiations under the CBD.
Discussions on a new fund for biodiversity derailed biodiversity talks in Cali, Colombia, in autumn 2024, requiring resumed talks a few months later.
Despite this, finance was barely on the agenda at the SBI meetings in Rome. Delegates discussed three studies on the relationship between debt sustainability and implementation of nature plans, but the more substantive talks are set to take place at the next SBI meeting in Nairobi.
Several parties “highlighted concerns with the imbalance of work” on finance between these SBI talks and the next ones, reported Earth Negotiations Bulletin (ENB).
Lim Li Ching, senior researcher at Third World Network, noted that tensions around finance permeated every aspect of the talks. She told Carbon Brief:
“If you’re talking about the gender plan of action – if there’s little or no financial resources provided to actually put it into practice and implement it, then it’s [just] paper, right? Same with the reporting requirements and obligations.”
Monitoring and reporting
Closely linked to the issue of finance is the obligations of parties to report on their progress towards the goals and targets of the GBF.
Parties do so through the submission of national reports.
Several parties at the talks pointed to a lack of timely funding for driving delays in their reporting, according to ENB.
A note released by the CBD Secretariat in December said that no parties had submitted their national reports yet; by the time of the SBI meetings, only the EU had. It further noted that just 58 parties had submitted their national biodiversity plans, which were initially meant to be published by COP16, in October 2024.
Linda Krueger, director of biodiversity and infrastructure policy at the environmental not-for-profit Nature Conservancy, told Carbon Brief that despite the sparse submissions, parties are “very focused on the national report preparation”. She added:
“Everybody wants to be able to show that we’re on the path and that there still is a pathway to getting to 2030 that’s positive and largely in the right direction.”
Watch, read, listen
NET LOSS: Nigeria’s marine life is being “threatened” by “ghost gear” – nets and other fishing equipment discarded in the ocean – said Dialogue Earth.
COMEBACK CAUSALITY: A Vox long-read looked at whether Costa Rica’s “payments for ecosystem services” programme helped the country turn a corner on deforestation.
HOMEGROWN GOALS: A Straits Times podcast discussed whether import-dependent Singapore can afford to shelve its goal to produce 30% of its food locally by 2030.
‘RUSTING’ RIVERS: The Financial Times took a closer look at a “strange new force blighting the [Arctic] landscape”: rivers turning rust-orange due to global warming.
New science
- Lakes in the Congo Basin’s peatlands are releasing carbon that is thousands of years old | Nature Geoscience
- Natural non-forest ecosystems – such as grasslands and marshlands – were converted for agriculture at four times the rate of land with tree cover between 2005 and 2020 | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
- Around one-quarter of global tree-cover loss over 2001-22 was driven by cropland expansion, pastures and forest plantations for commodity production | Nature Food
In the diary
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean | Brasília
- 5 March: Nepal general elections
- 9-20 March: First part of the thirty-first session of the International Seabed Authority (ISA) | Kingston, Jamaica
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz.
Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org
The post Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits