Last week, around 180 scientists, researchers and legal experts gathered in Laxenburg, Austria to attend the first-ever international conference focused on the controversial topic of climate “overshoot”.
This hypothesised scenario would see global temperatures initially “overshoot” the Paris Agreement’s aspirational limit of 1.5C, before they are brought back down through techniques that would remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
(For more on the key talking points, new research and discussions that emerged from the three-day conference, see Carbon Brief’s full write-up of the event.)
On the sidelines of the conference, Carbon Brief asked a range of delegates what they consider to be the key “unknowns” around overshoot.
Below are their responses, first as sample quotes, then, in full:
- Dr James Fletcher: “Yes, there will be overshoot, but at what point will that overshoot peak? Are we peaking at 1.6C, 1.7C, 2.1C?”
- Prof Shobha Maharaj: “There are lots of places in the world where adaptation plans have been made to a 1.5C ceiling. The fact is that these plans are going to need to be modified or probably redeveloped.”
- Sir Prof Jim Skea: “There are huge knowledge gaps around overshoot and carbon dioxide removal.”
- Prof Kristie Ebi: “If there is going to be a peak – and, of course, we don’t know what that peak is – then how do you start planning?”
- Prof Lavanya Rajamani: “To me, a key governance unknown is the extent to which our current legal and regulatory architecture…will actually be responsive to the needs of an overshoot world.”
- Prof Nebojsa Nakicenovic: “One of my major concerns has been for a long time…is whether, even after reaching net-zero, negative emissions can actually produce a temperature decline.”
- Prof Debra Roberts: “For me, the big unknown is how all of these areas of increased impact and risk actually intersect with one another and what that means in the real world.”
- Prof Oliver Geden: “[A key unknown] is whether countries are really willing to commit to net-negative trajectories.”
- Dr Carl-Friedrich Schleussner: “This is a bigger concern that I have – that we are pushing the habitability in our societies on this planet above that limit and towards maybe existential limits.”
- Dr Anna Pirani: “I think that tracking global mean surface temperature on an overshoot pathway will be an important unknown.”
- Prof Richard Betts: “One of the key unknowns is are we going to continue to get the land carbon sink that the models produce.”
- Prof Hannah Daly: “The biggest unknown is whether countries can translate these global [overshoot] pathways into sustained domestic action…that is politically and socially feasible.”
- Dr Andrew King: “[W]e still have a lot of uncertainty around other elements in the climate system that relate more to what people actually live through.”
Former minister for public service, sustainable development, energy, science and technology for Saint Lucia and negotiator at COP21 in Paris.
The key unknown is where we’re going to land. At what point will we peak [temperatures] before we start going down, and how long will we stay in that overshoot period? That is a scary thing. Yes, there will be overshoot, but at what point will that overshoot peak? Are we peaking at 1.6C, 1.7C, 2.1C? All of these are scary scenarios for small island developing states – anything above 1.5C is scary. Every fraction of a degree matters to us. Where we peak is very important and how long we stay in this overshoot period is equally important. That’s when you start getting into very serious, irreversible impacts and tipping points.
Adjunct professor at the University of Fiji and a coordinating lead author for Working Group II of the IPCC’s seventh assessment
First of all, there is an assumption that we’re going to go back down from overshoot. Back down is not a given. And secondly, we are still in the phase where we are talking about uncertainty. Climate scientists don’t like uncertainty. We are not acknowledging that uncertainty is the new normal… But because we’re so bogged down in terms of uncertainties, we are not moving towards [the issue of] what we do about it. We know it’s coming. We know the temperatures are going to be high. But there is little talk about the action.
The focus seems to be more on how we can understand this or how we can model this, but not what we do on the ground. Especially when it comes to adaptation planning – [and around] how does this modify whatever the plans are? There are lots of places in the world where adaptation plans have been made to a 1.5C ceiling. The fact is that these plans are going to need to be modified or probably redeveloped. And no one is talking about this, especially in the areas that are least resourced in the world – which sets up a big, big problem.
Chair of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and emeritus professor at Imperial College London’s Centre for Environmental Policy
There are huge knowledge gaps around overshoot and carbon dioxide removal. As it’s very clear from the themes of this conference, we don’t altogether understand how the Earth would react in taking carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. We don’t understand the nature of the irreversibilities and we don’t understand the effectiveness of CDR techniques, which might themselves be influenced by the level of global warming, plus all the equity and sustainability issues surrounding using CDR techniques.
Professor of global health at the University of Washington‘s Center for Health and the Global Environment
There are all kinds of questions about adaptation and how to approach effective adaptation. At the moment, adaptation is primarily assuming a continual increase in global mean surface temperature. If there is going to be a peak – and of course, we don’t know what that peak is – then how do you start planning? Do you change your planning? There are places, for instance when thinking about hard infrastructure, [where overshoot] may result in a change in your plan – because as you come down the backside, maybe the need would be less. For example, when building a bridge taller. And when implementing early warning systems, how do you take into account that there will be a peak and ultimately a decline? There is almost no work in that. I would say that’s one of the critical unknowns.
Professor of international environmental law at the University of Oxford
I think there are several scientific unknowns, but I would like to focus on the governance unknowns with respect to overshoot. To me, a key governance unknown is the extent to which our current legal and regulatory architecture – across levels of governance, so domestic, regional and international – will actually be responsive to the needs of an overshoot world and the consequences of actually not having regulatory and governance architectures in place to address overshoot.
Distinguished emeritus research scholar at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis and executive director of The World In 2050.
One of my major concerns has been for a long time – as it was clear that we are heading for an overshoot, as we are not reducing the emissions in time – is whether, even after reaching net-zero, negative emissions can actually produce a temperature decline…In other words, there might be asymmetry on the way down [in the global-temperature response to carbon removal] – it might not be symmetrical to the way up [as temperature rise in response to carbon emissions]. And this is really my major concern, that we are planning measures that are so uncertain that we don’t know whether they will reach the goal.
The last point I want to make is that I think that the scientific community should, under all conditions, make sure that the highest priority is on mitigation.
Honorary professor at the University of KwaZulu-Natal, coordinating lead author on the IPCC’s forthcoming special report on climate change and cities, board chair of the Red Cross Red Crescent Climate Centre and co-chair of Working Group II for the IPCC’s sixth assessment
Well, I think coming from the policy and practitioner community, what I’m hearing a lot about are the potential impacts that come from the exceedance component of overshoot. What I’m not hearing a lot about is the responses to overshoot and their impacts – and how those impacts might interact with the impacts from temperature exceedance. So there’s quite a complex risk landscape emerging. It’s three dimensional in many ways, but we’re only talking about one dimension and, for policymakers, we need to understand that three dimensional element in order to understand what options remain on the table. For me, the big unknown is how all of these areas of increased impact and risk actually intersect with one another and what that means in the real world.
Senior fellow and head of the climate policy and politics research cluster at the German Institute for International and Security Affairs and vice-chair of IPCC Working Group III
[A key unknown] is whether countries are really willing to commit to net-negative trajectories. We are assuming, in science, global pathways going net negative, with hardly any country saying they want to go there. So maybe it is just an academic thought experiment. So we don’t know yet if [overshoot] is even relevant. It is relevant in the sense that if we do, [the] 1.5C [target] stays on the table. But I think the next phase needs to be that countries – or the UNFCCC as a whole – needs to decide what they want to do.
Research group leader and senior research scholar at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
I’m convinced that there’s an upper limit of overshoot that we can afford – and it might be not far outside the Paris range [1.5C-2C] – before human societies will be overwhelmed with the task of bringing temperatures back down again. This [societal limit] is lower than the geophysical limits or the CDR limit.
The impacts of climate change and the challenges that will come with it will undermine society’s abilities to cooperatively engage in what is required to achieve long-term temperature reversal. This is a bigger concern that I have – that we are pushing the habitability in our societies on this planet above that limit and towards maybe existential limits. We may not be able to walk back from it, even if we wanted to. That is a big unknown to me.
I’m convinced that there is an upper limit to how much overshoot we can afford, and it might be just about 2C or a bit above – it might not be much more than that. But we do not have good evidence for this. But I think these scenarios of going to 3C and then assuming we can go back down – I have doubts that future societies grappling with the impacts of climate change will be in the position to embark on such an endeavour.
Senior research associate at the Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change (CMCC) and former head of the Technical Support Unit for Working Group I of the IPCC
I think that tracking global mean surface temperature on an overshoot pathway will be an important unknown – how to take account of natural variability in that context, to inform where we are on an overshoot pathway and how well we’re doing on it. I think, methodologically, that would prove to be a challenge. The fact that it occurs over many, many years – many decades – and, yet, we sort of think about it as a nice curve. We see these graphs that say “by the 2050s, we will be here and we’ll start declining and so on”. I think that what that actually translates to in the evolution of global surface temperatures is going to be very difficult to measure and track. Even how we report on that, internationally, in the UNFCCC [UN Framework Convention on Climate Change] context and what the WMO [World Meteorological Organization] does in terms of reporting an overshoot trajectory, that would be quite a challenge.
Head of climate impacts research in the Met Office Hadley Centre and professor at the University of Exeter
One of the key unknowns is are we going to continue to get the land carbon sink that the models produce. We have got model simulations of returning from an overshoot.
If you are lowering temperatures, you have got to reduce emissions. The amount you reduce emissions depends on how much carbon is taken up naturally by the system – by forests, oceans and so on. The models will do this; they give you an answer. But we don’t know whether they are doing the right thing. They have never been tested in this kind of situation.
In my field of expertise, one of the key [unknowns] is how these carbon sinks are going to behave in the future. That is why we are trying to get real-world data into the models – including through the Amazon FACE project – so we can really try and narrow the uncertainties in future carbon sinks. If the carbon sinks are weaker than the models think, it is going to be even harder to reduce emissions and we will need to remove even more by carbon capture and removal.
Professor of sustainable energy at University College Cork
We know ever more about the profound – and often irreversible – damages that will be felt as we overshoot 1.5C. Yet we seem no closer to understanding what will unlock the urgent decarbonisation that remains our only way to avoid the worst impacts of climate change.
Global models can show, on paper, what returning temperatures to safer levels after overshoot might look like. The biggest unknown is whether countries can translate these global pathways into sustained domestic action – over decades and without precedent in history – that is politically and socially feasible.
Associate professor in climate science at the University of Melbourne
I think, firstly, can we actually achieve net-negative emissions to bring temperatures down past a peak? It’s a completely different world and, unfortunately, it’s likely to be challenging and we’re setting ourselves up to need to do it more. So I think that’s a huge unknown.
But then, beyond that, I think also, whilst we’ve built some understanding of how global temperature would respond to net-zero or net-negative emissions, we still have a lot of uncertainty around other elements in the climate system that relate more to what people actually live through. In our warming world, we’ve seen that global warming relates to local warming being experienced by everyone at different amounts. But, in an overshoot climate, we would see quite diverse changes for different people, different areas of the world, experiencing very different changes in our local climates. And also definitely worsening of some climate hazards and possibly reversibility in others, so a very different risk landscape as well, emerging post net-zero – and I think we still don’t know very much about that as well.
The post Experts: The key ‘unknowns’ of overshooting the 1.5C global-warming limit appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Experts: The key ‘unknowns’ of overshooting the 1.5C global-warming limit
Greenhouse Gases
Our strategy for 2026 and beyond
Our strategy for 2026 and beyond
During his Fall Conference opening remarks last fall, CCL Executive Director Ricky Bradley outlined the next chapter of CCL’s work — one that is firmly rooted in our values, but guided by a sharper strategy. Now that 2026 is getting underway, we’re entering that next chapter in earnest.
“Today’s political landscape, and our country, desperately needs our respectful approach and our bridge-building ethos — and the climate needs our efforts to be more effective than ever,” Ricky said in November.
 “Over the past few months, CCL’s leadership team and I have been hard at work on a strategic planning process to achieve that. We’ve drilled down on everything, getting clear about CCL’s mission, our contributions to the overall goal of solving climate change, and the training and programs necessary to get us there.”
“Over the past few months, CCL’s leadership team and I have been hard at work on a strategic planning process to achieve that. We’ve drilled down on everything, getting clear about CCL’s mission, our contributions to the overall goal of solving climate change, and the training and programs necessary to get us there.”
Our work identified three elements that we think are crucial to advancing climate solutions in Congress. For members of Congress to pass climate policy, they need to see climate as a salient issue — in other words, they need to think it matters to people, including the people they listen to most. They need to see climate action as feasible. And engaging on the issue needs to be politically safe. Satisfying these conditions is how we’re going to achieve the legislative action necessary to solve climate change.
Part of getting there is making sure that our volunteers have the skills they need to transcend partisanship, build trust across divides, and forge the relationships and alliances that lead to enduring climate action. Enter: Our new BRIDGE Advocacy Program. Launching this weekend during our January Monthly Meeting, this robust new program will strengthen your communication skills and deepen your relationships with congressional offices in the year ahead.
All of this and more is outlined in CCL’s 2026 Strategic Plan document. Dive into the strategic plan to see CCL’s objectives for the new year and beyond, and learn more on Saturday during our first monthly meeting of 2026. We can’t wait to enter this next chapter with you!
The post Our strategy for 2026 and beyond appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
Greenhouse Gases
Analysis: UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
The UK’s fleet of wind, solar and biomass power plants all set new records in 2025, Carbon Brief analysis shows, but electricity generation from gas still went up.
The rise in gas power was due to the end of UK coal generation in late 2024 and nuclear power hitting its lowest level in half a century, while electricity exports grew and imports fell.
In addition, there was a 1% rise in UK electricity demand – after years of decline – as electric vehicles (EVs), heat pumps and data centres connected to the grid in larger numbers.
Other key insights from the data include:
- Electricity demand grew for the second year in a row to 322 terawatt hours (TWh), rising by 4TWh (1%) and hinting at a shift towards steady increases, as the UK electrifies.
- Renewables supplied more of the UK’s electricity than any other source, making up 47% of the total, followed by gas (28%), nuclear (11%) and net imports (10%).
- The UK set new records for electricity generation from wind (87TWh, +5%), solar (19TWh, +31%) and biomass (41TWh, +2%), as well as for renewables overall (152TWh, +6%).
- The UK had its first full year without any coal power, compared with 2TWh of generation in 2024, ahead of the closure of the nation’s last coal plant in September of that year.
- Nuclear power was at its lowest level in half a century, generating just 36TWh (-12%), as most of the remaining fleet paused for refuelling or outages.
Overall, UK electricity became slightly more polluting in 2025, with each kilowatt hour linked to 126g of carbon dioxide (gCO2/kWh), up 2% from the record low of 124gCO2/kWh, set last year.
The National Energy System Operator (NESO) set a new record for the use of low-carbon sources – known as “zero-carbon operation” – reaching 97.7% for half an hour on 1 April 2025.
However, NESO missed its target of running the electricity network for at least 30 minutes in 2025 without any fossil fuels.
The UK inched towards separate targets set by the government, for 95% of electricity generation to come from low-carbon sources by 2030 and for this to cover 100% of domestic demand.
However, much more rapid progress will be needed to meet these goals.
Carbon Brief has published an annual analysis of the UK’s electricity generation in 2024, 2023, 2021, 2019, 2018, 2017 and 2016.
Record renewables
The UK’s fleet of renewable power plants enjoyed a record year in 2025, with their combined electricity generation reaching 152TWh, a 6% rise from a year earlier.
Renewables made up 47% of UK electricity supplies, another record high. The rise of renewables is shown in the figure below, which also highlights the end of UK coal power.
While the chart makes clear that gas-fired electricity generation has also declined over the past 15 years, there was a small rise in 2025, with output from the fuel reaching 91TWh. This was an increase of 5TWh (5%) and means gas made up 28% of electricity supplies overall.
The rise in gas-fired generation was the result of rising demand and another fall in nuclear power output, which reached the lowest level in half a century, while net imports and coal also declined.

The year began with the UK’s sunniest spring and by mid-December had already become the sunniest year on record. This contributed to a 5TWh (31%) surge in electricity generation from solar power, helped by a jump of roughly one-fifth in installed generating capacity.
The new record for solar power generation of 19TWh in 2025 comes after years of stagnation, with electricity output from the technology having climbed just 15% in five years.
The UK’s solar capacity reached 21GW in the third quarter of 2025. This is a substantial increase of 3 gigawatts (GW) or 18% year-on-year.
These are the latest figures available from the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ). The DESNZ timeseries has been revised to reflect previously missing data.
UK wind power also set a new record in 2025, reaching 87TWh, up 4TWh (5%). Wind conditions in 2025 were broadly similar to those in 2024, with the uptick in generation due to additional capacity.
The UK’s wind capacity reached 33GW in the third quarter of 2025, up 1GW (4%) from a year earlier. The 1.2GW Dogger Bank A in the North Sea has been ramping up since autumn 2025 and will be joined by the 1.2GW Dogger Bank B in 2026, as well as the 1.4GW Sofia project.
These sites were all awarded contracts during the government’s third “contracts for difference” (CfD) auction round and will be paid around £53 per megawatt hour (MWh) for the electricity they generate. This is well below current market prices, which currently sit at around £80/MWh.
Results from the seventh auction round, which is currently underway, will be announced in January and February 2026. Prices are expected to be significantly higher than in the third round, as a result of cost inflation.
Nevertheless, new offshore wind capacity is expected to be deliverable at “no additional cost to the billpayer”, according to consultancy Aurora Energy Research.
The UK’s biomass energy sites also had a record year in 2025, with output nudging up by 1TWh (2%) to 41TWh. Approximately two-thirds (roughly 27TWh) of this total is from wood-fired power plants, most notably the Drax former coal plant in Yorkshire, which generated 15TWh in 2024.
The government recently awarded new contracts to Drax that will apply from 2027 onwards and will see the amount of electricity it generates each year roughly halve, to around 6TWh. The government is also consulting on how to tighten sustainability rules for biomass sourcing.
Rising demand
The UK’s electricity demand has been falling for decades due to a combination of more efficient appliances and lightbulbs, as well as ongoing structural shifts in the economy.
Experts have been saying for years that at some point this trend would be reversed, as the UK shifts to electrified heat and transport supplies using EVs and heat pumps.
Indeed, the Climate Change Committee (CCC) has said that demand would more than double by 2050, with electrification forming a key plank of the UK’s efforts to reach net-zero.
Yet there has been little sign of this effect to date, with electricity demand continuing to fall outside single-year rebounds after economic shocks, such as the 2020 Covid lockdowns.
The data for 2025 shows hints that this turning point for electricity demand may finally be taking place. UK demand increased by 4TWh (1%) to 322TWh in 2025, after a 1TWh rise in 2024.
After declining for more than two decades since a peak in 2005, this is the first time in 20 years that UK demand has gone up for two years in a row, as shown in the figure below.
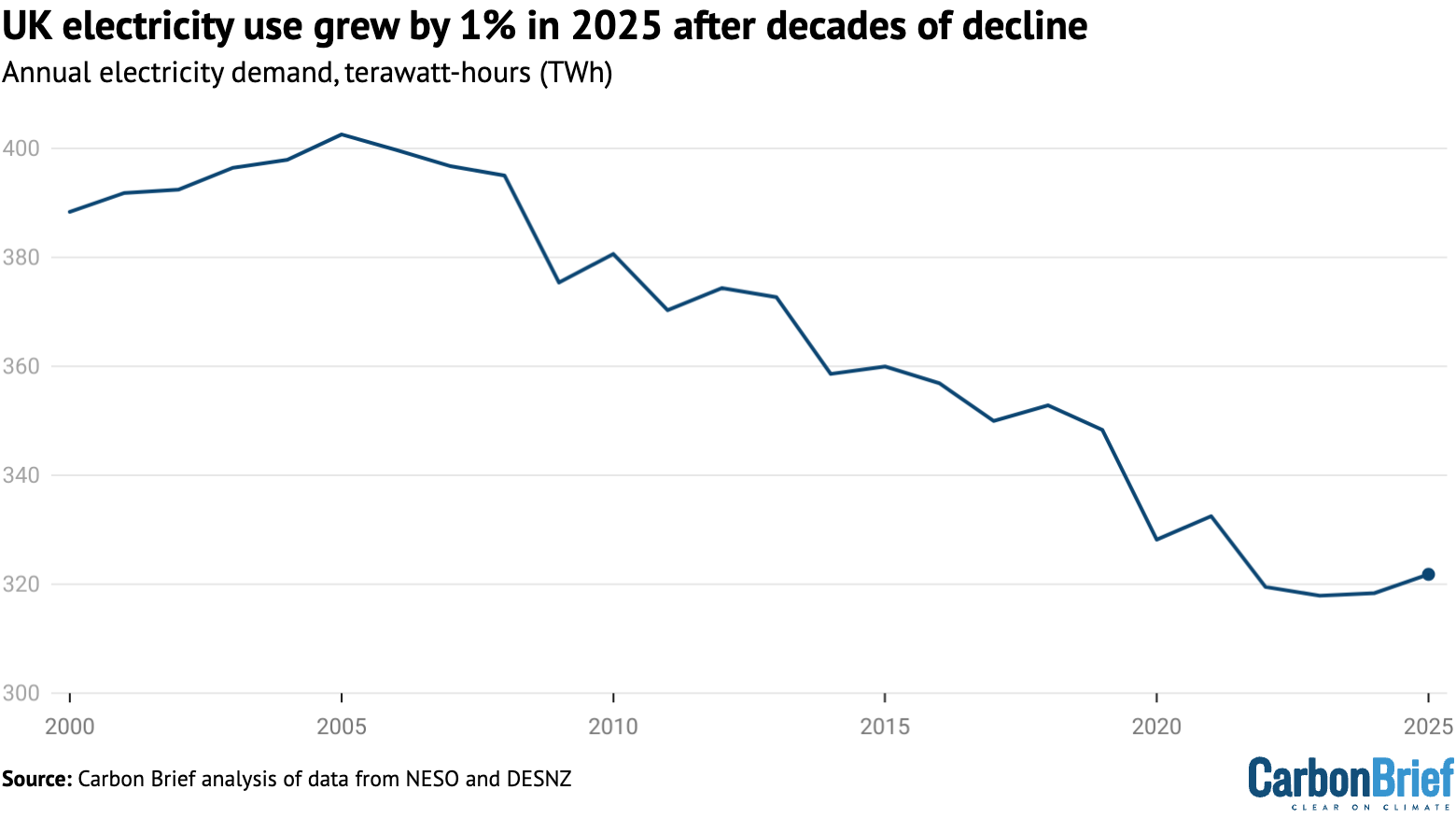
While detailed data on underlying electricity demand is not available, it is clear that the shift to EVs and heat pumps is playing an important role in the recent uptick.
There are now around 1.8m EVs on the UK’s roads and another 1m plug-in hybrids. Of this total, some 0.6m new EVs and plug-in hybrids were bought in 2025 alone. In addition, around 100,000 heat pumps are being installed each year. Sales of both technologies are rising fast.
Estimates from the NESO “future energy scenarios” point to an additional 2.0TWh of demand from new EVs in 2025, compared with 2024. They also suggest that newly installed heat pumps added around 0.2TWh of additional demand, while data centres added 0.4TWh.
By 2030, NESO’s scenarios suggest that electricity use for these three sources alone will rise by around 30TWh, equivalent to around 10% of total demand in 2025.
EVs would have the biggest impact, adding 17TWh to demand by 2030, NESO says, with heat pumps adding another 3TWh. Data-centre growth is highly uncertain, but could add 12TWh.
Gas growth
At the same time as UK electricity demand was growing by 4TWh in 2025, the country also lost a total of 10TWh of supply as a result of a series of small changes.
First, 2025 was the UK’s first full year without coal power since 1881, resulting in the loss of 2TWh of generation. Second, the UK’s nuclear fleet saw output falling to the lowest level in half a century, after a series of refuelling breaks and outages, which cut generation by 5TWh.
Third, after a big jump in imports in 2024, the UK saw a small decline in 2025, as well as a more notable increase in the amount of electricity exported to other countries. This pushed the country’s net imports down by 1TWh (4%).
The scale of cross-border trade in electricity is expected to increase as the UK has significantly expanded the number of interconnections with other markets.
However, the government’s clean-power targets for 2030 imply that the UK would become a net exporter, sending more electricity overseas than it receives from other countries. At present, it remains a significant net importer, with these contributions accounting for 109% of supplies.
Finally, other sources of generation – including oil – also declined in 2025, reducing UK supplies by another 2TWh, as shown in the figure below.
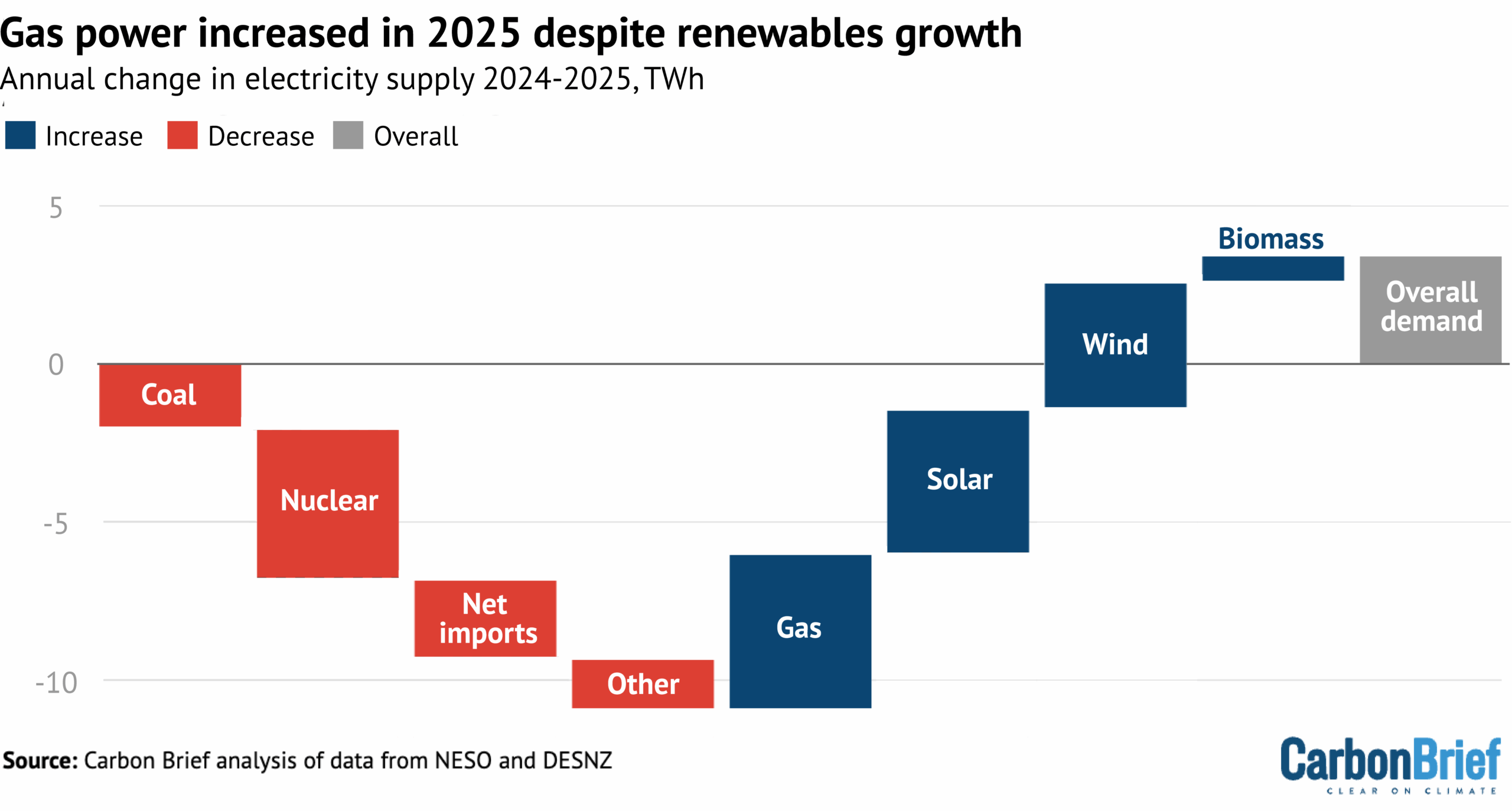
These losses in UK electricity supply were met by the already-mentioned increases in generation from gas, solar, wind and biomass, as shown in the figure above.
The government’s targets for decarbonising the UK’s electricity supplies will face similar challenges in the years to come as electrification – and, potentially, data centres – continue to push up demand.
All but one of the UK’s existing nuclear power plants are set to retire by 2030, meaning the loss of another 27TWh of nuclear generation.
This will be replaced by new nuclear capacity, but only slowly. The 3.2GW Hinkley Point C plant in Somerset is set to start operating in 2030 at the earliest and its sister plant, Sizewell C in Suffolk, not until at least another five years later.
Despite backing from ministers for small modular reactors, the timeline for any buildout is uncertain, with the latest government release referring to the “mid-2030s”.
Meanwhile, biomass generation is likely to decline as the output of Drax is scaled back from 2027.
Stalling progress
Taken together, the various changes in the UK’s electricity supplies in 2025 mean that efforts to decarbonise the grid stalled, with a small increase in emissions per unit of generation.
The 2% increase in carbon intensity to 126gCO2/kWh is illustrated in the figure below and comes after electricity was the “cleanest ever” in 2024, at 124gCO2/kWh.
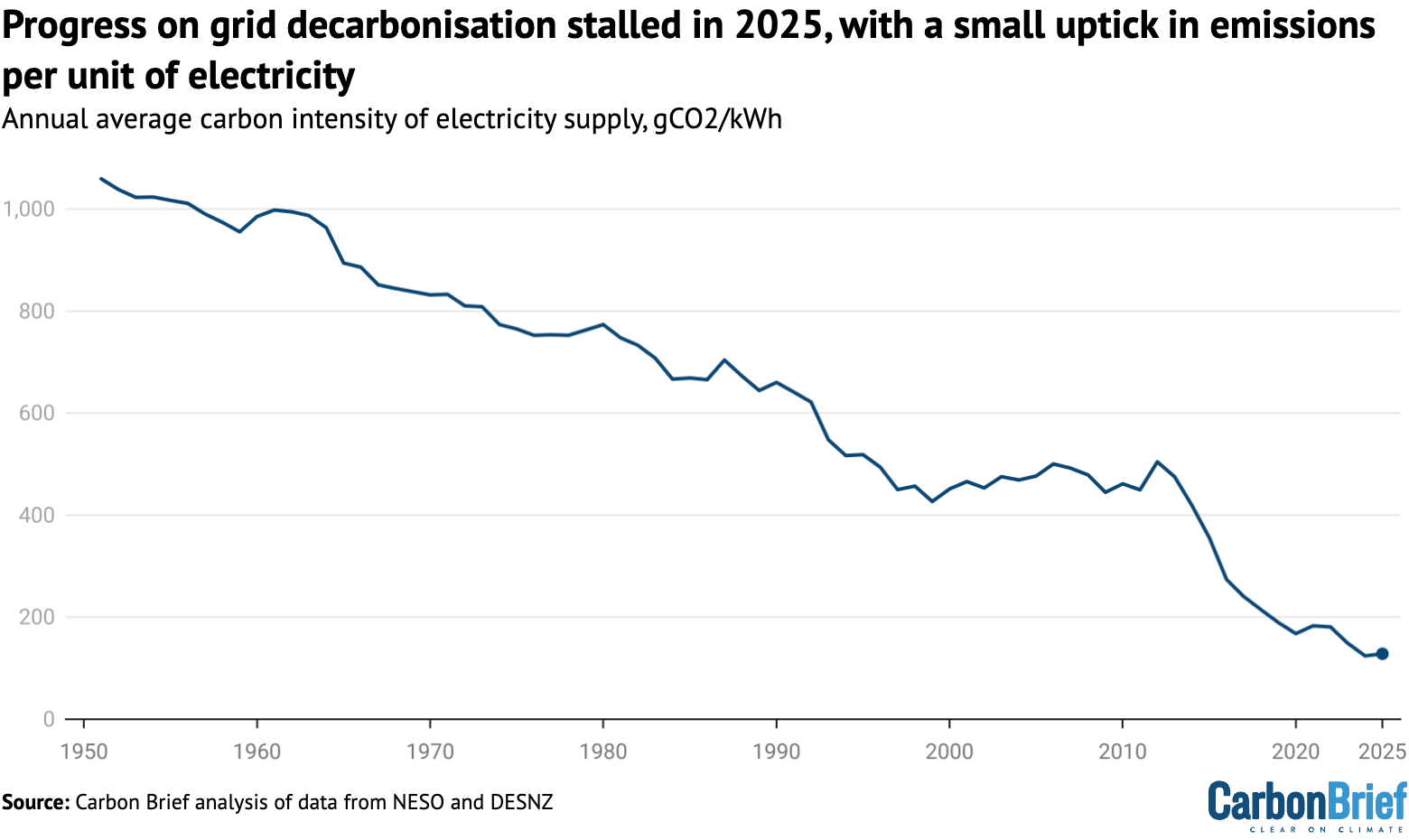
The stalling progress on cleaning up the UK’s grid reflects the balance of record renewables, rising demand and rising gas generation, along with poor output from nuclear power.
Nevertheless, a series of other new records were set during 2025.
NESO ran the transmission grid on the island of Great Britain (GB; namely, England, Wales and Scotland) with a record 97.7% “zero-carbon operation” (ZCO) on 1 April 2025.
Note that this measure excludes gas plants that also generate heat – known as combined heat and power, or CHP – as well as waste incinerators and all other generators that do not connect to the transmission network, which means that it does not include most solar or onshore wind.
NESO was unable to meet its target – first set in 2019 – for 100% ZCO during 2025, meaning it did not succeed in running the transmission grid without any fossil fuels for half an hour.
Other records set in 2025 include:
- GB ran on 100% clean power, after accounting for exports, for a record 87 hours in 2025, up from 64.5 hours in 2024.
- Total GB renewable generation from wind, solar, biomass and hydro reached a record 31.3GW from 13:30-14:00 on 4 July 2025, meeting 84% of demand.
- GB wind generation reached a record 23.8GW for half an hour on 5 December 2025, when it met 52% of GB demand.
- GB solar reached a record 14.0GW at 13:00 on 8 July 2025, when it met 40% of demand.
The government has separate targets for at least 95% of electricity generation and 100% of demand on the island of Great Britain to come from low-carbon sources by 2030.
These goals, similar to the NESO target, exclude Northern Ireland, CHP and waste incinerators. However, they include distributed renewables, such as solar and onshore wind.
These definitions mean it is hard to measure progress independently. The most recent government figures show that 74% of qualifying generation in GB was from low-carbon sources in 2024.
Carbon Brief’s figures for the whole UK show that low-carbon sources made up a record 58% of electricity supplies overall in 2025, up marginally from a year earlier.
Similarly, low-carbon sources made up 65% of electricity generation in the UK overall. This was unchanged from a year earlier.
Methodology
The figures in the article are from Carbon Brief analysis of data from DESNZ Energy Trends, chapter 5 and chapter 6, as well as from NESO. The figures from NESO are for electricity supplied to the grid in Great Britain only and are adjusted here to include Northern Ireland.
In Carbon Brief’s analysis, the NESO numbers are also adjusted to account for electricity used by power plants on site and for generation by plants not connected to the high-voltage national grid.
NESO already includes estimates for onshore windfarms, but does not cover industrial gas combined heat and power plants and those burning landfill gas, waste or sewage gas.
Carbon intensity figures from 2009 onwards are taken directly from NESO. Pre-2009 estimates are based on the NESO methodology, taking account of fuel use efficiency for earlier years.
The carbon intensity methodology accounts for lifecycle emissions from biomass. It includes emissions for imported electricity, based on the daily electricity mix in the country of origin.
DESNZ historical electricity data, including years before 2009, is adjusted to align with other figures and combined with data on imports from a separate DESNZ dataset. Note that the data prior to 1951 only includes “major” power producers.
The post Analysis: UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: UK renewables enjoy record year in 2025 – but gas power still rises
Greenhouse Gases
Ricky Bradley named Citizens’ Climate Executive Director after strategic and legislative progress during interim leadership role
Ricky Bradley named Citizens’ Climate Executive Director after strategic and legislative progress during interim leadership role
 Dec. 22, 2025 – After a six month interim period, Ricky Bradley has been appointed Executive Director of Citizens’ Climate Lobby and Citizens’ Climate Education. The decision was made by the CCL and CCE boards of directors in a unanimous vote during their final joint board meeting of 2025.
Dec. 22, 2025 – After a six month interim period, Ricky Bradley has been appointed Executive Director of Citizens’ Climate Lobby and Citizens’ Climate Education. The decision was made by the CCL and CCE boards of directors in a unanimous vote during their final joint board meeting of 2025.
“Citizens’ Climate Lobby is fortunate to have someone with Ricky Bradley’s experience, commitment, and demeanor to lead the organization,” said CCL board chair Bill Blancato. “I can’t think of anyone with as much knowledge about CCL and its mission who is held in such high regard by CCL’s staff and volunteers.”
Bradley has been active with Citizens’ Climate for more than 13 years. Prior to his former roles as Interim Executive Director and Vice President of Field Operations, he has also served as a volunteer Group Leader and volunteer Regional Coordinator, all of which ground him in Citizens’ Climate’s grassroots model. Bradley has also led strategic planning and implementation efforts at HSBC, helping a large team adopt new approaches and deliver on big organizational goals.
“We are confident that Ricky has the skills to guide CCL during a challenging time for organizations trying to make a difference on climate change,” Blancato added.
Since stepping into the Interim Executive Director role in July 2025, Bradley has led Citizens’ Climate through a season of high volunteer engagement and effective advocacy on Capitol Hill. Under his leadership, CCL staff and volunteers organized a robust virtual lobby week with 300+ constituent meetings, despite an extended government shutdown, and executed a targeted mobilization to support the bipartisan passage of climate-friendly forestry legislation through the Senate Agriculture Committee.
“We have heard nothing but glowing descriptions of Ricky’s ability as a leader, as a manager, and as a team player,” said CCE board chair Dr. Sandra Kirtland Turner. “We’ve been absolutely thrilled with how Ricky’s brought the team together over the last six months to deliver on a new strategic plan for the organization.”
The strategic plan, which launched during CCL’s Fall Conference in November, details Citizens’ Climate’s unique role in the climate advocacy space, its theory of change for effectively moving federal climate legislation forward, and its strategic goals for 2026.
“Ricky has the heart of a CCLer and the strategic chops to take us into the next chapter as an organization,” Dr. Kirtland Turner said.
Bradley shared his vision for that next chapter in his conference opening remarks last month and, most recently, during the organization’s December monthly meeting.
“There’s a lot that we don’t control in today’s politics, but we do know who we are. The power of our persistent, nonpartisan advocacy is unmistakable,” Bradley said. “If we stay true to that, deepen our skills, and walk forward together, I know we’re going to meet this moment and deliver real results for the climate.”
CONTACT: Flannery Winchester, CCL Vice President of Marketing and Communications, 615-337-3642, flannery@citizensclimate.org
###
Citizens’ Climate Lobby is a nonprofit, nonpartisan, grassroots advocacy organization focused on national policies to address climate change. Learn more at citizensclimatelobby.org.
The post Ricky Bradley named Citizens’ Climate Executive Director after strategic and legislative progress during interim leadership role appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
-
Climate Change5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Greenhouse Gases5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval

























