Elizabeth Rush, author of “The Quickening, Creation, and Community at the Ends of the Earth”
Episode 94: Antarctic Awakenings: Unveiling Climate Change at the Ends of the Earth with Elizabeth Rush and Brett Cease
In this episode of Citizens’ Climate Radio, co-hosts Peterson Toscano and Erica Valdez explore the theme of climate change and its impact on Antarctica. They interviewed Elizabeth Rush, author of “The Quickening, Creation, and Community at the Ends of the Earth,” who shares her experiences and insights from a research expedition to Thwaites Glacier.
 They also spoke with Brett Cease, Vice President of Programs for Citizens’ Climate Lobby, who traveled to Antarctica and shared his observations. Additionally, they discuss sustainable fashion, resilience, and the Great School Electrification Challenge.
They also spoke with Brett Cease, Vice President of Programs for Citizens’ Climate Lobby, who traveled to Antarctica and shared his observations. Additionally, they discuss sustainable fashion, resilience, and the Great School Electrification Challenge.
Journey to Thwaites Glacier with writer Elizabeth Rush
Elizabeth Rush joined a research expedition aboard an icebreaker in 2019 and headed for Thwaites Glacier for 54 days. This remote and deteriorating glacier is critical in understanding global sea level rise. Her book documents this journey, weaving together the awe-inspiring encounters with icebergs and the intense efforts of scientific labor.
A Deep Feminist Rewriting of Antarctic History
During her time on the icebreaker, Elizabeth embraced her role as writer-in-residence to shift the narrative focus. Antarctic history, often dominated by tales of conquest by wealthy, white men from the Global North, is ripe for reexamination. Elizabeth spent considerable time engaging with the ship’s diverse crew members, including engineers and cooks from the Philippines, whose stories are usually overshadowed by scientists’ stories. By doing so, she highlights the essential labor that makes scientific discovery possible and challenges the traditional narrative that has long defined Antarctic expeditions.
 Life Aboard the Icebreaker
Life Aboard the Icebreaker
Elizabeth’s account transcends typical adventure narratives, offering a glimpse into the daily realities of life on a research vessel. The absence of the internet and the close quarters created an environment of authenticity and camaraderie among the crew. This unique setting allowed genuine interactions and reflections that are rare in our every day, digitally-saturated lives.
A Thoughtful Dialogue on Climate Change and Parenthood
“The Quickening” provocatively explores the intersections of climate change and the decision to bring children into the world. Elizabeth tackles this complex topic not by dictating what to think but by inviting readers to engage in a thoughtful dialogue. The narrative steers clear of simplifying the issue to mere carbon footprints, instead enriching the discussion with nuanced perspectives on regeneration and balance.
About Elizabeth Rush
Elizabeth Rush is a distinguished author known for her impactful exploration of climate change and its effects on communities. Her acclaimed book, “Rising: Dispatches from the New American Shore,” was a Pulitzer Prize finalist and has garnered praise for its deeply felt portrayal of frontline communities facing environmental challenges. Rush’s writing is characterized by her commitment to listening to marginalized voices, whether they are those affected by climate change, the melting glaciers of Antarctica, or individuals excluded from environmental conversations.
“Rising” has been lauded as a vital contribution to the discourse on climate change and sea levels, earning acclaim from publications like the New York Times and the Chicago Tribune. Rush’s work extends beyond her book, with her writings appearing in prestigious publications such as Orion and Guernica. Rush has received numerous fellowships from institutions like the National Endowment for the Arts, National Geographic, and the Andrew Mellon Foundation. Currently based in Providence, Rhode Island, she teaches creative nonfiction at Brown University while living with her husband and two children.
This is the fourth time CCR has featured Elizabeth Rush on the show. She also appears in Episode 26 In Deep Water, Episode 29, Truth, Fact, and Cli-Fi, and Episode 47, Eco-Grief in a Time of Coronavirus Mourning.
Brett Cease’s Antarctic Adventure
 Brett Cease, Vice President of Programs for Citizens’ Climate Lobby, shared his enlightening journey to the Antarctic Peninsula. His voyage on the Ushuaia, a research vessel turned expedition ship, offered firsthand insights into Antarctica’s harsh realities and stunning beauty.
Brett Cease, Vice President of Programs for Citizens’ Climate Lobby, shared his enlightening journey to the Antarctic Peninsula. His voyage on the Ushuaia, a research vessel turned expedition ship, offered firsthand insights into Antarctica’s harsh realities and stunning beauty.
Navigating through towering waves and enduring 24-hour daylight, Brett’s expedition highlighted the Southern Ocean’s raw power and unpredictability. The trip provided an up-close view of the continent’s dramatic landscapes and unique wildlife, including several species of penguins.
Penguins and the Impact of Climate Change
 One of the most striking aspects of the journey was observing the effects of climate change on local wildlife. The Adelie penguins, in particular, suffer as rising temperatures cause the sea ice they depend on to form later and melt earlier each year.
One of the most striking aspects of the journey was observing the effects of climate change on local wildlife. The Adelie penguins, in particular, suffer as rising temperatures cause the sea ice they depend on to form later and melt earlier each year.
Brett vividly described the overwhelming smell of penguin colonies, a mix of old cigarettes, ammonia, and rotten shrimp, illustrating the less glamorous side of these adorable but squalid creatures.
Ice Loss and Its Global Implications
The voyage underscored the dramatic ice loss in Antarctica, with the continent shedding approximately 150 billion tons of ice annually. Witnessing these changes was humbling and a stark reminder of the urgent need for global climate action.
Listen Now!
Resilience Corner
Tamara Staton explores the surprising relationship between puppies and climate change. Through her experience with her puppy, Mica, Tamara highlights how pets contribute to our well-being, from reducing stress to promoting physical activity and combating loneliness. She emphasizes how the positive effects of pet ownership can indirectly support climate action by fostering healthier, happier individuals. Tamara invites us to consider pet ownership or pet-sitting as a means of experiencing these benefits.
To learn more about building resilience in the face of climate challenges, visit the Resilience Hub. Share your resiliency questions with Tamara via email at radio @ citizensclimate.org or you can text or leave a message at 619-512-9646.
CCL Youth Corner with Veda Ganesan
 Veda tells us about the Great School Electrification Challenge, an initiative spearheaded by CCL National Youth Action Team that aims to transform schools into hubs of sustainability by advocating for the electrification of various systems, including HVAC, transportation, and energy sources like solar panels. Through the stories of youth teams in Cincinnati, Ohio, and Dallas, Texas, Veda showcases the grassroots efforts to engage school boards, policymakers, and the community in adopting clean energy practices. Highlighting the recent success of the Cincinnati team in getting their electrification resolution unanimously passed, she encourages listeners to join the cause and participate in the challenge.
Veda tells us about the Great School Electrification Challenge, an initiative spearheaded by CCL National Youth Action Team that aims to transform schools into hubs of sustainability by advocating for the electrification of various systems, including HVAC, transportation, and energy sources like solar panels. Through the stories of youth teams in Cincinnati, Ohio, and Dallas, Texas, Veda showcases the grassroots efforts to engage school boards, policymakers, and the community in adopting clean energy practices. Highlighting the recent success of the Cincinnati team in getting their electrification resolution unanimously passed, she encourages listeners to join the cause and participate in the challenge.
Veda Genesan is a high school student from Texas and the host of the Sustainable Cents podcast.
Good News
 Erica Valdez shares the adverse environmental effects of the fashion industry, as it uses resources and generates emissions to produce, package, and transport clothing. The good news is there are many groups taking action and bringing this issue to light.
Erica Valdez shares the adverse environmental effects of the fashion industry, as it uses resources and generates emissions to produce, package, and transport clothing. The good news is there are many groups taking action and bringing this issue to light.
Erica highlights the Scrounger’s Center for Reusable Art Parts (SCRAP), a nonprofit center for creative reuse in San Francisco.
Through after-school programs like Sustainable Fashion Design for Teens, SCRAP educates students about the environmental effects of the fashion industry and teaches them how to reuse and revitalize clothing materials. This program empowers young people with hands-on workshops and educational sessions. It also provides a space to learn and process climate information and connect with other young advocates. SCRAP is a perfect example of how important individual and collective action is and how creative it can look.
Monthly Question
If you could advocate for the climate through art, what kind of art piece would you create?
This can be music, dance, film, writing, or other mediums you’ve used in rural climate work. We want to hear about it. Please email your answer to radio @ citizens climate.org. You can also text or leave a voicemail at 619-512-9646. Tell us your story of using art in your climate work.
Listener Survey
We want to hear your feedback about this episode. After you listen, feel free to fill in this short survey. Your feedback will help us make new decisions about the show’s content, guests, and style. You can fill it out anonymously and answer whichever questions you like. You can also reach us by email: radio @citizensclimatelobby.org
You can hear Citizens’ Climate Radio on:
Also, feel free to connect with other listeners, suggest program ideas, and respond to programs in the Citizens’ Climate Radio Facebook group, on X (formerly known as Twitter) @CitizensCRadio, Instagram @CitizensClimateRadio, LinkedIn, or TikTok @ClimateChangePodcast
Read the Transcript
Episode 94: Antarctic Awakenings: Unveiling Climate Change at the Ends of the Earth with Elizabeth Rush and Brett Cease
SPEAKERS
Elizabeth Rush, Tamara Staton, Brett Cease, Peterson Toscano, Veda Ganesan, Erica Valdez
Peterson Toscano 00:00
Welcome to Citizens’ Climate Radio, your climate change podcast.
Erica Valdez 00:05
In this show, we highlight people’s stories. We celebrate your successes, and together we share strategies for talking about climate change.
Peterson Toscano 00:12
I’m your host, Peterson Toscano,
Erica Valdez 00:14
and I’m your other host, Erica Valdez. Welcome to Episode 94 of Citizens’ Climate Radio, a project of Citizens’ Climate Education.
Peterson Toscano 00:22
This episode is airing on Friday, April 26 2024. Hey, Erica, Welcome to the show.
Erica Valdez 00:30
Hey, Peterson, I’m happy to be here.
Peterson Toscano 00:32
Congratulations, being co host first time, well done.
Erica Valdez 00:35
Thank you.
Peterson Toscano 00:36
We have a very, very full show today. lots of moving parts. What’s something you’re excited about listeners hearing on today’s show?
Erica Valdez 00:44
I’m especially looking forward to hearing from Elizabeth Rush. She talks about her new book, The Quickening. It’s about her experience on a trip to Antarctica and how she sees this continent being impacted by humans. I’m always looking for a good environmental book recommendation. And I just love hearing personal stories about other climate advocates.
Peterson Toscano 01:01
Yeah, she’s an amazing writer. She’ll give us a reading as well. I’m super excited about your good news story that you worked on. You researched it? You recorded it. You did all the audio and it’s about sustainable fashion. I’m super excited about that. Yeah, me too. Well, with this Antarctica theme, we also have a segment with Brett Cease from Citizens’ Climate Lobby, he traveled to Antarctica to and he shares with us the sights, the sounds and the smells, which I didn’t realize they were so strong in Antarctica.
Erica Valdez 01:32
And we also have a CCL Youth Corner. Today, we’re bringing you a special episode focusing on the Great School Electrification Challenge. They talk about what electrification is all about, and how either igniting change in their schools and how you can inspire youth to join the cause.
Peterson Toscano 01:48
We have a new section thanks to you questions and answers with listeners. So thanks for that suggestion. So are you ready, Erica?
Erica Valdez 01:56
Yep. Are you?
Peterson Toscano 01:57
I think so. Let’s do it.
Peterson Toscano 02:00
Elizabeth Rush is the author of Rising, Dispatches from the New American Shore, a Pulitzer Prize finalist. Her work focuses on listening to marginalized voices and frontline climate-affected communities, and she explores the crucial questions of our responsibilities and emotional responses in a rapidly changing world. Elizabeth returns to Citizens’ Climate Radio to tell us about her newest book, The Quickening: Creation and Community at the Ends of the Earth.
Erica Valdez 02:34
In 2019 Elizabeth Rush joined a research expedition aboard an icebreaker to Thwaites Glacier, a remote and rapidly deteriorating region critical to understanding global sea level rise. Her book, The Quickening, documents this journey, blending on inspiring encounters with icebergs and intense scientific labor, while pondering the profound personal question of what it means to bring a child into a world undergoing radical change.
Elizabeth Rush 02:59
When I took a position on this boat as like the writer in residence, I knew that I wanted to spend a lot of time on this ship, interviewing and speaking to people whose voices are traditionally left out of Antarctic stories. It turns out, as I like delved into Antarctic research, that like if you’re not a wealthy white dude from the global north like you’ve definitely been written out of Antarctic history, I did very purposefully spend a lot of time during the expedition talking to like the engineers, and the able-bodied seaman who all came from the Philippines, the cooks on board, because our modern Antarctic stories tend to center the work of the scientists that are trying to do climate science or groundbreaking science in Antarctica. And if you just look at like the crew list on our boat, the Nathanial B. Palmer. We were 50/50 support staff and scientists federally funded scientists, so I was really interested in like whose labor makes the scientific discovery possible. Who aren’t we hearing from?
Elizabeth Rush 04:12
I mean, it’s a book about Antarctic history. It’s a book about how in the little bit of time that human beings have had contact with Antarctica, we’ve really like crushed this continent of ice into like a very limited masculine narrative of conquest and derring do and Antarctica serves as like a backdrop and that story, I sometimes say it’s like a deep feminist rewriting of Antarctica. A lot of these books tend to be about like extreme environments. And I was like, you know, for all the time I spent in Antarctica, the reality is most of it was inside a climate controlled boat with like four meals a day cooked for me and stuff. So I tried to kind of lean into what it was actually like and not to over dramatize it, there was no choice but to be yourself. People really didn’t perform for each other, there was a certain amount of like deep authenticity that being on this boat just demanded, because otherwise you would wear yourself out by like day three.
Elizabeth Rush 04:13
I don’t think I’ve ever been in a situation like that. The closest is sort of like summer camp when I was 10, or something. I mean, I don’t know how people felt about summer camp, but, I don’t know just like there’s like a deep sense of camaraderie that developed amongst us going through this like really strange experience together. I think all the characters in the book come across as very authentic, and they just kind of like shed their armor, and let it all hang out.
Elizabeth Rush 05:48
The mechanism of the book is one where you’re kind of a fly on the wall eavesdropping on really interesting people for like two and a half months as they, I don’t know, plow into the ice and like go sedate elephant seals, and then play bridge for hours on end because they have nothing else to do. We had no internet, like no functional internet, which was awesome. Like, you just had to be with each other. It was really fun. I think it was some of the happiest of my adult life. Without internet, there was none of that kind of like knee-jerk. Oh, I’m like standing waiting for my groceries, let me read the newspaper. My time became way more expansive, because it wasn’t divided into these smaller and smaller chunks constantly, which I really, really, really liked.
Elizabeth Rush 06:43
It was after dinner and you’re sort of like, oh, I don’t know what to do with myself, you’re not like wow, let me just like read something on Twitter. Maybe I should walk up to the bridge and look to see if there are whales out there. And maybe I’ll chat with someone, I felt that there was a lot more sort of very low-stakes socializing that happened. And that replaced the internet a little bit like it replaced Twitter, it replaced social media. But with actual human beings, it was wonderful, I really felt liberated.
Elizabeth Rush 07:17
Experiencing something extraordinary with other human beings, there’s nothing quite like it. And it doesn’t have to be a glacier, it can just be a shared space. It can be a fire at the end of the day. I want to make the reader feel like they’re pulling close to this glacier, and looking at it, and having to kind of like consider it fully, physically, spiritually. The book really doesn’t tell you what to think about climate change and parenthood. Instead, I hope it creates a meaningful space for the reader to like engage in their own thinking on that quandary. It’s not you should have kids, you shouldn’t have kids. There’s no shoulds at all. It’s just, man, this is complicated. Here are lots of ways to think about it.
Elizabeth Rush 08:17
When I read about climate change and Parenthood in the news, it often gets sort of reduced to like conversations on the carbon footprint. And like, oh, a kid is like your biggest contribution to your carbon footprint. And I just think that’s a bunch of BS, and I could go down that rabbit hole. We don’t have to right now, but choosing to have a kid is not the same as like getting a Jetta, or a Prius, or whatever. And I really don’t appreciate the comparison because I think it denies folks the opportunity to have a real conversation about like what does regeneration mean as the planet tips out of balance? I really wanted the book to have space for like a thoughtful conversation around those subjects without getting prescriptive.
Erica Valdez 09:02
Elizabeth agreed to read from the quickening.
Peterson Toscano 09:05
Think of this section as a monologue spoken in the voice of Peter, one of the researchers aboard the ship.
Elizabeth Rush 09:14
So this is Peter. I had a moment yesterday. Do you ever just stop and think: what the eff am I doing? That we’re about to sail to the goddamn Southern Ocean? Why would anybody in their right mind go to Antarctica, which is like the great beyond? I just had one of those moments where I went, What am I doing? I’m from Norfolk, I shouldn’t be here. Most of my friends who are not scientists think I’m kind of mad. Antarctica is bad enough, but Thwaites? They look at me like really? Is there a need? They find the fact that it’s called a cruise particularly entertaining because you know, a cruise to them means rattling around the Caribbean on the QM2 with a cocktail in hand.
Elizabeth Rush 10:00
On our cruise, there’s no alcohol, you have to share a cabin, you eat what you’re given, and it’s freezing bloody cold. And the thing is, you can’t get off if you don’t like us. If there’s someone you really hate, you can’t get away from them. It’s the same on all the scientific cruises, no matter where you go. At breakfast, they’re there. They spent all night on the same boat as you, you have no choice but to make it work. Otherwise, you’d throw yourself off the side. It may surprise you to find that I’m a quite sociable person. So to cut myself off from all my friends almost completely? Well, I’ve got to find some sustenance somewhere. Here we are, on this boat with this motley crew of people who most of us just met, and now will embark on this incredibly intense journey. That is its own kind of social experiment.
Elizabeth Rush 10:57
All right, and then this is arriving at Thwaites. This is the night into morning that we arrive at Thwaites. That night sound sleep eludes me. I wake often, each time hopeful that we’ve arrived. Finally around five o’clock in the morning I rise, shuffle up the four flights of stairs, undog the door by the ice tower, and walk out on the bridge wings. Thwaite’s gray margin wobbles in the gloaming. We wind alongside entering small coves and rounding odd promontories. Our pace slow to hold this precarious line. The ice face soft as dunes. The night’s new hint of darkness gives way to the bruised light of dawn, and many others appear to watch what each of us has been working toward for weeks for years, and in some cases for decades, come into sharp focus. We don’t talk. When someone wants to say something, they whisper as though we’re in a giant, roofless cathedral. We, who’ve been at sea for so long, finally gaze upon the glacier that has already given us one another. Rick stands attentive at the ship’s helm. The captain next to him, steering us along the edges of Thwaites’ unfathomable fracturing, its hemorrhaging heart of milk.
Peterson Toscano 12:55
That was Elizabeth Rush, author of The Quickening: Creation and Community at the Ends of the Earth, which is available wherever books are sold.
Erica Valdez 13:05
To learn more about Elizabeth and her other publications, visit elizabethrush.net
Peterson Toscano 13:13
It turns out, you don’t need to be a fancy scientist or a creative writer to visit Antarctica. There are tourist cruises you can take. Well, not luxury cruises, but you can travel with scientists who are doing their research.
Erica Valdez 13:29
Brett Cease, Citizens’ Climate’s vice president of programming, traveled to Antarctica with his father and sister. He shares some of his experiences with us, including the shocking truth about penguins.
Brett Cease 13:42
We were on a boat called the Ushuaia, named for the city, obviously, that you leave from South America to get to the peninsula on. It’s a 279-foot ice-strengthened expedition ship, specifically that was built for NOAA as a research vessel back in 1970, it tops out at about 16 miles an hour. So, it goes very slowly, chugging along with its old diesel engines. It’s about 52 feet wide, and there was space enough for 90 passengers and 38 crew. And it now serves as not only as a transportation for those scientists to get to the peninsula but for tourists and individuals that are interested, like my family was, to go along with them and during the journey, learn about the research that they’re doing, get educated and have the chance to interact with those people as we made the voyage.
Brett Cease 14:36
These were the people in the world that are doing some of the front line research, trying to understand the changing climate of Antarctica, the early signals that we’re already detecting and impacts that it’s going to have on a whole system of food chains. Just imagine a house-sized wave crashing over your boat, your, the bow of the boat every five to 10 seconds for two days straight. Yo u literally kind of have to velcro your head to your pillow, or else you’ll roll out the bed. The winds and the current swirling around, this endless surging raw power of the Southern Ocean. It felt like being at the bottom of an endless grandfather clock pendulum.
Brett Cease 15:16
It wasn’t too cold, we were in the Antarctic summer. There’s no darkness, that is another beautiful thing. You know, imagine being in a world of 23+ plus of light. And yes, we, just like Elizabeth, we reveled in the chance to share and get to know the other travelers in the crew. Just to get into the flow of the season, and the wildlife, and the quiet ice passing by us. It was unforgettable. You’re struck immediately by how quickly the mountains rise up from the ocean. It’s actually the highest, and driest, and windiest continent of the world, not just the coldest. It’s known for its katabatic winds, which have speeds of over 200 miles an hour. And it’s constantly there.
Brett Cease 16:02
There are three types of penguins in the Antarctic Peninsula that we all got to see during the expedition: the gentoo penguin, the chinstrap penguin, and the adelie penguin. And here is where climate change rears its head. Rising temperatures on the Antarctic Peninsula are actually hammering the region’s adelie penguins and the sea ice that they depend. Ice forms continually later each year, it melts earlier, and that whole species is disappearing entirely from that Peninsula. Some of the sounds that you might, kind of, imagine with penguins include the cooing, the beautiful squawks that they give to each other as mates. Penguins make affectionally for life. So, it was really inspiring to see both the male and the female parents take care of their young chicks, and build up their stone nests with little pebbles that they’d wobble over across all the mud to collect.
Brett Cease 16:56
On top of being adored lovable birds that we all just enjoy looking at, penguins live in absolute squalor. This is one of the things that I wasn’t prepared for. It’s detailed by an NPR article that I love replicating here. They say the best way for you here at home, listener, to recreate the old factory experience for your own nose is to take some old cigarettes, soak them in ammonia, mix in some rotten shrimp, put this all in a bottle if you will. And then let it sit out on your windowsill in the sun for several days. Mix it up, and then take a big whiff in. And then breathe that in constantly, and that is the smell of penguin guano. Because of their sheer scale, these colonies that we visited were literally hundreds of thousands of birds. You can imagine that that gets overpowering pretty quickly.
Brett Cease 17:49
Antarctica is losing ice mass, that means it’s melting at an average rate of 150 billion tons of ice each year. Witnessing these icebergs that are floating now in the cold, open channels of the ocean, hundreds and hundreds of them, we got to see icebergs calving, we got to see the ship being navigated through channels that were clogged with them. They were composed of snow that had been compacted long before I was born, long before even, on some of them, the dawn of humankind. And thinking about the impact that all of us have in changing, so dramatically and so quickly, this entire landscape was incredibly humbling in harrowing.
Peterson Toscano 18:45
That was Brett Cease, vice president of programming for CCL.
Erica Valdez 18:50
Visit cclusa.org/radio to see some of Brett’s photos. Still to come, you hear some good news for me about a program that teaches school students about making fashion sustainably. We also learned about resilience and puppies from Tamara Staton. And hear the next installment of the CCL youth corner. Stay tuned!
Peterson Toscano 19:20
Now it is time for the resilience corner with Tamra Staton.
Tamara Staton 19:24
Hi, I’m Tamara Staton, CCL’s education and resilience coordinator. And this is Resilient Climateering Through Unexpected Climate Connections. Today’s topic is puppies and climate, two seemingly unrelated concepts that actually relate to one another in quite a few interesting ways. And to be clear, while this episode highlights the relationship between puppies and climate change, you could easily substitute puppies for kittens or many other sweet pets that regularly bring you joy.
Tamara Staton 19:54
In March, we got a puppy and we named her Mika she’s almost a year now, and it’s been quite an amazing journey. I don’t know if you’ve ever had a puppy, especially a working breed like a German Shepherd, but as much work as she’s been, I’m so happy that she’s in our lives. When Mika was just a few months, old romping around in the backyard, I found myself wondering if there’s a connection between puppies and climate change. While it may seem like a stretch at first, I actually see a boatload of connections.
Tamara Staton 20:25
In a nutshell, puppies, and the pets that we love, offer so many benefits to our lives, which end up helping us in our efforts to address climate change. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, for example, simply petting a dog, or a pet, lowers the stress hormone, cortisol. And the social interaction between people and their dogs actually increases levels of the feel good hormone, oxytocin. As highlighted from the National Institutes of Health, oxytocin can induce anti stress-like effects, such as reduction of blood pressure and cortisol levels. It increases pain thresholds, and stimulates various types of positive social interaction. It also promotes growth and healing. When we’re growing, healing, and healthy, climate action gets to take a front seat in our lives. Pets and puppies can help us stay healthier, and naturally reduce the stress that many of us feel on a regular basis when we think about climate change.
Tamara Staton 21:24
In addition to lowering my stress, and blood pressure, at least most of the time, my puppy, Mika, forces me to be more active and more present and to go outside. I take her on walks in the sun and the rain, I head to the park, and walk through the trees. I meander through my neighborhood speeding up at times, but also slowing down so that we can both take in our surroundings and be fully present with whatever we see, hear, and smell. And perhaps most importantly, at least for me, having a puppy leaves me feeling more fulfilled and less lonely. Granted, she’s on on their climate advocate working on the same cause. But the opportunity to snuggle with her on a regular basis, to feel her love to feel her loyalty? Those are sensations that are hard to replicate even with other people.
Tamara Staton 22:14
In fact, one study in 2011 found that pets provided greater social support than humans in mitigating depression. And another study found that pet owners had better self-esteem. Maybe you’re not up for a puppy, or a kitten, or a pet of your own anytime soon. There’s definitely a time and a place for taking that on. But maybe you consider pet sitting or time sharing or borrowing a snuggly pet from a friend or family member. Or maybe, you just lean into the love that you recognize that your own pet offers you. I’m Tamara Staton with the Resilience Corner. Thank you for listening and for your commitment to progress. To learn more about tools, training, and resources for staying strong through the climate challenge, check out our resilience hub at cclusa.org/resilience. And until next month, remember this. Find your passion, let it guide you, and you’ll do amazing things for our world.
Peterson Toscano 23:14
Thank you, Tamara. You know, Erica, now I definitely need a puppy. Desperately.
Erica Valdez 23:19
You and me both. Do you have a question for Tamara? She’s very happy to consider your resilience questions, conundrums, and suggestions. Send an email to radio@citizensclimate.org. That’s radio @ citizensclimate.org or text us at 619-512-9646.
Peterson Toscano 23:39
The resilience corner is made possible through a collaboration with Tamara Staton, education and resilience coordinator for Citizens’ Climate Education. Now it is time for the CCL youth corner with Veda Ganessan, our youth correspondent.
Veda Ganesan 23:55
Welcome to Citizens’ Climate Radio’s Youth Corner. We’ll delve into the latest developments in climate action and environmental issues, all from the youth’s point of view. I’m Veda Ganessan, CCL’s national youth podcast lead. Today, we’re bringing you a special episode focusing on the Great School Electrification Challenge. What is electrification all about? How are youth igniting change in their schools? And how can you inspire youth to join the cause? Oh, and I’ll be telling you about one team that got their resolution passed.
Veda Ganesan 24:36
Schools are among the largest energy consumers in the public sector. They generate emissions equivalent to those of 18 million cars each year. We students hope to change that. Enter the Great School Electrification Challenge. This initiative was launched by CCL’s national youth action team. In this challenge, teams of students are calling on their school boards to pledge to electrify everything in their schools. That means HVAC systems, lawn maintenance, school bus fleets, and even adding solar panels. It’s about embracing clean energy and sustainability in the places where we learn and grow. We’re gearing up for round two of the challenge right now.
Veda Ganesan 25:15
Sharon Bagatell, the CCL youth action coordinator, describes the challenge as fun, informative, and empowering. And it’s no wonder. Students hold a unique position as the primary users of school facilities, giving them the right to influence and advocate for change. The challenge is also about creating a safer, more comfortable school environment that fosters better academic performance. Now, the big question: how do students make it happen? I’ll tell you about two different use teams, one in Cincinnati, Ohio, and one in Dallas, Texas.
Veda Ganesan 25:48
First, let’s take a look at DFW Gen Green. Led by me and Care Share, our team in Texas has developed a meticulous roadmap that includes electric school bus fleets and solar panel installations. We’ve convened high-level discussions with representatives from critical departments. These include the school superintendent, CFO, facilities, energy construction and contracts to enhance our efforts. We’ve connected with the community through tabling at local events, publishing op-eds, and organizing district-wide art shows. This ambitious endeavor comes at a crucial time for the district, particularly amidst budgetary challenges.
Veda Ganesan 26:25
Now, zooming in on the Electrified Cincinnati Schools Team, we see that they have been developing relationships with board members and influential policymakers to make changes. They’ve even hosted discussions with guest speakers and local environmental activists. And just recently, the Cincinnati Board of Education unanimously passed the team’s electrification resolution. They’re the first team to do so in the national youth action team.
Veda Ganesan 26:48
With 11 more teams across the United States, including the Los Alamos High Eco Club and the Tahoe Youth Action Team, the opportunity to get involved awaits you. To learn more and to register, visit youth.citizensclimatelobby.org/school-electrification. Again, that’s youth.citizensclimatelobby.org/school-electrification. The Electrification Challenge is an invitation to contribute to a greater cause, affect real change within the community, and ignite inspiration for others. The top three electrification teams in round one will be receiving cash prizes for their hard work. Learn more at youth.citizensclimatelobby.org/school-electrification.
Veda Ganesan 27:35
As a high school student, I see the great electrification challenge as a symbol of our commitment to a brighter, greener and more sustainable future. It empowers us to be innovators, forward thinkers, and environmental stewards. So let’s embrace the challenge, ignite change, and create a world we’re proud to pass on to future generations. We’ll report more on this in future episodes as more teams join the challenge.
Veda Ganesan 28:00
So that concludes our time with you. Thank you for joining us for the CCL youth corner and stay tuned for our next episode on the goat campaign. To learn more about CCL youth, visit cclusa.org/youth.
Erica Valdez 28:18
Thank you, Veda. That was Veda Ganessan with the CCL youth corner. Now it’s time for our good news story.
Peterson Toscano 28:40
This story was researched, written, and produced by you, Erica Valdez; thank you so much.
Erica Valdez 28:46
Do you know which of these products takes more water to produce? Is it our food, our clothing, our cars? If you guess clothing, you’re right. The fashion industry is the second most water-intensive industry in the world. To produce and packaged clothing takes a lot of resources, not to mention the greenhouse gas emissions it produces to transport all of them. These processes have a huge impact on the environment. And it’s hard for us as individuals to steer clear from the consumer culture when things have become so accessible.
Erica Valdez 29:16
The good news is, that groups are stepping up to bring this issue to light and support individuals in taking action. One of these groups is the Scroungers Center for Reusable Art Parts, or SCRAP. I had a great conversation with Danielle grant. She’s a programs director at SCRAP. She told me about the background of the nonprofit and how it’s empowering young people in the climate conversation.
Erica Valdez 29:39
Here are some quick facts about SCRAP. It’s the oldest and largest creative reuse nonprofit center in the United States. Scrap was started in response to the defunding of arts education in the San Francisco School District. And it was established nearly 50 years ago, in 1976. At this time, the environmental movement was gaining momentum worldwide. I mean, it was the 70s. This decade brought the first Earth Day and the Environmental Protection Agency. People were advocating for the climate by sharing the science, protesting, and collaborating with others across the world.
Erica Valdez 30:11
I love that SCRAP is open to the public. People can shop, explore how to use materials, and attend educational workshops. What caught my attention was one of SCRAP’s after-school programs that teaches students how to reuse and revitalize clothing materials. This program is called Sustainable Fashion Design for Teens. In this program, students usually have two classes per week. One is more learning and curriculum based where they discuss the fashion industry worldwide and its environmental effects. The second is a hands-on workshop. Over 12 weeks, students work up to a final project, or fashion show, to present to their friends and family.
Erica Valdez 30:43
SCRAP’s main objectives with these school programs are to 1.) keep materials out of landfills and reuse them in schools. And 2.) to teach a young generation the importance of reducing waste in the fashion industry. While talking with Danielle, it’s obvious that these students need these spaces. SCRAP provides a space to learn and process climate information. Students not only hear about our shifting climate, but they also experience it in the Bay Area of San Francisco. They see and breathe in wildfire smoke and they also experienced a new phenomenon: the atmospheric river bringing extreme amounts of rainfall. This is a very heavy topic and SCRAP gives them tools to cope with climate anxiety. They also get to connect with other teens and make an impact.
Erica Valdez 31:24
Danielle phrased it perfectly. Quote, “This program gives students a little bit of hope and agency around participating in the fight that lies ahead” end quote. Sustainable Fashion Design for Teens is just one of many programs that SCRAP offers. And it’s not the only one doing this work. In fact, when looking for sustainable fashion groups to feature in this episode, I found so many around the world, I had trouble narrowing it down to just one. These groups show how important individual and collective action is, and how creative it can look.
Erica Valdez 31:52
Want to get involved? SCRAP has worked with other reuse nonprofits to help them implement similar programs. And they’re looking to collaborate in other areas and schools to create more learning opportunities like these. You can find more information about SCRAP programs at scrap-sf.org. Again, that’s scrap-sf.org. I put that link in the show notes for you. And there, you can also find photos of the students SCRAP projects. Just visit cclusa.org/radio.
Peterson Toscano 32:19
Thank you Erica. If you have good news you want to share send us an email radio @ citizensclimate.org.
Erica Valdez 32:26
You can also text us at 619-512-9646.
Peterson Toscano 32:31
Last month, we asked listeners to tell us about the role they play in the climate movement. Are you a helper, advocate, organizer, or a rebel? Tanya wrote to say she is a helper, but reading her message, you can see she’s also an advocate. Tanya wrote, quote, “I made a decision to live a more sustainable life and do things like buy bamboo toilet paper, and try really hard to stay away from plastic. I also sometimes make calls for the environmental voter project. And I belong to my local chapter of CCL. I make calls to my congressmen and senators when asked, and before all of this, I actually met with my congressman on my own and gave him a presentation and specific asks.” Thank you, Tanya, so much for that message.
Erica Valdez 33:16
We want to give listeners a chance to respond just like Tanya did. So, if you could advocate for the climate through art, what kind of piece would you create? This can be music, dance, film, writing or other mediums you’ve used in your climate work. We want to hear about it! So feel free to send us an email radio @ citizensclimate.org. You can also text or leave a voicemail at 619-512-9646 and tell us your story of using art and your climate work.
Peterson Toscano 33:43
Thank you for joining us for episode 94 of Citizens’ Climate Radio. Our show is written and produced by Erica Valdez.
Erica Valdez 33:52
And Peterson Toscano along with Horace Mo. Other technical support from Ricky Bradley and Brett cease social media assistance from Flannery Winchester. Moral support from Madeline Para.
Peterson Toscano 34:02
Over the last month, many of you have shared our post on your social media. Here are some of the people and organizations that have shown us some love: CCL groups in Boulder, Colorado in Arkansas, Austin, Texas and San Diego. Many thanks also to Robin Elsebeth Jenkins, Robert D. Evans, Michael Cooper, and Bill Nash. Thank you so much.
Erica Valdez 34:26
You can now follow us on Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, Facebook and TikTok. Call our listener voicemail hotline- not hotline.
Peterson Toscano 34:34
I like hotline.
Erica Valdez 34:35
Yeah? Caller listener voicemail line at 619-512-9646. That number again is 619-512-9646. Visit cclusa.org/radio to see our show notes and find links toward guests.
Peterson Toscano 34:51
Citizens’ Climate Radio is a project of Citizens’ Climate Education.
The post Episode 94: Antarctic Awakenings appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
https://citizensclimatelobby.org/blog/podcast/episode-94-antarctic-awakenings/
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 15 August 2025: Raging wildfires; Xi’s priorities; Factchecking the Trump climate report
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Blazing heat hits Europe
FANNING THE FLAMES: Wildfires “fanned by a heatwave and strong winds” caused havoc across southern Europe, Reuters reported. It added: “Fire has affected nearly 440,000 hectares (1,700 square miles) in the eurozone so far in 2025, double the average for the same period of the year since 2006.” Extreme heat is “breaking temperature records across Europe”, the Guardian said, with several countries reporting readings of around 40C.
HUMAN TOLL: At least three people have died in the wildfires erupting across Spain, Turkey and Albania, France24 said, adding that the fires have “displaced thousands in Greece and Albania”. Le Monde reported that a child in Italy “died of heatstroke”, while thousands were evacuated from Spain and firefighters “battled three large wildfires” in Portugal.
UK WILDFIRE RISK: The UK saw temperatures as high as 33.4C this week as England “entered its fourth heatwave”, BBC News said. The high heat is causing “nationally significant” water shortfalls, it added, “hitting farms, damaging wildlife and increasing wildfires”. The Daily Mirror noted that these conditions “could last until mid-autumn”. Scientists warn the UK faces possible “firewaves” due to climate change, BBC News also reported.
Around the world
- GRID PRESSURES: Iraq suffered a “near nationwide blackout” as elevated power demand – due to extreme temperatures of around 50C – triggered a transmission line failure, Bloomberg reported.
- ‘DIRE’ DOWN UNDER: The Australian government is keeping a climate risk assessment that contains “dire” implications for the continent “under wraps”, the Australian Financial Review said.
- EXTREME RAINFALL: Mexico City is “seeing one of its heaviest rainy seasons in years”, the Washington Post said. Downpours in the Japanese island of Kyushu “caused flooding and mudslides”, according to Politico. In Kashmir, flash floods killed 56 and left “scores missing”, the Associated Press said.
- SOUTH-SOUTH COOPERATION: China and Brazil agreed to “ensure the success” of COP30 in a recent phone call, Chinese state news agency Xinhua reported.
- PLASTIC ‘DEADLOCK’: Talks on a plastic pollution treaty have failed again at a summit in Geneva, according to the Guardian, with countries “deadlocked” on whether it should include “curbs on production and toxic chemicals”.
15
The number of times by which the most ethnically-diverse areas in England are more likely to experience extreme heat than its “least diverse” areas, according to new analysis by Carbon Brief.
Latest climate research
- As many as 13 minerals critical for low-carbon energy may face shortages under 2C pathways | Nature Climate Change
- A “scoping review” examined the impact of climate change on poor sexual and reproductive health and rights in sub-Saharan Africa | PLOS One
- A UK university cut the carbon footprint of its weekly canteen menu by 31% “without students noticing” | Nature Food
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
Factchecking Trump’s climate report
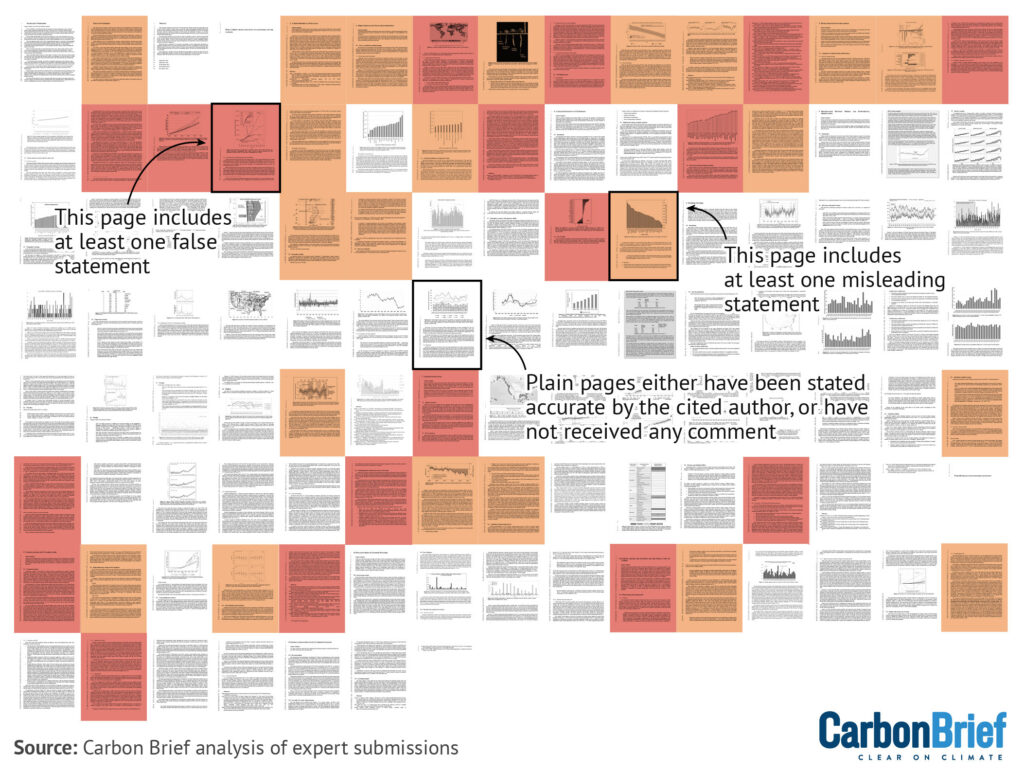
A report commissioned by the US government to justify rolling back climate regulations contains “at least 100 false or misleading statements”, according to a Carbon Brief factcheck involving dozens of leading climate scientists. The report, compiled in two months by five hand-picked researchers, inaccurately claims that “CO2-induced warming might be less damaging economically than commonly believed” and misleadingly states that “excessively aggressive [emissions] mitigation policies could prove more detrimental than beneficial”80
Spotlight
Does Xi Jinping care about climate change?
This week, Carbon Brief unpacks new research on Chinese president Xi Jinping’s policy priorities.
On this day in 2005, Xi Jinping, a local official in eastern China, made an unplanned speech when touring a small village – a rare occurrence in China’s highly-choreographed political culture.
In it, he observed that “lucid waters and lush mountains are mountains of silver and gold” – that is, the environment cannot be sacrificed for the sake of growth.
(The full text of the speech is not available, although Xi discussed the concept in a brief newspaper column – see below – a few days later.)
In a time where most government officials were laser-focused on delivering economic growth, this message was highly unusual.
Forward-thinking on environment
As a local official in the early 2000s, Xi endorsed the concept of “green GDP”, which integrates the value of natural resources and the environment into GDP calculations.
He also penned a regular newspaper column, 22 of which discussed environmental protection – although “climate change” was never mentioned.
This focus carried over to China’s national agenda when Xi became president.
New research from the Asia Society Policy Institute tracked policies in which Xi is reported by state media to have “personally” taken action.
It found that environmental protection is one of six topics in which he is often said to have directly steered policymaking.
Such policies include guidelines to build a “Beautiful China”, the creation of an environmental protection inspection team and the “three-north shelterbelt” afforestation programme.
“It’s important to know what Xi’s priorities are because the top leader wields outsized influence in the Chinese political system,” Neil Thomas, Asia Society Policy Institute fellow and report co-author, told Carbon Brief.
Local policymakers are “more likely” to invest resources in addressing policies they know have Xi’s attention, to increase their chances for promotion, he added.
What about climate and energy?
However, the research noted, climate and energy policies have not been publicised as bearing Xi’s personal touch.
“I think Xi prioritises environmental protection more than climate change because reducing pollution is an issue of social stability,” Thomas said, noting that “smoggy skies and polluted rivers” were more visible and more likely to trigger civil society pushback than gradual temperature increases.
The paper also said topics might not be linked to Xi personally when they are “too technical” or “politically sensitive”.
For example, Xi’s landmark decision for China to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 is widely reported as having only been made after climate modelling – facilitated by former climate envoy Xie Zhenhua – showed that this goal was achievable.
Prior to this, Xi had never spoken publicly about carbon neutrality.
Prof Alex Wang, a University of California, Los Angeles professor of law not involved in the research, noted that emphasising Xi’s personal attention may signal “top” political priorities, but not necessarily Xi’s “personal interests”.
By not emphasising climate, he said, Xi may be trying to avoid “pushing the system to overprioritise climate to the exclusion of the other priorities”.
There are other ways to know where climate ranks on the policy agenda, Thomas noted:
“Climate watchers should look at what Xi says, what Xi does and what policies Xi authorises in the name of the ‘central committee’. Is Xi talking more about climate? Is Xi establishing institutions and convening meetings that focus on climate? Is climate becoming a more prominent theme in top-level documents?”
Watch, read, listen
TRUMP EFFECT: The Columbia Energy Exchange podcast examined how pressure from US tariffs could affect India’s clean energy transition.
NAMIBIAN ‘DESTRUCTION’: The National Observer investigated the failure to address “human rights abuses and environmental destruction” claims against a Canadian oil company in Namibia.
‘RED AI’: The Network for the Digital Economy and the Environment studied the state of current research on “Red AI”, or the “negative environmental implications of AI”.
Coming up
- 17 August: Bolivian general elections
- 18-29 August: Preparatory talks on the entry into force of the “High Seas Treaty”, New York
- 18-22 August: Y20 Summit, Johannesburg
- 21 August: Advancing the “Africa clean air programme” through Africa-Asia collaboration, Yokohama
Pick of the jobs
- Lancaster Environment Centre, senior research associate: JUST Centre | Salary: £39,355-£45,413. Location: Lancaster, UK
- Environmental Justice Foundation, communications and media officer, Francophone Africa | Salary: XOF600,000-XOF800,000. Location: Dakar, Senegal
- Politico, energy & climate editor | Salary: Unknown. Location: Brussels, Belgium
- EnviroCatalysts, meteorologist | Salary: Unknown. Location: New Delhi, India
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 15 August 2025: Raging wildfires; Xi’s priorities; Factchecking the Trump climate report appeared first on Carbon Brief.
DeBriefed 15 August 2025: Raging wildfires; Xi’s priorities; Factchecking the Trump climate report
Greenhouse Gases
Cropped 13 August 2025: Fossil-fuelled bird decline; ‘Deadly’ wildfires; Empty nature fund
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
‘Deadly’ wildfires
WINE BRAKE: France experienced its “largest wildfire in decades”, which scorched more than 16,000 hectares in the country’s southern Aude region, the Associated Press said. “Gusting winds” fanned the flames, Reuters reported, but local winemakers and mayors also “blam[ed] the loss of vineyards”, which can act as a “natural, moisture-filled brake against wildfires”, for the fire’s rapid spread. It added that thousands of hectares of vineyards were removed in Aude over the past year. Meanwhile, thousands of people were evacuated from “deadly” wildfires in Spain, the Guardian said, with blazes ongoing in other parts of Europe.
MAJOR FIRES: Canada is experiencing its second-worst wildfire season on record, CBC News reported. More than 7.3m hectares burned in 2025, “more than double the 10-year average for this time of year”, the broadcaster said. The past three fire seasons were “among the 10 worst on record”, CBC News added. Dr Mike Flannigan from Thompson Rivers University told the Guardian: “This is our new reality…The warmer it gets, the more fires we see.” Elsewhere, the UK is experiencing a record year for wildfires, with more than 40,000 hectares of land burned so far in 2025, according to Carbon Brief.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “Cropped” email newsletter. A fortnightly digest of food, land and nature news and views. Sent to your inbox every other Wednesday.
WESTERN US: The US state of Colorado has recorded one of its largest wildfires in history in recent days, the Guardian said. The fire “charred” more than 43,300 hectares of land and led to the temporary evacuation of 179 inmates from a prison, the newspaper said. In California, a fire broke out “during a heatwave” and burned more than 2,000 hectares before it was contained, the Los Angeles Times reported. BBC News noted: “Wildfires have become more frequent in California, with experts citing climate change as a key factor. Hotter, drier conditions have made fire seasons longer and more destructive.”
FIRE FUNDING: “Worsening fires” in the Brazilian Amazon threaten new rainforest funding proposals due to be announced at the COP30 climate summit later this year, experts told Climate Home News. The new initiatives include the Tropical Forests Forever Facility, which the outlet said “aims to generate a flow of international investment to pay countries annually in proportion to their preserved tropical forests”. The outlet added: “If fires in the Amazon continue to worsen in the years to come, eligibility for funding could be jeopardised, Brazil’s environment ministry acknowledged.”
Farming impacts
OUT OF ORBIT: US president Donald Trump moved to “shut down” two space missions which monitor carbon dioxide and plant health, the Associated Press reported. Ending these NASA missions would “potentially shu[t] off an important source of data for scientists, policymakers and farmers”, the outlet said. Dr David Crisp, a retired NASA scientist, said the missions can detect the “glow” of plant growth, which the outlet noted “helps monitor drought and predict food shortages that can lead to civil unrest and famine”.
FARM EXTREMES: Elsewhere, Reuters said that some farmers are considering “abandoning” a “drought-hit” agricultural area in Hungary as “climate change cuts crop yields and reduces groundwater levels”. Scientists warned that rising temperatures and low rainfall threaten the region’s “agricultural viability”, the newswire added. Meanwhile, the Premium Times in Nigeria said that some farmers are “harvest[ing] crops prematurely” due to flooding fears. A community in the south-eastern state of Imo “has endured recurrent floods, which wash away crops and incomes alike” over the past decade, the newspaper noted.
SECURITY RISKS: Food supply chains in the UK face “escalating threats from climate impacts and the migration they are triggering”, according to a report covered by Business Green. The outlet said that £3bn worth of UK food imports originated from the 20 countries “with the highest numbers of climate-driven displacements” in 2024, based on analysis from the Energy and Climate Intelligence Unit. The analysis highlighted that “climate impacts on food imports pose a threat to UK food security”. Elsewhere, an opinion piece in Dialogue Earth explored how the “role of gender equity in food security remains critically unaddressed”.
Spotlight
Fossil-fuelled bird decline
This week, Carbon Brief covers a new study tracing the impact of fossil-fuelled climate change on tropical birds.
Over the past few years, biologists have recorded sharp declines in bird numbers across tropical rainforests – even in areas untouched by humans – with the cause remaining a mystery.
A new study published this week in Nature Ecology and Evolution could help to shed light on this alarming phenomenon.
The research combined ecological and climate attribution techniques for the first time to trace the fingerprint of fossil-fuelled climate change on declining bird populations.
It found that an increase in heat extremes driven by climate change has caused tropical bird populations to decline by 25-38% in the period 1950-2020, when compared to a world without warming.
In their paper, the authors noted that birds in the tropics could be living close to their “thermal limits”.
Study lead author Dr Maximilian Kotz, a climate scientist at the Barcelona Supercomputing Center in Spain, explained to Carbon Brief:
“High temperature extremes can induce direct mortality in bird populations due to hyperthermia and dehydration. Even when they don’t [kill birds immediately], there’s evidence that this can then affect body condition which, in turn, affects breeding behaviour and success.”
Conservation implications
The findings have “potential ramifications” for commonly proposed conservation strategies, such as increasing the amount of land in the tropics that is protected for nature, the authors said. In their paper, they continued:
“While we do not disagree that these strategies are necessary for abating tropical habitat loss…our research shows there is now an additional urgent need to investigate strategies that can allow for the persistence of tropical species that are vulnerable to heat extremes.”
In some parts of the world, scientists and conservationists are looking into how to protect wildlife from more intense and frequent climate extremes, Kotz said.
He referenced one project in Australia which is working to protect threatened wildlife following periods of extreme heat, drought and bushfires.
Prof Alex Pigot, a biodiversity scientist at University College London (UCL), who was not involved in the research, said the findings reinforced the need to systematically monitor the impact of extreme weather on wildlife. He told Carbon Brief:
“We urgently need to develop early warning systems to be able to anticipate in advance where and when extreme heatwaves and droughts are likely to impact populations – and also rapidly scale up our monitoring of species and ecosystems so that we can reliably detect these effects.”
There is further coverage of this research on Carbon Brief’s website.
News and views
EMPTY CALI FUND: A major voluntary fund for biodiversity remains empty more than five months after its launch, Carbon Brief revealed. The Cali Fund, agreed at the COP16 biodiversity negotiations last year, was set up for companies who rely on nature’s resources to share some of their earnings with the countries where many of these resources originate. Big pharmaceutical companies did not take up on opportunities to commit to contributing to the fund or be involved in its launch in February 2025, emails released to Carbon Brief showed. Just one US biotechnology firm has pledged to contribute to the fund in the future.
LOSING HOPE: Western Australia’s Ningaloo reef – long considered a “hope spot” among the country’s coral reefs for evading major bleaching events – is facing its “worst-ever coral bleaching”, Australia’s ABC News reported. The ocean around Ningaloo has been “abnormally” warm since December, resulting in “unprecedented” bleaching and mortality, a research scientist told the outlet. According to marine ecologist Dr Damian Thomson, “up to 50% of the examined coral was dead in May”, the Sydney Morning Herald said. Thomson told the newspaper: “You realise your children are probably never going to see Ningaloo the way you saw it.”
‘DEVASTATION BILL’: Brazil’s president, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, signed a “contentious” environmental bill into law, but “partially vetoed” some of the widely criticised elements, the Financial Times reported. Critics, who dubbed it the “devastation bill”, said it “risked fuelling deforestation and would harm Brazil’s ecological credentials” just months before hosting the COP30 climate summit. The newspaper said: “The leftist leader struck down or altered 63 of 400 provisions in the legislation, which was designed to speed up and modernise environmental licensing for new business and infrastructure developments.” The vetoes need to be approved by congress, “where Lula lacks a majority”, the newspaper noted.
RAINFOREST DRILLING: The EU has advised the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) against allowing oil drilling in a vast stretch of rainforest and peatland that was jointly designated a “green corridor” earlier this year, Climate Home News reported. In May, the DRC announced that it planned to open the conservation area for drilling, the publication said. A spokesperson for the European Commission told Climate Home News that the bloc “fully acknowledges and respects the DRC’s sovereign right to utilise its diverse resources for economic development”, but that it “highlights the fact that green alternatives have facilitated the protection of certain areas”.
NEW PLAN FOR WETLANDS: During the 15th meeting of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, held in Zimbabwe from 23 to 31 July, countries agreed on the adoption of a new 10-year strategic plan for conserving and sustainably using the world’s wetlands. Down to Earth reported that 13 resolutions were adopted, including “enhancing monitoring and reporting, capacity building and mobilisation of resources”. During the talks, Zimbabwe’s environment minister announced plans to restore 250,000 hectares of degraded wetlands by 2030 and Saudi Arabia entered the Convention on Wetlands. Panamá will host the next COP on wetlands in July 2028.
MEAT MADNESS: DeSmog covered the details of a 2021 public relations document that revealed how the meat industry is trying to “make beef seem climate-friendly”. The industry “may have enlisted environmental groups to persuade people to ‘feel better’ about eating beef”, the outlet said, based on this document. The strategy was created by a communications agency, MHP Group, and addressed to the Global Roundtable for Sustainable Beef. One of the key messages of the plan was to communicate the “growing momentum in the beef industry to protect and nurture the Earth’s natural resources”. MHP Group did not respond to a request for comment, according to DeSmog.
Watch, read, listen
MAKING WAVES: A livestream of deep-sea “crustaceans, sponges and sea cucumbers” has “captivated” people in Argentina, the New York Times outlined.
BAFFLING BIRDS: The Times explored the backstory to the tens of thousands of “exotic-looking” parakeets found in parks across Britain.
PLANT-BASED POWER: In the Conversation, Prof Paul Behrens outlined how switching to a plant-based diet could help the UK meet its climate and health targets.
MARINE DISCRIMINATION: Nature spoke to a US-based graduate student who co-founded Minorities in Shark Science about her experiences of racism and sexism in the research field.
New science
- Applying biochar – a type of charcoal – to soils each year over a long period of time can have “sustained benefits for crop yield and greenhouse gas mitigation”, according to a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences study.
- New research, published in PLOS Climate, found that nearly one-third of highly migratory fish species in the US waters of the Atlantic Ocean have “high” or “very high” vulnerability to climate change, but the majority of species have “some level of resilience and adaptability”.
- A study in Communications Earth & Environment found a “notable greening trend” in China’s wetlands over 2000-23, with an increasing amount of carbon being stored in the plants growing there.
In the diary
- 18-29 August: Second meeting of the preparatory commission for the Agreement on Marine Biological Diversity of Areas beyond National Jurisdiction | New York
- 24-28 August: World Water Week | Online and Stockholm, Sweden
- 26-29 August: Sixth forum of ministers and environment authorities of Asia Pacific | Nadi, Fiji
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz. Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org
The post Cropped 13 August 2025: Fossil-fuelled bird decline; ‘Deadly’ wildfires; Empty nature fund appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Cropped 13 August 2025: Fossil-fuelled bird decline; ‘Deadly’ wildfires; Empty nature fund
Greenhouse Gases
Holding the line on climate: EPA
CCL submits a formal comment on EPA’s proposed endangerment finding rollback
By Dana Nuccitelli, CCL Research Manager
On July 29, the EPA proposed to rescind its 2009 endangerment finding that forms the basis of all federal climate pollution regulations.
Without the endangerment finding, the EPA may not be allowed or able to regulate greenhouse gas pollution from sources like power plants or vehicle tailpipes, as they have done for years. News coverage has framed this as a “radical transformation” and a “bid to scrap almost all pollution regulations,” so it has appropriately alarmed many folks in the climate and environment space.
At CCL, we focus our efforts on working with Congress to implement durable climate policies, and so we don’t normally take actions on issues like this that relate to federal agencies or the courts. Other organizations focus their efforts on those branches of the government and are better equipped to spearhead this type of moment, and we appreciate those allies.
But in this case, we did see an opportunity for CCL’s voice — and our focus on Congress — to play a role here. We decided to submit a formal comment on this EPA action for two reasons.
First, this decision could have an immense impact by eliminating every federal regulation of climate pollutants in a worst case scenario. Second, this move relates to our work because the EPA is misinterpreting the text and intent of laws passed by Congress. Our representatives have done their jobs by passing legislation over the past many decades that supports and further codifies the EPA’s mandate to regulate climate pollution. That includes the Clean Air Act, and more recently, the Inflation Reduction Act. We at CCL wanted to support our members of Congress by making these points in a formal comment.
There has been a tremendous public response to this action. In just over one week, the EPA already received over 44,000 public comments on its decision, and the public comment period will remain open for another five weeks, until September 15.
To understand more about the details and potential outcomes of the EPA’s actions, read my article on the subject at Yale Climate Connections, our discussion on CCL Community, and CCL’s formal comment, which represents our entire organization. As our comment concludes,
“In its justifications for rescinding the 2009 endangerment finding, the Reconsideration has misinterpreted the text of the Clean Air Act, Congress’ decadeslong support for the EPA’s mandate to regulate greenhouse gas emissions from motor vehicles and other major sources, and the vast body of peer-reviewed climate science research that documents the increasingly dangerous threats that those emissions pose to Americans’ health and welfare. Because the bases of these justifications are fundamentally flawed, CCL urges the EPA to withdraw its ill-conceived Reconsideration of the 2009 endangerment finding. The EPA has both the authority and the responsibility to act. Americans cannot afford a retreat from science, law, and common sense in the face of a rapidly accelerating climate crisis.”
After the EPA responds to the public comment record and finalizes its decision, this issue will ultimately be decided by the Supreme Court several years from now.
In the meantime, CCL will continue to focus our efforts on areas where we can make the biggest difference in preserving a livable climate. Right now, that involves contacting our members of Congress to urge them to fully fund key climate and energy programs and protect critical work at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and Department of Energy. We’ve set an ambitious goal of sending 10,000 messages to our members of Congress, so let’s all do what CCL does best and make our voices heard on this critical issue.
This action by the EPA also reminds us that federal regulations are fragile. They tend to change with each new administration coming into the White House. Legislation passed by Congress – especially when done on a bipartisan basis – is much more durable. That’s why CCL’s work, as one of very few organizations engaging in nonpartisan advocacy for long-lasting climate legislation, is so critical.
That’s especially true right now when we’re seeing the Trump administration slam shut every executive branch door to addressing climate change. We need Congress to step up now more than ever to implement durable solutions like funding key climate and energy programs, negotiating a new bipartisan comprehensive permitting reform bill, implementing healthy forest solutions like the Fix Our Forests Act, and advancing conversations about policies to put a price on carbon pollution. Those are the kinds of effective, durable, bipartisan climate solutions that CCL is uniquely poised to help become law and make a real difference in preserving a livable climate.
For other examples of how CCL is using our grassroots power to help ensure that Congress stays effective on climate in this political landscape, see our full “Holding the Line on Climate” blog series.
The post Holding the line on climate: EPA appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Greenhouse Gases1 year ago
Greenhouse Gases1 year ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Climate Change1 year ago
Climate Change1 year ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint1 year ago
Carbon Footprint1 year agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Why airlines are perfect targets for anti-greenwashing legal action
-
Renewable Energy2 months ago
US Grid Strain, Possible Allete Sale
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Some firms unaware of England’s new single-use plastic ban