Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
US budget bill ‘would kill IRA’
WAYS AND MEANS: The future of Joe Biden’s signature climate policy, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), is in doubt after Republicans on two key Congressional committees passed budget proposals that “would effectively kill” it, reported Heatmap News. The proposals would end clean-energy tax credits and rebates for electric vehicle (EV) purchases, “claw back” climate grants and “slash” related spending, said Reuters.
DEFENCE DOUBTS: While a “small subset” of House Republicans have been trying to defend the IRA, it is unclear if they would block passage of the wider budget bill to get their way, according to E&E News. In the Senate, Politico said “some” Republicans are “pushing back” on the current proposals. A New York Times feature said Republican districts “have the most to lose” if all of the IRA tax credits are repealed. Semafor reported Republicans were “wrestling with possible failure” of the bill, in the face of opposition from Democrats and their own ranks. (Law firm Grant Thornton said policymakers were hoping to pass the bill by 4 July.)
SOCIAL COST: Meanwhile, a new White House memo directed US government agencies to disregard economic damages from climate change, reported E&E News. Under a headline asking, “What’s the cost of pollution? Trump says zero”, the New York Times explained that the “social cost of carbon” had been used for more than two decades to help weigh the costs and benefits of federal policies and regulations. It said the move could face legal challenges.
Around the world
- DOWNPOUR DEATHS: More than 100 people were killed by floods in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Agence-France Presse reported. Extreme rainfall also killed at least seven people in Somalia, the Associated Press said.
- PARIS PERIL: A UK opposition minister falsely attacked climate science and said his party could exit the Paris Agreement if elected, the Guardian said. The Guardian also reported on how Australia’s new opposition leader “could abandon net-zero”.
- GERMAN GAS: New economy minister Katharina Reiche wants more gas-fired power plants, according to Die Zeit. The country’s climate council warned the new government’s plans could breach climate goals, said Clean Energy Wire.
- DENGUE DANGER: Colombia’s El Espectador reported on rising climate-driven risks from dengue fever in Brazil, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Mexico and Panama.
- COP30 CREW: The Brazilian COP30 presidency has appointed 30 envoys, including “key liaisons” for strategic regions such as China’s Xie Zhenhua, Jonathan Pershing from the US and former UNFCCC chief Patricia Espinosa, Climate Home News said.
60%
The yearly rise in EV sales in emerging markets in Asia and Latin America in 2024, according to new data from the International Energy Agency.
Latest climate research
- Even passing 1.5C of global warming temporarily would trigger a “significant” risk of Amazon forest “dieback”, said research covered by Carbon Brief.
- Rapidly rising emissions from China’s agricultural machinery could “hinder” the country’s push towards net-zero, according to a study covered by Carbon Brief.
- Findings in Environmental Research Letters found that the benefits of CO2 “fertilisation” on forests are likely to be constrained by warming.
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
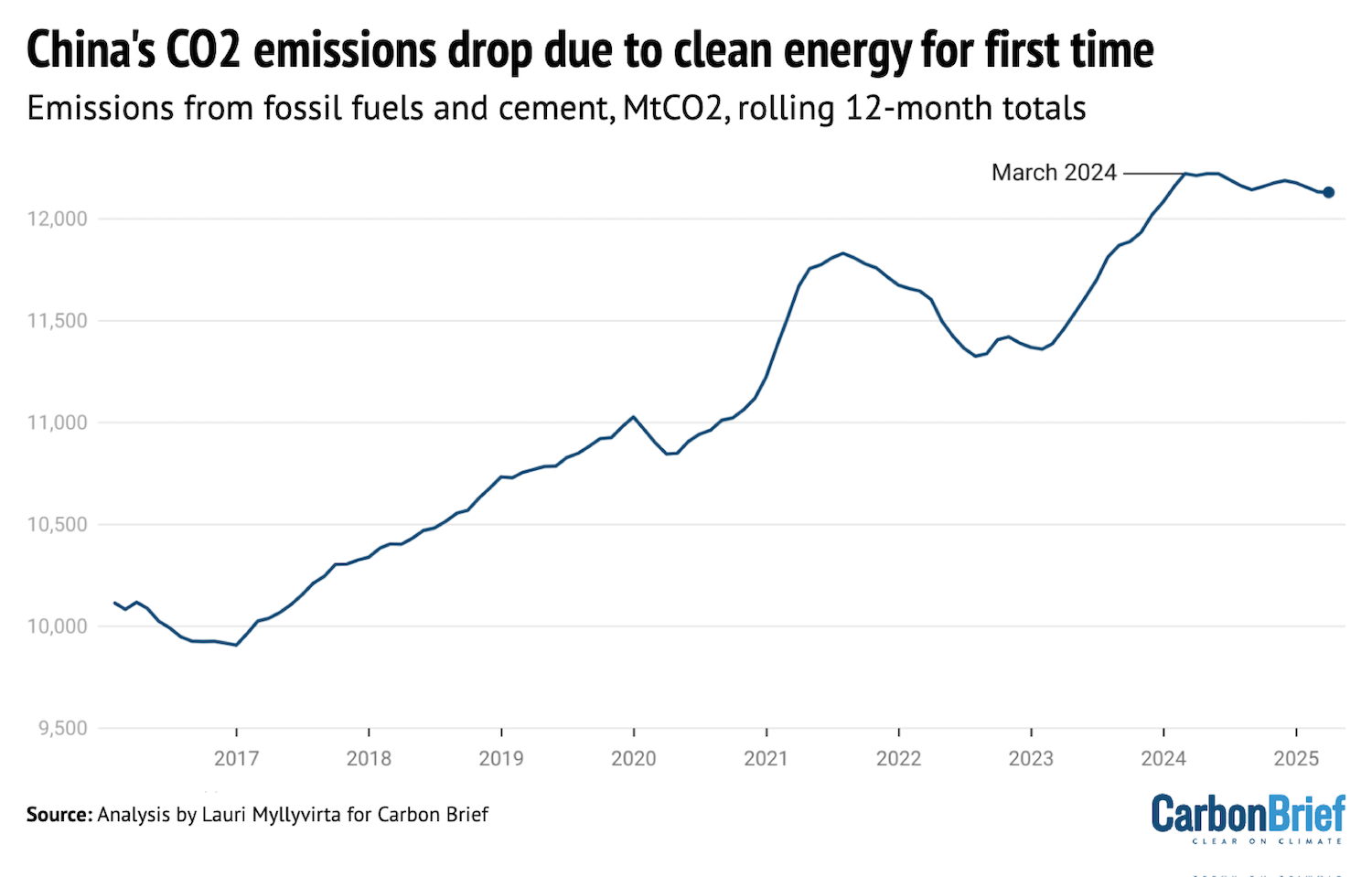
For the first time on record, China’s CO2 emissions have fallen as a result of clean energy expansion rather than weak growth in electricity demand, according to new analysis for Carbon Brief. The analysis, which has been covered by outlets including AFP, Semafor and the New York Times, found that China’s emissions from fossil fuels and cement fell 1.6% in the first quarter of 2025 and are now 1% below the peak reached in March 2024. The months ahead will be critical for what comes next, as Beijing is working to finalise its next international climate pledge for 2035 and its five-year plan for 2026-2030.
Spotlight
How Poland started speeding away from coal power
This week, Carbon Brief reports on coal falling to barely half of Poland’s power supplies.
The first round of Poland’s presidential election is on Sunday and Rafał Trzaskowski, from prime minister Donald Tusk’s centre-right party Civic Platform, is favoured to win.
Long seen as one of the world’s most coal-reliant countries, Poland’s electricity system is in the midst of dramatic and increasingly rapid change.
When Poland joined the EU in 2004, coal-fired power stations supplied 93% of the country’s electricity. Coal accounted for more than three-quarters of the total as recently as 2018, the year the country hosted COP24 in Katowice.
Since then, a gradual shuffle away from coal has turned to a sprint.
In 2024, coal generated little more than half of Poland’s electricity, according to data from thinktank Ember – and a coal power phaseout by 2035 is now seen as a realistic prospect.
While the topic has not played a big role in the election campaign, there is now broad public acceptance that “coal is over in Poland”, said Joanna Maćkowiak-Pandera, president of Polish thinktank Forum Energii. She told Carbon Brief:
“The extreme rightwing tries to claim that coal is the future and there is coal for [another] 400 years…[But] even the coal-mining sector does not believe it.”
As of 2024, coal contributed just 53.5% of electricity generation in Poland, with wind and solar making up 23.5%, gas power 12.1% and other renewables another 6.3%.
Coal ‘death spiral’
The “death spiral” for coal power is due to the high cost of coal mining in Poland, the old age of coal power plants, pressure from climate policies such as the EU emissions trading system (EUETS) and a loss of market share to renewables, said Maćkowiak-Pandera:
“You can be pro-coal, but you will not change the economics, physics, geology and the reality of the financial market.”
Until 2023, the right-wing Law and Justice party (PiS) had held the reins of government, having won the 2015 election after promising to protect the coal industry.
Following power cuts that summer, however, PiS increasingly accepted that renewbles – particularly solar power – could support energy security, explained Maćkowiak-Pandera.
(Renewables enjoy broad public support and are associated with energy security, she said.)
With backing from government policy, Poland’s solar capacity leapt from just 200 megawatts in 2015 to more than 20 gigawatts in 2024 – a 100-fold increase.
Still, PiS strongly resisted calls to phase out coal. In 2020, it struck a deal with unions to subsidise the Polish coal-mining industry until 2049. The subsidies remain in place.
After winning parliamentary elections in 2023, Tusk promised a “much faster energy transition” based on renewables and nuclear power, said Maćkowiak-Pandera.
While utility firms would “really love” to phase out coal plants within as little as three to five years, there is a growing consensus around 2035 as a more achievable end date, she said:
“It’s really not controversial any more…I speak with politicians, with utilities, with [electricity] transmission system operators, even with miners. Everybody is aware of the situation.”
Instead, there is a practical conversation around how best to replace coal at the lowest cost, explained Maćkowiak-Pandera.
This will mean more renewables, but also the flexible capacity needed to manage the grid – including some new gas-fired power plants – as well as energy storage and market reforms, she said.
Poland’s rapid transition may not have made many headlines, but other major coal-burning countries are starting to pay attention.
Maćkowiak-Pandera has welcomed delegations from China, South Africa, Mexico and Brazil, eager to learn about Poland’s experience. She added:
“For Chinese partners, it’s interesting because they like [our] pragmatic approach…they like that Poland [is] sometimes not mentioning climate, [but] is doing it anyhow.”
Watch, read, listen
CHINESE CROWING: A widely shared blog post on nationalist media outlet Guancha said China was taking climate action to “win the future energy revolution” and, among other things, to “save at least $600bn” on imported oil by shifting to EVs.
‘RUNNING BLIND’: For the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists, climate scientist Peter Gleick said the Trump administration’s “purges” of climate research were “threats to national security”.
‘REALISM’ REJECTED: The Wicked Problems podcast discussed the “defeatism” behind a recent initiative calling for “climate realism”, as well as the “abundance agenda”.
Coming up
- 18 May: Poland presidential election
- 19 May: EU-UK summit, London
- 19-23 May: First UN climate week 2025, Panama City, Panama
- 19-27 May: World Health Assembly 2025, Geneva, Switzerland
Pick of the jobs
- European Commission, programme manager (climate change and sustainable energy) | Salary: Unknown. Location: Brussels, Belgium
- Dialogue Earth, southeast Asia editor | Salary: £43,370. Location: London
- Royal Botanic Gardens Kew, postdoctoral research associate in genomics and climate change | Salary: £43,751. Location: London
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 16 May 2025: Has China’s CO2 peaked?; US bill ‘would kill IRA’; Poland’s coal collapse appeared first on Carbon Brief.
DeBriefed 16 May 2025: Has China’s CO2 peaked?; US bill ‘would kill IRA’; Poland’s coal collapse
Climate Change
New summit in Colombia seeks to revive stalled UN talks on fossil fuel transition
A landmark conference hosted by Colombia and the Netherlands will aim to lay the foundations for renewed talks on transitioning away from fossil fuels at COP31, though organisers say it remains unclear what concrete outcomes it will deliver.
The First Conference on the Transition Away from Fossil Fuels will take place in April in the city of Santa Marta, on Colombia’s Caribbean coast, where first-moving countries, states and cities will seek to restart last year’s stalled push for a global roadmap away from coal, oil and gas.
Bastiaan Hassing, head of international climate policy for the Dutch government, told an online briefing last week that the “most obvious” impact of the conference would be for its hosts to report back to the UN climate summit on what was agreed in Santa Marta.
“Ideally, but this is also more complicated, we discuss with each other (at COP) what next steps we could take in the implementation, for instance, of paragraph 28 of the COP decision in Dubai, which talks about the global transition away from fossil fuels,” Hassings said.
He noted that there are many options for how the conference can influence UN talks on implementing the global transition away from fossil fuels, but the exact possibilities would depend on the outcome of the talks. “Rest assured that we will be looking into this,” he added.
At last year’s COP30, a bloc of 80 countries, including small island states, as well as some Latin American, European, and African countries, called for the creation of a roadmap to transition away from fossil fuels.
But major oil and gas producers and consumers blocked the initiative in Belém. As a compromise, Brazil’s COP presidency promised to draft proposals for two voluntary roadmaps: one to end deforestation and another to guide the transition away from fossil fuels.
Brazil has launched consultations seeking input for those plans, asking governments and stakeholders about technological and economic barriers, climate justice considerations and examples of best practice. Last week, COP30 president André Corrêa do Lago told Brazilian media that he would hold discussions on his roadmap proposal at the Santa Marta conference.
Colombia’s environment minister Irene Vélez Torres told reporters last week that “this is the moment to be honest about the challenges involved in transitioning away from fossil fuels”.
“It is not easy. It involves commitments from both the Global North and South. It involves interests and tensions at the subnational level,” she added. “Yet none of this diminishes its urgency or the need to reach agreements at the international multilateral level”.
Process to end fossil fuels
Vélez Torres said she hoped the Santa Marta meeting would help establish an ongoing process to advance discussions that often stall in the formal UN negotiations, where decisions are made by consensus and fossil fuel producers resist stronger language.
“This is the first conference, and we want it to be followed by another. We also want to establish a technical secretariat to sustain these debates,” said Vélez Torres, who added that the initiative would be “articulated with [the] COP30 and COP31” presidencies.
Colombia has been one of the few fossil fuel-producing countries that pledged to halt all new coal, oil and gas exploration. The move triggered backlash from industry and political opponents – with former president Iván Duque calling the decision “political and economic suicide”. The South American country depends on fossil fuels for about 10% of fiscal revenues and 4% of GDP, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Organisers of the Santa Marta conference said they expect between 40 and 80 high-level representatives from governments, both at national and subnational levels. Colombian president Gustavo Petro is expected to participate, and invitations have been extended to California governor Gavin Newsom and Dutch prime minister Rob Jetten.
Deep divisions persist as plastics treaty talks restart at informal meeting
No turning back
The conference comes amid renewed volatility in global energy markets. As the US and Israel’s war in Iran disrupts oil and gas supplies and threatens to cause severe global economic damage, analysts say governments should seek to reduce their dependency on fossil fuels through investments in renewables and energy efficiency.
The upcoming Santa Marta conference should build momentum to plan that transition away from fossil fuels and signal that “there is no turning back”, said Peter Newell, professor of international relations at the University of Sussex and one of the main proponents of a fossil fuel non-proliferation treaty.
“Its outcomes, which might include a declaration on key principles and next steps (for the fossil fuel transition), should give renewed vigour to efforts within the UN climate negotiations to drive the agenda forward,” Newell said.
Because major fossil fuel producers have effectively “vetoed” discussions on a fossil fuel phase-out at COPs, he added, willing countries must move forward independently with initiatives like the Santa Marta conference.
Andreas Sieber, head of political strategy at the NGO 350.org, agreed that the push away from fossil fuels is “both necessary and economically inevitable”, adding that a conference on phasing out fossil fuels would have been “unthinkable just five years ago”.
Countries moving forward
COP30 host Brazil has taken the lead in developing its own national roadmap away from fossil fuels, which President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva requested his government to draft late last year. The roadmap is expected to be formally developed this year.
The plan – expected to include a dedicated energy transition fund – was initially due in February but has not yet been made public as ministers continue technical discussions.
In Europe, governments have also stepped up efforts to curb fossil fuel use following the energy shocks triggered by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the conflict in the Middle East.
Leo Roberts, a fossil fuel transition analyst at the climate think tank E3G, said the recent surge in gas prices linked to the Iran conflict reinforces the case for accelerating the transition to boost energy security and protect people from price shocks.
“Hopefully, Santa Marta is able to really demonstrate that not only is there momentum at the international sphere through the COP30 roadmap process, but there’s huge momentum away from fossil fuels in the real world,” he said.
The post New summit in Colombia seeks to revive stalled UN talks on fossil fuel transition appeared first on Climate Home News.
New summit in Colombia seeks to revive stalled UN talks on fossil fuel transition
Climate Change
The US’s critical minerals club threatens an equitable clean energy transition
Nick Dearden is the director of Global Justice Now.
The US push for nations to join a club that would coordinate the trade of critical minerals outside China signals a giant shift in Washington’s vision for how to govern the global economy But it will, unfortunately, also hinder the clean energy transition.
Critical minerals such as lithium, nickel, copper and rare earths are needed to manufacture clean energy technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines and batteries on which the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy depends.
But these minerals also have applications for a wide range of advanced technologies, not least military equipment and digital infrastructure. In recent years, AI deployment and the build out of data centres have become the primary political justification for mineral extraction.
No US official mentioned clean energy technologies as they promoted the new minerals club in Washington last month. Instead, the trading bloc aims to break China’s dominance over mineral supply chains and ensure US access to the resources it needs for digital and military sectors.
Analysis by Global Justice Now found that almost one in five of the 33 minerals that the UK identified as critical in 2024 are not needed to achieve the International Energy Agency’s decarbonisation pathways. A further 15 play only a very small role and only seven require significant production increases for the clean energy transition.
Prioritise minerals for the energy transition
The urgency of addressing climate change means we must prioritise the use of minerals to rapidly and equitably wean the global economy off coal, oil and gas while reducing resource overconsumption in the Global North. The US approach could make this prioritisation a lot harder.
For Washington, this isn’t about addressing climate change, but America’s ever deepening rivalry with China, a renewable energy superpower. In contrast, Donald Trump has called climate change “a hoax” and overseen unprecedented climate deregulation in favour of fossil fuels.
The minerals trading bloc risks diverting mineral resources towards carbon-intensive military and technology build-up in the US, which is directly at odds with the need to use these resources to manufacture clean energy technologies.
What’s more, for the green transition to be just, fair and equitable, resource-rich governments must be able to refine and add value to their resources, creating jobs and economic development in the process. But Trump’s trading bloc is intended to tell “partner” countries what role they should play in the global mineral supply chains to best serve US interests.
Serving US interests rather than clean energy
Countries with the smallest and least developed economies stand to lose out.
More than a dozen countries have signed bilateral deals with the Trump administration. The terms of the deals appear to get better the richer a country is.
At the poorer end is the deal with DRC – an outright piece of imperialism with one-sided obligations that override the country’s mineral sovereignty by giving the US first dibs on a range of strategic mining sites and the energy needed to power these sites.
‘America needs you’: US seeks trade alliance to break China’s critical mineral dominance
In the middle, Malaysia committed to facilitate American involvement in its mineral sector and refrain from banning or imposing quotas on exports of raw minerals to the US. This risks restricting the development of Malaysia’s refining capacities, making value addition harder.
At the top end is the UK, which has signed a deal that includes a commitment to streamline mineral permitting, but appears more focused on facilitating financial services to members of the trading bloc.
Wherever countries sit in the pecking order, the agreements signed with the US limit governments’ strategic sovereignty over their resources and stifle their ability to create a more sustainable economy which meets people’s needs.
Tools for a way forward
There is some hope, however. Trump’s mineral trading bloc would operate with profoundly different rules than the neoliberal trade deals, which we have become used to.
Some of its components – like price floors and state ownership – have not been seen in trade deals for a long time. In the right hands, these tools could help governments plan, coordinate and prioritise a globally just green transition and break away from the ‘market knows best’ logic which has long locked poorer countries into low-value exports of raw materials.
If governments work together, outside the coercive US trade bloc, to adopt some of these tools and policies, they might be able to draw local benefits from their mineral wealth and build a genuinely fair and equitable trade in transition minerals.
The post The US’s critical minerals club threatens an equitable clean energy transition appeared first on Climate Home News.
The US’s critical minerals club threatens an equitable clean energy transition
Climate Change
Greenpeace urges governments to defend international law, as evidence suggests breaches by deep sea mining contractors
SYDNEY/FIJI, Monday 9 March 2026 — As the International Seabed Authority (ISA) opens its 31st Session today, Greenpeace International is calling on member states to take firm and swift action if breaches by subsidiaries and subcontractors of The Metals Company (TMC) are established. Evidence compiled and submitted to the ISA’s Secretary General suggests that violations of exploration contracts may have occurred.
Louisa Casson, Campaigner, Greenpeace International, said: “In July, governments at the ISA sent a clear message: rogue companies trying to sidestep international law will face consequences. Turning that promise into action at this meeting is far more important than rushing through a Mining Code designed to appease corporate interests rather than protect the common good. As delegations from around the world gather today, they must unite and confront the US and TMC’s neo-colonial resource grab and make clear that deep sea mining is a reckless gamble humanity cannot afford.”
The ISA launched an inquiry at its last Council meeting in July 2025, in response to TMC USA seeking unilateral deep sea mining licences from the Trump administration. If the US administration unilaterally allows mining of the international seabed, it would be considered in violation of international law.
Greenpeace International has compiled and submitted evidence to the ISA Secretary-General, Leticia Carvalho, to support the ongoing inquiry into deep sea mining contractors. This evidence shows that those supporting these unprecedented rogue efforts to start deep sea mining unilaterally via President Trump could be in breach of their obligations with the ISA.
The analysis focuses on TMC’s subsidiaries — Nauru Ocean Resources Inc (NORI) and Tonga Offshore Mining Ltd (TOML) — as well as Blue Minerals Jamaica (BMJ), a company linked to Dutch-Swiss offshore engineering firm Allseas, one of TMC’s subcontractors and largest shareholders. The information compiled indicates that their activities may violate core contractual obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). If these breaches are confirmed, NORI and TOML’s exploration contracts, which expire in July 2026 and January 2027 respectively, the ISA should take action, including considering not renewing the contract.
Letícia Carvalho has recently publicly advocated for governments to finalise a streamlined deep sea mining code this year and has expressed her own concerns with the calls from 40 governments for a moratorium. At a time when rogue actors are attempting to bypass or weaken the international system, establishing rules and regulations that will allow mining to start could mean falling into the trap of international bullies. A Mining Code would legitimise and drive investment into a flagging industry, supporting rogue actor companies like TMC and weakening deterrence against unilateral mining outside the ISA framework.
Casson added: “Rushing to finalise a Mining Code serves the interests of multinational corporations, not the principles of multilateralism. With what we know now, rules to mine the deep sea cannot coexist with ocean protection. Governments are legally obliged to only authorise deep sea mining if it can demonstrably benefit humanity – and that is non-negotiable. As the long list of scientific, environmental and social concerns with this industry keeps growing, what is needed is a clear political signal that the world will not be intimidated into rushing a mining code by unilateral threats and will instead keep moving towards a moratorium on deep sea mining.”
—ENDS—
Key findings from the full briefing:
- Following TMC USA’s application to mine the international seabed unilaterally, NORI and TOML have amended their agreements to provide payments to Nauru and Tonga, respectively, if US-authorised commercial mining goes ahead. This sets up their participation in a financial mechanism predicated on mining in contradiction to UNCLOS.
- NORI and TOML have signed intercompany intellectual property and data-sharing agreements with TMC USA, and the data obtained by NORI and TOML under the ISA exploration contracts has been key to facilitating TMC USA’s application under US national regulations.
- Just a few individuals hold key decision-making roles across the TMC and all relevant subsidiaries, making claims of independent management ungrounded. NORI, TOML, and TMC USA, while legally distinct, are managed as an integrated corporate group with a single, coordinated strategy under the direct control and strategic direction of TMC.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits









