Welcome to Carbon Brief’s Cropped.
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
Key developments
G7 eyes food progress
ITALY MEETING: The Group of Seven (G7) nations met in Italy last week to discuss a range of issues spanning war and hunger to climate change and energy. The summit saw the seven major economies launch a new initiative for tackling hunger, Reuters reported. Known as the G7 Apulia Food Systems Initiative (AFSI) – named after the Southern Italian region where the summit took place – the proposal aims to “overcome structural barriers to food security and nutrition”, according to a declaration published after the event. According to the newswire, the initiative will focus on low-income countries and support projects in Africa, “one of the top priorities under Italy’s rotating G7 presidency this year”. It added that details of the scheme will be agreed by G7 development ministers in the coming months.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “Cropped” email newsletter. A fortnightly digest of food, land and nature news and views. Sent to your inbox every other Wednesday.
AFRICA LEFT OUT: Despite having a focus on Africa, agricultural leaders from the continent told Reuters they were not consulted about the new scheme. Ibrahima Coulibaly, president of the West African Network of Peasants and Agricultural Producers, told the newswire: “It is missing family farmers organisations that have not been involved even though small-scale producers will be key to its success.” In African Arguments, Madagascar’s agricultural minister Suzelin Rakotoarisolo Ratohiarijaona was also critical of the lack of involvement of African smallholder farmers in the new scheme, saying: “It’s telling that the Apulia Initiative was developed without their input. If this doesn’t change, it can’t hope to understand or address the daily challenges they face.” He added that the scheme must channel new finance towards grassroots groups and “encourage a shift to more diverse and nature-friendly forms of agriculture”.
‘ZERO’ HARVESTS: The new initiative came as the chief officer of the World Food Programme told BBC News that parts of Africa, as well as the Middle East and Latin America, are now unable to sustain crops due to constant floods and droughts, leaving people completely reliant on humanitarian aid. WFP director Martin Frick told the broadcaster that some of the poorest regions had now reached a tipping point of having “zero” harvests left, as “extreme weather was pushing already degraded land beyond use”. In the east African nation of Burundi, months of heavy rain and flooding has left 10% of all farmland unusable, Frick told BBC News. In the Darfur region of Sudan, cereal crop yields are 78% below the average for the previous five-year average amid drought and civil war, he added.
Food price spikes continue
MULTIPLE CROPS AND CAUSES: Consumers have recently experienced sustained increases in the prices of a range of foods. These price spikes have been attributed to various factors, ranging from climate change and harmful agricultural practices to the international economy and geopolitical tensions. Carbon Brief has just published an article that gathers the views of experts in the agrifood sector on the major causes of this global problem that is already putting pressure on producers, intermediaries and consumers.
CLIMATE-RELATED IMPACTS: Extreme weather events and diseases are hampering harvests and driving up orange prices in Brazil and Florida, Axios reported. The outlet added that in Florida, citrus production has declined 3% on average annually since 2003 and that, according to the International Monetary Fund, the price of oranges globally rose from $2.76 in 2023 to $3.68 in April this year. Prof Andy Challinor, professor of climate impacts at the University of Leeds, told Carbon Brief that “climate change is beginning to outpace us because it is interacting with our complex interrelated economic and food systems”.
CONFLICT REPERCUSSIONS: Dr Rob Vos, director for markets, trade and institutions at the International Food Policy Research Institute, told Carbon Brief that the highest inflation rates have been seen in countries with food systems “disrupted by intensified conflict”, such as Ethiopia, Gaza, Haiti and Sudan. He added that countries with macroeconomic constraints and weak currencies, such as Argentina, Venezuela and Turkey, are also particularly hard-hit. Bloomberg reported that access to agricultural land and workforce reduction due to the war in Gaza has caused Israel’s 29 largest food companies to increase their prices by as much as 30% since January.
UNSUSTAINABLE FARMING: Levi Sucre, coordinator of the Mesoamerican Alliance of Peoples and Forests, told Carbon Brief that overexploitation of land and the use of agrochemicals have increased the demand for fertilisers and the costs of production. For instance, Dr Innocent Okuku, executive secretary of the West African Fertiliser Association, told the Nigerian newspaper Daily Trust that application of fertilisers by smallholder farmers “is getting lower because of the issues around availability and cost”. The most affected are “people with the least resources”, says Sucre. Amongst those “highly vulnerable to food insecurity” are small island developing states, given that less than 1% of their land is devoted to agriculture, 70% of them face the risk of water scarcity and all have lost almost 7% of their agricultural GDP to climate-related disasters, Forbes reported.
Spotlight
Progress on agrifood systems at Bonn
In this spotlight, Carbon Brief explores the progress made regarding agriculture and food security at the recent Bonn climate talks.
The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) formally addresses issues and works towards solutions in agriculture and food systems through the Sharm el-Sheikh joint work on implementation of climate action on agriculture and food security (SSJW).
When SSJW negotiations ended at COP28 in Dubai, several experts told Carbon Brief that those outcomes had been disastrous, with the only tangible result of the summit being an “informal note”, which “essentially means, ‘we talked, we’ll talk again’”, Teresa Anderson, global climate justice lead at ActionAid, told Carbon Brief at the time.
The major sticking points at COP28 were the subject matter of a series of workshops to be held under the SSJW umbrella and the creation of a “coordination group” to oversee the implementation of the recommendations from those workshops.
‘Surprisingly sensible’
In contrast to COP28, this round of negotiations at Bonn were “surprisingly sensible”, Anderson said. Marie Cosquer, an advocacy analyst at Action Against Hunger, told Carbon Brief that “the vibe was nothing like Dubai” and the “parties started to engage constructively from the beginning”.
To begin with, Cosquer said, a “non-paper” with proposals, circulated by the EU negotiators ahead of the negotiations, allowed parties to react and “slowly became a way forward for consensus”. In addition, the G77 plus China negotiating group – who had advocated strenuously for the coordination group in Dubai – took a less hardline stance on the creation of the group.
The negotiators ultimately agreed upon two workshop topics: one on “systemic and holistic approaches to implementation of climate action on agriculture, food systems and food security” and the other on “progress, challenges and opportunities related to identifying needs and accessing means of implementation for climate action in agriculture and food security”.
Roadmap
The draft conclusions from Bonn also provide a roadmap for the remainder of the SSJW’s mandate, which runs to COP31 in November 2026. It lays out that the online portal, where parties will be able to upload their submissions for each workshop, should be developed over the next five months and presented at COP29 in November.
Clement Metivier, acting head of international advocacy at WWF-UK, said the roadmap was an “important and positive breakthrough”. It represented a “prime opportunity for governments to prioritise systemic and holistic approaches to transforming our food systems and make them healthy, resilient and equitable”, he added:
“There is no time to waste.”
News and views
EU RESTORATION LAW: EU ministers have approved the bloc’s nature restoration law, “despite stiff opposition to the plans and threats by Austria that it would seek to annul the outcome of the vote”, the Financial Times reported. The FT said “last-minute changes of heart from Austria and Slovakia” allowed the law to pass. However, the vote from Austria came from climate minister Leonore Gewessler, a Green party politician, who did not obtain approval from her coalition government partner, the conservative Austrian People’s Party, the FT said. In a letter to Belgium, which is currently holding the EU presidency, Austria’s chancellor Karl Nehammer, from the People’s Party, said Austria’s vote was “unlawful” and that his party would seek criminal charges against Gewessler for “alleged abuse of power”, the FT added.
FLOODS AND FOOD: Flooding in southern Brazil that started last month has caused $2.2bn in damages, including $680m in agricultural losses, according to Brazil Reports. The outlet added that “agribusiness is by far the most affected economic sector”, citing a study that found that the floods could cut agricultural GDP by up to 3.5%. Meanwhile, extreme weather in China is “raising concerns about food security” there, CNN reported. High temperatures and severe drought are impacting the northern part of the country while “heavy rains inundate the south”, the outlet said. It noted that the spring and summer planting seasons have been disrupted in key rice- and wheat-producing regions.
COTTON CROPS: High temperatures are “threatening cotton production” in the world’s fifth-largest cotton producer, Pakistan, Bloomberg reported. Nearly 10% of the total crop in Sindh – “one of the country’s most fertile provinces” – has been damaged by heat already, the outlet added, and “the situation is poised to get worse”. According to the country’s meteorological department, the month of June will bring rapid-onset “flash” drought, which can result in water shortages, wildfire and crop failure. Bloomberg added: “Besides cotton, excessive heat is also affecting sugarcane, exportable fruits like mangoes, citrus, banana and seasonal vegetables like chillies, tomato, potato and some lentils.”
ALGERIA RIOTS: The Associated Press reported that “violent riots erupted in a drought-stricken Algerian desert city last weekend after months of water shortages left taps running dry and forced residents to queue to access water for their households”. In the central Algerian city of Tiaret, “protestors wearing balaclavas set tires aflame and set up make-shift barricades blocking roads to protest their water being rationed”, AP said. It continued: “The unrest followed demands from President Abdelmajid Tebboune to rectify the suffering. At a council of ministers meeting last week, he implored his cabinet to implement ‘emergency measures’ in Tiaret. Several government ministers were later sent to ‘ask for an apology from the population’ and to promise that access to drinking water would be restored.”
Watch, read, listen
MOSQUITOES TO THE RESCUE: NPR reported on how scientists are transporting hundreds of thousands of mosquitoes to Hawaii to try to save their native bird species.
DEEP DIVE: On Last Week Tonight, comedian John Oliver dived into the controversy surrounding deep-sea mining. (Note, unfortunately, this is not available to watch in the UK.)
ANCESTRAL FORESTS: Nautilus chronicled an expedition to Hoh Rainforest in Washington state, “one of the largest old-growth temperate rainforests in the world”.
AFFECTED FISHERMEN: A multimedia story by InfoNile explored the impacts of overexploitation and illegal taxes by militias on fish production in Africa’s Lake Edward.
New science
Communications Earth & Environment
The increasing number of days without sea ice in southern and western Hudson Bay, an inland marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean in Canada, could make the loss of polar bears from this region “inevitable”, even if efforts are pursued to limit future climate change, new research found. The study drew on the latest high-resolution climate models to project the length of the ice-free period in Hudson Bay. The authors said: “Limiting global warming to 2C above pre-industrial levels may prevent the ice-free period from exceeding 183 days…providing some optimism for adult polar bear survival. However, with longer ice-free periods already substantially impacting recruitment, extirpation for polar bears in this region may already be inevitable.”
Intensified future heat extremes linked with increasing ecosystem water limitation
Earth System Dynamics
According to a new study, increasing water stress in land ecosystems will likely amplify the effects of extreme heat on people and wildlife globally. The researchers explained that while heat extremes “are mostly introduced by atmospheric circulation patterns”, they can be mitigated by ecosystems, which can provide a natural cooling service through plant transpiration and soil evaporation when there are ample water supplies. However, when water supplies in ecosystems are limited, heat extremes can be amplified, the new research found. The authors said: “We identify hotspot regions in tropical South America and across Canada and northern Eurasia where relatively strong trends towards increased ecosystem water limitation jointly occur with amplifying heat extremes.”
Early-stage loss of ecological integrity drives the risk of zoonotic disease emergence
Journal of the Royal Society Interface
The emergence of new diseases from animals – known as “zoonotic diseases” – is “strongly linked” to human pressures on biodiversity, new research suggested. The study updated the most comprehensive zoonotic emerging infectious disease event database with the latest reported events to analyse the relationship between new outbreaks and human pressures on ecosystems. The authors said: “We found emerging infectious disease risk was strongly predicted by structural integrity metrics such as human footprint and ecoregion intactness, in addition to environmental variables such as tropical rainforest density and mammal species richness.” Emerging infectious disease events “were more likely to occur in areas with intermediate levels of compositional and structural integrity, underscoring the risk posed by human encroachment into pristine, undisturbed lands”, the authors added.
In the diary
- 17-20 June: 67th meeting of the Global Environment Fund (GEF) council | Washington DC
- 18-21 June: ICLEI (Local governments for sustainability) World Congress 2024 | São Paulo, Brazil
- 19-21 June: G20 third climate and environment sustainability working group meeting | Manaus, Brazil
- 24-26 June: Organisational meeting of the Preparatory Commission for the Entry Into Force of the BBNJ Agreement and the convening of the first meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the agreement | New York City
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz. Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org.
The post Cropped 19 June 2024: Why food prices are spiking; Bonn climate talks; Plunging polar bear populations appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
DeBriefed 6 February 2026: US secret climate panel ‘unlawful’ | China’s clean energy boon | Can humans reverse nature loss?
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Secrets and layoffs
UNLAWFUL PANEL: A federal judge ruled that the US energy department “violated the law when secretary Chris Wright handpicked five researchers who rejected the scientific consensus on climate change to work in secret on a sweeping government report on global warming”, reported the New York Times. The newspaper explained that a 1972 law “does not allow agencies to recruit or rely on secret groups for the purposes of policymaking”. A Carbon Brief factcheck found more than 100 false or misleading claims in the report.
DARKNESS DESCENDS: The Washington Post reportedly sent layoff notices to “at least 14” of its climate journalists, as part of a wider move from the newspaper’s billionaire owner, Jeff Bezos, to eliminate 300 jobs at the publication, claimed Climate Colored Goggles. After the layoffs, the newspaper will have five journalists left on its award-winning climate desk, according to the substack run by a former climate reporter at the Los Angeles Times. It comes after CBS News laid off most of its climate team in October, it added.
WIND UNBLOCKED: Elsewhere, a separate federal ruling said that a wind project off the coast of New York state can continue, which now means that “all five offshore wind projects halted by the Trump administration in December can resume construction”, said Reuters. Bloomberg added that “Ørsted said it has spent $7bn on the development, which is 45% complete”.
Around the world
- CHANGING TIDES: The EU is “mulling a new strategy” in climate diplomacy after struggling to gather support for “faster, more ambitious action to cut planet-heating emissions” at last year’s UN climate summit COP30, reported Reuters.
- FINANCE ‘CUT’: The UK government is planning to cut climate finance by more than a fifth, from £11.6bn over the past five years to £9bn in the next five, according to the Guardian.
- BIG PLANS: India’s 2026 budget included a new $2.2bn funding push for carbon capture technologies, reported Carbon Brief. The budget also outlined support for renewables and the mining and processing of critical minerals.
- MOROCCO FLOODS: More than 140,000 people have been evacuated in Morocco as “heavy rainfall and water releases from overfilled dams led to flooding”, reported the Associated Press.
- CASHFLOW: “Flawed” economic models used by governments and financial bodies “ignor[e] shocks from extreme weather and climate tipping points”, posing the risk of a “global financial crash”, according to a Carbon Tracker report covered by the Guardian.
- HEATING UP: The International Olympic Committee is discussing options to hold future winter games earlier in the year “because of the effects of warmer temperatures”, said the Associated Press.
54%
The increase in new solar capacity installed in Africa over 2024-25 – the continent’s fastest growth on record, according to a Global Solar Council report covered by Bloomberg.
Latest climate research
- Arctic warming significantly postpones the retreat of the Afro-Asian summer monsoon, worsening autumn rainfall | Environmental Research Letters
- “Positive” images of heatwaves reduce the impact of messages about extreme heat, according to a survey of 4,000 US adults | Environmental Communication
- Greenland’s “peripheral” glaciers are projected to lose nearly one-fifth of their total area and almost one-third of their total volume by 2100 under a low-emissions scenario | The Cryosphere
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
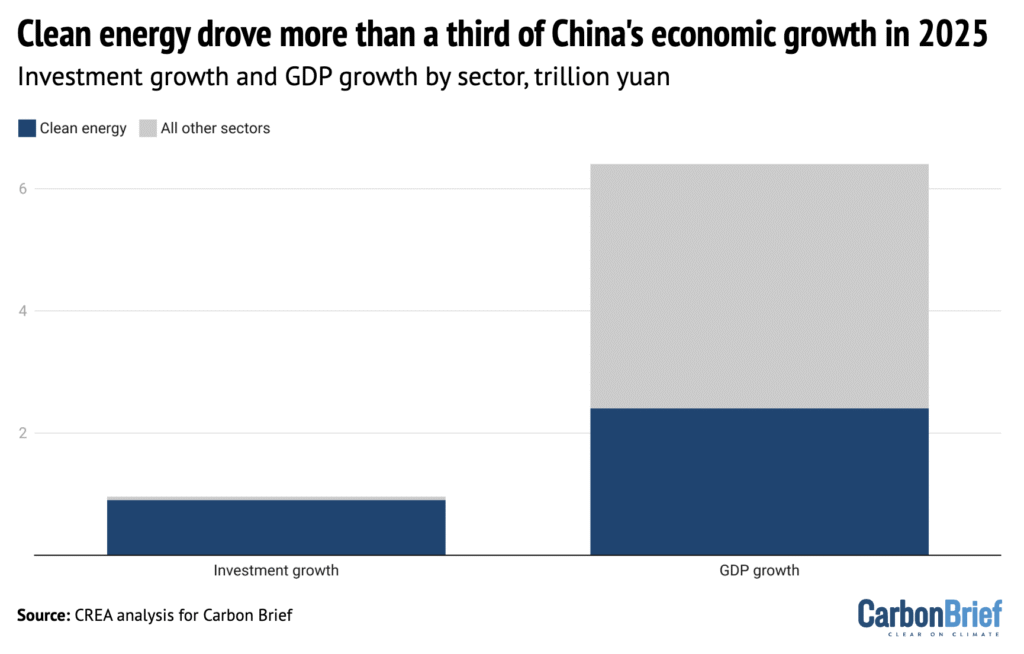
Solar power, electric vehicles and other clean-energy technologies drove more than a third of the growth in China’s economy in 2025 – and more than 90% of the rise in investment, according to new analysis for Carbon Brief (shown in blue above). Clean-energy sectors contributed a record 15.4tn yuan ($2.1tn) in 2025, some 11.4% of China’s gross domestic product (GDP) – comparable to the economies of Brazil or Canada, the analysis said.
Spotlight
Can humans reverse nature decline?
This week, Carbon Brief travelled to a UN event in Manchester, UK to speak to biodiversity scientists about the chances of reversing nature loss.
Officials from more than 150 countries arrived in Manchester this week to approve a new UN report on how nature underpins economic prosperity.
The meeting comes just four years before nations are due to meet a global target to halt and reverse biodiversity loss, agreed in 2022 under the landmark “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF).
At the sidelines of the meeting, Carbon Brief spoke to a range of scientists about humanity’s chances of meeting the 2030 goal. Their answers have been edited for length and clarity.
Dr David Obura, ecologist and chair of Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES)
We can’t halt and reverse the decline of every ecosystem. But we can try to “bend the curve” or halt and reverse the drivers of decline. That’s the economic drivers, the indirect drivers and the values shifts we need to have. What the GBF aspires to do, in terms of halting and reversing biodiversity loss, we can put in place the enabling drivers for that by 2030, but we won’t be able to do it fast enough at this point to halt [the loss] of all ecosystems.
Dr Luthando Dziba, executive secretary of IPBES
Countries are due to report on progress by the end of February this year on their national strategies to the Convention on Biological Diversity [CBD]. Once we get that, coupled with a process that is ongoing within the CBD, which is called the global stocktake, I think that’s going to give insights on progress as to whether this is possible to achieve by 2030…Are we on the right trajectory? I think we are and hopefully we will continue to move towards the final destination of having halted biodiversity loss, but also of living in harmony with nature.
Prof Laura Pereira, scientist at the Global Change Institute at Wits University, South Africa
At the global level, I think it’s very unlikely that we’re going to achieve the overall goal of halting biodiversity loss by 2030. That being said, I think we will make substantial inroads towards achieving our longer term targets. There is a lot of hope, but we’ve also got to be very aware that we have not necessarily seen the transformative changes that are going to be needed to really reverse the impacts on biodiversity.
Dr David Cooper, chair of the UK’s Joint Nature Conservation Committee and former executive secretary of the Convention on Biological Diversity
It’s important to look at the GBF as a whole…I think it is possible to achieve those targets, or at least most of them, and to make substantial progress towards them. It is possible, still, to take action to put nature on a path to recovery. We’ll have to increasingly look at the drivers.
Prof Andrew Gonzalez, McGill University professor and co-chair of an IPBES biodiversity monitoring assessment
I think for many of the 23 targets across the GBF, it’s going to be challenging to hit those by 2030. I think we’re looking at a process that’s starting now in earnest as countries [implement steps and measure progress]…You have to align efforts for conserving nature, the economics of protecting nature [and] the social dimensions of that, and who benefits, whose rights are preserved and protected.
Neville Ash, director of the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre
The ambitions in the 2030 targets are very high, so it’s going to be a stretch for many governments to make the actions necessary to achieve those targets, but even if we make all the actions in the next four years, it doesn’t mean we halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030. It means we put the action in place to enable that to happen in the future…The important thing at this stage is the urgent action to address the loss of biodiversity, with the result of that finding its way through by the ambition of 2050 of living in harmony with nature.
Prof Pam McElwee, Rutgers University professor and co-chair of an IPBES “nexus assessment” report
If you look at all of the available evidence, it’s pretty clear that we’re going to keep experiencing biodiversity decline. I mean, it’s fairly similar to the 1.5C climate target. We are not going to meet that either. But that doesn’t mean that you slow down the ambition…even though you recognise that we probably won’t meet that specific timebound target, that’s all the more reason to continue to do what we’re doing and, in fact, accelerate action.
Watch, read, listen
OIL IMPACTS: Gas flaring has risen in the Niger Delta since oil and gas major Shell sold its assets in the Nigerian “oil hub”, a Climate Home News investigation found.
LOW SNOW: The Washington Post explored how “climate change is making the Winter Olympics harder to host”.
CULTURE WARS: A Media Confidential podcast examined when climate coverage in the UK became “part of the culture wars”.
Coming up
- 2-8 February: 12th session of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), Manchester, UK
- 8 February: Japanese general election
- 8 February: Portugal presidential election
- 11 February: Barbados general election
- 11-12 February: UN climate chief Simon Stiell due to speak in Istanbul, Turkey
Pick of the jobs
- UK Met Office, senior climate science communicator | Salary: £43,081-£46,728. Location: Exeter, UK
- Canadian Red Cross, programme officer, Indigenous operations – disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation | Salary: $56,520-$60,053. Location: Manitoba, Canada
- Aldersgate Group, policy officer | Salary: £33,949-£39,253. Location: London (hybrid)
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 6 February 2026: US secret climate panel ‘unlawful’ | China’s clean energy boon | Can humans reverse nature loss? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
China Briefing 5 February 2026: Clean energy’s share of economy | Record renewables | Thawing relations with UK
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s China Briefing.
China Briefing handpicks and explains the most important climate and energy stories from China over the past fortnight. Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
Solar and wind eclipsed coal
‘FIRST TIME IN HISTORY’: China’s total power capacity reached 3,890 gigawatts (GW) in 2025, according to a National Energy Administration (NEA) data release covered by industry news outlet International Energy Net. Of this, it said, solar capacity rose 35% to 1,200GW and wind capacity was up 23% to 640GW, while thermal capacity – which is mostly coal – grew 6% to just over 1,500GW. This marks the “first time in history” that wind and solar capacity has outranked coal capacity in China’s power mix, reported the state-run newspaper China Daily. China’s grid-related energy storage capacity exceeded 213GW in 2025, said state news agency Xinhua. Meanwhile, clean-energy industries “drove more than 90%” of investment growth and more than half of GDP growth last year, said the Guardian in its coverage of new analysis for Carbon Brief. (See more in the spotlight below.)

DAWN FOR SOLAR: Solar power capacity alone may outpace coal in 2026, according to projections by the China Electricity Council (CEC), reported business news outlet 21st Century Business Herald. It added that non-fossil sources could account for 63% of the power mix this year, with coal falling to 31%. Separately, the China Renewable Energy Society said that annual wind-power additions could grow by between 600-980GW over the next five years, with annual additions of 120GW expected until 2028, said industry news outlet China Energy Net. China Energy Net also published the full CEC report.
STATE MEDIA VOICE: Xinhua published several energy- and climate-related articles in a series on the 15th five-year plan. One said that becoming a low-carbon energy “powerhouse” will support decarbonisation efforts, strengthen industrial innovation and improve China’s “global competitive edge and standing”. Another stated that coal consumption is “expected” to peak around 2027, with continued “growth” in the power and chemicals sector, while oil has already peaked. A third noted that distributed energy systems better matched the “characteristics of renewable energy” than centralised ones, but warned against “blind” expansion and insufficient supporting infrastructure. Others in the series discussed biodiversity and environmental protection and recycling of clean-energy technology. Meanwhile, the communist party-affiliated People’s Daily said that oil will continue to play a “vital role” in China, even after demand peaks.
Starmer and Xi endorsed clean-energy cooperation
CLIMATE PARTNERSHIP: UK prime minister Keir Starmer and Chinese president Xi Jinping pledged in Beijing to deepen cooperation on “green energy”, reported finance news outlet Caixin. They also agreed to establish a “China-UK high-level climate and nature partnership”, said China Daily. Xi told Starmer that the two countries should “carry out joint research and industrial transformation” in new energy and low-carbon technologies, according to Xinhua. It also cited Xi as saying China “hopes” the UK will provide a “fair” business environment for Chinese companies.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “China Briefing” email newsletter. All you need to know about the latest developments relating to China and climate change. Sent to your inbox every Thursday.
OCTOPUS OVERSEAS: During the visit, UK power-trading company Octopus Energy and Chinese energy services firm PCG Power announced they would be starting a new joint venture in China, named Bitong Energy, reported industry news outlet PV Magazine. The move “marks a notable direct entry” of a foreign company into China’s “tightly regulated electricity market”, said Caixin.
PUSH AND PULL: UK policymakers also visited Chinese clean-energy technology manufacturer Envision in Shanghai, reported finance news outlet Yicai. It quoted UK business secretary Peter Kyle emphasising that partnering with companies “like Envision” on sustainability is a “really important part of our future”, particularly in terms of job creation in the UK. Trade minister Chris Bryant told Radio Scotland Breakfast that the government will decide on Chinese wind turbine manufacturer Mingyang’s plans for a Scotland factory “soon”. Researchers at the thinktank Oxford Institute for Energy Studies wrote in a guest post for Carbon Brief that greater Chinese competition in Europe’s wind market could “help spur competition in Europe”, if localisation rules and “other guardrails” are applied.
More China news
- LIFE SUPPORT: China will update its coal capacity payment mechanism, which will raise thresholds for coal-fired power plants and expand to cover gas-fired power and pumped and new-energy storage, reported current affairs outlet China News.
- FRONTIER TECH: The world’s “largest compressed-air power storage plant” has begun operating in China, said Bloomberg.
- PARTNERSHIP A ‘MISTAKE’: The EU launched a “foreign subsidies” probe into Chinese wind turbine company Goldwind, said the Hong Kong-based South China Morning Post. EU climate chief Wopke Hoekstra said the bloc must resist China’s pull in clean technologies, according to Bloomberg.
- TRADE SPAT: The World Trade Organization “backed a complaint by China” that the US Inflation Reduction Act “discriminated against” Chinese cleantech exports, said Reuters.
- NEW RULES: China has set “new regulations” for the Waliguan Baseline Observatory, which provides “key scientific references for the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”, said the People’s Daily.
Captured

New or reactivated proposals for coal-fired power plants in China totalled 161GW in 2025, according to a new report covered by Carbon Brief.
Spotlight
Clean energy drove China’s economic growth in 2025
New analysis for Carbon Brief finds that clean-energy sectors contributed the equivalent of $2.1tn to China’s economy last year, making it a key driver of growth. However, headwinds in 2026 could restrict growth going forward – especially for the solar sector.
Below is an excerpt from the article, which can be read in full on Carbon Brief’s website.
Solar power, electric vehicles (EVs) and other clean-energy technologies drove more than a third of the growth in China’s economy in 2025 – and more than 90% of the rise in investment.
Clean-energy sectors contributed a record 15.4tn yuan ($2.1tn) in 2025, some 11.4% of China’s gross domestic product (GDP)
Analysis shows that China’s clean-energy sectors nearly doubled in real value between 2022-25 and – if they were a country – would now be the 8th-largest economy in the world.
These investments in clean-energy manufacturing represent a large bet on the energy transition in China and overseas, creating an incentive for the government and enterprises to keep the boom going.
However, there is uncertainty about what will happen this year and beyond, particularly due to a new pricing system, worsening industrial “overcapacity” and trade tensions.
Outperforming the wider economy
China’s clean-energy economy continues to grow far more quickly than the wider economy, making an outsized contribution to annual growth.
Without these sectors, China’s GDP would have expanded by 3.5% in 2025 instead of the reported 5.0%, missing the target of “around 5%” growth by a wide margin.
Clean energy made a crucial contribution during a challenging year, when promoting economic growth was the foremost aim for policymakers.
In 2024, EVs and solar had been the largest growth drivers. In 2025, it was EVs and batteries, which delivered 44% of the economic impact and more than half of the growth of the clean-energy industries.
The next largest subsector was clean-power generation, transmission and storage, which made up 40% of the contribution to GDP and 30% of the growth in 2025.
Within the electricity sector, the largest drivers were growth in investment in wind and solar power generation capacity, along with growth in power output from solar and wind, followed by the exports of solar-power equipment and materials.
But investment in solar-panel supply chains, a major growth driver in 2022-23, continued to fall for the second year, as the government made efforts to rein in overcapacity and “irrational” price competition.
Headwinds for solar
Ongoing investment of hundreds of billions of dollars represents a gigantic bet on a continuing global energy transition.
However, developments next year and beyond are unclear, particularly for solar. A new pricing system for renewable power is creating uncertainty, while central government targets have been set far below current rates of clean-electricity additions.
Investment in solar-power generation and solar manufacturing declined in the second half of the year.
The reduction in the prices of clean-energy technology has been so dramatic that when the prices for GDP statistics are updated, the sectors’ contribution to real GDP – adjusted for inflation or, in this case deflation – will be revised down.
Nevertheless, the key economic role of the industry creates a strong motivation to keep the clean-energy boom going. A slowdown in the domestic market could also undermine efforts to stem overcapacity and inflame trade tensions by increasing pressure on exports to absorb supply.
Local governments and state-owned enterprises will also influence the outlook for the sector.
Provincial governments have a lot of leeway in implementing the new electricity markets and contracting systems for renewable power generation. The new five-year plans, to be published this year, will, therefore, be of major importance.
This spotlight was written for Carbon Brief by Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst at Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), and Belinda Schaepe, China policy analyst at CREA. CREA China analysts Qi Qin and Chengcheng Qiu contributed research.
Watch, read, listen
PROVINCE INFLUENCE: The Institute for Global Decarbonization Progress, a Beijing-based thinktank, published a report examining the climate-related statements in provincial recommendations for the 15th five-year plan.
‘PIVOT’?: The Outrage + Optimism podcast spoke with the University of Bath’s Dr Yixian Sun about whether China sees itself as a climate leader and what its role in climate negotiations could be going forward.
COOKING FOR CLEAN-TECH: Caixin covered rising demand for China’s “gutter oil” as companies “scramble” to decarbonise.
DON’T GO IT ALONE: China News broadcast the Chinese foreign ministry’s response to the withdrawal of the US from the Paris Agreement, with spokeswoman Mao Ning saying “no country can remain unaffected” by climate change.
$6.8tn
The current size of China’s green-finance economy, including loans, bonds and equity, according to Dr Ma Jun, the Institute of Finance and Sustainability’s president,in a report launch event attended by Carbon Brief. Dr Ma added that “green loans” make up 16% of all loans in China, with some areas seeing them take a 34% share.
New science
- China’s official emissions inventories have overestimated its hydrofluorocarbon emissions by an average of 117m tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (mtCO2e) every year since 2017 | Nature Geoscience
- “Intensified forest management efforts” in China from 2010 onwards have been linked to an acceleration in carbon absorption by plants and soils | Communications Earth and Environment
Recently published on WeChat
China Briefing is written by Anika Patel and edited by Simon Evans. Please send tips and feedback to china@carbonbrief.org
The post China Briefing 5 February 2026: Clean energy’s share of economy | Record renewables | Thawing relations with UK appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
Congress rescues aid budget from Trump’s “evisceration” but climate misses out
Under pressure from Congress, President Donald Trump quietly signed into law a funding package that provides billions of dollars more in foreign assistance spending than he had originally wanted to for the fiscal year between October 2025 and September 2026.
The legislation allocates $50 billion, $9 billion less than the level agreed the previous year under President Biden but $19 billion more than Trump proposed, restoring health and humanitarian aid spending to near pre-Trump levels.
Democratic Senator Patty Murray, vice-chair of the committee on appropriations, said that “while including some programmatic funding cuts, the bill rejects the Trump administration’s evisceration of US foreign assistance programmes”.
But, with climate a divisive issue in the US, spending on dedicated climate programmes was largely absent. Clarence Edwards, executive director of E3G’s US office, told Climate Home News that “the era of large US government investment in climate policy is over, at least for the foreseeable future”.
The package ruled out any support for the Climate Investment Funds’ Clean Technology Fund, which supports low-carbon technologies in developing countries and had received $150 million from the US in the previous fiscal year.
The US also made no pledge to the Africa Development Fund (ADF) – a mechanism run by the African Development Bank that provides grants and low-interest loans to the poorest African nations. A government spokesperson told Reuters that decision reflected concerns that “like too many other institutions, the ADF has adopted a disproportionate focus on climate change, gender, and social issues”.
GEF spared from cuts
Trump did, however, agree to Congress’s request to make $150 million – more than last year – available for the Global Environment Facility (GEF), which tackles environmental issues like biodiversity loss, land degradation and climate change.
Edwards said that GEF funding “survived due to Congressional pushback and a refocus on non-climate priorities like biodiversity, plastics and ocean ecosystems, per US Treasury guidance”.
Congress also pressured Trump into giving $54 million to the Rome-based International Fund for Agricultural Development. Its goals include helping small-scale farmers adapt to climate change and reduce emissions.
Without any pressure from Congress, Trump approved tens of millions of dollars each for multilateral development banks in Asia, Africa and Europe and just over a billion dollars for the World Bank’s International Development Association, which funds development projects in the world’s poorest countries.
As most of these banks have climate programmes and goals, much of this money is likely to be spent on climate action. The largest lender, the World Bank, aims to devote 45% of its finance to climate programmes, although, as Climate Home News has reported, its definition of climate spending is considered too loose by some analysts.
The bill also earmarks $830 million – nearly triple what Trump originally wanted – for the Millennium Challenge Corporation, a George W. Bush-era institution that has increasingly backed climate-focussed projects like transmission lines to bring clean hydropower to cities in Nepal.
No funding boost for DFC
While Congress largely increased spending, it rejected Trump’s call for nearly $4 billion for the Development Finance Corporation (DFC), granting just under $1 billion instead – similar to previous years.
Under Biden, there had been a push to get the DFC to support clean energy projects. But the Trump administration ended DFC’s support for projects like South Africa’s clean energy transition.
At a recent board meeting, the DFC’s board – now dominated by Trump administration officials – approved US financial support for Chevron Mediterranean Limited, the developers of an Israeli gas field.
Kate DeAngelis, deputy director at Friends of the Earth US told Climate Home News it was good for the climate that Trump had not been able to boost the DFC’s budget. “DFC seems set up to focus mainly on the dirtiest deals without any focus on development,” she said.
US Congressional elections in November could lead to Democrats retaking control of one or both houses of Congress. Edwards said that “Democratic gains might restore funding [in the next fiscal year], while Republican holds would likely extend cuts”.
But he warned that “budgetary pressures and a murky economic environment don’t hold promise of increases in US funding for foreign assistance and climate programs, regardless of which party controls Congress”.
The post Congress rescues aid budget from Trump’s “evisceration” but climate misses out appeared first on Climate Home News.
Congress rescues aid budget from Trump’s “evisceration” but climate misses out
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-
Renewable Energy2 years ago
GAF Energy Completes Construction of Second Manufacturing Facility