A voluntary plan to curb fossil fuels, a goal to triple adaptation finance and new efforts to “strengthen” climate targets have been launched at the COP30 climate summit in Brazil.
After all-night negotiations in the Amazonian city of Belém, the Brazilian presidency released a final package termed the “global mutirão” – a name meaning “collective efforts”.
It was an attempt to draw together controversial issues that had divided the fortnight of talks, including finance, trade policies and meeting the Paris Agreement’s 1.5C temperature goal.
A “mechanism” to help ensure a “just transition” globally and a set of measures to track climate-adaptation efforts were also among COP30’s notable outcomes.
Scores of nations that had backed plans to “transition away” from fossil fuels and “reverse deforestation” instead accepted COP30 president André Corrêa do Lago’s compromise proposal of “roadmaps” outside the formal UN regime.
Billed as a COP of “truth” and “implementation”, the event – which took place 10 years on from the Paris Agreement – was seen as a moment to showcase international cooperation.
Yet, the lack of consensus on key issues and rising salience of “unilateral trade measures” and financial shortfalls revealed deep divisions.
The event itself also faced numerous logistical challenges, including a lengthy delay to negotiations when a fire broke out, forcing thousands of attendees to evacuate.
Here, Carbon Brief provides in-depth analysis of all the key outcomes in Belém – both inside and outside the COP.
(See Carbon Brief’s coverage of COP29, COP28, COP27, COP26, COP25, COP24, COP23, COP22, COP21 and COP20.)
Formal negotiations
Brazilian leadership
Brazilian president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva first made his bid to host an “Amazon COP” at COP27 in Egypt in 2022, fresh from an election victory.
Speaking in front of a cheering crowd, he laid out a vision for reversing deforestation in Brazil and hosting a rainforest COP in 2025, telling delegates:
“I advocate in a very strong way that the conference should be held in the Amazon.”
Lula faced no challenges from other countries and, at COP28 in Dubai in 2023, it was formally confirmed that Brazil would host COP30, representing the Latin American and Caribbean Group (GRULAC).
Lula’s insistence that COP should take place in the Amazon left only a few viable host city options, including Manaus, the capital of Amazonas state, and Belém, capital of Pará state.
Though Manaus offered some advantages, such as having its own stadium built for the World Cup in 2014, Lula opted for Belém – with some suggesting the decision was linked to Pará state governor, Helder Barbadlho, being a key ally of Lula’s Workers’ party.
After Belém was chosen, concerns were immediately raised that the city would not have enough accommodation for COP30’s 56,000 registered delegates.
In February, Lula caused consternation when, according to Folha de São Paulo, he responded to the fears by saying:
“If you don’t have a four-star hotel, sleep in a three-star hotel. If you don’t have a three-star hotel, sleep [under the] stars in the sky, which will be wonderful…They have to know how much a carapanã [a common mosquito in the Amazon] bite hurts.”
Though rumours swirled that the conference would have to be relocated to Rio de Janeiro, preparations in Belém continued, with the number of available rooms increasing from 18,000 to 36,000 from January to May, according to Brasil de Fato.
In August, just three months before COP30, the Brazilian government launched the summit’s accommodation booking platform, following pressure to do so from a UN committee, Climate Home News reported.
Despite this, “markups and sky-high prices remained”, raising worries that delegates from developing countries would not be able to afford to access the talks, it added.
Just days before the talks began, the COP30 presidency attempted to address concerns by offering free cabins on cruise ships to delegates from African countries, small island states and the least-developed countries (LDCs) group, Reuters said.
The environmental credentials of Lula’s government also came under scrutiny in the run up to the talks.
In August, Lula signed into law what many called the “devastation bill” for its impact on Brazil’s environmental licensing structure, after it was approved by the nation’s largely opposition-led congress, Sumaúma reported.
Just weeks before the talks, Lula’s government approved new oil and gas drilling at the mouth of the Amazon river, drawing condemnation from environmental groups, Mongabay said.
Unusually for a COP, the two-day “high level segment” – where world leaders give speeches with their views and plans on climate change – took place before the summit’s official opening from 6-7 November.
The COP30 presidency said this was to allow more time to rally action – and to avoid the summit’s accommodation crisis.
Reflecting a difficult geopolitical situation heading into COP30, the leaders of China, the US and India – the “planet’s three biggest polluters” – were “notably absent” from the leaders summit, reported the Associated Press.
Lula used his speech at the event to call for “roadmaps” away from deforestation and fossil fuels – he later repeated this in his speech during COP30’s opening. (His call sparked a movement of countries to push for roadmaps in Belém. (See: Fossil-fuel roadmap and deforestation.)
André Corrêa do Lago – a Brazilian economist, diplomat and former climate negotiator – was appointed the president of COP30. (He is the first former negotiator to take up this position.)

Ahead of the opening plenary on the summit’s first day, his team managed to avoid a time-consuming “agenda fight” by telling parties that the presidency would hold consultations on four items some blocs had sought to add to the agenda. These “big four” were on trade measures, climate finance, ambitions to keep global warming to 1.5C and data transparency.
Corrêa do Lago said that the presidency consultations would be followed by a special “stocktaking plenary” on Wednesday, where it would be decided how to take the discussions forward.
Proceedings were disrupted on Tuesday evening, when dozens of Indigenous protesters forced their way into COP’s “blue zone”, leading to clashes with security staff who sustained minor injuries, Reuters said. The protesters were expressing anger at a lack of access to the negotiations, according to the newswire.
The breach prompted UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) executive secretary, Simon Stiell, to write to both the COP30 presidency and the Brazilian government, to raise concerns about the “wellbeing of delegates and personnel”, Bloomberg reported.
Along with security concerns, Stiell said that delegates had been facing dangerously high temperatures due to faulty air conditioning units, in addition to water leakages and flooding inside the venue, the publication said. The presidency responded by promising to resolve all issues as quickly as possible.
At a press conference on Wednesday afternoon in the first week, COP30 strategy director Túlio Andrade gave an update on the presidency consultations for the additional items on trade measures, climate finance, 1.5C and transparency.
He said that seven hours of consultations had been held and stated that parties had been working together in a manner not witnessed in a “long, long time”.
Alongside him, Corrêa do Lago promised that the stocktaking plenary, scheduled for later that day, would bring “good news” for all, and agreed that the consultations had been “super constructive”.
However, when the plenary began just a few hours later, it ended abruptly, with Corrêa do Lago announcing that more consultations were needed and that the meeting would be rescheduled for Saturday.
As days passed with few new updates, some delegates theorised that the additional items would most likely be taken forward by some kind of “cover text” – an overarching political document that COP presidencies can choose to introduce, to summarise key negotiated outcomes, along with issues not on the official agenda.
However, Corrêa do Lago refused to be drawn on the possibility of a cover text in daily press conferences.
He also largely batted away questions about whether the outcome would include a reference to a “fossil-fuel roadmap” – as called for by Lula and a growing number of developed and developing countries at the summit.
On Thursday, the presidency announced the ministerial pairs of developed and developing nations that would steer key topics in the second week of negotiations.
This included the UK and Kenya on finance, Norway and UAE on the “global stocktake”, Germany and Gambia on adaptation, Spain and Egypt on mitigation, as well as Poland and Mexico on just transition.
On Saturday evening, Corrêa do Lago held the stocktaking plenary session, where he said the presidency consultations had been “rich with ideas”.
The following night, he then published a five-page “summary note”, which listed various options for how the discussions could be taken forward.
One of the possible outcomes listed was a “mutirão decision”, widely interpreted as a possible overarching text containing the key agreements from COP30.
On Monday afternoon, Corrêa do Lago held a muddled press conference, where he floated the possibility of “two packages” coming out of the summit: a “political package” covering the “big four” themes in consultations and another on negotiated tracks, plus other items.
After Corrêa do Lago rushed out to resume meetings, COP30 CEO Ana Toni became the first in the presidency to make an open reference to a “cover text”.
The presidency later followed up with a letter clarifying its position that it was looking to pursue an overall “Belém political package”, rather than a cover text.
The letter added that the presidency hoped to “complete a significant part of our work by tomorrow [Tuesday] evening, so that a plenary to gavel the Belém political package may take place by the middle of the week”.
The idea of finding agreement on the summit’s key text several days before the COP was scheduled to finish was something that had never been achieved before at international climate talks.
In the end, an early deal failed to materialise.
‘Global mutirão’
COP30 saw countries agree to a new “global mutirão” decision, a text calling for a tripling of adaptation finance by 2035 (later than some hoped), a new “Belem mission” to increase collective actions to cut emissions and – to the disappoint of many countries – no new “roadmaps” on transitioning away from fossil fuels and reversing deforestation.
(See Carbon Brief’s snap analysis and further detail in: Adaptation; Ambition and 1.5C, “Unilateral trade measures”; Fossil-fuel roadmap; and Deforestation.)
The first draft “global mutirão” text appeared during the summit’s second week, in the early hours of Tuesday morning.
“Mutirão” is a Portuguese word originating in the Indigenous Tupi-Guarani language that refers to people working together towards a common aim with a community spirit – something the COP30 presidency was keen to emphasise.
The presidency was also keen to stress that the mutirão text was not a cover text (sometimes referred to as a “cover decision”). However, like a cover text, it sought to bring together important issues that were not on the formal agenda with negotiated targets, acting as the key agreement from COP30.
The first draft drew together the “big four” issues of finance, trade, transparency and ambition.
For most of the major elements, the first draft listed various options.
For example, paragraph 56 listed three different options for how developed countries might triple spending on adaptation finance, while paragraph 35 floated three options for a possible “roadmap” away from fossil fuels, including one that simply said “no text”.
The first draft drew immediate condemnation from a group of 82 nations that wanted to see a more ambitious and certain call for a fossil-fuel “roadmap” included in the mutirão.
However, COP30 CEO Ana Toni told a press conference attended by Carbon Brief later that day that a “great majority” of country groups they had consulted saw a fossil-fuel roadmap as a “red line”. (A list of such countries was never made public.)
Lula returned to Belém on Wednesday and – as hopes of an early deal evaporated – he spent his time conducting bilateral meetings with delegations from different negotiating groups with the hope of moving negotiations forward.
Despite negotiations running late into the night on Wednesday, no new mutirão texts emerged by Thursday.
At around 2pm on Thursday, a major fire broke out in the Africa pavilion inside the COP venue, with large orange flames engulfing the surrounding area and burning a hole through the roof. The fire sent delegates in the pavilions area running for the exits.
The COP30 presidency and UNFCCC put out a joint statement saying the fire was extinguished within six minutes, all delegates were evacuated safely and 13 people were treated for smoke inhalation.
Pará state governor Helder Barbalho told local news outlet G1 that a generator failure or a short circuit in the pavilion may have started the fire, NPR reported.
(Carbon Brief understands there was also a fire in the green zone in the first week of the summit, also caused by an electrical fault.)
The fire temporarily put the negotiations on pause, but they were able to resume after 8pm on Thursday night, organisers said.
Early on Friday morning, a long-awaited second version of the draft “mutirão” text emerged.
This text called “for efforts to triple adaptation finance” by 2030, a presidency-led “Belém mission to 1.5C” and a voluntary “implementation accelerator”, as well as a series of “dialogues” on trade.
It did not refer to a “fossil-fuel roadmap”, sparking condemnation from some countries and campaigners. (See: Fossil-fuel roadmap.)
With different countries still poles apart on key issues in the mutirão, negotiations dragged all through Friday.
At one point on Friday afternoon, talks had “descended into turmoil”, as the presidency tried to move discussions into three “huddles” on trade, adaptation finance and ambition, according to several observers speaking to Carbon Brief.
Many countries objected to the lack of a huddle on fossil fuels, while Saudi Arabia said the idea of targeting the energy sector was “off the table”, the observers told Carbon Brief.
After a break, talks resumed, with four huddles being formed, including one on fossil fuels.
During the night, as tensions were rising, UK special climate envoy Rachel Kyte posted on LinkedIn saying that “ministers and negotiators are clutched in huddles, trying to negotiate with each other as opposed to having everything mediated through the Brazilian presidency”.
Speaking to a group of journalists on Saturday morning, EU climate commissioner Wopke Hoekstra described it as a “difficult and intense evening”.
At 10am, the presidency sent an email to delegates saying a new text would soon be circulated and that a closing plenary would follow.
The final version of the mutirão text emerged, “calling for” a tripling of adaptation finance, but with no clear baseline year and a target date of 2035, five years later than an earlier draft. It also contained no fossil-fuel roadmap. (See: Adaptation.)
At a closing plenary, the text was adopted with no objections.
After brief applause, Corrêa do Lago acknowledged that some countries were hoping for “more ambitious” outcomes from the text.
He then announced that the COP30 presidency would bring forward two roadmaps, on transitioning away from fossil fuels and deforestation, to present at the next COP.
He added that the fossil-fuel roadmap will be guided by an upcoming conference on transitioning away from fossil fuels hosted by Colombia and the Netherlands in April.
Corrêa do Lago went on to rapidly gavel more of COP30’s key texts, including on the “global goal on adaptation” (GGA), and the just transition and mitigation work programmes.
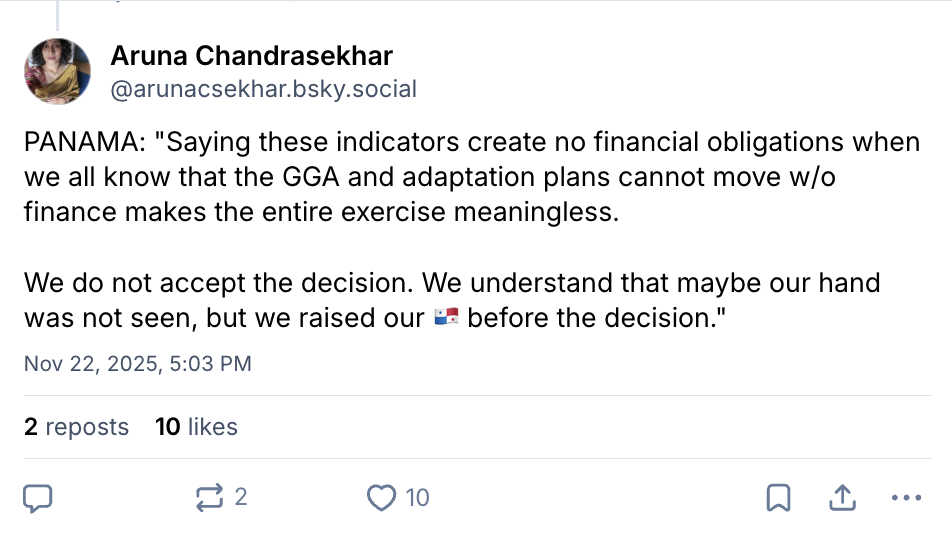
However, Panama, supported by other Latin American countries and the EU, took to the floor in plenary to say its attempt to raise an intervention ahead of the GGA being gavelled was ignored by the Brazilian presidency.
Colombia also took the floor, to say that its attempt to raise a flag before the adoption of the mitigation work programme was also ignored.
The closing plenary was suspended for an hour to allow for further consultations between the presidency and parties unhappy with the adoption process.
After the plenary resumed, delegates spent another six hours gavelling through more texts, including on gender equality and a host of more technical items, in addition to hearing more statements from countries and observers.
According to Carbon Brief calculations, in total, there were more than 150 pages of decision text adopted across the various bodies meeting at the COP.
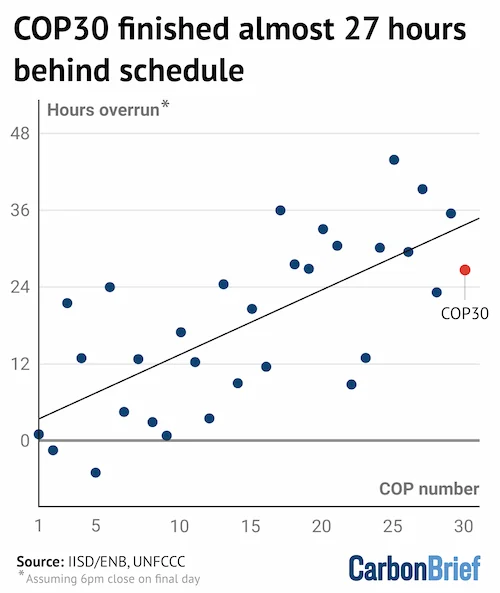
COP30 officially finished at 8:44pm on Saturday evening, making it only the 11th longest climate talks in history.
Adaptation
One of the biggest negotiated outcomes at COP30 concerned efforts to adapt to the impacts of climate change, with Corrêa do Lago dubbing it the “COP of adaptation”.
In particular, negotiators were expected to agree to a list of “indicators” that would allow countries to measure their progress under the global goal on adaptation (GGA). A much-reduced set of indicators was, ultimately, agreed at COP30.
However, calls for a new adaptation finance target quickly drew focus. The key “global mutirão” decision at the talks “calls on” countries to triple adaptation finance by 2035.
This followed a request from the LDCs at climate talks in Bonn earlier this year for a target to triple adaptation finance by 2030.
In 2021, a target to double adaptation finance to $40bn by 2025 was agreed at COP26 in Glasgow, UK.
However, a recent report from the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) found that, in 2023, developed nations provided just $26bn in adaptation finance to developing nations.
This marks a drop from $28bn in 2022 and is far short of the annual adaptation-finance needs for these nations, which UNEP puts at around $310bn annually out to 2035.
UNEP warned that, based on current trends, developed nations will miss the Glasgow goal.
A negotiation on a new adaptation-finance target for the years after 2025 was not included in the COP30 agenda. Over the course of the first week, a new goal was proposed in discussions on the GGA, national adaptation plans (NAPs) and the adaptation fund.
The LDCs’ proposal to triple finance to $120bn by 2030 was supported by small-island states (AOSIS), the African group, Grupo Sur and others.
It faced opposition, primarily from developed countries in the EU and the Environmental Integrity Group (EIG), the latter of whom noted that reference to such a target would be construed as an attempt to renegotiate the “new collective quantified goal” (NCQG).
Speaking during a press huddle, Aichetou Seck, an LDC adaptation negotiator from Senegal, said:
“We cannot keep returning to debate figures; the figures will only grow if action does not follow. What is needed now is a COP that elevates adaptation and sends a clear signal that adaptation finance is indispensable.”
With no official home, the question of a new adaptation-finance target was taken up within the presidency consultations. (See: Global mutirão.)
The first mutirão draft included a number of options, including one to “establish a goal” of developed countries tripling their provision of adaptation finance, with options for this to come exclusively “from public sources” and proposed deadlines of either 2030 or 2035.
There were also less ambitious proposals, merely “urging” a tripling of adaptation finance or “acknowledging” the need for a general increase in this finance.

Simultaneously, negotiations got underway on the GGA. Over the past two years, experts worked to turn a list of 10,000 potential indicators for tracking adaptation into just 100.
Cracks quickly emerged at COP30. Unity within the G77 and China coalition of developing countries fractured on the first day of negotiations, when the African group proposed a two-year “political refinement” process ahead of indicator adoption. Latin American countries called for adoption at COP30.
The African group argued that the indicators were “intrusive” and that African countries required more adaptation finance to take them on.
Richard Muyungi, African group chair, told Carbon Brief in the first week:
“We need to put guardrails or caveats on the adoption [of the indicators]. For example…the indicators should not infringe on the sovereignty of countries, asking countries to change their laws, their strategies. I mean, you cannot ask my country to change laws, because they want to address the global goal.”
Speaking during a press conference, Jacobo Ocharan, head of political strategies at Climate Action Network (CAN) International, noted that 48 of the indicators required support and finance in order to be actionable.
He asked: “What are you going to measure…in two years if that finance is not there?”
Other areas of disagreement within the GGA included opposing views on topics such as the Baku adaptation roadmap, the concept of “transformational adaptation” and language on “cross-cutting considerations”.
However, the key sticking point remained the indicators. Jeffrey Qi, policy advisor with IISD’s resilience program, told Carbon Brief that negotiators were trying to find a “tricky” balance. He said this included keeping indicators around domestic resource mobilisation that developed countries wanted, but which developing nations opposed.
The issue was complicated by the continued divide within the developing-country groups.
Speaking in a media huddle, Latin American ministers highlighted adaptation finance, but continued to emphasise the need to adopt the indicators. Edgardo Ortuño Silva, environment minister of Uruguay, said:
“We will not accept less in our conference than the adoption of action indicators and implementation means consistent with the [UNFCCC] and the Paris Agreement.”
Draft negotiation texts showed little progress in the second week, with the number of undecided, bracketed parts of the text doubling to nearly 100.
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Bethan Laughlin, senior policy specialist at the Zoological Society of London, said that the “massive elephant in the room is the lack of adaptation finance”, but that a goal within the presidency text could “unlock a huge amount of it”.
As negotiations drew to a close a new text seemingly found a landing ground. It included an annex of 59 of the potential 100 indicators, emphasising that they “do not create new financial obligations or commitments”.
The text also contained plans for a two-year “Belém-Addis vision” to further refine the indicators.
The only remaining bracket within the text was a placeholder for the final adaptation finance target from the mutirão.
This text was released on the same day and included weakened language that merely “call[ed] for efforts” to triple adaptation finance compared to 2025 levels by 2030.
Ana Mulio Alvarez, researcher on adaptation at thinktank E3G, told Carbon Brief that the indicator compromise was “satisfactory”, as it allowed the framework to advance while including further refinement, but that some aspects remained “ambiguous”.
She added that a small group of negotiators had altered some of the indicators, “render[ing] some unusable, suggesting the list may need to be revised again”.
The final GGA text retained the adoption of the 59 indicators and the two-year programme “aimed at developing guidance for operationalising the Belém adaptation indicators”.
The GGA was gavelled through during the closing plenary, but met with a mixed response. While there was clapping in the room, Latin American countries, the EU, Canada and others voiced criticism and said they could not support the outcome.
Panama, for example, referred to it as a “rushed draft” and argued that this “is not how we reach a global goal on adaptation”. The statement was met with a round of applause.
Following a pause in the plenary, Corrêa do Lago requested further work on the GGA at the Bonn climate talks in June 2026.
The GGA text retained the placeholder for an adaptation-finance goal within the final mutirão text.
Ultimately, this “reaffirm[ed]” the doubling goal from Glasgow, “call[ed] for efforts” to triple adaptation finance and “urge[ed]” developed countries to increase the “trajectory” of their finance provisions, largely mirroring the previous draft.

However, the deadline for the tripling target was pushed back by five years and the reference to 2025 as the baseline for this goal was removed.
Joe Thwaites, a senior advocate for international climate finance at NRDC, told Carbon Brief there was “ambiguity” in the goal, but added:
“The decision to triple was taken in 2025 and the old goal expires in 2025, so absent anything saying otherwise, that should be the assumption.”
Carbon Brief understands that, with no baseline officially in the text, the Standing Committee on Finance could provide a space where the baseline is defined by parties.
Beyond the GGA and adaptation finance, negotiations on NAPs followed on from tense sessions at COP29 and in Bonn, both of which ended without agreement.
According to Qi, within the NAP negotiations, “finance is the main issue…if you look at the text, it’s the same issue over and over again. So you just need to streamline everything.”
Ultimately, a decision was adopted in COP30’s closing plenary, marking an end to the stalemate in NAP negotiations.
Additionally, negotiations took place under the Adaptation Fund, with countries announcing financial pledges towards its annual target of $300m. The final text “notes with concern” that the target could not be met and “underscores the urgency of scaling up financial resources”.
Ambition and 1.5C
The key “global mutirão” decision at COP30 aims to keep the limit of 1.5C “within reach”, but says that the “carbon budget” for this is “now small and being rapidly depleted”.
For the first time in a COP text, it also acknowledges that there is likely to be an “overshoot” of 1.5C, saying that both the extent and duration of this needs to be “limit[ed]”.
It responds to this by launching two ill-defined voluntary initiatives, led by the COP presidencies: a “global implementation accelerator” (GIA) and a “Belém mission to 1.5C”.

It also “calls on” countries to “accelerat[e] the full implementation” of their climate pledges and to “striv[e] to do better”, as well as “inviting” them to draw up “implementation and investment plans”, to align their climate strategies with plans for economic development.
These measures fall well short of the outcomes that had been demanded by a broad coalition, including the EU and small-island states (AOSIS).
The decision does not mention fossil fuels, the largest source of planet-warming emissions, or a mooted “roadmap” to transition away from their use. (See: Fossil-fuel roadmap.)
In the closing plenary, the EU called the decision a “missed opportunity”. During heated negotiations on the penultimate day, it had called for a “concrete, annual process to…keeping 1.5C alive not in speeches, but in practice”. The outcome does not deliver this.
Fernanda Carvalho, head of policy for climate and energy at WWF, told Carbon Brief that the outcome reflected the “lowest common denominator, therefore [it] is weak”.
Countries had arrived in Brazil as a series of reports made clear that they remained badly off track for limiting warming to 1.5C, even though the outlook has improved since 2015.
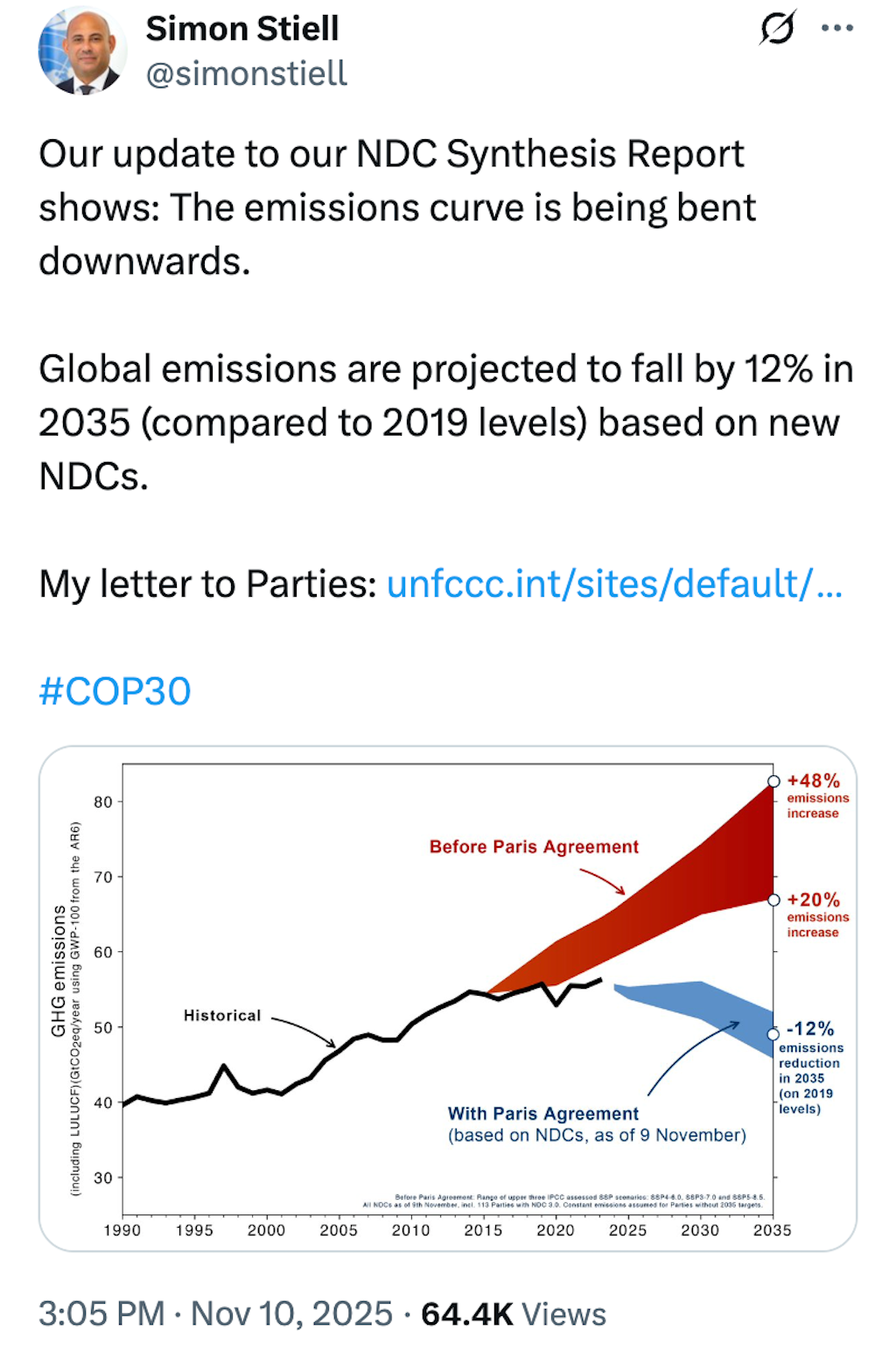
Despite countries submitting more than 100 new climate plans, known as “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs), the world remains on track for 2.3-2.5C of warming by 2100.
Ahead of the summit, this had prompted AOSIS to propose a “dedicated space” on the COP agenda in which to “assess collective progress…and drive ambition toward 1.5C”.
This idea was not added to the official agenda. Instead, it was taken up in “presidency consultations” along with three other contentious topics, which went on to be combined into a single COP30 decision known as the “global mutirão”. (See: Global mutirão.)
After a week of closed-door discussions, the presidency published a draft of this outcome that included options related to the call from AOSIS and others. In paragraph 44, one option would have created annual NDC discussions linked to a “transition away from fossil fuels”.

Although this option reflected some of the priorities put forward by AOSIS, it did not include a clear process through which to take the “annual consideration of NDCs” forwards.
Separately, this draft also included an option making a direct link back to paragraphs 28 and 33 of the global stocktake, which called for fossil-fuel transition and ending deforestation.
However, this direct link back to the stocktake and the idea of annual discussions on NDCs were both opposed by the like-minded developing countries (LMDCs, including China, India and Saudi Arabia) and the African group, according to the Earth Negotiations Bulletin.
The second draft of the mutirão text, published on 21 November, made no mention of fossil fuels, roadmaps, paragraph 28 of the global stocktake or annual discussions on NDCs.
The final draft – published on 22 November after all-night negotiations – is broadly similar, but fleshes out the GIA, among other changes.
It adds “information sessions” to be held under the GIA in Bonn in June 2026 and at COP31 – where the COP30 and COP31 presidencies will report back – as well as a related “high-level event”.
It also ties the GIA to the “UAE consensus” – the overarching outcome of COP28, where the global stocktake and its paragraph 28 on energy transition was adopted.
This “implicitly keeps the transition away from fossil fuels alive”, said Cosima Cassel, climate diplomacy lead at E3G. The Belém mission to 1.5C also “has potential” to be linked to roadmaps on fossil fuels and deforestation launched by Brazil. She told Carbon Brief:
“Given the resistance from major [fossil-fuel] producers, even maintaining that implicit link was hard-won…What we have is essentially the most that could be agreed without triggering a veto. The ambition is lower than many wanted, but the political hooks do exist. Much will depend on how Brazil, Australia and Turkey choose to drive this agenda forward.”
(Notably, the G20 declaration, published after the COP30 deal had been wrapped up, includes text that explicitly “welcomes” the outcome of the stocktake, even as similar language had proved elusive in Belém.)
Catherine Abreu, director of the International Climate Politics Hub, told Carbon Brief that, in order for the UN climate talks to “get real”, they would need to address the key issues raised by different groups of countries, including finance, trade and the “social dimensions of transition”, as well as a “laser focus” on the biggest emissions sources, fossil fuels and deforestation. She said:
“Yet the final decisions made on these issues rely on dialogues and coalitions that aren’t binding and have few accountability anchors within the UN climate process. It will take diligent attention from countries and COP presidencies – and civil society – to ensure the processes launched in Belém actually work to drive implementation.”
There were also related discussions in Belém on taking forward the outcomes of the first global stocktake under the “UAE dialogue”. Efforts to agree what this dialogue should talk about had failed at COP29 in Baku.
At COP30, countries initially remained deeply divided, between groups that only wanted it to discuss climate finance and those that wanted to talk about all of the stocktake outcomes.
After a “bridging proposal” offering compromise language was put forward by Latin American countries (AILAC), negotiations closed in on a broad scope for the UAE dialogue, covering all outcomes of the stocktake, but with a particular focus on finance.
The final decision on the dialogue says it will be held at the Bonn meetings in 2026 and 2027, with countries and observers invited to submit their views three months in advance.
Reports of these sessions will feed into the second stocktake in 2028 and the UAE dialogue itself will conclude with a ministerial “roundtable” at COP32 in 2027.
The decision also “encourages” the scientific community, including the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), to “consider how best to provide inputs for the global stocktake in a timely manner”.
Manjeet Dhakal, adviser to the least-developed countries (LDCs) told Carbon Brief that “significant compromises” had been made in order to “keep the process moving”. He said:
“There is now a clear need for strong implementation and tracking of the first GST [global stocktake] outcome through the UAE dialogue next year. Looking ahead, the IPCC AR7 working group reports should serve as critical inputs for the second GST. The global stocktake must help drive ambition to keep 1.5C within reach and close the implementation gap.”
Climate finance
Finance to help developing countries deal with climate change was not top of the agenda at COP30, but still influenced much of the event.
An effort by India, Arab states and other developing countries to elevate the issue ended up forming part of the Belém summit’s core “mutirão” package. (See: Global mutirão.)
The package launched a new “work programme” for countries to discuss concerns about climate finance, as well as a new goal to triple adaptation finance. (See: Adaptation.)
Most finance-related issues at COP30 could be traced back to a new target agreed last year, which included a $300bn-a-year goal, as well as a vaguer effort to reach $1.3tn, both by 2035.
This “new collective quantified goal” (NCQG) faced a backlash from many developing countries at the time, who argued it was insufficient.
The parties responsible for providing finance – including the EU, the UK and Japan – have been unwilling to consider more ambitious targets, often citing domestic fiscal pressures.
These divergences spilled over into COP30. As negotiators debated fossil-fuel phaseout, just transition and adaptation, developing countries argued that they needed more finance for all these activities.
In particular, there was a focus on Article 9.1 of the Paris Agreement, which says developed countries “shall provide” climate finance. In practice, this means public money.

In contrast, the $300bn target covers both funds “provided” and climate finance from a “wide variety of sources”, such as “mobilised” private spending.
Some developing countries argue that this formulation will enable developed countries, many of which have cut their aid budgets, to meet the goal without raising their contributions much.
Ahead of COP30, the LMDCs and Arab group – together representing around 40 countries, including India, China and Saudi Arabia – called for a three-year “work programme” on implementing Article 9.1. They also had support from the African group.
Chandni Raina, the Indian climate-finance negotiator who caused a stir last year when she publicly rejected the NCQG, told Carbon Brief:
“[Article] 9.1 is the catalyst that can enable us to mobilise finance of the kind that we need for climate action…We understood that the developed countries didn’t want to discuss 9.1 at all, because that puts the onus on them.”
EU lead negotiator Jacob Werksman said the bloc’s view was that the whole of Article 9 – covering “a wide variety of sources” – was important. He told a press conference: “We are prepared to talk about 9.1, but in the context of Article 9 as a whole.”
Developed-country representatives also stressed the importance of expanding the donor base to include wealthy, developing countries and changing global financial architecture to boost finance.
The LMDC-Arab grouping’s push for an Article 9.1 work programme formed part of the wider presidency discussions that dominated so much of COP30. (See: Global mutirão.)
Not all developing countries appeared to feel as strongly about the issue of Article 9.1, specifically. Ziaul Haque, additional director general at the Bangladesh Ministry of Environment, told Carbon Brief:
“We need to have good discussions around 9.1, but whether there is dedicated space or not…We are flexible.”
In the end, the mutirão text contains the compromise of a two-year programme covering all of Article 9 and a footnote stating the decision does not “prejudge” NCQG implementation.

Avantika Goswami, a climate policy lead at the Centre for Science and Environment, told Carbon Brief that, despite being “suboptimal”, the programme would provide “a concrete space to raise various issues on climate finance in the coming years, including on public finance flows”.
Another finance element that made it into the mutirão package was the “Baku to Belém roadmap”. Launched as part of the NCQG, this presidency-led initiative was meant to lay out how the $1.3tn part of the goal could be met.
Independent analysis commissioned for the roadmap suggests the vast majority will likely come from private-sector investment.
The roadmap was launched just before COP30. During the first week of the summit there was a “high-level” event in which the Brazilian and Azerbaijani presidencies laid out the next steps.
Major donors voiced their support for the Baku to Belém roadmap at the event, while both Kenya and AILAC indicated that they wanted it reflected in COP30 negotiated outcomes. However, the roadmap was a lower priority than other finance issues for many developing countries.
“We are more interested in the $300bn goal, that is where the provision and mobilisation will primarily take place,” Raju Pandit Chhetri, an LDC advisor, told Carbon Brief.
In the end, the mutirão package only “takes note” of the roadmap. However, the text also “decides” – a relatively strong active verb from a legal perspective – to “urgently advance actions” to scale up finance to $1.3tn.

There were a number of other negotiating tracks that involved climate finance at COP30.
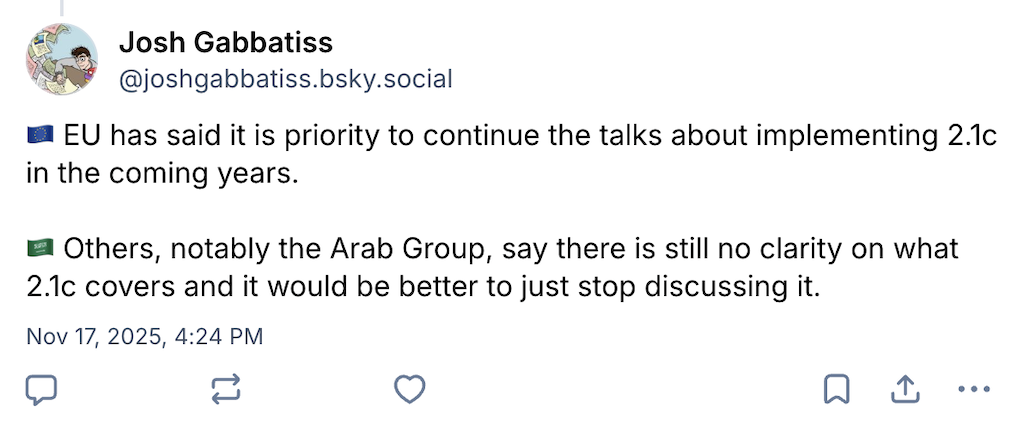
One track focused on Article 2.1c of the Paris Agreement, which concerns “making finance flows consistent” with climate goals.
The breadth of this topic is potentially huge, so countries have been engaged in a “dialogue” to arrive at a more shared understanding.
Ultimately, parties at COP30 decided to keep discussing the issue under a new “Veredas dialogue” until 2028, despite the Arab group initially wanting to end discussions.
Finally, another track saw negotiators discuss “biennial communications”, in which developed countries lay out plans for future climate-finance provision.
Parties had a chance at COP30 to update the information they should provide, to help developing countries plan for the future, but ultimately the changes were modest.
With little space for finance in formal negotiations, this workstream became an opportunity for developing countries to make ambitious demands, which did not make it into the final text. These included calling for the NCQG goal to exceed $300bn and for the developed nations to “reform [their] budgetary processes”.
‘Unilateral trade measures’
After several failed attempts to bring climate-related “unilateral trade measures” (UTMs) onto the agenda at previous COPs, the issue was taken up in Belém as part of presidency-led discussions and reflected in the key outcome of the summit, the “global mutirão”.
This decision creates three annual “dialogues” on trade, to be held at the Bonn meetings in 2026, 2027 and 2028. It also “reaffirms” that climate measures, “including unilateral ones, should not constitute” trade restrictions that are “arbitrary” or “discriminat[ory”.
This is the first-ever mention of trade measures in a COP cover decision.

In Belém, the issue of such trade measures had once again been raised by Bolivia on behalf of the like-minded developing countries (LMDCs, including China, India and others).
Within the presidency-led consultations, the LMDCs called for a recurring agenda item on trade, Tuvalu supported a dialogue and the African group proposed a system for countries to report trade measures to the UNFCCC.
Russia, meanwhile, warned that “killing off” UTMs again “will poison other issues and result in distrust”, reported the Earth Negotiations Bulletin (ENB).
On Sunday, the presidency published a summary of its consultations, containing five options for a decision on trade measures, including dialogues, roundtables or the creation of a platform.

In a first draft of the mutirão text, published on 18 November, the options had been refined to four.
David Waskow, director of the World Resources Institute’s international climate initiative, told a media briefing that trade is a “real issue” for some countries and not just a “bargaining tactic or some sort of chit that’s being put on the table”.
He added that the EU “feels strongly” about the ways trade measures support climate action, but also developing countries have “real concerns” about how those measures play out.
On what was scheduled to be the last day of COP30, the presidency published a second draft of the mutirão text “request[ing]” the subsidiary bodies to hold an annual dialogue in Bonn from 2026-2028 on trade and international cooperation.

Avantika Goswami, climate policy lead at Delhi-based thinktank the the Centre for Science and Environment, told Carbon Brief that, while “it is not ideal to not have a formal agenda item” on UTMs, the reference to the UN climate convention in the text “is welcomed”, as well as the dialogues that will take place over the next three years. Goswami added:
“At the very least, this will elevate the issue of unilateral trade measures to be more high-profile within the COP space and will provide a forum for countries to discuss their concerns and challenges, as well as possible solutions for the way forward.”
Alongside the discussions under the presidency, UTMs continued to crop up within different negotiation streams, including on just transition, “response measures” and technology.
In Baku in 2024, a four-year work plan to discuss response measures included an item on the “cross-border impacts” of “measures taken to combat” climate change. This established a formal space for trade-related climate measures and their impacts to be discussed and assessed, for the first time in climate talks.
Early options in draft texts for the response measures workstream at COP30 referred to presidency consultations on UTMs and to “cross-border impacts” of climate measures.

Subsequent drafts dropped the reference to UTMs, but retained language on cross-border impacts.
By the penultimate day of the talks, the presidency proposed a decision text for the response measures forum. This included a two-day global dialogue on response measures each year from 2026-29. After relatively few changes, this decision was adopted.
UTMs were also discussed in relation to just transition work programme (JTWP), following on from a LMDC proposal in Bonn to have them added to the agenda. The compromise in June was that trade measures were added to the work programme.
In Belém, Saudi Arabia said that unilateral trade measures would “hinder [climate] ambition, violate the right to development and exacerbate poverty, clearly attacking the very concept of just transitions”, according to Third World Network (TWN).
Meanwhile, China called UTMs “the new injustice”, whereas Japan did not support UTMs being discussed in the JTWP, TWN reported.
There was a particular focus on the EU’s “carbon border adjustment mechanism” (CBAM), with a draft text published in the second week, “not[ing] with concern” its potential impact.
Speaking during an EU press conference, European commissioner Wopke Hoekstra said the bloc is “more than happy to discuss” CBAM, but pushed back on criticism. He added that CBAM was not a unilateral trade measure, but “part of our climate toolbox”.
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Meena Raman, head of the climate change programme at Third World Network, said:
“This is the issue about equity, linking it to the trade measure. So it’s not about saying that what the EU is doing is not important for its own industry, but it’s being viewed as a protectionist, discriminatory measure rather than cooperating. It feels punishing.”
However, the final decision on the JTWP removed all references to trade. Similarly, all references to “trade barriers” were removed in the final decision on the “technology implementation programme”.
Climate science
Bangladesh, the EU and the UK were among those left “disappointed” by COP30 conclusions on climate science, reached at the end of the first week of the summit.
The text on “research and systematic observation” (RSO) failed to endorse the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) as the “best available science”.
It noted the need for “the integrity of climate change information”, but – unlike an earlier draft – it made no mention of the need to “counter misinformation on climate change”.
The text also failed to mention the latest findings on the state of the climate, as presented to the summit by the IPCC, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and others.
Speaking in the closing plenary of the first week of COP30, Bangladesh said it was “deeply concerned” about efforts to avoid endorsing the IPCC. It said:
“We are also deeply concerned about the consistent attempt to weaken the reference of the IPCC as the provider of the best available science, not only under this agenda item, but across several others. The IPCC remains the cornerstone of credible policy-relevant climate knowledge and its integrity must be protected.”
Similar interventions came from Australia, Canada and New Zealand. In contrast, Saudi Arabia, speaking for the Arab group, as well as Iran, called for finance to support further climate research.
(The headline “global mutirão” decision, adopted a week later, “recognises the centrality of equity and the best available science…as provided by the IPCC”.)
The UK said it was “deeply concerned that…it was not possible to capture vital scientific observations of the state of the climate in our conclusions”.
(An earlier draft had noted that 2025 was on track to be among the three hottest years on record, “primarily [as a] result of greenhouse gas emissions”. It had also flagged “record increases” in CO2 concentrations and “irreversible changes” in the Earth’s icy regions.)
The EU contrasted this inability to acknowledge the state of the world’s climate with Brazilian president Lula’s description of the summit as the “COP of truth”.
According to the Earth Negotiations Bulletin, the Arab group and India opposed references to the IPCC and to specific findings from the WMO. It also reported that Saudi Arabia had “called for deleting a reference to enhancing efforts to ‘counter misinformation’.”
Several sources who were not authorised to speak with the media tell Carbon Brief that COP discussions on climate science have been “getting harder” and “more political”. One says that a “very small group of countries” is behind this resistance.
However, a summary of the first week at the COP from the research consortium CGIAR stresses the need to understand the motivations behind these tensions. It says:
“[T]o truly understand these tensions, we must go beyond labels like ‘anti-science’ or ‘denial’. As some observers noted, resistance to scientific references often stems from legitimate concerns about fairness, representation and historical imbalance in how science – especially the IPCC – is shaped.”
Still, a number of scientists expressed their “concern” over the COP30 outcome. Prof Pamela McElwee at Rutgers University said the situation “mirrors” recent discussions under the Convention on Biological Diversity, calling this a “concerning moment”.
Prof Piers Forster, director of the Priestley Centre, said it had been an “honour” to present the Indicators of Global Climate Change study to the COP.
He added that it had been “gutting to see paragraphs describing our work and that of WMO and IPCC colleagues removed and eroded”.
Similarly, Prof Joeri Rogelj, director of research at the Grantham Research Institute, responded to the situation by saying that it was “very disappointing”.
COP30 was also unable to agree on asking the IPCC to align its seventh assessment cycle (AR7) with the second “global stocktake” under the Paris Agreement, due in 2028.
This is a reprisal of ongoing disputes, which have also been taking place at the IPCC.
Instead, a separate decision “encourages” the scientific community to “provide the best available scientific inputs” and “invites” organisations including the IPCC to “consider how best to provide inputs for the [next] global stocktake in a timely manner”.
Finally, the RSO text does “note…with concern” the funding issues reported by the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS), described by Agence France-Presse as a “crucial UN-backed programme that tracks and evaluates data on the atmosphere, land and ocean”.
In an interview with the newswire, GCOS deputy chair Peter Thorne said budget cuts from the US left the system “under considerable strain”, adding:
“This is possibly the first time we’re looking at an acute reversal in our capability to monitor the Earth, just when we need it the most.…GCOS itself will close its doors at the end of 2027 without additional funds.”
Just transition work programme
The outcome of the “just transition work programme” (JTWP) at COP30 has been hailed by many in civil society as a “victory”, thanks to the adoption of a new institutional mechanism.
Ahead of the summit, a number of civil society groups put together a proposal for a mechanism they dubbed the “Belém action mechanism” (BAM). This would provide a centralised hub to support just transitions around the world.
Over the course of the two weeks, organisations published an open letter calling for the creation of the mechanism, numerous “actions” took place within the corridors of COP, banners bearing the “BAM!” logo were carried during the people’s protest and badges were worn by delegates.

On the second day of negotiations, the G77 plus China put forward a proposal for a just transition “mechanism”, which would provide technical assistance, international cooperation and help foster partnerships in an effort to address implementation gaps.
This proposal “fires the starting gun on serious negotiations,” Teresa Anderson, global lead on climate justice for ActionAid International, said in a statement.
Norway, the UK and others, however, opposed the creation of a mechanism, arguing it would duplicate existing systems, take at least five years to set up and citing a lack of funding, according to the Earth Negotiations Bulletin (ENB).
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Dr Leon Sealey-Huggins, a senior campaigner at the charity War on Want, said a mechanism would help resolve areas of duplication that already exist in the just transition space, by providing a centralised home for resources.
At the end of the first week, the EU proposed a just-transition “action plan” as an alternative to a mechanism, according to the ENB. It suggested this would be hosted by the UNFCCC and facilitate knowledge exchange, enhance capacity and ensure participation of non-party stakeholders.
JTWP co-chair Joseph Teo noted that there was overlap between the proposals for an action plan or a mechanism. However, Dr Amiera Sawas, head of research and policy at the Fossil Fuel Non Proliferation Treaty Initiative, told Carbon Brief that an action plan was a “less ambitious proposal” that was “more about mapping and understanding what potential initiative exists”.
In the second week of COP30, negotiators tried to find agreement on either a mechanism or an action plan.
A text published on 17 November listed both as options. Additionally, it included language on the “meaningful participation” of a range of groups, including, for the first time, people of African descent. This language made it into the final text.

Anabella Rosemberg, senior advisor on just transition at NGO umbrella group CAN International, told Carbon Brief that developed countries disliked the word “mechanism” more than the functions proposed within the text. But she said that the alternative proposal for an action plan had flaws, adding:
“It doesn’t give the sense [that] this is the single address where I can send my request and I will get an answer on where I can be supported. It sounds very silly, but there is a difference if you have a coordinating entity or you don’t. Because if you don’t, it’s just a dialogue. It’s a series of events.”
By the end of the summit, negotiations were able to converge on the idea of establishing a just transition “mechanism”, as set out in the final text.
Dr Sealey-Huggins welcomed the outcome, despite wider aspects of COP30 “falling short”. He added:
“This mechanism is not the end of the struggle, but it is a vital victory that anchors our fights for justice within the UN… BAM shows the power of grassroots and frontline leadership.”
However, other elements of the text were ultimately “watered down”, according to Antonio Hill, advisor at the Natural Resource Governance Institute (NRGI).
Other points of contention within the just-transition negotiations included the cross-border impact of climate-related trade measures (see: Unilateral trade measures) and suggestions for the inclusion of a footnote on gender (see: Gender).
There was also disagreement on some language in the texts, including on connecting a 1.5C warming limit with a just transition and mentions of a transition away from fossil fuels. There was also disagreement on the role of “transition fuels” and text about integrating the outcomes of the first “global stocktake” into the work programme.
Additionally, earlier drafts of texts included a paragraph that “recognise[d]” the “risks arising from the extraction and processing of critical minerals”.
This was the first time that minerals have been included in a text within the UNFCCC process. However, there were diverging views on the inclusion, Hill told Carbon Brief:
“The main opponent – and, possibly, really the only major obstacle – was China…That points to a bit of a schism within the G77 and China, because, while they’re all supportive of the mechanism, clearly they have differences on this point. Both LDCs and Africa Groups still told us…that the minerals piece is important for them.”
Ultimately, the final text gavelled through during the closing plenary did not include references to critical minerals, transitioning away from fossil fuels or trade measures.
Nevertheless, the creation of an institutional mechanism around just transition saw the adoption of this text being greeted by extended applause in the COP30 closing plenary.
Reflecting on the outcome, Rosemberg celebrated the “victory” and told Carbon Brief::
“The just transition mechanism comes with the most progressive rights-based framing we have ever seen in a COP decision. For the first time, labour rights, human rights, the right to a clean environment, ‘free, prior and informed consent’ and the inclusion of marginalised groups are all recognised as core to achieving more ambitious climate action…This is our victory, carved out despite all odds.”
Loss and damage
Despite tense disagreements, “loss and damage” negotiators managed to agree on a number of texts, including a “review” that has proved difficult to wrap up over the past year.
Loss and damage caused by climate-related disasters featured in multiple COP30 negotiating tracks, with the focus restricted to technical and procedural matters.
Developed countries have historically blocked discussions on the topic, but the Belém summit saw a small number of developing countries hold up proceedings.
Observers and negotiators told Carbon Brief there was frustration over the slow progress in negotiations, as well as the lack of new financial pledges from developed countries.
Finance for the loss and damage in developing countries has long been a fraught topic at UN climate talks. Despite being established two years ago at COP28, progress in “filling” the UN fund for responding to loss and damage (FRLD) has been slow.
At a week-one COP30 event, the fund launched its first-ever call for funding requests, in a process called the “Barbados implementation modalities”.
So far, mostly developed countries have collectively pledged $790m to the FRLD, but only $397m of this has been paid into the fund. The initial round will distribute $250m of grants over the next six months to nations in need of support.
Jorge Gastelumendi, an FRLD board member representing Peru, told Carbon Brief this would serve as a demonstration phase to “show that you can move money fast” and justify more future contributions.
The FRLD figures being discussed are a fraction of developing countries’ annual needs, which are in the hundreds of billions of dollars.
NGOs and climate-vulnerable nations had hoped to see strong language in a negotiated “report of the FRLD” that would encourage developed countries to pay more into the fund.
These hopes largely failed to materialise in the final text. However, it does link the FRLD to the new climate-finance goal agreed at COP29 last year.
Another loss-and-damage stream concerned a joint annual report of the Warsaw International Mechanism (WIM) executive committee and the Santiago Network. These bodies focus on research and technical support for developing countries.
Negotiators managed to adopt the report at the end of the first week in Belém, but it was only “noted”, rather than “welcomed”, due to a last-minute Arab group request.
(There is a range of verbs that can be used to offer “praise or recognition” in UN legal texts. To “note” something is the least effusive option available.)
Parties had wanted to wrap up the annual report quickly so they could spend time on a more complicated matter – the long-delayed third WIM review.
Early on, AILAC and Vanuatu called for the review text to reflect the recent International Court of Justice (ICJ) advisory opinion, which found that states can be held legally accountable for emissions and that climate victims may be entitled to “reparations”.
The Arab group rejected this idea, calling for more time in closed-door briefings rather than advancing the text.
Lien Vandamme, a senior campaigner at the Centre for International Environmental Law (CIEL), told Carbon Brief this was likely due to parties in the group being “addicted to fossil fuels production”, meaning the ICJ’s opinion “is not good news for them”
Ultimately, there was no reference to the ICJ in the text.
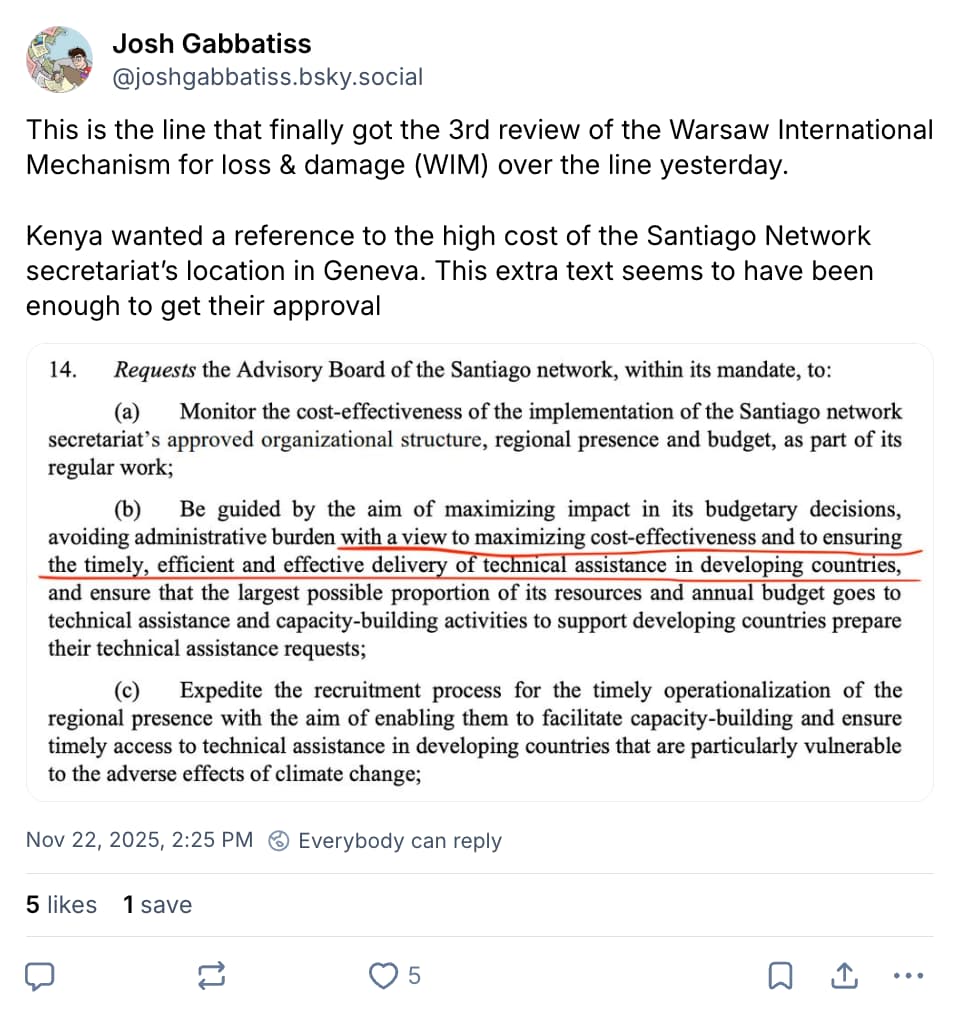
Kenya was also charged with blocking progress right into the final hours, due to a long-standing grievance about the location of the Santiago Network secretariat, which it had wanted to host in Nairobi.
Given this, Kenya was keen to include text stressing the high costs of the secretariat’s ultimate location in Geneva, Switzerland. Observers told Carbon Brief that Kenya refused to back down, despite unanimity across other parties.
In the end, tweaked wording in the paragraph about “cost-effectiveness” appeared to satisfy the Kenyan delegation.
By the end of COP30, negotiators had spent more than 80 hours discussing the WIM review since 2024. Hafij Khan, a co-chair of the WIM executive committee, highlighted the slow pace of the talks compared to the needs of climate-vulnerable communities.
“No more of these negotiations here, please. It is enough. It [has taken] more than a decade to develop this landscape,” he told Carbon Brief.
Gender
At COP30, rows over the definition of gender emerged across some high-profile negotiation streams.
Argentina, Paraguay and the Holy See – the governing body of the Vatican – among others, sought to emphasise binary approaches to gender in COP decisions.
For example, in the just transition work programme (JTWP) negotiations, Paraguay proposed the inclusion of a footnote saying that it “understands the term gender…as referring to the female and male sexes”. Ultimately, this was rejected.
This reflects a trend, which has been highlighted repeatedly at UN climate talks, where religiously conservative and right-wing governments object to more progressive language on gender.
Anabella Rosemberg, senior advisor on just transition at NGO umbrella group CAN International, told Carbon Brief that this approach was also “very dangerous for the process”, cautioning that, if parties are allowed to define terminology in this way, it “opens a whole Pandora’s box about how we build up decisions here”.
At COP30, parties were officially tasked with adopting a new “gender action plan” (GAP), following the renewal of the Lima work programme on gender at COP29 in Baku.
While the Lima work programme establishes the overarching principles for addressing gender equality under the UNFCCC, the GAP sets out specific actions for implementing gender-responsive climate action. The GAP also provides indicators for parties to measure their progress on gender-related issues.
The GAP sets out five “priority areas” for action:
- Capacity-building, knowledge management and communication.
- Gender balance, participation and women’s leadership.
- Coherence across different workstreams, processes and other UN conventions.
- [Gender-responsive] implementation and means of implementation.
- Monitoring and reporting.
In a press conference on 19 November, Mary Robinson, former president of Ireland, UN high commissioner for human rights and chair of the Elders, said:
“Gender equality isn’t an add-on to climate policy, it’s a measure of its effectiveness. When women and gender-diverse people are at the table, climate policies are more ambitious, more inclusive and more durable.”
The draft GAP that came out of the Bonn intersessional meeting in June, contained 99 bracketed areas of disagreement, including on language around reproductive and sexual health and rights, as well as the equal participation of women in UNFCCC processes.
Indeed, divergent political and cultural stances on gender became a key point of contention at the meeting.
Countries’ views only became more divergent as the negotiations in Belém stretched on. The second draft of the GAP, released on 14 November, contained 275 brackets, while a third iteration released on 18 November had 496 areas of disagreement.
Several countries sought to add footnotes to the GAP, amending the definitions of gender that had previously been agreed under the UNFCCC.

Three days later, as COP30 entered its final hours, a new draft was published with just one set of brackets remaining, around the entire text.
While this was ultimately adopted during the closing plenary, the Holy See again raised an objection, recalling its declaration that references to gender “be understood as grounded on the biological sexual identity that is male and female”.
It added that it “upholds and promotes a holistic and integrated approach that is firmly centered on the human dignity and integral human development of every person”, requesting that its statement be reflected in the report of the COP.
The intervention was met by booing from many gathered in the plenary hall.
Article 6
In Baku last year, countries had finally agreed on the rules for carbon trading under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement. In theory, this meant that there would be no more formal negotiations on Article 6 until 2028, when these rules are up for a scheduled review.
However, the bureaucratic matters on the table in Belém were more complicated to settle than expected. In the end, the decisions that were adopted “add marginal improvements” to the Article 6 rulebook, says Isa Mulder, a policy expert at NGO Carbon Market Watch.
There are relatively few rules under Article 6.2, which governs country-to-country carbon trading, but countries must detail their activities via “initial reports”.
These reports are scrutinised by a “technical export review”. The first six of these have now been completed, covering Ghana, Guyana, Suriname, Switzerland, Thailand and Vanuatu.
In Belém, negotiations focused on whether and how to request more detail and transparency in this reporting and review process. A particular issue was the fact that, to date, “all trades” under Article 6.2 have been flagged with “inconsistencies” during expert review.
The COP30 decision simply “notes” these inconsistencies and “urges” countries to sort them out, while adding that the reporting and review process is still “in the early stages”. It also asks reviewers to “clearly explain” any issues they find and how to resolve them.

In contrast, there is now a complex set of standards, methodologies and guidance that is being built to govern the new international carbon market under Article 6.4.
At COP30, negotiations focused on the annual report of the “supervisory body” that is in charge of this. The body had been given standard-setting autonomy at COP29.
It had recently adopted a standard on non-permanence, which had been the subject of heated debate in the sector. The standard describes how to handle the risk of a project removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, selling this removal as a carbon credit and then seeing the stored carbon released into the atmosphere once again, known as “reversal”.
In a joint letter, a group of NGOs and carbon-trading advocates said this and other standards “could exclude all land-based activities”, such as forests, from the Article 6.4 market.
They called for new guidance to be given to the supervisory body to prevent this from happening. Their recommendations – which were opposed by some scientists and other NGOs – were picked up and reflected in an early draft text at COP30.
In the end, however, such detailed guidance to the body was rejected. Many countries saw this as an attempt to “micro-manage” its work.
The debate shows there is an “ongoing challenge” to balance robust rules with a system that can drive investment and near-term climate action, said Beatriz Granziera, senior policy adviser at The Nature Conservancy (TNC), one of the signatories of the joint letter.
COP30 also debated the limits on the terms of the supervisory body members, which some countries wanted to extend. Instead, the final text leaves the term limits in place and decides to look at them again as part of the wider review of the rules that is already due in 2028.
This was a “good” outcome, says Andrea Bonzanni, international policy director at industry group the International Emissions Trading Association (IETA). He told Carbon Brief:
“It is good they did not agree to reopen the rules…It would have set a bad precedent and increased uncertainty in carbon markets. If the signal is that all rules are up for litigation every year, it is difficult to make investment decisions and unlock finance.”
The COP30 decision also “reiterates” that supervisory body members should not have “any financial or other interests” that could affect – or be seen to affect – their impartiality.

The Article 6.4 decision text gives a six-month extension, until June 2026, for carbon-credit projects registered under the “clean development mechanism” (CDM) of the Kyoto Protocol to “transition” into the Paris Agreement’s new carbon market.
In theory, this could allow up to another 760m tonnes of CO2 equivalent (MtCO2e) of credits to enter the Paris Agreement regime. Most would not be “additional” CO2 reductions, because the linked projects will operate even if they cannot sell new carbon credits.
Finally, in a related decision, COP30 says the CDM will close by the end of 2026. It also loans $26.8m from the CDM “trust fund” to the equivalent fund for Article 6.4.
Agriculture and food security
With agribusiness giant Brazil hosting this year’s summit, many expected COP30 to have a stronger focus on agriculture and food than previous years.
Formal negotiations for agriculture and food systems at the UNFCCC fall under the Sharm el-Sheikh joint work on the implementation of climate action on agriculture and food security (SJWA). COP30 ended without a substantive outcome for the SJWA.
The current four-year mandate of SJWA – which runs workshops, is developing an online portal and prepares an annual synthesis report of agriculture-relevant work undertaken by UNFCCC bodies – began in 2022 and runs out at COP31 next year.
At COP30, the main points of discussion for countries were a consideration of the outcomes of a workshop on “systemic and holistic approaches” to implementing climate action on food and agriculture, as well as countries weighing in on a special forum of the standing committee on finance (SCF) on financing for sustainable food systems and agriculture.
As the summit got underway in Belém, several parties began pushing the idea of capturing key messages from the workshop and forum into a formal SJWA decision.
Observers told Carbon Brief that Argentina, the African group and the LDCs wanted “means of implementation” – shorthand for finance – added to the text, while the EU opposed references to “Article 9.1” in the agriculture workstream. (See: Climate finance.)

The next day, various blocs circulated text proposals on recognising the workshop outcome, seen by Carbon Brief. These included proposals from EU and EIG on food systems “which span the entire value chain”, links to biodiversity, “precision agriculture” and market-based rewards for farmers.
G77 and China, meanwhile, flagged 13 points for inclusion in the draft text, including recognising the “fundamental priority of ending hunger” and a call for developed countries to “significantly scale up…grant-based finance for adaptation actions in agriculture”.
Language from all of these proposals was incorporated into a draft text released on the first Thursday of COP30.
This draft – with 23 square brackets, indicating text not yet agreed – included many references, ranging from agroecology to AI-farming and using “high-integrity carbon-market approaches under Article 6” to reward farmers.
It also recognised that the World Trade Organization (WTO) “can be useful in ensuring a stable, predictable global agricultural trade underpinned by rules” that support climate action.

Five hours later, this was replaced by a brief draft, which postponed further discussions until June next year, taking into account the earlier text.

Many observers expressed their dismay at negotiations finishing so abruptly, before the end of week one and without a substantive outcome.
Teresa Anderson, global climate justice lead at Action Aid International, tells Carbon Brief that negotiations “took a turn for the worse” after Australia and the EIG “pushed for dodgy language” on what could be considered “systemic” and “holistic”. Anderson says:
“In June, many countries talked about agroecology. And yet here in the COP, Australia and others just submitted language on precision agriculture, on AI and just basically a lot of corporate greenwash…[C]ountries weren’t able to agree on [this] because there was just too much new nonsense in there.”
The final draft conclusions “recognised that progress was made at these sessions” and “noted that more time is needed to conclude the discussions thereon”.
Mitigation work programme
The mitigation work programme (MWP) was one of the less contentious agenda items at COP30. It was established at COP26 to “urgently scale up mitigation ambition and implementation in this critical decade”, but has consistently failed to deliver.
The three main areas of discussion at COP30 were the potential for a digital platform, the dialogues held this year and the future of the work programme.
Echoing disagreements seen at the Bonn negotiations in June, parties quickly split over the potential development of a digital platform. Some delegations questioned whether it would just duplicate other existing ones, noting that it could be a resource drain.
Speaking to Carbon Brief, Lola Vallejo, diplomacy and partnerships director at the European Climate Foundation (which funds Carbon Brief) and former co-chair of the MWP, explained that the potential for a platform has come out of the “pitch hubs” that take place within the work programme’s dialogues.
These essentially “matchmake” mitigation projects with finance, she continued, adding:
“The open question for a lot of negotiators is still to what extent should the secretariat itself be involved in kind of providing this matchmaking, considering it requires a lot of skills, and you have [other] organisations…supporting the emergence of these projects…So, to what extent will that fall under the UNFCCC and MWP itself?”
Within the first sets of draft texts on the MWP, several “options” suggested a platform could be launched using the mitigation component of the UNFCCC’s existing “NMA platform”.
Ultimately, both the final text and the draft decisions released on 21 November, “takes note of the NMA platform”, requests that parties “consider ways to implement additional functionalities” on the platform and requests that the secretariat prepare a technical paper.
Two dialogues were held under the MWP in 2025, one focused on forests and one on waste, captured in a report ahead of COP30.
Teppo Säkkinen, advisor on climate, energy and industries at the Finland Chamber of Commerce, told Carbon Brief that these discussions have been “helpful”. He said:
“In some instances, the MWP has been helpful. There have been texts on cities, urban areas, [and] now on forests and waste, going really into the practicalities of decarbonisation. On the other hand, it has been such a struggle…to get anything on ambition.”
With the MWP coming to an end next year, Säkkinen noted that the “big question for after 2026 is if the MWP is a dead horse, or if it can really have some practicality and kind of be an avenue for that mitigation discussion”.
There remains a lack of clarity about what is next for the MWP, including the topics for dialogues over the coming year, which were not specified in the final text gavelled through on Saturday 22 November.
Indeed, within the closing plenary, Colombia objected to the MWP text due to the exclusion of specified dialogue topic for 2026.
It called for them to be focused on “industry and the pathways for implementing the transition away from fossil fuels, in a just, orderly and equitable manner in line with the best available science”.
Following a pause in the plenary, Corrêa do Lago requested further work on the MWP in Bonn next year, in recognition of the interventions.
COP reform
There is a rising clamour for reform of the UN climate process. It was on the COP agenda for the first time in Belém, under the title, “arrangements for intergovernmental meetings” (AIM).
Ideas on the table included capping the size of national delegations, as well as “sunsetting” agenda items and limiting the number of new issues that could be added.
Ultimately, COP30 adopted very limited conclusions that simply “invited parties to pursue efficiency in the consideration of agenda items at sessions”. Talks will continue next year.
The outcome was a “nothingburger”, said Erika Lennon, senior attorney at the Center for International Environmental Law (CIEL). She told Carbon Brief: “Normally AIM is not a COP agenda item and it didn’t seem parties were keen to have a lot on it here.”
The need to make the UN climate regime more efficient had been recognised by the Brazilian COP presidency in a letter published in May, which stated:
“Recognising growing calls for change at COPs, the COP30 presidency invites all parties to reflect on the future of the process itself.”
Any hopes that this might lead to substantive reform were quickly snuffed out by the first draft text on the agenda item, published on 13 November.
This ran to just five paragraphs, “not[ing] the efforts of the secretariat to cluster mandated events” and agreeing to continue discussions in Bonn in June 2026.
A longer draft appeared on 14 November, recalling and reaffirming text agreed at the Bonn meeting in June. This went on to be formally adopted at the end of the first week of talks.
However, it bears little relation to the more substantive ideas put forward by experts, ranging from the introduction of voting through to restrictions on which countries can host the COP.
The process has become “increasingly messy and procedurally complex”, says Dr Joanna Depledge, an expert on the international climate negotiations at the Cambridge Centre for Environment, Energy and Natural Resource Governance. She told Carbon Brief:
“A handful of items have been on the COP agenda for years, but are essentially dormant. Others are duplicated…for political reasons. Still more – like in Belém – receive all the political attention, despite being excluded from the agenda…The agenda urgently needs decluttering and rationalising”.
Some observers were hoping that a separate agenda item, called “cooperation with other international organisations”, could see a substantive new outcome on bringing together more closely the work of the three Rio conventions on climate change, biodiversity loss and desertification.
(Scientists and politicians have for years called for climate change and biodiversity loss to be tackled in a more cohesive way.)
After pledging to make COP30 a “nature COP”, the presidency held consultations on this item, attempting to rally support for an ambitious new outcome.
A draft “areas of interest” text linked to the issue spoke of “creat[ing] a space for continuous discussions to enhance cooperation among the Rio conventions” and the “establishment of a process to come up with a set of recommendations on how to enhance cooperation and policy coherence”.
However, several nations, including Saudi Arabia, vocally opposed the progression of a substantive outcome – and the final version of the “synergies” text is just five paragraphs long, containing little that is new.
Observers pointed out to Carbon Brief that Saudi Arabia’s opposition was particularly puzzling, given it currently holds the presidency for the desertification COP.
In an interview with Carbon Brief, Dr Osama Faqeeha, deputy environment minister for Saudi Arabia and chief adviser to the COP16 desertification presidency, said that the nation does not “support dissolving the conventions”.
Around the COP
Fossil-fuel roadmap
The call for a new fossil-fuel “roadmap” dominated headlines and some countries’ priority lists at COP30 – despite not being part of the summit’s official agenda.
Speaking during the world leaders summit in Belém ahead of the talks, Brazilian president Lula said that the world “need[s] roadmaps to justly and strategically reverse deforestation [and] overcome dependence on fossil fuels”. (He later reiterated his call during COP30’s opening plenary.)
Lula’s speech marked the first public call for a new “roadmap” away from fossil fuels to be a key feature of the talks.
However, an observer close to the process told Carbon Brief that the COP30 presidency had, in fact, been consulting on the possibility of a roadmap months earlier – drawing help from the Beyond Oil and Gas Alliance, a small group of nations who have pledged to phase out all fossil fuels.
While Brazil was the first country to support the fossil-fuel roadmap, it was joined in the first few days of COP by the seven Latin American countries that form the Alliance of Latin America and the Caribbean (AILAC) and by the Environmental Integrity Group (EIG), which includes Mexico, Liechtenstein, Monaco, South Korea, Switzerland and Georgia.
The call for a roadmap was also backed by the Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS), a group of 39 small low-lying island nations.
As momentum grew, questions were raised about whether the fossil-fuel roadmap, if agreed, would be included in COP’s formal negotiations or be decided separately.
At a press briefing on Saturday 15 November attended by Carbon Brief, UK special climate envoy Rachel Kyte said that “how to land” the roadmap was “up to the presidency”, noting that a “process outside of the negotiated outcomes” could “speed up delivery”.
On Tuesday 18 November, the idea of a fossil-fuel “roadmap” was brought into the negotiations space when it was referenced in the first draft of the “global mutirão” text, the key negotiated outcome of the Belém talks. (See: Global mutirão.)
Paragraph 35 of the text listed three options for where a reference to a fossil-fuel roadmap map might be incorporated, including one option for “no text”.
![Screenshot of text, saying: 35. Option 1: [Decides to convene a workshop for Parties to] [Invites Parties to] share domestic opportunities and success stories on the just, orderly and equitable transition towards low carbon solutions, taking into account countries' different national circumstances, pathways and approaches, and the principles and provisions of the Paris Agreement; Option 2: Encourages all Parties to cooperate for and contribute to the global efforts referred to in paragraphs 28 and 33 of decision 1/CMA.5 in a nationally determined manner, taking into account the Paris Agreement, and decides to convene a high-level ministerial round table on different national circumstances, pathways and approaches with a view to supporting countries to developed just, orderly and equitable transition roadmaps, including to progressively overcome their dependency on fossil fuels and towards halting and reversing deforestation; Option 3: no text;](https://breakingclimatechange.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Daisy_Ragout__35_-2.png)
Later that day, ministers and climate envoys from more than 20 countries united for a packed-out press conference, where they called the current reference to the fossil-fuel roadmap “weak”, adding that it must be “strengthened and adopted”.
At the sidelines of the conference, Kyte told journalists that around 80 countries now backed the call for a roadmap.
Carbon Brief obtained the list of countries that expressed their support, which grew to 86. It includes both developed and developing countries and some nations with significant government revenues from fossil fuels, such as Colombia, Australia, Norway, Guyana and Brazil.
However, COP30 CEO Ana Toni told a press conference later that evening that a “great majority” of country groups they had consulted saw a fossil-fuel roadmap as a “red line”.
It was claimed that this group also numbered around 80 countries, including some petrostates, such as Saudi Arabia and Russia. However, some observers questioned this figure and a list of opposing countries was never made public.
In an interview with Carbon Brief, Dr Osama Faqeeha, deputy environment minister for Saudi Arabia, refused to be drawn on whether a fossil-fuel roadmap was a red line, but said:
“I think the issue is the emissions, it’s not the fuel. And our position is that we have to cut emissions regardless.”
The next day, the EU officially threw its weight behind the call for a fossil-fuel roadmap, after initial delay caused by hesitation from Italy and Poland to join the movement, Climate Home News reported.
The EU circulated its own proposal for how a fossil-fuel roadmap could be referenced in the global mutirão text, the publication added.
However, on Friday morning, a second draft “mutirão” text emerged – this time with no reference to a fossil-fuel roadmap.
A group of at least 29 countries, including Colombia, Germany, Palau, Mexico and the UK, sent a letter to the presidency – seen by Carbon Brief – saying they could not “support an outcome that does not include a roadmap [on fossil fuels]”, according to the Guardian.
At a separate press conference held on Friday morning, a group of 24 countries signed a new “Belém declaration on the just transition away from fossil fuels”, pledging to “work collectively towards a just, orderly and equitable transition away from fossil fuels”.
Countries supporting the declaration included Australia, Austria, Belgium, Cambodia, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Denmark, Fiji, Finland, Ireland, Jamaica, Kenya, Luxembourg, Marshall Islands, Mexico, Micronesia, Nepal, Netherlands, Panama, Spain, Slovenia, Vanuatu and Tuvalu.
The event also saw Colombia and the Netherlands announce that they will co-host the first international conference on transitioning away from fossil fuels from 28-29 April 2026, in the Colombian city of Santa Marta.
At the sidelines of the press conference, Colombian environment minister Irene Vélez Torres told journalists that she hoped to see a “change to the text” to include a reference to the fossil-fuel roadmap.
Negotiations dragged all through Friday night, with countries split on the inclusion of the fossil-fuel roadmap.
On Saturday morning, a new mutirão text appeared – this one also without any reference to a fossil-fuel roadmap.
A few hours later, a closing plenary was held and the text was adopted with no objections.
After brief applause, Corrêa do Lago acknowledged that some countries were hoping for “more ambitious” outcomes from the text.
He then announced that the COP30 presidency would bring forward two roadmaps, on transitioning away from fossil fuels and deforestation, to present at the next COP. (See: Deforestation.) These will sit outside the formal COP process.
He added that the fossil-fuel roadmap will be guided by the upcoming conference in April on transitioning away from fossil fuels co-hosted in Santa Marta by Colombia and the Netherlands.
‘Action agenda’
A decade on from the Paris Agreement, there has been a growing sense that COPs are disconnected from real-world climate action.
In this context, COP30 was widely framed, by the Brazilian presidency and many others, as an “implementation COP” that would speak directly to this disconnect.
COP30 strategy director Túlio Andrade told a week-one press conference:
“This is the COP we finally transition from negotiation to implementation, so the results and the measure of success are going to be different as well.”
The presidency firmly linked “implementation” to its plans for “action agenda” reform.
First initiated by the Peruvian and French COP presidencies in 2014, the action agenda aims to mobilise voluntary climate initiatives, led by non-state actors from outside the UN climate process.
On top of these action-agenda initiatives, COPs have also been venues for nations to launch their own headline-grabbing pledges that align with their interests.
The UK COP26 presidency’s commitments on “coal, cars, cash and trees” exemplify this.
This has all led to an unwieldy situation, as Cosima Cassel, climate diplomacy lead at E3G, told Carbon Brief:
“There has been a massive proliferation of different pledges…A lot of initiatives doing the same thing, a lot of initiatives not speaking to each other.”
In one of his pre-COP letters, Corrêa do Lago explained that the Brazilian presidency would seek an “ambitious and integrated” action agenda, which compiled and “streamlined” existing projects.
He set out six broad themes and 30 “key objectives” that initiatives would be grouped under, including issues such as “transitioning away from fossil fuels” and “reversing deforestation”.
The Brazilian plan takes in both government-led initiatives – such as those announced by COP presidencies – and various non-state actors such as businesses, NGOs and cities.
Corrêa do Lago said this framework would support the implementation of targets every country agreed to in the “global stocktake” (GST) in 2023. He wrote that this approach would “transform climate action from cacophony into an orchestrated symphony”.
Brazil’s “high-level climate champion” Dan Ioschpe, who led on the action agenda for COP30, told Carbon Brief:
“We are not the ones proposing new initiatives or new pledges…We need to speed up the existing ones, because really we are talking about implementation.”
In total, the presidency team reached out to around 700 existing climate initiatives in the months prior to COP30. Only 482 of these initiatives engaged with the process. (As it stands, 261 of them appear on the official portal.)
The presidency declined to share the full list with Carbon Brief, but this suggests there could be hundreds of international initiatives that – for whatever reason – are no longer operating.
In the run-up to COP30, initiatives that responded to the presidency’s callout were encouraged to report their progress on another UN portal.
Those initiatives with overlapping goals joined together to create 117 “plans to accelerate solutions”, each under a specific “host” organisation, to consolidate their work. Each plan set out actions for the initiatives involved to take by 2028, the end of the current GST period.
While all of these “plans” were technically launched at the start COP30, some were announced formally during the event, including one to “accelerate expansion and resilience of power grids” and another dubbed the “Belém health action plan”.
(The latter led to a major announcement in week one when a range of philanthropies, including Wellcome, Rockefeller Foundation, Gates Foundation, Bloomberg Philanthropies and IKEA Foundation, pledged $300m “aimed at developing data and figuring out the best investments for tackling rising risks [to human health] from extreme heat, air pollution and infectious disease”, as reported by Reuters.)
There was also a full schedule of COP30 events where those running the various initiatives, experts and country delegates could discuss the plans.
A “five-year vision” was set out to continue this revised action agenda. It includes annual reviews to track progress towards the key objectives, as well as a broader review of priorities after the second global stocktake in 2028.
Dr Jennifer Allan, a global environmental politics researcher at Cardiff University, told Carbon Brief this process was a “good effort”. She added:
“I think it’s a really good effort just to start to map this all out and bring it nominally under one roof to track…This initiative won’t be able to tell the UN-REDD or the global methane pledge what to do, but it might provide another level of scrutiny.”
As the formal negotiations faced familiar roadblocks, some also saw the action agenda as a way to ensure more ambitious outcomes at the COP overall.
Mauricio Voivodic, executive director at WWF-Brazil, told Carbon Brief the action agenda was becoming a “safe space for discussing contentious topics and for finding ways to overcome obstacles in the negotiations”.
Former French negotiator Paul Watkinson, who has championed the idea of a reformed action agenda, told Carbon Brief that it should be “a key part of the outcome” of COP30.
Watkinson suggested at the start of week two that, without consensus on the fossil-fuel transition and ending deforestation, it might be better to deal with such issues outside the negotiated outcome.
“It is also a way that points to how the COP process could evolve in future,” he told Carbon Brief.
This sentiment was mirrored in the Brazilian presidency’s decision to avoid disputes in the final “mutirão” text by announcing new presidency-led “roadmaps” for dealing with deforestation and fossil fuels outside the UN climate process.
Deforestation
At COP30, there were several key announcements around deforestation, including the “Tropical Forest Forever Facility” (TFFF) and a future “roadmap” to be developed on ending deforestation.
During the Belém talks, momentum began to build around agreeing a roadmap to end deforestation – but it was largely overshadowed by the push for a similar fossil-fuel plan (See: Fossil-fuel roadmap).
At COP26, more than 130 countries had pledged to halt and reverse deforestation by 2030. Although the rate of deforestation is reducing, countries are off track to meet this goal.
A roadmap aimed to help achieve this deforestation target did not appear in the final mutirão decision agreed at COP30. However, in the closing plenary of the summit, Corrêa do Lago said the Brazilian presidency would work to create deforestation and fossil-fuel roadmaps outside the COP negotiation process.
Before COP30 began, in a speech at the opening of the leaders’ summit, Lula had called for roadmaps to “reverse deforestation, overcome dependence on fossil fuels and mobilise the resources required to achieve these goals in a fair and planned manner”.
By the second week of negotiations, around 45 countries backed a deforestation roadmap, including Brazil, Colombia, Mexico, the EU and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, according to a Carbon Brief tracker. This increased to at least 92 countries by Friday 21 November, after a large group of more than 50 rainforest nations got behind the proposal.
The first draft of the mutirão decision put forward by the Brazilian presidency on 18 November included optional text to create a “high-level ministerial round table”, aimed at supporting countries to develop their own national roadmaps on transitioning away from fossil fuels and halting and reversing deforestation.
The language around this was criticised as weak by some observers, but its inclusion was widely welcomed.

WWF and Greenpeace had urged countries to adopt the deforestation roadmap “as a formal outcome at COP30”, while Colombia’s environment minister Irene Vélez-Torres wrote in Backchannel:
“We need to see the global north come behind a roadmap – and quickly.”
However, the next draft published on 21 November removed mention of both deforestation and fossil-fuel roadmaps, as was the case with the final text signed off on 22 November.
Although more than 90 countries backed the deforestation roadmap, “wider political will to secure this in Belém was lacking”, WWF said in a statement.
Carolina Pasquali, executive director of Greenpeace Brazil, said that Lula’s government had “set the bar high” in calling for deforestation and fossil fuel roadmaps, but the “divided multilateral landscape was unable to hurdle it”.
The final decision did mention deforestation once, emphasising the importance of boosting efforts to halt and reverse deforestation by 2030 to help achieve the Paris temperature goal.
Meanwhile, Brazil’s forest fund, the TFFF, was officially launched at the COP30 leaders’ summit, in the week prior to the start of the formal negotiations.
This facility aims to pay countries for keeping their tropical forests standing. To that end, it is designed as a “blended finance vehicle”, which seeks to raise $25bn from “sponsor” countries – mainly developed nations – and philanthropies.
The TFFF hopes to use this capital to attract another $100bn from private investors in the global bond market.
During the launch, the facility received $5.5bn from Norway, Brazil, Portugal, France and Netherlands and another $1.1bn from Germany. It was endorsed by 53 countries, including 34 tropical forest countries and 19 potential sovereign investors.
The COP30 presidency described it as a “significant milestone [that] marks the beginning of a new era of global collaboration between public and private investment”.
This scheme is expected to benefit 74 tropical forest countries, including those in the Amazon and the Congo basin.
Experts have questioned various requirements countries would need to meet in order to receive the investment, such as transparent financial management and allocation of 20% of the funds to Indigenous peoples.
Additionally, some have cautioned that conservation funding for climate-critical forests should not depend on “betting on stock market prices”, questioning how much the fund would actually raise in “rainforest rewards” and instead call for new biodiversity finance.
The facility still needs to clarify certain operating rules and has received both supportive and critical responses.
Sandra Guzmán, founder and general director of the Climate Finance Group for Latin America and the Caribbean (GFLAC), said that while the fund has positive aspects, such as promoting financial innovation to include the private sector, it also has contributed to spreading limited funds more thinly. She told Carbon Brief:
“[Brazil’s government] tried to [boost] the TFFF and did not put their political and diplomatic strength into other mechanisms, for example, the Baku to Belém Roadmap agreed upon at COP29 with the aim of mobilising up to $1.3tn by 2035.”
After the launch of the TFFF, it was rejected by 150 civil society groups and Indigenous peoples’ organisations, who said it “does not seek to address the true structural causes of forest destruction” and “does not prioritise Indigenous peoples and local communities”.
Patricia Suárez, advisor of the Organization of Indigenous Peoples of the Colombian Amazon (OPIAC), told Carbon Brief that Indigenous peoples from Brazil and Colombia have advised the fund so that the resources from the facility reach Indigenous territories.
She noted that the Amazon peoples are working for the Indigenous fund INDII – launched in 2024 by OPIAC and the Inter-American Development Bank – to channel any funds going to the Amazon, such as the TFFF, to Indigenous territories and governments.
China at COP30
The absence of the US from talks in Belém sparked expectations that China would assume the mantle of leader.
However, Chinese climate leaders consistently refuted these calls. Chinese climate envoy Liu Zhenmin said that the commentators were just “the west giving us a ‘tall hat’” – meaning trying to flatter China.
Wang Yi, vice-chair of China’s expert panel on climate change, said in an interview with the Guardian that he did not think China “would like to play a leadership role”.
At the China pavilion, the word “leadership” (领导) was rarely, if ever, uttered by the nations’ delegates.
However, they still sought to position the country as a strong advocate for multilateral climate action and the global energy transition.
Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) head Huang Runqiu said during the first session at the China pavilion, attended by Carbon Brief: “We have become a committed actor and active contributor to green and low-carbon development.”
Any mentions of leadership by Chinese representatives typically were within the context of the country’s leading position as a provider of a specific “climate good”, such as clean-energy technologies.
The topic was more frequently raised by speakers representing non-Chinese institutions at the pavilion.
For example, Selwin Hart, special adviser to the secretary-general on climate action and just transition at the UN, told a crowd at the China pavilion that “we are certain to count on the leadership of China over the course of the next two weeks”.
China’s status in the climate talks underpinned a significant sticking point in discussions – the question of the provision of “financial resources” from developed to developing countries under Article 9.1. (See: Climate finance.)
As part of the LMDC group, China called for implementation of this paragraph to be included in the COP30 agenda.
While it is officially considered a developing country at the UNFCCC, there has been speculation that it could adopt greater responsibility in climate action – especially around climate finance – due to the rapid growth of both its economy and emissions over recent decades.
With discussions of climate finance looming large at COP30, China proposed during the second week the development of a “practical roadmap for implementation”, by developed countries predominantly, of the $300bn NCQG climate-finance goal.
Li Gao, MEE vice-minister and China’s head of delegation, said this would help “avoid blame-shifting…and prevent further erosion of trust” on climate finance.
In the end, while COP30 resulted in a plan within the mutirão decision to develop a “two-year work programme on climate finance” that included a mention of Article 9.1, it was situated within the “context of Article 9…as a whole”. This means that developing countries’ contributions also fall under its scope.

The tone of China’s arguments in Belém stood in firm contrast to COP29, when executive vice-premier Ding Xuexiang chose to make a link between China’s overseas financing and climate finance, sparking commentary that the country could be open to providing climate funding to other global-south countries in future.
“The EU needed to spend its biggest leverage [at COP30] to adjust the adaptation-finance goal,” Kate Logan, director of the China climate hub and climate diplomacy at the Asia Society Policy Institute (ASPI), told Carbon Brief. (See: Adaptation.)
During the leaders summit in Belém on the eve of COP30, Ding’s speech contained few surprises and did not mention China’s provision of south-south climate finance.
Instead, he said that “developed countries should fulfill their obligations to take the lead” on cutting emissions, delivering finance and providing technological and capacity-building support.
China also refrained from contributing to Brazil’s new forest fund, the TFFF, despite news reports in June saying it had signalled interest in investing. (See: Deforestation.)
Carbon Brief heard multiple explanations from analysts for this decision, including: questions by China around the operation of the fund; challenges reaching an agreement between different ministries; a desire for greater say in the fund’s design; and concerns around what contributing would mean for China’s position on climate finance.
China’s role in south-south cooperation nevertheless remained a major theme of its activities at COP30, building on months of momentum from high-level exchanges with Brazil and other emerging economies.
A “high-level summit” on south-south cooperation was held in the China pavilion on the first day of COP30 – signalling the importance China placed on the topic. Speakers included Huang, Hart and COP30 CEO Ana Toni, among others.
“We pay attention to the needs of developing countries,” Huang said at the summit, attended by Carbon Brief. He noted that China had signed a number of agreements with other global-south countries on climate as a sign of its commitment.
China also launched several initiatives at the pavilion aimed to support global-south countries’ climate action, including a training dataset for AI-driven extreme-weather early warning systems and a clean-stove initiative with Kenya and Malawi.
The pavilion often received visitors from global-south countries, with the south-south cooperation session being particularly well-attended.
Tyler Harlan, associate professor of urban and environmental studies at Loyola Marymount University, spoke with many global-south delegates about their impression of China’s presentations.
He told Carbon Brief that many delegates were interested in China’s provision of clean-energy technologies and its role as an example of what a “rapid transition” could look like – although he noted that the concepts and language often “didn’t fully resonate”.
By contrast, there was a marked lack of EU-China coordination, despite efforts to develop a united stance in July.
There were some signs of cooperation between the two parties, such as an early announcement that they both would join Brazil’s carbon-market coalition and the launch of two reports co-developed by Chinese and European bodies.
(Brazil, China and the UK also co-led a summit on methane, pledging to “accelerate global action” on non-CO2 greenhouse gases.)
However, any initial atmosphere of EU-China cooperation quickly dissipated. Multiple observers told Carbon Brief that early negotiations featured a rancorous back-and-forth between the two on the ambitiousness of their respective 2035 emissions reduction targets.
Comments by EU climate commissioner Wopke Hoeskstra ahead of the COP that China’s target was a “missed opportunity” drew a response from Chinese climate envoy Liu Zhenmin that the EU’s own target was “not so good”.
Another point of contention between the two was the role of “unilateral trade measures” (UTMs). (See: Unilateral trade measures.)
These referred not only to the EU’s CBAM – from which Carbon Brief understands China does not expect to see a significant impact – but also policies such as the EU’s tariffs on Chinese-made electric vehicles (EVs).
The LMDCs again asked for UTMs to be included on the agenda, stating that they “penalise developing countries and impact their ability to take action to address climate change”.
Japan, the EU and others argued that other fora would be “more appropriate” for discussions. The EU also implied that China’s critical-mineral export restrictions could also fall into the scope of discussion, should the item be included.
Ultimately, China and others secured its inclusion in the mutirão text, which says that “measures taken to combat climate change, including unilateral ones, should not constitute a means of arbitrary or unjustifiable discrimination or a disguised restriction on international trade”.
It added that three annual dialogues on UTMs will be conducted, resulting in a “high-level event” and report in 2028.
Separately, China and the UK were among the countries present for the COP30 presidency’s launch of an integrated forum on climate change and trade. However, Carbon Brief understands that neither country has formally joined the platform.
Meanwhile, a mention of critical minerals in a draft just-transition text – a potential first for COP – was deleted by the final version. (See: Just transition work programme.)
Joseph Dellatte, head of energy and climate studies at the Institut Montaigne, told Carbon Brief: “Even though the EU is worried about China’s trade measures on [critical materials], it still wants to strike a deal with Beijing.”
China also faced significant pressure on its approach to mitigating emissions.
The country was not a signatory to calls for developing a roadmap away from fossil fuels. It was also opposed to calls to emphasise the 1.5C temperature limit, instead “requesting the entire Paris Agreement temperature goal…be mentioned”.
Fossil fuels were not explicitly mentioned in the final mutirão text and language on a “Belém mission to 1.5C” was weakened. (See: Global mutirão.)
Arguments by China that the UAE dialogue should not become a “mini-GST” also seem to have been considered, with no mention of an annual agenda item in the final outcomes. (See: Ambition and 1.5C.)
The mutirão text “sends a red alert” on the consensus on fossil fuels, Greenpeace East Asia’s global policy advisor Yao Zhe told Carbon Brief, adding that the outcome reflected the “lowest common denominator”.
Li Shuo, director of ASPI’s China climate hub, said that, despite this, China’s prior agreement to transition away from fossil fuels would “guide its domestic energy reforms”.
MEE vice-minister Li told the state-run newspaper China Daily that the outcome of COP30 was a “milestone”, steering the Paris Agreement into a decade of implementation.
A common view across COP was that China’s clean-tech economy will set the real direction of climate action in the years ahead, more than its approach to climate diplomacy.
Chinese auto-makers supplied EVs for use at the negotiations, while Chinese companies from Tencent and Three Gorges to Longi and CATL attended the summit.
Several side events highlighted Chinese cleantech’s contribution to the global energy transition.
The BRI International Green Development Coalition – headed by former MEE vice-minister Zhao Yingmin – launched a new platform for “best practices” on low-carbon development.
At the launch, Toni told Carbon Brief and other attendees that the programme was “exactly the type of example we want for this COP – implementation, implementation, implementation”.
Global leaders
Unusually for a COP, the two-day “high-level segment” – where world leaders give speeches with their views and plans on climate change – took place before the summit’s official opening, from 6-7 November.
Valter Correia, special secretary of COP30, said in a statement that Brazil decided to hold the leaders summit before COP to “give us time for more in-depth reflection, without the pressure from hotels or the city”. (COP30 was plagued by concerns over accommodation shortages and high costs.)
Brazilian president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva used his intervention to call for “roadmaps” away from fossil fuels and deforestation, Bloomberg reported. According to the publication, he said:
“Despite our difficulties and contradictions, we need roadmaps to justly and strategically reverse deforestation, overcome dependence on fossil fuels and mobilise the necessary resources to achieve these goals.”
(He reiterated similar language in his speech at the opening of COP30.)
Lula’s call sparked the start of a movement from countries to get references for fossil-fuel and deforestation roadmaps included in the COP’s final negotiated outcome.
Reflecting what many observers called a “difficult geopolitical situation” heading into COP30, the leaders of China, the US and India – the “planet’s three biggest polluters” – were “notably absent” from the leaders summit, reported the Associated Press.
Some Latin American leaders “were openly critical” of US president Donald Trump’s stance on climate change in their speeches, noted the Financial Times.
Speaking at the summit, UN secretary-general António Guterres described countries’ failure to keep global temperatures from crossing 1.5C as a “moral failure and deadly negligence”, reported the Guardian. According to the publication, Guterres added:
“Every fraction of a degree means more hunger, displacement and loss – especially for those least responsible.”
Country pledges
This year was particularly key for countries’ climate pledges, as it was the deadline to submit new “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs) to the UN. These plans outline countries’ ambitions for slashing emissions out to 2035.
Countries were meant to submit new NDCs to the UN by 10 February, but 95% of countries missed that deadline, according to Carbon Brief analysis.
In a bid to rally action from countries, Brazil and the UN held a virtual climate summit focused on NDCs in April and an in-person event at the sidelines of the UN general assembly in New York in September.
At the New York event, the world’s biggest annual emitter China announced the emissions target of its NDC. (See Carbon Brief’s full analysis of China’s climate plan.)
(The world’s second annual largest emitter, the US, announced its NDC while former president Joe Biden was still in office. However, after Trump resumed power, he signed an order to take the nation out of the Paris Agreement – making the US NDC effectively void.)
Following the event in September, countries representing around 50% of global emissions had either submitted or announced their NDCs, Carbon Brief analysis found. However, still only one-third of countries had submitted or announced their plans.
Shortly before COP in October, the UN released a NDC synthesis report, drawing only on the available plans.
The report found that the latest round of NDCs will cause global emissions to drop 10% by 2035 from 2019 levels, “bending the emissions curve downwards for the first time”, but falling “drastically short” of the 60% cut needed to keep 1.5C in sight, said the Guardian.
On the first day of COP30 on 10 November, UNFCCC executive secretary Simon Stiell sent a letter to all parties saying 22 new NDCs had been submitted since the NDC synthesis report was published, bringing the projected global emissions drop to 12%.
Nations continued to submit new NDCs to the UN during COP itself. This included Belarus, Bhutan, Burundi, Ukraine, Djibouti, Iraq, Costa Rica, Yemen and Mexico. South Korea also announced its intention to submit its NDC.
By the end of the summit, some 122 countries had submitted their new pledges, earning praise in the “global mutirão” decision adopted at the closing plenary. The text “urges” those that have not yet made new pledges to do so “as soon as possible”.
At the summit, there was much speculation on whether the world’s third biggest emitter, India, would come forward with its new NDC.
India’s climate minister Bhupender Yadav provided little clarity in a speech, but, when pressed later, he clarified that “it will be by December”, according to India’s Economic Times.
Countries had also been asked to come forward with their first “biennial transparency reports” (BTRs) by December 2024.
BTRs are a new type of report under the Paris Agreement, which requires all countries to submit progress updates every two years. (Previously, developed and developing countries were subject to different emissions reporting requirements.)
The reports contain information about countries’ emissions and progress towards their NDCs, adaptation plans and commitments to deliver climate finance.
By the end of COP30, 131 countries had submitted their BTRs – around 67% of all parties.
New climate science
Coming soon
Food systems and water
Food systems featured in a number of new pledges at COP30.
During the world leaders’ summit in the days before the official start of negotiations, 43 countries and the EU adopted the Belém declaration on hunger, poverty and human-centred climate action.
This aims to address the “unequal distribution of climate impacts” through actions including expanding social-protection systems and supporting climate adaptation for small farmers.
On 13 November, the UN Environment Programme launched a food waste initiative to help halve food waste by 2030 and also reduce methane emissions by up to 7%. The pledge was supported by Brazil, Japan and the UK, alongside several cities and private companies.
The themed days for food and agriculture on 19 and 20 November saw a raft of new announcements, including Brazil launching an initiative called resilient agriculture investment for net-zero land degradation (RAIZ).
This is aimed at bringing together governments and investors to restore degraded farmland. It was backed by 10 countries, including the UK, Canada and Saudi Arabia.
Brazil and the UK also put forward a declaration to spur action around reducing the environmental impact of fertilisers.
Some initiatives launched at previous COPs were updated in Belém. For example, Colombia, Italy and Vietnam joined the alliance of champions for food systems transformation – a coalition of countries pledging to take strong action on transforming food systems, first launched at COP28.

Elsewhere, private funders put forward some money for food and agriculture, including the Gates Foundation committing $1.4bn for smallholder farmer climate adaptation.
A number of reports released during COP30 looked at how food systems were included in national climate pledges, known as NDCs. A report from WWF and Climate Focus found that 93% of new NDCs included at least one measure around agriculture or food systems.
Another NGO assessment of how food systems were incorporated into 10 NDCs found that pledges from Somalia and Switzerland were “very strong” in this regard and included actions from across the entire food system. Climate pledges from Brazil and New Zealand, on the other hand, were ranked as “weak”, the report said.
In terms of water and ocean outcomes, six more countries joined the “blue NDC challenge”. This is an initiative launched by Brazil and France earlier this year that encouraged nations to integrate ocean measures into their climate pledges.
Finally, analysis from the World Resources Institute, Ocean & Climate Platform and Ocean Conservancy found that more than 90% of new NDCs submitted by coastal and island countries included ocean-based climate actions.
Protests and access
COP30 was, according to Bloomberg, the first climate summit to be “held in a democratic country” since COP26 in Glasgow, ushering in the return of large, loud and colourful protests.
On the middle Saturday of COP, which is traditionally the protest day, around 70,000 protesters filled the streets of Belém calling for climate justice, along with the protection of nature and Indigenous rights.
It marked the first time that protests have been able to take place in the streets of a COP host city since 2021. At COP27, COP28 and COP29, much smaller demonstrations took place inside the “blue zone” – the official negotiations area – which is, technically, UN soil for the fortnight.
Earlier in week one of COP30, dozens of Indigenous protesters forced their way into the summit’s blue zone, leading to violent clashes with security, Reuters said. The protesters were expressing anger at a lack of access to the negotiations and “were upset with ongoing industry and development projects” in the Amazon, the newswire added.
An Indigenous group of around 50 people also briefly blockaded the main entrance of COP in protest of extractive activities in the Amazon, CNN reported. COP30 president André Corrêa do Lago met with the group to discuss their concerns, the outlet said.
On 17 November, more than 200 NGOs wrote to the UNFCCC’s Simon Stiell urging him to request Brazil “to reduce the presence of security forces in the vicinity of the COP30 venue and the city of Belém as a whole”.
Climate Home News reported that, according to the Coalition of Indigenous Peoples of Brazil, around 2,500 Indigenous representatives came to Belém to take part in proceedings – the largest turnout of its kind at a COP. However, out of this group, only 14% had access to the blue zone.
Hundreds of Indigenous representatives arrived in Belém on a flotilla of boats sailing down the Amazon river, a separate Climate Home News story said. The group participated in the “people’s summit”, an event held parallel to talks attended by 20,000 people, according to Agência Brasil. BBC News reported on 18 November: “Brazil creates new Indigenous territories during protest-hit COP30.”
Ahead of the summit, concerns were raised that “sky-high” accommodation costs would prevent negotiators and civil society from developing countries from being able to participate, the Guardian said.
Just days before the talks began, the COP30 presidency attempted to address concerns by offering free cabins on cruise ships to delegates from African countries, small island states and the LDCs group, Reuters said.
Road to COP31 and beyond
After more than three years of dispute, it was agreed at COP30 that next year’s summit will take place in Antalya, Turkey, with rival bidder Australia acting as “president of negotiations”.
It was also agreed that COP32 will be held in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia in 2027. This will be the first-ever COP hosted by one of the least-developed countries.
Speaking to the press in Belém, Australian climate minister Chris Bowen explained that there would be a pre-COP meeting in the Pacific next year. Bowen added:
“As COP president of negotiations, I would have all the powers of COP presidency to manage, to handle the negotiations, to appoint co-facilitators, to prepare draft text and to issue the cover decision.”
The details of the deal reached between Australia and Turkey are set out in a two-page document published towards the end of the talks in Belém. Turkey will act as host and “COP31 president”, while Australia will be “president of negotiations”.
According to Dr Joanna Depledge, there has been a clear split between the COP host and presidency on six occasions. For example, at COP25 in Spain, Chile retained the presidency despite being unable to host the talks due to violent protests. Similarly, the COP presidency was held by Fiji in 2017, when the summit was hosted in Bonn, Germany.
Depledge said that the more complex deal for COP31 is “unprecedented”, but that she is willing to “wait and see” whether it can work. She told Carbon Brief:
“This unprecedented trilateral model could go both ways: it could either be a recipe for confusion and chaos or, if Turkey, Australia and the [Pacific island states] work together in good faith, it could bring more political weight to bear on the negotiations and, in future, allow a wider range of countries to preside or host.”
Arthur Wyns, research fellow at the University of Melbourne and a former adviser to the COP28 presidency, told Carbon Brief that the deal was a “huge risk” for Australia, which “might work all year towards an outcome it has no final control over”. He added:
“The ultimate question is, who will be holding the gavel at the closing plenary? And, in the current arrangement, that seems to be Turkey.”
In the table below, Carbon Brief has compiled the key meetings and milestones leading up to COP31 in Turkey, as well as the dates and locations for COP32 and COP33.
| 8-12 December 2025 | United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA7), Nairobi, Kenya |
| 15-18 January 2026 | 15-18 January 2026 Climate Action Week, Maldives |
| March 2026 | Deadline to submit views for the first UAE dialogue |
| 28-29 April 2026 | Conference on a just transition away from fossil fuels, Santa Marta, Colombia |
| 8-18 June 2026 | UNFCCC intersessional meeting, Bonn, Germany |
| 14-16 June 2026 | G7 summit, Évian, France |
| 20-28 June 2026 | London climate action week, London, UK |
| September 2026 | Climate week, New York City, US |
| 8-22 September | UN general assembly (UNGA81), New York City, US |
| 19-30 October 2026 | UN biodiversity summit COP17,, Yerevan, Armenia |
| 9-20 November 2026 | COP31, Antalya, Turkey |
| 8-19 November 2027 | COP32, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia |
| 6-17 November 2028 | COP33, Asia-Pacific region |
The post COP30: Key outcomes agreed at the UN climate talks in Belém appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter.
Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
Food inflation on the rise
DELUGE STRIKES FOOD: Extreme rainfall and flooding across the Mediterranean and north Africa has “battered the winter growing regions that feed Europe…threatening food price rises”, reported the Financial Times. Western France has “endured more than 36 days of continuous rain”, while farmers’ associations in Spain’s Andalusia estimate that “20% of all production has been lost”, it added. Policy expert David Barmes told the paper that the “latest storms were part of a wider pattern of climate shocks feeding into food price inflation”.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “Cropped” email newsletter. A fortnightly digest of food, land and nature news and views. Sent to your inbox every other Wednesday.
NO BEEF: The UK’s beef farmers, meanwhile, “face a double blow” from climate change as “relentless rain forces them to keep cows indoors”, while last summer’s drought hit hay supplies, said another Financial Times article. At the same time, indoor growers in south England described a 60% increase in electricity standing charges as a “ticking timebomb” that could “force them to raise their prices or stop production, which will further fuel food price inflation”, wrote the Guardian.
‘TINDERBOX’ AND TARIFFS: A study, covered by the Guardian, warned that major extreme weather and other “shocks” could “spark social unrest and even food riots in the UK”. Experts cited “chronic” vulnerabilities, including climate change, low incomes, poor farming policy and “fragile” supply chains that have made the UK’s food system a “tinderbox”. A New York Times explainer noted that while trade could once guard against food supply shocks, barriers such as tariffs and export controls – which are being “increasingly” used by politicians – “can shut off that safety valve”.
El Niño looms
NEW ENSO INDEX: Researchers have developed a new index for calculating El Niño, the large-scale climate pattern that influences global weather and causes “billions in damages by bringing floods to some regions and drought to others”, reported CNN. It added that climate change is making it more difficult for scientists to observe El Niño patterns by warming up the entire ocean. The outlet said that with the new metric, “scientists can now see it earlier and our long-range weather forecasts will be improved for it.”
WARMING WARNING: Meanwhile, the US Climate Prediction Center announced that there is a 60% chance of the current La Niña conditions shifting towards a neutral state over the next few months, with an El Niño likely to follow in late spring, according to Reuters. The Vibes, a Malaysian news outlet, quoted a climate scientist saying: “If the El Niño does materialise, it could possibly push 2026 or 2027 as the warmest year on record, replacing 2024.”
CROP IMPACTS: Reuters noted that neutral conditions lead to “more stable weather and potentially better crop yields”. However, the newswire added, an El Niño state would mean “worsening drought conditions and issues for the next growing season” to Australia. El Niño also “typically brings a poor south-west monsoon to India, including droughts”, reported the Hindu’s Business Line. A 2024 guest post for Carbon Brief explained that El Niño is linked to crop failure in south-eastern Africa and south-east Asia.
News and views
- DAM-AG-ES: Several South Korean farmers filed a lawsuit against the country’s state-owned utility company, “seek[ing] financial compensation for climate-related agricultural damages”, reported United Press International. Meanwhile, a national climate change assessment for the Philippines found that the country “lost up to $219bn in agricultural damages from typhoons, floods and droughts” over 2000-10, according to Eco-Business.
- SCORCHED GRASS: South Africa’s Western Cape province is experiencing “one of the worst droughts in living memory”, which is “scorching grass and killing livestock”, said Reuters. The newswire wrote: “In 2015, a drought almost dried up the taps in the city; farmers say this one has been even more brutal than a decade ago.”
- NOUVELLE VEG: New guidelines published under France’s national food, nutrition and climate strategy “urged” citizens to “limit” their meat consumption, reported Euronews. The delayed strategy comes a month after the US government “upended decades of recommendations by touting consumption of red meat and full-fat dairy”, it noted.
- COURTING DISASTER: India’s top green court accepted the findings of a committee that “found no flaws” in greenlighting the Great Nicobar project that “will lead to the felling of a million trees” and translocating corals, reported Mongabay. The court found “no good ground to interfere”, despite “threats to a globally unique biodiversity hotspot” and Indigenous tribes at risk of displacement by the project, wrote Frontline.
- FISH FALLING: A new study found that fish biomass is “falling by 7.2% from as little as 0.1C of warming per decade”, noted the Guardian. While experts also pointed to the role of overfishing in marine life loss, marine ecologist and study lead author Dr Shahar Chaikin told the outlet: “Our research proves exactly what that biological cost [of warming] looks like underwater.”
- TOO HOT FOR COFFEE: According to new analysis by Climate Central, countries where coffee beans are grown “are becoming too hot to cultivate them”, reported the Guardian. The world’s top five coffee-growing countries faced “57 additional days of coffee-harming heat” annually because of climate change, it added.
Spotlight
Nature talks inch forward
This week, Carbon Brief covers the latest round of negotiations under the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), which occurred in Rome over 16-19 February.
The penultimate set of biodiversity negotiations before October’s Conference of the Parties ended in Rome last week, leaving plenty of unfinished business.
The CBD’s subsidiary body on implementation (SBI) met in the Italian capital for four days to discuss a range of issues, including biodiversity finance and reviewing progress towards the nature targets agreed under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
However, many of the major sticking points – particularly around finance – will have to wait until later this summer, leaving some observers worried about the capacity for delegates to get through a packed agenda at COP17.
The SBI, along with the subsidiary body on scientific, technical and technological advice (SBSTTA) will both meet in Nairobi, Kenya, later this summer for a final round of talks before COP17 kicks off in Yerevan, Armenia, on 19 October.
Money talks
Finance for nature has long been a sticking point at negotiations under the CBD.
Discussions on a new fund for biodiversity derailed biodiversity talks in Cali, Colombia, in autumn 2024, requiring resumed talks a few months later.
Despite this, finance was barely on the agenda at the SBI meetings in Rome. Delegates discussed three studies on the relationship between debt sustainability and implementation of nature plans, but the more substantive talks are set to take place at the next SBI meeting in Nairobi.
Several parties “highlighted concerns with the imbalance of work” on finance between these SBI talks and the next ones, reported Earth Negotiations Bulletin (ENB).
Lim Li Ching, senior researcher at Third World Network, noted that tensions around finance permeated every aspect of the talks. She told Carbon Brief:
“If you’re talking about the gender plan of action – if there’s little or no financial resources provided to actually put it into practice and implement it, then it’s [just] paper, right? Same with the reporting requirements and obligations.”
Monitoring and reporting
Closely linked to the issue of finance is the obligations of parties to report on their progress towards the goals and targets of the GBF.
Parties do so through the submission of national reports.
Several parties at the talks pointed to a lack of timely funding for driving delays in their reporting, according to ENB.
A note released by the CBD Secretariat in December said that no parties had submitted their national reports yet; by the time of the SBI meetings, only the EU had. It further noted that just 58 parties had submitted their national biodiversity plans, which were initially meant to be published by COP16, in October 2024.
Linda Krueger, director of biodiversity and infrastructure policy at the environmental not-for-profit Nature Conservancy, told Carbon Brief that despite the sparse submissions, parties are “very focused on the national report preparation”. She added:
“Everybody wants to be able to show that we’re on the path and that there still is a pathway to getting to 2030 that’s positive and largely in the right direction.”
Watch, read, listen
NET LOSS: Nigeria’s marine life is being “threatened” by “ghost gear” – nets and other fishing equipment discarded in the ocean – said Dialogue Earth.
COMEBACK CAUSALITY: A Vox long-read looked at whether Costa Rica’s “payments for ecosystem services” programme helped the country turn a corner on deforestation.
HOMEGROWN GOALS: A Straits Times podcast discussed whether import-dependent Singapore can afford to shelve its goal to produce 30% of its food locally by 2030.
‘RUSTING’ RIVERS: The Financial Times took a closer look at a “strange new force blighting the [Arctic] landscape”: rivers turning rust-orange due to global warming.
New science
- Lakes in the Congo Basin’s peatlands are releasing carbon that is thousands of years old | Nature Geoscience
- Natural non-forest ecosystems – such as grasslands and marshlands – were converted for agriculture at four times the rate of land with tree cover between 2005 and 2020 | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
- Around one-quarter of global tree-cover loss over 2001-22 was driven by cropland expansion, pastures and forest plantations for commodity production | Nature Food
In the diary
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean | Brasília
- 5 March: Nepal general elections
- 9-20 March: First part of the thirty-first session of the International Seabed Authority (ISA) | Kingston, Jamaica
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz.
Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org
The post Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
Climate Change
Battery passport plan aims to clean up the industry powering clean energy
For millions of consumers, the sustainability scheme stickers found on everything from bananas to chocolate bars and wooden furniture are a way to choose products that are greener and more ethical than some of the alternatives.
Inga Petersen, executive director of the Global Battery Alliance (GBA), is on a mission to create a similar scheme for one of the building blocks of the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy systems: batteries.
“Right now, it’s a race to the bottom for whoever makes the cheapest battery,” Petersen told Climate Home News in an interview.
The GBA is working with industry, international organisations, NGOs and governments to establish a sustainable and transparent battery value chain by 2030.
“One of the things we’re trying to do is to create a marketplace where products can compete on elements other than price,” Petersen said.
Under the GBA’s plan, digital product passports and traceability would be used to issue product-level sustainability certifications, similar to those commonplace in other sectors such as forestry, Petersen said.
Managing battery boom’s risks
Over the past decade, battery deployment has increased 20-fold, driven by record-breaking electric vehicle (EV) sales and a booming market for batteries to store intermittent renewable energy.
Falling prices have been instrumental to the rapid expansion of the battery market. But the breakneck pace of growth has exposed the potential environmental and social harms associated with unregulated battery production.
From South America to Zimbabwe and Indonesia, mineral extraction and refining has led to social conflict, environmental damage, human rights violations and deforestation. In Indonesia, the nickel industry is powered by coal while in Europe, production plants have been met with strong local opposition over pollution concerns.
“We cannot manage these risks if we don’t have transparency,” Petersen said.
The GBA was established in 2017 in response to concerns about the battery industry’s impact as demand was forecast to boom and reports of child labour in the cobalt mines of the Democratic Republic of the Congo made headlines.
The alliance’s initial 19 members recognised that the industry needed to scale rapidly but with “social, environmental and governance guardrails”, said Petersen, who previously worked with the UN Environment Programme to develop guiding principles to minimise the environmental impact of mining.

Digital battery passport
Today, the alliance is working to develop a global certification scheme that will recognise batteries that meet minimum thresholds across a set of environmental, social and governance benchmarks it has defined along the entire value chain.
Participating mines, manufacturing plants and recycling facilities will have to provide data for their greenhouse gas emissions as well as how they perform against benchmarks for assessing biodiversity loss, pollution, child and forced labour, community impacts and respect for the rights of Indigenous peoples, for example.
The data will be independently verified, scored, aggregated and recorded on a battery passport – a digital record of the battery’s composition, which will include the origin of its raw materials and its performance against the GBA’s sustainability benchmarks.
The scheme is due to launch in 2027.
A carrot and a stick
Since the start of the year, some of the world’s largest battery companies have been voluntarily participating in the biggest pilot of the scheme to date.
More than 30 companies across the EV battery and stationary storage supply chains are involved, among them Chinese battery giants CATL and BYD subsidiary FinDreams Battery, miner Rio Tinto, battery producers Samsung SDI and Siemens, automotive supplier Denso and Tesla.
Petersen said she was “thrilled” about support for the scheme. Amid a growing pushback against sustainability rules and standards, “these companies are stepping up to send a public signal that they are still committed to a sustainable and responsible battery value chain,” she said.

There are other motivations for battery producers to know where components in their batteries have come from and whether they have been produced responsibly.
In 2023, the EU adopted a law regulating the batteries sold on its market.
From 2027, it mandates all batteries to meet environmental and safety criteria and to have a digital passport accessed via a QR code that contains information about the battery’s composition, its carbon footprint and its recycling content.
The GBA certification is not intended as a compliance instrument for the EU law but it will “add a carrot” by recognising manufacturers that go beyond meeting the bloc’s rules on nature and human rights, Petersen said.
Raising standards in complex supply chain
But challenges remain, in part due to the complexity of battery supply chains.
In the case of timber, “you have a single input material but then you have a very complex range of end products. For batteries, it’s almost the reverse,” Petersen said.
The GBA wants its certification scheme to cover all critical minerals present in batteries, covering dozens of different mining, processing and manufacturing processes and hundreds of facilities.
“One of the biggest impacts will be rewarding the leading performers through preferential access to capital, for example, with investors choosing companies that are managing their risk responsibly and transparently,” Petersen said.
It could help influence public procurement and how companies, such as EV makers, choose their suppliers, she added. End consumers will also be able to access a summary of the GBA’s scores when deciding which product to buy.
US, Europe rush to build battery supply chain
Today, the GBA has more than 150 members across the battery value chain, including more than 50 companies, of which over a dozen are Chinese firms.
China produces over three-quarters of batteries sold globally and it dominates the world’s battery recycling capacity, leaving the US and Europe scrambling to reduce their dependence on Beijing by building their own battery supply chains.
Petersen hopes the alliance’s work can help build trust in the sector amid heightened geopolitical tensions. “People want to know where the materials are coming from and which actors are involved,” she said.
At the same time, companies increasingly recognise that failing to manage sustainability risks can threaten their operations. Protests over environmental concerns have shut down mines and battery factories across the world.
“Most companies know that and that’s why they’re making these efforts,” Petersen added.
The post Battery passport plan aims to clean up the industry powering clean energy appeared first on Climate Home News.
Battery passport plan aims to clean up the industry powering clean energy
Climate Change
Reheating plastic food containers: what science says about microplastics and chemicals in ready meals
How often do you eat takeaway food? What about pre-prepared ready meals? Or maybe just microwaving some leftovers you had in the fridge? In any of these cases, there’s a pretty good chance the container was made out of plastic. Considering that they can be an extremely affordable option, are there any potential downsides we need to be aware of? We decided to investigate.
Scientific research increasingly shows that heating food in plastic packaging can release microplastics and plastic chemicals into the food we eat. A new Greenpeace International review of peer-reviewed studies finds that microwaving plastic food containers significantly increases this release, raising concerns about long-term human health impacts. This article summarises what the science says, what remains uncertain, and what needs to change.
There’s no shortage of research showing how microplastics and nanoplastics have made their way throughout the environment, from snowy mountaintops and Arctic ice, into the beetles, slugs, snails and earthworms at the bottom of the food chain. It’s a similar story with humans, with microplastics found in blood, placenta, lungs, liver and plenty of other places. On top of this, there’s some 16,000 chemicals known to be either present or used in plastic, with a bit over a quarter of those chemicals already identified as being of concern. And there are already just under 1,400 chemicals that have been found in people.
Not just food packaging, but plenty of household items either contain or are made from plastic, meaning they potentially could be a source of exposure as well. So if microplastics and chemicals are everywhere (including inside us), how are they getting there? Should we be concerned that a lot of our food is packaged in plastic?
Greenpeace analysis of 24 articles in peer-reviewed scientific journals found that the plastics we use to package our food are directly risking our health.
Heating food in plastic packaging dramatically increases the levels of microplastics and chemicals that leach into our food.
Plastic food packaging: the good, the bad, and the ugly
The growing trend towards ready meals, online shopping and restaurant delivery, and away from home-prepared meals and individual grocery shopping, is happening in every region of the world. Since the first microwaveable TV dinners were introduced in the US in the 1950s to sell off excess stock of turkey meat after Thanksgiving holidays, pre-packaged ready meals have grown hugely in sales. The global market is worth $190bn in 2025, and is expected to reach a total volume of 71.5 million tonnes by 2030. It’s also predicted that the top five global markets for convenience food (China, USA, Japan, Mexico and Russia) will remain relatively unchanged up to 2030, with the most revenue in 2019 generated by the North America region.
A new report from Greenpeace International set out to analyse articles in peer-reviewed, scientific journals to look at what exactly the research has to say about plastic food packaging and food contact plastics.
Here’s what we found.
Our review of 24 recent articles highlights a consistent picture that regulators, businesses and
consumers should be concerned about: when food is packaged in plastic and then microwaved, this significantly increases the risk of both microplastic and chemical release, and that these microplastics and chemicals will leach into the food inside the packaging.
And not just some, but a lot of microplastics and chemicals.
When polystyrene and polypropylene containers filled with water were microwaved after being stored in the fridge or freezer, one study found they released anywhere between 100,000-260,000 microplastic particles, and another found that five minutes of microwave heating could release between 326,000-534,000 particles into food.
Similarly there are a wide range of chemicals that can be and are released when plastic is heated. Across different plastic types, there are estimated to be around 16,000 different chemicals that can either be used or present in plastics, and of these around 4,200 are identified as being hazardous, whilst many others lack any form of identification (hazardous or otherwise) at all.
The research also showed that 1,396 food contact plastic chemicals have been found in humans, several of which are known to be hazardous to human health. At the same time, there are many chemicals for which no research into the long-term effects on human health exists.
Ultimately, we are left with evidence pointing towards increased release of microplastics and plastic chemicals into food from heating, the regular migration of microplastics and chemicals into food, and concerns around what long-term impacts these substances have on human health, which range from uncertain to identified harm.
The known unknowns of plastic chemicals and microplastics
The problem here (aside from the fact that plastic chemicals are routinely migrating into our food), is that often we don’t have any clear research or information on what long-term impacts these chemicals have on human health. This is true of both the chemicals deliberately used in plastic production (some of which are absolutely toxic, like antimony which is used to make PET plastic), as well as in what’s called non-intentionally added substances (NIAS).
NIAS refers to chemicals which have been found in plastic, and typically originate as impurities, reaction by-products, or can even form later when meals are heated. One study found that a UV stabiliser plastic additive reacted with potato starch when microwaved to create a previously unknown chemical compound.
We’ve been here before: lessons from tobacco, asbestos and lead
Although none of this sounds particularly great, this is not without precedence. Between what we do and don’t know, waiting for perfect evidence is costly both economically and in terms of human health. With tobacco, asbestos, and lead, a similar story to what we’re seeing now has played out before. After initial evidence suggesting problems and toxicity, lobbyists from these industries pushed back to sow doubt about the scientific validity of the findings, delaying meaningful action. And all the while, between 1950-2000, tobacco alone led to the deaths of around 60 million people. Whilst distinguishing between correlation and causation, and finding proper evidence is certainly important, it’s also important to take preventative action early, rather than wait for more people to be hurt in order to definitively prove the point.
Where to from here?
This is where adopting the precautionary principle comes in. This means shifting the burden of proof away from consumers and everyone else to prove that a product is definitely harmful (e.g. it’s definitely this particular plastic that caused this particular problem), and onto the manufacturer to prove that their product is definitely safe. This is not a new idea, and plenty of examples of this exist already, such as the EU’s REACH regulation, which is centred around the idea of “no data, no market” – manufacturers are obligated to provide data demonstrating the safety of their product in order to be sold.

Greenpeace analysis of 24 articles in peer-reviewed scientific journals found that the plastics we use to package our food are directly risking our health.
Heating food in plastic packaging dramatically increases the levels of microplastics and chemicals that leach into our food.
But as it stands currently, the precautionary principle isn’t applied to plastics. For REACH in particular, plastics are assessed on a risk-based approach, which means that, as the plastic industry itself has pointed out, something can be identified as being extremely hazardous, but is still allowed to be used in production if the leached chemical stays below “safe” levels, despite that for some chemicals a “safe” low dose is either undefined, unknown, or doesn’t exist.
A better path forward
Governments aren’t acting fast enough to reduce our exposure and protect our health. There’s no shortage of things we can do to improve this situation. The most critical one is to make and consume less plastic. This is a global problem that requires a strong Global Plastics Treaty that reduces global plastic production by at least 75% by 2040 and eliminates harmful plastics and chemicals. And it’s time that corporations take this growing threat to their customers’ health seriously, starting with their food packaging and food contact products. Here are a number of specific actions policymakers and companies can take, and helpful hints for consumers.
Policymakers & companies
- Implement the precautionary principle:
- For policymakers – Stop the use of hazardous plastics and chemicals, on the basis of their intrinsic risk, rather than an assessment of “safe” levels of exposure.
- For companies – Commit to ensure that there is a “zero release” of microplastics and hazardous chemicals from packaging into food, alongside an Action Plan with milestones to achieve this by 2035
- Stop giving false assurances to consumers about “microwave safe” containers
- Stop the use of single-use and plastic packaging, and implement policies and incentives to foster the uptake of reuse systems and non-toxic packaging alternatives.
Consumers
- Encourage your local supermarkets and shops to shift away from plastic where possible
- Avoid using plastic containers when heating/reheating food
- Use non-plastic refill containers
Trying to dodge plastic can be exhausting. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, you’re not alone. We can only do so much in this broken plastic-obsessed system. Plastic producers and polluters need to be held accountable, and governments need to act faster to protect the health of people and the planet. We urgently need global governments to accelerate a justice-centred transition to a healthier, reuse-based, zero-waste future. Ensure your government doesn’t waste this once-in-a-generation opportunity to end the age of plastic.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits