World leaders gathered in Paris this week to pledge to make 2024 the “pivotal year” for improving access to clean cooking.
At an International Energy Agency (IEA) summit attended on Tuesday by heads of state and ministers from 27 countries, a total of $2.2bn was pledged to boost uptake of clean cooking technologies.
The summit focused on improving access to clean cooking in sub-Saharan Africa, where nearly four out of five people still rely on open fires to prepare food.
Ensuring global access to clean cooking by 2030 could save 2.5 million people – mostly women and children – from premature deaths associated with breathing fire smoke, the IEA says. It could also save 1.5bn tonnes of CO2 equivalent (tCO2e), around the same as a year of global shipping and aviation emissions.
But while the case for achieving universal clean cooking is clear, questions remain over how finance should be leveraged and what kind of solutions should be pursued.
The conference featured speeches from a number of fossil-fuel executives, who argued that cookstoves using liquified petroleum gas (LPG) offer the quickest and “cleanest” solution for boosting cooking access.
This drew criticism from African commentators, who noted that fossil-fuel representatives actually outnumbered African women, who made up just 17% of the people at the summit.
The role that carbon offsets should play in helping to distribute clean cookstoves in Africa was also much touted by heads of state and industry representatives.
Academic research has found that the “carbon credits” issued by cookstove projects in the past have been “largely worthless”. But advocates told the conference that new guidelines could enable the development of “high integrity” credits for projects in Africa.
Carbon Brief attended the summit at the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) headquarters in Paris and spoke to experts about what the new global pledge could mean for climate, energy, nature and gender goals.
- How could clean cooking aid climate, nature and gender goals?
- What are the solutions on offer for clean cooking in Africa?
- How will improved access to clean cooking be financed?
How could clean cooking aid climate, nature and gender goals?
Around 2.3 billion people – close to a third of the global population – lack access to clean cooking facilities, relying instead on wood, kerosene or coal as their primary cooking fuel.
The number of people without access to clean cooking is declining in Asia and Latin America. But in sub-Saharan Africa, continued population growth means the number of people without clean cooking access is still increasing.
Household air pollution, mostly from the inhalation of cooking smoke, is linked to around 3.7 million premature deaths each year, the IEA says. In Africa, women and children, who spend the most time at home, account for 60% of early deaths related to smoke inhalation and indoor air pollution.
Ensuring global access to clean cooking by 2030 is a key component of goal seven of the Sustainable Development Goals.
According to IEA projections, meeting this target could save 2.5 million people – mostly women and children – from premature deaths associated with breathing fire smoke.
In sub-Saharan Africa, many women and children are burdened with collecting firewood for hours each day in order to prepare a meal. The IEA projects that universal access to clean cooking could save the average household nearly 1.5 hours a day, which would likely, in turn, increase female participation in schooling and employment.
In addition to this, the IEA estimates that universal access to clean cooking – achieved in the way their scenario suggests – could save a total of 1.5bntCO2e from a combination of reduced combustion emissions and avoided deforestation for firewood.
At the summit in Paris on 14 May, heads of state and high-level private-industry figures repeatedly emphasised the clear benefits of improving clean cooking access in Africa – with many admitting they had neglected the issue for too long.
In his opening remarks to the summit, Akinwumi Adesina, a former Nigerian agricultural minister who is now president of the African Development Bank Group, spoke candidly of his experiences growing up in a low-income neighbourhood without access to clean cooking.
“I don’t wear glasses just because I went to university,” he told the summit, explaining that, as a child, he spent years standing over fire smoke, which likely damaged his vision.
He told the story of a female friend that died in a kerosene accident after fetching the fuel for use in cooking. Her family could not afford to buy a gas stove.
“How can we let these things happen?” he asked the conference.
Many speakers emphasised that, compared to other parts of the energy sector, such as heavy industry, improving access to clean cooking is “solvable”, as the technology needed is already available at a relatively low cost.
The IEA estimates that $4bn will need to be leveraged annually until 2030 in order to achieve universal clean cooking access. By comparison, total clean energy technology investment will need to reach $4tn per year by 2030 to meet net-zero, IEA says.
The clean cooking summit itself raised $2.2bn for clean cooking, the IEA said. IEA executive director Dr Fatih Birol promised that his agency would track where each penny was spent and reveal the results in a year.
Despite the new financial pledges and renewed focus, some lamented the lack of inclusion of African women at the conference.
Writing for African Arguments, the Ugandan climate activist Vanessa Nakate noted that the number of fossil-fuel executives outnumbered African women, who made up just 17% of the people in attendance.
One male session chair even cracked a joke about the lack of women speaking at the summit, telling the audience that the IEA should be pleased that clean cooking will no longer be viewed as “just a women’s issue”.

Later on at the summit, Graça Machel, a former Tanzanian education minister and deputy chair of the Elders, a group of global leaders started by former South African president Nelson Mandela, appealed for African women to be directly involved in high-level decision making on clean cooking. She told the conference:
“We need to build the capacity of women themselves so they aren’t just recipients. African women – we want to be investors, entrepreneurs, managers and customers. Any policy has to have the face of women, taking into account the magnitude [of our presence]. In our countries, we are millions. Clean cooking is about African women.”
What are the solutions on offer for clean cooking in Africa?
More than 238 million people in sub-Saharan Africa live in informal housing, making the distribution of clean cooking technologies challenging.
Traditional “unclean” cooking involves a pot perched on top of a simple fire burning wood or waste products, or a kerosene dispenser.
According to the IEA, the main options for clean cooking include:
- Improved biomass stoves: An enclosed stove that burns solid fuel, but keeps heat from escaping and improves combustion, thereby reducing polluting smoke.
- E-cooking or electric stoves: Primarily hot plates, induction stovetops, rice cookers or electric pressure cookers that are plugged into an electricity source, which can come from renewable power.
- LPG stoves: A fossil-fuel burner that uses a mixture of propane and butane distributed in large pressurised cylinders.
- Biodigesters: A large vessel where organic matter (animal manure, agriculture residues or food waste) is decomposed into biogas. This biogas is then used in a burner-type stove.
- Ethanol: A simple burner that attaches to a small canister containing alcohol fuel made from crops, such as corn or sugar, that has been fermented and distilled.
- Gas stoves: A burner that uses fossil-fuel gas typically delivered to customers via distribution pipelines.
The IEA infographic below demonstrates how each of these methods work.

At the summit, fossil-fuel executives from companies such as TotalEnergies, Shell, Eni, Indian Oil and Equinor were keen to stress the role that LPG cookstoves should play in providing clean cooking access in Africa.
Patrick Pouyanné, chairman of the board and chief executive officer at TotalEnergies – one of the fossil fuel companies behind the controversial East African oil pipeline project – told the summit that his company will invest more than $400m in the development of LPG for cooking by 2030.
Eirik Wærness, senior vice president and chief economist at Equinor – a key funder of the controversial Rosebank oil field in UK waters – boasted that his company already supplies 10% of India’s LPG. He told the conference:
“We should not let the best – which is renewable energy – stand in the way of the good [LPG]. We will do all that we can to provide LPG – and also LNG [liquified natural gas] – as a viable, clean fuel.”
The IEA’s scenario for achieving universal clean cooking access sees a key role of LPG cookstoves. It notes that, in the last decade, 70% of people who gained “clean” cooking access globally did so through LPG.
In its scenario, LPG remains the “primary solution to deliver clean cooking access”, representing nearly half of new household access in 2030.
Below, an IEA graphic breaks down the numbers of households gaining access to different types of clean cooking in 2022 (left) and how its scenario expects households to gain access from 2023-2030.

At the sidelines of the summit, Carbon Brief spoke to Dr Donnee Alexander, chief science officer for the Clean Cooking Alliance, a UN-backed NGO which helped to coordinate the summit.
Asked about whether a focus on LPG cookstoves over renewable-energy methods could risk locking African nations into further fossil-fuel dependency, she responded:
“I think Africa should be able to transition however they so desire. Because they have no energy. For me to say, ‘you need to transition in a certain way’, when a woman is cooking over an open fire and dying prematurely because she’s experiencing smoke inhalation every day of her life, who am I to say that she should not be transitioning to a much cleaner option compared to the baseline?”
But several African commentators reject the idea that fossil fuels are the key solution to Africa’s clean cooking crisis.
In her commentary on the summit, Nakate says:
“Natural gas is not clean…burning LPG or methane at home emits nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide and benzene, all [of] which can potentially trigger respiratory complications, including childhood asthma…Instead of trying to make gas affordable, the summit should seek to unlock investments that establish and scale ambitious and people-centred energy programmes. This is the most reasonable way to deliver decentralised energy to communities on the continent.”
Her thoughts are echoed by Mohamed Adow, founder and director of the Power Shift Africa thinktank in Kenya.
In a statement, he said there is “no evidence” that gas is the solution to providing clean cooking access in Africa, adding:
“What we need is a woman-centred approach that puts their needs first, not those of a greedy private sector looking to make profits. Rather than subsidies for private companies, that money would be better used investing in high efficiency, low-cost electric cookers for Africans.”
While most of the speakers at the summit focused on LPG, there was some recognition that renewable energy could be a way forward for providing clean cooking.
Stanlake Samkange, assistant executive director at the World Food Programme, said that his organisation had traditionally focused on supplying cleaner fuel stoves, but that “2024 is a departure”. He added:
“We are not just focusing on fuel efficient stoves but clean cooking…We are looking at electronic stoves and e-cooking. In Madagascar, we are looking to link that to solar panels.”
How will improved access to clean cooking be financed?
The IEA estimates that $4bn will need to be leveraged annually until 2030 in order to achieve universal clean cooking access.
The clean cooking summit raised $2.2bn from public and private sources. This included new pledges from the EU, France, Denmark, the US, the UK and firms, including fossil-fuel companies.
It follows on from a high-level clean cooking event at the COP28 climate summit in Dubai, where the African Development Bank pledged to allocate a separate $2bn for clean cooking over the next decade.
At the Paris summit, Birol pledged that the IEA will closely monitor where the finance is spent and reveal the results in a year.
Throughout the conference, heads of state, ministers and company CEOs made it clear that they saw clean cookstove carbon-offset projects as key for leveraging finance and distributing new technologies in Africa.
Offsetting involves developed nations or companies paying for projects that distribute clean cookstoves, allowing them to then claim they have reduced their own emissions by paying to cut carbon in another country. (For a full breakdown, see Carbon Brief’s carbon offsets explainer.)
Stephanie Mbombo, presidential special envoy for the new climate economy for the Democratic Republic of the Congo, said that her president saw carbon offsets as the “key driver” for access to clean cooking, telling the summit:
“[With] carbon credits, we will save the world, but we will also save ourselves.”
The CEOs of clean cookstove carbon-offset companies were invited to speak alongside senior political figures and made bold claims about how they could play a pivotal role.
“With carbon credits, it’s solved, it’s done,” said Peter Scott, the CEO of the cookstove company BURN Manufacturing.

This sentiment was echoed in the declaration issued from the summit.
It said that participants “acknowledge the significant role that carbon credits and climate finance have already played in scaling clean cooking efforts, recognising the potential for further expansion of this support”.
But academic research has found that clean cookstove carbon-offset projects are “largely worthless” in emissions reductions terms.
A study in the journal Nature Sustainability found that nine in 10 of the 96m cookstove credits certified by leading carbon registries do not avoid the emissions they claim.
What is more, investigations by journalists, including at Climate Home News, have uncovered serious faults with clean cookstove projects, such as faulty stoves being distributed without communities being given access to repairs or replacements.
Gilles Dufrasne, policy lead at Carbon Market Watch, a watchdog of carbon offsets, told Carbon Brief that cookstove projects have “perhaps” been the least successful at achieving emissions reductions out of all types of carbon-offset projects. He added:
“This is a case of projects that very likely have significant positive impacts for sustainable development, and likely also positive climate impacts, but where the quantification of these impacts is extremely shaky. Most projects issue many more credits than they should, and that’s a problem if countries use it to meet their nationally determined contributions – as this [clean cooking summit declaration] suggests they could.”
Acknowledging the need for more “high integrity” cookstove credits, the conference saw the Clean Cooking Alliance launch new “principles for responsible carbon finance in clean cooking”.
Alexander told Carbon Brief the goal of the principles was to “address the challenges in the carbon market to ensure that we have both higher integrity but also higher demand”.
She said that the new principles could bring about tangible ways of improving the outcomes of cookstove carbon-offsets projects:
“We’re saying let’s measure reduction in fuel use [from distributing clean cookstoves], utilising standard methodologies. Or let’s have digital monitoring and verification so we know exactly when the stove is used. Things like that start to bring more integrity into the system.”
Dufrasne added to Carbon Brief that, with current projects offering little guarantee that promised emissions reductions will be achieved, there is a risk that the sale of more carbon credits to developed nations will lead to these countries reducing their emissions by less than if they had invested in alternative climate measures:
“Getting countries and companies to pledge finance to a fund, which then finances cookstove projects – with or without credits – is likely to be a better way.”
The post Clean cooking: What new global pledge means for climate, nature and gender goals appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Clean cooking: What new global pledge means for climate, nature and gender goals
Greenhouse Gases
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter.
Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
Food inflation on the rise
DELUGE STRIKES FOOD: Extreme rainfall and flooding across the Mediterranean and north Africa has “battered the winter growing regions that feed Europe…threatening food price rises”, reported the Financial Times. Western France has “endured more than 36 days of continuous rain”, while farmers’ associations in Spain’s Andalusia estimate that “20% of all production has been lost”, it added. Policy expert David Barmes told the paper that the “latest storms were part of a wider pattern of climate shocks feeding into food price inflation”.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “Cropped” email newsletter. A fortnightly digest of food, land and nature news and views. Sent to your inbox every other Wednesday.
NO BEEF: The UK’s beef farmers, meanwhile, “face a double blow” from climate change as “relentless rain forces them to keep cows indoors”, while last summer’s drought hit hay supplies, said another Financial Times article. At the same time, indoor growers in south England described a 60% increase in electricity standing charges as a “ticking timebomb” that could “force them to raise their prices or stop production, which will further fuel food price inflation”, wrote the Guardian.
‘TINDERBOX’ AND TARIFFS: A study, covered by the Guardian, warned that major extreme weather and other “shocks” could “spark social unrest and even food riots in the UK”. Experts cited “chronic” vulnerabilities, including climate change, low incomes, poor farming policy and “fragile” supply chains that have made the UK’s food system a “tinderbox”. A New York Times explainer noted that while trade could once guard against food supply shocks, barriers such as tariffs and export controls – which are being “increasingly” used by politicians – “can shut off that safety valve”.
El Niño looms
NEW ENSO INDEX: Researchers have developed a new index for calculating El Niño, the large-scale climate pattern that influences global weather and causes “billions in damages by bringing floods to some regions and drought to others”, reported CNN. It added that climate change is making it more difficult for scientists to observe El Niño patterns by warming up the entire ocean. The outlet said that with the new metric, “scientists can now see it earlier and our long-range weather forecasts will be improved for it.”
WARMING WARNING: Meanwhile, the US Climate Prediction Center announced that there is a 60% chance of the current La Niña conditions shifting towards a neutral state over the next few months, with an El Niño likely to follow in late spring, according to Reuters. The Vibes, a Malaysian news outlet, quoted a climate scientist saying: “If the El Niño does materialise, it could possibly push 2026 or 2027 as the warmest year on record, replacing 2024.”
CROP IMPACTS: Reuters noted that neutral conditions lead to “more stable weather and potentially better crop yields”. However, the newswire added, an El Niño state would mean “worsening drought conditions and issues for the next growing season” to Australia. El Niño also “typically brings a poor south-west monsoon to India, including droughts”, reported the Hindu’s Business Line. A 2024 guest post for Carbon Brief explained that El Niño is linked to crop failure in south-eastern Africa and south-east Asia.
News and views
- DAM-AG-ES: Several South Korean farmers filed a lawsuit against the country’s state-owned utility company, “seek[ing] financial compensation for climate-related agricultural damages”, reported United Press International. Meanwhile, a national climate change assessment for the Philippines found that the country “lost up to $219bn in agricultural damages from typhoons, floods and droughts” over 2000-10, according to Eco-Business.
- SCORCHED GRASS: South Africa’s Western Cape province is experiencing “one of the worst droughts in living memory”, which is “scorching grass and killing livestock”, said Reuters. The newswire wrote: “In 2015, a drought almost dried up the taps in the city; farmers say this one has been even more brutal than a decade ago.”
- NOUVELLE VEG: New guidelines published under France’s national food, nutrition and climate strategy “urged” citizens to “limit” their meat consumption, reported Euronews. The delayed strategy comes a month after the US government “upended decades of recommendations by touting consumption of red meat and full-fat dairy”, it noted.
- COURTING DISASTER: India’s top green court accepted the findings of a committee that “found no flaws” in greenlighting the Great Nicobar project that “will lead to the felling of a million trees” and translocating corals, reported Mongabay. The court found “no good ground to interfere”, despite “threats to a globally unique biodiversity hotspot” and Indigenous tribes at risk of displacement by the project, wrote Frontline.
- FISH FALLING: A new study found that fish biomass is “falling by 7.2% from as little as 0.1C of warming per decade”, noted the Guardian. While experts also pointed to the role of overfishing in marine life loss, marine ecologist and study lead author Dr Shahar Chaikin told the outlet: “Our research proves exactly what that biological cost [of warming] looks like underwater.”
- TOO HOT FOR COFFEE: According to new analysis by Climate Central, countries where coffee beans are grown “are becoming too hot to cultivate them”, reported the Guardian. The world’s top five coffee-growing countries faced “57 additional days of coffee-harming heat” annually because of climate change, it added.
Spotlight
Nature talks inch forward
This week, Carbon Brief covers the latest round of negotiations under the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), which occurred in Rome over 16-19 February.
The penultimate set of biodiversity negotiations before October’s Conference of the Parties ended in Rome last week, leaving plenty of unfinished business.
The CBD’s subsidiary body on implementation (SBI) met in the Italian capital for four days to discuss a range of issues, including biodiversity finance and reviewing progress towards the nature targets agreed under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
However, many of the major sticking points – particularly around finance – will have to wait until later this summer, leaving some observers worried about the capacity for delegates to get through a packed agenda at COP17.
The SBI, along with the subsidiary body on scientific, technical and technological advice (SBSTTA) will both meet in Nairobi, Kenya, later this summer for a final round of talks before COP17 kicks off in Yerevan, Armenia, on 19 October.
Money talks
Finance for nature has long been a sticking point at negotiations under the CBD.
Discussions on a new fund for biodiversity derailed biodiversity talks in Cali, Colombia, in autumn 2024, requiring resumed talks a few months later.
Despite this, finance was barely on the agenda at the SBI meetings in Rome. Delegates discussed three studies on the relationship between debt sustainability and implementation of nature plans, but the more substantive talks are set to take place at the next SBI meeting in Nairobi.
Several parties “highlighted concerns with the imbalance of work” on finance between these SBI talks and the next ones, reported Earth Negotiations Bulletin (ENB).
Lim Li Ching, senior researcher at Third World Network, noted that tensions around finance permeated every aspect of the talks. She told Carbon Brief:
“If you’re talking about the gender plan of action – if there’s little or no financial resources provided to actually put it into practice and implement it, then it’s [just] paper, right? Same with the reporting requirements and obligations.”
Monitoring and reporting
Closely linked to the issue of finance is the obligations of parties to report on their progress towards the goals and targets of the GBF.
Parties do so through the submission of national reports.
Several parties at the talks pointed to a lack of timely funding for driving delays in their reporting, according to ENB.
A note released by the CBD Secretariat in December said that no parties had submitted their national reports yet; by the time of the SBI meetings, only the EU had. It further noted that just 58 parties had submitted their national biodiversity plans, which were initially meant to be published by COP16, in October 2024.
Linda Krueger, director of biodiversity and infrastructure policy at the environmental not-for-profit Nature Conservancy, told Carbon Brief that despite the sparse submissions, parties are “very focused on the national report preparation”. She added:
“Everybody wants to be able to show that we’re on the path and that there still is a pathway to getting to 2030 that’s positive and largely in the right direction.”
Watch, read, listen
NET LOSS: Nigeria’s marine life is being “threatened” by “ghost gear” – nets and other fishing equipment discarded in the ocean – said Dialogue Earth.
COMEBACK CAUSALITY: A Vox long-read looked at whether Costa Rica’s “payments for ecosystem services” programme helped the country turn a corner on deforestation.
HOMEGROWN GOALS: A Straits Times podcast discussed whether import-dependent Singapore can afford to shelve its goal to produce 30% of its food locally by 2030.
‘RUSTING’ RIVERS: The Financial Times took a closer look at a “strange new force blighting the [Arctic] landscape”: rivers turning rust-orange due to global warming.
New science
- Lakes in the Congo Basin’s peatlands are releasing carbon that is thousands of years old | Nature Geoscience
- Natural non-forest ecosystems – such as grasslands and marshlands – were converted for agriculture at four times the rate of land with tree cover between 2005 and 2020 | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
- Around one-quarter of global tree-cover loss over 2001-22 was driven by cropland expansion, pastures and forest plantations for commodity production | Nature Food
In the diary
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean | Brasília
- 5 March: Nepal general elections
- 9-20 March: First part of the thirty-first session of the International Seabed Authority (ISA) | Kingston, Jamaica
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz.
Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org
The post Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
Greenhouse Gases
Dangerous heat for Tour de France riders only a ‘question of time’
Rising temperatures across France since the mid-1970s is putting Tour de France competitors at “high risk”, according to new research.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, uses 50 years of climate data to calculate the potential heat stress that athletes have been exposed to across a dozen different locations during the world-famous cycling race.
The researchers find that both the severity and frequency of high-heat-stress events have increased across France over recent decades.
But, despite record-setting heatwaves in France, the heat-stress threshold for safe competition has rarely been breached in any particular city on the day the Tour passed through.
(This threshold was set out by cycling’s international governing body in 2024.)
However, the researchers add it is “only a question of time” until this occurs as average temperatures in France continue to rise.
The lead author of the study tells Carbon Brief that, while the race organisers have been fortunate to avoid major heat stress on race days so far, it will be “harder and harder to be lucky” as extreme heat becomes more common.
‘Iconic’
The Tour de France is one of the world’s most storied cycling races and the oldest of Europe’s three major multi-week cycling competitions, or Grand Tours.
Riders cover around 3,500 kilometres (km) of distance and gain up to nearly 55km of altitude over 21 stages, with only two or three rest days throughout the gruelling race.
The researchers selected the Tour de France because it is the “iconic bike race. It is the bike race of bike races,” says Dr Ivana Cvijanovic, a climate scientist at the French National Research Institute for Sustainable Development, who led the new work.
Heat has become a growing problem for the competition in recent years.
In 2022, Alexis Vuillermoz, a French competitor, collapsed at the finish line of the Tour’s ninth stage, leaving in an ambulance and subsequently pulling out of the race entirely.
Two years later, British cyclist Sir Mark Cavendish vomited on his bike during the first stage of the race after struggling with the 36C heat.
The Tour also makes a good case study because it is almost entirely held during the month of July and, while the route itself changes, there are many cities and stages that are repeated from year to year, Cvijanovic adds.
‘Have to be lucky’
The study focuses on the 50-year span between 1974 and 2023.
The researchers select six locations across the country that have commonly hosted the Tour, from the mountain pass of Col du Tourmalet, in the French Pyrenees, to the city of Paris – where the race finishes, along the Champs-Élysées.
These sites represent a broad range of climatic zones: Alpe d’ Huez, Bourdeaux, Col du Tourmalet, Nîmes, Paris and Toulouse.
For each location, they use meteorological reanalysis data from ERA5 and radiant temperature data from ERA5-HEAT to calculate the “wet-bulb globe temperature” (WBGT) for multiple times of day across the month of July each year.
WBGT is a heat-stress index that takes into account temperature, humidity, wind speed and direct sunlight.
Although there is “no exact scientific consensus” on the best heat-stress index to use, WBGT is “one of the rare indicators that has been originally developed based on the actual human response to heat”, Cvijanovic explains.
It is also the one that the International Cycling Union (UCI) – the world governing body for sport cycling – uses to assess risk. A WBGT of 28C or higher is classified as “high risk” by the group.
WBGT is the “gold standard” for assessing heat stress, says Dr Jessica Murfree, director of the ACCESS Research Laboratory and assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Murfree, who was not involved in the new study, adds that the researchers are “doing the right things by conducting their science in alignment with the business practices that are already happening”.
The researchers find that across the 50-year time period, WBGT has been increasing across the entire country – albeit, at different rates. In the north-west of the country, WBGT has increased at an average rate of 0.1C per decade, while in the southern and eastern parts of the country, it has increased by more than 0.5C per decade.
The maps below show the maximum July WBGT for each decade of the analysis (rows) and for hourly increments of the late afternoon (columns). Lower temperatures are shown in lighter greens and yellows, while higher temperatures are shown in darker reds and purples.
Six Tour de France locations analysed in the study are shown as triangles on the maps (clockwise from top): Paris, Alpe d’ Huez, Nîmes, Toulouse, Col du Tourmalet and Bordeaux.
The maps show that the maximum WBGT temperature in the afternoon has surpassed 28C over almost the entire country in the last decade. The notable exceptions to this are the mountainous regions of the Alps and the Pyrenees.
The researchers also find that most of the country has crossed the 28C WBGT threshold – which they describe as “dangerous heat levels” – on at least one July day over the past decade. However, by looking at the WBGT on the day the Tour passed through any of these six locations, they find that the threshold has rarely been breached during the race itself.
For example, the research notes that, since 1974, Paris has seen a WBGT of 28C five times at 3pm in July – but that these events have “so far” not coincided with the cycling race.
The study states that it is “fortunate” that the Tour has so far avoided the worst of the heat-stress.
Cvijanovic says the organisers and competitors have been “lucky” to date. She adds:
“It has worked really well for them so far. But as the frequency of these [extreme heat] events is increasing, it will be harder and harder to be lucky.”
Dr Madeleine Orr, an assistant professor of sport ecology at the University of Toronto who was not involved in the study, tells Carbon Brief that the paper was “really well done”, noting that its “methods are good [and its] approach was sound”. She adds:
“[The Tour has] had athletes complain about [the heat]. They’ve had athletes collapse – and still those aren’t the worst conditions. I think that that says a lot about what we consider safe. They’ve still been lucky to not see what unsafe looks like, despite [the heat] having already had impacts.”
Heat safety protocols
In 2024, the UCI set out its first-ever high temperature protocol – a set of guidelines for race organisers to assess athletes’ risk of heat stress.
The assessment places the potential risk into one of five categories based on the WBGT, ranging from very low to high risk.
The protocol then sets out suggested actions to take in the event of extreme heat, ranging from having athletes complete their warm-ups using ice vests and cold towels to increasing the number of support vehicles providing water and ice.
If the WBGT climbs above the 28C mark, the protocol suggests that organisers modify the start time of the stage, adapt the course to remove particularly hazardous sections – or even cancel the race entirely.
However, Orr notes that many other parts of the race, such as spectator comfort and equipment functioning, may have lower temperatures thresholds that are not accounted for in the protocol, but should also be considered.
Murfree points out that the study’s findings – and the heat protocol itself – are “really focused on adaptation, rather than mitigation”. While this is “to be expected”, she tells Carbon Brief:
“Moving to earlier start times or adjusting the route specifically to avoid these locations that score higher in heat stress doesn’t stop the heat stress. These aren’t climate preventative measures. That, I think, would be a much more difficult conversation to have in the research because of the Tour de France’s intimate relationship with fossil-fuel companies.”
The post Dangerous heat for Tour de France riders only a ‘question of time’ appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Dangerous heat for Tour de France riders only a ‘question of time’
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 20 February 2026: EU’s ‘3C’ warning | Endangerment repeal’s impact on US emissions | ‘Tree invasion’ fuelled South America’s fires
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Preparing for 3C
NEW ALERT: The EU’s climate advisory board urged countries to prepare for 3C of global warming, reported the Guardian. The outlet quoted Maarten van Aalst, a member of the advisory board, saying that adapting to this future is a “daunting task, but, at the same time, quite a doable task”. The board recommended the creation of “climate risk assessments and investments in protective measures”.
‘INSUFFICIENT’ ACTION: EFE Verde added that the advisory board said that the EU’s adaptation efforts were so far “insufficient, fragmented and reactive” and “belated”. Climate impacts are expected to weaken the bloc’s productivity, put pressure on public budgets and increase security risks, it added.
UNDERWATER: Meanwhile, France faced “unprecedented” flooding this week, reported Le Monde. The flooding has inundated houses, streets and fields and forced the evacuation of around 2,000 people, according to the outlet. The Guardian quoted Monique Barbut, minister for the ecological transition, saying: “People who follow climate issues have been warning us for a long time that events like this will happen more often…In fact, tomorrow has arrived.”
IEA ‘erases’ climate
MISSING PRIORITY: The US has “succeeded” in removing climate change from the main priorities of the International Energy Agency (IEA) during a “tense ministerial meeting” in Paris, reported Politico. It noted that climate change is not listed among the agency’s priorities in the “chair’s summary” released at the end of the two-day summit.
US INTERVENTION: Bloomberg said the meeting marked the first time in nine years the IEA failed to release a communique setting out a unified position on issues – opting instead for the chair’s summary. This came after US energy secretary Chris Wright gave the organisation a one-year deadline to “scrap its support of goals to reduce energy emissions to net-zero” – or risk losing the US as a member, according to Reuters.
Around the world
- ISLAND OBJECTION: The US is pressuring Vanuatu to withdraw a draft resolution supporting an International Court of Justice ruling on climate change, according to Al Jazeera.
- GREENLAND HEAT: The Associated Press reported that Greenland’s capital Nuuk had its hottest January since records began 109 years ago.
- CHINA PRIORITIES: China’s Energy Administration set out its five energy priorities for 2026-2030, including developing a renewable energy plan, said International Energy Net.
- AMAZON REPRIEVE: Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon has continued to fall into early 2026, extending a downward trend, according to the latest satellite data covered by Mongabay.
- GEZANI DESTRUCTION: Reuters reported the aftermath of the Gezani cyclone, which ripped through Madagascar last week, leaving 59 dead and more than 16,000 displaced people.
20cm
The average rise in global sea levels since 1901, according to a Carbon Brief guest post on the challenges in projecting future rises.
Latest climate research
- Wildfire smoke poses negative impacts on organisms and ecosystems, such as health impacts on air-breathing animals, changes in forests’ carbon storage and coral mortality | Global Ecology and Conservation
- As climate change warms Antarctica throughout the century, the Weddell Sea could see the growth of species such as krill and fish and remain habitable for Emperor penguins | Nature Climate Change
- About 97% of South American lakes have recorded “significant warming” over the past four decades and are expected to experience rising temperatures and more frequent heatwaves | Climatic Change
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
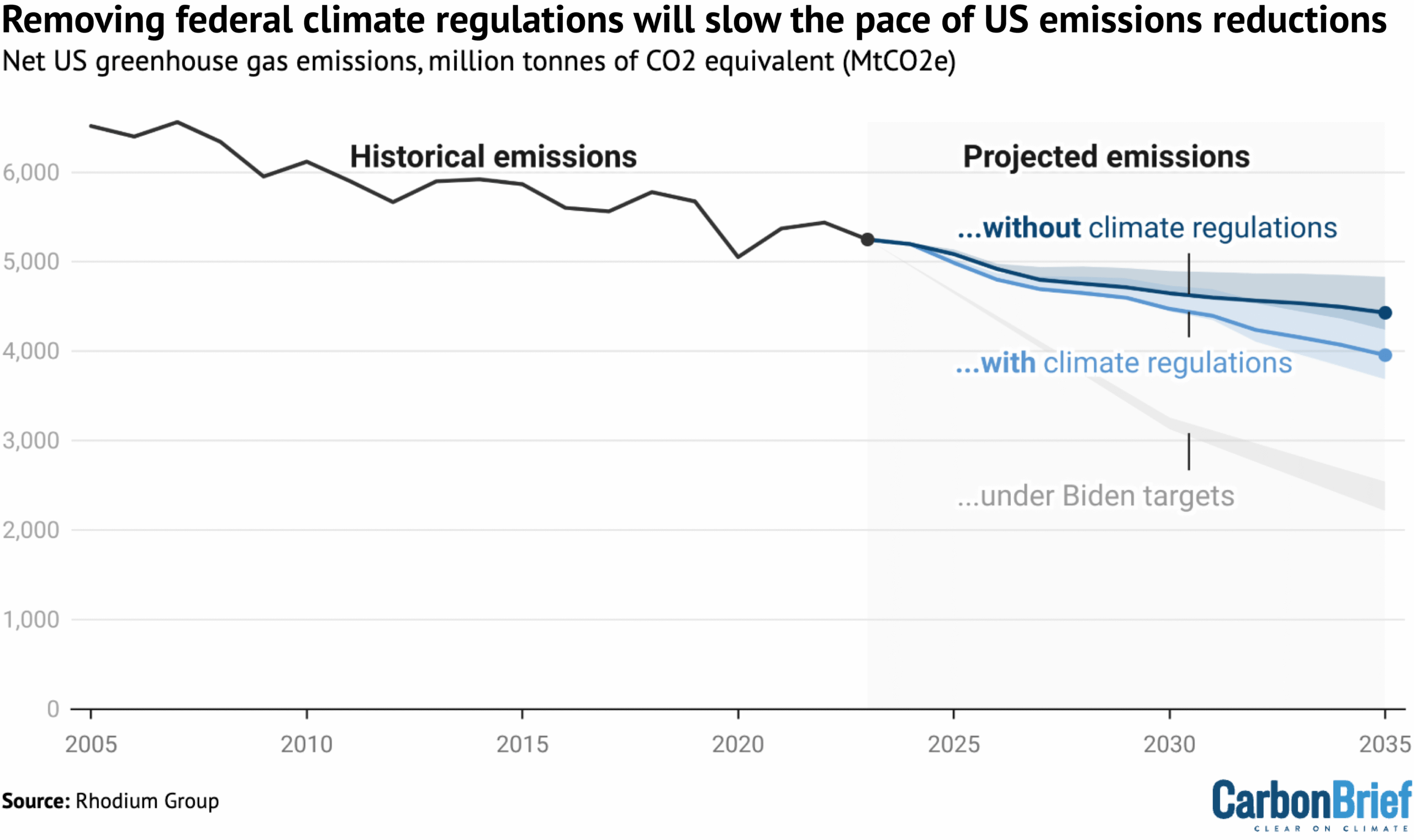
Repealing the US’s landmark “endangerment finding”, along with actions that rely on that finding, will slow the pace of US emissions cuts, according to Rhodium Group visualised by Carbon Brief. US president Donald Trump last week formally repealed the scientific finding that underpins federal regulations on greenhouse gas emissions, although the move is likely to face legal challenges. Data from the Rhodium Group, an independent research firm, shows that US emissions will drop more slowly without climate regulations. However, even with climate regulations, emissions are expected to drop much slower under Trump than under the previous Joe Biden administration, according to the analysis.
Spotlight
How a ‘tree invasion’ helped to fuel South America’s fires
This week, Carbon Brief explores how the “invasion” of non-native tree species helped to fan the flames of forest fires in Argentina and Chile earlier this year.
Since early January, Chile and Argentina have faced large-scale and deadly wildfires, including in Patagonia, which spans both countries.
These fires have been described as “some of the most significant and damaging in the region”, according to a World Weather Attribution (WWA) analysis covered by Carbon Brief.
In both countries, the fires destroyed vast areas of native forests and grasslands, displacing thousands of people. In Chile, the fires resulted in 23 deaths.
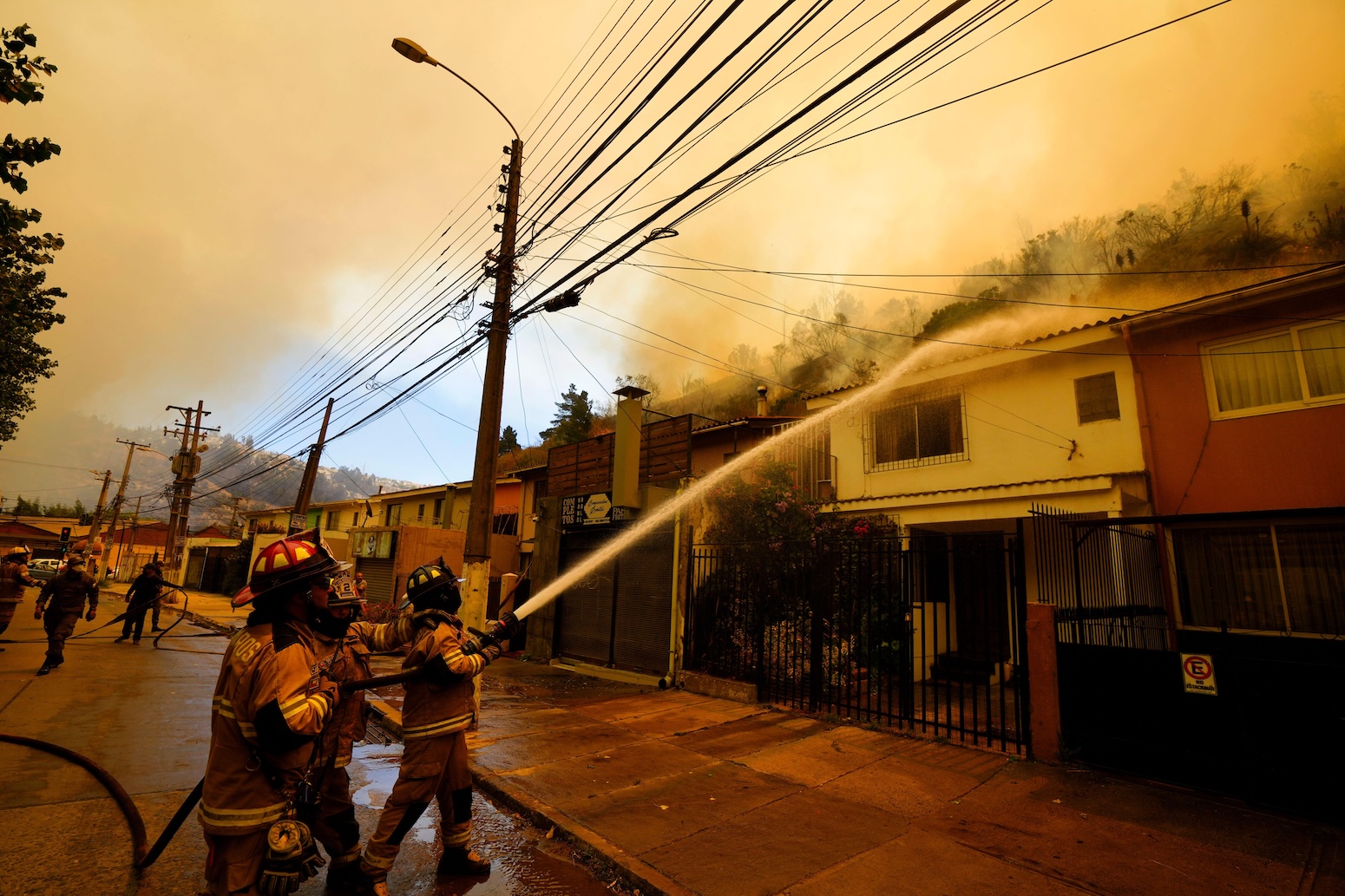

Multiple drivers contributed to the spread of the fires, including extended periods of high temperatures, low rainfall and abundant dry vegetation.
The WWA analysis concluded that human-caused climate change made these weather conditions at least three times more likely.
According to the researchers, another contributing factor was the invasion of non-native trees in the regions where the fires occurred.
The risk of non-native forests
In Argentina, the wildfires began on 6 January and persisted until the first week of February. They hit the city of Puerto Patriada and the Los Alerces and Lago Puelo national parks, in the Chubut province, as well as nearby regions.
In these areas, more than 45,000 hectares of native forests – such as Patagonian alerce tree, myrtle, coigüe and ñire – along with scrubland and grasslands, were consumed by the flames, according to the WWA study.
In Chile, forest fires occurred from 17 to 19 January in the Biobío, Ñuble and Araucanía regions.
The fires destroyed more than 40,000 hectares of forest and more than 20,000 hectares of non-native forest plantations, including eucalyptus and Monterey pine.
Dr Javier Grosfeld, a researcher at Argentina’s National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) in northern Patagonia, told Carbon Brief that these species, introduced to Patagonia for production purposes in the late 20th century, grow quickly and are highly flammable.
Because of this, their presence played a role in helping the fires to spread more quickly and grow larger.
However, that is no reason to “demonise” them, he stressed.
Forest management
For Grosfeld, the problem in northern Patagonia, Argentina, is a significant deficit in the management of forests and forest plantations.
This management should include pruning branches from their base and controlling the spread of non-native species, he added.
A similar situation is happening in Chile, where management of pine and eucalyptus plantations is not regulated. This means there are no “firebreaks” – gaps in vegetation – in place to prevent fire spread, Dr Gabriela Azócar, a researcher at the University of Chile’s Centre for Climate and Resilience Research (CR2), told Carbon Brief.
She noted that, although Mapuche Indigenous communities in central-south Chile are knowledgeable about native species and manage their forests, their insight and participation are not recognised in the country’s fire management and prevention policies.
Grosfeld stated:
“We are seeing the transformation of the Patagonian landscape from forest to scrubland in recent years. There is a lack of preventive forestry measures, as well as prevention and evacuation plans.”
Watch, read, listen
FUTURE FURNACE: A Guardian video explored the “unbearable experience of walking in a heatwave in the future”.
THE FUN SIDE: A Channel 4 News video covered a new wave of climate comedians who are using digital platforms such as TikTok to entertain and raise awareness.
ICE SECRETS: The BBC’s Climate Question podcast explored how scientists study ice cores to understand what the climate was like in ancient times and how to use them to inform climate projections.
Coming up
- 22-27 February: Ocean Sciences Meeting, Glasgow
- 24-26 February: Methane Mitigation Europe Summit 2026, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 25-27 February: World Sustainable Development Summit 2026, New Delhi, India
Pick of the jobs
- The Climate Reality Project, digital specialist | Salary: $60,000-$61,200. Location: Washington DC
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), science officer in the IPCC Working Group I Technical Support Unit | Salary: Unknown. Location: Gif-sur-Yvette, France
- Energy Transition Partnership, programme management intern | Salary: Unknown. Location: Bangkok, Thailand
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 20 February 2026: EU’s ‘3C’ warning | Endangerment repeal’s impact on US emissions | ‘Tree invasion’ fuelled South America’s fires appeared first on Carbon Brief.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits