Biofuel
Introduction Biofuel Production in Sweden
Sweden has emerged as a global leader in the production and implementation of biofuels, making significant strides towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving sustainability targets.
Biofuels are a type of renewable energy derived from organic materials, such as crops, agricultural waste, or forestry residues. They are considered a viable alternative to fossil fuels due to their lower carbon emissions and potential for reducing dependence on finite resources.
In Sweden, biofuel production has gained considerable momentum as the country aims to transition to a more sustainable and carbon-neutral society. Several factors have contributed to the growth of biofuel production in Sweden, including government policies, technological advancements, and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
One of the key biofuels produced in Sweden is bioethanol, which is primarily derived from agricultural crops such as wheat, barley, and sugar beet.
The production process involves fermenting the sugars present in these crops to obtain ethanol, which can then be blended with gasoline or used as a standalone fuel. Bioethanol production in Sweden has been steadily increasing, with a focus on developing advanced technologies to improve efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
Another significant biofuel produced in Sweden is biodiesel, which is typically derived from vegetable oils or animal fats through a process called transesterification. Biodiesel can be used as a direct replacement for conventional diesel fuel or blended with it. Sweden has been actively promoting the use of biodiesel by implementing policies that require a certain percentage of biofuels in transportation fuels.
Sweden has also made substantial progress in utilizing forest biomass for bioenergy production. Forest residues, such as branches, bark, and sawdust, are converted into wood pellets or chips, which can be burned to generate heat and electricity. This biomass-based bioenergy plays a crucial role in reducing the country’s reliance on fossil fuels and provides a sustainable alternative for heating and power generation.
To support and incentivize biofuel production, the Swedish government has implemented various policies and regulations. These include tax exemptions, financial incentives, and sustainability criteria that ensure biofuels meet certain environmental standards. Additionally, Sweden has been actively involved in international collaborations and research projects to advance biofuel technologies and share knowledge with other countries.
The progress made in biofuel production in Sweden aligns with the country’s ambitious goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. By promoting the use of biofuels and investing in renewable energy infrastructure, Sweden is at the forefront of sustainable energy transitions, setting an example for other nations striving to achieve a greener future.
Fact and data Biofuel Production in Sweden
Here are some facts and data regarding biofuel production in Sweden:
Leading Producer
Sweden is one of the leading producers of biofuels in Europe. The country has made significant investments in biofuel research, development, and production.
Bioethanol Production
Sweden has a strong focus on bioethanol production. In 2020, the country produced around 380 million liters of bioethanol.
Biodiesel Production
Sweden also has a substantial biodiesel production capacity. In 2020, the country produced approximately 560,000 tons of biodiesel.
Renewable Energy Targets
Sweden has set ambitious renewable energy targets. The country aims to have 70% of its total energy consumption from renewable sources by 2030.
Sustainable Feedstocks
Sweden utilizes sustainable feedstocks for biofuel production. These include agricultural crops, forest residues, and waste materials.
Forest Biomass
Forest biomass plays a significant role in Sweden’s bioenergy production. The country has vast forest resources and effectively utilizes residues from forestry activities to produce bioenergy.
Government Policies
The Swedish government has implemented several policies to support biofuel production. These include tax exemptions, financial incentives, and mandates for blending biofuels in transportation fuels.
Advanced Technologies
Sweden is actively involved in the development and implementation of advanced biofuel technologies. These technologies aim to improve production efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
International Collaborations
Sweden participates in international collaborations and research projects related to biofuels. This facilitates knowledge sharing and advancements in biofuel technologies.
Carbon Emission Reduction
Biofuel production in Sweden contributes to significant reductions in carbon emissions. Biofuels have lower lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping Sweden meet its climate goals.
It’s important to note that specific production figures and targets may vary over time, so it’s advisable to consult up-to-date sources for the latest data on biofuel production in Sweden.
Company who support Biofuel Production in Sweden
Several companies in Sweden actively support and contribute to biofuel production.
Here are a few notable examples:
SEKAB: SEKAB is a Swedish company that specializes in bio-based chemicals and biofuels. They are a key player in the production of advanced biofuels, including cellulosic ethanol derived from forest residues and agricultural waste.
Preem: Preem is the largest fuel company in Sweden and is actively involved in biofuel production. They have invested in biofuel refineries and focus on producing biodiesel from renewable feedstocks like rapeseed oil and tall oil (a byproduct of the forest industry).
Lantmännen: Lantmännen is a Swedish agricultural cooperative that is engaged in various sectors, including biofuels. They produce bioethanol from grain crops like wheat and barley, contributing to Sweden’s biofuel production capacity.
Södra: Södra is a forest industry cooperative in Sweden that supports biofuel production through the utilization of forest biomass. They supply wood chips and pellets made from forest residues for energy production, including bioenergy and heat generation.
St1: St1 is a Finnish energy company that operates in Sweden and is committed to developing sustainable solutions, including biofuels. They produce and distribute bioethanol and biodiesel, contributing to Sweden’s renewable fuel supply.
Neste: Although Neste is a Finnish company, it has a significant presence and operations in Sweden. Neste is a global leader in renewable diesel production and operates a renewable diesel refinery in Porvoo, Finland, which supplies biofuels to the Swedish market.
These companies play a vital role in supporting and advancing biofuel production in Sweden through their investments, research, and development efforts. It’s worth noting that the biofuel industry is dynamic, and there may be additional companies involved in biofuel production in Sweden beyond those listed here.
Conclusion for Biofuel Production in Sweden
Sweden has made significant progress in biofuel production, establishing itself as a global leader in the field.
The country has embraced biofuels as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, with a strong commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving its renewable energy targets.
Key highlights of biofuel production in Sweden include the production of bioethanol and biodiesel, utilization of forest biomass for bioenergy, government support through policies and incentives, and active participation in international collaborations and research projects. Companies such as SEKAB, Preem, Lantmännen, Södra, St1, and Neste are among the major players supporting and contributing to biofuel production in Sweden. Through these efforts, Sweden is setting an example for other nations in transitioning to a greener and more sustainable future
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/05/biofuel-production-in-sweden.html
Renewable Energy
California’s Next Governor?
 What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
What does the most affluent state in America need in its next governor? I’m pretty sure it not a Trump supporter.
Yes, we have traffic, which we hate. But that’s because everybody and his dog wants to be here for our economic opportunities and our natural beauty.
In general, we reject racism, ignorance, corruption, and environmental destruction.
Renewable Energy
Understanding Social Democracy
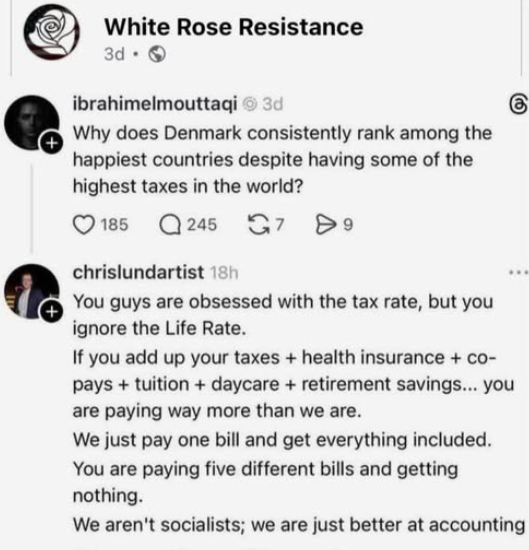 I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
I can’t swear that the content of the meme here is accurate; in fact, most affluent Scandinavians I run across admit that they pay higher taxes than Americans.
They claim that the attraction is that they aren’t forced to live among uneducated slobs where people are dying of treatable diseases with masses of impoverished people living on the streets.
Isn’t there something to be said for that?
Renewable Energy
What Kids Need from Their Parents
 Well, here’s a controversial statement.
Well, here’s a controversial statement.
Apparently, there are people who believe kids should be raised by dishonest imbeciles.
https://www.2greenenergy.com/2026/03/05/what-kids-need-from-their-parents/
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits






