As a budget freeze for Argentina’s public universities amid soaring inflation leaves campuses unable to pay their electricity bills and climate science under threat, the country’s researchers and students are taking to the streets in a nationwide demonstration on Tuesday.
The dire outlook for Argentina’s renowned higher education system under President Javier Milei, a right-wing populist, was highlighted on April 22 – Earth Day – by Argentine plant ecologist Pedro Jaureguiberry, who was announced as a finalist in the prestigious Frontiers Planet Prize.
“The current budget for universities in 2024 is insufficient, adding to the fact that in recent years we have only received 20% of the budget we asked for conducting research at our lab,” Jaureguiberry, an assistant researcher with the Multidisciplinary Institute of Plant Biology at the National University of Córdoba (UNC), told Climate Home.
The 44-year-old scientist, who has spent his entire academic career in Argentina, was shortlisted for the award as one of 23 national champions drawn from science research teams across six continents, in recognition of a study he led on the drivers of human-caused biodiversity loss.

Dr Jaureguiberry conducting fieldwork in central western Argentina. (Photo: Diego Gurvich)
Of the finalists, three international winners will be announced in June in Switzerland, receiving prize money of $1.1 million each for their role in groundbreaking scientific research.
Global billionaires tax to fight climate change, hunger rises up political agenda
With annual inflation running close to 300%, this year’s freeze on Argentina’s government budget for universities and scientific research amounts to a spending cut in real terms of around 80%, according to the University of Buenos Aires, which this month declared itself in an “economic emergency”.
On Tuesday, university teaching staff and students, backed by trade unions, will march in Buenos Aires and other cities “in defence of public education”, which they say faces a grave threat from the budget squeeze.
Met office hit by layoffs
Argentine meteorologist Carolina Vera, former vice-chair of a key working group responsible for the latest assessment report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, said that in four decades of teaching and research she had never seen “such a level of dismantling through the reduction of research grants and programs with such disdain for knowledge”.
“This is very serious for atmospheric and ocean sciences, key to issues such as climate change, placing a whole new generation of meteorologists and climatologists in danger,” she told Climate Home from Trevelin, in the southern province of Chubut.
There has been widespread condemnation of 86 layoffs affecting administrative and other contractors at the National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET), while Vera added that she is concerned about the situation at the National Meteorological Service, where 73 technicians have been let go. That, she warned, would affect the functionality of early warning and disaster prevention systems.
Canadian minister vows to fight attempts to weaken plastic pollution treaty
Climatic and meteorological challenges are increasing in Argentina, from heavy rains due to the El Niño weather phenomenon – which has caused an ongoing dengue epidemic – to extreme heat and wildfires.
A significant drought is forecast for the southern hemisphere summer of 2024-2025, from November to February, as El Niño gives way to an expected La Niña, with the National Meteorological Service having a key role to play in predicting conditions and disseminating information about them ahead of time.
Vera added that the budget restrictions on CONICET would also limit its research capabilities, particularly relating to climate change. “We hope that this will be reversed soon,” she added.
Greenlight for extractive industries
Milei has branded climate change a “socialist lie” since 2021 and has also questioned public education for “brainwashing people” with Marxist ideology.
Sergio Federovisky, deputy minister of environment during the previous presidency of Alberto Fernández, said Milei is not only disdainful of scientific views on global warming but also on broader environmental protection. For example, Milei – a former university professor and television pundit – said during his presidential campaign that “a company can pollute a river all it wants”.
“Climate denialism is not a scientific position, but rather an argument used to release all types of extractive actions that could be hindered by an environmental policy on the use of natural resources and the concentration of wealth,” Federovisky told Climate Home from Buenos Aires.

Meeting between Argentine President Javier Milei and Elon Musk in Texas, United States, at the Tesla factory on April 12 2024, forging a partnership through which the government is betting on attracting investment to Argentina. (Photo: Prensa Casa Rosada via / Latin America News Agency / Reuters)
In an economic review published on February 1, which unlocked $4.7 billion to support the new government’s policies, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) expressed its support for investment to increase the exploitation of oil and gas reserves and metals mining in Argentina, in order to boost exports and government revenues.
World Bank head Ajay Banga told journalists before last week’s Spring Meetings that the Argentine economy is going through a “whole economic realignment”. The bank “is supportive of the direction of that economy” and looks forward “to working closely with their leadership to help them as they go forward”, he added.
Yet he also noted that the bank’s latest review of economic prospects for the region highlighted challenges, including the impacts of Argentina’s correction, with regional GDP projected to expand by 1.6 percent in 2024, one of the lowest rates in the world and insufficient to drive prosperity.
World Bank climate funding greens African hotels while fishermen sink
The IMF’s support for Milei’s neoliberal economic policies has been strongly criticised by the International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC), which said on Friday that fiscal austerity “is not the answer when people’s lives and their democratic rights are at stake”.
“The IMF is celebrating the budget surplus in Argentina, but it’s indefensible to ignore the human cost of this economic shock therapy,” the ITUC’s General Secretary Luc Triangle said in a statement.
“Pensions have been slashed, thousands of public sector workers fired, public services are on the verge of collapse, unemployment is growing and food poverty spreading.”
Last week the government attempted to head off Tuesday’s protest by announcing a last-minute budget increase for maintenance costs for universities. But that was rejected by a national council of rectors and has not deterred the movement against the austerity measures, with large numbers set to come out onto the streets as planned.
(Reporting by Julián Reingold; editing by Megan Rowling)
The post Argentinian scientists condemn budget cuts ahead of university protest appeared first on Climate Home News.
Argentinian scientists condemn budget cuts ahead of university protest
Climate Change
On the Farm, the Hidden Climate Cost of America’s Broken Health Care System
American farmers are drowning in health insurance costs, while their German counterparts never worry about medical bills. The difference may help determine which country’s small farms are better prepared for a changing climate.
Samantha Kemnah looked out the foggy window of her home in New Berlin, New York, at the 150-acre dairy farm she and her husband, Chris, bought last year. This winter, an unprecedented cold front brought snowstorms and ice to the region.
On the Farm, the Hidden Climate Cost of the Broken U.S. Health Care System
Climate Change
A Little-Used Maneuver Could Mean More Drilling and Mining in Southern Utah’s Redrock Country
Two Utah Congress members have introduced a resolution that could end protections for Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument. Conservation groups worry similar maneuvers on other federal lands will follow.
Lawmakers from Utah have commandeered an obscure law to unravel protections for the Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, potentially delivering on a Trump administration goal of undoing protections for public conservation lands across the country.
A Little-Used Maneuver Could Mean More Drilling and Mining in Southern Utah’s Redrock Country
Climate Change
Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes
Drought and heatwaves occurring together – known as “compound” events – have “surged” across the world since the early 2000s, a new study shows.
Compound drought and heat events (CDHEs) can have devastating effects, creating the ideal conditions for intense wildfires, such as Australia’s “Black Summer” of 2019-20 where bushfires burned 24m hectares and killed 33 people.
The research, published in Science Advances, finds that the increase in CDHEs is predominantly being driven by events that start with a heatwave.
The global area affected by such “heatwave-led” compound events has more than doubled between 1980-2001 and 2002-23, the study says.
The rapid increase in these events over the last 23 years cannot be explained solely by global warming, the authors note.
Since the late 1990s, feedbacks between the land and the atmosphere have become stronger, making heatwaves more likely to trigger drought conditions, they explain.
One of the study authors tells Carbon Brief that societies must pay greater attention to compound events, which can “cause severe impacts on ecosystems, agriculture and society”.
Compound events
CDHEs are extreme weather events where drought and heatwave conditions occur simultaneously – or shortly after each other – in the same region.
These events are often triggered by large-scale weather patterns, such as “blocking” highs, which can produce “prolonged” hot and dry conditions, according to the study.
Prof Sang-Wook Yeh is one of the study authors and a professor at the Ewha Womans University in South Korea. He tells Carbon Brief:
“When heatwaves and droughts occur together, the two hazards reinforce each other through land-atmosphere interactions. This amplifies surface heating and soil moisture deficits, making compound events more intense and damaging than single hazards.”
CDHEs can begin with either a heatwave or a drought.
The sequence of these extremes is important, the study says, as they have different drivers and impacts.
For example, in a CDHE where the heatwave was the precursor, increased direct sunshine causes more moisture loss from soils and plants, leading to a drought.
Conversely, in an event where the drought was the precursor, the lack of soil moisture means that less of the sun’s energy goes into evaporation and more goes into warming the Earth’s surface. This produces favourable conditions for heatwaves.
The study shows that the majority of CDHEs globally start out as a drought.
In recent years, there has been increasing focus on these events due to the devastating impact they have on agriculture, ecosystems and public health.
In Russia in the summer of 2010, a compound drought-heatwave event – and the associated wildfires – caused the death of nearly 55,000 people, the study notes.

The record-breaking Pacific north-west “heat dome” in 2021 triggered extreme drought conditions that caused “significant declines” in wheat yields, as well as in barley, canola and fruit production in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada, says the study.
Increasing events
To assess how CDHEs are changing, the researchers use daily reanalysis data to identify droughts and heatwaves events. (Reanalysis data combines past observations with climate models to create a historical climate record.) Then, using an algorithm, they analyse how these events overlap in both time and space.
The study covers the period from 1980 to 2023 and the world’s land surface, excluding polar regions where CDHEs are rare.
The research finds that the area of land affected by CDHEs has “increased substantially” since the early 2000s.
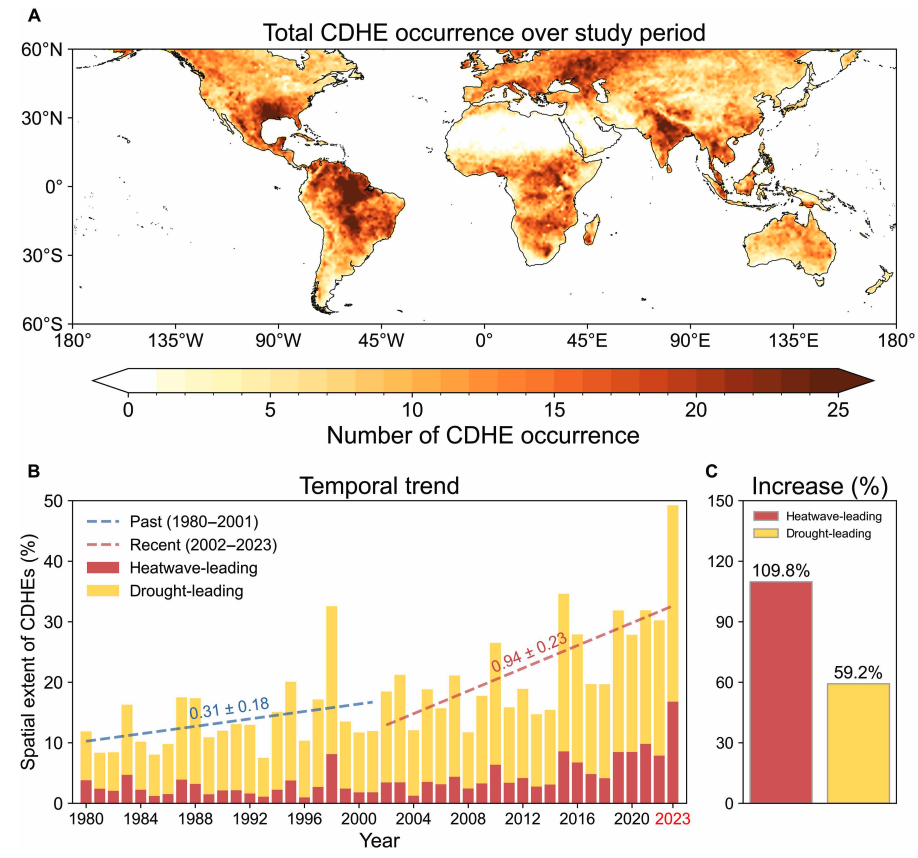
Heatwave-led events have been the main contributor to this increase, the study says, with their spatial extent rising 110% between 1980-2001 and 2002-23, compared to a 59% increase for drought-led events.
The map below shows the global distribution of CDHEs over 1980-2023. The charts show the percentage of the land surface affected by a heatwave-led CDHE (red) or a drought-led CDHE (yellow) in a given year (left) and relative increase in each CDHE type (right).
The study finds that CDHEs have occurred most frequently in northern South America, the southern US, eastern Europe, central Africa and south Asia.
Threshold passed
The authors explain that the increase in heatwave-led CDHEs is related to rising global temperatures, but that this does not tell the whole story.
In the earlier 22-year period of 1980-2001, the study finds that the spatial extent of heatwave-led CDHEs rises by 1.6% per 1C of global temperature rise. For the more-recent period of 2022-23, this increases “nearly eightfold” to 13.1%.
The change suggests that the rapid increase in the heatwave-led CDHEs occurred after the global average temperature “surpasse[d] a certain temperature threshold”, the paper says.
This threshold is an absolute global average temperature of 14.3C, the authors estimate (based on an 11-year average), which the world passed around the year 2000.
Investigating the recent surge in heatwave-leading CDHEs further, the researchers find a “regime shift” in land-atmosphere dynamics “toward a persistently intensified state after the late 1990s”.
In other words, the way that drier soils drive higher surface temperatures, and vice versa, is becoming stronger, resulting in more heatwave-led compound events.
Daily data
The research has some advantages over other previous studies, Yeh says. For instance, the new work uses daily estimations of CDHEs, compared to monthly data used in past research. This is “important for capturing the detailed occurrence” of these events, says Yeh.
He adds that another advantage of their study is that it distinguishes the sequence of droughts and heatwaves, which allows them to “better understand the differences” in the characteristics of CDHEs.
Dr Meryem Tanarhte is a climate scientist at the University Hassan II in Morocco, and Dr Ruth Cerezo Mota is a climatologist and a researcher at the National Autonomous University of Mexico. Both scientists, who were not involved in the study, agree that the daily estimations give a clearer picture of how CDHEs are changing.
Cerezo-Mota adds that another major contribution of the study is its global focus. She tells Carbon Brief that in some regions, such as Mexico and Africa, there is a lack of studies on CDHEs:
“Not because the events do not occur, but perhaps because [these regions] do not have all the data or the expertise to do so.”
However, she notes that the reanalysis data used by the study does have limitations with how it represents rainfall in some parts of the world.
Compound impacts
The study notes that if CDHEs continue to intensify – particularly events where heatwaves are the precursors – they could drive declining crop productivity, increased wildfire frequency and severe public health crises.
These impacts could be “much more rapid and severe as global warming continues”, Yeh tells Carbon Brief.
Tanarhte notes that these events can be forecasted up to 10 days ahead in many regions. Furthermore, she says, the strongest impacts can be prevented “through preparedness and adaptation”, including through “water management for agriculture, heatwave mitigation measures and wildfire mitigation”.
The study recommends reassessing current risk management strategies for these compound events. It also suggests incorporating the sequences of drought and heatwaves into compound event analysis frameworks “to enhance climate risk management”.
Cerezo-Mota says that it is clear that the world needs to be prepared for the increased occurrence of these events. She tells Carbon Brief:
“These [risk assessments and strategies] need to be carried out at the local level to understand the complexities of each region.”
The post Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Heatwaves driving recent ‘surge’ in compound drought and heat extremes
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits






