Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Shifting political players
EU LEADERSHIP: Ursula von der Leyen has secured another five years as president of the European Commission following a vote yesterday in which she won the backing of 401 MEPs – 40 more than needed, reported Bloomberg. In her reelection bid, von der Leyen committed to EU climate goals including the still-pending 90% emissions reduction by 2040 target and a new Clean Industrial Deal, Euractiv reported. However, the publication noted that her comments on nature protection were limited to “positive rhetoric” only.
PARIS PM: Elsewhere in Europe, veteran climate negotiator Laurence Tubiana has been proposed as the next French prime minister, with backing from the Socialist, Green and Communist parties in the current hung parliament, reported Climate Home News. Tubiana, who is currently CEO at the European Climate Foundation [which funds Carbon Brief], was one of the “architects” of the Paris Agreement in 2015, according to Bloomberg.
VANCE’S STANCE: In the US, Donald Trump’s newly selected running mate JD Vance has come under scrutiny for his climate scepticism. The Republican vice presidential candidate is “a staunch supporter of the oil and gas industry and an opponent of renewable energy”, according to the Independent, but has reportedly only held such views in recent years, a shift that coincides with his bid for Trump support. He also has investments in “green” technologies, reported E&E News, but the New York Times emphasised his public anti-climate sentiments and his sponsorship of green legislation repeals as a senator for Ohio.
AFRICAN COAL: In South Africa, a political ecologist wrote in the Conversation that the country’s newly appointed environment minister has shown support for continuing to use coal and said his government would not be “bullied” into transitioning away from fossil fuels too quickly. It comes as Agence France-Presse reported that the country’s president Cyril Ramaphosa has “reaffirmed the coal-dependent nation’s commitment to moving towards renewable energy, but insisted that communities and workers must not lose out”.
Labour must ‘make up lost ground’
KING’S SPEECH: The UK’s new Labour government has confirmed a legislative agenda with the environment “front and centre”, reported the Guardian. The king’s speech mentioned that the government will set up the publicly owned GB Energy to “own, manage and operate clean power projects” across the UK, reported BBC News. The company is set to be capitalised with an £8.3bn investment. Meanwhile, Politico reported that Labour is set to appoint a climate envoy, a role that has been empty for more than a year.
NEW ADVICE: The Climate Change Committee (CCC), which advises the UK government on its climate policies, released its annual progress report on Thursday, urging Labour to “make up lost ground” after a lack of sufficient action under the last Conservative government. Carbon Brief covered the recommendations in detail (more on this below). Elsewhere, the Times reported that Emma Pinchbeck, chief executive of the industry group Energy UK, has been appointed “preferred candidate” for the next chief executive of the CCC.
Around the world
- ‘HELLISHLY HOT’: A heatwave across southern Europe and the Balkans has led governments to issue severe weather warnings, said France 24, with temperatures rising above 40C.
- CHINA ‘THIRD PLENUM’: A communique from China’s highly influential “third plenum” meeting called for a “coordinated approach to carbon cutting, pollution reduction, green development and economic growth”, as well as for the country to “actively respond to climate change”, according to state news agency Xinhua.
- CARIBBEAN VULNERABILITY: In the aftermath of Hurricane Beryl, which killed at least a dozen people and destroyed infrastructure across the Caribbean, the Associated Press reported that officials are demanding more funding from “financial and development institutions” to rebuild and address climate change.
- PROTEST IN PERIL: Five UK climate activists from Just Stop Oil received record-length jail sentences of up to five years for a plan to block London’s M25 motorway, reported Reuters. Meanwhile, the right to peaceful protest in Australia is also “in peril”, the Guardian reported.
- GLOBAL FLOODS: Downpours and flooding have killed hundreds in South Asia, caused “emergency alerts” in China, left more than 50 people dead in Niger and caused damage in Toronto, Canada.
$8.4bn
The amount of debt eradicated through “debt-for-nature” swaps from 1987-2023.
$7.6tn
The total amount of debt service paid by low- and middle-income countries over the same timescale, illustrating how swap schemes are “far too small to have any impact”, experts told the Carbon Brief.
Latest climate research
- European “fire weather” – conditions favourable to the ignition and spread of wildfires – will become “more severe” due to climate change, showed a new study in Environmental Research Letters.
- Optimising the conversion of organic waste into biogas for energy has considerable decarbonisation potential in China, said new research in Nature Communications, which found that their proposed system could contribute 3.77% of the emissions reduction needed for the country’s 1.5C-aligned target.
- Nature-based solutions have “consistently proven to be a cost-effective approach” to address disaster risk, reported researchers in Science of the Total Environment.
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured

UK emissions have been falling steadily for years, largely driven by the phaseout of coal and the growth of renewable power. However, only one-third of the reductions required to achieve the UK’s goal under the Paris Agreement of cutting emissions 68% by 2030 are covered by plans the CCC deems to be “credible”, according to its latest progress report. There is an even larger credibility gap for the sixth carbon budget for 2033-2037, with only a quarter of the cuts needed covered by “credible” policies. This is illustrated in the chart above, which shows the emissions cuts needed to reach net-zero (red), compared to cuts expected from policies that the CCC deems “credible”.
Spotlight
The climate impact of generative AI
Carbon Brief investigates the climate implications of the accelerating use of generative AI tools.
Google’s latest environmental report indicated that its total emissions have increased by almost 50% since 2019 and 13% year-on-year – a change it puts down to the growth of its data centres and rising emissions in its supply chain.
The report added that rolling out artificial intelligence (AI) services might make it “challenging” to cut emissions due to the “increasing energy demands from the greater intensity of AI compute”.
Since March, Google has been integrating its generative AI tool Gemini into search functions, matching the exponential uptick in day-to-day AI use through Chat-GPT, Microsoft Copilot and other such tools. (“Generative AI” is AI that is capable of generating text, images, videos or other data from scratch in response to a prompt.)
But there’s a catch: when a query is sent to a generative AI model (a process known as inference), it uses a lot more energy than a traditional search, creating an expectation that the energy demand of data centres will shoot up as a result.
Soaring energy demand
A recent study, still awaiting peer review, found that a multipurpose AI system could use up to 33 times more energy than computers running task-specific software and that generating two images with AI uses as much energy as charging a smartphone.
Dr Sasha Luccioni, AI and climate lead at AI company Hugging Face and lead author of the study, explained to Carbon Brief that multipurpose models “tend to be larger in size” and are trained for several different outputs, “which makes them more computationally-intensive”.
Training AI models before they are available for use also takes large amounts of energy. OpenAI’s GPT-3 required 1,287MWh during training, enough electricity to power 120 average US households for one year.
Direct energy consumption is not the only factor to consider. Felippa Amanta, a PhD researcher of digital services at the University of Oxford’s Environmental Change Institute, told Carbon Brief that “generative AI can have quite unpredictable indirect energy effects from how they’re being used by households”.
People are also using AI assistants for things they never needed it for before – a phenomenon Amanta explained as “induced demand”.
AI is changing our day-to-day behaviour, “from finding recipes, to writing emails, making CVs and the list goes on”, she said. It is this increase in user inference that can drive up data centre energy demands.
A report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), released today, said that the rise of AI was putting an increased focus on the energy use of data centres. (AI currently accounts for around 10% of data-centre electricity use.)
It said that electricity consumption from data centres as a whole accounted for a “limited” 1-1.3% share of global electricity demand in 2022. This could rise to between 1.5% and 3% by 2026, according to its projections. (By contrast, electric vehicles are expected to account for between less than 1.5% and 2% by 2026.)
The agency noted that expectations of future data centre energy demand growth were highly uncertain, depending on the uptake of AI services and the efficiency of the chips used to run them. (It noted that chipmaker Nvidia recently unveiled a new chip that was 25 times more energy efficient than previous models.)
As with any electricity-intensive technology, the climate impact of surging AI use will be determined by the extent to which renewables can meet the demand. In April, the Financial Times reported that fossil-fuel companies are hoping that surging energy demand from AI use will “usher in a golden era” for gas production.
Efficiency and regulation
On the flip side, AI has the potential to be a tool for climate action, chiefly by increasing energy efficiency. For example, AI could be used to improve the efficiency of power grids or daily commutes.
But as generative AI tools become integrated into our lives, there is a risk of a rebound effect, where the ease and ubiquity of AI solutions make us use services more, countering any efficiency savings, Amanta said.
Another issue facing the rapidly changing AI environment is a lack of transparency.
The climate impacts of AI models can potentially be mitigated by increasing their computational efficiency, powering data centres with clean energy, or using more task-specific models – but a lack of transparent data is slowing the development of legislation to regulate this shift, Dr Luccioni told Carbon Brief:
“The fact that we can’t get an accurate estimate of the energy usage or emissions of the many AI-enabled tools used by millions of people daily is problematic.”
Without understanding the scope of the issue, it is difficult to regulate energy intensity or add constraints on companies, she added. The IEA’s report also called for more reliable data.
Amanta pointed to examples of policies being proposed in the US and Singapore that recognise the environmental impacts of AI’s growth and aim to regulate their efficiency and sources of energy. The EU’s AI Act, which came into force in June, includes environmental considerations.
Watch, read, listen
SEA LEVEL RISE: A coastal village in Myanmar is being eroded away due to rising sea levels and residents are struggling to access fresh groundwater, reported the Mekong Eye.
CLIMATE CONFLICT: Earthrise released a video exploring the intersectionality of climate change and conflict, speaking to Sudanese climate activist, Watan Mohamed.
FACTCHECKING TWISTERS: The new tornado disaster film gets a lot of things right about climate science, said experts in Nature.
Coming up
- 15 July-2 August: Second part of the 29th Session of the International Seabed Authority Assembly and Council, Kingston, Jamaica
- 22-26 July: 27th Session of the FAO Committee on Forestry, Rome
- 25-26 July: G20 3rd Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors meeting, Rio de Janeiro
Pick of the jobs
- International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD), senior communications officer, India energy programme | Salary: Unknown. Location: Delhi, India (remote)
- Environment America, climate solutions associate | Salary: $32,500. Location: Pennsylvania, US
- Climate Outreach, fundraising administrator | Salary: £23,000. Location: Oxford, UK (remote)
Climate Central, vice president for science | Salary: $140,000-$160,000. Location: Princeton, New Jersey, US (remote)
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 19 July 2024: New political players in EU and US; UK govt urged to make up ‘lost ground’ on targets; AI’s climate impact appeared first on Carbon Brief.
https://www.carbonbrief.org/debriefed-19-july-2024-new-political-players-in-eu-and-us-uk-govt-urged-to-make-up-lost-ground-on-targets-ais-climate-impact/
Greenhouse Gases
Our Fix Our Forests advocacy in 2025
Our Fix Our Forests advocacy in 2025
By Elissa Tennant
Healthy forests are a key part of the climate puzzle — and they’ve been a big part of our advocacy in 2025!
In January of this year, CCL volunteers sent 7,100 messages to Congress urging them to work together to reduce wildfire risk. Soon after, the Fix Our Forests Act was introduced in the House as H.R. 471 and passed the House by a bipartisan vote of 279–141.
At our Conservative Climate Conference and Lobby Day in March, we raised the Fix Our Forests Act as a secondary ask in 47 lobby meetings on Capitol Hill. The next month, an improved version of the bill was then introduced in the Senate as S. 1462 and referred to the Senate Agriculture Committee.
The bill was scheduled for a committee vote in October. CCLers placed more than 2,000 calls to senators on the committee and generated a flurry of local media in their states before the vote. In October, the bill passed the Senate Agriculture Committee with strong bipartisan support.
It’s clear that this legislation has momentum! As the Fix Our Forests Act now awaits a floor vote in the Senate, let’s take a look back at our 2025 advocacy efforts to advance this bill — and why it’s so important.
Protecting forests and improving climate outcomes
Wildfires are getting worse. In the U.S., the annual area burned by wildfires has more than doubled over the past 30 years. In California alone, the acreage burned by wildfires every year has more than tripled over the past 40 years.
American forests currently offset 12% of our annual climate pollution, with the potential to do even more. We need to take action to reduce wildfire, so forests can keep doing their important work pulling climate pollution out of the atmosphere.
The bipartisan Fix Our Forests Act:
- Protects America’s forests by supporting time-tested tools, like prescribed fire and reforestation, that make our forests healthy and able to better withstand and recover from severe wildfire and other extreme weather.
- Protects communities across the nation by reducing wildfire risks to people, homes, and water supplies and adopting new technologies.
- Protects livelihoods by supporting rural jobs and recreation areas and sustaining the forests that house and feed us.
CCL supports this bill alongside many organizations including American Forests, The Nature Conservancy, Environmental Defense Fund, National Audubon Society, The Western Fire Chiefs Association, The Federation of American Scientists and more.
A deeper dive into our efforts
All year long, CCL’s Government Relations staff has been in conversation with congressional offices to share CCL’s perspective on the legislation and understand the opportunities and challenges facing the bill. Our Government Relations team played a key role in helping us understand when and how to provide an extra grassroots push to keep the bill moving.
Starting Sept. 9 through the committee vote, CCLers represented by senators on the Senate Agriculture Committee made 2,022 calls to committee members in support of FOFA. CCL also signed a national coalition letter to Senate leadership in support of the bill, joining organizations like the American Conservation Coalition Action, Bipartisan Policy Center Action, the International Association of Fire Chiefs, and more.
In October, we launched a local media initiative in support of FOFA, focused on states with senators on the Agriculture Committee. Volunteers published letters to the editor and op-eds in California, Minnesota, Colorado, and more. In one state, the senator’s office saw a CCLer’s op-ed in the local newspaper, and reached out to schedule a meeting with those volunteers to discuss the bill! CCL’s Government Relations team joined in to make the most of the conversation.
As soon as the committee vote was scheduled for October 21, our Government Relations staff put out a call for volunteers to generate local endorsement letters from trusted messengers. CCL staff prepared short endorsement letter templates for each state that chapters could personalize and submit to their senator’s office. Each version included clear instructions, contact info, and space for volunteers to add their local context, like a short story or relevant example of how wildfires have impacted their area.
Then, CCL state coordinators worked with the CCL chapters in their states to make sure they prepared and sent the signed letters to the appropriate senate office, and to alert CCL’s Government Affairs staff so they could follow up and keep the conversation going on Capitol Hill.
Individually, our voices as climate advocates struggle to break through and make change. But it’s this kind of coordinated nationwide effort, with well-informed staff partnering with motivated local volunteers, that makes CCL effective at moving the needle in Congress.
On October 21, the Fix Our Forests Act officially passed the Senate Agriculture Committee with a vote of 18-5.
Building on the momentum
After committee passage, FOFA is now waiting to be taken up by the full Senate for a floor vote. It’s not clear yet if it will move as a standalone bill or included in a package of other legislation.
But to continue building support, we spent a large portion of our Fall Conference training our volunteers on the latest information about the bill, and we included FOFA as a primary ask in our Fall Lobby Week meetings.
Volunteers are now messaging all senators in support of FOFA. If you haven’t already, add your voice by sending messages to your senators about this legislation. With strategy, organization, and a group of dedicated people, we can help pass the Fix Our Forests Act, reducing wildfire risk and helping forests remove more climate pollution.
Help us keep the momentum going! Write to your Senator in support of the Fix Our Forests Act.
The post Our Fix Our Forests advocacy in 2025 appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 5 December: Deadly Asia floods; Adaptation finance target examined; Global south IPCC scientists speak out
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Deadly floods in Asia
MOUNTING DEVASTATION: The Associated Press reported that the death toll from catastrophic floods in south-east Asia had reached 1,500, with Indonesia, Sri Lanka and Thailand most affected and hundreds still missing. The newswire said “thousands” more face “severe” food and clean-water shortages. Heavy rains and thunderstorms are expected this weekend, it added, with “saturated soil and swollen rivers leaving communities on edge”. Earlier in the week, Bloomberg said the floods had caused “at least $20bn in losses”.
CLIMATE CHANGE LINKS: A number of outlets have investigated the links between the floods and human-caused climate change. Agence France-Presse explained that climate change was “producing more intense rain events because a warmer atmosphere holds more moisture and warmer oceans can turbocharge storms”. Meanwhile, environmental groups told the Associated Press the situation had been exacerbated by “decades of deforestation”, which had “stripped away natural defenses that once absorbed rainfall and stabilised soil”.
‘NEW NORMAL’: The Associated Press quoted Malaysian researcher Dr Jemilah Mahmood saying: “South-east Asia should brace for a likely continuation and potential worsening of extreme weather in 2026 and for many years.” Al Jazeera reported that the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies had called for “stronger legal and policy frameworks to protect people in disasters”. The organisation’s Asia-Pacific director said the floods were a “stark reminder that climate-driven disasters are becoming the new normal”, the outlet said.
Around the world
- REVOKED: The UK and Netherlands withdrew $2.2bn of financial backing from a controversial liquified natural gas (LNG) project in Mozambique, Reuters reported. The Guardian noted that TotalEnergies’ “giant” project stood accused of “fuelling the climate crisis and deadly terror attacks”.
- REVERSED: US president Donald Trump announced plans to “significantly weaken” Biden-era fuel efficiency requirements for cars, the New York Times said.
- RESTRICTED: EU leaders agreed to ban the import of Russian gas from autumn 2027, the Financial Times reported. Meanwhile, Reuters said it is “likely” the European Commission will delay announcing a plan on auto sector climate targets next week, following pressure to “weaken” a 2035 cut-off for combustion engines.
- RETRACTED: An influential Nature study that looked at the economic consequences of climate change has been withdrawn after “criticism from peers”, according to Bloomberg. [The research came second in Carbon Brief’s ranking of the climate papers most covered by the media in 2024.]
- REBUKED: The federal government of Canada faced a backlash over an oil pipeline deal struck last week with the province of Alberta. CBC News noted that First Nations chiefs voted “unanimously” to demand the withdrawal of the deal and Canada’s National Observer quoted author Naomi Klein as saying that the prime minister was “completely trashing Canada’s climate commitments”.
- RESCHEDULED: The Indonesian government has cancelled plans to close a coal plant seven years early, Bloomberg reported. Meanwhile, Bloomberg separately reported that India is mulling an “unprecedented increase” in coal-power capacity that could see plants built “until at least 2047”.
$518 billion a year
The projected coastal flood damages for the Asia-Pacific region by 2100 if current policies continue, according to a Scientific Reports study covered this week by Carbon Brief.
Latest climate research
- More than 100 “climate-sensitive rivers” worldwide are experiencing “large and severe changes in streamflow volume and timing” | Environmental Research Letters
- Africa’s forests have switched from a carbon sink into a source | Scientific Reports
- Increasing urbanisation can “substantially intensify warming”, contributing up to 0.44C of additional temperature rise per year through 2060 | Communications Earth & Environment
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
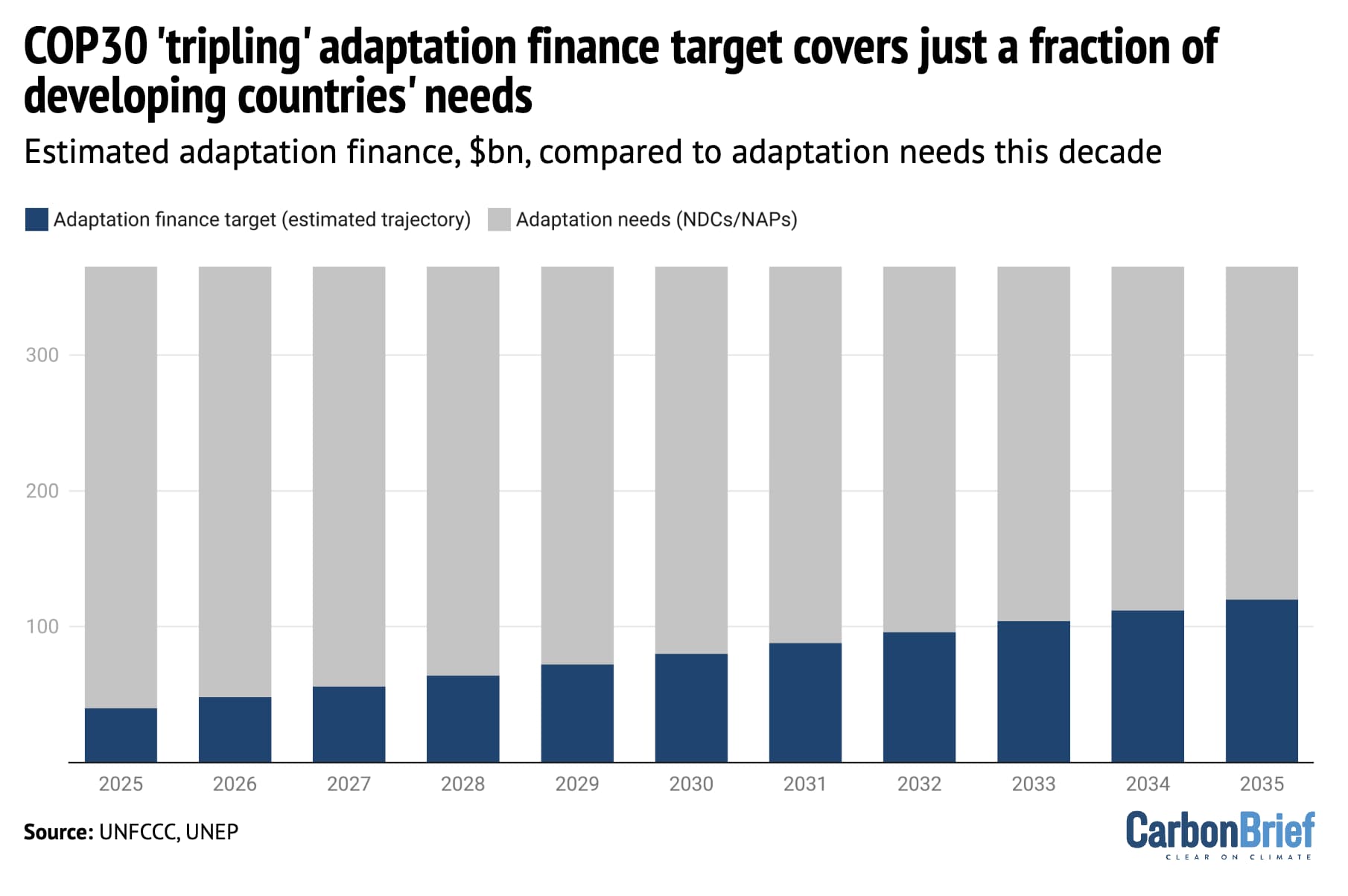
A new target for developed nations to triple adaptation finance by 2035, agreed at the COP30 climate summit, would not cover more than a third of developing countries’ estimated needs, Carbon Brief analysis showed. The chart above compares a straight line to meeting the adaptation finance target (blue), alongside an estimate of countries’ adaptation needs (grey), which was calculated using figures from the latest UN Environmental Programme adaptation gap report, which were based on countries’ UN climate plans (called “nationally determined contributions” or NDCs) and national adaptation plans (NAPs).
Spotlight
Inclusivity at the IPCC
This week, Carbon Brief speaks to an IPCC lead author researching ways to improve the experience of global south scientists taking part in producing the UN climate body’s assessments.
Hundreds of climate scientists from around the world met in Paris this week to start work on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC’s) newest set of climate reports.
The IPCC is the UN body responsible for producing the world’s most authoritative climate science reports. Hundreds of scientists from across the globe contribute to each “assessment cycle”, which sees researchers aim to condense all published climate science over several years into three “working group” reports.
The reports inform the decisions of governments – including at UN climate talks – as well as the public understanding of climate change.
The experts gathering in Paris are the most diverse group ever convened by the IPCC.
Earlier this year, Carbon Brief analysis found that – for the first time in an IPCC cycle – citizens of the global south make up 50% of authors of the three working group reports. The IPCC has celebrated this milestone, with IPCC chair Prof Jim Skea touting the seventh assessment report’s (AR7’s) “increased diversity” in August.
But some IPCC scientists have cautioned that the growing involvement of global south scientists does not translate into an inclusive process.
“What happens behind closed doors in these meeting rooms doesn’t necessarily mirror what the diversity numbers say,” Dr Shobha Maharaj, a Trinidadian climate scientist who is a coordinating lead author for working group two (WG2) of AR7, told Carbon Brief.
Global south perspective
Motivated by conversations with colleagues and her own “uncomfortable” experience working on the small-islands chapter of the sixth assessment cycle (AR6) WG2 report, Maharaj – an adjunct professor at the University of Fiji – reached out to dozens of fellow contributors to understand their experience.
The exercise, she said, revealed a “dominance of thinking and opinions from global north scientists, whereas the global south scientists – the scientists who were people of colour – were generally suppressed”.
The perspectives of scientists who took part in the survey and future recommendations for the IPCC are set out in a peer-reviewed essay – co-authored by 20 researchers – slated for publication in the journal PLOS Climate. (Maharaj also presented the findings to the IPCC in September.)
The draft version of the essay notes that global south scientists working on WG2 in AR6 said they confronted a number of diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) issues, including “skewed” author selection, “unequal” power dynamics and a “lack of respect and trust”. The researchers also pointed to logistical constraints faced by global south authors, such as visa issues and limited access to journals.
The anonymous quotations from more than 30 scientists included in the essay, Maharaj said, are “clear data points” that she believes can advance a discussion about how to make academia more inclusive.
“The literature is full of the problems that people of colour or global south authors have in academia, but what you don’t find very often is quotations – especially from climate scientists,” she said. “We tend to be quite a conservative bunch.”
Road to ‘improvement’
Among the recommendations set out in the essay are for DEI training, the appointment of a “diversity and inclusion ombudsman” and for updated codes of conduct.
Marharaj said that these “tactical measures” need to occur alongside “transformative approaches” that help “address value systems, dismantle power structures [and] change the rules of participation”.
With drafting of the AR7 reports now underway, Maharaj said she is “hopeful” the new cycle can be an improvement on the last, pointing to a number of “welcome” steps from the IPCC.
This includes holding the first-ever expert meeting on DEI this autumn, new mechanisms where authors can flag concerns and the recruitment of a “science and capacity officer” to support WG2 authors.
The hope, Maharaj explained, is to enhance – not undermine – climate science.
“The idea here was to move forward and to improve the IPCC, rather than attack it,” she said. “Because we all love the science – and we really value what the IPCC brings to the world.”
Watch, read, listen
BROKEN PROMISES: Climate Home News spoke to communities in Nigeria let down by the government’s failure to clean up oil spills by foreign companies.
‘WHEN A ROAD GOES WRONG’: Inside Climate News looked at how a new road from Brazil’s western Amazon to Peru has become a “conduit for rampant deforestation and illegal gold mining”.
SHADOWY COURTS: In the Guardian, George Monbiot lamented the rise of investor-state dispute settlements, which he described as “undemocratic offshore tribunals” that are already having a “chilling effect” on countries’ climate ambitions.
Coming up
- 1-12 December: UN Environment Assembly 7, Nairobi, Kenya
- 7 December: Hong Kong legislative elections
- 11 December: Falkland Islands legislative assembly elections
Pick of the jobs
- Greenpeace International, engagement manager – climate and energy | Salary: Unknown. Location: Various
- The Energy, newsletter editor | Salary: Unknown. Location: Australia (remote)
- University of Groningen, PhD position in motivating people to contribute to societal transitions | Salary: €3,059-€3,881 per month. Location: Groningen, the Netherlands
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 5 December: Deadly Asia floods; Adaptation finance target examined; Global south IPCC scientists speak out appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Greenhouse Gases
Cropped 3 December 2025: Extreme weather in Africa; COP30 roundup; Saudi minister interview
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
COP30 roundup
FOOD OFF THE MENU: COP30 wrapped up in the Brazilian Amazon city of Belém, with several new announcements for forest protection, but with experts saying that food systems were seemingly “erased” from official negotiations, Carbon Brief reported. Other observers told the Independent that the lack of mention of food in some of the main negotiated outcomes was “surprising” and “deeply disappointing”. The outlet noted that smallholder farmers spend an “estimated 20 to 40% of their annual income on adaptive measures…despite having done next to nothing to contribute to the climate crisis”.
‘BITTERSWEET’: Meanwhile, Reuters said that the summit’s outcomes for trees and Indigenous peoples were “unprecedented”, but “bittersweet”. It noted that countries had “unlocked billions in new funds for forests” through the Tropical Forest Forever Facility. (For more on that fund, see Carbon Brief’s explainer.) However, the newswire added, “nations failed to agree on a plan to keep trees standing as they have repeatedly promised to do in recent summits”. Mongabay noted that pledges to the new forest fund totalled “less than a quarter of the $25bn initially required for a full-scale rollout”.
‘MIXED OUTCOMES’: A separate piece in Mongabay said that COP30 “delivered mixed outcomes” for Indigenous peoples. One positive outcome was a “historic pledge to recognise Indigenous land tenure rights over 160m hectares” of tropical forest land, the outlet said. This was accompanied by a monetary pledge of $1.8bn to support “Indigenous peoples, local and Afro-descendant communities in securing land rights over the next five years”, it added. However, Mongabay wrote, there were some “major disappointments” around the summit’s outcomes, particularly around the absence of mention of critical minerals and fossil-fuel phaseout in the final texts.
Africa on edge
SOMALIA DROUGHT: Somalia officially declared a drought emergency last month “after four consecutive failed rainy seasons left millions at risk of hunger and displacement”, allAfrica reported, with 130,000 people in “immediate life-threatening need”. According to Al Jazeera, more than 4.5 million people “face starvation”, as “failed rains and heat devastated” the country, with displaced communities also “escaping fighting” in their villages and aid cuts impacting relief. Down to Earth, meanwhile, covered an Amnesty International report that demonstrated that Somalia failed to “implement a functional social-security system for the marginalised, particularly those negatively affected by drought”.
COCOA CRASH: Ivory Coast’s main cocoa harvest is expected to “decline sharply for [the] third consecutive year” due to erratic rainfall, crop disease, ageing farms and poor investment, Reuters reported. Africa Sustainability Matters observed that the delayed implementation of the EU’s deforestation law – announced last week – could impact two million smallholder farmers, who may see “delays in certification processes ripple through payment cycles and export volumes”. Meanwhile, SwissInfo reported that the “disconnect between high global cocoa prices and the price paid to farmers” is leading to “unprecedented cocoa smuggling” in Ghana.
‘FERTILISER CRISIS’: Nyasa Times reported that, “for the first time”, Malawian president Peter Mutharika admitted that the country is “facing a planting season…for which his government is dangerously unprepared”. According to the paper, Mutharika acknowledged that the country is “heading into the rains without adequate fertiliser and with procurement dangerously behind schedule” at a meeting with the International Monetary Fund’s Africa director. “We are struggling with supplies… We are not yet ready in terms of fertiliser,” Mutharika is quoted as saying, with the paper adding that his administration is “overwhelmed” by a fertiliser crisis.
News and views
PLANT TALKS COLLAPSE: “Decade-long” talks aimed at negotiating new rules for seed-sharing “collapsed” after week-long negotiations in Lima, Euractiv reported. The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture allows “any actor to access seed samples of 64 major food crops stored in public gene banks”, but “virtually no money flows back to countries that conserve and share seed diversity”, the outlet said. Observers “criticised the closed-door nature of the final talks”, which attempted to postpone a decision on payments until 2027, it added.
UNSUSTAINABLE: The UK food system is driving nature loss and deepening climate change, according to a new WWF report. The report analysed the impacts on nature, climate and people of 10 UK retailers representing 90% of the domestic grocery market. Most of the retailers committed in 2021 to halving the environmental impact of the UK grocery market by 2030. However, the report found that the retailers are “a long way off” on reducing their emissions and sourcing products from deforestation-free areas.
GREY CARBON: A “flurry” of carbon-credit deals “covering millions of hectares of landmass” across Africa struck by United Arab Emirates-based firm Blue Carbon on the sidelines of COP28 “have gone nowhere”, according to a joint investigation by Agence-France Presse and Code for Africa. In Zimbabwe – where the deal included “about 20% of the country’s landmass” – national climate change authorities said that the UAE company’s memorandum of understanding “lapsed without any action”. AFP attempted multiple ways to contact Blue Carbon, but received no reply. Meanwhile, research covered by New Scientist found that Africa’s forests “are now emitting more CO2 than they absorb”.
UK NATURE: The UK government released an updated “environmental improvement plan” to help England “meet numerous legally binding goals” for environmental restoration, BusinessGreen reported. The outlet added that it included measures such as creating “wildlife-rich habitats” and boosting tree-planting. Elsewhere, a study covered by the Times found that England and Wales lost “almost a third of their grasslands” in the past 90 years. The main causes of grassland decline were “increased mechanisation on farms, new agrochemicals and crop-growing”, the Times said.
IN DANGER: The Trump administration proposed changes to the US Endangered Species Act that “could clear the way for more oil drilling, logging and mining” in key species habitats, reported the New York Times. This act is the “bedrock environmental law intended to prevent animal and plant extinctions”, the newspaper said, adding that one of the proposals could make it harder to protect species from future threats, such as the effects of climate change. It added: “Environmental groups are expected to challenge the proposals in court once they are finalised.”
‘ALREADY OVERSTRETCHED’: Producing enough food to feed the world’s growing population by 2050 “will place additional pressure on the world’s already overstretched” resources, according to the latest “state of the world’s land and water resources” report from the UN Food and Agriculture Organization. The report said that degradation of agricultural lands is “creating unprecedented pressure on the world’s agrifood systems”. It also found that urban areas have “more than doubled in size in just two decades”, consuming 24m hectares “of some of the most fertile croplands” in the process.
Spotlight
Saudi minister interviewed
During the second week of COP30 in Belém, Carbon Brief’s Daisy Dunne conducted a rare interview with a Saudi Arabian minister.
Dr Osama Faqeeha is deputy environment minister for Saudi Arabia and chief adviser to the COP16 presidency on desertification.
Carbon Brief: Thank you very much for agreeing to this interview. You represent the Saudi Arabia COP16 presidency on desertification. What are your priorities for linking desertification, biodiversity and climate change at COP30?
Dr Osama Faqeeha: First of all, our priority is to really highlight the linkages – the natural linkage – between land, climate and biodiversity. These are all interconnected, natural pillars for Earth. We need to pursue actions on the three together. In this way, we can achieve multiple goals. We can achieve climate resilience, we can protect biodiversity and we can stop land degradation. And this will really give us multiple benefits – food security, water security, climate resilience, biodiversity and social goals.
CB: Observers have accused Saudi Arabia, acting on behalf of the Arab group, of blocking an ambitious outcome on a text on synergies between climate change and biodiversity loss, under the item on cooperation with international organisations. [See Carbon Brief’s full explanation.] What is your response?
OF: We support synergies in the action plans. We support synergies in the financial flows. We support synergies in the political [outcome]. What we don’t support is trying to reduce all of the conventions. We don’t support dissolving the conventions. We need a climate convention, we need a biodiversity convention and we need a desertification convention. There was this incident, but the discussion continued after that and has been clarified. We support synergies. We oppose dissolution. This way we dilute the issues. No. This is a challenge. But we don’t have to address them separately. We need to address them in a comprehensive way so that we can really have a win-win situation.
CB: But as the president of the COP16 talks on desertification, surely more close work on the three Rio conventions would be a priority for you?
OF: First of all, we have to realise the convention is about land. Preventing land degradation and combating drought. These are the two major challenges.

CB: We’re at COP30 now and we’re at a crucial point in the negotiations where a lot of countries have been calling for a roadmap away from fossil fuels. What is Saudi Arabia’s position on agreeing to a roadmap away from fossil fuels?
OF: I think the issue is the emissions, it’s not the fuel. And our position is that we have to cut emissions regardless. In Saudi Arabia, in our nationally determined contribution [NDC], we doubled [the 2030 emissions reductions target] – from 130MtCO2 to 278MtCO2 – on a voluntary basis. So we are very serious about cutting emissions.
CB: The presidency said that some countries see the fossil-fuel roadmap as a red line. Is Saudi Arabia seeing a fossil-fuel roadmap as a red line for agreement in the negotiations?
OF: I think people try to put pressure on the negotiation to go in one way or another. And I think we should avoid that because, trying to demonise a country, that’s not good. Saudi Arabia is a signatory to the Paris Agreement. Saudi Arabia made the Paris Agreement possible. We are committed to the Paris Agreement.
[Carbon Brief obtained the “informal list” of countries that opposed a fossil-fuel roadmap at COP30, which included Saudi Arabia.]
CB: You mention that you feel sometimes the media demonises Saudi Arabia. So could you clarify, what do you hope to be Saudi Arabia’s role in guiding the negotiations to conclusion here at this COP?
OF: I think we have to realise that there is common but differentiated responsibilities. We have developed countries and developing countries. We have to realise that this is very well established in the convention. We can reach the same end point, but with different pathways. And this is what the negotiation is all about. It’s not one size fits all. What works with a certain country may not work with another country. So, I think people misread the negotiations. We, as Saudi Arabia, officially announced that we will reach carbon neutrality by 2060 – and we are putting billions and billions of dollars to reach this goal. But it doesn’t mean that we agree on everything. On every idea. We agree to so many things, you never hear that. Saudi Arabia agrees on one thousand points and we disagree on one point, then suddenly it becomes the news. Now, why does the media do that? Maybe that gives them more attention. I don’t know. But all I can tell you is that Saudi Arabia is part of the process. Saudi Arabia is making the process work.
This interview has been edited for length.
Watch, read, listen
NEW CHALLENGE: CNN discussed the environmental impacts of AI usage and how scientists are using it to conserve biodiversity.
AMAZON COP: In the Conversation, researchers argued that hosting COP30 in the Amazon made the “realities of climate and land-use change jarringly obvious” and Indigenous voices “impossible to ignore”.
DUBIOUS CLAIMS: DeSmog investigated an EU-funded “campaign blitz” that “overstated the environmental benefits of eating meat and dairy, while featuring bizarre and misleading claims”.
WASP’S NEST: In a talk for the Leverhulme Centre for Nature Recovery, Prof Seirian Sumner explained the “natural capital” of wasps and why it is important to “love the unlovable parts of nature”.
New science
- Climate change can “exacerbate” the abundance and impacts of plastic pollution on terrestrial, freshwater and marine ecosystems | Frontiers in Science
- The North Sea region accounts for more than 20% of peatland-related emissions within the EU, UK, Norway and Iceland, despite accounting for just 4% of the region’s peatland area | Nature Communications
- Economic damages from climate-related disasters in the Brazilian Amazon rose 370% over 2000-22, with farming experiencing more than 60% of total losses | Nature Communications
In the diary
- 1-5 December: Meeting of the implementation review committee of the UN desertification convention | Panama City
- 2-5 December: Meeting of the contracting parties to the Barcelona Convention on the protection of the Mediterranean Sea | Cairo
- 5 December: World soil day
- 8-12 December: International Water Association water and development congress and exhibition | Bangkok
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz. Ayesha Tandon also contributed to this issue. Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org
The post Cropped 3 December 2025: Extreme weather in Africa; COP30 roundup; Saudi minister interview appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Cropped 3 December 2025: Extreme weather in Africa; COP30 roundup; Saudi minister interview
-
Climate Change4 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Greenhouse Gases4 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Why airlines are perfect targets for anti-greenwashing legal action