Weather Guard Lightning Tech

Vestas Buys LM Wind Power Factory, Increased Data Center Demand
This week we discuss uncertainty surrounding the IRA bill, GEV Wind Power’s acquisition by Certek, and the sale of an LM Wind Power factory to Vestas. Plus Blackstone is in talks to acquire TXNM Energy, pointing to increase data center demand. Register for the next SkySpecs webinar!
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly email update on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary Barnes’ YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
You are listening to the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast, brought to you by build turbines.com. Learn, train, and be a part of the Clean Energy Revolution. Visit build turbines.com today. Now here’s your hosts, Allen Hall, Joel Saxum, Phil Totaro, and Rosemary Barnes.
Allen Hall: Well, welcome to the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast, Joel and Rosemary.
It’s been an exciting week. A lot going on in a, in America in regards to what’s gonna happen with the IRA bill. Nobody knows the, it’s like, uh, as tense, as tense can be. You, you don’t even really see a lot of articles about it at the moment. Everybody’s just in, in kind of hold mode, like, hold your breath and hope something bad doesn’t happen.
Joel Saxum: I think the interesting thing there is when something like this pops up, you would tend to see a lot of LinkedIn opinions and you’re not. I think a lot of, a lot of people are kind of moved. They’re kind of, [00:01:00] nobody’s really saying too much. We’re kind of waiting to see,
Allen Hall: yeah, waiting for that spicy take.
Usually from Rosemary, but she hasn’t written that article yet. It must be coming. Rosemary.
Rosemary Barnes: Well, I haven’t been writing a lot of anything on LinkedIn recently. Um, yeah, a bit, I’m bit busy. I got, I got really sick of, uh, LinkedIn as well when I, I over posted for a few months and. I got over it. Started, started to hate it when people would, would write a comment on my post.
Yeah. And I’m like, just stop talking to me. Go away. And I’m like, yeah, you were the one who made this post. So you That was my, that was my sign to, um, yeah, to, to move away for a little while. Yeah. But it’s also, uh, I mean, you know, like I, it’s not a topic that I am an expert in. ’cause obviously I’m, you know, I don’t live there, so I’m not, yeah.
I have. I have heard a few podcasts talking about it. Um, there’s that one. Um, uh, do you guys listen to that podcast? That’s, it’s like [00:02:00] the original Energy gang crew, but none of them are on the Energy Gang anymore. Now they’ve got their own new podcast. It’s like Dig Ashore. And, um, the other two, sorry, I don’t, I don’t remember their, their names.
Joel Saxum: They just started
Allen Hall: that one.
Rosemary Barnes: It’s called, maybe it’s called Open Circuit.
Allen Hall: Oh, maybe I have, yes, I know what you’re talking about.
Rosemary Barnes: It, it’s really good. It’s very, uh, it’s too American Central for me to listen to every episode, but for, you know, Americans then, I’m sure that that’s, uh, that’s good. Um, they, they speculate a fair bit about it.
Um, and also the, um, podcast that has Jesse Jenkins on it, which is called Shift Key, um, they talk about it a bit as well. So I have, I have heard a fair few takes on it, but, um. Yeah, I don’t know. I’m, I’m waiting to see, to, to be honest, as a non-American, I’ve just written off American Wind Power for the next few years and, uh, you know, just like, wait, wait, wait a little while to like, uh, get started again.
But it, you know, it doesn’t affect me so much. I don’t, I, I don’t have [00:03:00]projects in America. Um, so I. Not affected day to day,
Joel Saxum: a and a half a dozen part load leads that I was in a hand, but now I’m not gonna
Rosemary Barnes: do. You know what though? I, it is actually incredibly challenging for me too because, um, Australians and probably every non-American, like I, my business insurance will not cover me in the us They just absolutely not.
There is not, it is not possible for me to get insurance. To do projects in the us Um, and it would only be possible if I actually started an American company. That would be the only way to do it. So, um, that is a big disincentive for me to expand into America. Um, just ’cause your legal system is very, very different to the rest of the world and um, yeah, insurance companies won’t take that risk so.
That’s why that, that’s why I’m not expending to America. But you know, the rest of the world is a big place. So,
Allen Hall: well, if you don’t spend all your time on LinkedIn, then maybe you can then join us on the webinar. We have an up on Wednesday, May 28th at 11:00 AM East Coast, US and it’s about lightning damage and lightning [00:04:00] strikes and it’s one of another, one of the monthly Sky Specs webinars with uh, PES Wind and the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast.
We have some really interesting guests. In this one, Matthew Stead from eLog Ping and Matt Segal from EDF. So if you know Matt Segal, uh, he knows his way around blades and blade repair and he has a really solid approaches on how to deal with the damage, that’s gonna be a great discussion. So if you have lightning damage and pretty much every operator that I’ve talked to has some lightning damage at the moment, uh, you’re gonna want to attend that.
Webinars free. So it’s Wednesday, May 28th, 11:00 AM. East Coast and you just sign up in the show notes below. Really simple
Joel Saxum: as busy wind energy professionals, staying informed is crucial, and let’s face it difficult. That’s why the Uptime podcast recommends PES Wind Magazine. I. PES Wind offers a diverse range of in-depth articles and expert [00:05:00] insights that dive into the most pressing issues facing our energy future.
Whether you’re an industry veteran or new to wind, PES Wind has the high quality content you need. Don’t miss out. Visit PS wind.com today.
Allen Hall: So the big news of the week, well there’s actually a couple, uh, big news articles this week. Uh, GEV, wind Power, which is a large repair company. Based in the uk, but they have a lot of their business in the United States.
Uh, was acquired by a company called CEC and Joel just doing some research on cec. It looks like a holding company. That’s what it seems like to me. It’s owned by David Harrison, who is based in the uk and it just looks like they’re gonna continue to, uh, try to grow GEV, but it also includes Wind Power Lab from Denmark and rig com.
Joel Saxum: From Australia. Yeah, they group their ctec. Um, I know that GEV Wind Power is, um, they, they have huge plans for growth, right? They’ve got the office in Dallas office in [00:06:00] Poland, the Wind Power Lab office in Copenhagen. Rig com office, I believe is in Melbourne, down in Australia, down by Rosemary. And then they have of course the big office for the UK and Hull and that’s for offshore and onshore.
Uh, but they’ve also just not opened another office up in Canada. So big, big expansion plans for GE v windpower. This CEC capital injection, uh, is gonna help for sure, right? They’ve got a, they’ve got a existing our infrastructure, uh, for the GEV WINDPOWER group. Uh, and they’re gonna keep ’em all in place and they’re just gonna con continue to grow.
So, uh, look to see some more things coming out of the, uh, GEV group. Put this injection to cash.
Allen Hall: Yeah, because GEV, when Power Lab and Rcom were part of the Bridges Fund, which was owned by Hojo
Joel Saxum: Well Bridge, so Bridges was a technically a think minority shareholder in the GEV group. Uh, but that was Goldman Sachs money, uh, bridges was right.
So now, now we’re going, CTEC is Macquarie money, so [00:07:00] Australian money. Being injected in. Well,
Allen Hall: that does make a little bit of sense though. Australia is gonna be a huge renewable powerhouse. It already is. So it makes sense that a Australian money would be involved in this because, uh, yeah, there’s gonna be a lot more wind turbines in solar activity in Australia.
It’s gonna pick up pretty well, so might as well grab a company early while you can and, and continue to grow it. The other thing that that happened today was LM wind power. Selling a factory up in Poland to Vestus. Now, we’ve all talked internally about what is happening at LM Wind Power because they’ve had a a number of staff reductions over the last year or so, and then they had the blade problem up in Canada.
It does seem like a lot of the design activities are moving towards the United States from GEs point of view. [00:08:00] That leaves a lot of LM factories with that are making blades for somebody else. Rosemary, when you were there, uh, LM did make blades for almost everybody for quite a while. It looks like they still do, but now they’re selling off the non GE factories.
Is that the plan?
Rosemary Barnes: I, I don’t know what the plan is. Uh, um, yeah, not inside anymore, so I don’t have any insider info, but, uh, I did spend. Quite a lot of time actually at that factory in Glen. And it’s definitely one of my favorite, favorite wind turbine blade manufacturing facilities that I ever visited. Um, they get a lot, they get a lot done there.
That is like what I could say. The team there is amazing. They, the amount of stuff they can get through in, you know, one shift is like. Double what it is in some other factories. So I think, you know, from, from that perspective, without knowing what best has paid for it, I think it’s a, um, a good call if they get to keep the personnel.
Um, so yeah, [00:09:00] it, um, good for Besters. I was actually looking at some information recently, something unrelated, but I, I came across some, um, research reports. Actually. There were academic papers and it had, um, they had gone through all Vista’s recent, um. Like, uh, all of their annual reports and also all the other listed companies.
So there’s, you know, there’s a few listed wind, turbine blade manufacturer, wind turbine manufacturers, um, where they will give, you know, a breakdown, public information, a breakdown of how their money is spent in profits and that sort of thing. Um, and they had this little chart that showed how much, um, the different manufacturers that they looked at, how much they were spending on their staff, and how much they were spending on research and development.
Vest, uh, staff were paid far more than the other, um, manufacturers that were on there.
Joel Saxum: That’s geopolitical though, right? Like Siemens, Siemens Committee said a lot of employees in Spain, they just, they’re cheaper employees, a cheaper labor force than it is in Denmark or Germany.
Rosemary Barnes: But also, so that, but also, [00:10:00] um, investors spent way more on research and development than, than the others.
And that’s like, I have gotten that impression, you know, ’cause like a lot of what I do with my YouTube channel is. Looking at new, new kinds of things that people are doing. And time after time, it was vest that had investigated this interesting thing. You know, like vesters are the one that have the, um, have tried a multi rotor design out and like actually to the point of making a prototype and, um, installing it.
Vesters are the ones that have done the in cable stayed, um, tower and, yeah, like again, put it up the, you know, like over and over again. There were these things where they maybe didn’t even believe that there was an imminent commercial case for this technology, but they were doing it to, to learn and just improve their general knowledge and to also.
Um, be ahead of the curve when things changed enough to make this new technology maybe make sense now they would have the information they needed to move, move fast on that. Well, that’s my, my take on why that makes sense to them. So, yeah, I, I, I do, I am starting to get the impression, and I’ve never worked at [00:11:00] Vestas or even, I never even did a blade project for Vestas while I was working at lm, but that’s definitely the impression that I’m getting, that the, you know, they’re kind of retaining more of the essence of the original.
Danish wind turbine companies, then the others have more become globalized, Americanized or yeah, like, um, Spain fight or you know, like what, whatever. From all the mergers that have happened, um, the culture has been diluted, but, but festers, I still, still see pushing the envelope. I mean, they haven’t always been profitable, so, um, you know, is the strategy right or not?
But then, you know, every western manufacturer and every. Every, every wind turbine manufacturer, no matter where they are in the world, including China, um, have had periods of unprofitability. That’s for sure. So, yeah. Um, I, I just think it’s interesting that they’re taking a real different approach.
Joel Saxum: Well, that’s what I was gonna say, uh, kind of rosemary before you jumped, said it’s cultural thing, right?
Like, they’re vestas, they’re Denmark, they’re the, the, you know, I guess you can, you could have this argument [00:12:00] between the Danish and the Dutch about who wind power kind of. First, there’s a cultural thing there too, right? Like you have DTU right there, you have the university at our, I wanna say it, right, orus.
Uh, but you have, you have all of these different facilities there that are also lending to that research, right? There’s a lot of grant money that gets funneled through DTU. And if you look at those projects with those couple of universities there in Denmark, you see a lot of times Vesta is tanked. On those projects.
There may be some other, um, third party companies or a lot of it being sponsored by the university, but you see Vestas in a lot of those. So I think it’s a, I’d like you said, I think it’s a cultural thing that the Danish still haven’t be, that still haven’t, that it’s a good thing that they’re doing what they’re doing.
I, in my opinion, but that they haven’t become. This larger global fired thing, right? Where they’re still kind of sticking to their roots?
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah, I mean, I like it as an engineer and I will say that a lot of, um, my best ex colleagues from LM have ended up at Vestas. Um, so, you know, I think that they are, they do, they do [00:13:00] attract, you know, like people who like to work on really interesting problems.
But I also have been around long enough to know that, um. The most interesting engineering problems are not always the most business savvy things to be working on. So that’s why I don’t wanna comment about it, you know, as a business strategy or, you know, suggest that, you know, investors are definitely going to, you know, remain dominant in the future.
Um, because a lot of the times the, you know, like over engineering is a thing and, uh, you can’t be competitive if you have you, you know, like a good, good engineering is really about. Doing the minimum that you, that you need to make the product that succeeds in the, in the market. Uh, doing any more than that is very satisfying to an engineer, but, um, it is not the, not usually the smartest thing to do for, you know, making a profitable business.
So
Allen Hall: good engineering is knowing when to stop. Which is the hardest part of engineering. ’cause you never wanna stop. You need to stop and make some money. Yeah. [00:14:00] Don’t let blade damage catch you off guard. OGs. Ping sensors detect issues before they become expensive. Time consuming problems from ice buildup and lightning strikes to pitch misalignment and internal blade cracks.
OGs Ping has you covered The cutting edge sensors are easy to install, giving you the power to stop damage before it’s too late. Visit eLog ping.com and take control of your turbine’s health today. So private equity, giant Blackstone’s infrastructure arm is reportedly and talks to acquire TX and M Energy, which is Texas and New Mexico.
And so utility companies serving about 800,000 homes and businesses across the New Mexico, Texas area. Uh, the discussions are still fluid. There’s not a lot of details. However, it does seem like this is a play by Blackstone to maybe set up some data centers and to get. In line to get a data center set up is really hard to do right now because you have to talk to an existing operator and [00:15:00]get them to get approvals and there’s paperwork and there’s applications.
Once you buy, uh, a large energy producer, you can kind of control that a little bit and there’s reasons to do it because Texas and New Mexico, there’s a lot of real estate there. Renewables are really easy to install. It makes this acquisition. Much more desirable, I think just because of where it is now.
TX and M was going to be acquired a couple months ago, Joel, by Avan Grid, except that got stopped by the administration. Uh, that was about a year ago, right? Where that deal got canceled for. Was it competitive reasons or was it because it was. Avant grid, which is not a US entity is, is that what the deal was?
I don’t remember
Joel Saxum: exactly why it got canceled. I just know that it was a regulatory approval thing. It wasn’t a, it wasn’t a due diligence problem or anything like that. It was just regulatory approval, [00:16:00]
but.
When I, when I read this article, I thought immediately, have you guys ever, have you guys ever seen the movie Inception?
No.
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah, you gotta say Inception. What’s wrong with you, Alan? Oh my God.
Joel Saxum: In the movie Inception, they, they have an issue where they’re like, we need to convince the pilot of the plane to do this, and we need to convince the stewardesses to do this, and we need to convince the, the, this person to do this. And they have a really rich fellow with them.
And they’re like, how are we going to get past these problems? And he’s like, I’ll just buy the airline. So in the movie, the guy just buys the airline and then he gets to do whatever he wants with the airplane and, and how they do their inception tricks, whatever. That’s exactly what I thought about when I saw Blackstone do this, right?
We wanna get these data centers on, we wanna do this, we wanna do this. It’s like, man, this is gonna be, this is gonna be difficult. We’re gonna have to convince all these people. We’re gonna have to do this regulatory approvals and get in line and queues. It’s like, what if we just buy the power company?
Okay. Just do that and you can do whatever you want
like
that. That [00:17:00] makes sense. I think it’s a genius thing and I think it, I’m surprised that it’s taken this long to do it and there hasn’t been some other larger players that have tried it. So I just just saw a thing yesterday, a chart that said there’s over 5,300 data centers in the United States right now.
It’s like 5,386 or something, which is Corey way, way larger than I thought it was. And we’re, and if you look at a global scale, we’re way in front of the next person. And I don’t remember exactly what it was, but everybody you talk to in the energy world is going, Hey, more data centers, more data centers, more data centers.
And it is, it’s, it’s, I listened to a podcast theater. They’re talking about wait until you see the next six months. What’s gonna happen with data centers? As, as you see, Google searches declining for chat GT requests. It’s gonna be all data centers.
Allen Hall: So EPRI is saying 48% of utilities nationwide are now receiving data center requests exceeding one gigawatt with almost half facing requests that exceed [00:18:00] 50% of the system peak demand.
Wow. That’s a lot of energy to be requesting.
Joel Saxum: So last summer, peak demand in Ercot, and I’m gonna talk Texas right now, right? ’cause this is where a lot of these data centers are going. ’cause Ercot is gonna, the Wild West. T’S peak demand last summer was 87 gigawatts at one point in time. They have it projected by, I think it was like 2031.
That peak demand is gonna be 213 gigawatts. And
Allen Hall: is that based on population or is that based on data center growth,
Joel Saxum: data center growth. That’s only five years away, six years away, and you’re talking almost triple the demand.
Allen Hall: Can, can we veer off just slightly on this discussion, which is the existing talk about the IRA bill and how they wanna change it.
So it’s gonna be harder for renewable companies to apply for the tax credits and production tax credits and all these little nuances that add up to something much more massive. They’re, [00:19:00] if the administration does that. And Congress passes it and whatever else happens, okay, fine. But in this data center demand, you cannot get enough gas turbines built to support that.
You can’t order one
Joel Saxum: and receive it before 2030. Right. So what are we talking about? You have to put solar and wind on the grid right now. ’cause it’s the only energy generating facility that’s, that’s that’s timely enough to get to meet demand. Right.
Allen Hall: Those, we just do not have the infrastructure right now in the United States or elsewhere.
Like a Siemens who makes a lot of gas turbines, can’t supply the demand. That’s about to happen. So the demand is gonna get so dang high. You’re gonna, you’re gonna go from 20 29, 20 30, uh, order book to 2035 order book probably in the next six months, the way it sounds. What are they
Joel Saxum: gonna do? Could you see a player that doesn’t, that knows turbines but doesn’t [00:20:00] do gas fired turbines coming in?
I don’t know who all the players are, right? I know GE sells ’em. I know a couple others, but like, like a steam, like a Rolls Royce is Rolls Royce sell gas turbine power plant turbines. They know. They know turbine technology couldn’t. Why? If you were them, wouldn’t you look at this demand and go. We should start building these things.
Allen Hall: Joel, to build a gas turbine is really difficult. It’s like building a jet engine. On steroids, it’s, and to make it something that’s really reliable, it is not easy. That’s why it takes so long to build these things. It’s not just a startup. Well, yeah, what are you gonna do? Build a second factory next door to the one you have and spend a billion dollars to set this thing up.
But you’re not gonna be able to make the first turbine for at least five or six years. That makes zero sense, because all of a sudden if the data center, uh, compute goes away, like some software engineer figures out how to do this a lot with less power, basically a lot less power to do it. Then poof, all their order book disappears and all that money they spend on a [00:21:00] factory disappears and no one’s willing to take that risk.
So who’s steps in the middle of this besides wind and solar and some batteries? Wind and solar betters right to, that’s the fastest way to get power onto the grid, even if it’s disconnected from the main grid, right? Even if you go geothermal,
Joel Saxum: you still need turbines. You still need turbines. Turbines are not quick to make.
And you can’t build a nuclear plant in about 10
Allen Hall: years. No. So what are we, Rosemary? What are we doing? And here’s my thought this morning. I woke up this morning like, this is a huge problem. What are we gonna do? My first thought was like, well, everybody’s gonna go to Australia because the power is plentiful and it’s only a data cable to America.
That’s what’ll happen. Rosemary?
Rosemary Barnes: Uh, I don’t, I don’t think data centers, I think data centers is primarily a US problem, and then there’ll be a few, and not even like, it’s, it’s localized within the US as well. People aren’t just like, people think with this, you know, data center growth that it’s like.
Everyone’s gonna worry about it. But you need data [00:22:00] centers, um, near where the, you know, the tech companies, the AI companies are, because they don’t, you know, they can’t be located on the other side of the world from where their data center is, if they’re gonna be, you know, running all these, um, these learning models.
And then you need them near population centers as well for, um, you know, so that they have them, them close by. I think the biggest thing with data centers that’s gonna be different to what everybody’s panicking about is that it is not gonna be the, um, the, the demand people are predicting is not going to come, come true to anything.
Like the extent, extent that what has been predicted. I think it will grow and it will grow a lot, but I, I, you know, like the growth that people are predicted is, um. Well, IM implausible for a start to actually achieve it. But I think also, like if you look back through history, I mean, you know, people always predict, you know, that you get a big amount of growth early on and people don’t really know what the, you know, the size of the exponent is.
And so when they project out into the future, you can get things wildly wrong and we have a history of you, you know, look back through the predicted energy use of all sorts of new [00:23:00] technologies over the, um, decades or, you know, centuries. Then you’ll see predictions that were just crazy in hindsight.
We’re really early in the AI thing, so algorithms are gonna be refined. Um, chip designs are gonna be refined. Even, you know, like everything else around data center’s gonna be refined. Maybe quantum computing is gonna make a difference in a few years. You know, like maybe something that hasn’t been invented yet.
You know, like five years ago people didn’t think AI would be doing what it is today. There’ll be some other technology in five years that’s doing something that we couldn’t foresee. Um, so I, you know, I think that it’s more likely that the. Unexpected technology developments are on the side of bringing down the amount of power.
Allen Hall: Yeah. But the way that tends to go in industry is once you’re on a pathway, there’s very little that’s gonna deter you off that pathway. So even if there are significant improvements, you’ll see the main path still be followed. And that’s gonna be the trouble with these AI data centers, is that they’re gonna [00:24:00] project out, they’re gonna get their.
Mindset about doing it a certain way, and they’re gonna go, and if you talk about saving 10% here or there, they’re like, if it’s gonna take 10 more weeks to get that done, we’re not gonna do it. We’re gonna continue down this pathway.
Rosemary Barnes: No, but they’re doing it all the time. They heard about a, a data center, it was designed and, um, you know, planned for a certain amount of compute, and then the chip designs improved and they totally changed it.
And so now it, you know, it’s the same power, but it, um, processes much more. And we’re gonna. We’re gonna say a lot. A lot of that I think.
Allen Hall: I think the chat GPT usage and the AI usage is relatively low, and I know US engineers like to use those services because we like the new tech and we want to be involving our fingers in it and see what it’s all about.
I think the vast majority of humanity really hasn’t touched it yet. When they do, it’s gonna go
Joel Saxum: crazy. Did you see that Google’s alphabet stock? When they, they just released a, they did, it was an earnings report, but they released the end. This is the first time that their number of search engine [00:25:00] entries, whatever requests.
Dropped and it’s because, because, and their stock dropped by 10% that day that happened. Yeah. Like that’s, and and, and like you said, we, people that are in the know are using, I use it all day long. Right. My, uh, my partner uses it all day long, but the general populace hasn’t gotten into it yet. But once they do, it’s.
It’s so much better than Google, so much better than Google. Like you don’t have to know how to Google things anymore. You could just like ask a question that you’re talking to a person and it just gives you the answer,
Allen Hall: right? It is much more, uh, interactive, human, interactive, uh, interface than what Google ever was, and you still have to have little tricks to get Google to give you the right answer at times.
This is much more intuitive and if you think about your phone and how you try to Google things on your phone, it’s that interface is terrible. Absolutely terrible. It’s been terrible for five plus years. This AI interface, all of them, perplexity is the one that [00:26:00] I like at the minute, is really simple. It’s like asking somebody a question, like asking a librarian in the old days, where can I find this information?
Tell me what’s going on. Poof. There it is. And it provides justification, rationale behind it, all those kind of things you like to have as an engineer. But I do think the growth of this, if it is as powerful as it is today, the growth is gonna be phenomenal. And the power usage is gonna be nuts,
Rosemary Barnes: but I’m not sure that you are, um, aware of how much growth is baked into the forecast currently.
I’ve just brought up, um, an article that Michael Lere wrote on Bloomberg, NEF, um, about ai. And it, it’s interesting there because he goes through the economics of it, um, and he draws on some, uh. Questions that a guy David Kahn made, um, from Sequoia Capital that he says, David Kahn says that to justify the capital expenditures applied by NVIDIA’s [00:27:00] near term revenue pipeline, they would need to generate annual revenue from AI services of 200 billion.
And then, um, with their new updated NVIDIA sales forecast storing it, it’s been updated to 600 billion. Um, and that is, uh, yeah, like half of the aggregate revenue of Amazon, Microsoft Meta and Google Parent Alpha. So if you assume 600 billions will be, um, uh, it’ll be the world’s 100 million wealthiest people, then that’s $6,000 a year.
Um, and then, you know, like, obviously you can go a bit further down, but it, it’s um, like not impossible, but it’s also, that is a massive amount of growth that is already. Factored into the, that pipeline. So I think, I just think it’s more evidence that that is a, like a, that is a pretty optimistic take on, you know, immense growth and that it’s far more likely we’re gonna see less, less growth than that.
I still think we’re gonna see crazy growth, but. I think that the, [00:28:00] that the, the current pipeline that the, you know, current investments, if you, um, sorry, not investments, but the current plans for, for growth of companies like nvidia, they don’t just factor in incredible growth. It’s like incredible squared, incredible cubed growth that’s factored into their pipeline and it is gonna.
Scale, scale back again that I, I don’t think anyone can know, but that’s, that’s, I really think that that’s the most likely thing to happen.
Allen Hall: Building chips and building power plants are two wildly different things in terms of the time it takes to do it. Building a gigawatt of energy production takes time.
Building another chip is just clunk. There’s another one. It doesn’t take that much time. So I think the ability to create the chips is gonna far exceed the ability to power them.
Rosemary Barnes: Yeah, and that’s why you see like that project I talked about where they um, you know, the chip capability changed so much in between when they started the project and by the time they went to actually put the chips inside the building.
Um. You still see the power [00:29:00] stayed the same, but just the compute in increased. Um, so yeah, I think you’re right.
Joel Saxum: I still think that the, the good play is investing in a cable lay vessel. I’m telling you the the, the s the SF uptime cable lay vessel.
Allen Hall: This is my wild conspiracy theory at the moment, is that Elon with his satellite network, SpaceX and starlink and all that, allows you to put an AI center anywhere on the planet that it is cheap to power it.
Joel Saxum: A handful of geostationary satellites. Is and And if you devote them to one data center or to a family of data centers, somewhere that has to be cheaper than laying cables across the OS. Ocean.
Allen Hall: Yes, that’s what I’m saying. Elon’s gonna buy the center of Australia, lay out solar panels. Too hot. It’s gotta go somewhere cold.
I’m talking
Joel Saxum: Canada Green. Greenland. Greenland,
Allen Hall: [00:30:00] Greenland. Greenland. There you go. There’s a perfect conspiracy case right there, Joel. You hit all the triggers at one time. Well, well, we’re, we’re not gonna solve this this week. Uh, but it is an important issue and it is coming up a lot. And I know that it is not gonna stop the discussion.
It is ramping up and there’s a lot of energy being spent trying to figure out, can we even solve this problem? What’s happening with the IRA bill or the potential changes to the IRA bill can aggravate this and make it a lot harder. Uh, be prepared. Very interesting times. Joel Rosemary. Another great episode
Rosemary Barnes: and un unsupervised today.
I often wonder if these ones where we don’t have producer Claire here, um, you know, reigning us in, do we lose subscribers on these episodes or are people, you know, like really attracted to our tell it like it is, uh, kind of rambling, rambling style on these ones.
Allen Hall: Stay tuned and we’ll see you all here next week on the Uptime Wind Energy [00:31:00] Podcast.
https://weatherguardwind.com/vestas-lm-factory-data-centers/
Renewable Energy
Trump’s Popularity on “The Continent”
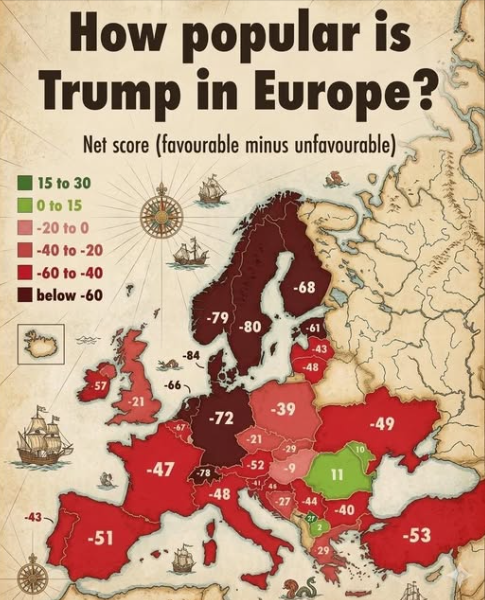 I can’t swear that the data at left is accurate, but it certainly rings true based on the considerable number of Europeans I meet each month. They tend to disapprove of lawlessness, stupidity, and wars that are unnecessary and illegal.
I can’t swear that the data at left is accurate, but it certainly rings true based on the considerable number of Europeans I meet each month. They tend to disapprove of lawlessness, stupidity, and wars that are unnecessary and illegal.
By comparison, Americans are uneducated savages.
Renewable Energy
Moray West Offline, Iberdrola in Australia
Moray West Offline, Iberdrola in Australia
Allen covers a substation failure that has left Scotland’s 882 MW Moray West farm half-offline since November, GE Vernova’s new Italy contract and Milan factory investment, Iberdrola’s sixth Australian acquisition of 2026, and Flender India’s new gearbox test rig near Chennai.
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly newsletter on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on YouTube, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary’s “Engineering with Rosie” YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
The wind industry had quite a week.
Let us start in Scotland, off the rugged north-east coast, where something has gone quietly wrong. Ocean Winds and Ignitis built Moray West, an eight hundred and eighty-two megawatt offshore wind farm — one of the largest in Scotland. But one of its two offshore substations has been offline since November. Half the farm’s capacity … gone dark. And there is more. The project missed a contractual milestone last September under an off-take agreement. That triggered an event of default under its project lending agreements. The lenders and the sponsors have agreed to a short-term waiver. Discussions are described as constructive. Commercial operations, originally expected last year, are now targeted for sometime in 2026. Eight hundred and eighty-two megawatts … waiting.
Now, let us travel south to Italy. GE Vernova has won a contract to supply seventeen onshore turbines to IVPC Group’s Fortore wind farm in the Benevento region of southern Italy. The project tops one hundred megawatts. Turbine deliveries begin in twenty twenty-seven. GE Vernova is also investing thirty million dollars to expand its Sesto San Giovanni plant outside Milan. That investment boosts production of transformer bushings, the insulating components that keep high-voltage equipment running. About fifty new jobs are coming to that facility. And GE Vernova’s two-piece blade design for its six-point-one megawatt turbines is already drawing attention as developers scramble to crack Italy’s notoriously complex logistics and permitting hurdles. Italy is a market in motion.
Now, to the other side of the world. Iberdrola has completed the acquisition of the Ararat wind farm in Victoria, Australia. Two hundred and forty-two megawatts. Operational since twenty seventeen. This is Iberdrola’s sixth transaction of twenty twenty-six alone, and it marks the Spanish giant’s first owned generation asset in Victoria, Australia’s second most populous state. Iberdrola now operates in five Australian states with more than twenty-five hundred megawatts of installed capacity. Victoria has set a target of ninety-five percent renewable energy by twenty thirty-five. Iberdrola intends to help get it there.
And finally, from Chennai, India, comes a story about getting ready for what is coming. Flender India has just inaugurated its largest and most advanced gearbox test rig for wind turbines at its Walajabad facility near Chennai. The project began in January of twenty twenty-five at Flender’s Voerde site in Germany. From start to finish, thirteen months. Final assembly, three months. This is a collaboration between Flender’s operations in Germany, China, and India. CEO Andreas Evertz called it a testament to their global commitment to driving renewable energy solutions worldwide. India’s wind market is growing fast, and Flender is making sure it can test every gearbox that growth demands.
So, let us step back and look at the picture. A Scottish offshore wind farm sits half-dark while its owners negotiate with lenders. GE Vernova plants its flag in southern Italy and invests thirty million dollars in an Italian factory. Iberdrola expands to a sixth Australian transaction in a single year. And Flender India builds the biggest gearbox test rig on the subcontinent. And that is the state of the wind industry for the ninth of March, twenty twenty-six. Join us for the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast tomorrow
Renewable Energy
Two Thousand Years Later, Society’s Relationship with Religion Hasn’t Changed Much
 As shown at left, the ancient Roman stoic philosopher Seneca had a viewpoint on religion that is shared 100% by modern atheists.
As shown at left, the ancient Roman stoic philosopher Seneca had a viewpoint on religion that is shared 100% by modern atheists.
Two Thousand Years Later, Society’s Relationship with Religion Hasn’t Changed Much
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits



