The choices made about how land is used and managed play a crucial role in tackling climate change.
The importance of the land use, land-use change and forestry sector (which is often referred to as LULUCF) is reflected in 118 of 143 countries including land-based emissions reductions and removals in their latest emissions pledges under the Paris Agreement.
However, there is a complication.
It arises because of a fundamental difference in how land-based emissions are treated by scientific models and the national greenhouse gas inventories submitted by parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Specifically, there are different definitions as to what constitutes “managed” land and the human-caused carbon removals on that land.
As we show in our new study, published in Nature, the result is a gap of 4-7bn tonnes of CO2 (GtCO2) between estimates from models and national inventories for net emissions from current land use. Even at the low end of this range, it equates to around 10% of global annual CO2 emissions today.
The knock-on impact of this gap is that it makes comparisons between the two difficult in critical policy processes such as the global stocktake – the five-yearly progress check on collective action towards the long-term goal of the Paris Agreement.
And, more fundamentally, our findings suggest that nations will need to increase the collective ambition of their climate targets to remain consistent with the Paris temperature limits.
Making sense of LULUCF accounting
In order to estimate the amount of carbon emissions or removals of carbon from land, scientists use so-called “bookkeeping” approaches.
These approaches, and the models that employ them, account for stocks and flows of carbon triggered by changes in land cover or land management practices and estimate the resulting “direct” carbon fluxes.
The term “direct” is used because the fluxes – that is, the exchange of CO2 between the land and atmosphere – are a result of direct human intervention. These actions, including deforestation, forest harvest and regrowth, are what scientific models consider as “anthropogenic” carbon fluxes.
This accounting approach is used by the models underpinning the concepts of the remaining carbon budget and net-zero timings in the assessment reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
But to understand the total amount of carbon flux on land, scientists need to use more detailed, process-based vegetation models. These models, collectively called “dynamic global vegetation models”, simulate biogeochemical and hydrological cycles and estimate future plant and forest carbon uptake and release.
These models explicitly include climate and environmental interactions and so they capture so-called “indirect” effects. These include the response of land to indirect human-induced climate and environmental changes, such as through CO2 fertilisation and warming-induced changes to temperatures and rainfall patterns, which affect plant growth.
These “indirect” fluxes are estimated for Earth’s full land surface area, including both land actively managed by humans as well as land with limited or no human activity in what global models consider as the “natural” terrestrial sink.
Taken together, both direct and indirect carbon fluxes on land provide a full picture of the land-related carbon balance, which is assessed each year by the Global Carbon Project.
However, countries estimate their LULUCF fluxes differently. This is because it is not practically possible to separate direct and indirect fluxes through observations, such as via national forest inventories or satellite data.
National GHG inventories follow reporting conventions that define human-caused fluxes using an area-based approach, whereby all fluxes occurring on managed land are considered anthropogenic. By contrast, fluxes on unmanaged land are not reported.
In addition to land that is actively managed for, say, agriculture and forestry practices, countries may consider other land as “managed”, such as national parks, wilderness preserves or areas under less frequent forest management.
But even if countries and models agreed on the amount of land which is considered “managed”, physical measurements and observations cannot distinguish between direct and indirect contributions to LULUCF fluxes.
As a result, national inventories include most of the indirect effect on a larger land area than is considered under scientific conventions. In short, countries consider “anthropogenic” part of the CO2 sink that models consider “natural”.
The infographic below outlines this mismatch. It shows how scientific models differentiate between direct (red) and indirect (blue) fluxes, while national inventories (green) do not.

Globally, this mismatch results in a difference between bookkeeping models and country inventories of around 4-7GtCO2. As the map below shows, the differences vary from country to country.
Overall, 53 and 56 countries report, respectively, LULUCF net removals (pale green shading) and emissions (purple) where models agree. Then 67 countries report net removals, but models suggest net emissions (dark green) and nine countries report net emissions while models show net removals (blue).

Shifting benchmarks
In our study, we propose a method for resolving these differences. We employ a reduced-complexity climate model called OSCAR, which has an explicit representation of the land carbon cycle. We use it to estimate the current and future evolution of indirect emissions to align IPCC pathways with aggregate estimates from national inventories.
We then estimate how this would affect mitigation benchmarks, such as the emissions reductions needed by 2030, the year of net-zero CO2 emissions and the total cumulative CO2 emitted until net-zero.
Across the board, we find that key global mitigation benchmarks become harder to achieve when calculated using conventions set in national inventories, requiring more ambitious mitigation action than when aiming for model-based outcomes.
For example, under inventory accounting conventions, we find that net-zero in emissions pathways that are consistent with 1.5C of warming is achieved one-to-five years earlier than in model-based conventions. Similarly, emissions reduction benchmarks this decade are three-to-six percentage points higher and cumulative CO2 emissions are 15-18% lower.
These shifts arise because of the additional land-based carbon removals in national inventories, or “alignment factor”, acts to lower current global emissions compared to model-based conventions. The alignment factor will diminish over time should the world succeed in reducing emissions drastically in the near-term.
| Benchmark | Change in 1.5C pathways | Change in 2C pathways |
|---|---|---|
| Year of net-zero CO2 | 1 to 5 years | -1 to 7 years |
| Emissions reductions by 2030 | 3.4 to 5.9% | 2.5 to 5% |
| Cumulative CO2 until net-zero | 54-95 GtCO2 (15-18%) | 93-167 GtCO2 (15-18%) |
Table shows difference in key mitigation benchmarks between pathways including fluxes aligned with model-based conventions vs. pathways including fluxes aligned with inventory-based conventions (5th-95th percentiles). Across the board, benchmarks are more difficult to reach when aligned with national inventories.
IPCC assessment
It is important to stress that our results do not conflict with the benchmarks assessed by the IPCC.
The use of simple climate models, such as MAGICC and FaIR, in IPCC assessments includes the “direct” LULUCF emissions from pathways as inputs and include in their simulations the “indirect” emissions due to climate and environmental responses to calculate the global temperature response to human-caused emissions.
In our analysis, we explicitly separate these two flux components, adding the indirect fluxes on “managed” land to our estimate of the direct fluxes. In short, we simply align different accounting practices, shifting fluxes on one side of the “ledger” to the other.
The climate outcome of each scenario we assess remains the same, but the benchmark – when viewed through the lens of inventory accounting conventions – shifts. Understanding this dynamic is critical, because ultimately countries will measure their progress towards achieving the long-term temperature goal of the Paris Agreement against their own accounting conventions.
Our findings show the danger of comparing apples to oranges: in order to achieve the global mitigation benchmarks assessed by the IPCC, global mitigation action needs to be stronger and more ambitious when using the national inventories perspective.
While our adjustment does not change the overall amount of decarbonisation effort necessary to reach the Paris Agreement goal, it changes where we currently stand relative to it.
In the absence of such adjustment, countries would collectively appear in a better position than they actually are.
Depending heavily on LULUCF
Our results also provide a warning to countries depending strongly on the land sector to achieve their national climate pledges under the Paris Agreement.
From a bookkeeping accounting perspective, sustainable land-management practices can both strongly reduce existing sources of emissions as well as enhance land-based carbon removal.
Across pathways assessed by the IPCC, “direct” emissions typically reduce strongly and stay net-negative through the rest of the century. However, in the pathways we reanalyse, inventory-aligned emissions on land begin to reverse around mid-century and become a net source of emissions in about a quarter of the assessed pathways by the end of the century. This is because the weakening of the indirect effect contributes more than the strengthening of the direct effect in these scenarios.
While inventory-aligned fluxes result in smaller net emissions today compared to model-based fluxes, depending on them to achieve national climate targets presents a “double-edged sword”.
The indirect component of these fluxes is due to climate and environmental effects, which will change based on how strongly and quickly the world is able to reduce emissions in the future.
In particular, with high levels of mitigation, as the rate that CO2 accumulates in the atmosphere slows down, the strength of indirect fluxes will decrease and may even reverse.
Thus, countries should take care when depending strongly on the land sector as enhanced “direct” emissions reductions and removals can be masked by weakening “indirect” fluxes.
Other important factors which we did not consider could make depending on land-based removals even riskier, such as disturbances from wildfires, which will likely increase as the world continues to warm.
The graphic below provides an illustration. It shows the impact on direct (red) and indirect (blue) carbon emissions (up arrows) and removals (down) for scenarios with low (top) and high (bottom) global mitigation, and unchanged (left) and increased (right) land-based mitigation. The overall impact of each combination on net emissions is shown by the green arrows.

Moving forward
Our study highlights the importance of comparing apples to apples when trying to evaluate and take stock of progress towards the Paris Agreement.
Part of the core enabling architecture of the agreement was its “bottom-up” nature, enabling countries to set targets and measure progress towards them in such a way that fits national circumstances. At the same time, care must be taken to comparing these efforts with pathways assessed by the global scientific community.
Here, we offer one way to use the “Rosetta Stone” approach to align IPCC-assessed pathways with national emissions inventories, which can be used to assess progress in the near-term. We offer a number of recommendations for improving this moving forward.
First, we suggest that national climate targets can be made more explicit by separating targets for land-based mitigation from other sector-based action. In this way, each can be measured and assessed separately and uncertainties due to accounting differences can be contained.
Second, we suggest that countries can be more explicit and clarify their deforestation pledges, as direct and indirect carbon fluxes vary greatly in different forest types.
Third, we suggest that scientific and policymaking communities convene to agree on an “operational translation system”. That is, something that would allow each to understand the other by addressing any remaining inconsistencies and develop methods for estimating country-considered indirect fluxes to support comparison with modelled pathways.
And, fourth, we suggest that modellers incorporate their own estimates of the indirect effect from the land-component of their integrated models. Together with efforts by policymaking communities, this would bring alignment directly into IPCC reports to improve comparability with global progress towards the Paris Agreement.
Countries will come together at COP28 this year to conclude the very first global stocktake of the Paris Agreement.
Our assessment shows that even more ambitious climate action is needed to achieve the benchmarks laid out by scientists when using national inventory accounting as a starting point, which will help future stocktakes.
It is critical that progress is measured in a like-for-like manner rather than the current situation comparing apples and oranges.
Even so, the overarching message remains loud and clear that the world must drastically cut emissions this decade, irrespective of accounting frameworks, to stay within the limits of the Paris Agreement. It is vital this message is not lost in the minutia of discussions around reporting technicalities.
The post Guest post: Why resolving how land emissions are counted is critical for tracking climate progress appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Guest post: Why resolving how land emissions are counted is critical for tracking climate progress
Climate Change
DeBriefed 27 February 2026: Trump’s fossil-fuel talk | Modi-Lula rare-earth pact | Is there a UK ‘greenlash’?
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Absolute State of the Union
‘DRILL, BABY’: US president Donald Trump “doubled down on his ‘drill, baby, drill’ agenda” in his State of the Union (SOTU) address, said the Los Angeles Times. He “tout[ed] his support of the fossil-fuel industry and renew[ed] his focus on electricity affordability”, reported the Financial Times. Trump also attacked the “green new scam”, noted Carbon Brief’s SOTU tracker.
COAL REPRIEVE: Earlier in the week, the Trump administration had watered down limits on mercury pollution from coal-fired power plants, reported the Financial Times. It remains “unclear” if this will be enough to prevent the decline of coal power, said Bloomberg, in the face of lower-cost gas and renewables. Reuters noted that US coal plants are “ageing”.
OIL STAY: The US Supreme Court agreed to hear arguments brought by the oil industry in a “major lawsuit”, reported the New York Times. The newspaper said the firms are attempting to head off dozens of other lawsuits at state level, relating to their role in global warming.
SHIP-SHILLING: The Trump administration is working to “kill” a global carbon levy on shipping “permanently”, reported Politico, after succeeding in delaying the measure late last year. The Guardian said US “bullying” could be “paying off”, after Panama signalled it was reversing its support for the levy in a proposal submitted to the UN shipping body.
Around the world
- RARE EARTHS: The governments of Brazil and India signed a deal on rare earths, said the Times of India, as well as agreeing to collaborate on renewable energy.
- HEAT ROLLBACK: German homes will be allowed to continue installing gas and oil heating, under watered-down government plans covered by Clean Energy Wire.
- BRAZIL FLOODS: At least 53 people died in floods in the state of Minas Gerais, after some areas saw 170mm of rain in a few hours, reported CNN Brasil.
- ITALY’S ATTACK: Italy is calling for the EU to “suspend” its emissions trading system (ETS) ahead of a review later this year, said Politico.
- COOKSTOVE CREDITS: The first-ever carbon credits under the Paris Agreement have been issued to a cookstove project in Myanmar, said Climate Home News.
- SAUDI SOLAR: Turkey has signed a “major” solar deal that will see Saudi firm ACWA building 2 gigawatts in the country, according to Agence France-Presse.
$467 billion
The profits made by five major oil firms since prices spiked following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine four years ago, according to a report by Global Witness covered by BusinessGreen.
Latest climate research
- Claims about the “fingerprint” of human-caused climate change, made in a recent US Department of Energy report, are “factually incorrect” | AGU Advances
- Large lakes in the Congo Basin are releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from “immense ancient stores” | Nature Geoscience
- Shared Socioeconomic Pathways – scenarios used regularly in climate modelling – underrepresent “narratives explicitly centring on democratic principles such as participation, accountability and justice” | npj Climate Action
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
The constituency of Richard Tice MP, the climate-sceptic deputy leader of Reform UK, is the second-largest recipient of flood defence spending in England, according to new Carbon Brief analysis. Overall, the funding is disproportionately targeted at coastal and urban areas, many of which have Conservative or Liberal Democrat MPs.
Spotlight
Is there really a UK ‘greenlash’?
This week, after a historic Green Party byelection win, Carbon Brief looks at whether there really is a “greenlash” against climate policy in the UK.
Over the past year, the UK’s political consensus on climate change has been shattered.
Yet despite a sharp turn against climate action among right-wing politicians and right-leaning media outlets, UK public support for climate action remains strong.
Prof Federica Genovese, who studies climate politics at the University of Oxford, told Carbon Brief:
“The current ‘war’ on green policy is mostly driven by media and political elites, not by the public.”
Indeed, there is still a greater than two-to-one majority among the UK public in favour of the country’s legally binding target to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, as shown below.
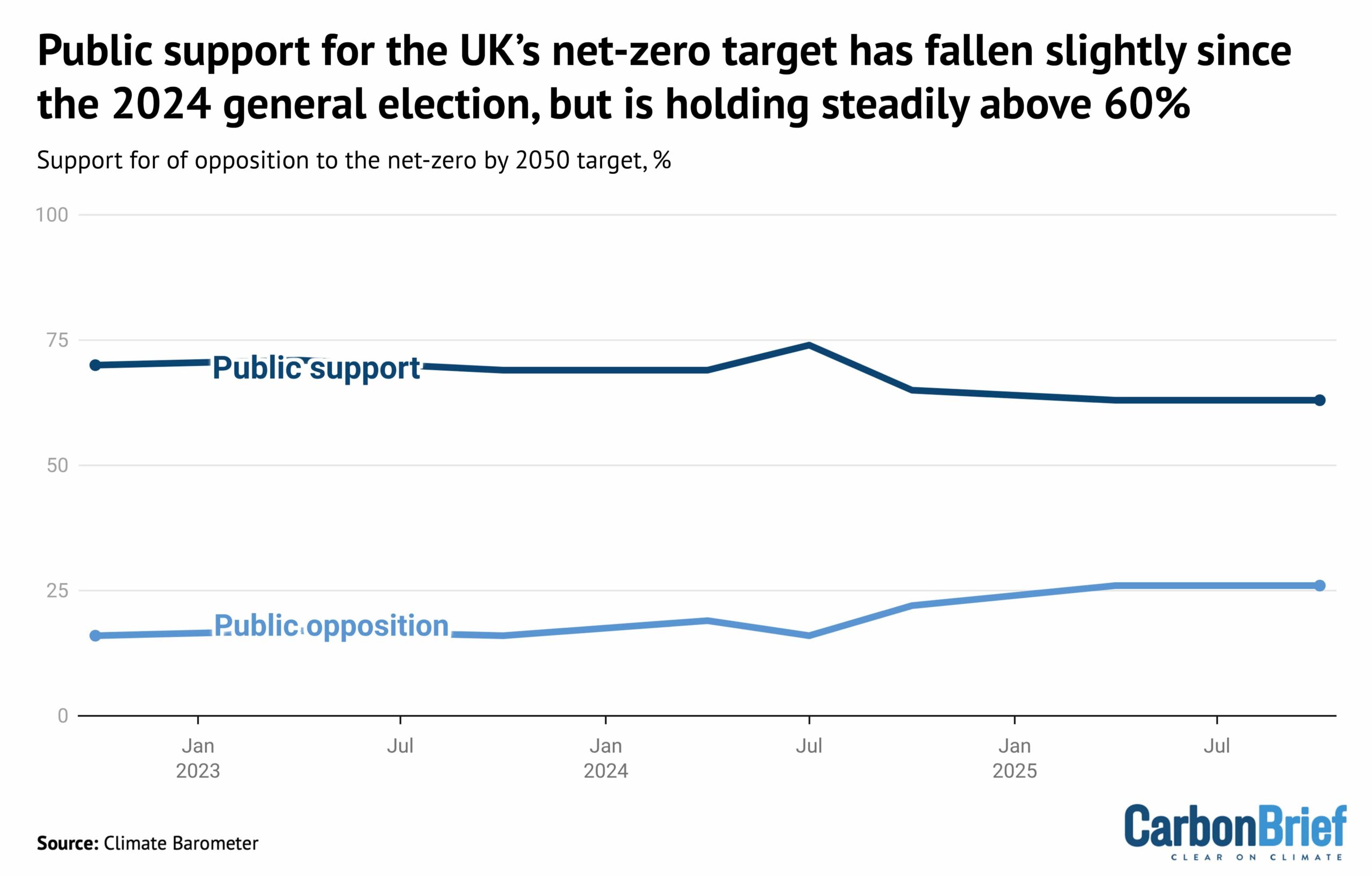
Steve Akehurst, director of public-opinion research initiative Persuasion UK, also noted the growing divide between the public and “elites”. He told Carbon Brief:
“The biggest movement is, without doubt, in media and elite opinion. There is a bit more polarisation and opposition [to climate action] among voters, but it’s typically no more than 20-25% and mostly confined within core Reform voters.”
Conservative gear shift
For decades, the UK had enjoyed strong, cross-party political support for climate action.
Lord Deben, the Conservative peer and former chair of the Climate Change Committee, told Carbon Brief that the UK’s landmark 2008 Climate Change Act had been born of this cross-party consensus, saying “all parties supported it”.
Since their landslide loss at the 2024 election, however, the Conservatives have turned against the UK’s target of net-zero emissions by 2050, which they legislated for in 2019.
Curiously, while opposition to net-zero has surged among Conservative MPs, there is majority support for the target among those that plan to vote for the party, as shown below.
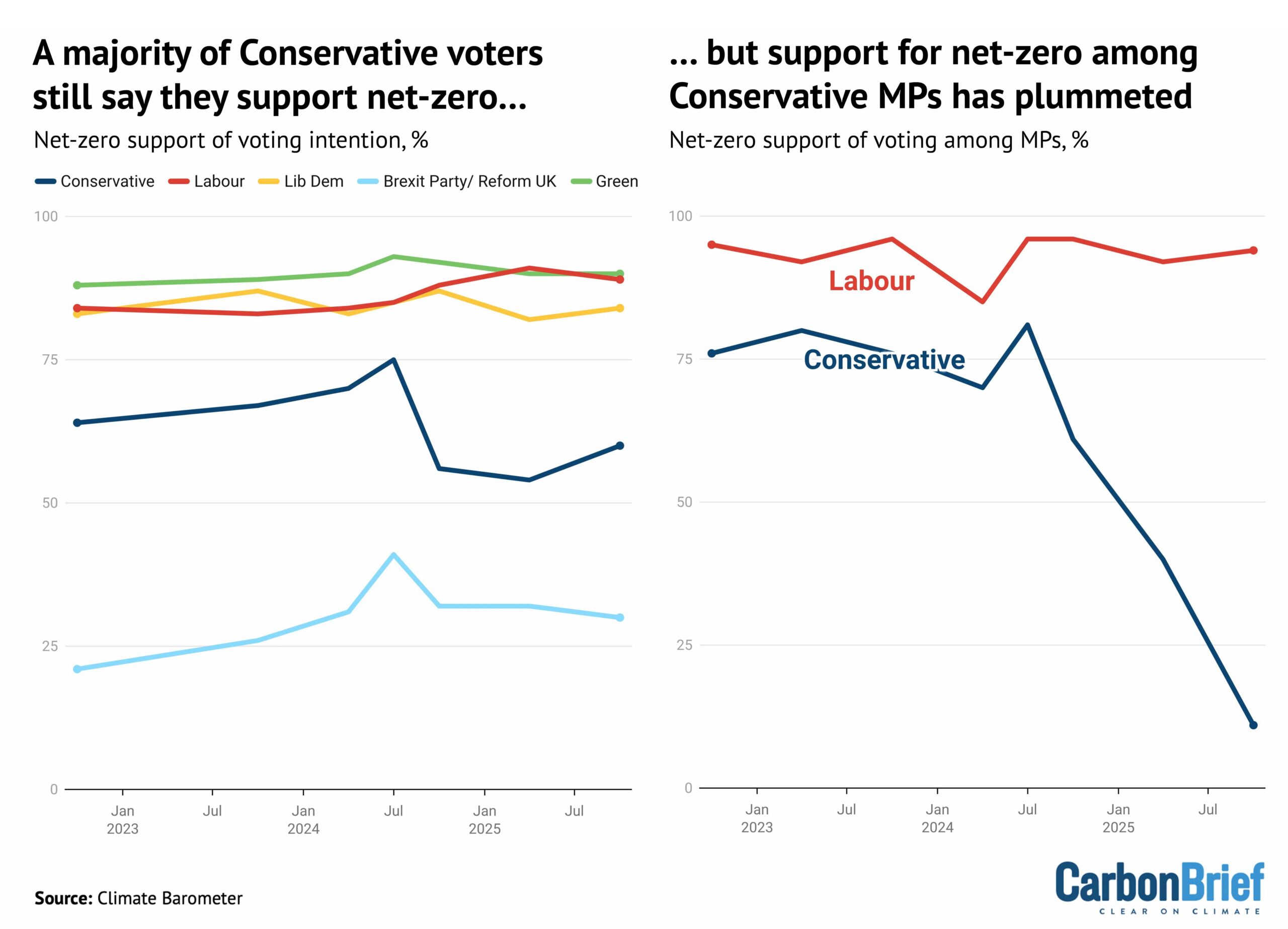
Dr Adam Corner, advisor to the Climate Barometer initiative that tracks public opinion on climate change, told Carbon Brief that those who currently plan to vote Reform are the only segment who “tend to be more opposed to net-zero goals”. He said:
“Despite the rise in hostile media coverage and the collapse of the political consensus, we find that public support for the net-zero by 2050 target is plateauing – not plummeting.”
Reform, which rejects the scientific evidence on global warming and campaigns against net-zero, has been leading the polls for a year. (However, it was comfortably beaten by the Greens in yesterday’s Gorton and Denton byelection.)
Corner acknowledged that “some of the anti-net zero noise…[is] showing up in our data”, adding:
“We see rising concerns about the near-term costs of policies and an uptick in people [falsely] attributing high energy bills to climate initiatives.”
But Akehurst said that, rather than a big fall in public support, there had been a drop in the “salience” of climate action:
“So many other issues [are] competing for their attention.”
UK newspapers published more editorials opposing climate action than supporting it for the first time on record in 2025, according to Carbon Brief analysis.
Global ‘greenlash’?
All of this sits against a challenging global backdrop, in which US president Donald Trump has been repeating climate-sceptic talking points and rolling back related policy.
At the same time, prominent figures have been calling for a change in climate strategy, sold variously as a “reset”, a “pivot”, as “realism”, or as “pragmatism”.
Genovese said that “far-right leaders have succeeded in the past 10 years in capturing net-zero as a poster child of things they are ‘fighting against’”.
She added that “much of this is fodder for conservative media and this whole ecosystem is essentially driving what we call the ‘greenlash’”.
Corner said the “disconnect” between elite views and the wider public “can create problems” – for example, “MPs consistently underestimate support for renewables”. He added:
“There is clearly a risk that the public starts to disengage too, if not enough positive voices are countering the negative ones.”
Watch, read, listen
TRUMP’S ‘PETROSTATE’: The US is becoming a “petrostate” that will be “sicker and poorer”, wrote Financial Times associate editor Rana Forohaar.
RHETORIC VS REALITY: Despite a “political mood [that] has darkened”, there is “more green stuff being installed than ever”, said New York Times columnist David Wallace-Wells.
CHINA’S ‘REVOLUTION’: The BBC’s Climate Question podcast reported from China on the “green energy revolution” taking place in the country.
Coming up
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean, Brasília
- 3 March: UK spring statement
- 4-11 March: China’s “two sessions”
- 5 March: Nepal elections
Pick of the jobs
- The Guardian, senior reporter, climate justice | Salary: $123,000-$135,000. Location: New York or Washington DC
- China-Global South Project, non-resident fellow, climate change | Salary: Up to $1,000 a month. Location: Remote
- University of East Anglia, PhD in mobilising community-based climate action through co-designed sports and wellbeing interventions | Salary: Stipend (unknown amount). Location: Norwich, UK
- TABLE and the University of São Paulo, Brazil, postdoctoral researcher in food system narratives | Salary: Unknown. Location: Pirassununga, Brazil
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 27 February 2026: Trump’s fossil-fuel talk | Modi-Lula rare-earth pact | Is there a UK ‘greenlash’? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
Pacific nations want higher emissions charges if shipping talks reopen
Seven Pacific island nations say they will demand heftier levies on global shipping emissions if opponents of a green deal for the industry succeed in reopening negotiations on the stalled accord.
The United States and Saudi Arabia persuaded countries not to grant final approval to the International Maritime Organization’s Net-Zero Framework (NZF) in October and they are now leading a drive for changes to the deal.
In a joint submission seen by Climate Home News, the seven climate-vulnerable Pacific countries said the framework was already a “fragile compromise”, and vowed to push for a universal levy on all ship emissions, as well as higher fees . The deal currently stipulates that fees will be charged when a vessel’s emissions exceed a certain level.
“For many countries, the NZF represents the absolute limit of what they can accept,” said the unpublished submission by Fiji, Kiribati, Vanuatu, Nauru, Palau, Tuvalu and the Solomon Islands.
The countries said a universal levy and higher charges on shipping would raise more funds to enable a “just and equitable transition leaving no country behind”. They added, however, that “despite its many shortcomings”, the framework should be adopted later this year.
US allies want exemption for ‘transition fuels’
The previous attempt to adopt the framework failed after governments narrowly voted to postpone it by a year. Ahead of the vote, the US threatened governments and their officials with sanctions, tariffs and visa restrictions – and President Donald Trump called the framework a “Green New Scam Tax on Shipping”.
Since then, Liberia – an African nation with a major low-tax shipping registry headquartered in the US state of Virginia – has proposed a new measure under which, rather than staying fixed under the NZF, ships’ emissions intensity targets change depending on “demonstrated uptake” of both “low-carbon and zero-carbon fuels”.
The proposal places stringent conditions on what fuels are taken into consideration when setting these targets, stressing that the low- and zero-carbon fuels should be “scalable”, not cost more than 15% more than standard marine fuels and should be available at “sufficient ports worldwide”.
This proposal would not “penalise transitional fuels” like natural gas and biofuels, they said. In the last decade, the US has built a host of large liquefied natural gas (LNG) export terminals, which the Trump administration is lobbying other countries to purchase from.
The draft motion, seen by Climate Home News, was co-sponsored by US ally Argentina and also by Panama, a shipping hub whose canal the US has threatened to annex. Both countries voted with the US to postpone the last vote on adopting the framework.
The IMO’s Panamanian head Arsenio Dominguez told reporters in January that changes to the framework were now possible.
“It is clear from what happened last year that we need to look into the concerns that have been expressed [and] … make sure that they are somehow addressed within the framework,” he said.
Patchwork of levies
While the European Union pushed firmly for the framework’s adoption, two of its shipping-reliant member states – Greece and Cyprus – abstained in October’s vote.
After a meeting between the Greek shipping minister and Saudi Arabia’s energy minister in January, Greece said a “common position” united Greece, Saudi Arabia and the US on the framework.
If the NZF or a similar instrument is not adopted, the IMO has warned that there will be a patchwork of differing regional levies on pollution – like the EU’s emissions trading system for ships visiting its ports – which will be complicated and expensive to comply with.
This would mean that only countries with their own levies and with lots of ships visiting their ports would raise funds, making it harder for other nations to fund green investments in their ports, seafarers and shipping companies. In contrast, under the NZF, revenues would be disbursed by the IMO to all nations based on set criteria.
Anais Rios, shipping policy officer from green campaign group Seas At Risk, told Climate Home News the proposal by the Pacific nations for a levy on all shipping emissions – not just those above a certain threshold – was “the most credible way to meet the IMO’s climate goals”.
“With geopolitics reframing climate policy, asking the IMO to reopen the discussion on the universal levy is the only way to decarbonise shipping whilst bringing revenue to manage impacts fairly,” Rios said.
“It is […] far stronger than the Net-Zero Framework that is currently on offer.”
The post Pacific nations want higher emissions charges if shipping talks reopen appeared first on Climate Home News.
Pacific nations want higher emissions charges if shipping talks reopen
Climate Change
Doubts over European SAF rules threaten cleaner aviation hopes, investors warn
Doubts over whether governments will maintain ambitious targets on boosting the use of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) are a threat to the industry’s growth and play into the hands of fossil fuel companies, investors warned this week.
Several executives from airlines and oil firms have forecast recently that SAF requirements in the European Union, United Kingdom and elsewhere will be eased or scrapped altogether, potentially upending the aviation industry’s main policy to shrink air travel’s growing carbon footprint.
Such speculation poses a “fundamental threat” to the SAF industry, which mainly produces an alternative to traditional kerosene jet fuel using organic feedstocks such as used cooking oil (UCO), Thomas Engelmann, head of energy transition at German investment manager KGAL, told the Sustainable Aviation Fuel Investor conference in London.
He said fossil fuel firms would be the only winners from questions about compulsory SAF blending requirements.
The EU and the UK introduced the world’s first SAF mandates in January 2025, requiring fuel suppliers to blend at least 2% SAF with fossil fuel kerosene. The blending requirement will gradually increase to reach 32% in the EU and 22% in the UK by 2040.
Another case of diluted green rules?
Speaking at the World Economic Forum in Davos in January, CEO of French oil and gas company TotalEnergies Patrick Pouyanné said he would bet “that what happened to the car regulation will happen to the SAF regulation in Europe”.
The EU watered down green rules for car-makers in March 2025 after lobbying from car companies, Germany and Italy.
“You will see. Today all the airline companies are fighting [against the EU’s 2030 SAF target of 6%],” Pouyanne said, even though it’s “easy to reach to be honest”.
While most European airline lobbies publicly support the mandates, Ryanair Group CEO Michael O’Leary said last year that the SAF is “nonsense” and is “gradually dying a death, which is what it deserves to do”.
EU and UK stand by SAF targets
But the EU and the British government have disputed that. EU transport commissioner Apostolos Tzitzikostas said in November that the EU’s targets are “stable”, warning that “investment decisions and construction must start by 2027, or we will miss the 2030 targets”.
UK aviation minister Keir Mather told this week’s investor event that meeting the country’s SAF blending requirement of 10% by 2030 was “ambitious but, with the right investment, the right innovation and the right outlook, it is absolutely within our reach”.
“We need to go further and we need to go faster,” Mather said.

SAF investors and developers said such certainty on SAF mandates from policymakers was key to drawing the necessary investment to ramp up production of the greener fuel, which needs to scale up in order to bring down high production costs. Currently, SAF is between two and seven times more expensive than traditional jet fuel.
Urbano Perez, global clean molecules lead at Spanish bank Santander, said banks will not invest if there is a perceived regulatory risk.
David Scott, chair of Australian SAF producer Jet Zero Australia, said developing SAF was already challenging due to the risks of “pretty new” technology requiring high capital expenditure.
“That’s a scary model with a volatile political environment, so mandate questioning creates this problem on steroids”, Scott said.
Others played down the risk. Glenn Morgan, partner at investment and advisory firm SkiesFifty, said “policy is always a risk”, adding that traditional oil-based jet fuel could also lose subsidies.


Asian countries join SAF mandate adopters
In Asia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand and Japan have recently adopted SAF mandates, and Matti Lievonen, CEO of Asia-based SAF producer EcoCeres, predicted that China, Indonesia and Hong Kong would follow suit.
David Fisken, investment director at the Australian Trade and Investment Commission, said the Australian government, which does not have a mandate, was watching to see how the EU and UK’s requirements played out.
The US does not have a SAF mandate and under President Donald Trump the government has slashed tax credits available for SAF producers from $1.75 a gallon to $1.
Is the world’s big idea for greener air travel a flight of fancy?
SAF and energy security
SAF’s potential role in boosting energy security was a major theme of this week’s discussions as geopolitical tensions push the issue to the fore.
Marcella Franchi, chief commercial officer for SAF at France’s Haffner Energy, said the Canadian government, which has “very unsettling neighbours at the moment”, was looking to produce SAF to protect its energy security, especially as it has ample supplies of biomass to use as potential feedstock.
Similarly, German weapons manufacturer Rheinmetall said last year it was working on plans that would enable European armed forces to produce their own synthetic, carbon-neutral fuel “locally and independently of global fossil fuel supply chain”.
Scott said Australia needs SAF to improve its fuel security, as it imports almost 99% of its liquid fuels.
He added that support for Australian SAF production is bipartisan, in part because it appeals to those more concerned about energy security than tackling climate change.
The post Doubts over European SAF rules threaten cleaner aviation hopes, investors warn appeared first on Climate Home News.
Doubts over European SAF rules threaten cleaner aviation hopes, investors warn
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits