The Trump administration in the US has imposed tariffs on all imports from China, Mexico and Canada, as well as on steel, aluminium and cars from around the world.
In response, the US has been hit with retaliatory tariffs from major trading partners, including the EU.
US president Donald Trump has said he intends to launch a further round of reciprocal tariffs on 2 April, targeting a broader range of countries.
This escalating “trade war” is expected to slow global growth and has also triggered warnings of a US recession.
Global energy flows and efforts to tackle climate change are already being affected by the escalating trade tensions.
The tariffs are expected to disrupt the global trade in clean technologies, from electric cars to the materials used to build wind turbines.
At the same time, as high-emitting industries face higher costs, some commentators have suggested that tariffs could hamper US plans for fossil-fuel expansion.
And as clean technology becomes more expensive to manufacture in the US, other nations – particularly China – are likely to step up to fill in any gaps.
Carbon Brief has asked a range of researchers and policy experts what they think Trump’s tariffs could mean for global climate action and energy supplies.
These are their responses, first as sample quotes, then, below, in full:
- Dr Kyle Chan: “With US automakers struggling to compete, Chinese electric vehicle companies will likely gain a stronger position.”
- Elisabetta Cornago: “China may redirect its exports towards the relatively open EU market, challenging homegrown clean-tech industries at a time when the EU is trying to support and revitalise them.”
- Dr Bentley Allan and Dr Tim Sahay: “G7 and G20 countries are strengthening their domestic economies with deficit financing and directed investments into strategic sectors, such as green and digital sectors”
- Alex Muresianu: “A less productive US economy, which must pay higher prices for key inputs, is one that can spare fewer resources to address climate change.”
- Antoine Vagneur-Jones: “The administration’s fondness for data centres requires significant grid investment and yet the US relies on its neighbours for its supply of large power transformers.”
- Jimena Blanco: “The US is mainly or wholly import-reliant for around four-fifths of its identified 50 critical minerals, including from its partners Canada and Mexico.”
- Dr Simi Thambi: “An increase in trade protectionism is not good for climate action.”
- Robert Rozansky: “One upside to Trump’s trade war is that it might stymie his efforts to push US liquified natural gas (LNG) expansion into overdrive.”
- Chris Severson-Baker: “The Canadian oil and gas lobby…has been using this moment to make the case for more oil and gas production and infrastructure.”
- Anne-Sophie Corbeau: “Trump’s tariffs have already had an impact on LNG trade…China has not imported a single US LNG cargo since 6 February.”
- Avantika Goswami: “Tariffs – if imposed widely – may hurt the exports of countries like India, which nurture aspirations to mimic China’s role as an exporter of green goods.”
- Tu Le: “If manufacturers have to move multiple factories, that changes, reduces or eliminates what would have likely been more investment in research and development for clean energy vehicles.”
- Ellie Belton: “A more unpredictable US could create opportunities for the UK and EU to attract low-carbon investment and gain a competitive edge in the energy transition.”
- Eileen Torres Morales: “The effects of Trump’s tariffs on the global transition to green iron and steelmaking are still uncertain.”
- Dr Aurélien Saussay: “When faced with increased economic pressures from tariffs, countries could be more tempted to relax environmental standards to maintain competitiveness.”
Dr Kyle Chan
Postdoctoral researcher and author of High Capacity
Trump’s tariffs will likely have wide-ranging effects on China’s clean-tech industry and global climate progress. Higher tariffs on China will directly impact US imports of Chinese clean tech goods, such as lithium batteries, which reached $1.9bn in December 2024.
Chinese solar manufacturing firms will also be hit indirectly through tariffs on production sites in south-east Asia, which collectively supplies 80% of US solar imports. Meanwhile, China’s retaliation could disrupt US access to critical minerals for its own clean-tech industry. This includes graphite for battery anodes and rare earth metals for wind turbines.
The impact on China’s electric vehicle industry in particular will be consequential, albeit less direct. Chinese electric vehicle imports to the US, which were already minimal, will not be significantly affected by Trump’s new tariffs.
However, the broader disruption to automotive supply chains across Mexico and Canada – along with rising steel and aluminium costs – will weaken the ability of US automakers to transition to electric vehicles. This will benefit Chinese electric vehicle makers, which continue to innovate and drive down costs.
With US automakers struggling to compete, Chinese electric vehicle companies will likely gain a stronger position, not just in China’s domestic market, but globally as well.
 Elisabetta Cornago
Elisabetta Cornago
Senior research fellow, EU energy and climate policy
Centre for European Reform
The Trump administration is walking back on US climate commitments, both domestically by threatening to cut back Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) support for clean-tech industries and internationally, [by] withdrawing from the Paris Agreement. US tariffs can also affect climate action and the energy transition globally, hitting global value chains for clean technologies.
The Trump administration has levied tariffs on primary materials, such as steel and aluminium, on the EU as well as on China. This will increase manufacturing costs for US-based producers of goods that rely on imports of those materials, such as wind turbines and electric vehicles.
But, at the same time, because of interconnections in global value chains, the EU will also be impacted by US tariffs that are currently limited to China.
Tariffs on Chinese exports of solar panels, electric vehicles and batteries to the US, for example, will reinforce China’s overcapacity in manufacturing in all these sectors, relative to weak Chinese demand. As a consequence, China may redirect its exports towards the relatively open EU market, challenging homegrown clean tech industries at a time when the EU is trying to support and revitalise them.
Trump’s self-harming retreat on climate and tariffs has caused uncertainty for clean energy, industry and trade. There is a macroeconomic slowdown that could negatively impact the rising green investments of the last decade.
However, countries are strategic actors, not just passive victims of US trade policy. We are observing G7 and G20 countries take anticipatory steps.
First, they are strengthening their domestic economies with deficit financing and directed investments into strategic sectors, such as green and digital sectors. A few examples:
- The monumental shift in German fiscal policy will now enable investments in climate.
- The overhaul of EU’s fiscal rules and greater funding of the EU’s industrial deal with over €100bn to support clean manufacturing.
- Brazilian president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva has unfurled Nova Industria Brasil to build green industrialisation.
- Mexican president Claudia Sheinbaum has announced and funded Plan Mexico for strategic investments.
Many nations are also diversifying their markets and multilateralist diplomacy. Targets of Trump tariff threats are involved in a flurry of trade and investment deals:
- Within Asia, there are negotiations to green the world’s largest trade bloc – the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
- Trade deals between Mexico-EU, EU-Brazil and Canada-EU are being revamped to allow more green trade.
- Countries such as Brazil and South Africa are leading diplomatic efforts through their presidencies of BRICS and G20 this year to articulate new trading and financial architecture that gives them the policy space to pursue green structural transformation to meet domestic and global climate goals.
 Alex Muresianu
Alex Muresianu
Senior policy analyst
Tax Foundation
At the most basic level, gains from trade are valuable. Historically, trade barriers have slowed the spread and adoption of new technology. The fight against climate change is just one example of the many economic challenges these tariffs will make more difficult.
Tariffs on important inputs make building more expensive and distort the US economy toward less productive activity. A less productive US economy, which must pay higher prices for key inputs, is one that can spare fewer resources to address climate change.
Advocates of Trump’s approach to trade often invoke competition with China as a justification. However, most of Trump’s tariffs are targeted at allied or friendly nations, such as Canada, Mexico and members of the EU. US policymakers are worried about losing an innovation race with China in areas like electric vehicles or other green technologies, but putting up barriers to other markets will make us less – not more – competitive in the long term.
 Antoine Vagneur-Jones
Antoine Vagneur-Jones
Head of trade and supply chains
BloombergNEF
The tariffs jar with priorities that are – at least rhetorically – at the heart of the Trump presidency.
The administration’s fondness for data centres requires significant grid investment and yet the US relies on its neighbours for its supply of large power transformers. Expanding manufacturing is another apparent priority, but increasing the cost of inputs will crimp domestic industry.
And by hurting cross-border value chains and taxing imported crude, the tariffs could conceivably disadvantage traditional internal combustion engine vehicles more than their electrified equivalents.
 Jimena Blanco
Jimena Blanco
Chief analyst
Verisk Maplecroft
Against a background of tariffs and disrupted trading relationships, we are seeing a more protectionist stance towards critical minerals emerging, further complicating clean-tech supply chains.
Our research shows resource nationalism is accelerating. Among the emerging markets, 17 major critical mineral producers have seen a significant increase in risk in the past five years, including Chile and Peru – both key sources of lithium and copper.
Exact details of the new US tariff regime won’t be known until 2 April, but it is likely that the next batch of tariffs will be levied most heavily on countries with the largest trade imbalances. These countries represent the majority of Washington’s key global trade partners, meaning disruptions to supply chains – including in minerals essential for the energy transition – are increasingly likely.
The US is mainly or wholly import-reliant for around four-fifths of its identified 50 critical minerals, including from its US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) partners Canada and Mexico. If Canada, for example, responds to the imposition of tariffs by the US with new export taxes, bans or restrictions on mineral exports, increasing costs or supply shortages are a prospect that US businesses will have to adapt to.
There is potential for US tariffs to slow the rollout of green policies if nations view renewables mandates or more stringent carbon regulation as adding additional burdens to their economy at a time of increasing trade friction. However, this could be counterbalanced somewhat by investments in low-carbon solutions such as carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) or hydrogen.
 Dr Simi Thambi
Dr Simi Thambi
Climate economist
FAIRR
An increase in trade protectionism is not good for climate action. Climate scientists have conceptualised this as a scenario of rising retaliatory tariffs – Shared Socioeconomic Pathway 3 (SSP3) – where challenges to mitigation and adaptation are high, making it unlikely for the world to limit temperature rise to 1.5C by the end of the century. This scenario could lead to up to four times more emissions than a sustainability-focused pathway with low challenges to mitigation and adaptation.
Mitigation is very challenging in this scenario because reducing emissions is more expensive, as investments needed to scale clean technologies are not prioritised. As a result, these technologies fail to penetrate well into the markets that need them most cost-effectively. For example, according to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) 2024 electric vehicle outlook, electric vehicle sales in emerging markets remain very low. Lowering global emissions without greening the transport sector in developing economies would be highly challenging.
Adaptation also faces considerable challenges in SSP3, because one can expect deforestation and cropland expansion to rise in this scenario, as countries focus on their national ambitions. Extensive deforestation would reduce ecosystems and biodiversity, reducing their adaptive capacity.
 Robert Rozansky
Robert Rozansky
Global LNG analyst and project manager, Europe gas tracker
Global Energy Monitor
The Trump administration has gone all in on promoting US LNG under its “America first”, “energy dominance” agenda. As it seeks to boost new LNG production projects that are still on the drawing board, such as the Alaska LNG project touted in the State of the Union address, the US could further exacerbate a global overbuild of LNG infrastructure that threatens international climate targets. At the same time, the Trump administration’s trade war may make these same proposed LNG projects more difficult to build and finance.
Tariffs will raise the cost of raw materials, such as steel, the “backbone of LNG facilities”. If tariffs lead to economy-wide inflation, labour could become more expensive, too. The LNG industry is no stranger to the toll of inflation. For example, the cost of the under-construction Golden Pass LNG Terminal rose by $2bn after its main contractor declared bankruptcy in May citing pandemic-related cost inflation and delays.
If it becomes more expensive to build LNG export terminals in the US, financiers committed to projects under construction may struggle to recover their investments and those evaluating proposed facilities may be hesitant to invest.
The longer proposed projects sit without financial backers, the less likely it is they will get off the ground at all. New US LNG terminals are already set to face steep competition from an incoming wave of export projects abroad and increasingly cheap renewable power, as an alternative to gas.
Given that LNG may be roughly as bad for the climate as coal, if not worse, one upside to Trump’s trade war is that it might stymie his efforts to push US LNG expansion into overdrive.
 Chris Severson-Baker
Chris Severson-Baker
Executive director
Pembina Institute
In Canada, this is unfolding into a national debate about how best to strengthen our economic resilience and ensure long-term prosperity in the face of a hostile US.
There is a risk that what president Trump is doing could cause knee-jerk reactions here in Canada. The Canadian oil and gas lobby, for example, has been using this moment to make the case for more oil and gas production and infrastructure, to get more of its products to markets outside the US.
While we agree that Canada needs to diversify its trading partners, doubling down on oil and gas exports would not provide the long-term economic resiliency and energy security our country is seeking right now. We should look instead at Europe, where governments are aggressively decarbonising their economies, not only for climate reasons. They also understand that clean energy and new technologies are associated with less price volatility and more secure supplies, as well as health and affordability benefits for citizens.
The EU’s forthcoming carbon border adjustment mechanism (CBAM) will give an advantage to low-carbon exports of steel, aluminium and cement. These are all industries that Canada is well-placed to lead on, given our abundance of emissions-free electricity to power them. However, this can only happen if we retain our nationwide industrial carbon pricing system.
That is also why the next big nation-building project we foresee in Canada is not oil and gas infrastructure, but widespread electrification, supported by a buildout and modernisation of our electricity grid. This would help Canadians become more resilient, both to the economic impacts of trade disputes and the physical and economic impacts of climate change.
 Anne-Sophie Corbeau
Anne-Sophie Corbeau
Global research scholar at the Center on Global Energy Policy
Columbia University
Trump’s tariffs have already had an impact on LNG trade. After the Trump administration imposed new tariffs on China in early February 2025, China retaliated by announcing, among other things, a 15% tariff on US LNG. China and the US are not too dependent on each other in LNG trade, with US LNG representing only 6% of China’s LNG supply in 2024. But China has not imported a single US LNG cargo since 6 February, as Chinese offtakers of US LNG are diverting their cargoes to other regions to avoid tariffs.
However, China and the US are respectively the largest LNG importer and exporter globally. Chinese buyers have contracted significant amounts of US LNG between 2021 and 2023. Should tariffs persist or even increase, US LNG will likely continue to be diverted to other countries, making the whole global LNG market less efficient. Meanwhile, Chinese buyers may become hesitant to contract more US LNG.
Another country that may be at risk if trade relations deteriorate is Mexico. Mexico’s energy system is very dependent on gas. It is also uniquely dependent on imports of US pipeline gas, which is cheaper than LNG imports. There are also a few Mexican LNG export projects at different stages of advancement that rely on US gas supplies and are therefore in competition with US-based LNG projects. Uncertainties over the bilateral relationship could become a source of risk for Mexico.
 Avantika Goswami
Avantika Goswami
Programme manager, climate change
Centre for Science and Environment
Donald Trump’s use of tariffs as an economic weapon is an attempt to regain dominance in the US’ trade relationships, for varying reasons – one being the US’ massive trade deficit.
From a climate perspective, tariffs need to be situated within a larger picture. They are likely to raise costs for general goods in the US – and green goods are not excluded from this calculus. This comes at a time when the US is lagging behind east and south-east Asia in the manufacturing of green technologies and has been slow in its domestic energy transition.
Tariffs may further raise the cost of the transition in the US. In tandem with attempts to expand oil and gas production in the domestic energy mix as Trump promises – and also any successful reindustrialisation efforts – this could see a rise in US domestic emissions. Meanwhile, fossil fuel exports will raise emissions elsewhere.
Tariffs – if imposed widely – may hurt the exports of countries like India, which nurture aspirations to mimic China’s role as an exporter of green goods. There has been an increase in the export of solar technology from India to the US, with India’s share of the country’s module imports rising from 2.5% in 2022 to 10.7% in 2024, amounting to approximately $2bn in 2023-24. For a country with aspirations in green manufacturing, tariffs on green goods could undermine this positive momentum for India.
This shift toward protectionism in the US does not necessarily spell the collapse of the global green goods market. Instead, it may serve to strengthen China’s role in the global green technology supply chain.
Lastly, the return to protectionism, particularly green protectionism, is an act of hypocrisy by nations like the US, which have spent years denouncing the same policies at the World Trade Organization when undertaken by developing countries.
 Tu Le
Tu Le
Managing director
Sino Auto Insights
It is important to take the Trump administration’s individual actions in totality, while also keeping in the back of your mind that the US is the second largest passenger vehicle market in the world. That drives the need for legacy automakers to sell into this market.
The tariffs force companies to review their long-term manufacturing strategy. If they have to move multiple factories, that changes, reduces or eliminates what would have likely been more investment in research and development for clean energy vehicles, due to their limited capital.
The Trump administration is also poised to eliminate the more stringent Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) vehicle emissions standards that would have taken effect in 2027. If successful, that would substantially reduce the urgency for global original equipment manufacturers to launch products with more efficient powertrains. And it pushes out the need for oil companies in Russia, the Middle East and the US to alter or reduce their investments in clean energy initiatives.
Legacy manufacturers play a role in this as well, since their leadership years ago seemed to be so bullish in their ability to easily move over to clean energy vehicles. Their initial sales forecasts for this timeframe were never realistic and it put a spotlight on this being a left versus right issue, when it should have been a discussion on energy independence all along.
The US and EU governments are likely to push out their net-zero targets [for vehicles]. They were arbitrary to begin with. Now, with the Trump administration in place and European automakers whining about their inability to meet the more stringent requirements, they seem more than likely to be delayed past 2035.
 Ellie Belton
Ellie Belton
Senior policy advisor – trade and climate
E3G
It is hard to imagine a scenario in which higher tariffs will benefit the global energy transition. Even if clean technologies are not directly targeted, the complex nature of international supply chains means that there will inevitably be knock-on effects, such as through increased costs for component parts like steel and aluminium.
Retaliatory tariffs against the US will also create a domino effect, distorting trade flows worldwide and altering countries’ comparative advantage in the clean economy. The biggest risk to climate action is the uncertainty this creates, which will damage investor confidence and distract governments from driving green ambition.
But a more unpredictable US could create opportunities for the UK and EU to attract low-carbon investment and gain a competitive edge in the energy transition. Continued efforts to provide public support for decarbonisation and seek mutual gains with cooperative trade partners will enable Europe to capitalise on the growing demand for renewable technologies globally.
Trade policy may have become a geopolitical game, but the urgent need to deliver a safe climate remains as critical as ever. The world is currently stuck in crisis response mode, but it is vital that we do not lose sight of the long-term direction of travel.
 Eileen Torres Morales
Eileen Torres Morales
Research associate
Stockholm Environment Institute
The effects of Trump’s tariffs on the global transition to green iron and steelmaking are still uncertain. It will take some time to see the impact, if any, such as increased steel prices in the short term, changed trade dynamics or long-term impacts on global green steel production.
The announcement of steel tariffs has forced exporting countries to rapidly reconsider how to stay competitive in the US market. The tariffs might benefit steel producers in the US, but a likely outcome is that both public and private consumers within the US will face rising steel prices regardless of whether the steel is green or not.
Trump’s administration’s interest in research and development of US-based green iron and steel production also remains unclear. It is not yet known if incentives for steel decarbonisation considered in the IRA will remain. For example, will the negotiations to advance green iron and steel production under the US Department of Energy’s industrial demonstrations programme continue or not?
Although the imposition of tariffs by the US may temporarily shift attention away from international competition and policies focused on heavy industry transition, this should not distract from progress in establishing a market for low-carbon products.
Policy instruments, such as the EU’s emissions trading system (ETS) and CBAM, should continue to be prioritised. Such tools can support the construction of a strong internal market for green steel, thus steering attention away from tariffs, back to driving innovation in low-carbon technology and emissions reductions that contribute to global climate action.
 Dr Aurélien Saussay
Dr Aurélien Saussay
Assistant professor at the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment
London School of Economics and Political Science
The looming threat of Trump’s tariffs is already reshaping energy policy decisions in concerning ways.
Perhaps most alarming, from a European standpoint, is European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen’s recent suggestion that Europe should increase its imports of US shale gas-derived LNG to appease the Trump administration and avoid tariffs. This move would seriously undermine the EU’s 2050 net-zero commitment.
This potential shift illustrates how trade tensions can indirectly sabotage climate progress. I’m particularly concerned by how these tariffs could undermine the viability of carbon-pricing schemes in major economies. When faced with increased economic pressures from tariffs, countries could be more tempted to relax environmental standards to maintain competitiveness.
The steel and aluminium sectors – already struggling to decarbonise – would be especially vulnerable. Many mills have begun investing in cleaner technologies, but tariffs could force them to prioritise cost-cutting over emissions reduction.
Furthermore, the uncertainty created by trade wars makes low-carbon investments riskier. Clean energy technologies, many of which are capital intensive, require stable policy environments to attract investments. The constant threat of retaliatory tariffs dampens investor confidence.
Perhaps most importantly, retaliatory tariffs on clean-energy technologies could significantly slow the global energy transition. This is particularly the case for tariffs targeting China, which is a leader in many of the key decarbonisation technologies. By increasing costs for solar panels, wind turbines and electric vehicles, these measures would hamper deployment rates precisely when acceleration is needed.
The post Experts: What do Trump’s tariffs mean for global climate action? appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Experts: What do Trump’s tariffs mean for global climate action?
Greenhouse Gases
Permitting reform: A major key to cutting climate pollution
Permitting reform: A major key to cutting climate pollution
By Dana Nuccitelli, CCL Research Coordinator
Permitting reform has emerged as the biggest and most important clean energy and climate policy area in the 119th Congress (2025-2026).
To make sure every CCL volunteer understands the opportunities and challenges ahead, CCL Vice President of Government Affairs Jennifer Tyler and I recently provided two trainings about the basics of permitting reform and understanding the permitting reform landscape.
These first introductory trainings set the stage for the rest of an ongoing series, which will delve into the details of several key permitting reform topics that CCL is engaging on. Read on for a recap of the first two trainings and a preview of coming attractions.
Permitting reform basics
Before diving into the permitting reform deep end, we need to first understand the fundamentals of the topic: what is “permitting”? What problems are we trying to solve with permitting reform? Why is it a key climate solution?
In short, a permit is a legal authorization issued by a government agency (federal and/or state and/or local) that allows a specific activity or project to proceed under certain defined conditions. The permitting process ensures that public health, safety, and the environment are protected during the construction and operation of the project.
But the permitting process can take a long time, and in some cases it’s taking so long that it’s unduly slowing down the clean energy transition. “Permitting reform” seeks to make the process more efficient while still ensuring that public health, safety, and the environment are protected.
There are a lot of factors involved in the permitting reform process, including environmental laws, limitations on lawsuits, and measures to expedite the building of electrical transmission lines that are key for expanding the capacity of America’s aging electrical grid in order to allow us to connect more clean energy and meet our energy affordability and security and climate needs.
But if we can succeed in passing a good, comprehensive permitting reform package through Congress, it could unlock enough climate pollution reductions to offset what we lost from this year’s rollback of the Inflation Reduction Act’s clean energy investments. Permitting reform is the big climate policy in the current session of Congress.
Understanding the permitting reform landscape
In the second training of this series, we sought to understand the players and the politics in the permitting reform space, learn about the challenges involved, and explore CCL’s framework and approach for weighing in on this policy topic.
Permitting reform has split some traditional alliances along two differing theories about how to best address climate change. Some groups with a theory of change relying on using permitting and lawsuits to slow and stop fossil fuel infrastructure are least likely to be supportive of a permitting reform effort. Groups like CCL that recognize the importance of quickly building lots of clean, affordable energy infrastructure are more supportive of permitting reform measures.
The subject has created some strange bedfellows, because clean energy and fossil fuel companies and organizations all want efficient permitting for their projects, and hence all tend to support permitting reform. For CCL, the key question is whether a comprehensive permitting reform package will be a net benefit to clean energy or the climate — and that’s what we’re working toward.
The two major political parties also have different priorities when it comes to permitting reform. Republicans tend to view it through a lens of reducing government red tape, ensuring that laws and regulations are only used for their intended purpose, and achieving energy affordability and security. Democrats prioritize building clean energy faster to slow climate change, addressing energy affordability, and protecting legacy environmental laws and community engagement.
As we discussed in the training, there are a number of key concepts that will require compromise from both sides of the aisle in order to reach a durable bipartisan permitting reform agreement. We’ll delve into the details of these in these upcoming trainings:
The Challenge of Energy Affordability and Security
First, with support from CCL’s Electrification Action Team, on February 5 I’ll examine what’s behind rising electricity rates and energy insecurity in the U.S. and how we can solve these problems. Electrification is a key climate solution in the transition to clean energy sources. But electricity rates are rising fast and face surging demand from artificial intelligence data centers. Permitting reform can play a key role in addressing these challenges.
Transmission Reform and Key Messages
Insufficient electrical transmission capacity is acting as a bottleneck slowing down the deployment of new clean energy sources in the U.S. Reforming cumbersome transmission permitting processes could unlock billions of tons of avoided climate pollution while improving America’s energy security and affordability. In this training on March 5, Jenn and I will dive into the details of the key clean energy and climate solution that is transmission reform, and the key messages to use when lobbying our members of Congress.
Clean energy projects often encounter long, complex permitting steps that slow construction and raise costs. Practical permitting reforms can help ensure that good projects move forward faster while upholding environmental and community protections. In this training on March 19, Jenn and I will examine permitting reforms to build energy infrastructure faster, some associated tensions and compromises that they may involve, and key messages for congressional offices.
Presidents from both political parties have taken steps to interfere with the permitting of certain types of energy infrastructure that they oppose. These executive actions create uncertainty that inhibits the development of new energy sources in the United States. For this reason, ensuring fair permitting certainty is a key aspect of permitting reform that enjoys bipartisan support. In this training on April 2, Jenn and I will discuss how Congress can ensure certainty in a permitting reform package, and key messages for congressional offices.
Community Engagement and Key Messages
It’s important for energy project developers to engage local communities in order to address any local concerns and adverse impacts that may arise from new infrastructure projects. But it’s also important to strike a careful balance such that community input can be heard and addressed in a timely manner without excessively slowing new clean energy project timelines. In this training on May 7, Jenn and I will examine how community engagement may be addressed in the permitting reform process, and key messages for congressional offices.
We look forward to nerding out with you in these upcoming advanced and important permitting reform trainings! 
Want to take action now? Use our online action tool to call Congress and encourage them to work together on comprehensive permitting reform.
The post Permitting reform: A major key to cutting climate pollution appeared first on Citizens' Climate Lobby.
Greenhouse Gases
DeBriefed 30 January 2026: Fire and ice; US formally exits Paris; Climate image faux pas
Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Fire and ice
OZ HEAT: The ongoing heatwave in Australia reached record-high temperatures of almost 50C earlier this week, while authorities “urged caution as three forest fires burned out of control”, reported the Associated Press. Bloomberg said the Australian Open tennis tournament “rescheduled matches and activated extreme-heat protocols”. The Guardian reported that “the climate crisis has increased the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including heatwaves and bushfires”.
WINTER STORM: Meanwhile, a severe winter storm swept across the south and east of the US and parts of Canada, causing “mass power outages and the cancellation of thousands of flights”, reported the Financial Times. More than 870,000 people across the country were without power and at least seven people died, according to BBC News.
COLD QUESTIONED: As the storm approached, climate-sceptic US president Donald Trump took to social media to ask facetiously: “Whatever happened to global warming???”, according to the Associated Press. There is currently significant debate among scientists about whether human-caused climate change is driving record cold extremes, as Carbon Brief has previously explained.
Around the world
- US EXIT: The US has formally left the Paris Agreement for the second time, one year after Trump announced the intention to exit, according to the Guardian. The New York Times reported that the US is “the only country in the world to abandon the international commitment to slow global warming”.
- WEAK PROPOSAL: Trump officials have delayed the repeal of the “endangerment finding” – a legal opinion that underpins federal climate rules in the US – due to “concerns the proposal is too weak to withstand a court challenge”, according to the Washington Post.
- DISCRIMINATION: A court in the Hague has ruled that the Dutch government “discriminated against people in one of its most vulnerable territories” by not helping them to adapt to climate change, reported the Guardian. The court ordered the Dutch government to set binding targets within 18 months to cut greenhouse gas emissions in line with the Paris Agreement, according to the Associated Press.
- WIND PACT: 10 European countries have agreed a “landmark pact” to “accelerate the rollout of offshore windfarms in the 2030s and build a power grid in the North Sea”, according to the Guardian.
- TRADE DEAL: India and the EU have agreed on the “mother of all trade deals”, which will save up to €4bn in import duty, reported the Hindustan Times. Reuters quoted EU officials saying that the landmark trade deal “will not trigger any changes” to the bloc’s carbon border adjustment mechanism.
- ‘TWO-TIER SYSTEM’: COP30 president André Corrêa do Lago believes that global cooperation should move to a “two-speed system, where new coalitions lead fast, practical action alongside the slower, consensus-based decision-making of the UN process”, according to a letter published on Tuesday, reported Climate Home News.
$2.3tn
The amount invested in “green tech” globally in 2025, marking a new record high, according to Bloomberg.
Latest climate research
- Including carbon emissions from permafrost thaw and fires reduces the remaining carbon budget for limiting warming to 1.5C by 25% | Communications Earth & Environment
- The global population exposed to extreme heat conditions is projected to nearly double if temperatures reach 2C | Nature Sustainability
- Polar bears in Svalbard – the fastest-warming region on Earth – are in better condition than they were a generation ago, as melting sea ice makes seal pups easier to reach | Scientific Reports
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
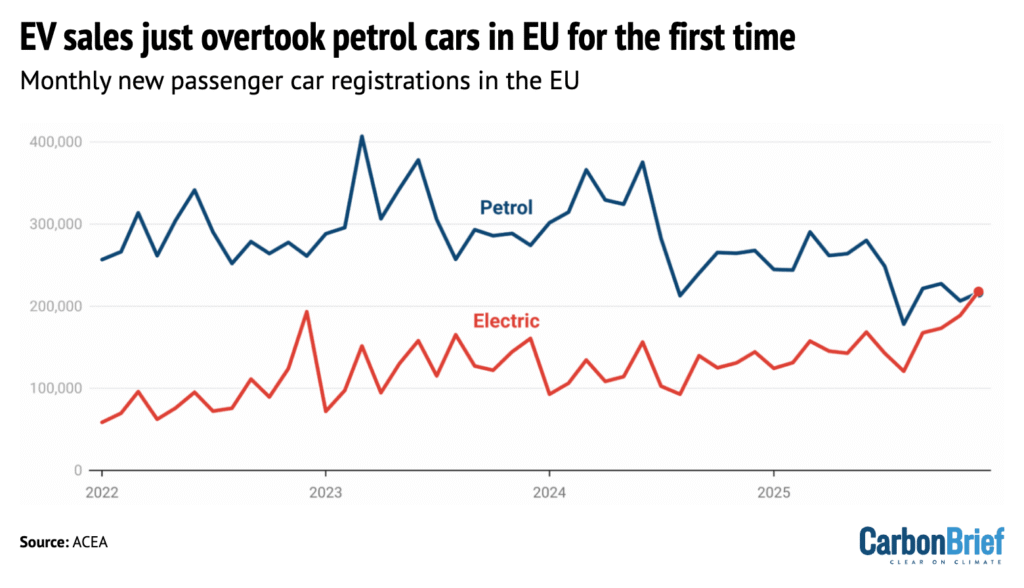
Sales of electric vehicles (EVs) overtook standard petrol cars in the EU for the first time in December 2025, according to new figures released by the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) and covered by Carbon Brief. Registrations of “pure” battery EVs reached 217,898 – up 51% year-on-year from December 2024. Meanwhile, sales of standard petrol cars in the bloc fell 19% year-on-year, from 267,834 in December 2024 to 216,492 in December 2025, according to the analysis.
Spotlight
Looking at climate visuals
Carbon Brief’s Ayesha Tandon recently chaired a panel discussion at the launch of a new book focused on the impact of images used by the media to depict climate change.
When asked to describe an image that represents climate change, many people think of polar bears on melting ice or devastating droughts.
But do these common images – often repeated in the media – risk making climate change feel like a far-away problem from people in the global north? And could they perpetuate harmful stereotypes?
These are some of the questions addressed in a new book by Prof Saffron O’Neill, who researches the visual communication of climate change at the University of Exeter.
“The Visual Life of Climate Change” examines the impact of common images used to depict climate change – and how the use of different visuals might help to effect change.
At a launch event for her book in London, a panel of experts – moderated by Carbon Brief’s Ayesha Tandon – discussed some of the takeaways from the book and the “dos and don’ts” of climate imagery.
Power of an image
“This book is about what kind of work images are doing in the world, who has the power and whose voices are being marginalised,” O’Neill told the gathering of journalists and scientists assembled at the Frontline Club in central London for the launch event.
O’Neill opened by presenting a series of climate imagery case studies from her book. This included several examples of images that could be viewed as “disempowering”.
For example, to visualise climate change in small island nations, such as Tuvalu or Fiji, O’Neill said that photographers often “fly in” to capture images of “small children being vulnerable”. She lamented that this narrative “misses the stories about countries like Tuvalu that are really international leaders in climate policy”.
Similarly, images of power-plant smoke stacks, often used in online climate media articles, almost always omit the people that live alongside them, “breathing their pollution”, she said.
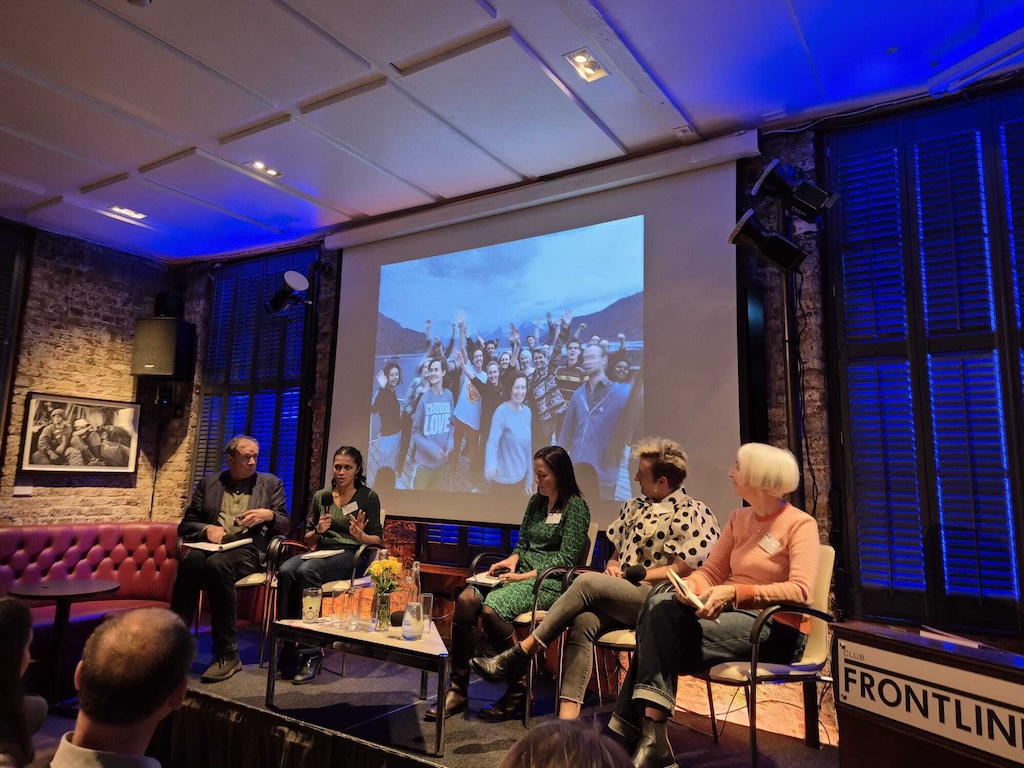

During the panel discussion that followed, panellist Dr James Painter – a research associate at the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism and senior teaching associate at the University of Oxford’s Environmental Change Institute – highlighted his work on heatwave imagery in the media.
Painter said that “the UK was egregious for its ‘fun in the sun’ imagery” during dangerous heatwaves.
He highlighted a series of images in the Daily Mail in July 2019 depicting people enjoying themselves on beaches or in fountains during an intense heatwave – even as the text of the piece spoke to the negative health impacts of the heatwave.
In contrast, he said his analysis of Indian media revealed “not one single image of ‘fun in the sun’”.
Meanwhile, climate journalist Katherine Dunn asked: “Are we still using and abusing the polar bear?”. O’Neill suggested that polar bear images “are distant in time and space to many people”, but can still be “super engaging” to others – for example, younger audiences.
Panellist Dr Rebecca Swift – senior vice president of creative at Getty images – identified AI-generated images as “the biggest threat that we, in this space, are all having to fight against now”. She expressed concern that we may need to “prove” that images are “actually real”.
However, she argued that AI will not “win” because, “in the end, authentic images, real stories and real people are what we react to”.
When asked if we expect too much from images, O’Neill argued “we can never pin down a social change to one image, but what we can say is that images both shape and reflect the societies that we live in”. She added:
“I don’t think we can ask photos to do the work that we need to do as a society, but they certainly both shape and show us where the future may lie.”
Watch, read, listen
UNSTOPPABLE WILDFIRES: “Funding cuts, conspiracy theories and ‘powder keg’ pine plantations” are making Patagonia’s wildfires “almost impossible to stop”, said the Guardian.
AUDIO SURVEY: Sverige Radio has published “the world’s, probably, longest audio survey” – a six-hour podcast featuring more than 200 people sharing their questions around climate change.
UNDERSTAND CBAM: European thinktank Bruegel released a podcast “all about” the EU’s carbon adjustment border mechanism, which came into force on 1 January.
Coming up
- 1 February: Costa Rican general election
- 3 February: UN Environment Programme Adaptation Fund Climate Innovation Accelerator report launch, Online
- 2-8 February: Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) 12th plenary, Manchester, UK
Pick of the jobs
- Climate Central, climate data scientist | Salary: $85,000-$92,000. Location: Remote (US)
- UN office to the African Union, environmental affairs officer | Salary: Unknown. Location: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- Google Deepmind, research scientist in biosphere models | Salary: Unknown. Location: Zurich, Switzerland
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 30 January 2026: Fire and ice; US formally exits Paris; Climate image faux pas appeared first on Carbon Brief.
DeBriefed 30 January 2026: Fire and ice; US formally exits Paris; Climate image faux pas
Greenhouse Gases
Factcheck: What it really costs to heat a home in the UK with a heat pump
Electric heat pumps are set to play a key role in the UK’s climate strategy, as well as cutting the nation’s reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Heat pumps took centre-stage in the UK government’s recent “warm homes plan”, which said that they could also help cut household energy bills by “hundreds of pounds” a year.
Similarly, innovation agency Nesta estimates that typical households could cut their annual energy bills nearly £300 a year, by switching from a gas boiler to a heat pump.
Yet there has been widespread media coverage in the Times, Sunday Times, Daily Express, Daily Telegraph and elsewhere of a report claiming that heat pumps are “more expensive” to run.
The report is from the Green Britain Foundation set up by Dale Vince, owner of energy firm Ecotricity, who campaigns against heat pumps and invests in “green gas” as an alternative.
One expert tells Carbon Brief that Vince’s report is based on “flimsy data”, while another says that it “combines a series of worst-case assumptions to present an unduly pessimistic picture”.
This factcheck explains how heat pumps can cut bills, what the latest data shows about potential savings and how this information was left out of the report from Vince’s foundation.
How heat pumps can cut bills
Heat pumps use electricity to move heat – most commonly from outside air – to the inside of a building, in a process that is similar to the way that a fridge keeps its contents cold.
This means that they are highly efficient, adding three or four units of heat to the house for each unit of electricity used. In contrast, a gas boiler will always supply less than one unit of heat from each unit of gas that it burns, because some of the energy is lost during combustion.
This means that heat pumps can keep buildings warm while using three, four or even five times less energy than a gas boiler. This cuts fossil-fuel imports, reducing demand for gas by at least two-fifths, even in the unlikely scenario that all of the electricity they need is gas-fired.
Since UK electricity supplies are now the cleanest they have ever been, heat pumps also cut the carbon emissions associated with staying warm by around 85%, relative to a gas boiler.
Heat pumps are, therefore, the “central” technology for cutting carbon emissions from buildings.
While heat pumps cost more to install than gas boilers, the UK government’s recent “warm homes plan” says that they can help cut energy bills by “hundreds of pounds” per year.
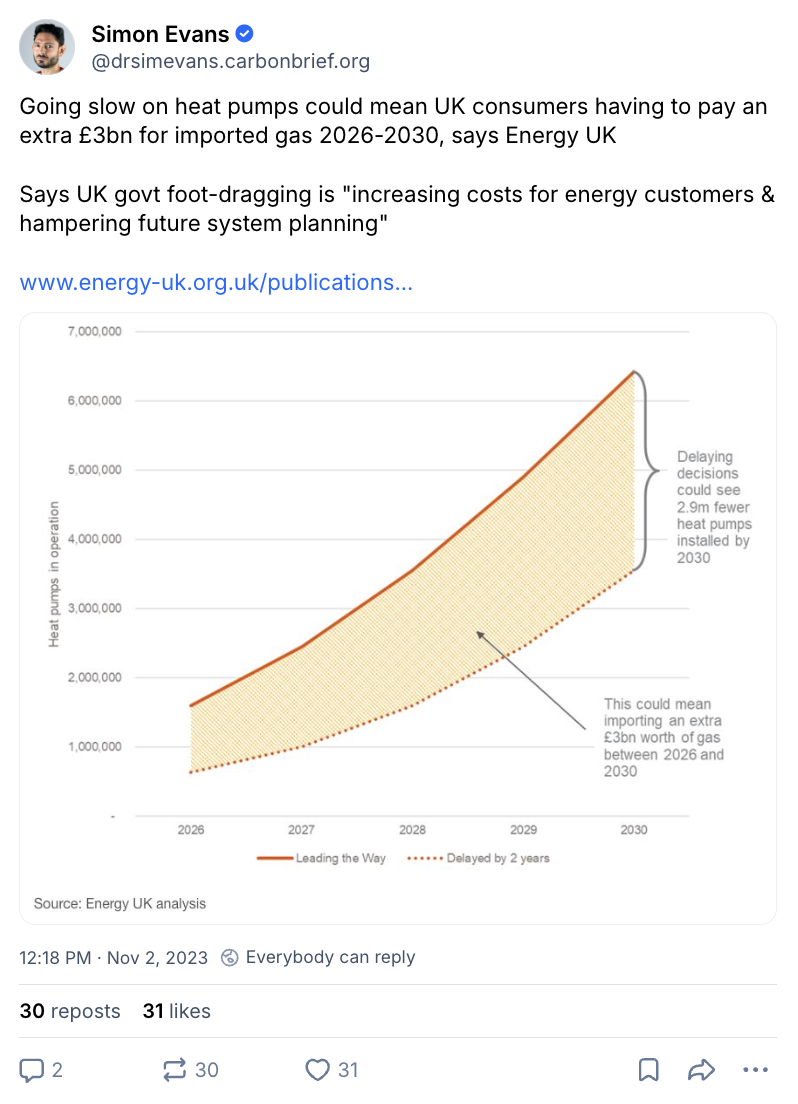
Similarly, Nesta published analysis showing that a typical home could cut its annual energy bill by £280, if it replaces a gas boiler with a heat pump, as shown in the figure below.
Nesta and the government plan say that significantly larger savings are possible if heat pumps are combined with other clean-energy technologies, such as solar and batteries.
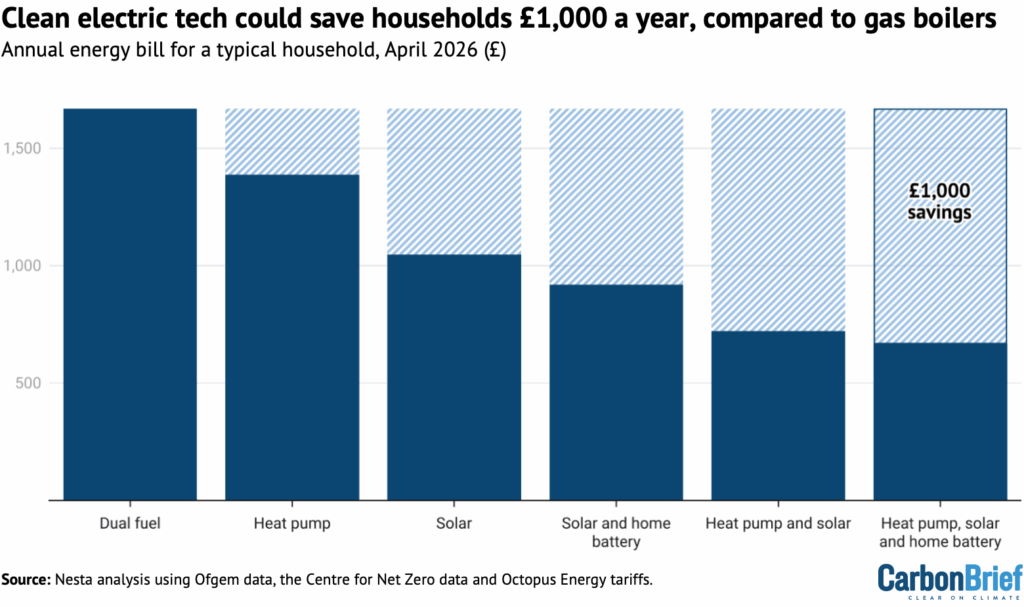
Both the government and Nesta’s estimates of bill savings from switching to a heat pump rely on relatively conservative assumptions.
Specifically, the government assumes that a heat pump will deliver 2.8 units of heat for each unit of electricity, on average. This is known as the “seasonal coefficient of performance” (SCoP).
This figure is taken from the government-backed “electrification of heat” trial, which ran during 2020-2022 and showed that heat pumps are suitable for all building types in the UK.
(The Green Britain Foundation report and Vince’s quotes in related coverage repeat a number of heat pump myths, such as the idea that they do not perform well in older properties and require high levels of insulation.)
Nesta assumes a slightly higher SCoP of 3.0, says Madeleine Gabriel, the organisation’s director of sustainable future. (See below for more on what the latest data says about SCoP in recent installations.)
Both the government and Nesta assume that a home with a heat pump would disconnect from the gas grid, meaning that it would no longer need to pay the daily “standing charge” for gas. This currently amounts to a saving of around £130 per year.
Finally, they both consider the impact of a home with a heat pump using a “smart tariff”, where the price of electricity varies according to the time of day.
Such tariffs are now widely available from a variety of energy suppliers and many have been designed specifically for homes that have a heat pump.
Such tariffs significantly reduce the average price for a unit of electricity. Government survey data suggests that around half of heat-pump owners already use such tariffs.
This is important because on the standard rates under the price cap set by energy regulator Ofgem, each unit of electricity costs more than four times as much as a unit of gas.
The ratio between electricity and gas prices is a key determinant of the size and potential for running-cost savings with a heat pump. Countries with a lower electricity-to-gas price ratio consistently see much higher rates of heat-pump adoption.
(Decisions taken by the UK government in its 2025 budget mean that the electricity-to-gas ratio will fall from April, but current forecasts suggest it will remain above four-to-one.)
In contrast, Vince’s report assumes that gas boilers are 90% efficient, whereas data from real homes suggests 85% is more typical. It also assumes that homes with heat pumps remain on the gas grid, paying the standing charge, as well as using only a standard electricity tariff.
Prof Jan Rosenow, energy programme leader at the University of Oxford’s Environmental Change Institute, tells Carbon Brief that Vince’s report uses “worst-case assumptions”. He says:
“This report cherry-picks assumptions to reach a predetermined conclusion. Most notably, it assumes a gas boiler efficiency of 90%, which is significantly higher than real-world performance…Taken together, the analysis combines a series of worst-case assumptions to present an unduly pessimistic picture.”
Similarly, Gabriel tells Carbon Brief that Vince’s report is based on “flimsy data”. She explains:
“Dale Vince has drawn some very strong conclusions about heat pumps from quite flimsy data. Like Dale, we’d also like to see electricity prices come down relative to gas, but we estimate that, from April, even a moderately efficient heat pump on a standard tariff will be cheaper to run than a gas boiler. Paired with a time-of-use tariff, a heat pump could save £280 versus a boiler and adding solar panels and a battery could triple those savings.”
What the latest data shows about bill savings
The efficiency of heat-pump installations is another key factor in the potential bill savings they can deliver and, here, both the government and Vince’s report take a conservative approach.
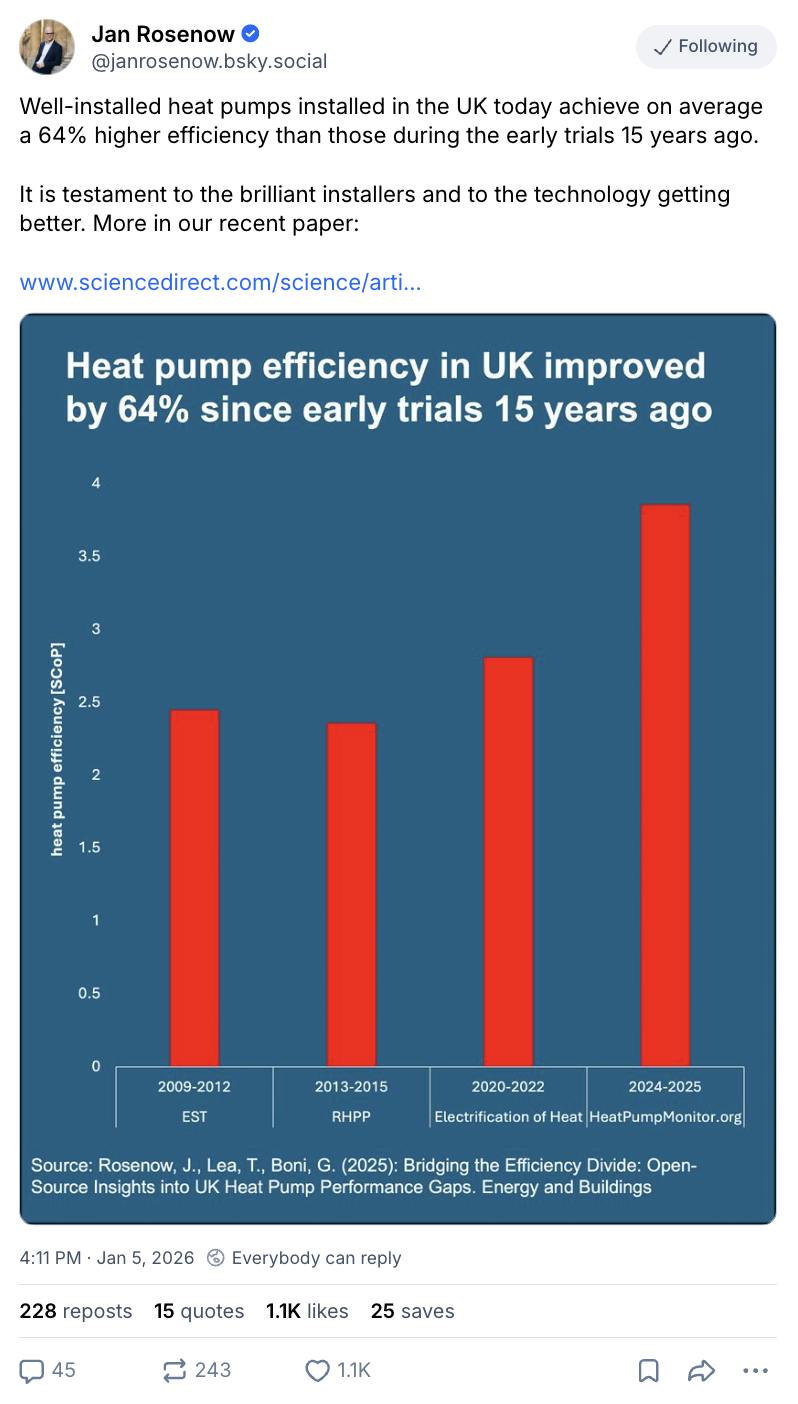
They rely on the “electrification of heat” trial data to use an efficiency (SCoP) of 2.8 for heat pumps. However, Rosenow says that recent evidence shows that “substantially higher efficiencies are routinely available”, as shown in the figure below.
Detailed, real-time data on hundreds of heat pump systems around the UK is available via the website Heat Pump Monitor, where the average efficiency – a SCoP of 3.9 – is much higher.
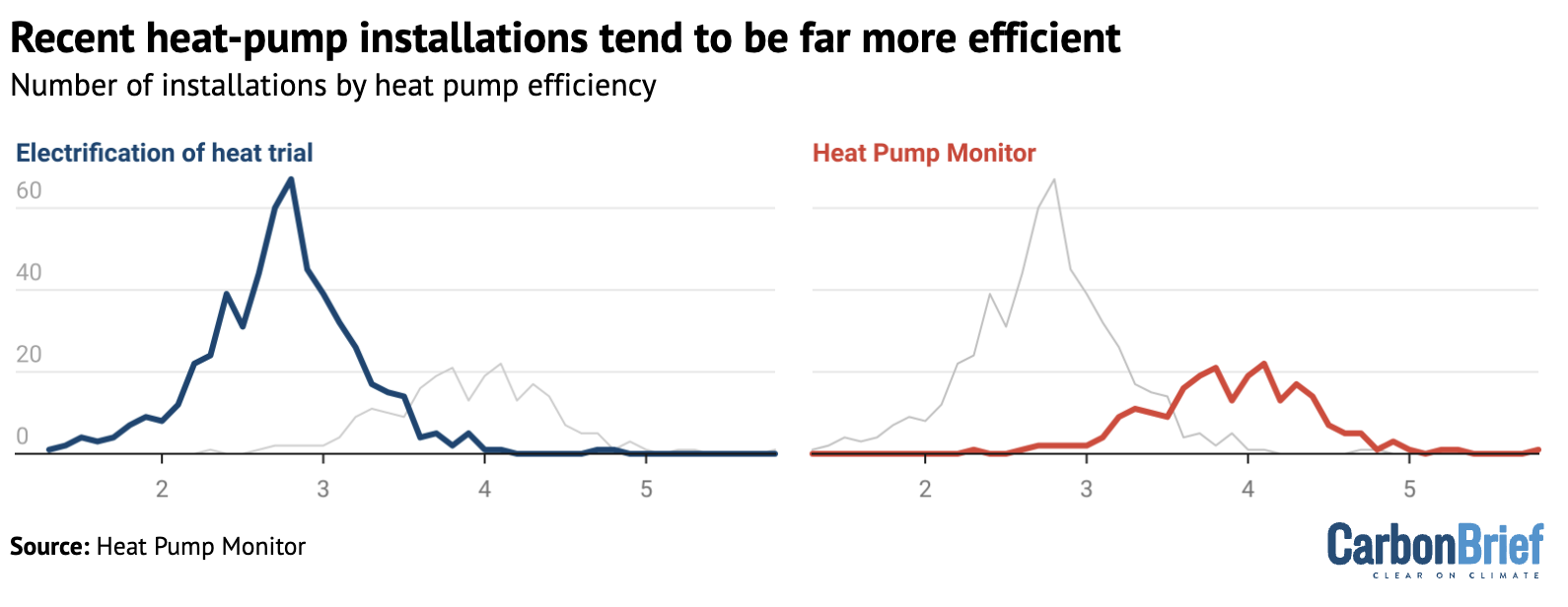
Homes with such efficient heat-pump installations would see even larger bill savings than suggested by the government and Nesta estimates.
Academic research suggests that there are simple and easy-to-implement reasons why these systems achieve much higher efficiency levels than in the electrification of heat trial.
Specifically, it shows that many of the systems in the trial have poor software settings, which means they do not operate as efficiently as their heat pump hardware is capable of doing.
The research suggests that heat pump installations in the UK have been getting more and more efficient over time, as engineers become increasingly familiar with the technology.
It indicates that recently installed heat pumps are 64% more efficient than those in early trials.
Notably, the Green Britain Foundation report only refers to the trial data from the electrification of heat study carried out in 2020-22 and the even earlier “renewable heat premium package” (RHPP). This makes a huge difference to the estimated running costs of a heat pump.
Carbon Brief analysis suggests that a typical household could cut its annual energy bills by nearly £200 with a heat pump – even on a standard electricity tariff – if the system has a SCoP of 3.9.
The savings would be even larger on a smart heat-pump tariff.
In contrast, based on the oldest efficiency figures mentioned in the Green Britain Foundation report, a heat pump could increase annual household bills by as much as £200 on a standard tariff.
To support its conclusions, the report also includes the results of a survey of 1,001 heat pump owners, which, among other things, is at odds with government survey data. The report says “66% of respondents report that their homes are more expensive to heat than the previous system”.
There are several reasons to treat these findings with caution. The survey was carried out in July 2025 and some 45% of the heat pumps involved were installed between 2021-23.
This is a period during which energy prices surged as a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the resulting global energy crisis. Energy bills remain elevated as a result of high gas prices.
The wording of the survey question asks if homes are “more or less expensive to heat than with your previous system” – but makes no mention of these price rises.
The question does not ask homeowners if their bills are higher today, with a heat pump, than they would have been with the household’s previous heating system.
If respondents interpreted the question as asking whether their bills have gone up or down since their heat pump was installed, then their answers will be confounded by the rise in prices overall.
There are a number of other seemingly contradictory aspects of the survey that raise questions about its findings and the strong conclusions in the media coverage of the report.
For example, while only 15% of respondents say it is cheaper to heat their home with a heat pump, 49% say that one of the top three advantages of the system is saving money on energy bills.
In addition, 57% of respondents say they still have a boiler, even though 67% say they received government subsidies for their heat-pump installation. It is a requirement of the government’s boiler upgrade scheme (BUS) grants that homeowners completely remove their boiler.
The government’s own survey of BUS recipients finds that only 13% of respondents say their bills have gone up, whereas 37% say their bills have gone down, another 13% say they have stayed the same and 8% thought that it was too early to say.
The post Factcheck: What it really costs to heat a home in the UK with a heat pump appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Factcheck: What it really costs to heat a home in the UK with a heat pump
-
Greenhouse Gases6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change6 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits