Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Eve of COP30
MULTILATERAL HOPES A gathering of world leaders kicked off in Belém, Brazil, ahead of the official opening of COP30 next week. The leaders of China, the US and India – the “planet’s three biggest polluters” – are “notably absent” from the two-day leaders summit, reported the Associated Press. Some Latin American leaders “were openly critical” of the US president’s stance on climate change in their speeches at the “diminished” summit, noted the Financial Times.
‘MORAL FAILURE’: Speaking at the world leaders summit, UN secretary-general António Guterres described failing to remain below 1.5C as a “moral failure and deadly negligence”, reported the Guardian. Guterres added: “Every fraction of a degree means more hunger, displacement and loss – especially for those least responsible.” The UN chief’s speech came as the World Meteorological Organization confirmed that 2025 is “on track to be the second or third warmest globally”, noted Reuters.
‘POSITIVE TIPPING POINT’: The Brazilian COP presidency published a “Baku to Belém roadmap” detailing how climate finance for developing nations could be scaled up to $1.3tn a year by 2035, Climate Home News reported. The roadmap was published ahead of the UN climate talks, but will not be formally discussed as part of the negotiations, the outlet added. Read Carbon Brief’s summary of what the roadmap means for climate finance.
FORESTS NOT FOREVER: Brazil also launched its Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF) this week, said Agence France-Presse, designed to help tropical countries protect their forests. Norway has joined France and Brazil in investing in the fund, while Germany will announce its contribution on Friday, noted Bloomberg. The Guardian dubbed the UK’s decision to opt out as “a major letdown”. For more on the TFFF, see Carbon Brief’s explainer.
UN report says world is heading for 2.8C
UNFULFILLING: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) annual “emissions gap” report warned that global temperature rise could be heading for 2.8C this century, if only current policies are fulfilled, the Financial Times reported. The rise could be limited to 2.5C, if unconditional national pledges are met in full – or to 2.3C, if pledges conditional on financial support are put into action, the newspaper noted.
STALLED PROGRESS: The world’s warming trajectory is now “0.3C lower than it was a year ago…meaning new plans announced this year have done little to move the needle”, noted Reuters. Some of this progress will be “cancelled” out, the New York Times added, once the US withdrawal from the Paris Agreement takes effect. See Carbon Brief’s in-depth coverage of the UNEP report.
Around the world
- WATERED DOWN: The EU finally confirmed a “significantly weakened” plan to cut emissions to 90% below 1990 levels by 2040, reported the Financial Times.
- DEADLY DISASTER: The Philippines is in a state of emergency after Typhoon Kalmaegi left at least 114 people dead and nearly 130 missing.
- DROPPING COMMITMENTS: The junior partner in Australia’s opposition Coalition – the Nationals – has formally abandoned a commitment to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, reported ABC News.
- MAYORAL WIN: Zohran Mamdani won New York City’s mayoral election, having “refram[ed] climate policy as a quality-of-life issue”, Inside Climate News reported.
100
The number of proposed indicators to track progress towards the “global goal on adaptation” that will be negotiated at COP, according to Carbon Brief‘s new Q&A.
Latest climate research
- Rising temperatures could affect the muscles that Arctic bumblebees use to generate their “charismatic buzz” | Nature Communications
- The release of CO2 from the the Southern Ocean has been “underestimated” by up to 40% in previous studies | Science
- Outdoor heat stress has led to a 10% decline in labour capacity in “rural to urban migration hotspots” in India | Environmental Research Letters
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
IPCC funding shortfall
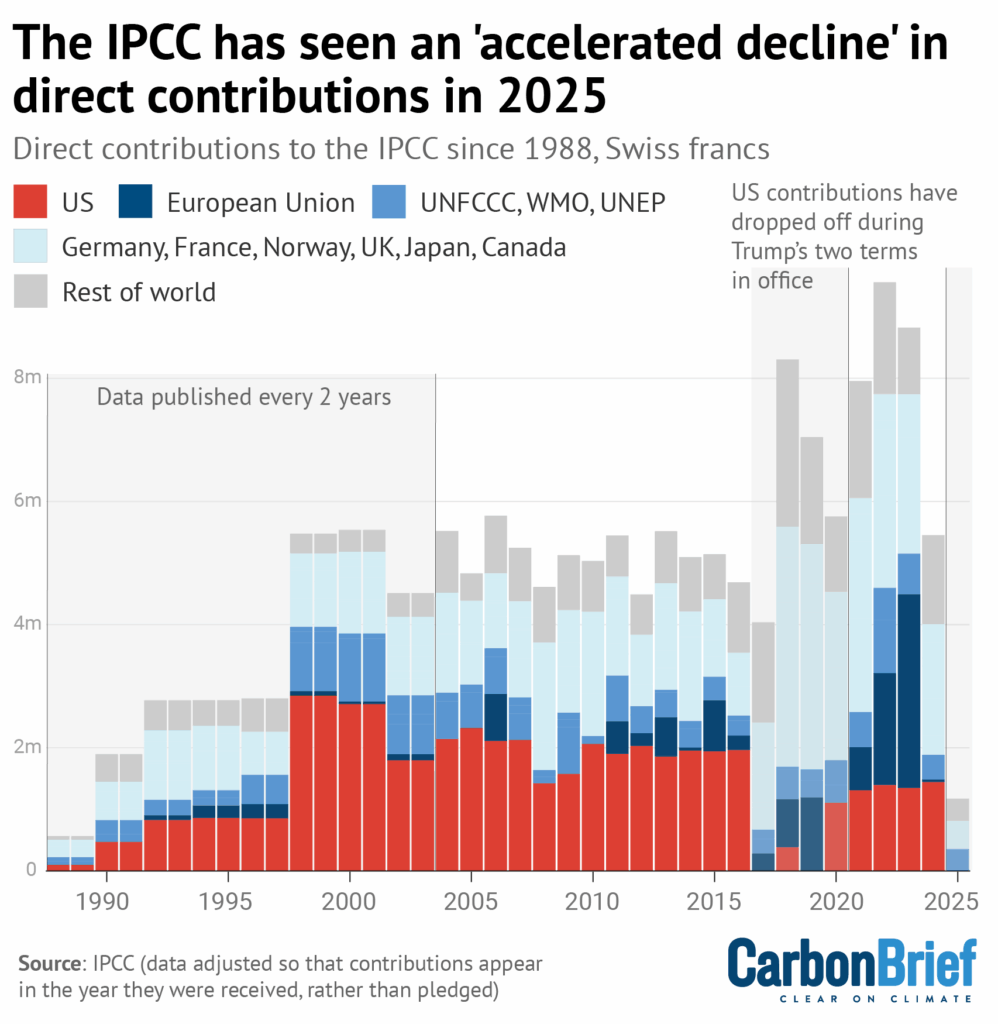
Carbon Brief covered the latest meeting of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in Lima, Peru. Alongside funding from parent organisations the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and UN Environment Programme, voluntary contributions by countries help pay for the work of the IPCC. The biggest contributors so far in 2025 are Norway, the UNFCCC, Canada and the WMO. The red bars show how US contributions have dropped off during Trump’s two terms in office. Having provided 30% of direct contributions throughout the IPCC’s history, the US has not made a contribution so far this year.
Spotlight
‘With knowledge comes responsibility’: the changing role of climate scientists in a warming world
This week, Carbon Brief speaks to a researcher about the different ways climate scientists are feeling and taking responsibility for the knowledge they hold.

From calling for action in Belém to defending science against attempts to discredit or downplay it, climate scientists are responding to world events in ever-more visible ways.
Dr Friederike Hartz is a research and policy associate at University College London.
For her PhD thesis, carried out at the University of Cambridge, Hartz interviewed 77 experts who participated in IPCC reports, the world’s most authoritative global assessments of climate science coordinated by the UN.
‘You can’t unsee it’
Hartz’s findings show how climate scientists can feel a sense of responsibility, as those who bear the knowledge and evidence of climate change.
Some interviewees felt a sense of “representational responsibility” – motivated by the wish to improve the lives of the vulnerable or underrepresented communities they belong to.
Others expressed a sense of “intergenerational responsibility”, resolving to contribute to a better world for their children and grandchildren.
Hartz called this the “inescapability” of climate knowledge. She told Carbon Brief:
“Once you know, you know. As one of my interviewees shared with me, you simply can’t unsee it. Especially as a scientist, you’re trained to see those things.”
Taking responsibility
Hartz’s research looked at what it means for climate scientists to act on the sense of responsibility they feel, beyond producing the science itself.
Some take part in formal IPCC assessments. Others “have come to accept and further embrace a responsibility for communicating” their knowledge, Hartz noted in her paper.
Beyond the IPCC, some scientists take on additional responsibility for evidence-based “advocacy” or even call for more “activism” in science.
Similarly, on the grounds that “with knowledge comes responsibility”, some have called for scientists to “step beyond their traditional roles” or act as “sentinels” to alert society to threats. Hartz told Carbon Brief:
“This is all part of what I call ‘science enactment’: putting science into action or putting it in the hands of other people who can act on it.”
Navigating what it means to take responsibility is a very individual thing, said Hartz, which speaks to late biologist Stephen Schneider’s “double ethical bind” – the balance between a commitment to the “scientific method” and the “wish to see the world a better place”.
Lived experience
Hartz pointed to research suggesting the traditional view – that engaging in activism or advocacy can damage a scientist’s credibility – may be unwarranted. But there can be other downsides, she noted, including the emotional toll. As one of her interviewees expressed it:
“As scientists, we are not droids…And, so, to say that we are not at all influenced by what is going on in science is not true.”
Hartz suggested that scientists can simultaneously experience feelings of enthusiasm about their work and frustration about its uptake. Or as she noted in her thesis, citing a seminal political science study:
“Knowledge can only speak ‘truth to power’ to the extent that ‘power listens to truth’.”
Watch, read, listen
‘WHITE HOUSE EFFECT’: A Netflix documentary looked at how a “crucial opportunity” to take climate action was “deliberately undermined” during the George HW Bush administration.
‘COP OF TRUTH’: Brazil’s president, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, wrote in the Guardian ahead of COP30 about the need to act “with the urgency the climate crisis demands”.
HUMAN STORIES: A video by the Grantham Institute at Imperial College London explored the pivotal moments leading to the historic establishment of a loss and damage fund.
Coming up
- 10 November: UN Climate Change conference (COP30) begins in Belém, Brazil
- 12 November: IEA World Energy Outlook 2025 launch, Paris
- 13 November: Global Carbon Budget annual update released
Pick of the jobs
- Project Drawdown, program manager, research fellow and senior analyst | Salary: Various. Location: Remote
- UK Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, laboratory assistant | £26,206 – £27,808. Location: Lancaster, UK
- Ofwat, Wales environmental policy lead | £57,783 – £72,000. Location: Cardiff, UK
- UNEP, mitigation expert on sand and dust storms | Salary: Not specified. Location: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Conservation International, senior manager, climate & landscape restoration | Salary: Not specified. Location: Acornhoek, South Africa.
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 7 November 2025: Belém COP begins; UN warns of 1.5C breach; changing roles of climate scientists appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
We handpick and explain the most important stories at the intersection of climate, land, food and nature over the past fortnight.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s fortnightly Cropped email newsletter.
Subscribe for free here.
Key developments
Food inflation on the rise
DELUGE STRIKES FOOD: Extreme rainfall and flooding across the Mediterranean and north Africa has “battered the winter growing regions that feed Europe…threatening food price rises”, reported the Financial Times. Western France has “endured more than 36 days of continuous rain”, while farmers’ associations in Spain’s Andalusia estimate that “20% of all production has been lost”, it added. Policy expert David Barmes told the paper that the “latest storms were part of a wider pattern of climate shocks feeding into food price inflation”.
-
Sign up to Carbon Brief’s free “Cropped” email newsletter. A fortnightly digest of food, land and nature news and views. Sent to your inbox every other Wednesday.
NO BEEF: The UK’s beef farmers, meanwhile, “face a double blow” from climate change as “relentless rain forces them to keep cows indoors”, while last summer’s drought hit hay supplies, said another Financial Times article. At the same time, indoor growers in south England described a 60% increase in electricity standing charges as a “ticking timebomb” that could “force them to raise their prices or stop production, which will further fuel food price inflation”, wrote the Guardian.
‘TINDERBOX’ AND TARIFFS: A study, covered by the Guardian, warned that major extreme weather and other “shocks” could “spark social unrest and even food riots in the UK”. Experts cited “chronic” vulnerabilities, including climate change, low incomes, poor farming policy and “fragile” supply chains that have made the UK’s food system a “tinderbox”. A New York Times explainer noted that while trade could once guard against food supply shocks, barriers such as tariffs and export controls – which are being “increasingly” used by politicians – “can shut off that safety valve”.
El Niño looms
NEW ENSO INDEX: Researchers have developed a new index for calculating El Niño, the large-scale climate pattern that influences global weather and causes “billions in damages by bringing floods to some regions and drought to others”, reported CNN. It added that climate change is making it more difficult for scientists to observe El Niño patterns by warming up the entire ocean. The outlet said that with the new metric, “scientists can now see it earlier and our long-range weather forecasts will be improved for it.”
WARMING WARNING: Meanwhile, the US Climate Prediction Center announced that there is a 60% chance of the current La Niña conditions shifting towards a neutral state over the next few months, with an El Niño likely to follow in late spring, according to Reuters. The Vibes, a Malaysian news outlet, quoted a climate scientist saying: “If the El Niño does materialise, it could possibly push 2026 or 2027 as the warmest year on record, replacing 2024.”
CROP IMPACTS: Reuters noted that neutral conditions lead to “more stable weather and potentially better crop yields”. However, the newswire added, an El Niño state would mean “worsening drought conditions and issues for the next growing season” to Australia. El Niño also “typically brings a poor south-west monsoon to India, including droughts”, reported the Hindu’s Business Line. A 2024 guest post for Carbon Brief explained that El Niño is linked to crop failure in south-eastern Africa and south-east Asia.
News and views
- DAM-AG-ES: Several South Korean farmers filed a lawsuit against the country’s state-owned utility company, “seek[ing] financial compensation for climate-related agricultural damages”, reported United Press International. Meanwhile, a national climate change assessment for the Philippines found that the country “lost up to $219bn in agricultural damages from typhoons, floods and droughts” over 2000-10, according to Eco-Business.
- SCORCHED GRASS: South Africa’s Western Cape province is experiencing “one of the worst droughts in living memory”, which is “scorching grass and killing livestock”, said Reuters. The newswire wrote: “In 2015, a drought almost dried up the taps in the city; farmers say this one has been even more brutal than a decade ago.”
- NOUVELLE VEG: New guidelines published under France’s national food, nutrition and climate strategy “urged” citizens to “limit” their meat consumption, reported Euronews. The delayed strategy comes a month after the US government “upended decades of recommendations by touting consumption of red meat and full-fat dairy”, it noted.
- COURTING DISASTER: India’s top green court accepted the findings of a committee that “found no flaws” in greenlighting the Great Nicobar project that “will lead to the felling of a million trees” and translocating corals, reported Mongabay. The court found “no good ground to interfere”, despite “threats to a globally unique biodiversity hotspot” and Indigenous tribes at risk of displacement by the project, wrote Frontline.
- FISH FALLING: A new study found that fish biomass is “falling by 7.2% from as little as 0.1C of warming per decade”, noted the Guardian. While experts also pointed to the role of overfishing in marine life loss, marine ecologist and study lead author Dr Shahar Chaikin told the outlet: “Our research proves exactly what that biological cost [of warming] looks like underwater.”
- TOO HOT FOR COFFEE: According to new analysis by Climate Central, countries where coffee beans are grown “are becoming too hot to cultivate them”, reported the Guardian. The world’s top five coffee-growing countries faced “57 additional days of coffee-harming heat” annually because of climate change, it added.
Spotlight
Nature talks inch forward
This week, Carbon Brief covers the latest round of negotiations under the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), which occurred in Rome over 16-19 February.
The penultimate set of biodiversity negotiations before October’s Conference of the Parties ended in Rome last week, leaving plenty of unfinished business.
The CBD’s subsidiary body on implementation (SBI) met in the Italian capital for four days to discuss a range of issues, including biodiversity finance and reviewing progress towards the nature targets agreed under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
However, many of the major sticking points – particularly around finance – will have to wait until later this summer, leaving some observers worried about the capacity for delegates to get through a packed agenda at COP17.
The SBI, along with the subsidiary body on scientific, technical and technological advice (SBSTTA) will both meet in Nairobi, Kenya, later this summer for a final round of talks before COP17 kicks off in Yerevan, Armenia, on 19 October.
Money talks
Finance for nature has long been a sticking point at negotiations under the CBD.
Discussions on a new fund for biodiversity derailed biodiversity talks in Cali, Colombia, in autumn 2024, requiring resumed talks a few months later.
Despite this, finance was barely on the agenda at the SBI meetings in Rome. Delegates discussed three studies on the relationship between debt sustainability and implementation of nature plans, but the more substantive talks are set to take place at the next SBI meeting in Nairobi.
Several parties “highlighted concerns with the imbalance of work” on finance between these SBI talks and the next ones, reported Earth Negotiations Bulletin (ENB).
Lim Li Ching, senior researcher at Third World Network, noted that tensions around finance permeated every aspect of the talks. She told Carbon Brief:
“If you’re talking about the gender plan of action – if there’s little or no financial resources provided to actually put it into practice and implement it, then it’s [just] paper, right? Same with the reporting requirements and obligations.”
Monitoring and reporting
Closely linked to the issue of finance is the obligations of parties to report on their progress towards the goals and targets of the GBF.
Parties do so through the submission of national reports.
Several parties at the talks pointed to a lack of timely funding for driving delays in their reporting, according to ENB.
A note released by the CBD Secretariat in December said that no parties had submitted their national reports yet; by the time of the SBI meetings, only the EU had. It further noted that just 58 parties had submitted their national biodiversity plans, which were initially meant to be published by COP16, in October 2024.
Linda Krueger, director of biodiversity and infrastructure policy at the environmental not-for-profit Nature Conservancy, told Carbon Brief that despite the sparse submissions, parties are “very focused on the national report preparation”. She added:
“Everybody wants to be able to show that we’re on the path and that there still is a pathway to getting to 2030 that’s positive and largely in the right direction.”
Watch, read, listen
NET LOSS: Nigeria’s marine life is being “threatened” by “ghost gear” – nets and other fishing equipment discarded in the ocean – said Dialogue Earth.
COMEBACK CAUSALITY: A Vox long-read looked at whether Costa Rica’s “payments for ecosystem services” programme helped the country turn a corner on deforestation.
HOMEGROWN GOALS: A Straits Times podcast discussed whether import-dependent Singapore can afford to shelve its goal to produce 30% of its food locally by 2030.
‘RUSTING’ RIVERS: The Financial Times took a closer look at a “strange new force blighting the [Arctic] landscape”: rivers turning rust-orange due to global warming.
New science
- Lakes in the Congo Basin’s peatlands are releasing carbon that is thousands of years old | Nature Geoscience
- Natural non-forest ecosystems – such as grasslands and marshlands – were converted for agriculture at four times the rate of land with tree cover between 2005 and 2020 | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
- Around one-quarter of global tree-cover loss over 2001-22 was driven by cropland expansion, pastures and forest plantations for commodity production | Nature Food
In the diary
- 2-6 March: UN Food and Agriculture Organization regional conference for Latin America and Caribbean | Brasília
- 5 March: Nepal general elections
- 9-20 March: First part of the thirty-first session of the International Seabed Authority (ISA) | Kingston, Jamaica
Cropped is researched and written by Dr Giuliana Viglione, Aruna Chandrasekhar, Daisy Dunne, Orla Dwyer and Yanine Quiroz.
Please send tips and feedback to cropped@carbonbrief.org
The post Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Cropped 25 February 2026: Food inflation strikes | El Niño looms | Biodiversity talks stagnate
Climate Change
Battery passport plan aims to clean up the industry powering clean energy
For millions of consumers, the sustainability scheme stickers found on everything from bananas to chocolate bars and wooden furniture are a way to choose products that are greener and more ethical than some of the alternatives.
Inga Petersen, executive director of the Global Battery Alliance (GBA), is on a mission to create a similar scheme for one of the building blocks of the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy systems: batteries.
“Right now, it’s a race to the bottom for whoever makes the cheapest battery,” Petersen told Climate Home News in an interview.
The GBA is working with industry, international organisations, NGOs and governments to establish a sustainable and transparent battery value chain by 2030.
“One of the things we’re trying to do is to create a marketplace where products can compete on elements other than price,” Petersen said.
Under the GBA’s plan, digital product passports and traceability would be used to issue product-level sustainability certifications, similar to those commonplace in other sectors such as forestry, Petersen said.
Managing battery boom’s risks
Over the past decade, battery deployment has increased 20-fold, driven by record-breaking electric vehicle (EV) sales and a booming market for batteries to store intermittent renewable energy.
Falling prices have been instrumental to the rapid expansion of the battery market. But the breakneck pace of growth has exposed the potential environmental and social harms associated with unregulated battery production.
From South America to Zimbabwe and Indonesia, mineral extraction and refining has led to social conflict, environmental damage, human rights violations and deforestation. In Indonesia, the nickel industry is powered by coal while in Europe, production plants have been met with strong local opposition over pollution concerns.
“We cannot manage these risks if we don’t have transparency,” Petersen said.
The GBA was established in 2017 in response to concerns about the battery industry’s impact as demand was forecast to boom and reports of child labour in the cobalt mines of the Democratic Republic of the Congo made headlines.
The alliance’s initial 19 members recognised that the industry needed to scale rapidly but with “social, environmental and governance guardrails”, said Petersen, who previously worked with the UN Environment Programme to develop guiding principles to minimise the environmental impact of mining.

Digital battery passport
Today, the alliance is working to develop a global certification scheme that will recognise batteries that meet minimum thresholds across a set of environmental, social and governance benchmarks it has defined along the entire value chain.
Participating mines, manufacturing plants and recycling facilities will have to provide data for their greenhouse gas emissions as well as how they perform against benchmarks for assessing biodiversity loss, pollution, child and forced labour, community impacts and respect for the rights of Indigenous peoples, for example.
The data will be independently verified, scored, aggregated and recorded on a battery passport – a digital record of the battery’s composition, which will include the origin of its raw materials and its performance against the GBA’s sustainability benchmarks.
The scheme is due to launch in 2027.
A carrot and a stick
Since the start of the year, some of the world’s largest battery companies have been voluntarily participating in the biggest pilot of the scheme to date.
More than 30 companies across the EV battery and stationary storage supply chains are involved, among them Chinese battery giants CATL and BYD subsidiary FinDreams Battery, miner Rio Tinto, battery producers Samsung SDI and Siemens, automotive supplier Denso and Tesla.
Petersen said she was “thrilled” about support for the scheme. Amid a growing pushback against sustainability rules and standards, “these companies are stepping up to send a public signal that they are still committed to a sustainable and responsible battery value chain,” she said.

There are other motivations for battery producers to know where components in their batteries have come from and whether they have been produced responsibly.
In 2023, the EU adopted a law regulating the batteries sold on its market.
From 2027, it mandates all batteries to meet environmental and safety criteria and to have a digital passport accessed via a QR code that contains information about the battery’s composition, its carbon footprint and its recycling content.
The GBA certification is not intended as a compliance instrument for the EU law but it will “add a carrot” by recognising manufacturers that go beyond meeting the bloc’s rules on nature and human rights, Petersen said.
Raising standards in complex supply chain
But challenges remain, in part due to the complexity of battery supply chains.
In the case of timber, “you have a single input material but then you have a very complex range of end products. For batteries, it’s almost the reverse,” Petersen said.
The GBA wants its certification scheme to cover all critical minerals present in batteries, covering dozens of different mining, processing and manufacturing processes and hundreds of facilities.
“One of the biggest impacts will be rewarding the leading performers through preferential access to capital, for example, with investors choosing companies that are managing their risk responsibly and transparently,” Petersen said.
It could help influence public procurement and how companies, such as EV makers, choose their suppliers, she added. End consumers will also be able to access a summary of the GBA’s scores when deciding which product to buy.
US, Europe rush to build battery supply chain
Today, the GBA has more than 150 members across the battery value chain, including more than 50 companies, of which over a dozen are Chinese firms.
China produces over three-quarters of batteries sold globally and it dominates the world’s battery recycling capacity, leaving the US and Europe scrambling to reduce their dependence on Beijing by building their own battery supply chains.
Petersen hopes the alliance’s work can help build trust in the sector amid heightened geopolitical tensions. “People want to know where the materials are coming from and which actors are involved,” she said.
At the same time, companies increasingly recognise that failing to manage sustainability risks can threaten their operations. Protests over environmental concerns have shut down mines and battery factories across the world.
“Most companies know that and that’s why they’re making these efforts,” Petersen added.
The post Battery passport plan aims to clean up the industry powering clean energy appeared first on Climate Home News.
Battery passport plan aims to clean up the industry powering clean energy
Climate Change
Reheating plastic food containers: what science says about microplastics and chemicals in ready meals
How often do you eat takeaway food? What about pre-prepared ready meals? Or maybe just microwaving some leftovers you had in the fridge? In any of these cases, there’s a pretty good chance the container was made out of plastic. Considering that they can be an extremely affordable option, are there any potential downsides we need to be aware of? We decided to investigate.
Scientific research increasingly shows that heating food in plastic packaging can release microplastics and plastic chemicals into the food we eat. A new Greenpeace International review of peer-reviewed studies finds that microwaving plastic food containers significantly increases this release, raising concerns about long-term human health impacts. This article summarises what the science says, what remains uncertain, and what needs to change.
There’s no shortage of research showing how microplastics and nanoplastics have made their way throughout the environment, from snowy mountaintops and Arctic ice, into the beetles, slugs, snails and earthworms at the bottom of the food chain. It’s a similar story with humans, with microplastics found in blood, placenta, lungs, liver and plenty of other places. On top of this, there’s some 16,000 chemicals known to be either present or used in plastic, with a bit over a quarter of those chemicals already identified as being of concern. And there are already just under 1,400 chemicals that have been found in people.
Not just food packaging, but plenty of household items either contain or are made from plastic, meaning they potentially could be a source of exposure as well. So if microplastics and chemicals are everywhere (including inside us), how are they getting there? Should we be concerned that a lot of our food is packaged in plastic?
Greenpeace analysis of 24 articles in peer-reviewed scientific journals found that the plastics we use to package our food are directly risking our health.
Heating food in plastic packaging dramatically increases the levels of microplastics and chemicals that leach into our food.
Plastic food packaging: the good, the bad, and the ugly
The growing trend towards ready meals, online shopping and restaurant delivery, and away from home-prepared meals and individual grocery shopping, is happening in every region of the world. Since the first microwaveable TV dinners were introduced in the US in the 1950s to sell off excess stock of turkey meat after Thanksgiving holidays, pre-packaged ready meals have grown hugely in sales. The global market is worth $190bn in 2025, and is expected to reach a total volume of 71.5 million tonnes by 2030. It’s also predicted that the top five global markets for convenience food (China, USA, Japan, Mexico and Russia) will remain relatively unchanged up to 2030, with the most revenue in 2019 generated by the North America region.
A new report from Greenpeace International set out to analyse articles in peer-reviewed, scientific journals to look at what exactly the research has to say about plastic food packaging and food contact plastics.
Here’s what we found.
Our review of 24 recent articles highlights a consistent picture that regulators, businesses and
consumers should be concerned about: when food is packaged in plastic and then microwaved, this significantly increases the risk of both microplastic and chemical release, and that these microplastics and chemicals will leach into the food inside the packaging.
And not just some, but a lot of microplastics and chemicals.
When polystyrene and polypropylene containers filled with water were microwaved after being stored in the fridge or freezer, one study found they released anywhere between 100,000-260,000 microplastic particles, and another found that five minutes of microwave heating could release between 326,000-534,000 particles into food.
Similarly there are a wide range of chemicals that can be and are released when plastic is heated. Across different plastic types, there are estimated to be around 16,000 different chemicals that can either be used or present in plastics, and of these around 4,200 are identified as being hazardous, whilst many others lack any form of identification (hazardous or otherwise) at all.
The research also showed that 1,396 food contact plastic chemicals have been found in humans, several of which are known to be hazardous to human health. At the same time, there are many chemicals for which no research into the long-term effects on human health exists.
Ultimately, we are left with evidence pointing towards increased release of microplastics and plastic chemicals into food from heating, the regular migration of microplastics and chemicals into food, and concerns around what long-term impacts these substances have on human health, which range from uncertain to identified harm.
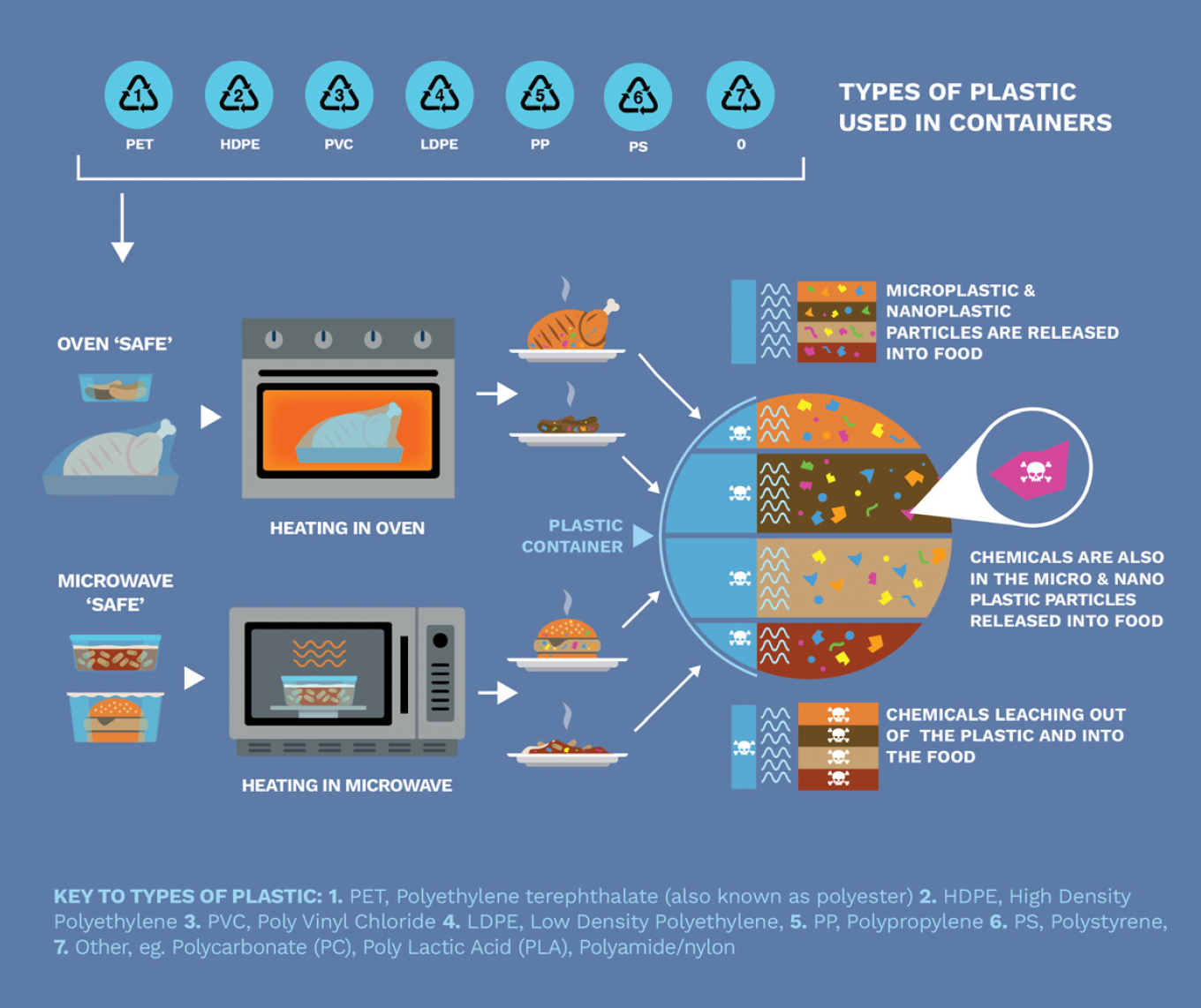
The known unknowns of plastic chemicals and microplastics
The problem here (aside from the fact that plastic chemicals are routinely migrating into our food), is that often we don’t have any clear research or information on what long-term impacts these chemicals have on human health. This is true of both the chemicals deliberately used in plastic production (some of which are absolutely toxic, like antimony which is used to make PET plastic), as well as in what’s called non-intentionally added substances (NIAS).
NIAS refers to chemicals which have been found in plastic, and typically originate as impurities, reaction by-products, or can even form later when meals are heated. One study found that a UV stabiliser plastic additive reacted with potato starch when microwaved to create a previously unknown chemical compound.
We’ve been here before: lessons from tobacco, asbestos and lead
Although none of this sounds particularly great, this is not without precedence. Between what we do and don’t know, waiting for perfect evidence is costly both economically and in terms of human health. With tobacco, asbestos, and lead, a similar story to what we’re seeing now has played out before. After initial evidence suggesting problems and toxicity, lobbyists from these industries pushed back to sow doubt about the scientific validity of the findings, delaying meaningful action. And all the while, between 1950-2000, tobacco alone led to the deaths of around 60 million people. Whilst distinguishing between correlation and causation, and finding proper evidence is certainly important, it’s also important to take preventative action early, rather than wait for more people to be hurt in order to definitively prove the point.
Where to from here?
This is where adopting the precautionary principle comes in. This means shifting the burden of proof away from consumers and everyone else to prove that a product is definitely harmful (e.g. it’s definitely this particular plastic that caused this particular problem), and onto the manufacturer to prove that their product is definitely safe. This is not a new idea, and plenty of examples of this exist already, such as the EU’s REACH regulation, which is centred around the idea of “no data, no market” – manufacturers are obligated to provide data demonstrating the safety of their product in order to be sold.

Greenpeace analysis of 24 articles in peer-reviewed scientific journals found that the plastics we use to package our food are directly risking our health.
Heating food in plastic packaging dramatically increases the levels of microplastics and chemicals that leach into our food.
But as it stands currently, the precautionary principle isn’t applied to plastics. For REACH in particular, plastics are assessed on a risk-based approach, which means that, as the plastic industry itself has pointed out, something can be identified as being extremely hazardous, but is still allowed to be used in production if the leached chemical stays below “safe” levels, despite that for some chemicals a “safe” low dose is either undefined, unknown, or doesn’t exist.
A better path forward
Governments aren’t acting fast enough to reduce our exposure and protect our health. There’s no shortage of things we can do to improve this situation. The most critical one is to make and consume less plastic. This is a global problem that requires a strong Global Plastics Treaty that reduces global plastic production by at least 75% by 2040 and eliminates harmful plastics and chemicals. And it’s time that corporations take this growing threat to their customers’ health seriously, starting with their food packaging and food contact products. Here are a number of specific actions policymakers and companies can take, and helpful hints for consumers.
Policymakers & companies
- Implement the precautionary principle:
- For policymakers – Stop the use of hazardous plastics and chemicals, on the basis of their intrinsic risk, rather than an assessment of “safe” levels of exposure.
- For companies – Commit to ensure that there is a “zero release” of microplastics and hazardous chemicals from packaging into food, alongside an Action Plan with milestones to achieve this by 2035
- Stop giving false assurances to consumers about “microwave safe” containers
- Stop the use of single-use and plastic packaging, and implement policies and incentives to foster the uptake of reuse systems and non-toxic packaging alternatives.
Consumers
- Encourage your local supermarkets and shops to shift away from plastic where possible
- Avoid using plastic containers when heating/reheating food
- Use non-plastic refill containers
Trying to dodge plastic can be exhausting. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, you’re not alone. We can only do so much in this broken plastic-obsessed system. Plastic producers and polluters need to be held accountable, and governments need to act faster to protect the health of people and the planet. We urgently need global governments to accelerate a justice-centred transition to a healthier, reuse-based, zero-waste future. Ensure your government doesn’t waste this once-in-a-generation opportunity to end the age of plastic.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits