Welcome to Carbon Brief’s DeBriefed.
An essential guide to the week’s key developments relating to climate change.
This week
Deadly Texas floods
EXTREME FLOODING: At least 120 people died and 173 remain missing one week after flash floods in Texas, NBC News reported. The floods were “one of the deadliest weather events in recent American history”, the New York Times said. The newspaper said it is “too early to say with certainty” the role of climate change, but this type of extreme rainfall is “precisely the kind of phenomenon that scientists say is becoming more common because of global warming”.
STORM CONDITIONS: Bloomberg noted that drought, the “abnormally hot Gulf of Mexico” and other factors fuelled the “storm that spawned the floods” in Kerr county. Climate scientists told Inside Climate News that the “torrential downpours on 4 July exemplify the devastating outcomes of weather intensified by a warming atmosphere”.
CUTS QUESTIONED: The Guardian reported on a warning from experts that such floods could become the “new normal” as “Donald Trump and his allies dismantle crucial federal agencies that help states prepare and respond to extreme weather and other hazards”. E&E News reported that “forecasts and warnings largely worked during the catastrophe in Texas”, but that “those systems are expected to degrade as Trump’s cuts take hold”.
HIMALAYAN FLOODS: Elsewhere, heavy rainfall “battered” two Himalayan states in India, “leading to widespread damage, disruption and loss of life”, India Today reported. Pakistan’s Dawn newspaper reported that “record high summer temperatures” have “accelerated the melting of glaciers”, leading to deadly flooding in some parts of the country.
Europe heat deaths
RAGING HEAT: Around 1,500 of the 2,300 heat deaths during the heatwave that “seared Europe at the end of June” can be attributed to climate change, according to World Weather Attribution analysis covered by the Guardian. The newspaper said that Milan was the “hardest-hit city” and that 88% of the “climate-driven deaths” were in people aged over 65.
MORE EXTREMES: Extreme heat continued to affect much of Europe this week. In Catalonia, Spain, more than 18,000 people were ordered to remain indoors as a “wildfire raged out of control, consuming almost 3,000 hectares of vegetation”, Reuters said. Marseille airport closed as a major wildfire encroached on the southern French city, Le Monde reported.
‘CLIMATE DELAYERS’: Meanwhile, a “far-right” political group successfully outbid other groups to lead negotiations for the EU’s next climate target on behalf of the European parliament, according to Politico. This role for the Patriots for Europe group “give[s] the far right unprecedented influence” over the 2040 target, the outlet said, adding that it “strongly opposes the EU’s climate policies”. An early attempt to curb the bloc’s influence failed, Reuters said.
Around the world
- LIBYAN OIL: BP and Shell have “signed agreements to assess new opportunities in Libya”, the Financial Times reported, joining several oil majors resuming exploration following the country’s civil war.
- SOLAR POWER: Trump issued an executive order targeting “unaffordable and unreliable ‘green’ energy sources”, reported Inside Climate News. But the outlet said it is unclear whether this will “have much of an effect”.
- CLIMATE MOTION: The UN Human Rights Council passed a motion on climate change and human rights – but only after the Marshall Islands withdrew a “divisive amendment” calling on states to recommit to a fossil fuel phase-out, Reuters said.
- BELÉM INCOMING: Meanwhile, the president of COP30 told Climate Home News that countries “already decided” to transition away from fossil fuels and climate negotiations can now focus on a “timeline or rules for how this transition will be made”.
- LAW: The International Court of Justice will issue a major opinion on the legal obligation of countries to address climate change on 23 July, reported Reuters. Although it is nonbinding, experts told the newswire that it “could set a precedent in climate change-driven lawsuits” around the world.
74%
The percentage of global wind and solar projects under construction that are located in China, according to a Global Energy Monitor report.
Latest climate research
- Annual meltwater from the Greenland ice sheet “significantly increased” in the past three decades | Nature Climate Change
- The wealthier and more democratic a nation, the less their citizens engage in climate activism | Journal of Environmental Psychology
- Climate change has “played an important role” in genetic and demographic changes in Tibetan macaques | Science Advances
(For more, see Carbon Brief’s in-depth daily summaries of the top climate news stories on Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday.)
Captured
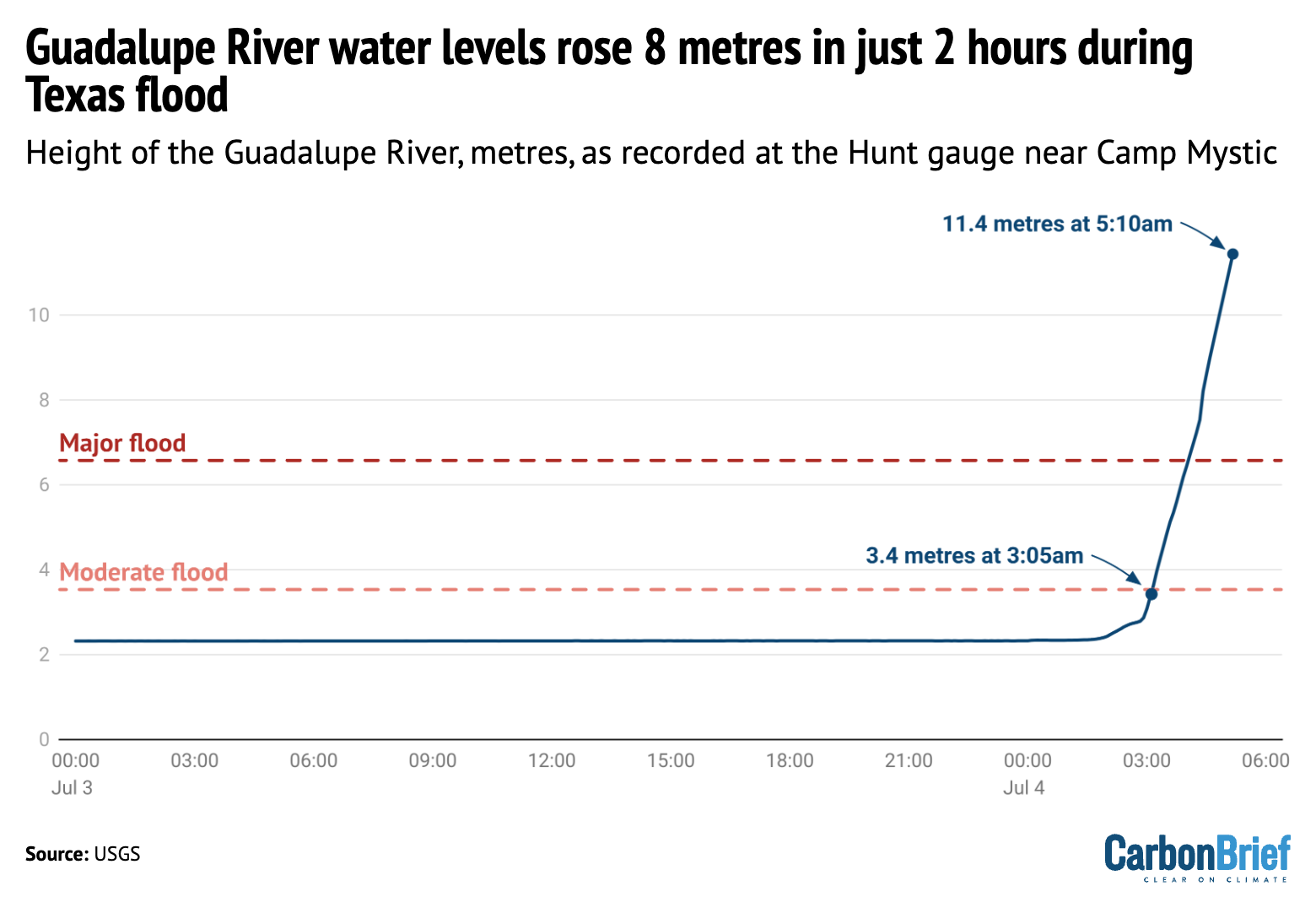
Water levels soared by more than eight metres in just over two hours on the Guadalupe River within an area known as “flash flood alley” in Texas on 4 July. The resulting floods caused devastation for people in nearby homes and summer camps. Satellite imagery in NBC News showed the scale of the impact. Carbon Brief examined the potential role of climate change in the flood and how it was covered by global media.
Spotlight
Ireland exits coal
This week, Carbon Brief looks at the significance of Ireland becoming the latest European country to end coal-powered electricity.
Ireland has joined the UK and a slew of other nations in burning its last lump of coal – the most polluting fossil fuel – to generate electricity.
Coal use ceased on 20 June at Moneypoint, the country’s last coal-burning power station, in line with a 2019 government pledge.
Spain and Italy are expected to become the next European countries to leave behind coal power, according to Beyond Fossil Fuels.
Ireland’s move offers an important “signal” for the country’s energy transition, said Margie McCarthy, the director of research and policy insights at the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI). She told Carbon Brief:
“We’ve put in place a lot of really ambitious legislation and climate action plans, but we are still more than 80% reliant on fossil fuels across all of our energy demands…Coal is a particularly carbon-intensive fossil fuel, so any movement away from that is a good step forward.”
Coal controversies
Gas (42.1% in 2024) and renewables (39.6%) generate the vast majority of Ireland’s electricity. Coal, despite its overall decline, experienced a mini-comeback in 2021 and 2022 – broadly in line with EU trends when gas prices soared as Russia restricted supplies and countries later dropped Russian fossil fuels following the country’s invasion of Ukraine.
The share of Ireland’s electricity coming from coal increased from 4% in 2020 to 14% in 2021. This fluctuated again in recent years, dropping to 4.6% in May 2025.

The ESB, the state-owned energy company that runs Moneypoint, was criticised in 2022 for resuming shipments from a controversial Colombian mine as an alternative to Russian coal. The company had stopped buying coal from the Cerrejón mine in 2018.
Cerrejón is “Latin America’s largest open-pit coal mine” – six times the size of Manchester, a recent article from the Bureau of Investigative Journalism said. Ireland’s national broadcaster RTÉ reported in 2024:
“According to local communities, lawyers’ organisations and court rulings, in its four decades of operation it has driven an environmental crisis that has destroyed the health, lives and culture of many thousands of Indigenous people.”
An ESB spokesperson told Carbon Brief that it sourced a “limited amount of coal from Cerrejón between April 2022 and August 2023”.
Next steps
Now that coal use has wound down, Moneypoint will remain available to generate electricity using oil on a back-up basis until 2029.
The ESB “expects low levels of running of the plant going forward”, a spokesperson said.
The company plans to turn Moneypoint into a “green energy hub”, with a major offshore windfarm, a wind turbine construction hub and a green hydrogen facility on site.
Looking at Ireland’s ongoing energy transition, McCarthy said that, although gas still plays a “significant” role, increases in wind, solar and electricity interconnection are “good signals to move in the right direction”. She added:
“We just need to keep the pace going. We need to accelerate quicker…and that we make sure we’re managing demand while we are trying to accelerate that pace.”
Data centre dilemma
A major cause of Ireland’s growing electricity demand is data centres, which consumed more than one-fifth of the country’s electricity supplies in 2024 – more than all urban households.
Ireland has become an “EU pioneer of data centres” thanks to “its low taxes, temperate climate and fibre cable access to the US and Europe”, according to the Financial Times.
McCarthy highlighted the importance of ensuring that “data centre demand is not undoing the renewable energy share, or the final energy consumption reductions that are required as part of our targets and obligations”. She added:
“It’s very fair to say that the efficiency measures in data centres have been significant…But the issue is that the demand is outpacing any efficiency measures that are being introduced.”
Watch, read, listen
OIL TO LITHIUM: A Climate Home News article looked at the challenges facing Nigeria’s efforts to “supply refined lithium to the electric vehicle battery industry”.
PODCAST CHAT: The Rest is Politics podcast spoke to the UK Climate Change Committee chief executive, Emma Pinchbeck, about net-zero and the energy transition.
BRRR: A BBC News “in depth” article explored the growing “battle” for control over the Arctic, along with the security challenges from climate change and other issues in “one of the world’s coldest places”.
Coming up
- 7-25 July: 30th session of the International Seabed Authority (part II), Kingston, Jamaica
- 14-23 July: UN high-level political forum on sustainable development, New York
- 17 July: UN General Assembly third informal dialogue on the Pact for the Future, New York
- 14-18 July:20th ordinary session of the African ministerial conference on the environment, Nairobi, Kenya
Pick of the jobs
- New Scientist, environment news reporter | Salary: £40,000-£50,000 (pro rata). Location: London
- Environmental Defense Fund, senior analyst, mission finance | Salary: €56,000-£61,000. Location: Belgium, the Netherlands or UK
- Daily Telegraph, environment editor | Salary: Unknown. Location: London
- United Nations Human Settlements Programme, junior nature-based solutions and climate consultant | Salary: Unknown. Location: Kenya
- Brookline.News, freelance environmental reporter | Salary: Unknown. Location: Massachusetts, US
DeBriefed is edited by Daisy Dunne. Please send any tips or feedback to debriefed@carbonbrief.org.
This is an online version of Carbon Brief’s weekly DeBriefed email newsletter. Subscribe for free here.
The post DeBriefed 11 July 2025: Texas floods; Global warming ‘tripled’ Europe heat deaths; Ireland exits coal appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Climate Change
A Tiny Caribbean Island Sued the Netherlands Over Climate Change, and Won
The case shows that climate change is a fundamental human rights violation—and the victory of Bonaire, a Dutch territory, could open the door for similar lawsuits globally.
From our collaborating partner Living on Earth, public radio’s environmental news magazine, an interview by Paloma Beltran with Greenpeace Netherlands campaigner Eefje de Kroon.
A Tiny Caribbean Island Sued the Netherlands Over Climate Change, and Won
Climate Change
Greenpeace organisations to appeal USD $345 million court judgment in Energy Transfer’s intimidation lawsuit
SYDNEY, Saturday 28 February 2026 — Greenpeace International and Greenpeace organisations in the US announce they will seek a new trial and, if necessary, appeal the decision with the North Dakota Supreme Court following a North Dakota District Court judgment today awarding Energy Transfer (ET) USD $345 million.

ET’s SLAPP suit remains a blatant attempt to silence free speech, erase Indigenous leadership of the Standing Rock movement, and punish solidarity with peaceful resistance to the Dakota Access Pipeline. Greenpeace International will also continue to seek damages for ET’s bullying lawsuits under EU anti-SLAPP legislation in the Netherlands.
Mads Christensen, Greenpeace International Executive Director said: “Energy Transfer’s attempts to silence us are failing. Greenpeace International will continue to resist intimidation tactics. We will not be silenced. We will only get louder, joining our voices to those of our allies all around the world against the corporate polluters and billionaire oligarchs who prioritise profits over people and the planet.
“With hard-won freedoms under threat and the climate crisis accelerating, the stakes of this legal fight couldn’t be higher. Through appeals in the US and Greenpeace International’s groundbreaking anti-SLAPP case in the Netherlands, we are exploring every option to hold Energy Transfer accountable for multiple abusive lawsuits and show all power-hungry bullies that their attacks will only result in a stronger people-powered movement.”
The Court’s final judgment today rejects some of the jury verdict delivered in March 2025, but still awards hundreds of millions of dollars to ET without a sound basis in law. The Greenpeace defendants will continue to press their arguments that the US Constitution does not allow liability here, that ET did not present evidence to support its claims, that the Court admitted inflammatory and irrelevant evidence at trial and excluded other evidence supporting the defense, and that the jury pool in Mandan could not be impartial.[1][2]
ET’s back-to-back lawsuits against Greenpeace International and the US organisations Greenpeace USA (Greenpeace Inc.) and Greenpeace Fund are clear-cut examples of SLAPPs — lawsuits attempting to bury nonprofits and activists in legal fees, push them towards bankruptcy and ultimately silence dissent.[3] Greenpeace International, which is based in the Netherlands, is pursuing justice in Europe, with a suit against ET under Dutch law and the European Union’s new anti-SLAPP directive, a landmark test of the new legislation which could help set a powerful precedent against corporate bullying.[4]
Kate Smolski, Program Director at Greenpeace Australia Pacific, said: “This is part of a worrying trend globally: fossil fuel corporations are increasingly using litigation to attack and silence ordinary people and groups using the law to challenge their polluting operations — and we’re not immune to these tactics here in Australia.
“Rulings like this have a chilling effect on democracy and public interest litigation — we must unite against these silencing tactics as bad for Australians and bad for our democracy. Our movement is stronger than any corporate bully, and grows even stronger when under attack.”
Energy Transfer’s SLAPPs are part of a wave of abusive lawsuits filed by Big Oil companies like Shell, Total, and ENI against Greenpeace entities in recent years.[3] A couple of these cases have been successfully stopped in their tracks. This includes Greenpeace France successfully defeating TotalEnergies’ SLAPP on 28 March 2024, and Greenpeace UK and Greenpeace International forcing Shell to back down from its SLAPP on 10 December 2024.
-ENDS-
Images available in Greenpeace Media Library
Notes:
[1] The judgment entered by North Dakota District Court Judge Gion follows a jury verdict finding Greenpeace entities liable for more than US$660 million on March 19, 2025. Judge Gion subsequently threw out several items from the jury’s verdict, reducing the total damages to approximately US$345 million.
[2] Public statements from the independent Trial Monitoring Committee
[3] Energy Transfer’s first lawsuit was filed in federal court in 2017 under the RICO Act – the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act, a US federal statute designed to prosecute mob activity. The case was dismissed in 2019, with the judge stating the evidence fell “far short” of what was needed to establish a RICO enterprise. The federal court did not decide on Energy Transfer’s claims based on state law, so Energy Transfer promptly filed a new case in a North Dakota state court with these and other state law claims.
[4] Greenpeace International sent a Notice of Liability to Energy Transfer on 23 July 2024, informing the pipeline giant of Greenpeace International’s intention to bring an anti-SLAPP lawsuit against the company in a Dutch Court. After Energy Transfer declined to accept liability on multiple occasions (September 2024, December 2024), Greenpeace International initiated the first test of the European Union’s anti-SLAPP Directive on 11 February 2025 by filing a lawsuit in Dutch court against Energy Transfer. The case was officially registered in the docket of the Court of Amsterdam on 2 July, 2025. Greenpeace International seeks to recover all damages and costs it has suffered as a result of Energy Transfers’s back-to-back, abusive lawsuits demanding hundreds of millions of dollars from Greenpeace International and the Greenpeace organisations in the US. The next hearing in the Court of Amsterdam is scheduled for 16 April, 2026.
Media contact:
Kate O’Callaghan on 0406 231 892 or kate.ocallaghan@greenpeace.org
Climate Change
Former EPA Staff Detail Expanding Pollution Risks Under Trump
The Trump administration’s relentless rollback of public health and environmental protections has allowed widespread toxic exposures to flourish, warn experts who helped implement safeguards now under assault.
In a new report that outlines a dozen high-risk pollutants given new life thanks to weakened, delayed or rescinded regulations, the Environmental Protection Network, a nonprofit, nonpartisan group of hundreds of former Environmental Protection Agency staff, warns that the EPA under President Donald Trump has abandoned the agency’s core mission of protecting people and the environment from preventable toxic exposures.
Former EPA Staff Detail Expanding Pollution Risks Under Trump
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits