Carbon Footprint
Microsoft (MSFT) Signs Solar Deal with Zelestra to Power Data Centers in Spain, Supporting Community Projects
Microsoft (MSFT) has signed a long-term Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with Zelestra for 95.7 MWAC of solar power. The energy will come from two new solar farms in Aragón, Spain — Escatrón II and Fuendetodos II, both under construction. This clean energy will help power Microsoft’s data centers and operations in the region. It also supports Microsoft’s wider climate goals.
A Solar Deal That Shines Beyond Power
Beyond simply buying solar power, Microsoft is tying this deal to benefits for the local community. The non-profit ECODES will run a “Community Fund” financed by this PPA. ECODES plans to use this fund to support sustainability projects in Aragón. They will invest in local infrastructure, social inclusion, and environmental education.
Zelestra calls its strategy “3 Es”: Education, Energy, and Environment. Microsoft sees this as part of its “Datacenter Community Pledge,” which aims to ensure its operations help local areas as well as reduce its carbon footprint.
Why Microsoft’s 95.7 MW Bet Matters
This solar agreement matters for several reasons:
- Reliable clean energy: The 95.7 MW solar supply gives Microsoft a stable source of renewable power.
- Social benefits: ECODES will channel money into projects that help local people and ecosystems.
- Long-term local commitment: Zelestra intends to stay in Aragón and work with communities for years.
This structure shows how a big company can use a clean energy deal not just for itself, but for shared community value.
Spain’s Solar Boom and Zelestra’s Expanding Footprint
Solar power in Spain is booming. In the last few years, the country has added thousands of megawatts of solar capacity. According to Informa’s DBK report, solar energy grew by 6,000 MW in just one year, reaching 32,350 MW by 2024.
Red Eléctrica (the Spanish grid operator) data shows that by early 2025, solar PV installed capacity passed 32,000 MW, making solar the largest source of power capacity in Spain.
This growth reflects a major shift in Spain’s energy mix. In 2024, solar PV generated a record 44,520 GWh of electricity, about 17% of the country’s total electricity output.
At the same time, renewables now make up around 66% of Spain’s total power generation capacity. These numbers show how central solar power has become to Spain’s energy transition.
The outlook is even more ambitious. According to GlobalData, Spain’s solar capacity could reach 152.8 GW by 2035, driven by strong policy support and growing investor confidence. To fuel this, many new projects are already in the permitting stage.

In 2025 alone, more than 5 GW of solar projects were submitted for environmental approval. Castilla‑La Mancha is a major one of those major regions, and it stands out in Zelestra’s portfolio.
Zelestra is a major player in this growth. In 2025, it secured €146.6 million to build six solar plants in Castilla‑La Mancha, totaling 237 MWdc. These projects will create jobs, generate around 467 GWh of clean energy per year, and avoid over 84,000 tons of CO₂ emissions annually.
Zelestra is also expanding its corporate partnerships, providing renewable electricity for companies like Microsoft and Graphic Packaging International. Its portfolio in Spain exceeds 6 GW, showing its strong commitment to the country’s clean energy transition and its role as a key developer of large-scale solar projects.
Inside Microsoft’s Push Toward Carbon Negativity
Microsoft has set strong climate goals. In 2020, it announced its plans to be carbon negative by 2030. That means by then, it wants to remove more carbon from the atmosphere than it emits.
To reach this, the tech giant is doing several things:
- It has contracted 34 GW of new renewable energy across 24 countries.
- It aims to match 100% of its electricity use with zero‑carbon power by 2025.
- It invests in carbon removal. In fiscal year 2024, Microsoft signed contracts for nearly 22 million metric tons of carbon removal.
- It uses a $1 billion Climate Innovation Fund to support new technologies.
Progress and Challenges in Emissions
Microsoft has made real progress, but it also faces big challenges. Its Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions (those from its own operations and electricity use) dropped 29.9% compared to 2020.

But its total emissions (including its supply chain, or “Scope 3”) rose by 23–26% since 2020. This increase comes mainly from its rapid growth in data centers and cloud services.
Because it makes a lot of servers, chips, and hardware, Microsoft’s construction and supply chain also generate emissions. To cut those, it is working with its suppliers. By 2030, Microsoft plans to require high-volume suppliers to use 100% carbon‑free electricity.
Microsoft’s clean energy capacity has grown steadily since 2013, starting with wind projects in the U.S. By 2022, capacity reached 900 MW with wind and solar projects in Europe and the U.S.

In 2024, Microsoft signed the largest corporate clean energy deal for 10.5 GW with Brookfield Renewable, delivering by 2030. This reflects Microsoft’s goal to power all operations with 100% renewable energy by 2030, underscoring its leadership in global sustainability efforts.
Carbon Removal and Long-Term Risks
Microsoft is not just cutting emissions, it is also removing carbon. It invests in two big types of removal:
- Nature-based removal: Microsoft has a deal with Chestnut Carbon to buy over 7 million tons of forest-based carbon credits.
- Advanced removal: Microsoft supports projects like bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS). It recently backed a project in Louisiana that could capture 6.75 million tons of CO₂ over 15 years.
Still, some experts warn that Microsoft’s climate strategy lacks targets beyond 2030. That could challenge its long-term impact.
SEE MORE on Microsoft:
- Microsoft (MSFT Stock) Emissions Up 23%, Invests in Waste-to-Energy Project to Capture 3 Million Tons of CO₂
- Microsoft (MSFT Stock) Tops Q2 2025 Record-Breaking Surge in Durable Carbon Removal Credit Purchases
- Microsoft Leads on Climate: $800M CIF Drives Clean Tech and AI Energy Deals with ADNOC, Masdar, and XRG
How the Solar Deal Fits into Microsoft’s Strategy?
The 95.7 MW deal in Spain ties directly into Microsoft’s overall carbon-negative goal. Here’s how it fits:
- It adds zero-carbon electricity to Microsoft’s grid mix.
- It supports Microsoft’s plan to match all its power use with clean energy.
- The deal’s community fund reinforces Microsoft’s aim to pair climate action with social value.
- It strengthens Microsoft’s global clean energy portfolio.
This helps Microsoft reduce its operational emissions (Scope 1 & 2) and supports its broader mission to remove carbon.
What’s Next for Microsoft, Zelestra, and Local Communities?
If all goes well, the two solar farms in Aragón will come online and deliver power to Microsoft for many years. The ECODES fund should start giving out grants to local groups, helping build greener projects in the community.
The tech giant must also keep pushing its carbon removal work and supplier engagement. It needs to make sure its long-term investments bring real, measurable climate impact.
Zelestra, for its part, will prove whether it can deliver reliable solar and meaningful social impact. If the model works, more companies may use similar “clean energy + community” contracts.
The agreement is more than just about cutting emissions — it’s also about helping local communities. At the same time, Microsoft’s push to be carbon negative by 2030 is ambitious and complex. It involves clean power, carbon removal, and changes in its entire supply chain.
This Spanish solar deal adds a new piece to Microsoft’s climate puzzle. It strengthens its clean energy supply and shows how corporate climate goals can benefit more than just the bottom line.
The post Microsoft (MSFT) Signs Solar Deal with Zelestra to Power Data Centers in Spain, Supporting Community Projects appeared first on Carbon Credits.
Carbon Footprint
Legal challenges in carbon offsetting: What recent lawsuits teach us
Over the past two years, the world of carbon offsetting has entered a new era—one defined by legal scrutiny, public demand for accuracy, and a deeper understanding of how complex carbon accounting truly is. This shift reflects a growing expectation that environmental claims must be both scientifically credible and communicated with absolute precision.
![]()
Carbon Footprint
Constellation Secures $1B DOE Loan to Restart Crane Clean Energy Center and Boost America’s Nuclear Energy Future
U.S. Secretary of Energy Chris Wright announced on November 18 that the Department of Energy’s Loan Programs Office has finalized a $1 billion loan to help lower energy costs and restart a Pennsylvania nuclear power plant. The funding will support Constellation Energy Generation, LLC in financing the Crane Clean Energy Center, an 835 MW facility located on the Susquehanna River in Londonderry Township, Pennsylvania. This loan marks a major step toward restoring reliable, carbon-free power to the region.
Energy Secretary Wright highlighted further,
“Thanks to President Trump’s bold leadership and the Working Families Tax Cut, the United States is taking unprecedented steps to lower energy costs and bring about the next American nuclear renaissance. Constellation’s restart of a nuclear power plant in Pennsylvania will provide affordable, reliable, and secure energy to Americans across the Mid-Atlantic region. It will also help ensure America has the energy it needs to grow its domestic manufacturing base and win the AI race.”
Constellation (Nasdaq: CEG) is the first company to receive a simultaneous conditional loan commitment and financial close from the DOE Loan Programs Office. Its strong finances and credit rating allowed the process to move quickly. The loan, provided through the Energy Dominance Financing Program, will lower financing costs and attract private investment to restart the plant. In addition, DOE noted the project will help the U.S. stay competitive in the global AI and digital economy, which is driving higher electricity demand.
Crane Clean Energy Center: Returning 835 MW of Carbon-Free Power
The Crane Clean Energy Center is an 835-megawatt nuclear plant on the Susquehanna River. Previously known as Three Mile Island Unit 1, it has a long and historic legacy. In March 1979, Three Mile Island Unit 2 suffered a partial meltdown and has remained in monitored storage ever since. Unit 1, however, continued operating safely for four decades before being shut down in September 2019 due to market conditions rather than safety concerns.
In September 2024, Constellation signed a 20-year power purchase agreement with Microsoft, which allows the tech giant to buy the carbon-free electricity generated by the restarted plant. Following the agreement, Constellation rebranded the facility as the Crane Clean Energy Center. As said before, once operational, the plant will provide 835 MW of nuclear energy.
DOE Loan Accelerates the Restart
Constellation (Nasdaq: CEG) is the first company to receive a simultaneous conditional loan commitment and financial close from the DOE Loan Programs Office. Its strong finances and credit rating allowed the process to move quickly. The loan, provided through the Energy Dominance Financing Program, will lower financing costs and attract private investment to restart the plant. In addition, DOE noted the project will help the U.S. stay competitive in the global AI and digital economy, which is driving higher electricity demand.
DOE stated that the Crane loan aligns with President Trump’s Executive Order on Reinvigorating the Nuclear Industrial Base. The project is the first under this administration to receive a simultaneous conditional commitment and financial close.
Because the reactor was never fully decommissioned, restarting it is faster and more cost-effective than building a new plant. The loan will fund equipment inspections, system upgrades, workforce training, and regulatory compliance. Once approved by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, the plant will supply enough electricity to power about 800,000 homes across the PJM Interconnection region. It will help lower electricity costs, strengthen grid reliability, and create hundreds of jobs.

READ MORE:
- Constellation Secures Groundbreaking $1 Billion Clean Nuclear Energy Deal with Federal Government
- Constellation and Calpine’s $16.4B Deal Boosts U.S. Clean Energy Transition
Pennsylvania Leads in Clean Energy and AI Power
Senator Dave McCormick praised the DOE loan, saying Pennsylvania is leading the nation in energy independence and AI innovation. He highlighted that the restart will deliver more than 800 MW of carbon-free electricity and create 3,400 direct and indirect jobs.
McCormick also noted Constellation’s ongoing investments across the state, including commitments announced at the Pennsylvania Energy and Innovation Summit. The restart comes amid unprecedented electricity demand from AI, cloud computing, and expanding data centers.
A Goldman Sachs report predicts that AI could increase data-center power demand by 160 percent. AI queries, like those used by tools such as ChatGPT, require nearly ten times more electricity than a standard Google search. Nuclear power is vital to meet this growing demand reliably.

Extending Nuclear Plant Life: Constellation’s Strategy for Reliable Power
Constellation has invested in local communities by committing over $1 million in charitable contributions over five years. In 2025 alone, the company donated $200,000 to support nonprofits, workforce programs, and local initiatives.
Significantly, restarting Crane is part of Constellation’s larger multi-billion-dollar plan to extend the life of America’s nuclear fleet, increase output, and ensure reliable power for decades.
The Crane Clean Energy Center is expected to deliver significant economic benefits to Pennsylvania. An analysis by the Pennsylvania Building and Construction Trades Council projected that the restart would create thousands of direct and indirect jobs. It could add more than $16 billion to the state’s GDP and generate over $3 billion in state and federal tax revenue.
The plant is already more than 80 percent staffed, with over 500 employees, including engineers, mechanics, technicians, and licensed operators. Regulatory reviews and technical inspections remain on schedule.
Joe Dominguez, president and CEO of Constellation, said:
“DOE’s quick action and leadership is another huge step towards bringing hundreds of megawatts of reliable nuclear power onto the grid at this critical moment. Under the Trump administration, the FERC and DOE have made it possible for us to vastly expedite this restart without compromising quality or safety. It’s a great example of how America first energy policies create jobs, growth and opportunities and make the grid more reliable. Utilities and grid operators are moving too slowly and need to make regulatory changes that will allow our nation to unlock its abundant energy potential. Constellation and nuclear energy are helping to lead the way and we are thankful to President Trump and Secretary Wright for putting the ‘energy’ back into DOE.”
Nuclear Power for America’s Clean Energy Future
The surge in AI, electrification, and cloud computing has made nuclear energy more critical than ever. Small modular reactors and advanced technologies are gaining interest from utilities and data-center developers.
The U.S. produces about 30 percent of the world’s nuclear electricity. Ninety-four reactors supply steady, clean power to millions of homes and industries nationwide. According to the World Nuclear Association, U.S. reactors generated 779 terawatt-hours in 2023, accounting for 19 percent of the nation’s total electricity output.
The administration aims to quadruple U.S. nuclear capacity to 400 gigawatts by 2050. The International Energy Agency projects 35 GW of new capacity by 2035 and 200 GW by 2050, nearly triple current levels. Restarting Crane contributes to this goal while providing reliable baseload power, supporting AI and digital growth, and boosting the economy.
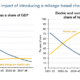
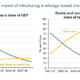
Electricity generation for data centres by fuel in the United States, Base Case, 2020-2035

The Crane Clean Energy Center restart is a key step toward clean, reliable energy. It shows how nuclear power can meet rising electricity needs, support innovation, and strengthen local economies.
The post Constellation Secures $1B DOE Loan to Restart Crane Clean Energy Center and Boost America’s Nuclear Energy Future appeared first on Carbon Credits.
-
Climate Change4 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Greenhouse Gases4 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits
-
Renewable Energy5 months ago
US Grid Strain, Possible Allete Sale