Australia’s oceans are heating at an alarming rate. In 2024, sea surface temperatures reached record highs, marking the hottest year on record for our surrounding waters.1 This isn’t just an abstract statistic—it’s a crisis unfolding beneath the waves, threatening marine life, coral reefs, and the livelihoods of those who depend on healthy oceans.
Why Are Our Oceans Heating Up?
The primary driver is human-induced climate change. The burning of fossil fuels—coal, oil, and gas—has led to a significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions, trapping heat in the atmosphere. The vast majority of this excess heat is absorbed by the ocean, causing surface temperatures to rise at an unprecedented rate.2
Rising sea surface temperatures contribute to phenomena such as marine heatwaves and coral bleaching. These disruptions are becoming more frequent and severe, pushing marine ecosystems past their limits.
Climate change is also disrupting ocean currents, which play a crucial role in regulating global temperatures. This could have serious implications for Australia and the Pacific, for example the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a key system regulating global temperatures, is slowing down due to climate change. If it worsened and collapsed, this could produce a La Niña-like pattern over eastern Australia—bringing more intense rainfall and flooding.3
Closer to home, the East Australian Current now extends further south, creating an area of more rapid warming in the Tasman Sea, where the warming rate is now twice the global average.4
What Happens When the Ocean Gets Too Hot?
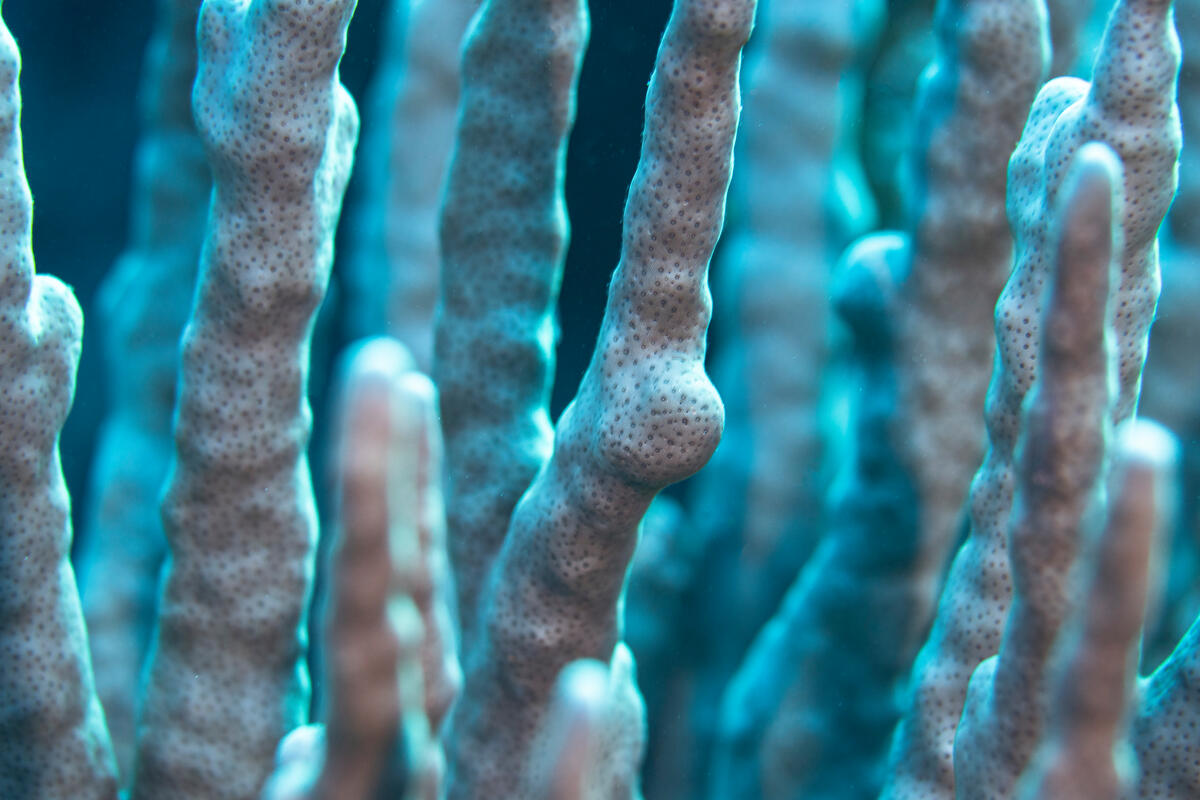
1. Coral Bleaching and Reef Degradation
Australia’s Great Barrier Reef has experienced widespread coral bleaching events in recent years. Coral bleaching occurs when corals, stressed by elevated sea temperatures, expel the symbiotic algae that provide them with energy and vibrant colours. Without these algae, corals can die, leading to the degradation of reef ecosystems that support a vast array of marine life.5
2. Marine Heatwaves and Mass Die-Offs
Marine heatwaves—periods of abnormally high sea temperatures—have become more frequent and intense. A recent marine heatwave off the coast of Western Australia caused the deaths of approximately 30,000 fish, an event scientists have linked directly to climate change. The extreme temperatures depleted oxygen levels and disrupted marine food chains, leaving fish and other marine life struggling to survive. Research indicates that such events are now up to 100 times more likely due to climate change.6
3. Disruption of Marine Ecosystems
Warmer oceans can alter the distribution and abundance of marine species. Many fish and other marine organisms are shifting their ranges toward cooler waters, disrupting existing ecosystems and affecting fisheries. Others that can’t migrate or adapt to changing temperatures are likely to die. These changes can have cascading effects throughout the food web, impacting species from the smallest plankton to the largest predators.4
4. Sea Level Rise and Coastal Impacts
As ocean temperatures rise, seawater expands, and melting polar ice contribute to sea level rise. Rising sea levels increase the risk of coastal flooding, erosion, and habitat loss, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.7 Pacific Island nations are already experiencing the severe effects of climate change: rising sea levels, extreme storms, tidal inundation, food and water insecurity, and displacement are becoming all too common. These impacts threaten not just physical survival, but the very culture and identity of Pacific communities.
The Solution: Protecting Our Oceans
To address these challenges, Greenpeace advocates for:
- Global Oceans Treaty: Protecting at least 30% of the world’s oceans by 2030 through a network of international marine sanctuaries can help safeguard biodiversity and allow ecosystems to recover.
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Transitioning away from fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources is crucial to mitigate climate change and its impacts on the oceans.
- Preventing Overfishing and Pollution: Implementing sustainable fishing practices and reducing pollution, including plastic waste, are essential steps to maintain healthy marine environments.
Australia is home to unique and diverse marine ecosystems, and we have a responsibility to protect them. The Global Ocean Treaty, agreed upon in 2023, provides a framework for creating ocean sanctuaries in international waters. We urge the Australian government to ratify this treaty and take bold action to protect our oceans.
We need urgent action from Environment Minister Tanya Plibersek and Foreign Minister Penny Wong to ratify the Global Ocean Treaty and protect critical marine habitats, including the South Tasman Sea and Lord Howe Rise.
Sign the petition now to demand ocean protection before it’s too late.
The ocean is our greatest ally in the fight against climate change. Often called the lungs of the Earth, the ocean produces around 50% of the planet’s oxygen, regulates global temperatures, and absorbs vast amounts of carbon dioxide. But with rising temperatures, acidification, and pollution, its ability to sustain life—both beneath the waves and above—is under serious threat. The time to act is now.
- https://theconversation.com/its-official-australias-ocean-surface-was-the-hottest-on-record-in-2024-249277
- https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/ocean-warming/
- https://theconversation.com/a-huge-atlantic-ocean-current-is-slowing-down-if-it-collapses-la-nina-could-become-the-norm-for-australia-184254
- https://www.csiro.au/en/research/environmental-impacts/climate-change/state-of-the-climate/oceans
- https://www.gbrmpa.gov.au/the-reef/reef-health/climate-change
- https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2025/feb/05/deaths-of-30000-fish-off-wa-coast-made-more-likely-by-climate-change-research-finds
Australia’s Oceans Just Hit Their Hottest Year on Record—Here’s Why That Matters
Climate Change
With Love: Living consciously in nature
I fell flat on my backside one afternoon this January and, weirdly, it made me think of you. Okay, I know that takes a bit of unpacking—so let me go back and start at the beginning.
For the last six years, our family has joined with half a dozen others to spend a week or so up at Wangat Lodge, located on a 50-acre subtropical rainforest property around three hours north of Sydney. The accommodation is pretty basic, with no wifi coverage—so time in Wangat really revolves around the bush. You live by the rhythm of the sun and the rain, with the days punctuated by swimming in the river and walking through the forest.
An intrinsic part of Wangat is Dan, the owner and custodian of the place, and the guide on our walks. He talks about time, place, and care with great enthusiasm, but always tenderly and never with sanctimony. “There is no such thing as ‘the same walk’”, is one of Dan’s refrains, because the way he sees it “every day, there is change in the world around you” of plants, animals, water and weather. Dan speaks of Wangat with such evident love, but not covetousness; it is a lightness which includes gentle consciousness that his own obligations arise only because of the historic dispossession of others. He inspires because of how he is.
One of the highlights this year was a river walk with Dan, during which we paddled or waded through most of the route, with only occasional scrambles up the bank. Sometimes the only sensible option is to swim. Among the life around us, we notice large numbers of tadpoles in the water, which is clean enough to drink. Our own tadpoles, the kids in the group, delight in the expedition. I overhear one of the youngest children declaring that she’s having ‘one of the best days ever’. Dan looks content. Part of his mission is to reintroduce children to nature, so that the soles of their feet may learn from the uneven ground, and their muscles from the cool of the water.
These moments are for thankfulness in the life that lives.
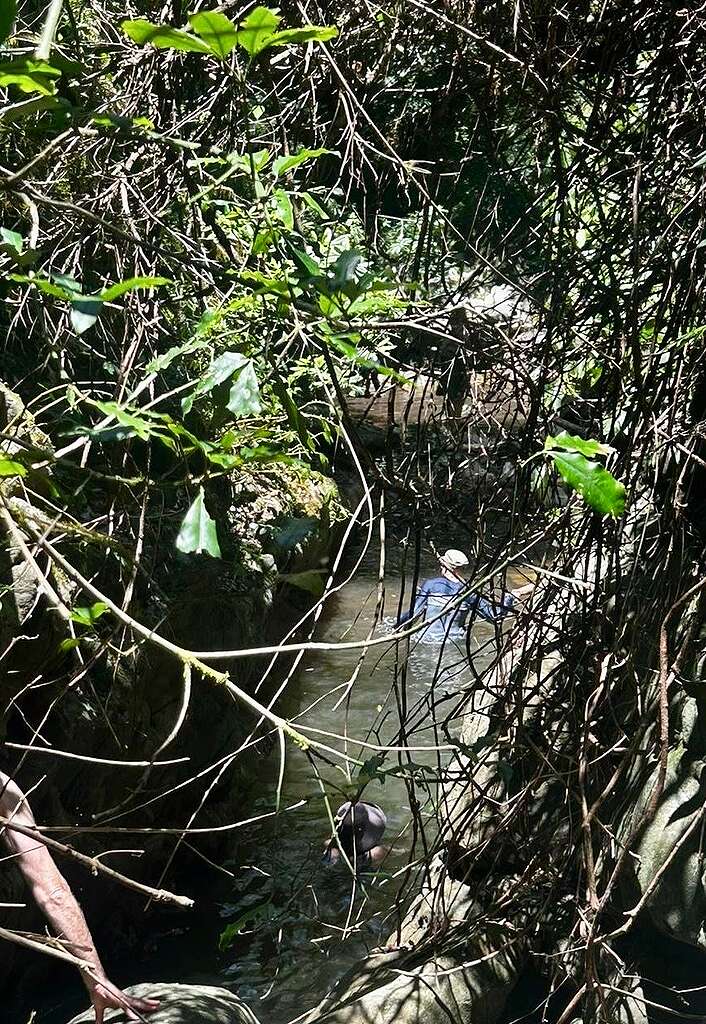

It is at the very end of the walk when I overbalance and fall on my arse—and am reminded of the eternal truth that rocks are hard. As I gingerly get up, my youngest daughter looks at me, caught between amusement and concern, and asks me if I’m okay.
I have to think before answering, because yes, physically I’m fine. But I feel too, an underlying sense of discomfort; it is that omnipresent pressure of existential awareness about the scale of suffering and ecological damage now at large in the world, made so much more immediately acute after Bondi; the dissonance that such horrors can somehow exist simultaneously with this small group being alive and happy in this place, on this earth-kissed afternoon.
How is it okay, to be “okay”? What is it to live with conscience in Wangat? Those of us who still have access to time, space, safety and high levels of volition on this planet carry this duality all the time, as our gift and obligation. It is not an easy thing to make sense of; but for me, it speaks to the question of ‘why Greenpeace’? Because the moral and strategic mission-focus of campaigning provides a principled basis for how each of us can bridge that interminable gulf.
The essence of campaigning is to make the world’s state of crisis legible and actionable, by isolating systemic threats to which we can rise and respond credibly, with resources allocated to activity in accordance with strategy. To be part of Greenpeace, whether as an activist, volunteer supporter or staff member, is to find a home for your worries for the world in confidence and faith that together we have the power to do something about it. Together we meet the confusion of the moment with the light of shared purpose and the confidence of direction.
So, it was as I was getting back up again from my tumble and considering my daughter’s question that I thought of you—with gratitude, and with love–-because we cross this bridge all the time, together, everyday; to face the present and the future.
‘Yes, my love’, I say to my daughter, smiling as I get to my feet, “I’m okay”. And I close my eyes and think of a world in which the fires are out, and everywhere, all tadpoles have the conditions of flourishing to be able to grow peacefully into frogs.
Thank you for being a part of Greenpeace.
With love,
David
Climate Change
Without Weighing Costs to Public Health, EPA Rolls Back Air Pollution Standards for Coal Plants
The federal Mercury and Air Toxics Standards for coal and oil-fired power plants were strengthened during the Biden administration.
Last week, when the Environmental Protection Agency finalized its repeal of tightened 2024 air pollution standards for power plants, the agency claimed the rollback would save $670 million.
Without Weighing Costs to Public Health, EPA Rolls Back Air Pollution Standards for Coal Plants
Climate Change
A Tiny Caribbean Island Sued the Netherlands Over Climate Change, and Won
The case shows that climate change is a fundamental human rights violation—and the victory of Bonaire, a Dutch territory, could open the door for similar lawsuits globally.
From our collaborating partner Living on Earth, public radio’s environmental news magazine, an interview by Paloma Beltran with Greenpeace Netherlands campaigner Eefje de Kroon.
A Tiny Caribbean Island Sued the Netherlands Over Climate Change, and Won
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits









