Nearly 60 countries have drastically scaled back their plans for building coal-fired power plants since the Paris Agreement in 2015, according to figures released by Global Energy Monitor (GEM).
Among those making cuts of 98% or more to their coal-power pipeline are some of the world’s biggest coal users, including Turkey, Vietnam and Japan.
The data also shows that 35 nations eliminated coal from their plans entirely over the past decade, including South Korea and Germany.
Global coal-fired electricity generation has increased since 2015 as more power plants have come online.
But the data on plants in “pre-construction” phases in 2024 shows what GEM calls a “dramatic drop” in proposals for future coal plants.
The number of countries still planning new coal plants has roughly halved to just 33, with the proposed capacity – the maximum electricity output of those proposed plants – dropping by around two-thirds.
China and India, the world’s largest coal consumers, have also both reduced their planned coal capacity by more than 60% over the same timeframe, from a total of 801 gigawatts (GW) to 298GW.
However, both countries still have a large number of coal projects in the pipeline and, together, made up 92% of newly proposed coal capacity globally in 2024.
‘Dramatic drop’
The Paris Agreement in 2015 had major implications for the use of fossil fuels. As the fossil fuel that emits the most carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned, coal has long been viewed by many as requiring a rapid phaseout.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA) both see steep declines in “unabated” coal use by 2030 as essential to limit global warming to 1.5C.
But coal power capacity has continued to grow, largely driven by China.
Global capacity hit 2,175GW in 2024, up 1% from the year before and 13% higher than in 2015, according to GEM’s global coal-plant tracker.
This growth disguises a collapse in plans for future coal projects.
GEM’s latest analysis charts a decade of developments since the Paris Agreement and the “dramatic drop” in the number of coal plant proposals.
In 2015, coal power capacity in pre-construction – meaning plants that had been announced, or reached either the pre-permit or permitted stage – stood at 1,179GW.
By 2024, this had fallen to 355GW – a 70% drop. This indicates that countries are increasingly turning away from their earlier plans for a continued reliance on coal.
In total, 23 nations reduced the size of their proposals over this period and another 35 completely eliminated coal power from their future energy plans. Together, these 58 countries account for 80% of global fossil fuel-related CO2 emissions.
The chart below shows these changes, with China and India shown on a different x-axis due to the scale of their proposals. (See section below for more information.)

2015 to 2024, gigawatts (GW), in all countries that saw declines over this period. Red arrows indicate countries that no longer have any plans to build coal power plants. Source: Global Energy Monitor.
According to GEM, of the coal plants that were either under pre-construction or construction in 2015, 55% ended up being cancelled, a third were completed and the remainder are still under development.
Many of the nations that have phased coal out of their electricity plans are either very small or only had modest ambitions for building coal power in the first place.
However, the list also includes countries such as Germany and South Korea. These nations are both in the top 10 of global coal consumers, but their governments have committed to significantly reducing or, in Germany’s case, phasing out coal use by the late 2030s.
Turkey, Vietnam and Japan are among the big coal-driven economies that are now approaching having zero new coal plants in the works. All have around 2% of the planned capacity they had a decade ago.
Other major coal consumers have also drastically reduced their coal pipelines. Indonesia, the fifth-biggest coal user, has reduced its coal proposals by 90% and South Africa – the seventh-biggest – has cut its planned capacity by 83%.
Of the 68 countries that were planning to build new coal plants in 2015, just nine have increased their planned capacity. Around 85% of the planned increase in capacity by these nations is in Russia and its central Asian neighbours.
China and India
China is by far the world’s largest coal consumer, with India the second largest.
There was 44GW of coal power added to the global fleet last year. China was responsible for 30.5GW of this while retiring just 2.5GW, and India added 5.8GW while retiring 0.2GW.
Between them, these nations contributed 70% of the global coal-plant construction in 2024.
Nevertheless, there were signs of change as newly operating coal capacity around the world reached its lowest level in 20 years.
China and India have also seen significant drops in their pre-construction coal capacity over the past decade.
In 2015, China had 560GW of coal power in its pipeline and India had 241GW. Both nations have seen their proposed capacity drop by more than 60% to reach 217GW and 81GW, respectively.
While this is a significant reduction, both nations still have more coal capacity planned now than any other nation did in 2015. China’s current 217GW is roughly four times more than the 57GW Turkey was planning at that time.
GEM attributes the “slowdown” in China’s new proposals to the nation’s record-breaking solar and wind growth, which saw more electricity generation capacity installed in 2023 and 2024 than in the rest of the world combined.
As for India, GEM says the “notable declines” in coal proposals and commissions came after a “coal-plant investment bubble that went bust in the early 2010s”.
It notes that India is now “encouraging and fast-tracking the development of large coal plants”. The government has cited the need to meet the large nation’s growing electricity demand, especially due to the increased need for cooling technologies during heatwaves.
As other nations move away from the fossil fuel, coal capacity is likely to become increasingly concentrated in these two nations. Together, they made up 92% of the 116GW in newly proposed capacity last year.
The post Analysis: Nearly 60 countries have ‘dramatically’ cut plans to build coal plants since 2015 appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Nearly 60 countries have ‘dramatically’ cut plans to build coal plants since 2015
Climate Change
Doubts over European SAF rules threaten cleaner aviation hopes, investors warn
Doubts over whether governments will maintain ambitious targets on boosting the use of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) are a threat to the industry’s growth and play into the hands of fossil fuel companies, investors warned this week.
Several executives from airlines and oil firms have forecast recently that SAF requirements in the European Union, United Kingdom and elsewhere will be eased or scrapped altogether, potentially upending the aviation industry’s main policy to shrink air travel’s growing carbon footprint.
Such speculation poses a “fundamental threat” to the SAF industry, which mainly produces an alternative to traditional kerosene jet fuel using organic feedstocks such as used cooking oil (UCO), Thomas Engelmann, head of energy transition at German investment manager KGAL, told the Sustainable Aviation Fuel Investor conference in London.
He said fossil fuel firms would be the only winners from questions about compulsory SAF blending requirements.
The EU and the UK introduced the world’s first SAF mandates in January 2025, requiring fuel suppliers to blend at least 2% SAF with fossil fuel kerosene. The blending requirement will gradually increase to reach 32% in the EU and 22% in the UK by 2040.
Another case of diluted green rules?
Speaking at the World Economic Forum in Davos in January, CEO of French oil and gas company TotalEnergies Patrick Pouyanné said he would bet “that what happened to the car regulation will happen to the SAF regulation in Europe”.
The EU watered down green rules for car-makers in March 2025 after lobbying from car companies, Germany and Italy.
“You will see. Today all the airline companies are fighting [against the EU’s 2030 SAF target of 6%],” Pouyanne said, even though it’s “easy to reach to be honest”.
While most European airline lobbies publicly support the mandates, Ryanair Group CEO Michael O’Leary said last year that the SAF is “nonsense” and is “gradually dying a death, which is what it deserves to do”.
EU and UK stand by SAF targets
But the EU and the British government have disputed that. EU transport commissioner Apostolos Tzitzikostas said in November that the EU’s targets are “stable”, warning that “investment decisions and construction must start by 2027, or we will miss the 2030 targets”.
UK aviation minister Keir Mather told this week’s investor event that meeting the country’s SAF blending requirement of 10% by 2030 was “ambitious but, with the right investment, the right innovation and the right outlook, it is absolutely within our reach”.
“We need to go further and we need to go faster,” Mather said.

SAF investors and developers said such certainty on SAF mandates from policymakers was key to drawing the necessary investment to ramp up production of the greener fuel, which needs to scale up in order to bring down high production costs. Currently, SAF is between two and seven times more expensive than traditional jet fuel.
Urbano Perez, global clean molecules lead at Spanish bank Santander, said banks will not invest if there is a perceived regulatory risk.
David Scott, chair of Australian SAF producer Jet Zero Australia, said developing SAF was already challenging due to the risks of “pretty new” technology requiring high capital expenditure.
“That’s a scary model with a volatile political environment, so mandate questioning creates this problem on steroids”, Scott said.
Others played down the risk. Glenn Morgan, partner at investment and advisory firm SkiesFifty, said “policy is always a risk”, adding that traditional oil-based jet fuel could also lose subsidies.
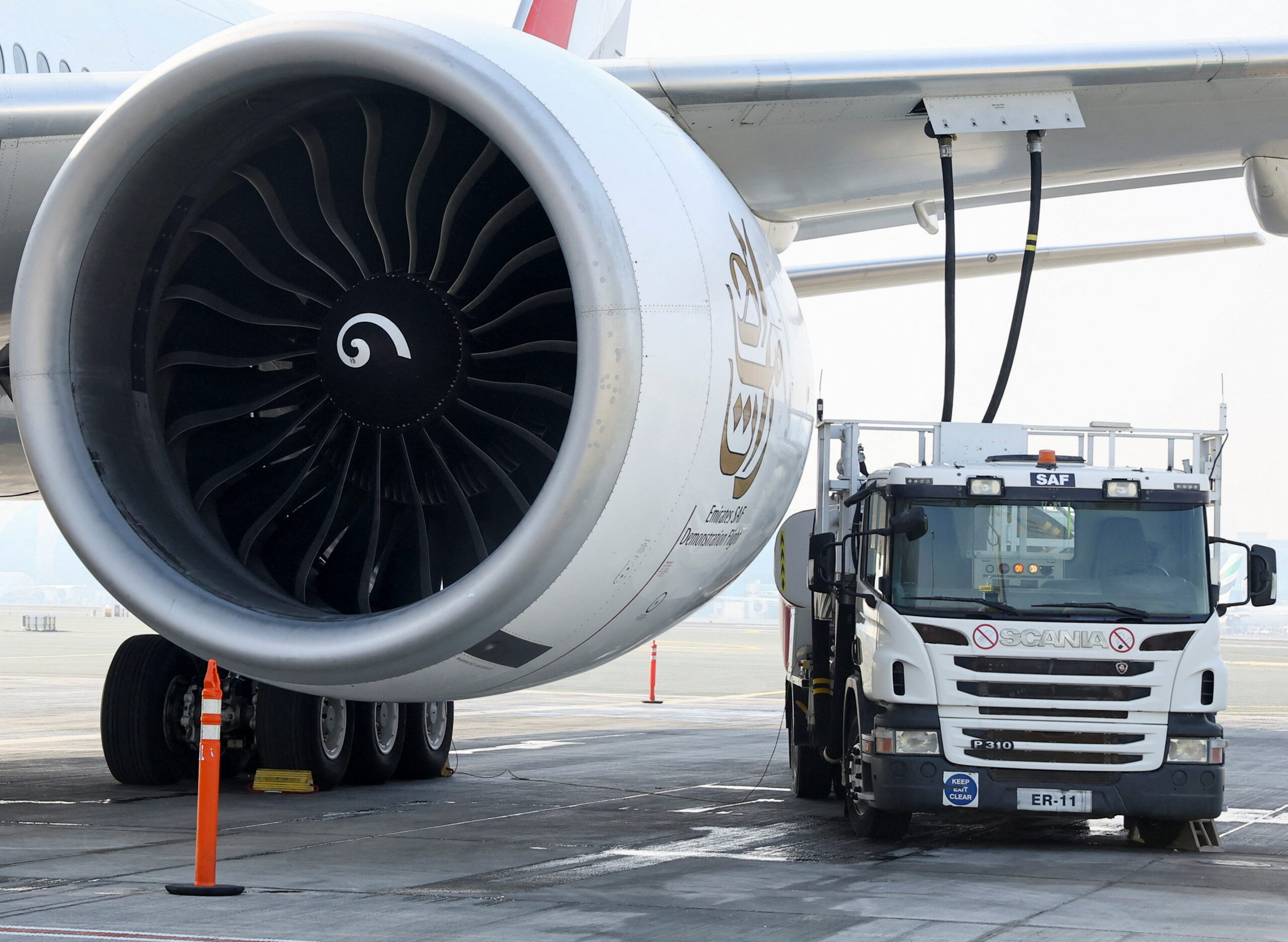


Asian countries join SAF mandate adopters
In Asia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand and Japan have recently adopted SAF mandates, and Matti Lievonen, CEO of Asia-based SAF producer EcoCeres, predicted that China, Indonesia and Hong Kong would follow suit.
David Fisken, investment director at the Australian Trade and Investment Commission, said the Australian government, which does not have a mandate, was watching to see how the EU and UK’s requirements played out.
The US does not have a SAF mandate and under President Donald Trump the government has slashed tax credits available for SAF producers from $1.75 a gallon to $1.
Is the world’s big idea for greener air travel a flight of fancy?
SAF and energy security
SAF’s potential role in boosting energy security was a major theme of this week’s discussions as geopolitical tensions push the issue to the fore.
Marcella Franchi, chief commercial officer for SAF at France’s Haffner Energy, said the Canadian government, which has “very unsettling neighbours at the moment”, was looking to produce SAF to protect its energy security, especially as it has ample supplies of biomass to use as potential feedstock.
Similarly, German weapons manufacturer Rheinmetall said last year it was working on plans that would enable European armed forces to produce their own synthetic, carbon-neutral fuel “locally and independently of global fossil fuel supply chain”.
Scott said Australia needs SAF to improve its fuel security, as it imports almost 99% of its liquid fuels.
He added that support for Australian SAF production is bipartisan, in part because it appeals to those more concerned about energy security than tackling climate change.
The post Doubts over European SAF rules threaten cleaner aviation hopes, investors warn appeared first on Climate Home News.
Doubts over European SAF rules threaten cleaner aviation hopes, investors warn
Climate Change
Southern Right Whales Are Having Fewer Calves; Scientists Say a Warming Ocean Is to Blame
After decades of recovery from commercial whaling, climate change is now threatening the whales’ future.
Southern right whales—once driven to near-extinction by industrial hunting in the 19th and 20th centuries—have long been regarded as a conservation success. After the International Whaling Commission banned commercial whaling in the 1980s, populations began a slow but steady rebound. New research, however, suggests climate change may be undermining that recovery.
Southern Right Whales Are Having Fewer Calves; Scientists Say a Warming Ocean Is to Blame
Climate Change
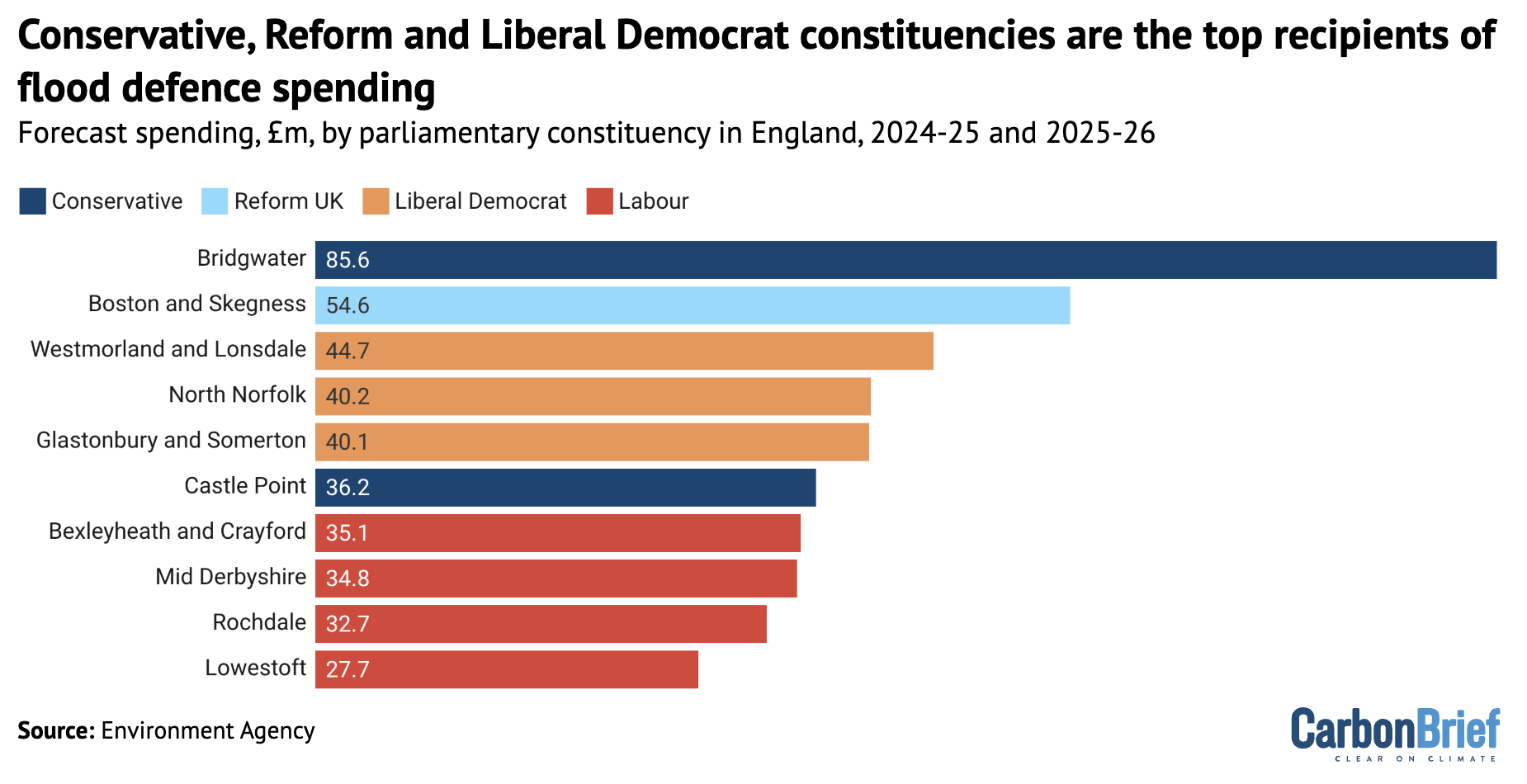
Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding
The Lincolnshire constituency held by Richard Tice, the climate-sceptic deputy leader of the hard-right Reform party, has been pledged at least £55m in government funding for flood defences since 2024.
This investment in Boston and Skegness is the second-largest sum for a single constituency from a £1.4bn flood-defence fund for England, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
Flooding is becoming more likely and more extreme in the UK due to climate change.
Yet, for years, governments have failed to spend enough on flood defences to protect people, properties and infrastructure.
The £1.4bn fund is part of the current Labour government’s wider pledge to invest a “record” £7.9bn over a decade on protecting hundreds of thousands of homes and businesses from flooding.
As MP for one of England’s most flood-prone regions, Tice has called for more investment in flood defences, stating that “we cannot afford to ‘surrender the fens’ to the sea”.
He is also one of Reform’s most vocal opponents of climate action and what he calls “net stupid zero”. He denies the scientific consensus on climate change and has claimed, falsely and without evidence, that scientists are “lying”.
Flood defences
Last year, the government said it would invest £2.65bn on flood and coastal erosion risk management (FCERM) schemes in England between April 2024 and March 2026.
This money was intended to protect 66,500 properties from flooding. It is part of a decade-long Labour government plan to spend more than £7.9bn on flood defences.
There has been a consistent shortfall in maintaining England’s flood defences, with the Environment Agency expecting to protect fewer properties by 2027 than it had initially planned.
The Climate Change Committee (CCC) has attributed this to rising costs, backlogs from previous governments and a lack of capacity. It also points to the strain from “more frequent and severe” weather events, such as storms in recent years that have been amplified by climate change.
However, the CCC also said last year that, if the 2024-26 spending programme is delivered, it would be “slightly closer to the track” of the Environment Agency targets out to 2027.
The government has released constituency-level data on which schemes in England it plans to fund, covering £1.4bn of the 2024-26 investment. The other half of the FCERM spending covers additional measures, from repairing existing defences to advising local authorities.
The map below shows the distribution of spending on FCERM schemes in England over the past two years, highlighting the constituency of Richard Tice.
By far the largest sum of money – £85.6m in total – has been committed to a tidal barrier and various other defences in the Somerset constituency of Bridgwater, the seat of Conservative MP Ashley Fox.
Over the first months of 2026, the south-west region has faced significant flooding and Fox has called for more support from the government, citing “climate patterns shifting and rainfall intensifying”.
He has also backed his party’s position that “the 2050 net-zero target is impossible” and called for more fossil-fuel extraction in the North Sea.
Tice’s east-coast constituency of Boston and Skegness, which is highly vulnerable to flooding from both rivers and the sea, is set to receive £55m. Among the supported projects are beach defences from Saltfleet to Gibraltar Point and upgrades to pumping stations.
Overall, Boston and Skegness has the second-largest portion of flood-defence funding, as the chart below shows. Constituencies with Conservative and Liberal Democrat MPs occupied the other top positions.
Overall, despite Labour MPs occupying 347 out of England’s 543 constituencies – nearly two-thirds of the total – more than half of the flood-defence funding was distributed to constituencies with non-Labour MPs. This reflects the flood risk in coastal and rural areas that are not traditional Labour strongholds.
Reform funding
While Reform has just eight MPs, representing 1% of the population, its constituencies have been assigned 4% of the flood-defence funding for England.
Nearly all of this money was for Tice’s constituency, although party leader Nigel Farage’s coastal Clacton seat in Kent received £2m.
Reform UK is committed to “scrapping net-zero” and its leadership has expressed firmly climate-sceptic views.
Much has been made of the disconnect between the party’s climate policies and the threat climate change poses to its voters. Various analyses have shown the flood risk in Reform-dominated areas, particularly Lincolnshire.
Tice has rejected climate science, advocated for fossil-fuel production and criticised Environment Agency flood-defence activities. Yet, he has also called for more investment in flood defences, stating that “we cannot afford to ‘surrender the fens’ to the sea”.
This may reflect Tice’s broader approach to climate change. In a 2024 interview with LBC, he said:
“Where you’ve got concerns about sea level defences and sea level rise, guess what? A bit of steel, a bit of cement, some aggregate…and you build some concrete sea level defences. That’s how you deal with rising sea levels.”
While climate adaptation is viewed as vital in a warming world, there are limits on how much societies can adapt and adaptation costs will continue to increase as emissions rise.
The post Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Constituency of Reform’s climate-sceptic Richard Tice gets £55m flood funding
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits