Russia, Saudi Arabia and other Gulf states have urged the World Bank to keep funding fossil fuel as a way to guarantee energy access across the world, as the lender pursues green reforms.
During a meeting of the bank’s steering committee in Marrakech, Morocco, they voiced opposition to reforms which are expected to channel more money into clean energy projects.
Mohammed Aljadaan, the Saudi finance minister, said “hydrocarbons will continue to play an important role in balancing the energy mix for the foreseeable future”, calling on the World Bank to reflect “these realities” in its financing.
He added that the lender should prioritise supporting universal electricity access, which requires “tapping all energy sources”.
His calls were echoed by Bahrain’s finance minister, Sheikh Salman Al Khalifa, who intervened at the meeting on behalf of a group of countries including neighbouring United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
“All sources of energy are essential and needed for economic growth and development,” he said before going on to make the case for the “indispensable role” of fossil gas as a source of “reliable and affordable” energy during the transition process.
Gulf states are among the world’s biggest producers and exporters of fossil fuels, which contribute to the vast majority of their national incomes.
Carbon capture pitch
Both Aljadaan and Al Khalifa also urged the World Bank to boost investment in carbon capture and storage (CCS) to allow for “a wide and reliable energy mix”. Saudi Arabia is a major proponent of CCS and has a history of promoting it in international summits, including talks over the IPCC scientific reports and UN climate talks.
Countries that produce or rely on fossil fuels particularly advocate the use CCS to trap their emissions, rather than ending the use of such fuels completely. However, the technology remains expensive and unproven at large scale.
According to the IPCC’s scientists, stopping a tonne of carbon dioxide with CCS costs between $50 and $200. Replacing fossil fuels with renewables usually saves money.
The International Energy Agency recently downgraded the role of the techno-fix in its net zero scenario, saying the history of CCS “has largely been one of unmet expectations”, marked by slow progress and flat deployment.
Green agenda attacked
Another voice in favour of fossil fuels around the World Bank committee table was that of Alexey Overchuk, Russia’s deputy prime minister. In a not-so-thinly veiled attack on the lender’s new agenda, he hit out at “unbalanced” energy and climate policies.
“An accelerated ‘greening’ of the global economy without considering the social effects and economic efficiency of decarbonization measures, along with massive underinvestment in fossil fuels, undermines energy security globally,” Overchuk said.
He added that the World Bank should recognise “the potential advantages of other energy sources, including gas and nuclear”. Russia is the second world’s largest gas producer, accounting for 18% of the global gas output in 2021.
World Bank and fossil fuels
The World Bank has reduced its financial backing of fossil fuel projects over the last few years. But last year it still provided over $1 billion of direct support to oil and gas, according to research by campaigning group Oil Change International.
A separate study found the lender’s private finance arm supplied $3.7bn in trade finance to oil and gas projects in 2022. Trade finance refers to a complex set of financial instruments in which money flows through intermediaries, like commercial banks, before reaching governments and businesses.
The World Bank – along its fellow development banks – recently agreed on principles to align its activities to the goals of the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C and to “pursue efforts” to keep it under 1.5°C.
But analysts raised concerns over the framework which does not explicitly prohibit financing for fossil fuel activities.
Climate finance leader
The World Bank says it is the largest provider of climate finance to developing countries. In 2022, it delivered $31.7 billion for climate-related investments – 36% of its lending.
At the meeting on Thursday in Marrakech, the World Bank’s shareholders endorsed its new vision, which puts a sharper focus on climate change.
The bank has expanded its historical objective to “end poverty” by adding that this should happen “on a livable planet”.
The reason for evolving the statement is to widen the aperture through which the bank looks at its task in the future, its chief Ajay Banga said on Wednesday. “If you can’t breathe and cannot drink clean water, there is little point in eradicating poverty,” he added.
The post Saudi Arabia, Russia urge World Bank to keep funding fossil fuels appeared first on Climate Home News.
Saudi Arabia, Russia urge World Bank to keep funding fossil fuels
Climate Change
Climate at Davos: Energy security in the geopolitical driving seat
The annual World Economic Forum got underway on Tuesday in the Swiss ski resort of Davos, providing a snowy stage for government and business leaders to opine on international affairs. With attention focused on the latest crisis – a potential US-European trade war over Greenland – climate change has slid down the agenda.
Despite this, a number of panels are addressing issues like electric vehicles, energy security and climate science. Keep up with top takeaways from those discussions and other climate news from Davos in our bulletin, which we’ll update throughout the day.
From oil to electrons – energy security enters a new era
Energy crises spurred by geopolitical tensions are nothing new – remember the 1970s oil shock spurred by the embargo Arab producers slapped on countries that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War, leading to rocketing inflation and huge economic pain.
But, a Davos panel on energy security heard, the situation has since changed. Oil now accounts for less than 30% of the world’s energy supply, down from more than 50% in 1973. This shift, combined with a supply glut, means oil is taking more of a back seat, according to International Energy Agency boss Fatih Birol.
Instead, in an “age of electricity” driven by transport and technology, energy diplomacy is more focused on key elements of that supply chain, in the form of critical minerals, natural gas and the security buffer renewables can provide. That requires new thinking, Birol added.
“Energy and geopolitics were always interwoven but I have never ever seen that the energy security risks are so multiplied,” he said. “Energy security, in my view, should be elevated to the level of national security today.”
In this context, he noted how many countries are now seeking to generate their own energy as far as possible, including from nuclear and renewables, and when doing energy deals, they are considering not only costs but also whether they can rely on partners in the long-term.
In the case of Europe – which saw energy prices jump after sanctions on Russian gas imports in the wake of Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine – energy security rooted in homegrown supply is a top priority, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said in Davos on Tuesday.
Outlining the bloc’s “affordable energy action plan” in a keynote speech at the World Economic Forum, she emphasised that Europe is “massively investing in our energy security and independence” with interconnectors and grids based on domestically produced sources of power.
The EU, she said, is trying to promote nuclear and renewables as much as possible “to bring down prices and cut dependencies; to put an end to price volatility, manipulation and supply shocks,” calling for a faster transition to clean energy.
“Because homegrown, reliable, resilient and cheaper energy will drive our economic growth and deliver for Europeans and secure our independence,” she added.
Comment – Power play: Can a defensive Europe stick with decarbonisation in Davos?
AES boss calls for “more technical talk” on supply chains
Earlier, the energy security panel tackled the risks related to supply chains for clean energy and electrification, which are being partly fuelled by rising demand from data centres and electric vehicles.
The minerals and metals that are required for batteries, cables and other components are largely under the control of China, which has invested massively in extracting and processing those materials both at home and overseas. Efforts to boost energy security by breaking dependence on China will continue shaping diplomacy now and in the future, the experts noted.
Copper – a key raw material for the energy transition – is set for a 70% increase in demand over the next 25 years, said Mike Henry, CEO of mining giant BHP, with remaining deposits now harder to exploit. Prices are on an upward trend, and this offers opportunities for Latin America, a region rich in the metal, he added.
At ‘Davos of mining’, Saudi Arabia shapes new narrative on minerals
Andrés Gluski, CEO of AES – which describes itself as “the largest US-based global power company”, generating and selling all kinds of energy to companies – said there is a lack of discussion about supply chains compared with ideological positioning on energy sources.
Instead he called for “more technical talk” about boosting battery storage to smooth out electricity supply and using existing infrastructure “smarter”. While new nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors are promising, it will be at least a decade before they can be deployed effectively, he noted.
In the meantime, with electricity demand rising rapidly, the politicisation of the debate around renewables as an energy source “makes no sense whatsoever”, he added.
The post Climate at Davos: Energy security in the geopolitical driving seat appeared first on Climate Home News.
Climate at Davos: Energy security in the geopolitical driving seat
Climate Change
A Record Wildfire Season Inspires Wyoming to Prepare for an Increasingly Fiery Future
As the Cowboy State faces larger and costlier blazes, scientists warn that the flames could make many of its iconic landscapes unrecognizable within decades.
In six generations, Jake Christian’s family had never seen a fire like the one that blazed toward his ranch near Buffalo, Wyoming, late in the summer of 2024. Its flames towered a dozen feet in the air, consuming grassland at a terrifying speed and jumping a four-lane highway on its race northward.
A Record Wildfire Season Inspires Wyoming to Prepare for an Increasingly Fiery Future
Climate Change
Analysis: UK newspaper editorial opposition to climate action overtakes support for first time
Nearly 100 UK newspaper editorials opposed climate action in 2025, a record figure that reveals the scale of the backlash against net-zero in the right-leaning press.
Carbon Brief has analysed editorials – articles considered the newspaper’s formal “voice” – since 2011 and this is the first year opposition to climate action has exceeded support.
Criticism of net-zero policies, including renewable-energy expansion, came entirely from right-leaning newspapers, particularly the Sun, the Daily Mail and the Daily Telegraph.
In addition, there were 112 editorials – more than two a week – that included attacks on Ed Miliband, continuing a highly personal campaign by some newspapers against the Labour energy secretary.
These editorials, nearly all of which were in right-leaning titles, typically characterised him as a “zealot”, driving through a “costly” net-zero “agenda”.
Taken together, the newspaper editorials mirror a significant shift on the UK political right in 2025, as the opposition Conservative party mimicked the hard-right populist Reform UK party by definitively rejecting the net-zero target that it had legislated for and the policies that it had previously championed.
Record climate opposition
Nearly 100 UK newspaper editorials voiced opposition to climate action in 2025 – more than double the number of editorials that backed climate action.
As the chart below shows, 2025 marked the fourth record-breaking year in a row for criticism of climate action in newspaper editorials.
This also marks the first time that editorials opposing climate action have overtaken those supporting it, during the 15 years that Carbon Brief has analysed.
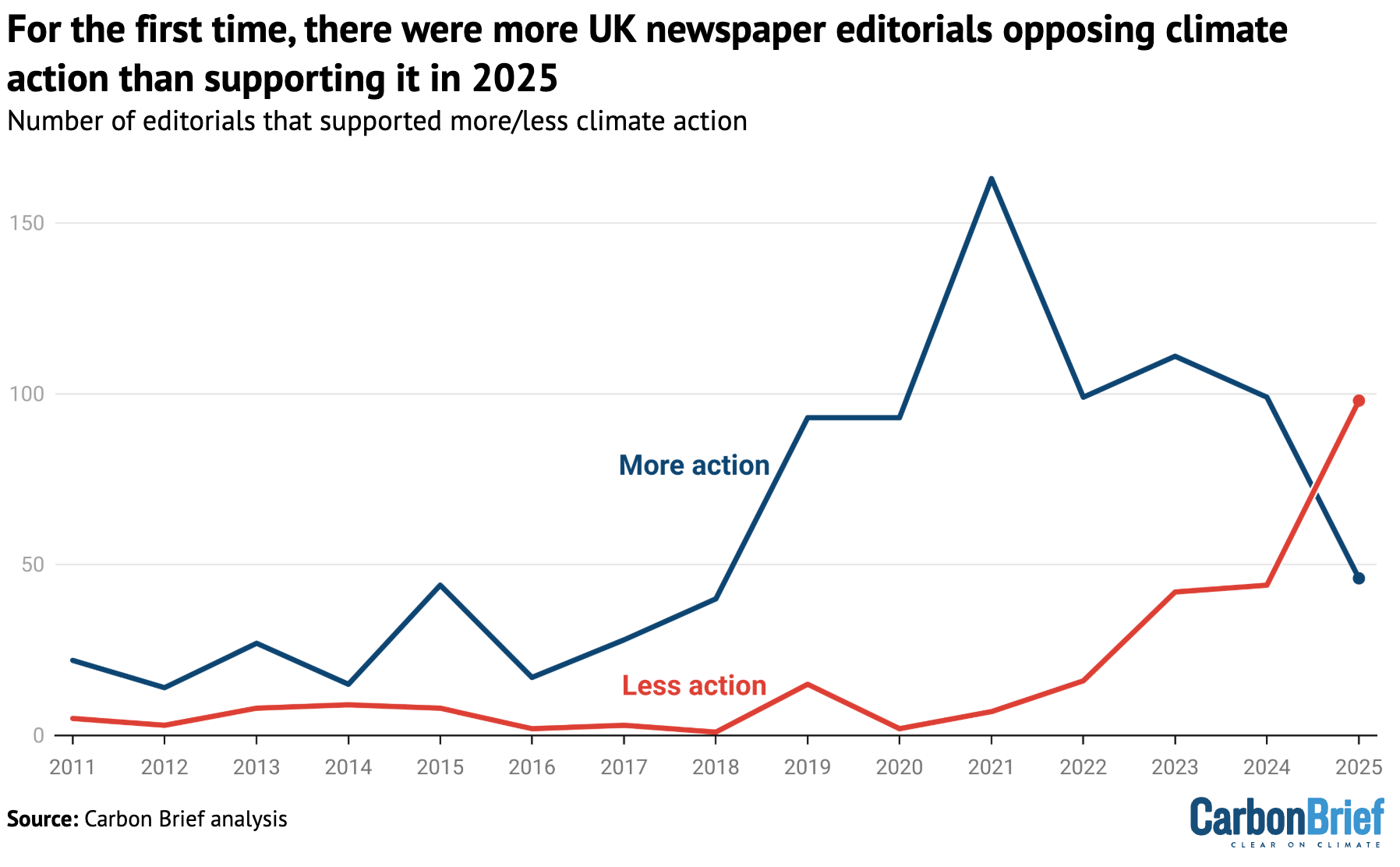
This trend demonstrates the rapid shift away from a long-standing political consensus on climate change by those on the UK’s political right.
Over the past year, the Conservative party has rejected both the “net-zero by 2050” target that it legislated for in 2019 and the underpinning Climate Change Act that it had a major role in creating. Meanwhile, the Reform UK party has been rising in the polls, while pledging to “ditch net-zero”.
These views are reinforced and reflected in the pages of the UK’s right-leaning newspapers, which tend to support these parties and influence their politics.
All of the 98 editorials opposing climate action were in right-leaning titles, including the Sun, the Daily Mail, the Daily Telegraph, the Times and the Daily Express.
Conversely, nearly all of the 46 editorials pushing for more climate action were in the left-leaning and centrist publications the Guardian and the Financial Times. These newspapers have far lower circulations than some of the right-leaning titles.
In total, 81% of the climate-related editorials published by right-leaning newspapers in 2025 rejected climate action. As the chart below shows, this is a marked difference from just a few years ago, when the same newspapers showed a surge in enthusiasm for climate action.
That trend had coincided with Conservative governments led by Theresa May and Boris Johnson, which introduced the net-zero goal and were broadly supportive of climate policies.
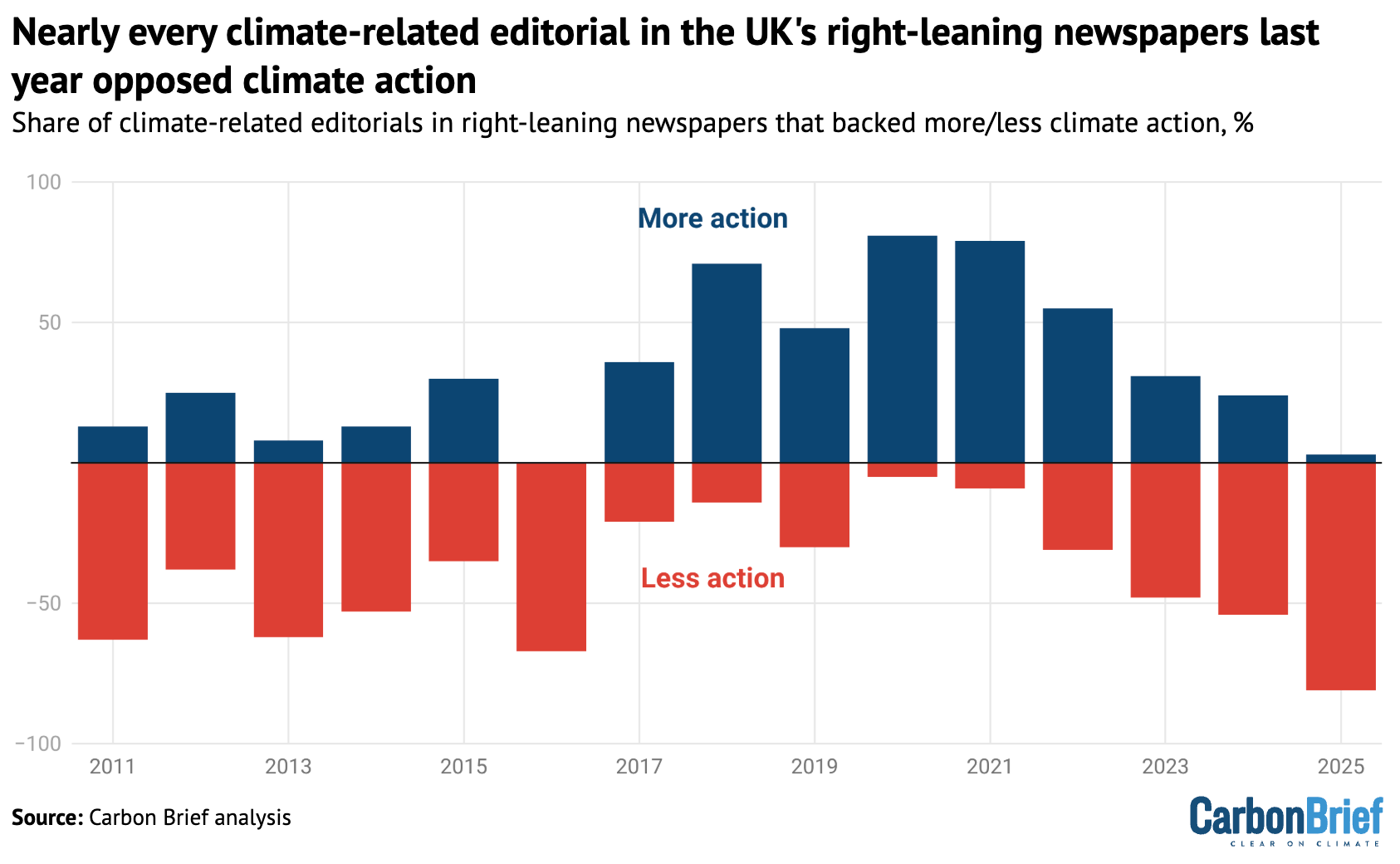
Notably, none of the editorials opposing climate action in 2025 took a climate-sceptic position by questioning the existence of climate change or the science behind it. Instead, they voiced “response scepticism”, meaning they criticised policies that seek to address climate change.
(The current Conservative leader, Kemi Badenoch, has described herself as “a net-zero sceptic, not a climate change sceptic”. This is illogical as reaching net-zero is, according to scientists, the only way to stop climate change from getting worse.)
In particular, newspapers took aim at “net-zero” as a catch-all term for policies that they deemed harmful. Most editorials that rejected climate action did not even mention the word “climate”, often using “net-zero” instead.
This supports recent analysis by Dr James Painter, a research associate at the University of Oxford, which concluded that UK newspaper coverage has been “decoupling net-zero from climate change”.
This is significant, given strong and broad UK public support for many of the individual climate policies that underpin net-zero. Notably, there is also majority support for the “net-zero by 2050” target itself.
Much of the negative framing by politicians and media outlets paints “net-zero” as something that is too expensive for people in the UK.
In total, 87% of the editorials that opposed climate action cited economic factors as a reason, making this by far the most common justification. Net-zero goals were described as “ruinous” and “costly”, as well as being blamed – falsely – for “driving up energy costs”.
The Sunday Telegraph summarised the view of many politicians and commentators on the right by stating simply that said “net-zero should be scrapped”.
While some criticism of net-zero policies is made in good faith, the notion that climate change can be stopped without reducing emissions to net-zero is incorrect. Alternative policies for tackling climate change are rarely presented by critical editorials.
Moreover, numerous assessments have concluded that the transition to net-zero can be both “affordable” and far cheaper than previously thought.
This transition can also provide significant economic benefits, even before considering the evidence that the cost of unmitigated warming will significantly outweigh the cost of action.
Miliband attacks intensify
Meanwhile, UK newspapers published 112 editorials over the course of 2025 taking personal aim at energy security and net-zero secretary Ed Miliband.
Nearly all of these articles were in right-leaning newspapers, with the Sun alone publishing 51. The Daily Mail, the Daily Telegraph and the Times published most of the remainder.
This trend of relentlessly criticising Miliband personally began last year in the run up to Labour’s election victory. However, it ramped up significantly in 2025, as the chart below shows.
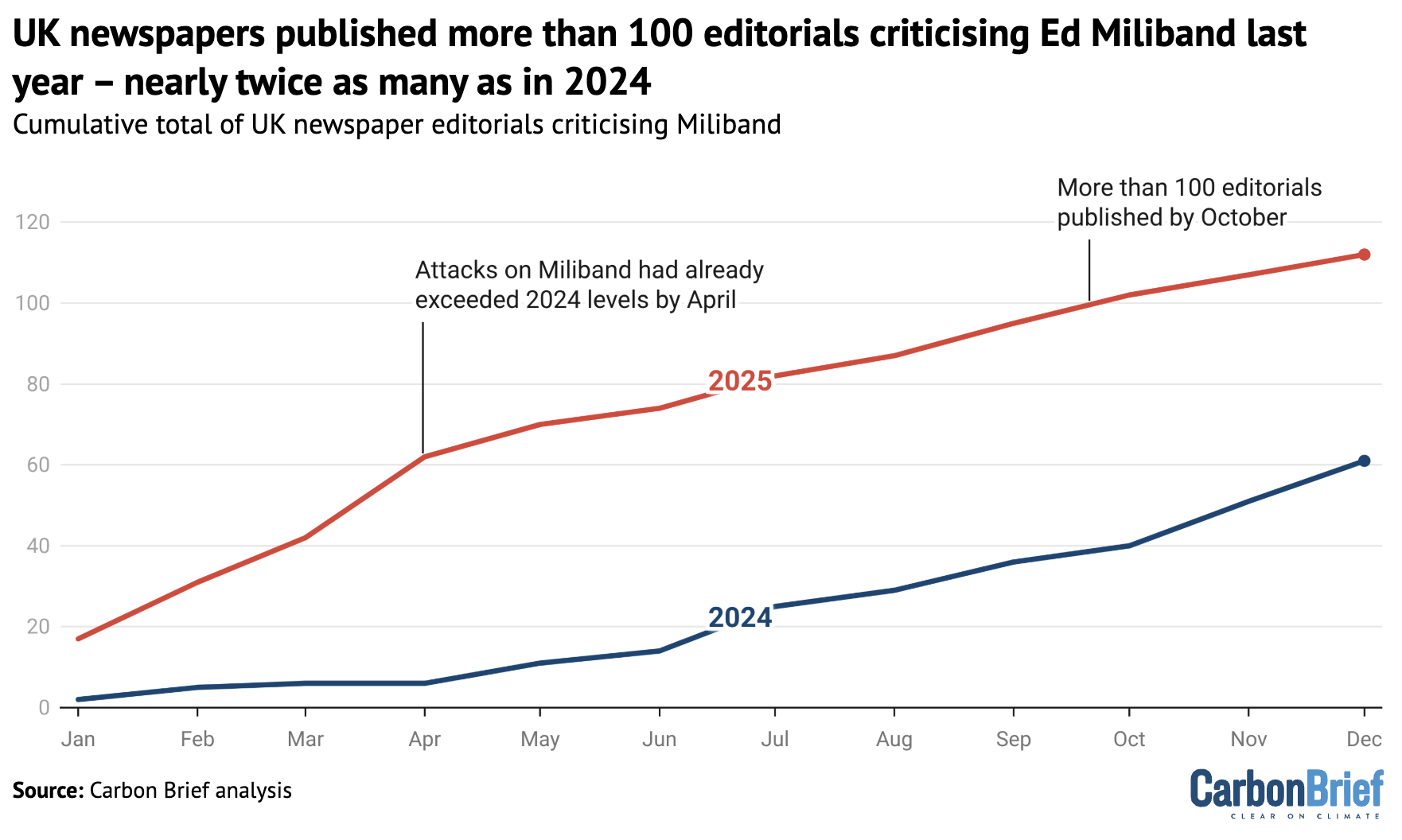
Around 58% of the editorials that opposed climate action used criticism of climate advocates as a justification – and nearly all of these articles mentioned Miliband, specifically.
Editorials denounced Miliband as a “loon” and a “zealot”, suffering from “eco insanity” and “quasi-religious delusions”. Nicknames given to him include “His Greenness”, the “high priest of net-zero” and “air miles Miliband”.
Many of these attacks were highly personal. The Daily Mail, for example, called Miliband “pompous and patronising”, with an “air of moral and intellectual superiority”.
Frequently, newspapers refer to “Ed Miliband’s net-zero agenda”, “Ed Miliband’s swivel-eyed targets” and “Mr Miliband’s green taxes”.
These formulations frame climate policies as harmful measures that are being imposed on people by the energy secretary.
In fact, the Labour government decisively won an election in 2024 with a manifesto that prioritised net-zero policies. Often, the “targets” and “taxes” in question are long-standing policies that were introduced by the previous Conservative government, with cross-party support.
Moreover, the government’s climate policy not only continues to rely on many of the same tools created by previous administrations, it is also very much in line with expert evidence and advice. This is to prioritise the expansion of clean power and to fuel an economy that relies on increasing levels of electrification, including through electric cars and heat pumps.
Despite newspaper editorials regularly calling for Miliband to be “sacked”, prime minister Keir Starmer has voiced his support both for the energy secretary and the government’s prioritisation of net-zero.
In an interview with podcast The Rest is Politics last year, Miliband was asked about the previous Carbon Brief analysis that showed the criticism aimed at him by right-leaning newspapers.
Podcast host Alastair Campbell asked if Miliband thought the attacks were the legacy of his strong stance, while Labour leader, during the Leveson inquiry into the practices of the UK press. Miliband replied:
“Some of these institutions don’t like net-zero and some of them don’t like me – and maybe quite a lot of them don’t like either.”
Renewable backlash
As well as editorial attitudes to climate action in general, Carbon Brief analysed newspapers’ views on three energy technologies – renewables, nuclear power and fracking.
There were 42 newspaper editorials criticising renewable energy in 2025. This meant that, for the first time since 2014, there were more anti-renewables editorials than pro-renewables editorials, as the chart below shows.
As with climate action more broadly, this was a highly partisan issue. The Times was the only right-leaning newspaper that published any editorials supporting renewables.
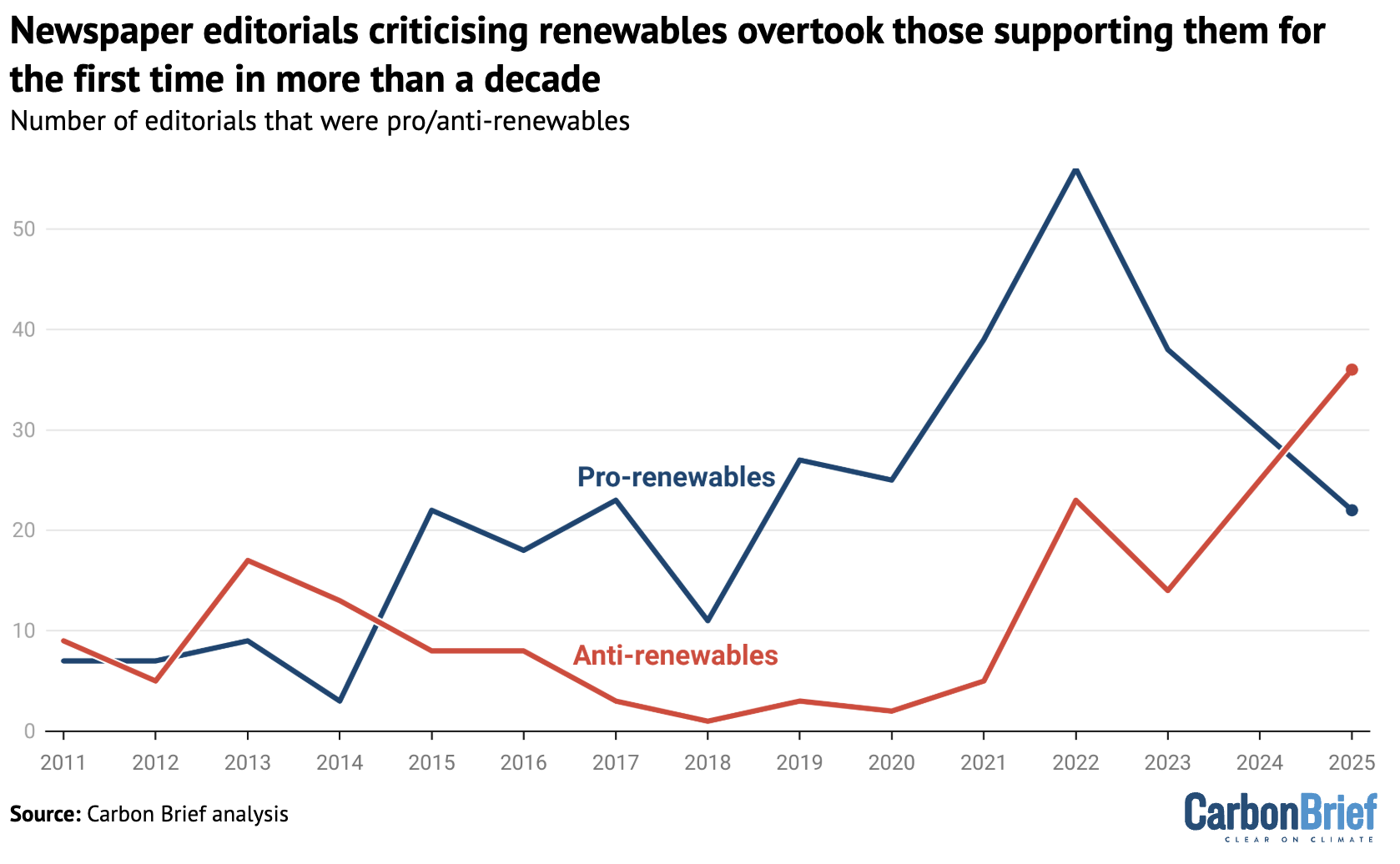
By far the most common stated reason for opposing renewable energy was that it is “expensive”, with 86% of critical editorials using economic arguments as a justification.
The Sun referred to “chucking billions at unreliable renewables” while the Daily Telegraph warned of an “expensive and intermittent renewables grid”.
At the same time, editorials in supportive publications also used economic arguments in favour of renewables. The Guardian, for example, stressed the importance of building an “affordable clean-energy system” that is “built on renewables”.
There was continued support in right-leaning publications for nuclear power, despite the high costs associated with the technology. In total, there were 20 editorials supporting nuclear power in 2025 – nearly all in right-leaning newspapers – and none that opposed it.
Fracking was barely mentioned by newspapers in 2023 and 2024, after a failed push by the Conservatives under prime minister Liz Truss to overturn a ban on the practice in 2022. This attempt had been accompanied by a surge in supportive right-leaning newspaper editorials.
There was a small uptick of 15 editorials supporting fracking in 2025, as right-leaning newspapers once again argued that it would be economically beneficial.
The Sun urged current Conservative leader Badenoch to make room for this “cheap, safe solution” in her future energy policy. The government plans to ban fracking “permanently”.
North Sea oil and gas remained the main fossil-fuel policy focus, with 30 editorials – all in right-leaning newspapers – that mentioned the topic. Most of the editorials arguing for more extraction from the North Sea also argued for less climate action or opposed renewable energy.
None of these editorials noted that the UK is expected to be significantly less reliant on fossil-fuel imports if it pursues net-zero, than if it rolls back on climate action and attempts to squeeze more out of the remaining deposits in the North Sea.
Methodology
This is a 2025 update of previous analysis conducted for the period 2011-2021 by Carbon Brief in association with Dr Sylvia Hayes, a research fellow at the University of Exeter. Previous updates were published in 2022, 2023 and 2024.
The count of editorials criticising Ed Miliband was not conducted in the original analysis.
The full methodology can be found in the original article, including the coding schema used to assess the language and themes used in editorials concerning climate change and energy technologies.
The analysis is based on Carbon Brief’s editorial database, which is regularly updated with leading articles from the UK’s major newspapers.
The post Analysis: UK newspaper editorial opposition to climate action overtakes support for first time appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: UK newspaper editorial opposition to climate action overtakes support for first time
-
Greenhouse Gases5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change5 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits









