Up
Introduction Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Finland
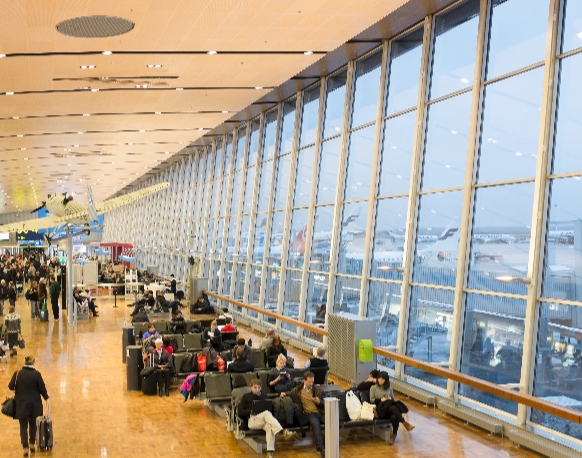
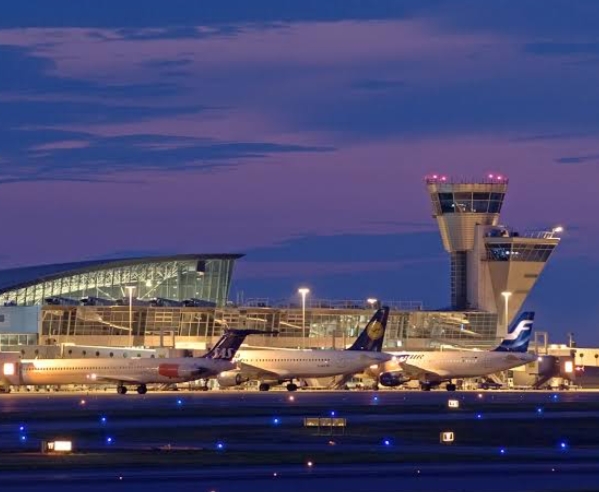
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, located in Vantaa, Finland, is the country’s premier international airport. Serving as a vital air transportation hub, it connects Finland to various global destinations.
With modern facilities, efficient services, and a strategic location, the airport plays a crucial role in facilitating both domestic and international travel.
Passengers at Helsinki-Vantaa Airport experience a seamless journey with its state-of-the-art terminals, offering a range of amenities from shopping and dining to lounges for relaxation. As a key hub for Finnair, the national airline, and a base for numerous other carriers, the airport contributes significantly to the region’s connectivity.
Notable for its Nordic design and efficiency, Helsinki-Vantaa Airport reflects Finland’s commitment to providing a world-class travel experience. Its well-connected transportation links, including a railway station directly connected to the airport, enhance accessibility for travelers.
Whether arriving or departing, Helsinki-Vantaa Airport stands as a modern gateway, embodying Finnish hospitality and functionality.
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Finland Profile data
Here is general profile information about Helsinki-Vantaa Airport :
– Location: Vantaa, Finland
– Type: International Airport
– Operator: Finavia
– Terminals: Two passenger terminals (T1 and T2)
– Airlines: Serves as a hub for Finnair and a base for numerous other carriers.
– Facilities: Modern amenities including shopping, dining, lounges, and conference services.
– Connectivity: Well-connected with a railway station directly linked to the airport.
– Importance: Key hub for both domestic and international air travel in Finland.
Sustainability in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Finland
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport has made notable strides in sustainability, here are some aspects of its sustainability initiatives:
1. Energy Efficiency: The airport has implemented measures to enhance energy efficiency, including the use of renewable energy sources where possible.
2. Waste Management: Efforts have been made to reduce waste and improve recycling practices within the airport premises.
3. Carbon Neutrality: Helsinki-Vantaa has worked towards carbon neutrality by investing in carbon offset projects and implementing energy-saving technologies.
4. Public Transportation: The airport encourages the use of public transportation, with a direct railway connection to the city center, contributing to reduced carbon emissions from passenger travel.
Energy Efficiency in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport has prioritized energy efficiency through various measures:
1. Renewable Energy: The airport has incorporated renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, to reduce its environmental impact.
2. Energy-Saving Technologies: Implementation of energy-efficient technologies and practices, including LED lighting and energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
3. Monitoring and Optimization: Continuous monitoring and optimization of energy consumption to identify areas for improvement and reduce overall energy usage.
4. Certifications: Pursuit of certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, indicating a commitment to sustainable practices.
These efforts align with the broader goals of reducing the airport’s carbon footprint and enhancing overall sustainability.
Waste Management in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport has implemented waste management initiatives to enhance sustainability:
1. Recycling Programs: The airport promotes recycling practices for various waste materials, including paper, plastic, and glass.
2. Waste Sorting Facilities: Adequate waste sorting facilities are available throughout the airport to facilitate proper disposal and recycling.
3. Reduction Strategies: Initiatives aimed at reducing overall waste generation, such as encouraging the use of reusable items and minimizing single-use plastics.
4. Collaboration: Collaboration with waste management partners and local authorities to ensure effective waste disposal and recycling processes.
By focusing on waste reduction and responsible disposal, Helsinki-Vantaa Airport aims to minimize its environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable aviation industry.
Monitoring and optimization of energy consumption in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport employs monitoring and optimization strategies for energy consumption, including:
1. Advanced Systems: Utilization of advanced systems for real-time monitoring of energy usage throughout the airport infrastructure.
2. Data Analysis: Regular analysis of energy consumption data to identify patterns, peak usage times, and areas where improvements can be made.
3. Energy-Efficient Technologies: Implementation of energy-efficient technologies and equipment to reduce overall energy consumption.
4. Continuous Improvement: Ongoing efforts to identify opportunities for improvement and implement changes to optimize energy efficiency.
By actively monitoring and optimizing energy usage, Helsinki-Vantaa Airport aims to enhance sustainability, reduce environmental impact, and contribute to more efficient operations.
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport Certifications
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport holds various certifications indicating its commitment to environmental and operational standards.
Some certifications include:
1. ISO 14001: This certification reflects adherence to international standards for environmental management systems, emphasizing the implementation of effective environmental practices.
2. ACA Certification: Airport Carbon Accreditation certifies airports for their efforts in managing and reducing carbon emissions. Helsinki-Vantaa Airport has been actively working toward carbon neutrality.
3. IATA’s CEIV Pharma: Certification for handling pharmaceutical products, ensuring compliance with international standards in the transportation of temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical goods.
Traffic Management Control in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Finland
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport employs a comprehensive Traffic Management Control system to ensure efficient and safe air traffic operations.
Key aspects include:
1. Air Traffic Control (ATC): The airport has an ATC tower overseeing arrivals and departures, providing instructions to pilots for safe and orderly movement on the ground and in the airspace.
2. Ground Control: Ground Control manages the movement of aircraft on the taxiways and runways, coordinating with the ATC tower to ensure smooth transitions between ground and air operations.
3. Collaboration with Airlines: Coordination with airlines to manage the flow of arriving and departing flights, optimizing scheduling to prevent congestion and delays.
4. Technology Integration: Integration of advanced technologies for radar surveillance, communication, and navigation to enhance overall traffic management efficiency.
Efficient traffic management is crucial for maintaining safety and minimizing delays at Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, contributing to a smooth travel experience for passengers and efficient operations for airlines.
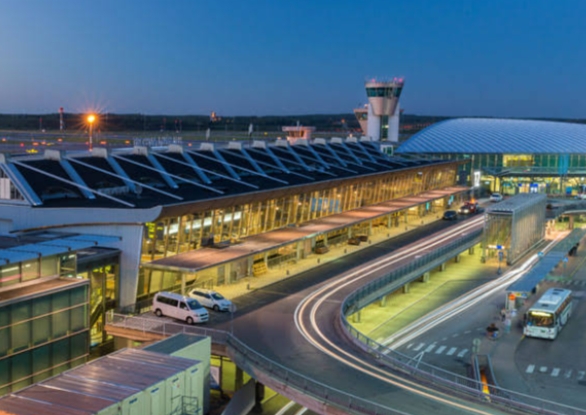
Latest Facilities in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport generally undergo continuous improvements and expansions to enhance passenger experience.
Common types of facilities in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport include:
1. Terminals: Modern and well-equipped terminals with amenities such as lounges, shopping, and dining options.
2. Technology Integration: Implementation of advanced technologies for check-in, security, and baggage handling to streamline processes.
3. Sustainable Initiatives: Integration of sustainable features, such as energy-efficient systems and waste management practices.
4. Transportation Links: Efficient transportation links, including direct rail connections and parking facilities.
Development of Helsinki-Vantaa Airport
The development of Helsinki-Vantaa Airport has been marked by ongoing efforts to enhance its infrastructure, services, and sustainability.
Key aspects of its development include:
1. Capacity Expansion: Periodic expansions to accommodate increasing passenger numbers and air traffic demand.
2. Terminal Upgrades: Renovations and upgrades to terminals, improving facilities, and providing a better passenger experience.
3. Technology Integration: Continued integration of advanced technologies for more efficient and secure operations.
4. Sustainability Initiatives: Emphasis on sustainability with measures such as energy-efficient systems, waste management, and certifications for environmental standards.
5. Collaboration with Airlines: Working closely with partner airlines to optimize flight schedules and improve overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion for Exploring Sustainability in Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Finland
Helsinki-Vantaa Airport in Finland exemplifies a commitment to sustainability through a multifaceted approach. From energy-efficient technologies and waste management programs to certifications and continuous development, the airport stands as a model for environmentally conscious aviation.
These initiatives not only reflect the airport’s dedication to reducing its environmental impact but also contribute to the broader goals of creating a more sustainable and resilient air travel industry. As Helsinki-Vantaa Airport continues to evolve and implement innovative practices, it sets a positive example for airports worldwide seeking to balance operational efficiency with environmental responsibility.
https://www.exaputra.com/2023/11/exploring-sustainability-in-helsinki.html
Renewable Energy
Trump’s Destruction of Renewable Energy Benefits His Support Base, and That’s All that Matters
 The death sentence that Trump has imposed on renewable energy in America is good for two groups: a) Big Oil and b) the MAGA crowd that rejects science and wants nothing more than to own the libs, aka “libtards.”
The death sentence that Trump has imposed on renewable energy in America is good for two groups: a) Big Oil and b) the MAGA crowd that rejects science and wants nothing more than to own the libs, aka “libtards.”
The unforeseen problem for the common American is that solar and wind are by far the least expensive sources of energy, so that the ratepayers in the U.S. are soon going to be shucking out huge amounts of extra cash each month.
Of course, this doesn’t account for the increases in the effects of climate change that, though they are devastating our planet, won’t be affecting the folks in Oklahoma too badly for the next few years while Trump does his best to profit by turning our Earth into a wasteland.
Trump’s Destruction of Renewable Energy Benefits His Support Base, and That’s All that Matters
Renewable Energy
WOMA 2026 Recap Live from Melbourne
Weather Guard Lightning Tech

WOMA 2026 Recap Live from Melbourne
Allen, Rosemary, and Yolanda, joined by Morten Handberg from Wind Power LAB, recap WOMA 2026 live from Melbourne. The crew discusses leading edge erosion challenges unique to Australia, the frustration operators face getting data from full service agreements, and the push for better documentation during project handovers. Plus the birds and bats management debate, why several operators said they’d choose smaller glass fiber blades over bigger carbon fiber ones, and what topics WOMA 2027 should tackle next year.
Sign up now for Uptime Tech News, our weekly newsletter on all things wind technology. This episode is sponsored by Weather Guard Lightning Tech. Learn more about Weather Guard’s StrikeTape Wind Turbine LPS retrofit. Follow the show on YouTube, Linkedin and visit Weather Guard on the web. And subscribe to Rosemary’s “Engineering with Rosie” YouTube channel here. Have a question we can answer on the show? Email us!
[00:00:00] The Uptime Wind Energy Podcast brought to you by Strike Tape protecting thousands of wind turbines from lightning damage worldwide. Visit strike tape.com and now your hosts. Welcome to the Uptime Winner Energy podcast. I’m your host, Alan Hall. I’m here with Yolanda Pone, Rosemary Barnes, and the Blade Whisperer, Morton Hamburg.
And we’re all in Melbourne at the Pullman on the park. We just finished up Woma 2026. Massive event. Over 200 people, two days, and a ton of knowledge. Rosemary, what did you think? Yeah, I mean it was a, a really good event. It was really nice ’cause we had event organization, um, taken care of by an external company this time.
So that saved us some headaches, I think. Um. But yeah, it was, it was really good. It was different than last year, and I think next year will be different again because yeah, we don’t need to talk about the same topics every single year. But, um, yeah, I got really great [00:01:00] feedback. So that’s shows we’re doing something right?
Yeah, a lot of the, the sessions were based upon feedback from Australian industry and, uh, so we did AI rotating bits, the, the drive train blades. Uh, we had a. Master class on lightning to start off. Uh, a number of discussions about BOP and electrical, BOP. All those were really good. Mm-hmm. Uh, the, the content was there, the expertise was there.
We had worldwide representation. Morton, you, you talked about blades a good bit and what the Danish and Worldwide experience was. You know, talked about the American experience on Blades. That opened up a lot of discussions because I’m never really sure where Australia is in the, uh, operations side, because a lot of it is full service agreements still.
But it does seem like from last year to this year. There’s more onboarding of the technical expertise internally at the operators. Martin, [00:02:00] you saw, uh, a good bit of it. This is your first time mm-hmm. At this conference. What were your impressions of the, the content and the approach, which is a little bit different than any other conference?
I see an industry that really wants to learn, uh, Australia, they really want to learn how to do this. Uh, and they’re willing to listen to us, uh, whether you live in Australia, in the US or in Europe. You know, they want to lean on our experiences, but they wanna, you know, they want to take it out to their wind farms and they ga then gain their own knowledge with it, which I think is really amicable.
You know, something that, you know, we should actually try and think about how we can copy that in Europe and the US. Because they, they are, they’re listening to us and they’re taking in our input, and then they try and go out. They go out and then they, they try and implement it. Um, so I think really that is something, uh, I’ve learned, you know, and, and really, um, yeah, really impressed by, from this conference.
Yeah. Yolanda, you were on several panels over the, the two days. What were your impressions of the conference and what were your thoughts [00:03:00] on the Australia marketplace? I think the conference itself is very refreshing or I think we all feel that way being on the, on the circuit sometimes going on a lot of different conferences.
It was really sweet to see everybody be very collaborative, as Morton was saying. Um, and it was, it was just really great about everybody. Yes, they were really willing to listen to us, but they were also really willing to share with each other, which is nice. Uh, I did hear about a few trials that we’re doing in other places.
From other people, just kind of, everybody wants to learn from each other and everybody wants to, to make sure they’re in as best a spot as they can. Yeah, and the, the, probably the noisiest part of the conferences were at the coffees and the lunch. Uh, the, the collaboration was really good. A lot of noise in the hallways.
Uh, just people getting together and then talking about problems, talking about solutions, trying to connect up with someone they may have seen [00:04:00]somewhere else in the part of the world that they were here. It’s a different kind of conference. And Rosemary, I know when, uh, you came up to with a suggestion like, Hey.
If there’s not gonna be any sales talks, we’re not gonna sit and watch a 30 minute presentation about what you do. We’re gonna talk about solutions. That did play a a different dynamic because. It allowed people to ingest at their own rate and, and not just sit through another presentation. Yeah. It was made it more engaging, I think.
Yeah, and I mean, anyway, the approach that I take for sales for my company that I think works best is not to do the hard sell. It’s to talk about smart things. Um, and if you are talking about describing a problem or a solution that somebody in the audience has that problem or solution, then they’re gonna seek you out afterwards.
And so. There’s plenty of sales happening in an event like this, but you’re just not like, you know, subjecting people to sales. It’s more presenting them with the information that they need. And then I, I think also the size of the conference really [00:05:00] helps ’cause yeah, about 200 people. Any, everybody is here for the same technical kind.
Content. So it’s like if you just randomly start talking to somebody while you’re waiting for a coffee or whatever, you have gonna have heaps to talk about with them, with ev every single other person there. And so I think that that’s why, yeah, there was so much talking happening and you know, we had social events, um, the first two evenings and so.
Mo like I was surprised actually. So many people stayed. Most people, maybe everybody stayed for those events and so just so much talking and yeah, we did try to have quite long breaks, um, and quite a lot of them and, you know, good enough food and coffee to keep people here. And I think that that’s as important as, you know, just sitting and listening.
Well, that was part of the trouble, some of the conference that you and I have been at, it’s just like six hours of sitting down listening to sort of a droning mm-hmm. Presenter trying to sell you something. Here we were. It was back and forth. A lot more panel talk with experts from around the world and then.[00:06:00]
Break because you just can’t absorb all that without having a little bit of a brain rest, some coffee and just trying to get to the next session. I, I think that made it, uh, a, a, a more of a takeaway than I would say a lot of other conferences are, where there’s spender booze, and. Brochures and samples being handed out and all that.
We didn’t have any of that. No vendor booze, no, uh, upfront sales going on and even into the workshop. So there was specific, uh, topics provided by people that. Provide services mostly, uh, speaking about what they do, but more on a case study, uh, side. And Rosie, you and I sat in on one that was about, uh, birds and bats, birds and bats in Australia.
That one was really good. Yeah, that was great. I learned, I learned a lot. Your mind was blown, but Totally. Yeah. It is crazy how much, how much you have to manage, um, bird and wildlife deaths related to wind farms in Australia. Like compared to, I mean, ’cause you see. Dead birds all the time, right? Cars hit [00:07:00] birds, birds hit buildings, power lines kill birds, and no one cares about those birds.
But if a bird is injured near a wind farm, then you know, everybody has to stop. We have to make sure that you can do a positive id. If you’re not sure, send it away for a DNA analysis. Keep the bird in a freezer for a year and make sure that it’s logged by the, you know, appropriate people. It’s, it’s really a lot.
And I mean, on the one hand, like I’m a real bird lover, so I am, I’m glad that birds are being taken seriously, but on the other hand, I. I think that it is maybe a little bit over the top, like I don’t see extra birds being saved because of that level of, of watching throughout the entire life of the wind farm.
It feels more like something for the pre-study and the first couple of years of operation, and then you can chill after that if everything’s under control. But I, I guess it’s quite a political issue because people do. Do worry about, about beds and bats? Mm-hmm. Yeah, I thought the output of that was more technology, a little or a little more technology.
Not a lot of technology in today’s world [00:08:00] because we could definitely monitor for where birds are and where bats are and, uh, you know. Slow down the turbines or whatever we’re gonna do. Yeah. And they are doing that in, in sites where there is a problem. But, um, yeah, the sites we’re talking about with that monitoring, that’s not sites that have a big, big problem at sites that are just Yeah, a few, a few birds dying every year.
Um, yeah. So it’s interesting. And some of the blade issues in Australia, or a little unique, I thought, uh, the leading edge erosion. Being a big one. Uh, I’ve seen a lot of leading edge erosion over the last couple of weeks from Australia. It is Texas Times two in some cases. And, uh, the discussion that was had about leading edge erosion, we had ETT junker from Stack Raft and, and video form all the way from Sweden, uh, talking to us live, which was really nice actually.
Uh, the, the amount of knowledge that the Global Blade group. Brought to the discussion and just [00:09:00] opening up some eyes about what matters in leading edge erosion. It’s not so much the leading edge erosion in terms of a EP, although there is some a EP loss. It’s more about structural damage and if you let the structure go too far.
And Martin, you’ve seen a lot of this, and I think we had a discussion about this on the podcast of, Hey, pay attention to the structural damage. Yeah, that’s where, that’s where your money is. I mean, if you go, if you get into structural damage, then your repair costs and your downtime will multiply. That is just a known fact.
So it’s really about keeping it, uh, coding related because then you can, you can, you can move really fast. You can get it the blade up to speed and you won’t have the same problems. You won’t have to spend so much time rebuilding the blade. So that’s really what you need to get to. I do think that one of the things that might stand out in Australia that we’re going to learn about.
Is the effect of hail, because we talked a lot about it in Europe, that, you know, what is the effect of, of hail on leading edge erosion? We’ve never really been able to nail it down, but down here I heard from an, [00:10:00] from an operator that they, they, uh, referenced mangoes this year in terms of hail size. It was, it was, it was incredible.
So if you think about that hitting a leading edge, then, uh, well maybe we don’t really need to, we don’t really get to the point where, so coding related, maybe we will be structural from the beginning, but. Then at least it can be less a structural. Um, but that also means that we need to think differently in terms of leading edge, uh, protection and what kinds of solutions that are there.
Maybe some of the traditional ones we have in Europe, maybe they just don’t work, want, they, they won’t work in some part of Australia. Australia is so big, so we can’t just say. Northern Territory is the same as as, uh, uh, um, yeah. Victoria or uh, or Queensland. Or Queensland or West Australia. I think that what we’re probably going to learn is that there will be different solutions fitting different parts of Australia, and that will be one of the key challenges.
Um, yeah. And Blades in Australia sometimes do. Arrive without leading edge protection from the OEMs. [00:11:00] Yeah, I’m sure some of the sites that I’ve been reviewing recently that the, the asset manager swears it’s got leading edge protection and even I saw some blades on the ground and. I don’t, I don’t see any leading edge protection.
I can’t feel any leading edge protection. Like maybe it’s a magical one that’s, you know, invisible and, um, yeah, it doesn’t even feel different, but I suspect that some people are getting blades that should have been protected that aren’t. Um, so why? Yeah, it’s interesting. I think before we, we rule it out.
Then there are some coatings that really look like the original coating. Mm. So we, we, I know that for some of the European base that what they come out of a factory, you can’t really see the difference, but they’re multilayer coating, uh, on the blades. What you can do is that you can check your, uh, your rotor certificate sometimes will be there.
You can check your, uh, your blade sheet, uh, that you get from manufacturer. If you get it. Um, if you get it, then it will, it will be there. But, um, yeah, I, I mean, it can be difficult to say, to see from the outset and there’s no [00:12:00]documentation then. Yeah, I mean. If I can’t see any leading edge erosion protection, and I don’t know if it’s there or not, I don’t think I will go so far and then start installing something on something that is essentially a new blade.
I would probably still put it into operation because most LEP products that can be installed up tower. So I don’t think that that necessarily is, is something we should, shouldn’t still start doing just because we suspect there isn’t the LEP. But one thing that I think is gonna be really good is, um, you know, after the sessions and you know, I’ve been talking a lot.
With my clients about, um, leading edge erosion. People are now aware that it’s coming. I think the most important thing is to plan for it. It’s not right to get to the point where you’ve got half a dozen blades with, you know, just the full leading edge, just fully missing holes through your laminate, and then your rest of your blades have all got laminate damage.
That’s not the time to start thinking about it because one, it’s a lot more expensive for each repair than it would’ve been, but also. No one’s got the budget to, to get through all of that in one season. So I do really [00:13:00] like that, you know, some of the sites that have been operating for five years or so are starting to see pitting.
They can start to plan that into their budget now and have a strategy for how they’re going to approach it. Um, yeah. And hopefully avoid getting over to the point where they’ve missing just the full leading edge of some of their blades. Yeah. But to Morton’s earlier point, I think it’s also important for people to stop the damage once it happens too.
If, if it’s something that. You get a site or for what, whatever reason, half of your site does look like terrible and there’s holes in the blade and stuff. You need to, you need to patch it up in some sort of way and not just wait for the perfect product to come along to, to help you with that. Some of the hot topics this week were the handover.
From, uh, development into production and the lack of documentation during the transfer. Uh, the discussion from Tilt was that you need to make sure it is all there, uh, because once you sign off. You probably can’t go back and get it. And [00:14:00] some of the frustration around that and the, the amount of data flow from the full service provider to the operator seemed to be a, a really hot topic.
And, and, uh, we did a little, uh, surveyed a about that. Just the amount of, um, I don’t know how to describe it. I mean, it was bordering on anger maybe is a way. Describe it. Uh, that they feel that operators feel like they don’t have enough insight to run the turbines and the operations as well as they can, and that they should have more insight into what they have operating and why it is not operat.
A certain way or where did the blades come from? Are there issues with those blades? Just the transparency WA was lacking. And we had Dan Meyer, who is from the States, he’s from Colorado, he was an xge person talking about contracts, uh, the turbine supply agreement and what should be in there, the full service [00:15:00] agreement, what should be in there.
Those are very interesting. I thought a lot of, uh, operators are very attentive to that, just to give themselves an advantage of what you can. Put on paper to help yourself out and what you should think about. And if you have a existing wind farm from a certain OEM and you’re gonna buy another wind farm from ’em, you ought to be taking the lessons learned.
And I, I thought that was a, a very important discussion. The second one was on repairs. And what you see from the field, and I know Yolanda’s been looking at a lot of repairs. Well, all of you have been looking at repairs in Australia. What’s your feeling on sort of the repairs and the quality of repairs and the amount of data that comes along with it?
Are we at a place that we should be, or do we need a little more detail as to what’s happening out there? It’s one of the big challenges with the full service agreements is that, you know, if everything’s running smoothly, then repairs are getting done, but the information isn’t. Usually getting passed on.
And so it’s seems fine and it seems like really good actually. Probably if you’re an [00:16:00] asset manager and everything’s just being repaired without you ever knowing about it, perfect. But then at some point when something does happen, you’ve got no history and especially like even before handover. You need to know all of the repairs that have happened for, you know, for or exchanges for any components because you know, you’re worried about, um, serial defects, for example.
You need every single one. ’cause the threshold is quite high to, you know, ever reach a serial defect. So you wanna know if there were five before there was a handover. Include that in your population. Um, yeah, so that’s probably the biggest problem with repairs is that they’re just not being. Um, the reports aren’t being handed over.
You know, one of the things that Jeremy Hanks from C-I-C-N-D-T, and he’s an NDT expert and has, has seen about everything was saying, is that you really need to understand what’s happening deep inside the blade, particularly for inserts or, uh, at the root, uh, even up in, with some, some Cory interactions happening or splicing that It’s hard to [00:17:00] see that hard to just take a drone inspection and go, okay, I know what’s happening.
You need a little more technology in there at times, especially if you have a serial defect. Why do you have a serial defect? Do you need to be, uh, uh, scanning the, the blade a little more deeply, which hasn’t really happened too much in Australia, and I think there’s some issues I’ve seen where it may come into use.
Yeah, I think it, it, it’ll be coming soon. I know some people are bringing stuff in. I’ve got emails sitting in my inbox I need to chase up, but I’m, I’m really going to, to get more into that. Yeah. And John Zalar brought up a very similar, uh, note during his presentation. Go visit your turbines. Yeah, several people said that.
Um, actually Liz said that too. Love it. And, um, let’s this, yeah, you just gotta go have a look. Oh, Barend, I think said bar said it too. Go on site. Have a look at the lunchroom. If the lunch room’s tidy, then you know, win turbine’s gonna be tidy too. And I don’t know about that ’cause I’ve seen some tidy lunchroom that were associated with some, you know, uh, less well performing assets, but it’s, you know, it’s [00:18:00] a good start.
What are we gonna hope for in 2027? What should we. Be talking about it. What do you think we’ll be talking about a year from now? Well, a few people, quite a few people mentioned to me that they were here, they’re new in the industry, and they heard this was the event to go to. Um, and so I, I was always asking them was it okay?
’cause we pitch it quite technical and I definitely don’t wanna reduce. How technical it is. One thing I thought of was maybe we start with a two to five minute introduction, maybe prerecorded about the, the topic, just to know, like for example, um, we had some sessions on rotating equipment. Um, I’m a Blades person.
I don’t know that much about rotating equipment, so maybe, you know, we just explain this is where the pitch bearings are. They do this and you know, there’s the main bearing and it, you know, it does this and just a few minutes like that to orient people. Think that could be good. Last, uh, this year we did a, a masterclass on lightning, a half day masterclass.
Maybe we change that topic every year. Maybe next year it’s blade design, [00:19:00] certification, manufacturing. Um, and then, you know, the next year, whatever, open to suggestions. I mean, in general, we’re open to suggestions, right? Like people write in and, and tell us what you’d wanna see. Um, absolutely. I think we could focus more on technologies might be an, an area like.
It’s a bit, it’s a bit hard ’cause it gets salesy, but Yeah. I think one thing that could actually be interesting and that, uh, there was one guy came up with an older turbine on the LPS system. Mm. Where he wanted to look for a solution and some of the wind farms are getting older and it’s older technology.
So maybe having some, uh, uh, some sessions on that. Because the older turbines, they are vastly different from what we, what we see in the majority with wind farms today. But the maintenance of those are just as important. And if you do that correctly, they’re much easier to lifetime extent than it will likely be for some of the nuance.
But, you know, let. Knock on wood. Um, but, but I think that’s something that could be really interesting and really relevant for the industry and something [00:20:00] that we don’t talk enough about. Yeah. Yeah, that’s true because I, I’m working on a lot of old wind turbines now, and that has been, um, quite a challenge for me because they’re design and built in a way that’s quite different to when, you know, I was poking, designing and building, uh, wind turbine components.
So that’s a good one. Other people mentioned end of life. Mm-hmm. Not just like end of life, like the life is over, but how do you decide when the life end of life is going to be? ’cause you know, like you have a planned life and then you might like to extend, but then you discover you’ve got a serial issue.
Are you gonna fix it? Or you know, how are you gonna fix it? Those are all very interesting questions that, um, can occur. And then also, yeah, what to do with the. The stuff at the end of the Wind Farm lifetime, we could make a half day around those kinds of sessions. I think recycling could actually be good to, to also touch upon and, and I think, yeah, Australia is more on the front of that because of, of your high focus on, on nature and sustainability.
So looking at, well, what do we do with these blades? Or what do we do with the towers of foundation once, uh, [00:21:00] once we do need to decommission them, you know, what is, what are we going to do in Australia about that? Or what is Australia going to do about that? But, you know, what can we bring to the, to the table that that can help drive that discussion?
I think maybe too, helping people sort of templates for their formats on, on how to successfully shadow, monitor, maybe showing them a bit mute, more of, uh. Like cases and stuff, so to get them going a bit more. ’cause we heard a lot of people too say, oh, we’re, we’re teetering on whether we should self operate or whether we continue our FSA, but we, we we’re kind of, we don’t know what we’re doing.
Yeah. In, in not those words. Right. But just providing a bit more of a guidance too. On that side, we say shadow monitoring and I think we all know what it means. If you’ve seen it done, if you haven’t seen it done before. It seems daunting. Mm-hmm. What do you mean shadow monitoring? You mean you got a crack into the SCADA system?
Does that mean I’ve gotta, uh, put CMS out there? Do I do, do I have to be out [00:22:00] on site all the time? The answer that is no to all of those. But there are some fundamental things you do need to do to get to the shadow monitoring that feels good. And the easy one is if there’s drone inspections happening because your FSA, you find out who’s doing the drone inspections and you pay ’em for a second set of drone inspections, just so you have a validation of it, you can see it.
Those are really inexpensive ways to shadow monitor. Uh, but I, I do think we say a lot of terms like that in Australia because we’ve seen it done elsewhere that. Doesn’t really translate. And I, if I, I’m always kind of looking at Rosemary, like, does it, this make sense? What I’m saying makes sense, Rosemary, because it’s hard to tell because so many operators are in sort of a building mode.
I, I see it as. When I talked to them a few years ago, they’re completely FSA, they had really small staffs. Now the staffs are growing much larger, which makes me feel like they’re gonna transition out an FSA. Do we need to provide a little more, uh, insight into how that is done deeper. [00:23:00] Like, these are the tools you, you will need.
This is the kind of people you need to have on staff. This is how you’re gonna organize it, and this is the re these are the resources that you should go after. Mm. Does that make a little si more sense? Yeah. That might be a good. Uh, idea for getting somebody who’s, you know, working for a company that is shadow monitoring overseas and bring them in and they can talk through what that, what that means exactly.
And that goes back to the discussion we were having earlier today by having operators talk about how they’re running their operations. Mm. And I know the last year we tried to have everybody do that and, and they were standoffish. I get it. Because you don’t want to disclose things that your company doesn’t want out in public.
And year two, it felt like there’s a little more. Openness about that. Yeah, there was a few people were quite open about, um, yeah, talking about challenges and some successes as well. I think we’ll have more successes next year ’cause we’ve got more, more things going on. But yeah, definitely would encourage any operators to think about what’s a you A case study that you could give about?
Yeah, it could just be a problem that’s unsolved and I bet you’ll find people that wanna help you [00:24:00] solve that problem. Or it could be something that you struggled with and then you’re doing a better job and Yeah, I mean the. Some operators think that they’re in competition with each other and some think that they’re not really, and the answer is somewhere, somewhere in the middle.
There are, you know, some at least small amounts of competition. But, you know, I just, I just really think that. We’re fighting against each other, trying to win within the wind industry. Then, you know, in 10, 20 years time, especially in Australia, there won’t be any new wind. It’ll just be wind and solar everywhere and, and the energy transition stalled because everyone knows that’s not gonna get us all the way to, you know, a hundred percent renewables.
So, um, I do think that we need to, first of all, fight for wind energy to improve. The status quo is not good enough to take us through the next 20 years. So we do need to collaborate to get better. And then, yeah, I don’t know, once we’re, once we’re one, wind has won, then we can go back to fighting amongst ourselves, I guess.
Is Australia that [00:25:00] laboratory? Yeah, I think I, I say it all the time. I think Australia is the perfect place because I, I do think we’re a little bit more naturally collaborative. For some reason, I don’t know why, it’s not really like a, a cultural thing, but seems to be the case in Australian wind. Um, and also our, our problems are harder than, uh, than what’s being faced elsewhere.
I mean, America has some specific problems right now that are, you know, worse, but in general, operating environment is very harsh Here. We’re so spread out. Everything is so expensive. Cranes are so expensive. Repairs are so expensive. Spares spare. Yeah, spares are crazy expensive. You know, I look every now and then and do reports for people about, you know, what, what’s the average cost for and times for repairs and you know, you get an American values and it’s like, okay, well at a minimum times by five Australia and you know, so.
It, there’s a lot more bang for buck. And the other thing is we just do not have enough, um, enough people, enough. Uh, we’ve got some really smart people. We need a lot more [00:26:00] people that are as smart as that. And you can’t just get that immediately. Like there has been a lot of good transfer over from related industries.
A lot of people that spoke so that, you know, they used to work for thermal power plants and, um, railway, a guy that spoke to a guy had come in from railway. Um. That’s, that’s really good. But it will take some years to get them up to speed. And so in the meantime, we just need to use technology as much as we can to be able to, you know, make the people that good people that we do have, you know, make them go a lot further, um, increase what they can do.
’cause yeah, I don’t think there’s a single, um, asset owner where they couldn’t, you know, double the number of asset managers they had and, you know, ev everyone could use twice as many I think. Yeah, I agree. Yeah. I think something that we really focused on this year is kind of removing the stones that are in people’s path or like helping at least like to, to say like, don’t trip over there.
Don’t trip over here. And I think part of that, like, like you mentioned, is that. [00:27:00] The, the collaborative manner that everyone seemed to have and just, I think 50% of our time that we were in those rooms was just people asking questions to experts, to anybody they really wanted to. Um, and it, it just, everybody getting the same answers, which is really just a really different way to, to do things, I think.
But more than, I mean, we, we we’re still. We’re still struggling with quality in Australia. That’s still a major issue on, on a lot of the components. So until we have that solved, we don’t really know how much of an influence the other factors they really have because it just overshadows everything. And yes, it will be accelerated by extreme weather conditions, but.
What will, how will it work if, if the components are actually fit, uh, fit for purpose in the sense that we don’t have wrinkles in the laminates, that we don’t have, uh, bond lines that are detaching. Mm-hmm. Maybe some of it is because of, uh, mango size hails hitting the blades. Maybe it’s because of extreme temperatures.
Maybe it’s [00:28:00] because of, uh, uh, yeah. At extreme topography, you know, creating, uh, wind conditions that the blades are not designed for. We don’t really know that. We don’t really know for sure. Uh, we just assume, um, Australia has some problems with, not problems, but some challenges with remoteness. We don’t, with, uh, with getting new, new spares that much is absolutely true.
We can’t do anything about that. We just have to, uh, find a way to, to mitigate that. Mm-hmm. But I think we should really be focused on getting quality, uh, getting the quality in, in order. You know, one thing that’s interesting about that, um, so yeah, Australia should be focused more on quality than anybody else, but in, in, in the industry, yeah.
Uh, entire world should be more focused on quality, but also Australia. Yeah. But Australia, probably more than anyone considering how hard it is to, you know, make up for poor quality here. Um. At the same time, Australia for some reason, loves to be the first one with a new technology, loves to have the biggest [00:29:00] turbine.
Um, and the, the latest thing and the newest thing, and I thought it was interesting. I mean, this was operations and maintenance, um, conference, so not really talking about new designs and manufacturing too much, but at least three or four people said, uh. Uh, I would be using less carbon fiber in blades. I would not be, not be going bigger and bigger and bigger.
If I was buying turbines for a new wind farm, I would have, you know, small glass blades and just more of them. So I think that that was really interesting to hear. So many people say it, and I wasn’t even one of them, even though, you know, I would definitely. Say that. I mean, you know, in terms of business, I guess it’s really good to get a lot of, a lot of big blades, but, um, because they just, people, I don’t think people understand that, that bigger blades just have dramatically more quality problems than the smaller ones.
Um, were really kind of exceeded the sweet spot for the current manufacturing methods and materials. I don’t know if you would agree, but it’s, it’s. Possible, but [00:30:00] it’s, it, you know, it’s not like a blade that’s twice as long, doesn’t have twice as many defects. It probably has a hundred times as many defects.
It’s just, uh, it’s really, really challenging to make those big blades, high quality, and no one is doing it all that well right now. I would, however, I got an interesting hypothetical and they’re. Congrats to her for, for putting out that out. But there was an operator that said to me at the conference, so what would you choose hypothetically?
A 70 meter glass fiber blade or a 50 meter carbon fiber blade, so a blade with carbon fiber reinforcement. And I did have to think quite a while about it because there was, it was she say, longer blades, more problems, but carbon blade. Also a lot of new problems. So, so what is it? So I, I ended up saying, well, glass fiber, I would probably go for a longer glass fiber blade, even though it will have some, some different challenges.
It’s easier to repair. Yeah, that’s true. So we can overcome some of the challenges that are, we can also repair carbon. We have done it in air, air, uh, aeronautics for many, many years. But wind is a different beast because we don’t have, uh, [00:31:00] perfect laboratory conditions to repair in. So that would just be a, a really extreme challenge.
So that’s, that’s why I, I would have gone for carbon if, for glass fiber, if, if I, if I could in that hypothe hypothetical. Also makes more energy, the 70 meter compared to it’s a win-win situation.
Well, it’s great to see all of you. Australia. I thought it was a really good conference. And thanks to all our sponsors, uh, til being the primary sponsor for this conference. Uh, we are starting to ramp up for 2027. Hopefully all of you can attend next year. And, uh, Rosie, it’s good to see you in person. Oh, it’s, uh, it’s, it’s exciting when we are actually on the same continent.
Uh, it doesn’t happen very often. And Morton, it’s great to see you too, Yolanda. I see you every day pretty much. So she’s part of our team, so I, it’s great to see you out. This is actually the first time, me and Rosie, we have seen each other. We’ve, we’ve known each other for years. Yeah. Yeah. The first time we actually, uh, been, been, yeah.
Within, uh, yeah. [00:32:00] Same room. Yep. And same continent. Yeah. Yeah. So that’s been awesome. And also it’s my first time meeting Yolanda in person too. So yeah, that’s our first time. And same. So thanks so much for everybody that attended, uh, woma 2026. We’ll see you at Woma 2027 and uh, check us out next week for the Uptime Wind Energy Podcast.
Renewable Energy
What Can Stop Climate Change?
 I looked through a few of the many thousands of responses to the question above on social media and have concluded:
I looked through a few of the many thousands of responses to the question above on social media and have concluded:
If you ask uneducated people who know essentially nothing about global warming, you’ll find that nothing can stop it, because it’s been going on since the origin of the planet. Others say that God controls the planet’s temperature.
If you ask climate scientists who work in laboratories around the globe who have been studying this subject for decades, you’ll find that there are two key answers: a) decarbonization of our transportation and energy sectors and b) halting the destruction of our rain forests.
As always, we have a choice to make: ignorance or science.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits