When I think about climate change nowadays, I think about how the places I consider home have changed, are changing, and will continue to change.
I think about how the things I enjoy can cease to exist. As someone who immigrated to Canada from the Philippines, I call those two countries my home; both have honed me into who I am today– from the culture I grew up with to the community I belong to. Given climate change’s dire impacts, I can’t help but feel anxious about how those places are also rapidly changing. I can see it right before my eyes: from the warmer summers and more intense typhoons in the Philippines to the warmer and shorter winters in Winnipeg, it feels odd and frightening to experience those changes instantly.
I grew up in the Philippines and as a child, my parents always made sure that we had food on the table and taught us to save up and be thrifty. My parents also taught me to refrain from littering anywhere and to throw away my garbage properly. However, prioritizing the environment was not at the top of the list and something as seemingly simple as recycling is not something that is emphasized. Flooding is common whenever it rains, which often means trash will flow from one place to another because even though I try to be mindful of my trash, others will leave trash in the streets. A lot of our rivers are known for water and plastic pollution. There weren’t a lot of trees and parks around in larger cities for people to enjoy. As a kid, all of these seemed expected in my environment.
When I moved to Canada in 2013 and began navigating a new environment, I realized I had to unlearn what I deemed typical back in the Philippines. One thing that stood out for me during my first year in Canada was how everywhere I went, there was a garbage and recycling bin. I only learned how to recycle properly when I moved to Canada. I thought, “If only the Philippines could have the same system, there would probably be less trash going to the rivers and streets.”
Despite this new recycling knowledge, my climate journey wouldn’t truly start until much later.
My climate journey began not too long ago. In fact, it only started in 2022 when I landed my current role at the Manitoba Museum as their Learning and Engagement Producer for Youth Climate Action. I knew what climate change and global warming were, but my understanding of those topics needed work. I remember when I interviewed at the museum, they asked me about eco-anxiety and I had no idea what that was. I knew what anxiety meant, but eco-anxiety? It was my first time hearing that term.


I was fortunate to get the job; I made sure to research, take notes, and deepen my understanding of climate change and its impacts. I didn’t have any formal education in the environment and sustainability discipline; all I had was my background in science, my strong interest in working with youth, and my determination to learn more about climate change and make an impact through my job.
My work at the museum has allowed me to gain a deeper understanding of the environment around me. I’ve learned to appreciate the many wonderful things that Mother Nature does for us. I have become more conscious of my actions and decisions that will impact the environment – in short, I have to walk the talk.
My role at the museum has also taught me the importance of climate education and having resources everyone can access.
For example, I run a group called Youth Climate Alliance at the Manitoba Museum. The program aims to give youth ages 14 – 18 a platform to pursue their climate change advocacy and to learn more about climate change and its impacts. Working with youth never fails to inspire me. I feel hopeful about the future because I can see how there are people out there who can come together and make the world a better place.
As I write this, I can’t help but reflect on how far I’ve come when it comes to my climate journey and how much more I need to learn and improve. There’s a phrase in Tagalog that goes “Malayo pa, pero malayo na” or in English, “Still a long way to go but have already gone a long way”- this is how I would summarize my climate story. There is still so much that I need to learn and unlearn about climate change and its impacts, and climate action, but I know that Mika a year and a half ago would be so proud of who she is today.

My name is Mika Pineda, and I am currently working at the Manitoba Museum as a Learning and Engagement producer for Youth Climate Action. I create and develop programming related to climate change for youth (K-12). Through the programs I develop, I hope to educate Manitoban youth about climate change and its impacts because it is such an important issue right now.
The post Malayo pa, pero malayo na (Still a long way to go, but have already gone a long way) appeared first on Climate Generation.
Malayo pa, pero malayo na (Still a long way to go, but have already gone a long way)
Climate Change
War in Iran Could Have ‘Historic’ Disruptions on Energy Markets
Oil prices jumped after the United States and Israel attacked Iran. Experts say the effects on oil and gas prices will depend on how long the war lasts and whether Iran damages energy infrastructure.
The U.S. and Israeli war against Iran is disrupting energy markets and driving oil and gas prices higher in the United States and globally. While those increases are modest so far, experts say the war has the potential to cause more severe and lasting impacts if Iran damages the region’s energy infrastructure or restricts shipping through the Strait of Hormuz.
War in Iran Could Have ‘Historic’ Disruptions on Energy Markets
Climate Change
Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting
Half of nations have met a UN deadline to report on how they are tackling nature loss within their borders, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
This includes 11 of the 17 “megadiverse nations”, countries that account for 70% of Earth’s biodiversity.
It also includes all of the G7 nations apart from the US, which is not part of the world’s nature treaty.
All 196 countries that are part of the UN biodiversity treaty were due to submit their seventh “national reports” by 28 February, of which 98 have done so.
Their submissions are supposed to provide key information for an upcoming global report on actions to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030, in addition to a global review of progress due to be conducted by countries at the COP17 nature summit in Armenia in October this year.
At biodiversity talks in Rome in February, UN officials said that national reports submitted late will not be included in the global report due to a lack of time, but could still be considered in the global review.
Tracking nature action
In 2022, nations signed a landmark deal to halt and reverse nature loss by 2030, known as the “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF).
In an effort to make sure countries take action at the domestic level, the GBF included an “implementation schedule”, involving the publishing of new national plans in 2024 and new national reports in 2026.
The two sets of documents were to inform both a global report and a global review, to be conducted by countries at COP17 in Armenia later this year. (This schedule mirrors the one set out for tackling climate change under the Paris Agreement.)
The deadline for nations’ seventh national reports, which contain information on their progress towards meeting the 23 targets of the GBF based on a set of key indicators, was 28 February 2026.
According to Carbon Brief’s analysis of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity’s online reporting platform, 98 out of the 196 countries that are part of the nature convention (50%) submitted on time.
The map below shows countries that submitted their seventh national reports by the UN’s deadline.
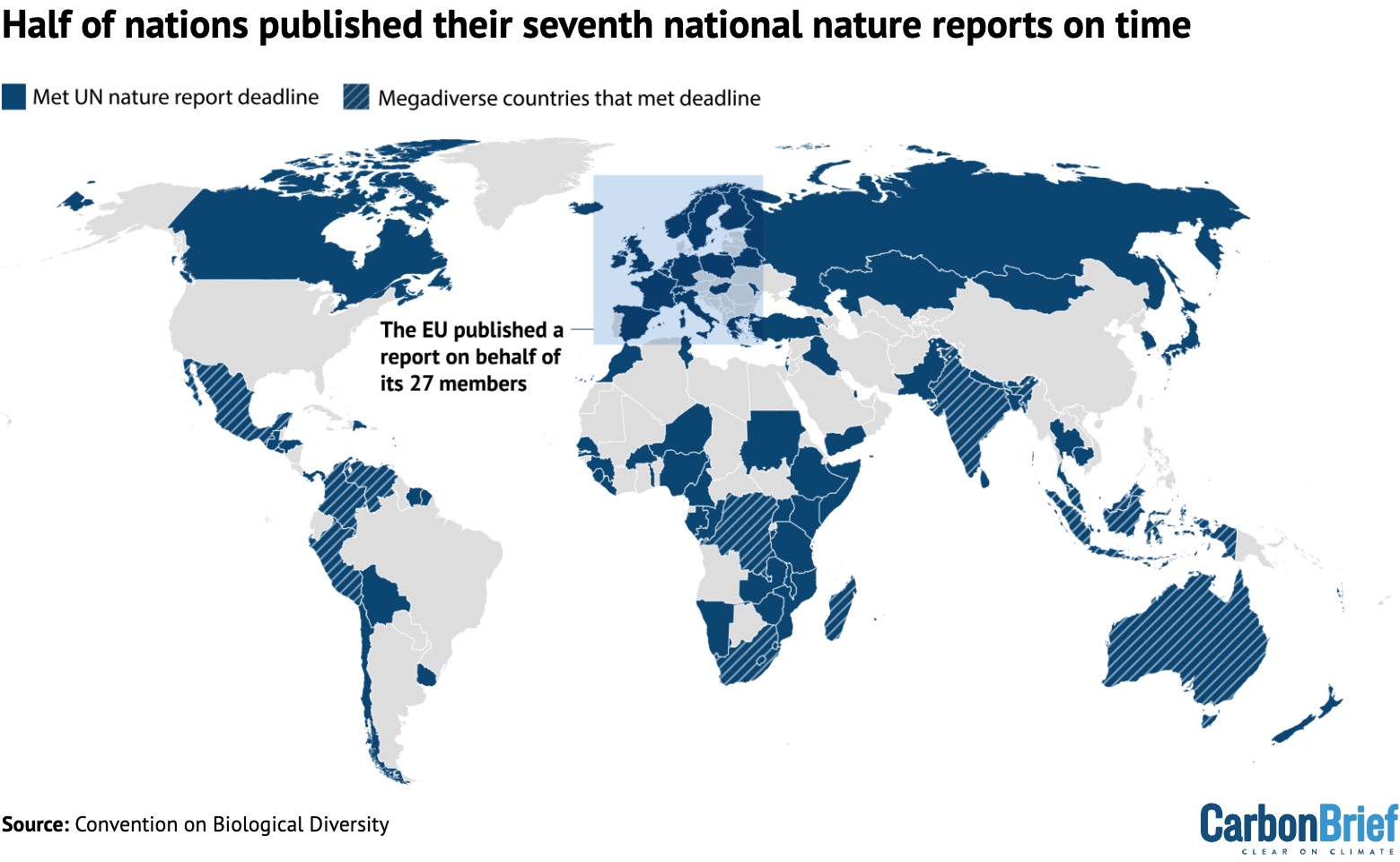
This includes 11 of the 17 “megadiverse nations” that account for 70% of Earth’s biodiversity.
The megadiverse nations to meet the deadline were India, Venezuela, Indonesia, Madagascar, Peru, Malaysia, South Africa, Colombia, Mexico, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Australia.
It also includes all of the G7 nations (France, Germany, the UK, Japan, Italy and Canada), excluding the US, which has never ratified the Convention on Biological Diversity.
The UK’s seventh national report shows that it is currently on track to meet just three of the GBF’s 23 targets.
This is according to a LinkedIn post from Dr David Cooper, former executive secretary of the CBD and current chair of the UK’s Joint Nature Conservation Committee, which coordinated the UK’s seventh national report,
The report shows the UK is not on track to meet one of the headline targets of the GBF, which is to protect 30% of land and sea for nature by 2030.
It reports that the proportion of land protected for nature is 7% in England, 18% in Scotland and 9% in Northern Ireland. (The figure is not given for Wales.)
National plans
In addition to the national reports, the upcoming global report and review will draw on countries’ national plans.
Countries were meant to have submitted their new national plans, known as “national biodiversity strategies and action plans” (NBSAPs), by the start of COP16 in October 2024.
A joint investigation by Carbon Brief and the Guardian found that only 15% of member countries met that deadline.
Since then, the percentage of countries that have submitted a new NBSAP has risen to 39%.
According to the GBF and its underlying documents, countries that were “not in a position” to meet the deadline to submit NBSAPs ahead of COP16 were requested to instead submit national targets. These submissions simply list biodiversity targets that countries will aim for, without an accompanying plan for how they will be achieved.
As of 2 March, 78% of nations had submitted national targets.
At biodiversity talks in Rome in February, UN officials said that national reports submitted late will not be included in the global report due to a lack of time, but could still be considered in the global review.
Funding ‘delays’
At the Rome talks, some countries raised that they had faced “difficulties in submitting [their national reports] on time”, according to the Earth Negotiations Bulletin.
Speaking on behalf of “many” countries, Fiji said that there had been “technical and financial constraints faced by parties” in the preparation of their seventh national reports.
In a statement to Carbon Brief, a spokesperson for the Global Environment Facility, the body in charge of providing financial and technical assistance to countries for the preparation of their national reports, said “delays in fund disbursement have occurred in some cases”, adding:
“In 2023, the GEF council approved support for the development of NBSAPs and the seventh national reports for all 139 eligible countries that requested assistance. This includes national grants of up to $450,000 per country and $6m in global technical assistance delivered through the UN Development Programme and UN Environment Programme.
“As of the end of January 2026, all 139 participating countries had benefited from technical assistance and 93% had accessed their national grants, with 11 countries yet to receive their funds. Delays in fund disbursement have occurred in some cases, compounded by procurement challenges and limited availability of technical expertise.”
The spokesperson added that the fund will “continue to engage closely with agencies and countries to support timely completion of NBSAPs and the seventh national reports”.
The post Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting
Climate Change
Dow Asks Texas to Legalize Plastic Pollution from its Seadrift Complex
Facing multiple lawsuits, Dow requests an “unprecedented” permit amendment to authorize its discharge of polyethylene pellets into coastal waters.
Two weeks ago, when Texas sued a massive Dow petrochemical plant over water pollution, state environmental regulators were already considering a novel proposal from the company that would effectively legalize discharges of plastic material from the 4,700–acre complex into waters feeding San Antonio Bay and the Gulf of Mexico.
Dow Asks Texas to Legalize Plastic Pollution from its Seadrift Complex
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits







