The Green Energy Evolution in Asia: A Landscape Defined by Growth and Transformation
Across the vast and diverse continent of Asia, a revolution is brewing – a shift towards a cleaner, greener future powered by renewable energy.
From the towering wind turbines dotting China’s plains to the sprawling solar farms gracing India’s deserts, a new energy landscape is taking shape. This article delves into the exciting developments, persistent challenges, and promising outlook of the Asian Green Energy Landscape.
A Region on the Rise:
- Installed Capacity Soars: Asia boasts over 1,400 Gigawatts of renewable energy capacity, leading the global charge with a staggering 60% share. China stands tall as the champion, followed by India, Japan, and Vietnam, showcasing a region united in its renewable ambitions.
- Energy Mix Transformation: While renewables fuel optimism, coal remains the dominant player, contributing to around 70% of the energy mix. This highlights the critical need for further diversification and a concerted push towards greener sources.
- Investment Boom Fuels Change: Driven by climate targets and economic potential, investments in Asian renewable energy projects have skyrocketed, reaching a record high in recent years. Solar and wind, with their declining costs and increasing efficiency, attract the lion’s share of these investments.
Drivers and Trends Shaping the Future:
- Ambitious Climate Goals: Countries across Asia, from China’s pledge to peak emissions by 2030 to India’s 40% renewable target by 2030, demonstrate a shared commitment to combating climate change, propelling the shift towards renewables.
- Technological Advancements: Cost reductions and efficiency improvements in solar, wind, and other renewable technologies have made them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels, paving the way for broader adoption.
- Economic Opportunities Beckon: Green energy represents a significant economic engine for Asian nations, attracting investments, creating jobs, and fostering innovation, further fueling the renewable energy push.
Challenges and Hurdles on the Path to Sustainability:
- Grid Integration Hinders Progress: Integrating large-scale renewable energy into existing grids poses a formidable challenge, requiring infrastructure upgrades and smart grid technologies to ensure seamless integration.
- Financing Needs Remain: Despite the investment boom, securing long-term financing for renewable energy projects, particularly in developing countries, remains a hurdle that needs to be addressed.
- Policy Inconsistencies Create Uncertainty: Clear and consistent policies are crucial for long-term investor confidence and sustained renewable energy growth. Inconsistencies can create uncertainty and hinder progress.
Regional Variations: A Diverse Landscape
While the overall picture paints a promising future, the green energy landscape within Asia exhibits significant regional variations:
- China: The global leader in renewable capacity, China grapples with grid integration challenges and rural electrification needs.
- India: Rapidly expanding its renewable sector, India must address financing gaps and improve grid infrastructure.
- Southeast Asia: This region boasts diverse renewable potential, with solar and hydropower playing key roles in its green energy journey.
A Look Ahead: The Promise of a Green Future
Despite the challenges, the future of green energy in Asia holds immense promise. Key factors driving optimism include:
- Continued cost reductions in renewable technologies
- Strong government commitment to climate goals
- Growing public support for clean energy
- Emergence of innovative financing mechanisms
As the region continues to innovate, collaborate, and address existing challenges, its green energy journey will be a defining chapter in the global transition towards a sustainable energy future. This is just a glimpse into the complex and dynamic world of Asian Green Energy.
Total Green Energy Consumption from Renewables and Growth in Asia
Percentage of Total Green Energy Consumption:
As of 2018, the share of modern renewable energy in Asia’s total final energy consumption was 8.5%. However, this number varies significantly across different countries and regions:
- East Asia: 14.81% (led by China with 16.8%)
- Southeast Asia: 4.1% (with significant variation among countries)
- South Asia: 11.4% (led by India with 14.8%)
It’s important to note that this excludes traditional biomass, which constitutes a larger share in some rural areas.
Growth in Renewable Energy Consumption:
The growth rate of renewable energy consumption in Asia is impressive:
- Between 2010 and 2020: average annual growth rate of 8.4%, compared to global average of 6.5%.
- Between 2020 and 2021: growth of 10.3%, despite the pandemic, exceeding the global average of 9.2%.
Regional variations:
- China: leads the region with the highest absolute growth due to its massive scale and ambitious targets.
- India: experiencing rapid growth, driven by government initiatives and falling solar costs.
- Southeast Asia: showing potential with diverse resources and increasing investments.
Looking Ahead:
- Projections suggest continued growth, possibly reaching 24% of total final energy consumption by 2030.
- This will depend on factors like continued policy support, technological advancements, and grid infrastructure development.
Green Energy Consumption and Growth in Asia
Green Energy Consumption and Growth in Asia: Table Summary
| Region | Share of Modern Renewables in 2018 (%) | Average Annual Growth (2010-2020) | Growth in 2021 (%) | Projected Share in 2030 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| East Asia | 14.81 | 8.9% | 11.2% | 27.5% |
| *** China** | 16.8 | 9.5% | 11.8% | 29.0% |
| Southeast Asia | 4.1 | 7.1% | 8.2% | 15.0% |
| South Asia | 11.4 | 7.8% | 9.7% | 22.0% |
| *** India** | 14.8 | 14.7% | 18.5% | 28.0% |
| Total Asia | 8.5 | 8.4% | 10.3% | 24.0% |
Notes:
- Modern renewables exclude traditional biomass used in rural areas.
- Projected share in 2030 is based on various estimations and may vary depending on future developments.
- Specific countries like China and India are highlighted due to their significant contribution and growth within their respective regions.
Future of Green Energy in Asia
The future of green energy in Asia is very promising, driven by several key factors:
Strong Growth Momentum:
- Asia is already the world leader in renewable energy investment and capacity, and this trend is expected to continue.
- China and India are expected to remain major drivers, with ambitious targets for increasing renewables penetration.
- Southeast Asia holds vast potential for solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower development.
Technological Advancements:
- Cost reductions in solar, wind, and battery storage technologies are making renewables increasingly competitive with fossil fuels.
- Innovations in grid integration, smart grids, and microgrids are improving the reliability and flexibility of renewable energy systems.
- Emerging technologies like offshore wind and green hydrogen offer further potential for decarbonization.
Supportive Policies:
- Many Asian governments have set ambitious renewable energy targets and are implementing supportive policies such as feed-in tariffs, auctions, and renewable energy zones.
- Regional cooperation initiatives are also fostering knowledge sharing and technology transfer.
- Growing public awareness and demand for clean energy are putting further pressure on policymakers to prioritize renewables.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Grid integration, financing, and land use remain key challenges that need to be addressed.
- Promoting innovation and developing domestic manufacturing capabilities for renewable energy technologies are crucial.
- Ensuring a just transition for workers in the fossil fuel sector is important to garner wider public support.
Potential Impacts:
- A successful green energy transition in Asia could bring numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality.
- Enhanced energy security and reduced dependence on fossil fuel imports.
- Creation of new jobs in the green energy sector.
- Economic growth and development opportunities.
However, achieving these goals requires significant investments, policy reforms, and technological advancements.
Overall, the future of green energy in Asia is bright, with the potential to transform the region’s energy landscape and contribute significantly to global climate goals. However, overcoming existing challenges and ensuring a just transition will be crucial for success.
https://www.exaputra.com/2024/02/green-energy-lansdcape-in-asia.html
Renewable Energy
Do We Need More Fallacious Hate Speech?
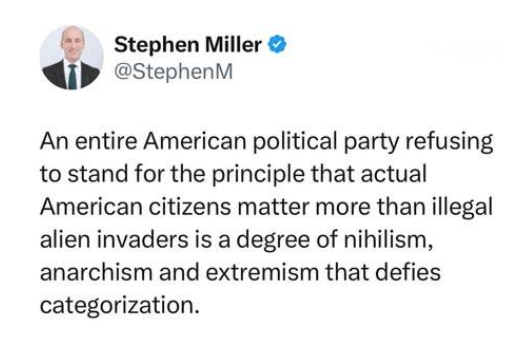 Unfortunately, there are tens of millions of morons who believe hateful garage like this.
Unfortunately, there are tens of millions of morons who believe hateful garage like this.
The average 10-year-old can understand that we can BOTH protect our citizens while obeying the U.S. Constitution and international law when it comes to treating the undocumented legally and humanely.
Again, this is what is called the logical fallacy of the “false dichotomy.” Only idiots believe we have to choose one over the other.
Renewable Energy
A Reader Asks: Should Energy Companies be Held Liable for Climate Change?
 I would say that the regulations on energy (and transportation) companies should be sufficient to put pressure on them to phase out fossil fuels and decarbonize in favor of renewables and nuclear.
I would say that the regulations on energy (and transportation) companies should be sufficient to put pressure on them to phase out fossil fuels and decarbonize in favor of renewables and nuclear.
A Reader Asks: Should Energy Companies be Held Liable for Climate Change?
Renewable Energy
In the U.S., We Live Among Experts
 One might think that being surrounded by experts would be eutopia, but it’s not everything it’s cracked up to be.
One might think that being surrounded by experts would be eutopia, but it’s not everything it’s cracked up to be.
At left is an expression of what life in the United States has become over the last decade, which differs greatly from the experiences of those in the rest of the world.
Trump supporters have, at various times, been experts in macroeconomics, epidemiology, and above all, climate science.
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits













