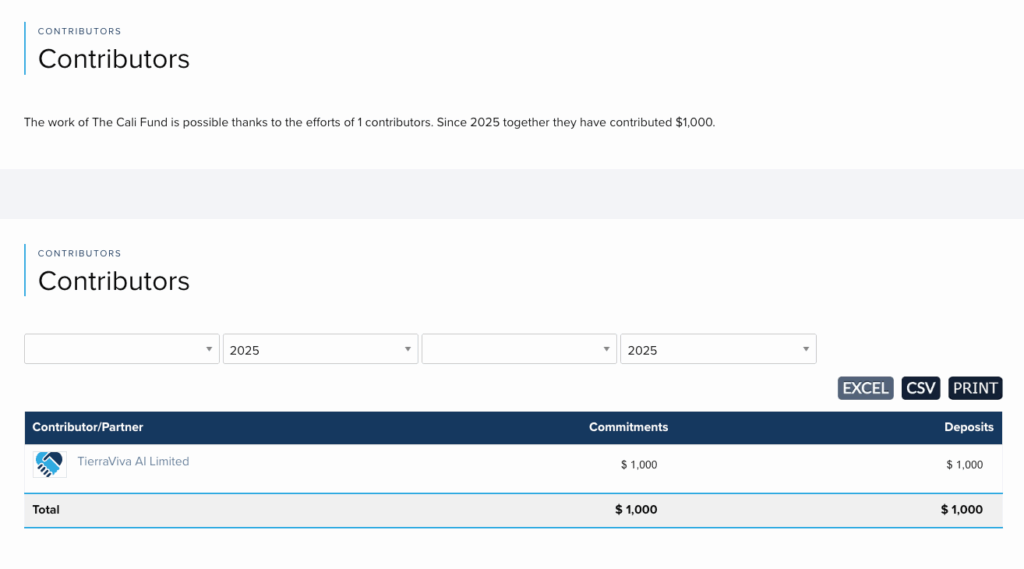
A major biodiversity fund – which could, in theory, generate billions of dollars annually for conservation – received its first donation of just $1,000 in November.
The Cali Fund was created under the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) at the COP16 nature negotiations in Cali, Colombia, last year.
On 19 November, nine months after the fund officially launched, UK start-up TierraViva AI put forward the first contribution.
The $1,000 payment is an “ice-breaker”, the company’s chief executive tells Carbon Brief, aimed at encouraging others “who may be hesitating” to pay in.
The fund is designed to be a way for companies that rely on nature’s genetic resources to share some of their earnings with the developing, biodiverse countries where many of the original resources are found.
Companies use genetic data from these materials to develop products, such as vaccines and skin cream.
One expert describes the $1,000 as a good “first step”, but says it is “time for larger actors to step forward”. Another says it “squarely points the finger to the profit-making enterprises that are not contributing”.
The CBD is “pleased” about the first payment, a spokesperson tells Carbon Brief, adding that “many discussions” are ongoing about future donations.
Funding biodiversity action
Companies all around the world use genetic materials from plants, animals, bacteria and fungi often found in biodiversity-rich, global south countries to develop their products.
There are existing rules in place to secure consent and ensure compensation if companies or researchers travel to a country to physically gather these materials.
Today, however, much of this information is available in online databases – with few rules in place around access. This genetic data is known as digital sequence information (DSI).
The Cali Fund is part of an effort to close this loophole.
The COP16 agreement on the creation of the fund outlined that large companies in several sectors, including pharmaceutical, cosmetic, biotechnology, agribusiness and technology, “should” contribute a cut of the money they earn from the use of these materials. (See: Carbon Brief’s infographic on DSI.)
The money is intended to fund biodiversity action, with 50% of resources going to Indigenous peoples and local communities who protect vast swathes of the world’s nature and biodiversity.
These contributions, however, are voluntary.
The fund officially launched at the resumed COP16 negotiations in Rome in February 2025, where a spokesperson for the CBD said that first contributions could be announced in spring.
However, Carbon Brief reported in August that the fund was still empty.
On 19 November, the first contribution was announced during the COP30 UN climate summit. At $1,000, the amount was significantly lower than the potential millions that larger companies could pay in.
A UK government press release described it as a “major milestone” that will “pav[e] the way for others to do the same and mobilise private sector finance for nature at scale”.
The payment was an “expression of our commitment to the objectives of the Cali Fund”, TierraViva AI chief executive Dr Paul Oldham wrote in a letter to the executive secretary of the CBD, Astrid Schomaker.
The $1,000 is an “initial contribution”, Oldham said, and the company plans to give more “as our business grows”. Based in the UK with a team of programmers in Nairobi, TierraViva AI was set up in 2023 and uses AI to support conservation.
An anthropologist who worked on Indigenous peoples’ rights in the Amazon, Oldham’s research helped inform the list of sectors most likely to “directly or indirectly benefit from the use of DSI”, including “generative biology” and AI companies.
Oldham noted in a speech at the sidelines of COP30 that although the company’s earnings are not large enough to meet the contribution thresholds set out in the Cali Fund agreement, its contribution showed that companies “of any size” can pay in.

He tells Carbon Brief that while “some” companies “are not serious about contributing and are seeking to delay” paying into the fund, others have different concerns, including the “need for a level playing field” and positive incentives to contribute:
“This will be hard-earned company money, so it’s reasonable enough to imagine that one of the first questions companies will want an answer to is: ‘well, what is this actually going to be spent on?’ And: ‘what is the benefit of this to us’, which is likely to vary by sector.
“In my view, the best way forward would be for companies that can to make contributions. That would give everybody, including governments, confidence that there might be constructive ways to address difficult topics.”
Future contributions
A spokesperson for the CBD tells Carbon Brief:
“We are pleased that the Cali Fund is not only ‘open for business’, but that this first contribution also demonstrates it is fully operational. We thank and congratulate TierraViva AI for being the first company to step up.”
“Many discussions” are ongoing around future donations to the fund, the spokesperson says, and the CBD is “hopeful that further announcements can be made soon”, ahead of the next UN biodiversity summit, COP17, in October 2026.
Asked whether the CBD was expecting more contributions at this stage, the spokesperson says the fund was set up in “very short order” and that the first payment shows that companies are “able to contribute”.
US biotechnology company Ginkgo Bioworks was the first to pledge to contribute to the fund earlier this year, but has so far not put forward any money. The company did not respond to Carbon Brief’s request for comment.
Carbon Brief reported earlier this year that at least two companies were contacted by a UK department with opportunities to be involved in the Cali Fund before its launch in February, but no company took up on the offer.

The first contribution coming from a “startup that has just begun operations squarely points the finger to the profit-making enterprises that are not contributing”, Dr Siva Thambisetty, associate professor of law at the London School of Economics, tells Carbon Brief. Thambisetty adds:
“Strident cries of lack of legal certainty, unfairness or stacking obligations [combining responsibilities from different agreements and laws] would be more credible if industry organisations encouraged large firms that use DSI to begin contributing, instead of denying the last 20 years of multilateral [negotiations] that have led to this point.”
Dr June Rubis – Indigenous peoples and local communities (IPLC) lead from Asia on the Cali Fund’s steering committee – welcomes TierraViva AI’s “first step”, but tells Carbon Brief that the “real test lies ahead” and that it is “now time for larger actors to step forward”.
She says the Cali Fund offers “clarity” on how the private sector can directly increase support to UN-backed funds at a time when “states are retreating” from their climate and biodiversity finance obligations:
“It’s not a voluntary offsetting scheme or a…risky or fringe fund; it’s a multilateral mechanism designed to meet the highest fiduciary and equity standards. We invite companies to see this not as philanthropy, but as participation in a globally endorsed system where trust is institutionalised, benefits are traceable and equity is operationalised.
“Contributing to the Cali Fund isn’t just ethical, it’s strategic. [But] It’s about more than funding: it’s about trust, power-sharing and making sure IPLCs are part of the decisions, not just the outcomes.”
The post ‘Cali Fund’ aiming to raise billions for nature receives first donation – of just $1,000 appeared first on Carbon Brief.
‘Cali Fund’ aiming to raise billions for nature receives first donation – of just $1,000
Climate Change
Environmental Groups Challenge Air Permit for Natural Gas Expansion at Atlanta Plant
The Sierra Club and Southern Environmental Law Center are suing over state regulators’ approval of new gas turbines at Plant Bowen, citing concerns about worsening air quality.
Atlanta has spent decades battling smog and air pollution. Now, state regulators have cleared the way for a major natural gas expansion at Georgia Power’s Plant Bowen, a massive coal-fired power plant roughly 40 miles northwest of downtown that could add hundreds of tons of new air pollution each year to a region already struggling with unhealthy air.
Environmental Groups Challenge Air Permit for Natural Gas Expansion at Atlanta Plant
Climate Change
War in Iran Could Have ‘Historic’ Disruptions on Energy Markets
Oil prices jumped after the United States and Israel attacked Iran. Experts say the effects on oil and gas prices will depend on how long the war lasts and whether Iran damages energy infrastructure.
The U.S. and Israeli war against Iran is disrupting energy markets and driving oil and gas prices higher in the United States and globally. While those increases are modest so far, experts say the war has the potential to cause more severe and lasting impacts if Iran damages the region’s energy infrastructure or restricts shipping through the Strait of Hormuz.
War in Iran Could Have ‘Historic’ Disruptions on Energy Markets
Climate Change
Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting
Half of nations have met a UN deadline to report on how they are tackling nature loss within their borders, Carbon Brief analysis shows.
This includes 11 of the 17 “megadiverse nations”, countries that account for 70% of Earth’s biodiversity.
It also includes all of the G7 nations apart from the US, which is not part of the world’s nature treaty.
All 196 countries that are part of the UN biodiversity treaty were due to submit their seventh “national reports” by 28 February, of which 98 have done so.
Their submissions are supposed to provide key information for an upcoming global report on actions to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030, in addition to a global review of progress due to be conducted by countries at the COP17 nature summit in Armenia in October this year.
At biodiversity talks in Rome in February, UN officials said that national reports submitted late will not be included in the global report due to a lack of time, but could still be considered in the global review.
Tracking nature action
In 2022, nations signed a landmark deal to halt and reverse nature loss by 2030, known as the “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework” (GBF).
In an effort to make sure countries take action at the domestic level, the GBF included an “implementation schedule”, involving the publishing of new national plans in 2024 and new national reports in 2026.
The two sets of documents were to inform both a global report and a global review, to be conducted by countries at COP17 in Armenia later this year. (This schedule mirrors the one set out for tackling climate change under the Paris Agreement.)
The deadline for nations’ seventh national reports, which contain information on their progress towards meeting the 23 targets of the GBF based on a set of key indicators, was 28 February 2026.
According to Carbon Brief’s analysis of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity’s online reporting platform, 98 out of the 196 countries that are part of the nature convention (50%) submitted on time.
The map below shows countries that submitted their seventh national reports by the UN’s deadline.
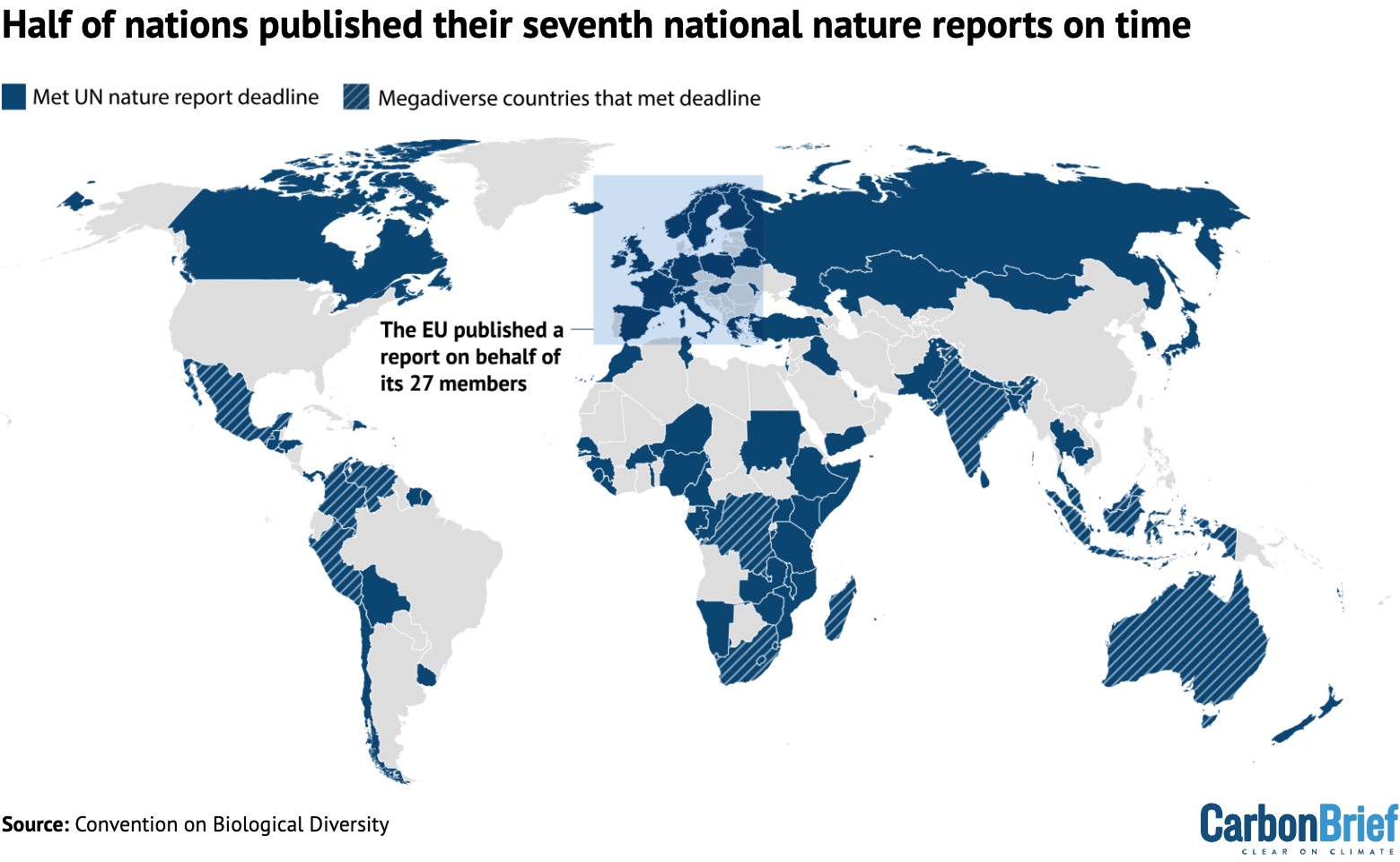
This includes 11 of the 17 “megadiverse nations” that account for 70% of Earth’s biodiversity.
The megadiverse nations to meet the deadline were India, Venezuela, Indonesia, Madagascar, Peru, Malaysia, South Africa, Colombia, Mexico, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Australia.
It also includes all of the G7 nations (France, Germany, the UK, Japan, Italy and Canada), excluding the US, which has never ratified the Convention on Biological Diversity.
The UK’s seventh national report shows that it is currently on track to meet just three of the GBF’s 23 targets.
This is according to a LinkedIn post from Dr David Cooper, former executive secretary of the CBD and current chair of the UK’s Joint Nature Conservation Committee, which coordinated the UK’s seventh national report,
The report shows the UK is not on track to meet one of the headline targets of the GBF, which is to protect 30% of land and sea for nature by 2030.
It reports that the proportion of land protected for nature is 7% in England, 18% in Scotland and 9% in Northern Ireland. (The figure is not given for Wales.)
National plans
In addition to the national reports, the upcoming global report and review will draw on countries’ national plans.
Countries were meant to have submitted their new national plans, known as “national biodiversity strategies and action plans” (NBSAPs), by the start of COP16 in October 2024.
A joint investigation by Carbon Brief and the Guardian found that only 15% of member countries met that deadline.
Since then, the percentage of countries that have submitted a new NBSAP has risen to 39%.
According to the GBF and its underlying documents, countries that were “not in a position” to meet the deadline to submit NBSAPs ahead of COP16 were requested to instead submit national targets. These submissions simply list biodiversity targets that countries will aim for, without an accompanying plan for how they will be achieved.
As of 2 March, 78% of nations had submitted national targets.
At biodiversity talks in Rome in February, UN officials said that national reports submitted late will not be included in the global report due to a lack of time, but could still be considered in the global review.
Funding ‘delays’
At the Rome talks, some countries raised that they had faced “difficulties in submitting [their national reports] on time”, according to the Earth Negotiations Bulletin.
Speaking on behalf of “many” countries, Fiji said that there had been “technical and financial constraints faced by parties” in the preparation of their seventh national reports.
In a statement to Carbon Brief, a spokesperson for the Global Environment Facility, the body in charge of providing financial and technical assistance to countries for the preparation of their national reports, said “delays in fund disbursement have occurred in some cases”, adding:
“In 2023, the GEF council approved support for the development of NBSAPs and the seventh national reports for all 139 eligible countries that requested assistance. This includes national grants of up to $450,000 per country and $6m in global technical assistance delivered through the UN Development Programme and UN Environment Programme.
“As of the end of January 2026, all 139 participating countries had benefited from technical assistance and 93% had accessed their national grants, with 11 countries yet to receive their funds. Delays in fund disbursement have occurred in some cases, compounded by procurement challenges and limited availability of technical expertise.”
The spokesperson added that the fund will “continue to engage closely with agencies and countries to support timely completion of NBSAPs and the seventh national reports”.
The post Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting appeared first on Carbon Brief.
Analysis: Half of nations meet UN deadline for nature-loss reporting
-
Greenhouse Gases7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-
Climate Change7 months ago
Guest post: Why China is still building new coal – and when it might stop
-

 Greenhouse Gases2 years ago
Greenhouse Gases2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Bill Discounting Climate Change in Florida’s Energy Policy Awaits DeSantis’ Approval
-
Climate Change2 years ago
Spanish-language misinformation on renewable energy spreads online, report shows
-

 Climate Change2 years ago
Climate Change2 years ago嘉宾来稿:满足中国增长的用电需求 光伏加储能“比新建煤电更实惠”
-
Climate Change Videos2 years ago
The toxic gas flares fuelling Nigeria’s climate change – BBC News
-

 Carbon Footprint2 years ago
Carbon Footprint2 years agoUS SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rules Spur Renewed Interest in Carbon Credits











